Integrable Multispecies Totally Asymmetric Stochastic Interacting Particle Systems with Homogeneous Rates
Abstract
1. Introduction
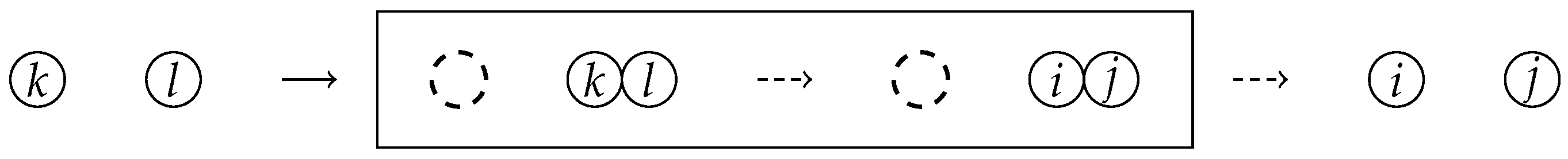
If a particle of species i with attempts to jump to a site occupied by a particle of species j, the two particles exchange positions. If , the jump is blocked.
Each particle of species i at site x independently jumps to site after an exponential waiting time with rate 1. If is occupied by a particle of species j, then the site temporarily accommodates both particles, with the particle of species occupying the left position and the particle of species the right position at . Immediately thereafter, the particle of species moves back to site x, resulting in an exchange of positions if , or no net movement if .
Summary of the Main Results
- We show that only 7 of the 28 two-species models classified in [34] extend naturally to integrable N-species systems.
- We construct new one- and two-parameter families of integrable models, which broaden and generalize these seven cases.
- For the remaining 21 cases, we introduce an alternative extension scheme that yields 8 further integrable N-species models.
- We provide explicit formulas for transition probabilities and demonstrate that all of the above results remain valid when the dynamics incorporate the drop–push interaction rule.
2. Preliminary
2.1. Notations
2.2. Natural Extension to the N-Species Case
2.3. Tensor Product
3. Integrability
3.1. Master Equations
3.1.1. Two-Particle Systems
- (i)
- If with , then
- (ii)
- If , then
3.1.2. General n-Particle Systems
- (i)
- If with , then
- (ii)
- If with , then
- (iii)
- If with , then
- (iv)
- If , then
3.2. Yang–Baxter Integrability
3.3. Generalizations
- (i)
- and for each
- (ii)
- and for .
- (iii)
- and for .
Each particle of species i at x independently jumps to site after an exponential waiting time with rate 1. If is occupied by a particle of species j, then temporarily accommodates both particles, with species i occupying the left position and species j the right position. If , the following infection rules apply:
- (a)
- (b)
Immediately after this interaction, the left particle moves back to x.
3.4. Asymmetric Extension to N-Species Cases
4. Discussion
4.1. Models with the Drop–Push Rule
4.2. Transition Probabilities
4.3. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Matrices for Two-Particle Interactions in Integrable “Two-Species” Models
- (i)
- Each column of sums to 1.
- (ii)
- All off-diagonal entries are either 0 or 1.
- (iii)
- The associated scattering matriceswhere denotes the identity matrix, and are spectral parameters, satisfy the relation (Yang–Baxter equation) between matrices:
References
- Liggett, T. Interacting Particle Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Liggett, T. Stochastic Interacting Systems: Contact, Voter and Exclusion Processes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Spohn, H. Large Scale Dynamics of Interacting Particles; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Schütz, G.M. Exactly solvable models for many-body systems far from equilibrium. In Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena; Domb, C., Lebowitz, J., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2000; Volume 19, pp. 1–251. [Google Scholar]
- Borodin, A.; Corwin, I. Macdonald processes. Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 2014, 158, 225–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodin, A.; Corwin, I.; Petrov, L.; Sasamoto, T. Spectral theory for interacting particle systems solvable by coordinate Bethe ansatz. Commun. Math. Phys. 2015, 339, 1167–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, I. The Kardar–Parisi–Zhang equation and universality class. Random Matrices Theory Appl. 2012, 1, 1130001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, G.M. Exact solution of the master equation for the asymmetric exclusion process. J. Stat. Phys. 1997, 88, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, C.; Widom, H. Integral formulas for the asymmetric simple exclusion process. Commun. Math. Phys. 2008, 279, 815–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, G.; Corwin, I.; Quastel, J. Probability distribution of the free energy of the continuum directed random polymer in 1+1 dimensions. Comm. Pure Appl. Math. 2011, 64, 466–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardar, M.; Parisi, G.; Zhang, Y.-C. Dynamic scaling of growing interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, T.; Sasamoto, T. Asymmetric simple exclusion process and modified random matrix ensembles. Nucl. Phys. B 2004, 699, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tracy, C.A.; Widom, H. Asymptotics in ASEP with step initial condition. Commun. Math. Phys. 2009, 290, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, M.; Lee, E. The transition probability and the probability for the left-most particle’s position of the q-totally asymmetric zero range process. J. Math. Phys. 2014, 55, 013301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. The current distribution of the multiparticle hopping asymmetric diffusion model. J. Stat. Phys. 2012, 149, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, E.; Wang, D. Distributions of a particle’s position and their asymptotics in the q-deformed totally asymmetric zero range process with site dependent jumping rates. Stoch. Processes Their Appl. 2019, 129, 1795–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povolotsky, A.M. Bethe ansatz solution for the zero-range process with nonuniform stationary state. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 061109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povolotsky, A.M.; Priezzhev, V.B.; Hu, C.-K. Asymmetric avalanche process. J. Stat. Phys. 2003, 111, 1149–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povolotsky, A.M. On the integrability of zero-range chipping models with factorized steady states. J. Phys. A 2013, 46, 465205. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Waugh, D. The transition probability of the q-TAZRP (q-Bosons) with inhomogeneous jump rates. SIGMA 2016, 12, 037. [Google Scholar]
- Borodin, A.; Bufetov, A. Color-position symmetry in interacting particle systems. Annal. Probab. 2021, 49, 1607–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Nicoletti, M.; Petrov, L. Colored interacting particle systems on the ring: Stationary measures from Yang–Baxter equation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.11865. [Google Scholar]
- Kuan, J. Determinantal expressions in multi-species TASEP. SIGMA 2020, 16, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gier, J.; Mead, W.; Wheeler, M. Transition probability and total crossing events in the multi-species asymmetric exclusion process. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2023, 56, 255204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyer, A.; Kuniba, A. Multispecies inhomogeneous—PushTASEP from antisymmetric fusion. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.00829. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyer, A.; Martin, J. The inhomogeneous multispecies PushTASEP: Dynamics and symmetry. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.09740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuniba, A.; Maruyama, S.; Okado, M. Multispecies TASEP and combinatorial R. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2015, 48, 34FT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuniba, A.; Okado, M.; Watanabe, S. Integrable Structure of Multispecies Zero Range Process. SIGMA 2017, 13, 044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, C.; Widom, H. On the distribution of a second-class particle in the asymmetric simple exclusion process. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2009, 42, 425002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, C.; Widom, H. On the asymmetric simple exclusion process with multiple species. J. Stat. Phys. 2013, 150, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamohammadi, A.; Fatollahi, A.H.; Khorrami, M.; Shariati, A. Multispecies reaction-diffusion systems. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 4642–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Karimipour, V.; Khorrami, M. Exact solution of a one-parameter family of asymmetric exclusion processes. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 57, 6370–6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Karimipour, V.; Khorrami, M. A two-parameteric family of asymmetric exclusion processes and its exact solution. J. Stat. Phys. 1999, 97, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Ahmadi, N. Class of integrable diffusion-reaction processes. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 1674–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roshani, F.; Khorrami, M. Annihilation-diffusion processes: An exactly solvable model. J. Math. Phys. 2002, 43, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshani, F.; Khorrami, M. Solvable multi-species extensions of the drop–push model. Eur. Phys. J. B 2003, 36, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. Exact formulas of the transition probabilities of the multi-species asymmetric simple exclusion process. SIGMA 2020, 16, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. Integrability of the multi-species symmetric simple exclusion process with long-range jumps on Z. Symmetry 2024, 16, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, G.M.; Ramaswamy, R.; Barma, M. Pairwise balance and invariant measures for generalized exclusion processes. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1996, 29, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodin, A.; Ferrari, P.L. Large time asymptotics of growth models on space-like paths I: PushASEP. Electron. J. Probab. 2008, 13, 1380–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, E.; Raimbekov, T. Integrable Multispecies Totally Asymmetric Stochastic Interacting Particle Systems with Homogeneous Rates. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091510
Lee E, Raimbekov T. Integrable Multispecies Totally Asymmetric Stochastic Interacting Particle Systems with Homogeneous Rates. Symmetry. 2025; 17(9):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091510
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Eunghyun, and Temirlan Raimbekov. 2025. "Integrable Multispecies Totally Asymmetric Stochastic Interacting Particle Systems with Homogeneous Rates" Symmetry 17, no. 9: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091510
APA StyleLee, E., & Raimbekov, T. (2025). Integrable Multispecies Totally Asymmetric Stochastic Interacting Particle Systems with Homogeneous Rates. Symmetry, 17(9), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17091510



