Optimization Design of High-Performance Hybrid Superconducting ECR Ion Source Magnet System Based on Particle Swarm Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Magnet System Model Design
2.1. ECR Conditions
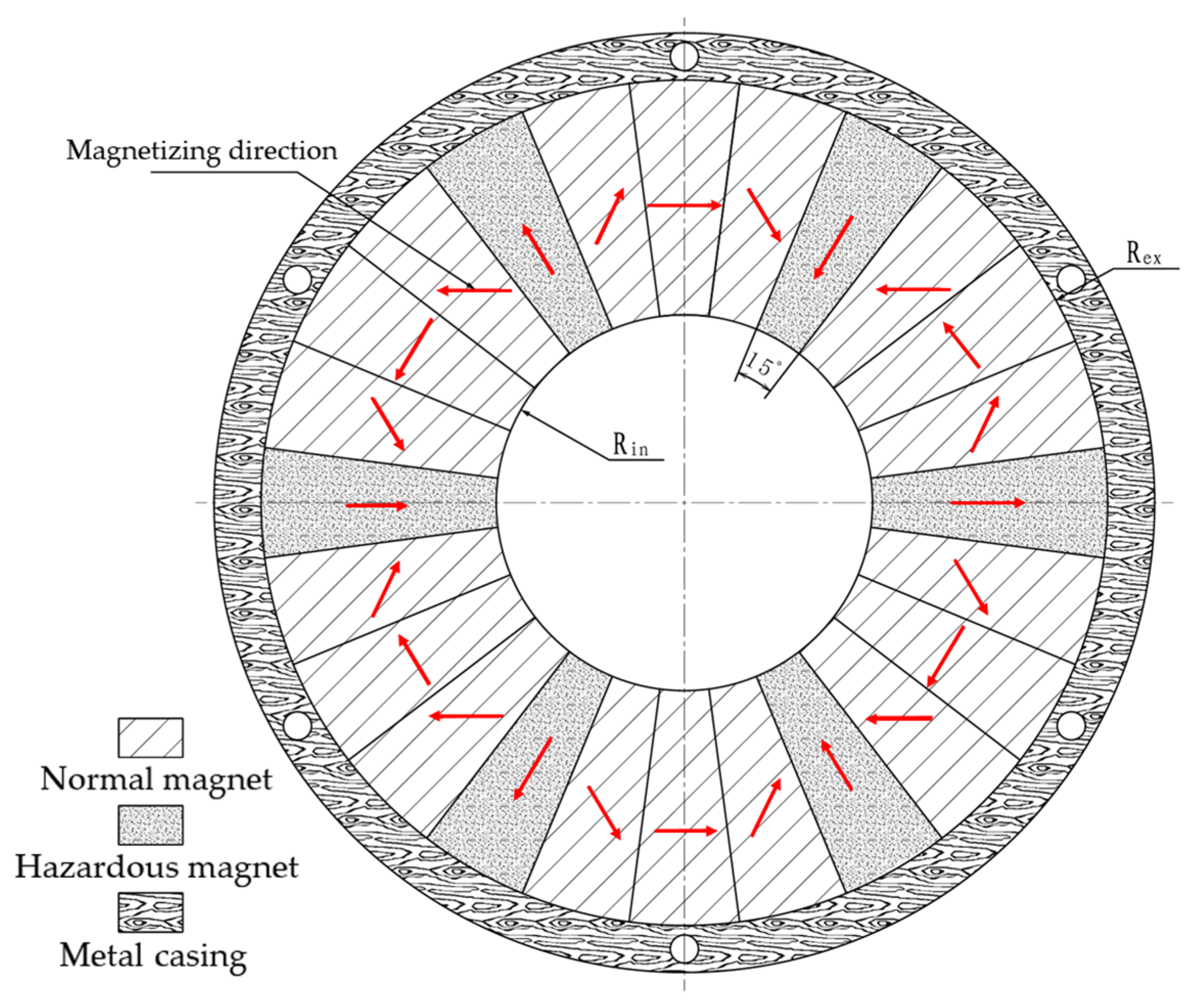
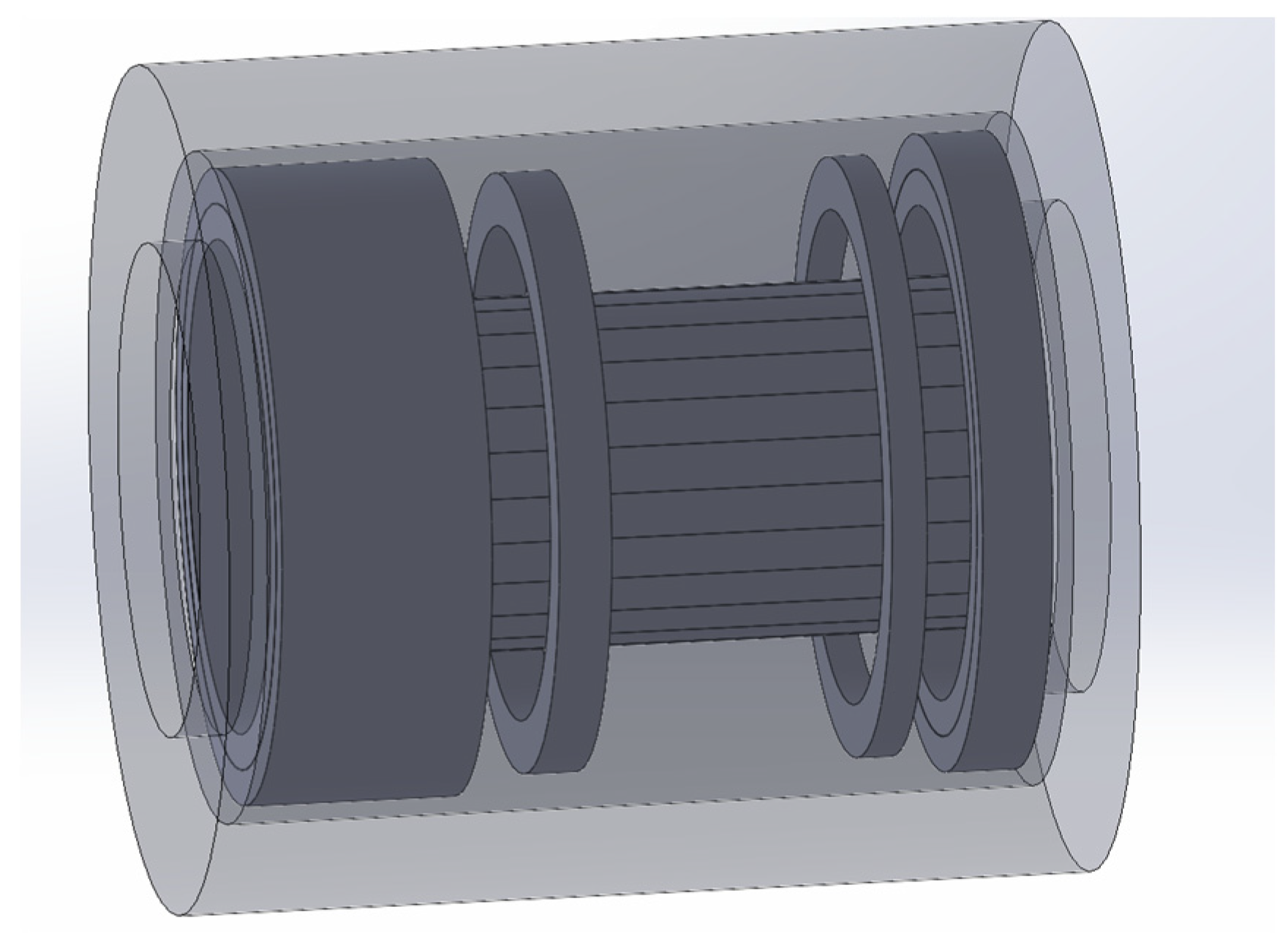
2.2. Configuration of the Hybrid Magnet System
3. Optimization of the Permanent Hexapole Magnet Based on Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
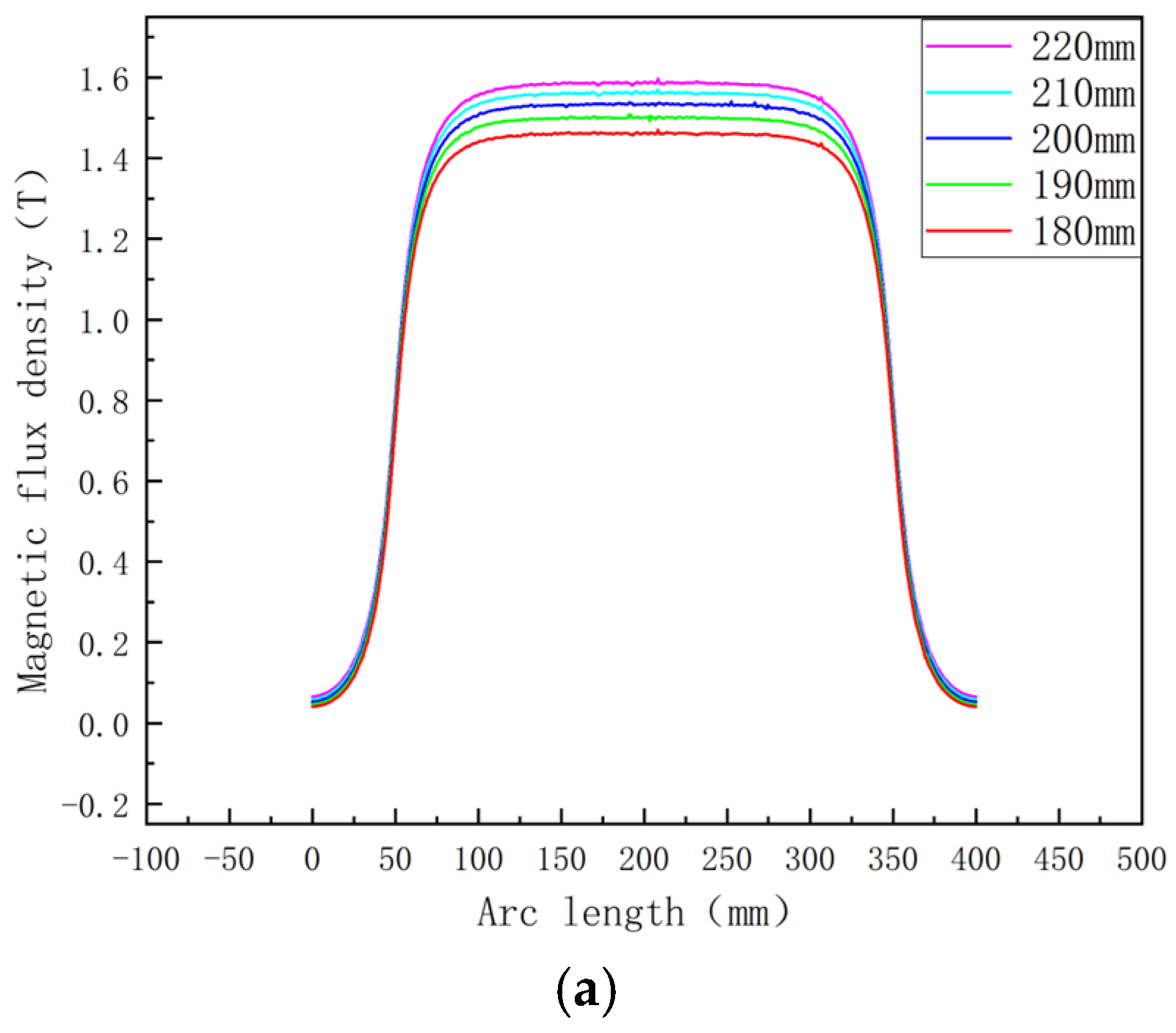
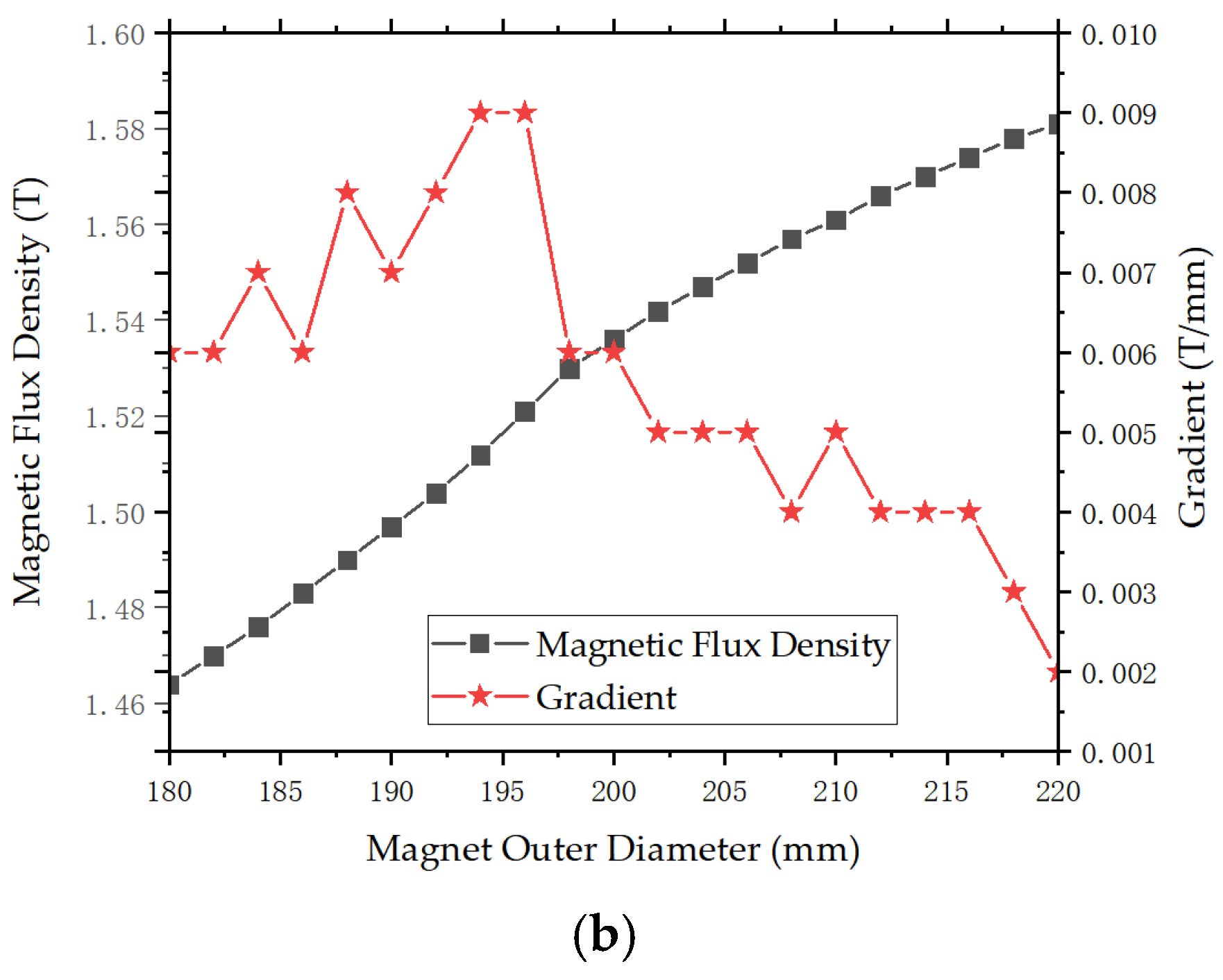
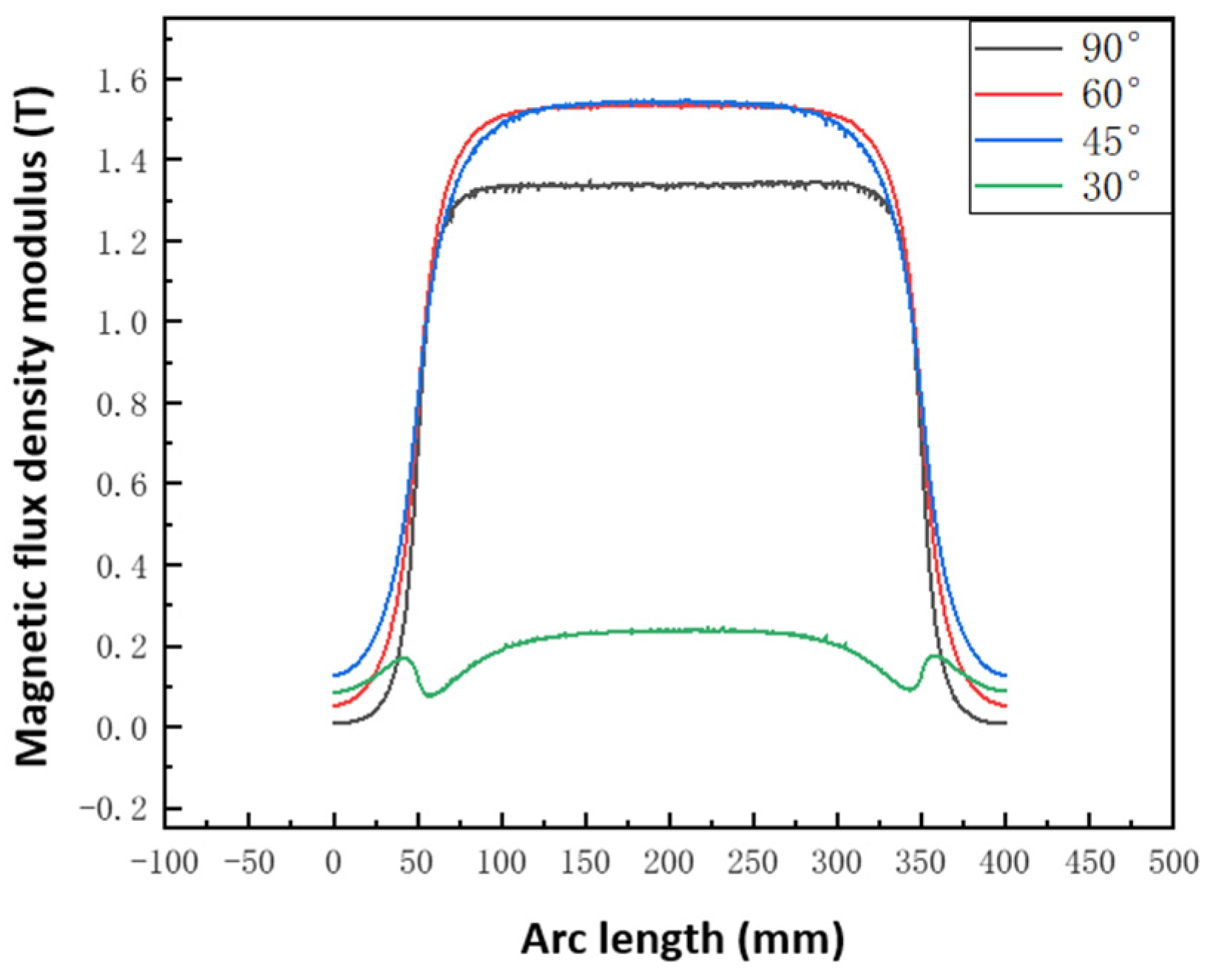
3.1. Parametric Analysis
3.2. PSO-Based Optimization Model and Implementation
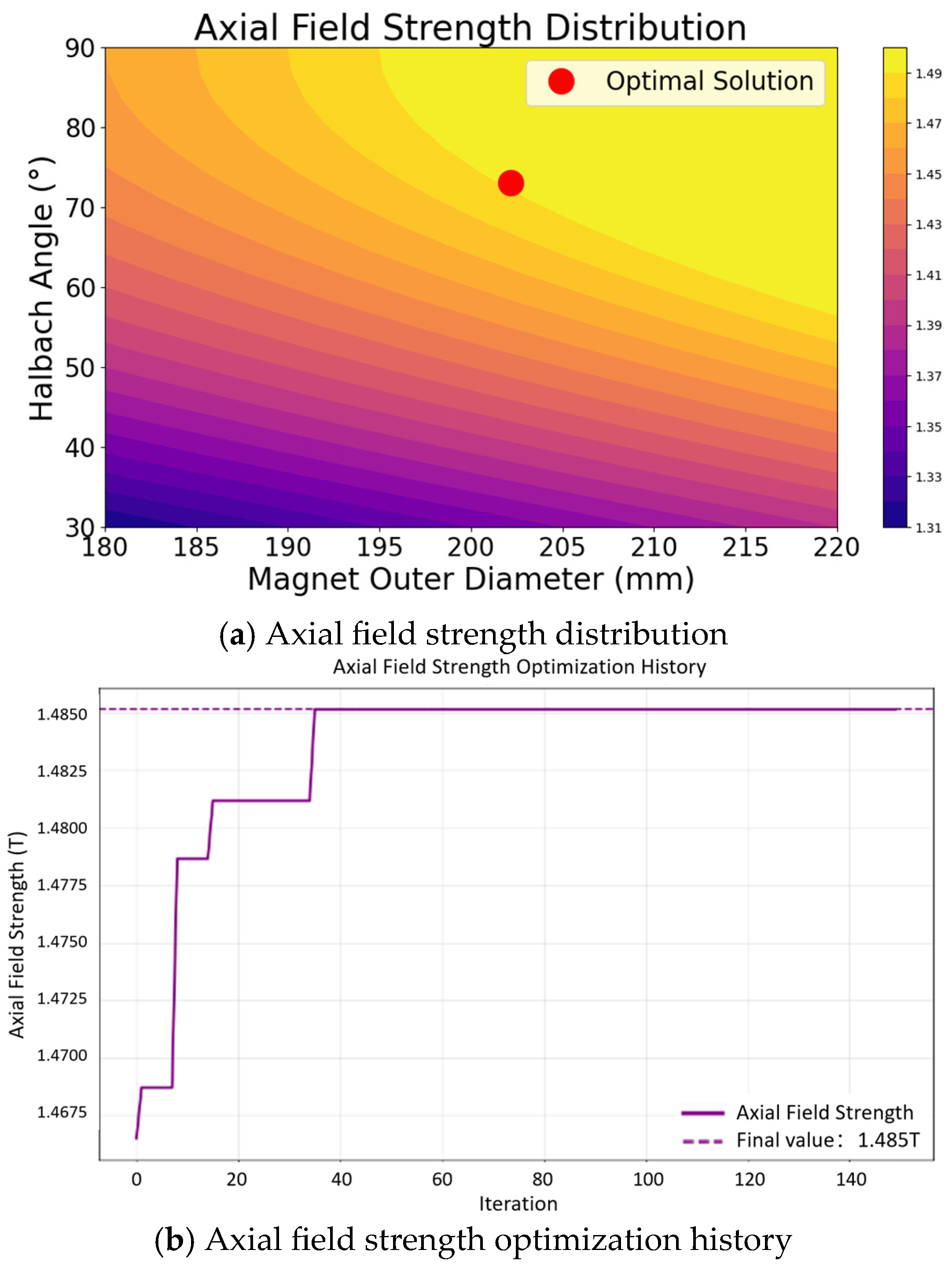
3.2.1. Optimization Problem Definition and Objective Function Formulation
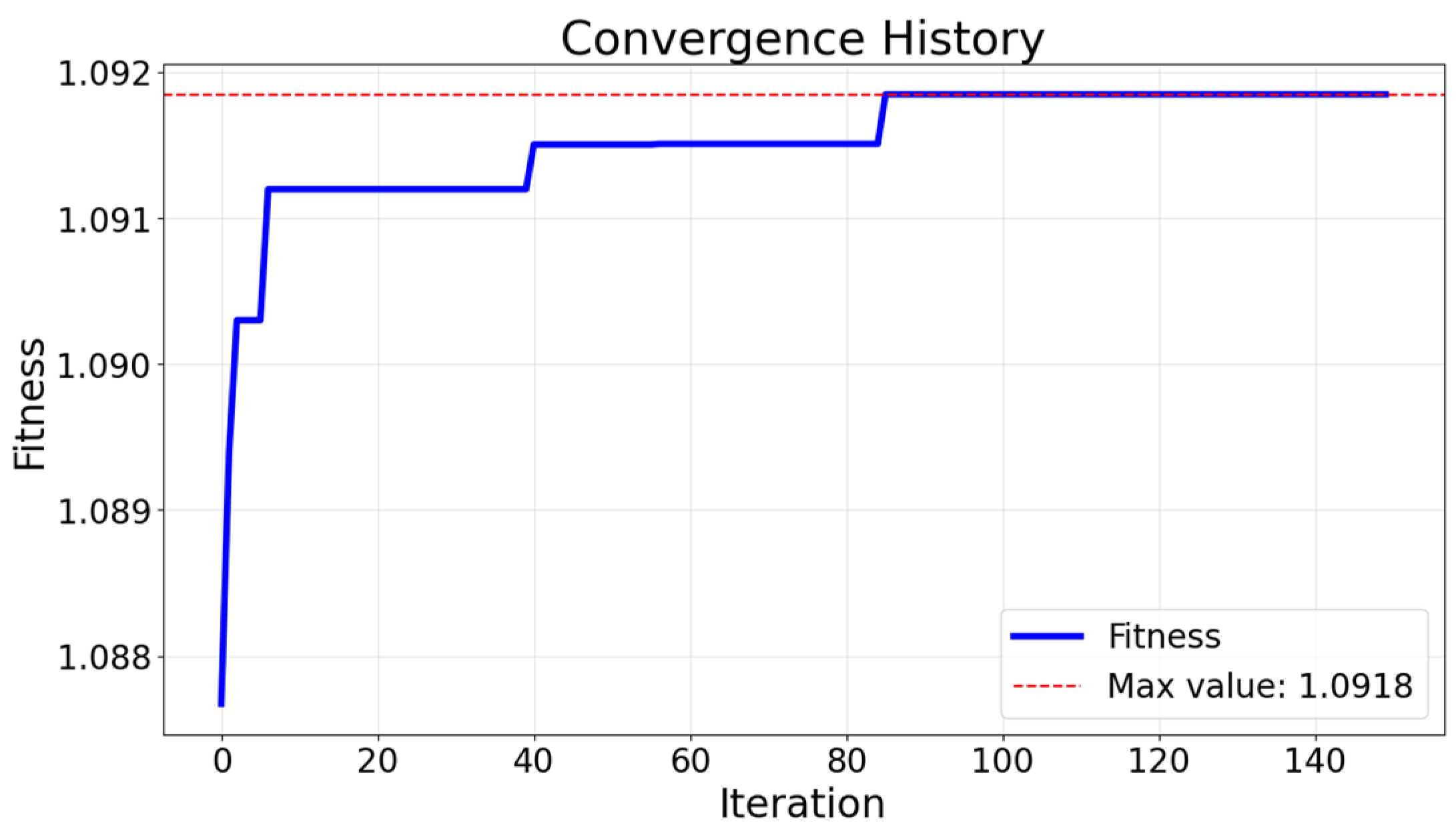
3.2.2. Implementation and Solution via Particle Swarm Optimization
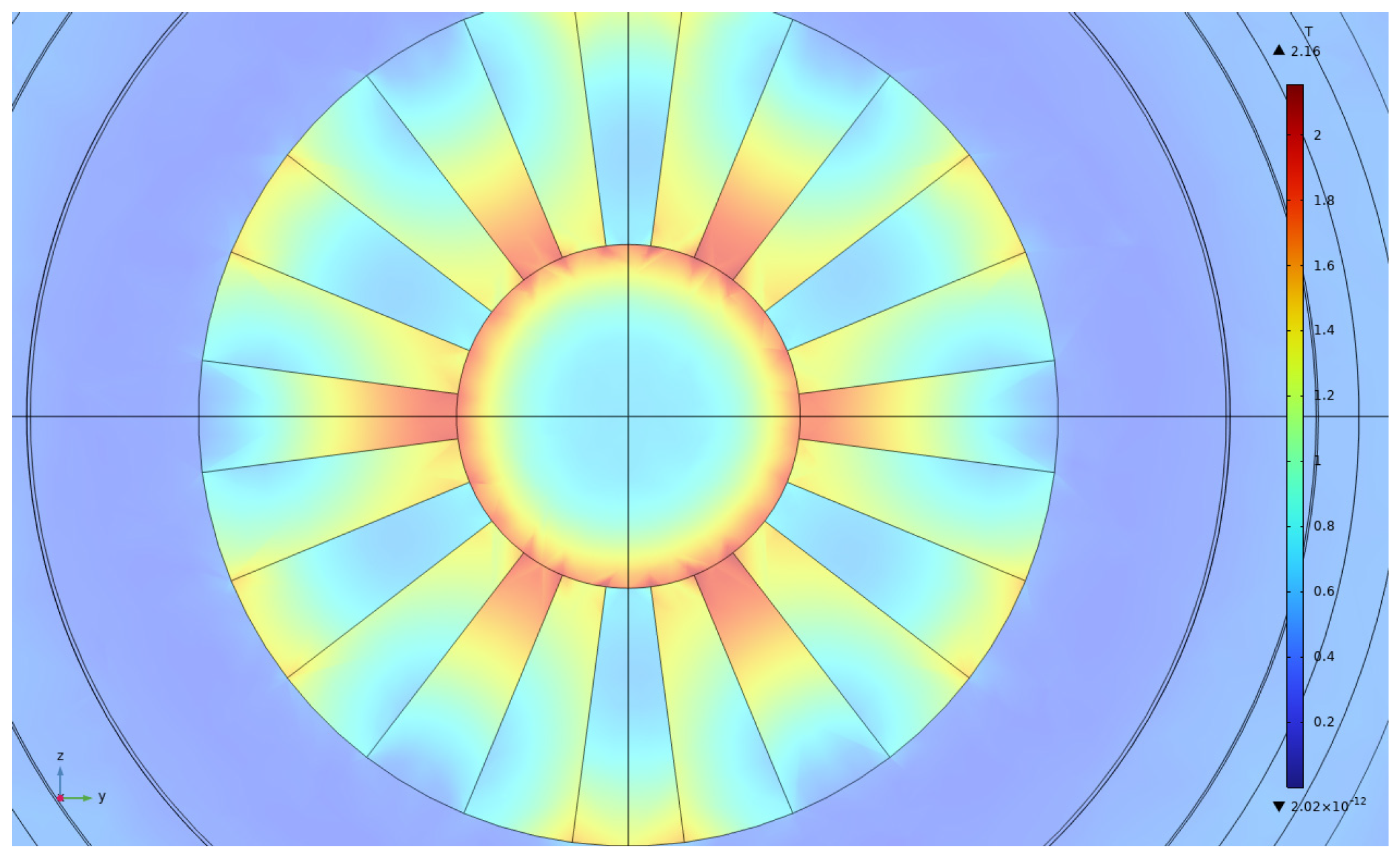
3.2.3. Optimization Results and Analysis
4. Optimization of Hybrid Superconducting Magnet Based on PSO
4.1. Basic Parameters Design and Analysis
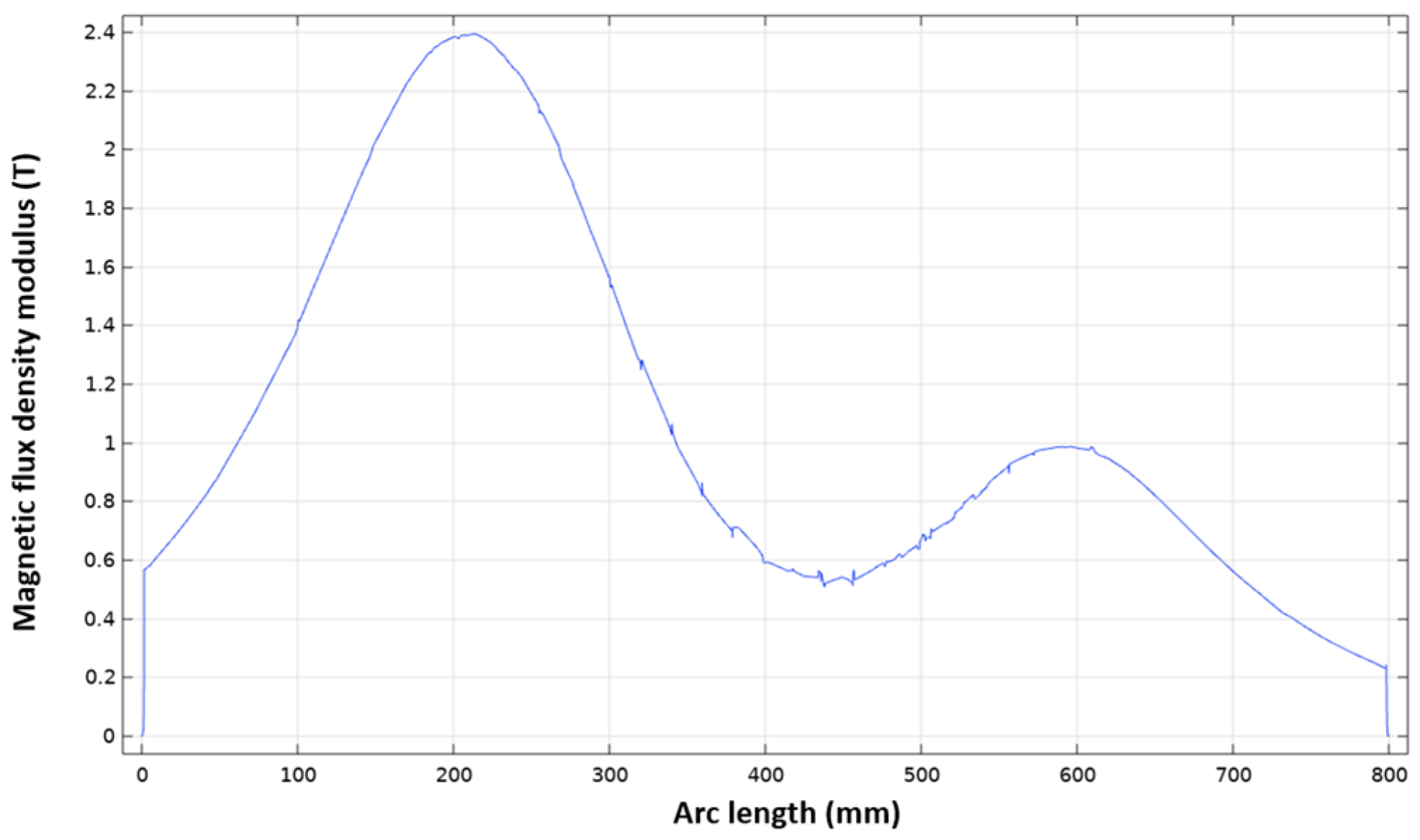
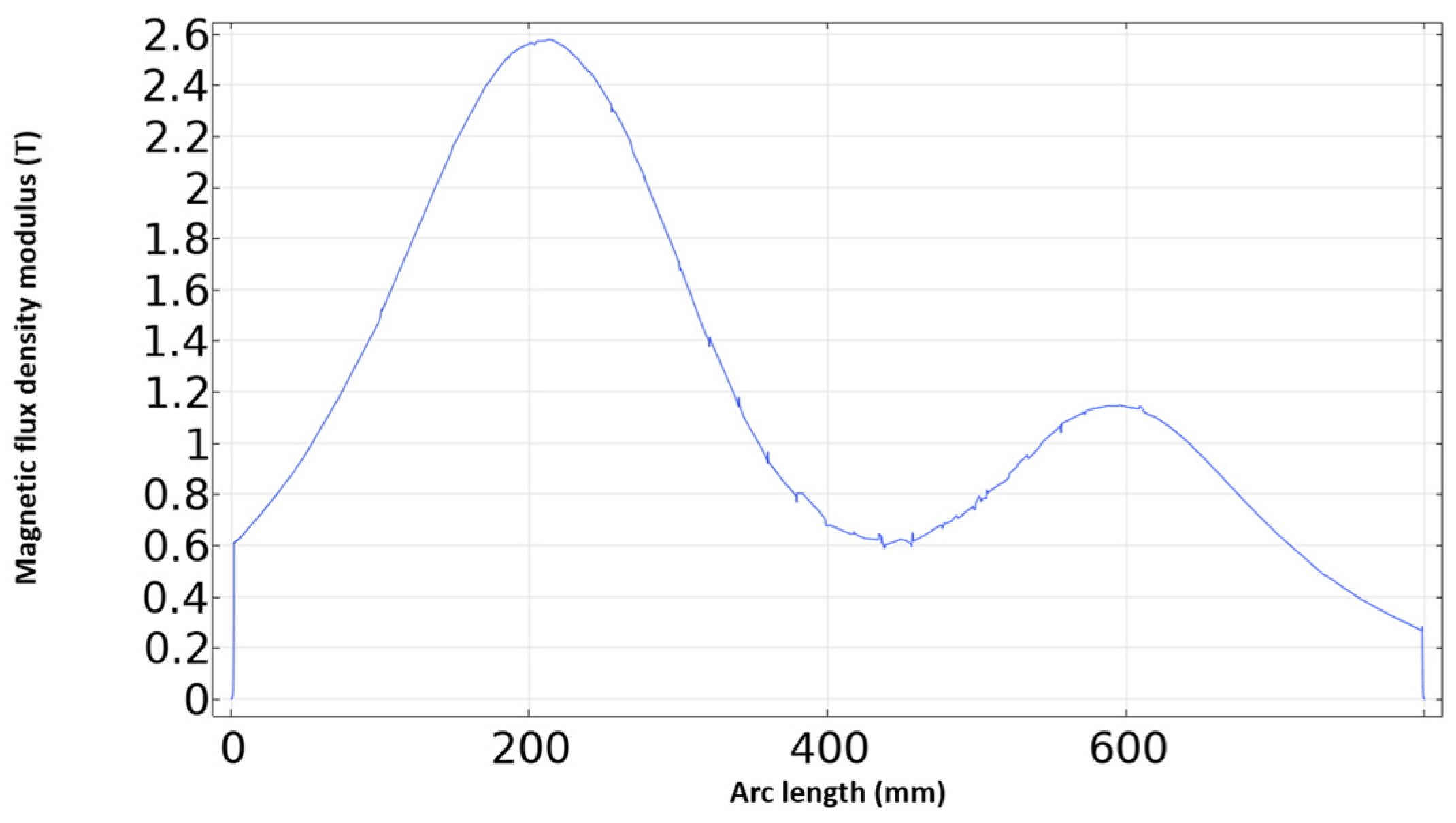
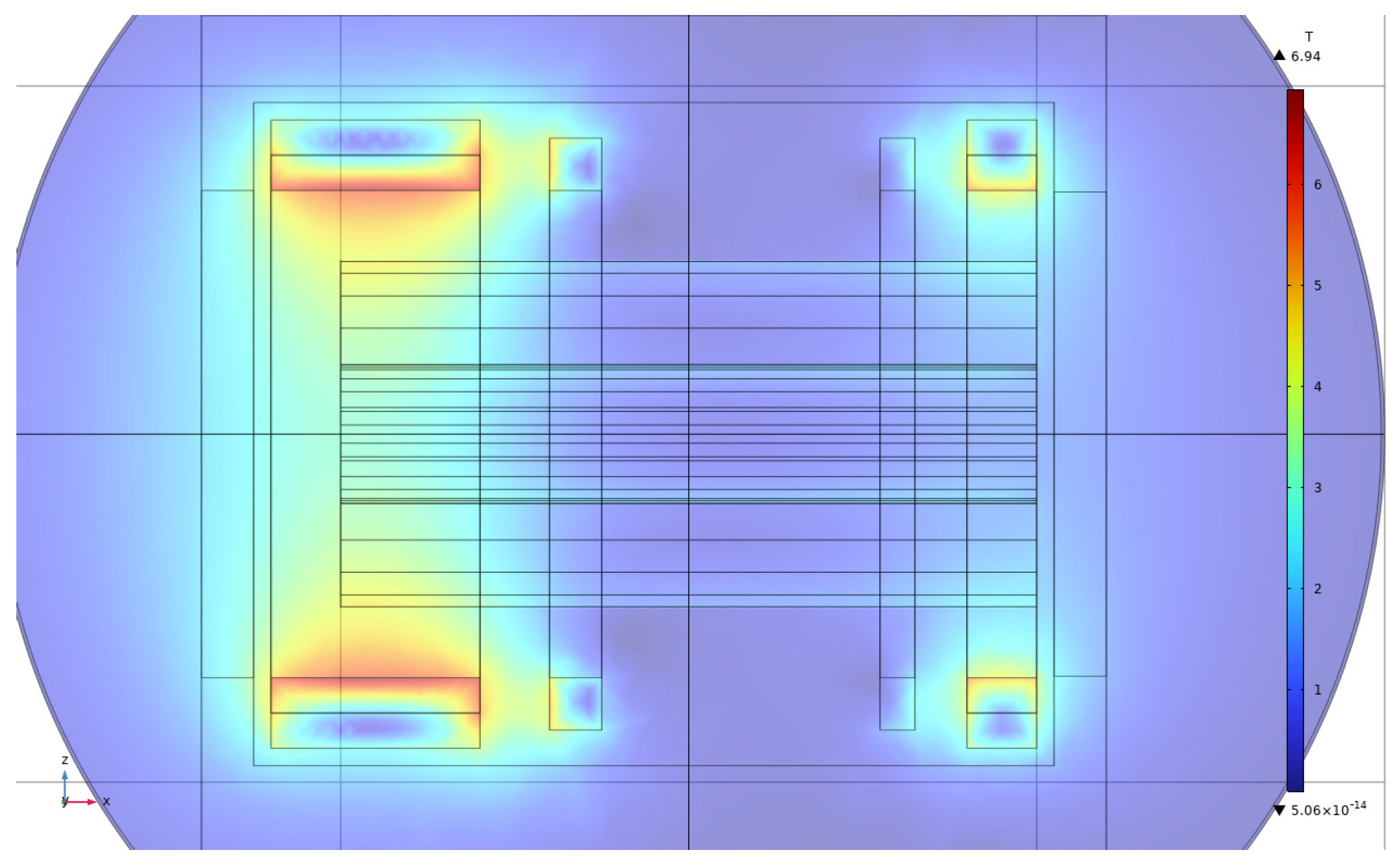
4.2. Finite Element Simulation Optimization Analysis
4.3. PSO-Based Current Optimization Model
4.3.1. Current Optimization Problem Definition and Objective Function Formulation
4.3.2. Implementation and Optimization Process
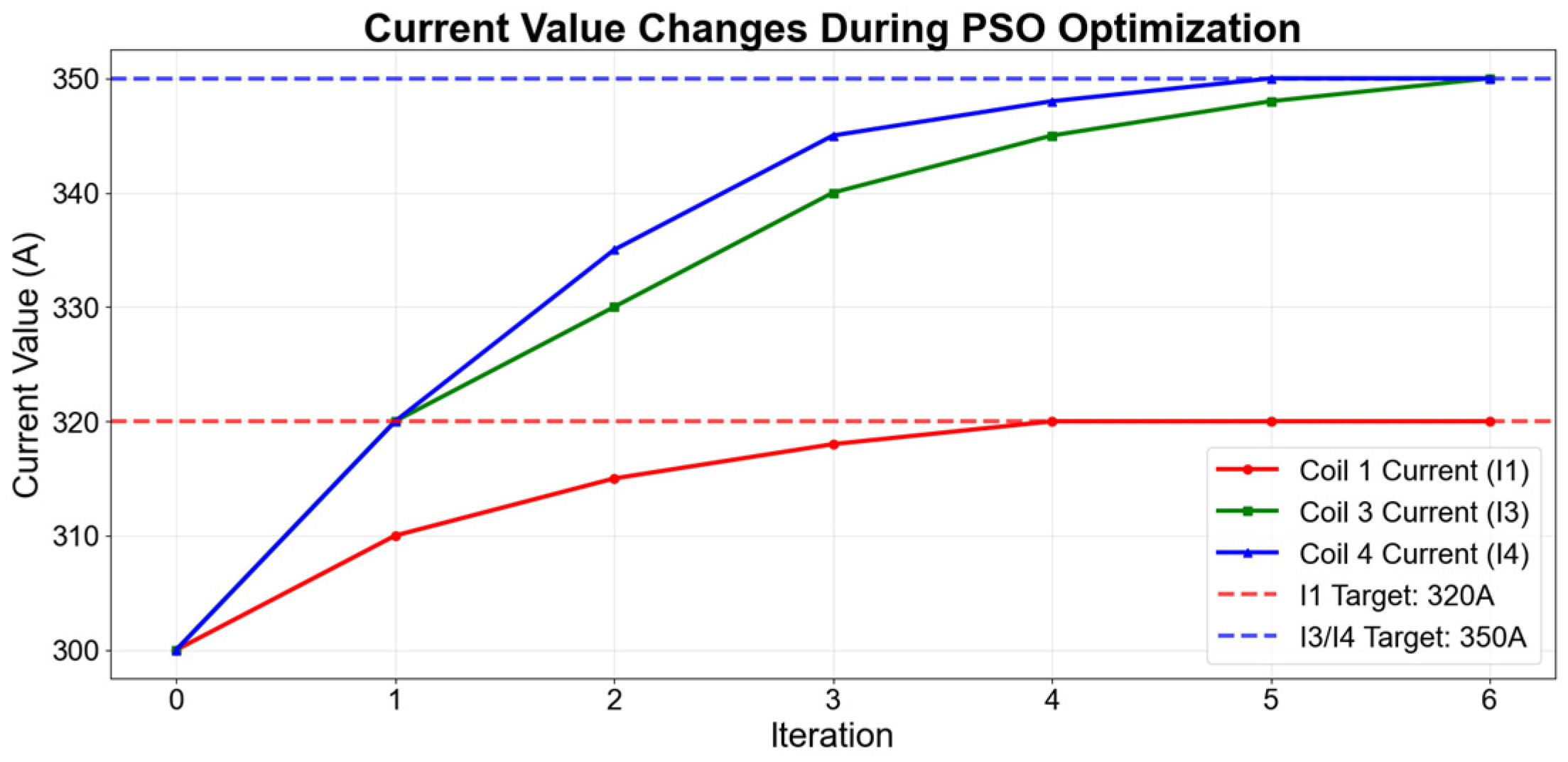
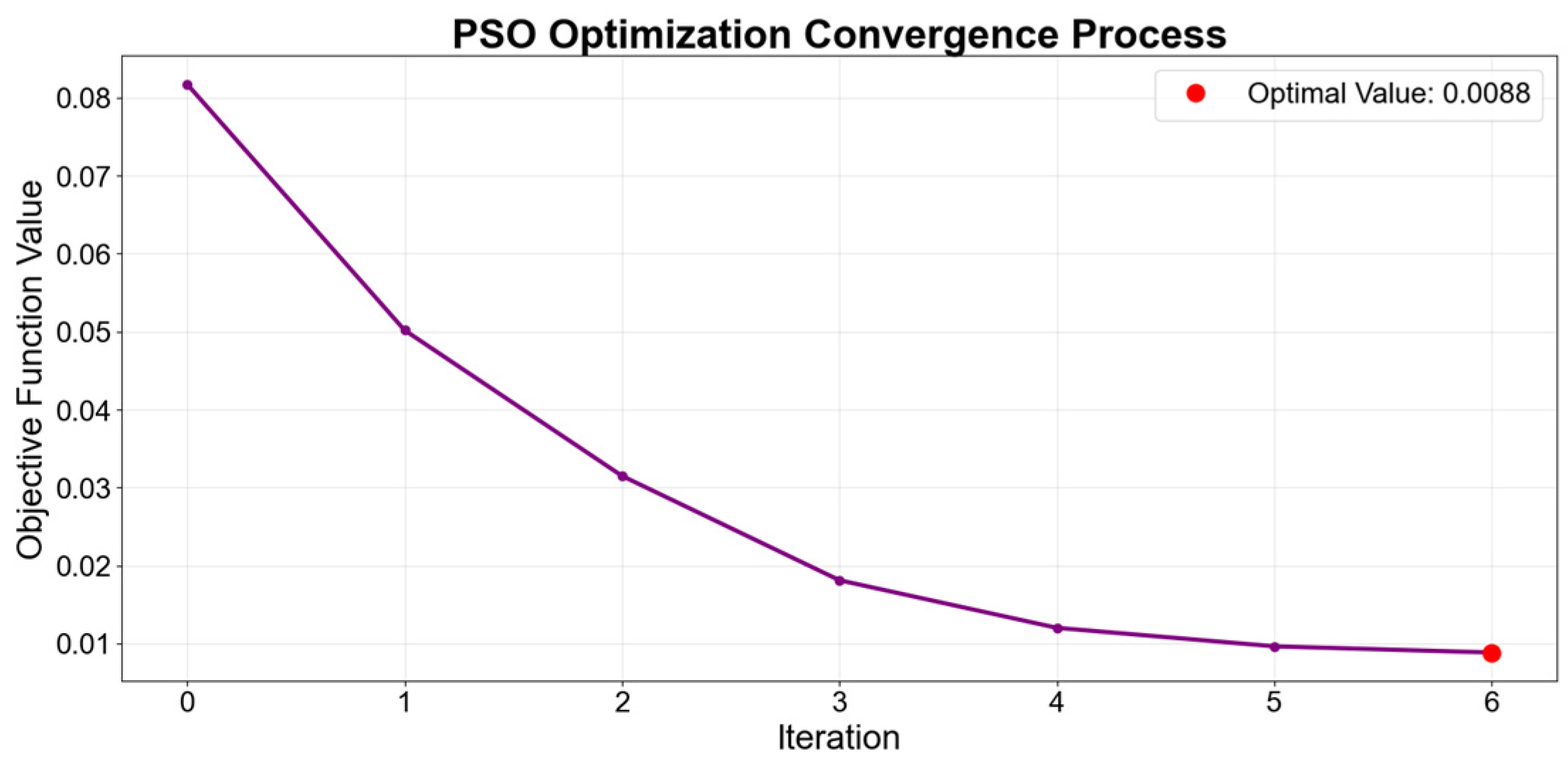
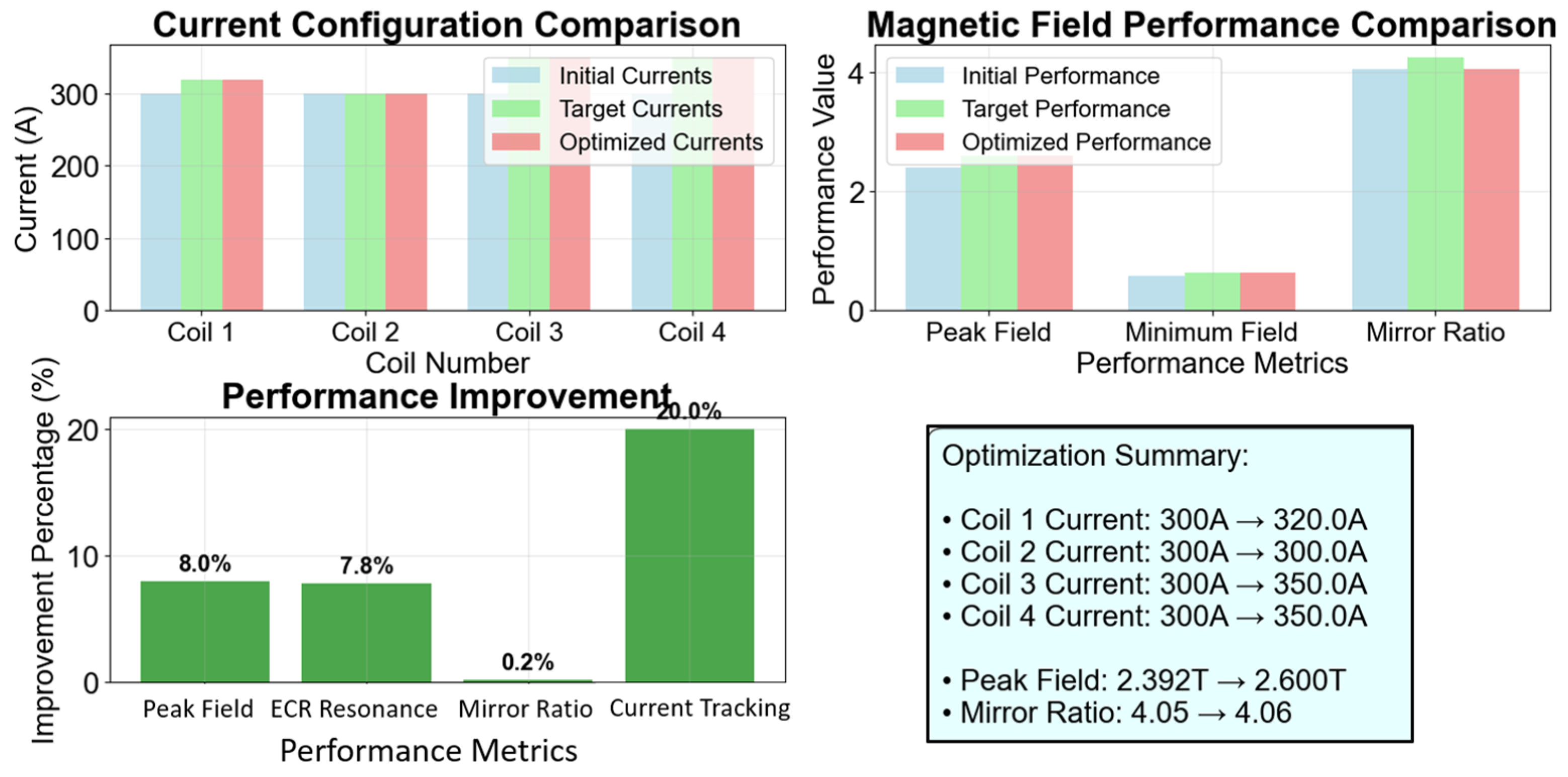
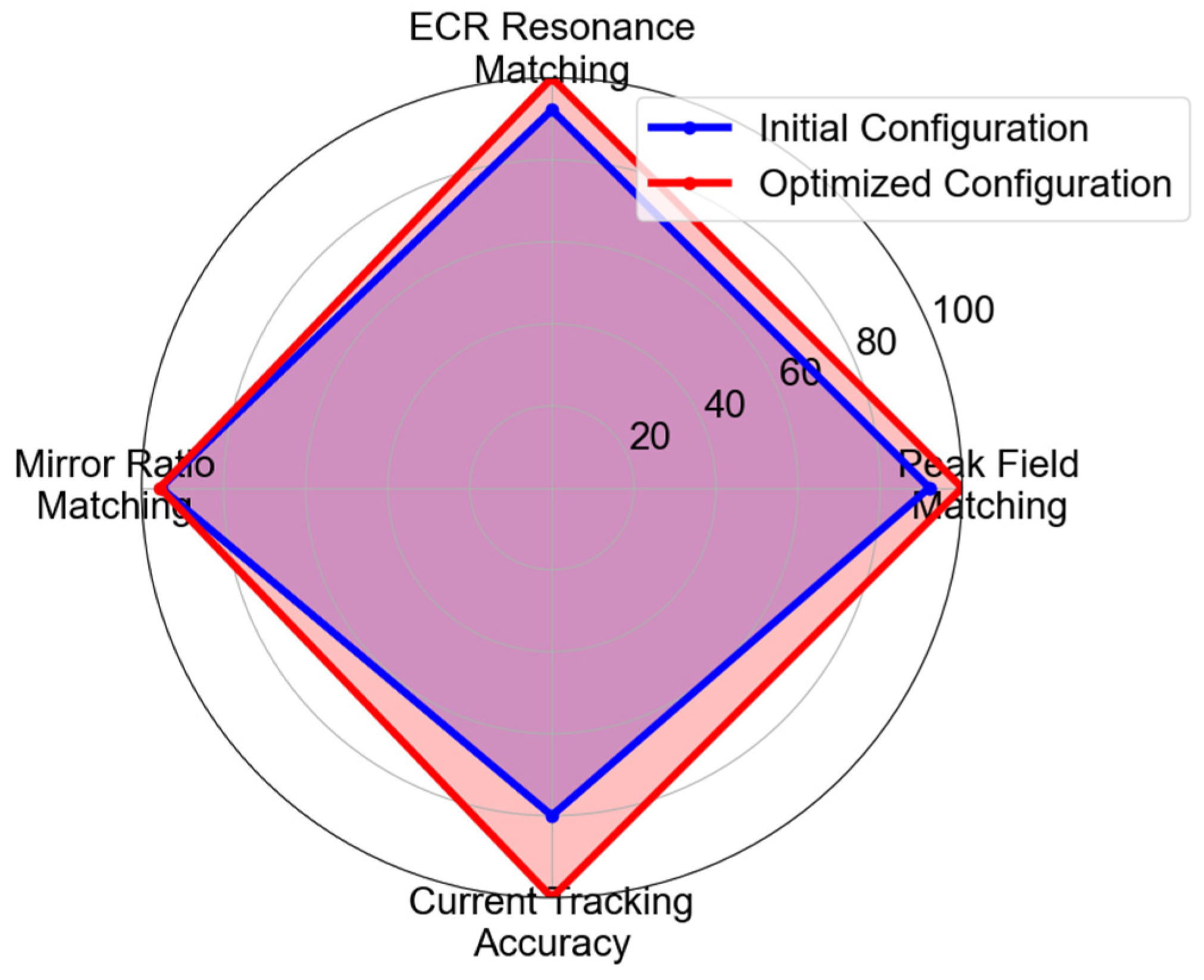
4.3.3. Optimization Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geller, R. Electron Cyclotron Resonance Ion Sources and ECR Plasmas; Institute of Physics Publishing: Bristol, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Xie, D.Z.; Zhang, X.Z.; Xiong, B.; Ruan, L.; Sha, S.; Zhang, W.H.; Cao, Y.; Lin, S.H.; Guo, J.W.; et al. Development of DRAGON electron cyclotron resonance ion source at Institute of Modern Physics. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 02A328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, T.H.; Fukuda, M.; Yorita, T.; Kanda, H.; Yasuda, Y.; Koay, H.W.; Morita, Y.; Takeda, K.; Hara, T.; Hisamatsu, M.; et al. Development of ECR ion source with high-temperature superconducting REBCO coils. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2244, 012108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Yang, Y.; Hafalia, R.; Juchno, M.; Lin, A.; Croteau, J.-F.; Higley, H.; Naus, M.; Pong, I.; Troitino, J.F.; et al. Design and Development of a 28 GHz Nb3Sn ECR Ion Source Superconducting Magnet. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 4301105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadoux, T.; Bakon, N.; Berriaud, C.; Felice, H.; Mora, E.F.; Graffin, P.; Guillo, T.; Minier, G.; Nunio, F.; Rochepault, E.; et al. Mechanical Design of the Superconducting Magnet for the 28 GHz ECR Ion Source ASTERICS. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, R.; Kennedy, J.; Blackwell, T. Particle Swarm Optimization: An Overview. Swarm Intell. 2007, 1, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tan, D.; Liu, L. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm: An Overview. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chou, N.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cui, J.; Li, G.; Xie, Y.M. Topological optimization of magnetic pulse welding coils with a connectivity-constrained particle swarm optimization algorithm. Mater. Des. 2022, 224, 111337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shami, T.M.; El-Saleh, A.A.; Alswaitti, M.; Al-Tashi, Q.; Summakieh, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Particle Swarm Optimization: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 10031–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L. Design and Experimental Research on High-Charge-State ECR Ion Sources. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Hitz, D.; Zhao, H. Design Study of Hexapole Permanent Magnets for ECR Ion Sources. High Energy Phys. Nucl. Phys. 2004, 28, 644–649. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z. Optimization Design and Experimental Research on S-type Superconducting Hexapole Magnet Based on ECR Ion Source. Ph.D. Thesis, Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J. Research on Microwave Coupling in High-Charge-State ECR Ion Sources. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, C. Generation of High-Current High-Charge-State Ion Beams and Device Development for ECR Ion Sources. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaque, K.; Salam, Z. A deterministic particle swarm optimization maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic system under partial shading condition. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3195–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, R.; Pan, M.; Zhou, X.; Song, J.; Tian, H.; Wen, S.; Deng, H. Influence of titanium on the clustering of vacancy, rhenium and osmium in tungsten-titanium alloys: First-principles study. Fusion Eng. Des. 2022, 178, 113098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Huang, Z.; Pang, M.; Bai, G.; Wang, Q.; Han, B. Optimized design of uniform-field coils system with a large uniform region by particle swarm optimization algorithm. Measurement 2024, 234, 114614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.M.; Kuckes, A.F.; Motley, R.W. Electron-Cyclotron Resonance Heating of Alkali Plasmas. J. Appl. Phys. 1967, 38, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, A.; Hitz, D.; Melin, G.; Serebrennikov, K. Electron cyclotron resonance plasmas and electron cyclotron resonance ion sources: Physics and technology (invited). Rev. Sci. Instruments 2004, 75, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, D.; Lyneis, C.; Abbott, S.; Collins, D.; Dwinell, R.; Galloway, M.; Leitner, M.; Todd, D. Next generation ECR ion sources: First results of the superconducting 28GHz ECRIS—VENUS. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interactions Mater. Atoms 2005, 235, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.W.; Sun, L.T.; Lu, W.; Zhang, X.Z.; Guo, X.H.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, H.Y.; Feng, Y.C.; Li, J.Y.; Ma, H.Y.; et al. New development of advanced superconducting electron cyclotron resonance ion source SECRAL (invited). Rev. Sci. Instruments 2010, 81, 02A202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
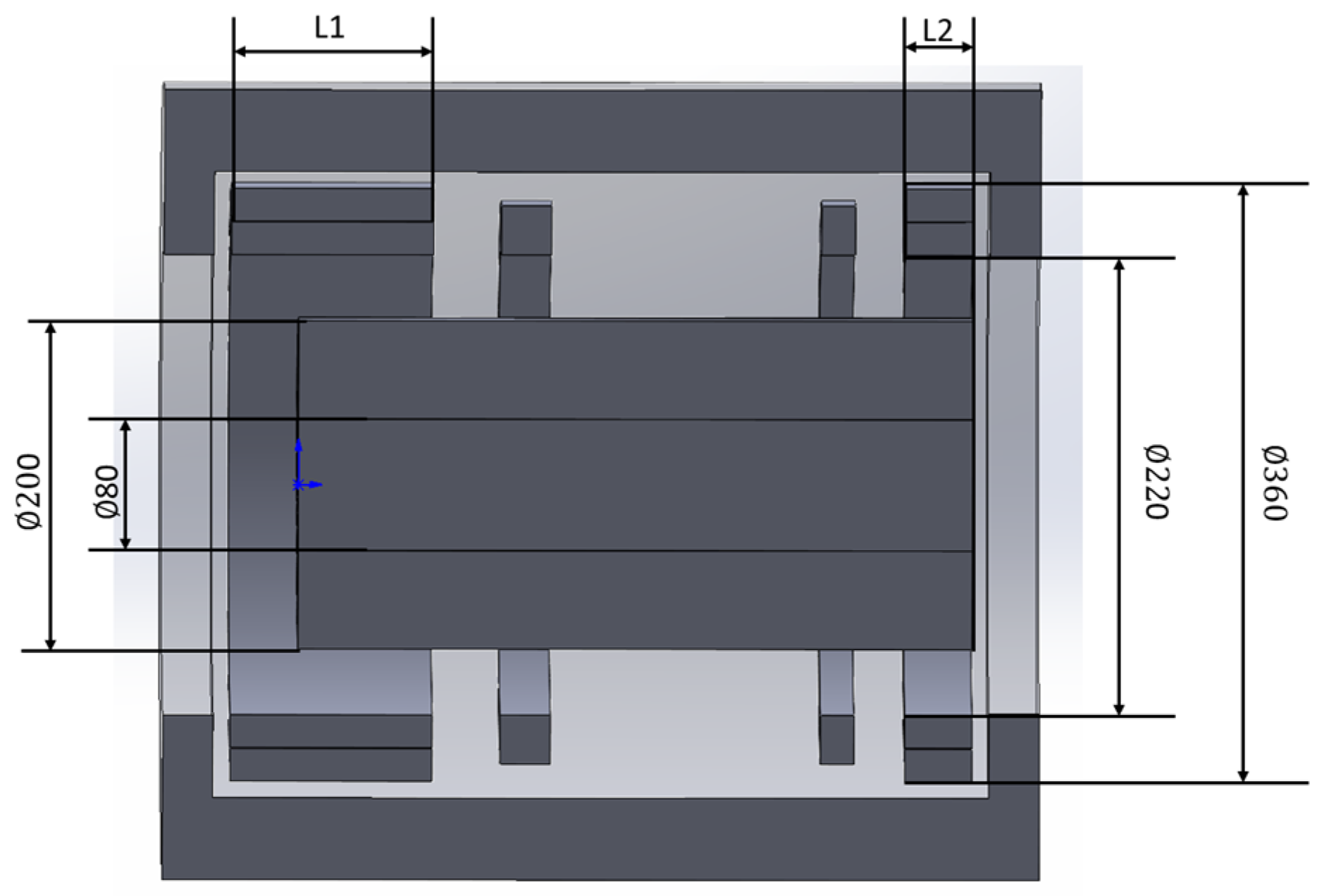
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Inner diameter of magnet/mm | 80 |
| Outer diameter of magnet/mm | 200 |
| Length of left magnet section (L1)/mm | 120 |
| Length of right magnet section (L2)/mm | 70 |
| Inner diameter of solenoid coil/mm | 220 |
| Outer diameter of solenoid coil/mm | 360 |
| Width of solenoid coils (from left to right)/mm | 100, 30, 30, 30 |
| Current of solenoid coils (from left to right)/A | +300, −300, −300, +300 |
| Number of turns of solenoid coils (from left to right) | 2400, 450, 300, 800 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Inner diameter of magnet/mm | 80 |
| Outer diameter of magnet/mm | 200 |
| Length of left magnet section (L1)/mm | 140 |
| Length of right magnet section (L2)/mm | 70 |
| Inner diameter of solenoid coil/mm | 220 |
| Outer diameter of solenoid coil/mm | 360 |
| Width of solenoid coils (left to right)/mm | 100, 30, 30, 40 |
| Current of solenoid coils (left to right)/A | +320, −300, −350, +350 |
| Number of turns of solenoid coils (left to right) | 2400, 450, 300, 800 |
| Performance Indicator | Designed Source | VENUS Source [22] | SECRAL Source [23] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microwave Frequency (GHz) | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| Axial Peak Field (T) | 2.6 | ~2.5 | 2.3–2.5 |
| Mirror Ratio | ~4.25 | ~4.0 | 3.5–4.0 |
| Minimum B-field in ECR Zone (T) | ~0.64 | ~0.44 | ~0.6–0.65 |
| Radial Peak Field (T) | ~1.3 | ~1.4 | ~1.2 |
| Magnet Technology | Hybrid (SC Solenoid + NdFeB PM) | All-SC (Nb3Sn & NbTi Coils) | All-SC (NbTi Coils) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H. Optimization Design of High-Performance Hybrid Superconducting ECR Ion Source Magnet System Based on Particle Swarm Algorithm. Symmetry 2026, 18, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym18010082
Xu M, Liu L, Liu Y, Lu Y, Wang H. Optimization Design of High-Performance Hybrid Superconducting ECR Ion Source Magnet System Based on Particle Swarm Algorithm. Symmetry. 2026; 18(1):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym18010082
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Manman, Lei Liu, Yongming Liu, Yimin Lu, and Huaiyang Wang. 2026. "Optimization Design of High-Performance Hybrid Superconducting ECR Ion Source Magnet System Based on Particle Swarm Algorithm" Symmetry 18, no. 1: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym18010082
APA StyleXu, M., Liu, L., Liu, Y., Lu, Y., & Wang, H. (2026). Optimization Design of High-Performance Hybrid Superconducting ECR Ion Source Magnet System Based on Particle Swarm Algorithm. Symmetry, 18(1), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym18010082






