Multi-Scale Pure Graphs with Multi-View Subspace Clustering for Salient Object Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- To depict the global structure and remove the noise of multi-view low-level features, multi-view low-rank sparse subspace clustering was applied to induce a shared affinity graph matrix.
- 2.
- To further capture the consistency and complementary intrinsic structure of multi-view features, multi-view subspace clustering was explored based on a low-rank representation with diversity regularization.
- 3.
- To clearly describe the local and global structure of multi-view low-level features, two-stage multi-scale pure graphs were constructed based on the above graph matrices.
- 4.
- Extensive experiments demonstrate that our two-stage, multi-scale pure graphs consistently achieve better saliency performance than several state-of-the-art graph models on five benchmark datasets.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
3.1. Multi-View Feature Extraction
3.2. Multi-View Pure Graph Construction
3.2.1. Adjacent Graph
3.2.2. Affinity Graph Learning
| Algorithm 1 Multi-scale pure graphs with multi-view subspace clustering for salient object detection |
| Require: Multi-view features , background seeds . Ensure: Saliency result .
|
4. Experimental Design and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Implementation Details
4.1.2. Benchmark Dataset
4.1.3. Baseline Models
4.1.4. Evaluation Metrics
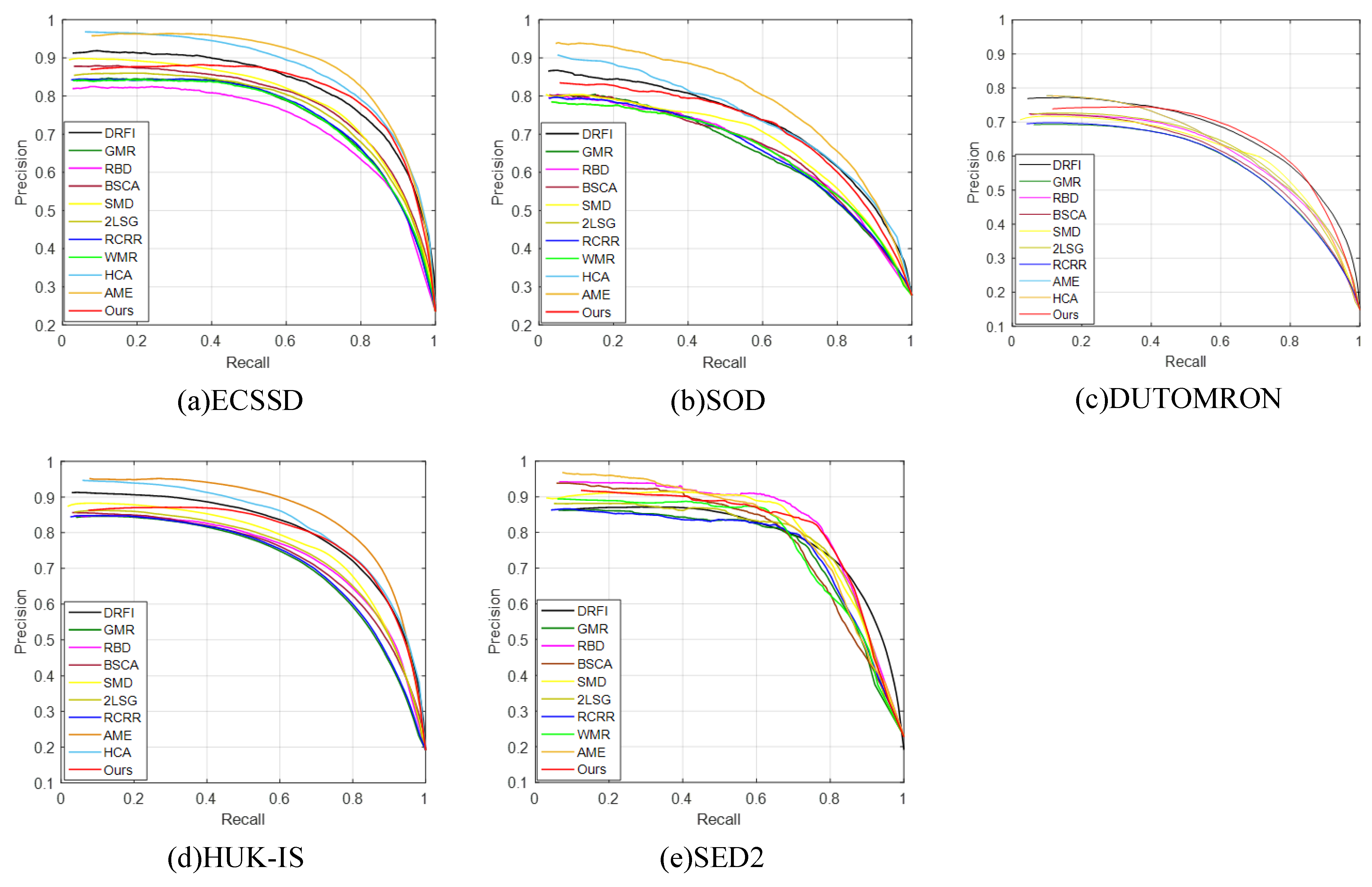
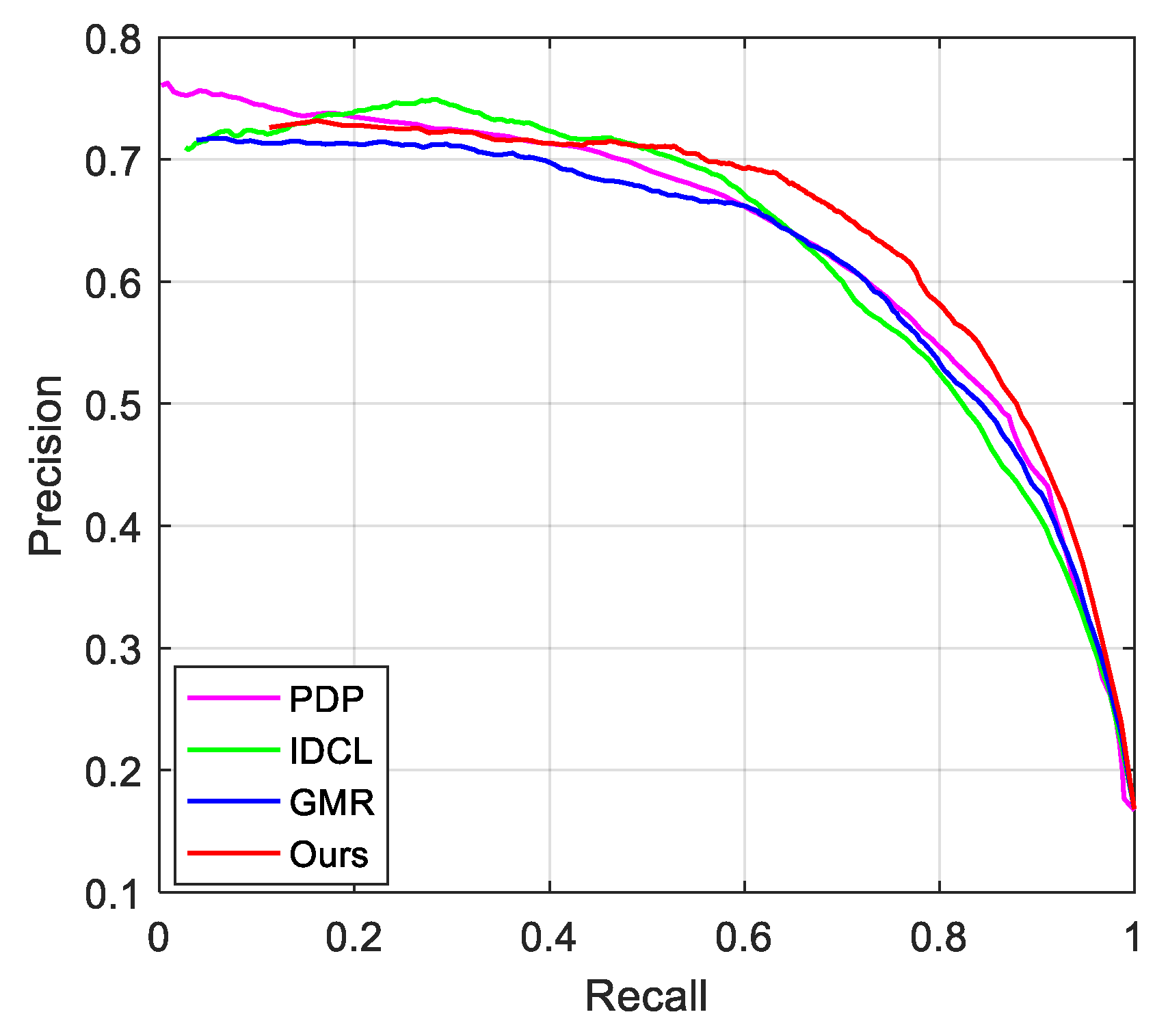
4.2. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
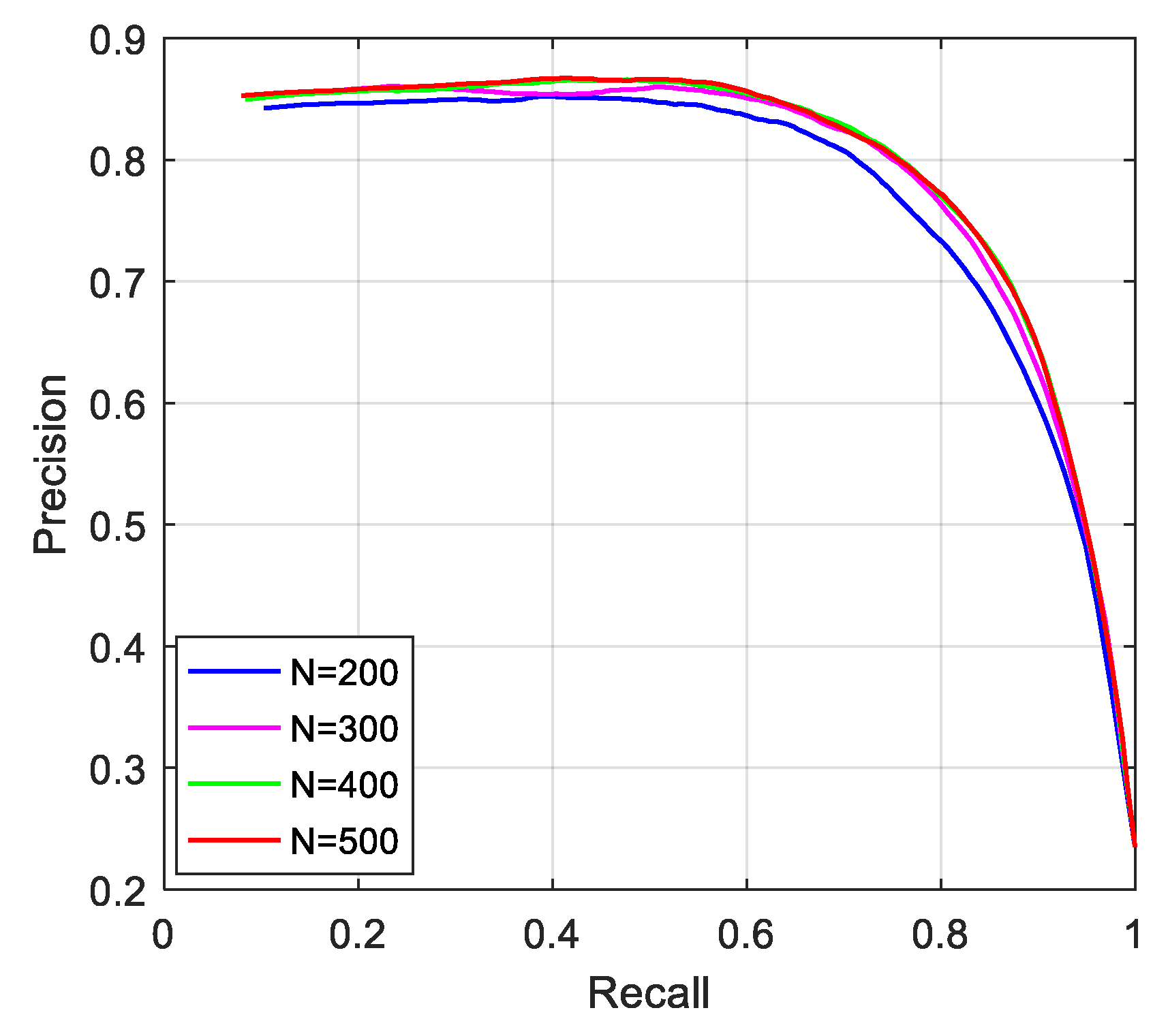
4.3. Comparison of Ablation Experiments
4.4. Extended Experiment on High-Resolution Dataset
4.5. Running Time
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, K.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chuang, Y.Y. DeepCO3: Deep Instance Co-Segmentation by Co-Peak Search and Co-Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8838–8847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qian, X.; Xue, Y. Scalable Mobile Image Retrieval by Exploring Contextual Saliency. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network Based on Salient Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 5009513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, F.; Xu, W. Saliency selection for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, China, 26–29 September 2010; pp. 2785–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, T.; Yang, K.; Li, Y.; Yan, H. Where Does the Driver Look? Top-Down-Based Saliency Detection in a Traffic Driving Environment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 2051–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A Model of Saliency-based Visual Attention for Rapid Scene Analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schölkopf, B.; Platt, J.; Hofmann, T. Graph-Based Visual Saliency. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19: Proceedings of the 2006 Conference; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, L. Saliency Detection: A Spectral Residual Approach. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Estrada, F.; Wils, P.; Süsstrunk, S. Salient Region Detection and Segmentation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achantay, R.; Hemamiz, S.; Estraday, F.; Süsstrunky, S. Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, CVPR Workshops 2009, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.M.; Zhang, G.X.; Mitra, N.; Huang, X.; Hu, S.M. Global Contrast Based Salient Region Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 37, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzi, F.; Krähenbühl, P.; Pritch, Y.; Hornung, A. Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, N.; Li, S. Salient Object Detection: A Discriminative Regional Feature Integration Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2083–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, M.H. Saliency Detection via Graph-Based Manifold Ranking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3166–3173. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Wei, L.; Yang, M.H.; Wu, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Ling, H.; Wang, J. DeepSaliency: Multi-Task Deep Neural Network Model for Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 25, 3919–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Han, J. DHSNet: Deep hierarchical saliency network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 678–686. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yu, Y. Visual Saliency Detection Based on Multiscale Deep CNN Features. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5012–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, C.; Wang, P.; Xu, H.; Wang, M.; Tian, J. Saliency Detection via Affinity Graph Learning and Weighted Manifold Ranking. Neurocomputing 2018, 312, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Du, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, K. Saliency Detection via Local Structure Propagation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2018, 52, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tseng, K.K.; Chow, T.W.; Wu, Q.J. Graph Model-based Salient Object Detection Using Objectness and Multiple Saliency Cues. Neurocomputing 2018, 323, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L. Salient Object Detection via Two-Stage Graphs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 29, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brbić, M.; Kopriva, I. Multi-view low-rank sparse subspace clustering. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 73, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L. Learning a Joint Affinity Graph for Multiview Subspace Clustering. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 1724–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, M.H. Saliency Detection via Absorbing Markov Chain. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1665–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, D. Salient Region Detection via Integrating Diffusion-Based Compactness and Local Contrast. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 3308–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Lu, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H. Saliency Detection via Cellular Automata. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, M.; Peng, G. Multiview diffusion-based affinity graph learning with good neighbourhoods for salient object detection. Appl. Intell. 2025, 55, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Razavian, A.S.; Azizpour, H.; Sullivan, J.; Carlsson, S. CNN Features Off-the-Shelf: An Astounding Baseline for Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Piramuthu, R. GraB: Visual Saliency via Novel Graph Model and Background Priors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 535–543. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P.; Song, H.Z.; Zhang, X.G. Local Regression Ranking for Saliency Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Li, K. Exploiting background divergence and foreground compactness for Salient object detection. Neurocomputing 2019, 383, 194–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Yang, X.; Nie, F.; Tao, D. Saliency Detection via a Multiple Self-Weighted Graph-Based Manifold Ranking. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 22, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, T.; Shen, S.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Liu, Q. Adaptive Graph Convolutional Network with Attention Graph Clustering for Co-Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9047–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Li, X.; Wei, L.; Wu, F.; Zhuang, Y. Context-Aware Graph Label Propagation Network for Saliency Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 8177–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, J.; Shao, X.; Wang, H. GroupTransNet: Group transformer network for RGB-D salient object detection. Neurocomputing 2024, 594, 127865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Sun, J.; Ren, P.; Wang, F.; Sun, F. MAGNet: Multi-scale Awareness and Global fusion Network for RGB-D salient object detection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2024, 299, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jia, Y.; Ma, L.; Yu, L. Recurrent Adaptive Graph Reasoning Network With Region and Boundary Interaction for Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5630720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lu, J.; Han, J.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S. Domain Separation Graph Neural Networks for Saliency Object Ranking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 3964–3974. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, W.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Dai, W.; Zou, J.; Xiong, H.; Frossard, P. 360Spred: Saliency Prediction for 360-Degree Videos Based on 3D Separable Graph Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 9979–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC Superpixels Compared to State-of-the-Art Superpixel Methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Ling, H.; Hu, W.; Xiong, W.; Maybank, S.J. Salient Object Detection via Structured Matrix Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, R.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Y.Y. Quaternionic Weber Local Descriptor of Color Images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2017, 27, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, Z.; Li, H. SDSP: A novel saliency detection method by combining simple priors. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, Australia, 15–18 September 2013; pp. 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, N.; Lu, H.; Ruan, X.; Yang, M.H. Salient Object Detection via Bootstrap Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1884–1892. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Xu, L.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Hierarchical Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 1155–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Movahedi, V.; Elder, J.H. Design and perceptual validation of performance measures for salient object segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yu, Y. Visual saliency based on multiscale deep features. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 5455–5463. [Google Scholar]
- Alpert, S.; Galun, M.; Brandt, A.; Basri, R. Image Segmentation by Probabilistic Bottom-Up Aggregation and Cue Integration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J. Saliency Optimization from Robust Background Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2814–2821. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, D. Salient Region Detection Using Diffusion Process on a Two-Layer Sparse Graph. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 5882–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Yu, S.; You, X. Coarse-to-fine salient object detection with low-rank matrix recovery. Neurocomputing 2020, 376, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, Y.J. RGB-‘D’ Saliency Detection With Pseudo Depth. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2126–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ai, J.; Jiang, B.; Lu, H.; Li, X. Saliency Detection via Absorbing Markov Chain With Learnt Transition Probability. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Feng, M.; Lu, H.; Cottrell, G.W. Hierarchical Cellular Automata for Visual Saliency. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2018, 126, 751–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Borji, A. Structure-Measure: A New Way to Evaluate Foreground Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4548–4557. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Gong, C.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Cheng, M.M.; Borji, A. Enhanced-alignment Measure for Binary Foreground Map Evaluation. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Main Track, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 698–704. [Google Scholar]
- Margolin, R.; Zelnik-Manor, L.; Tal, A. How to Evaluate Foreground Maps. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
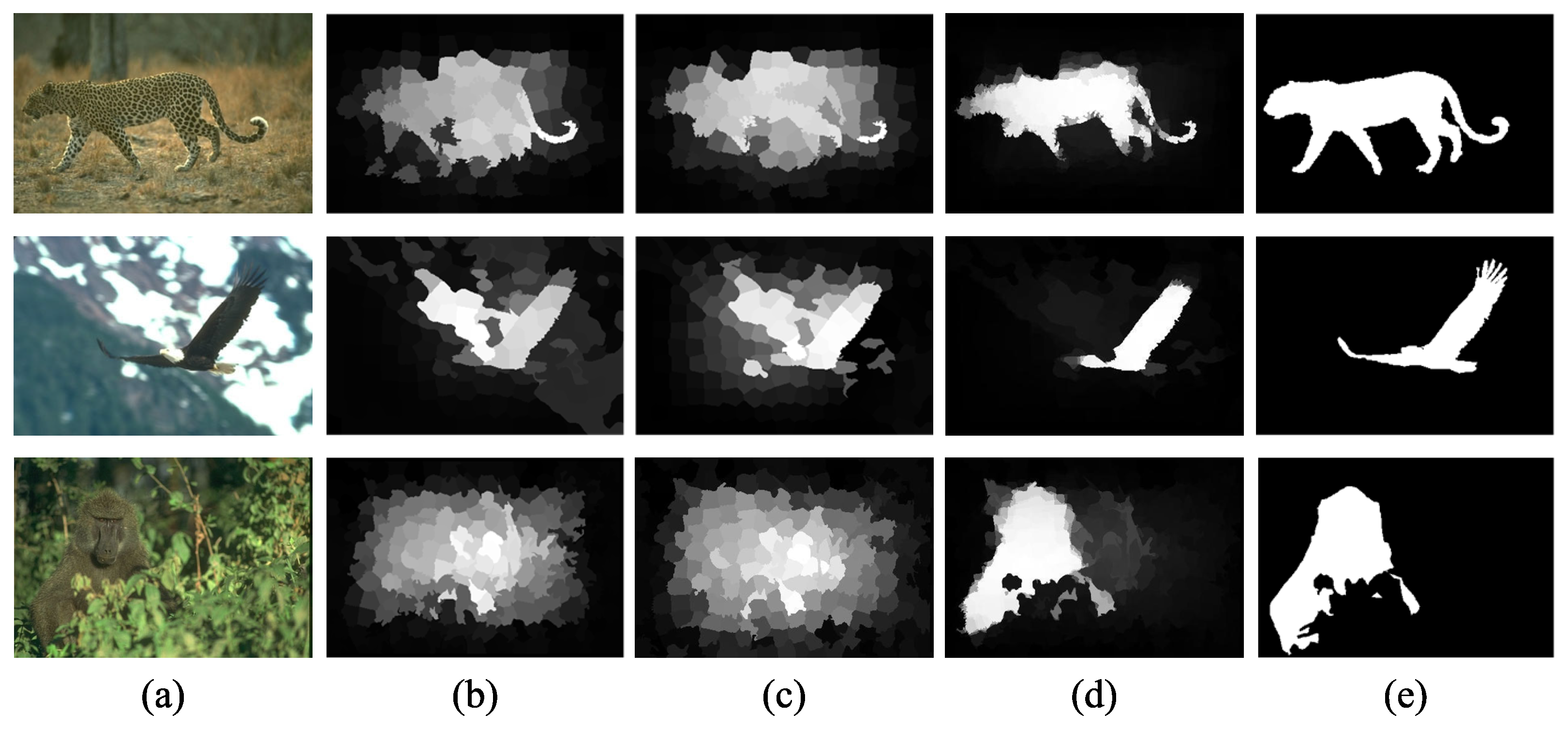
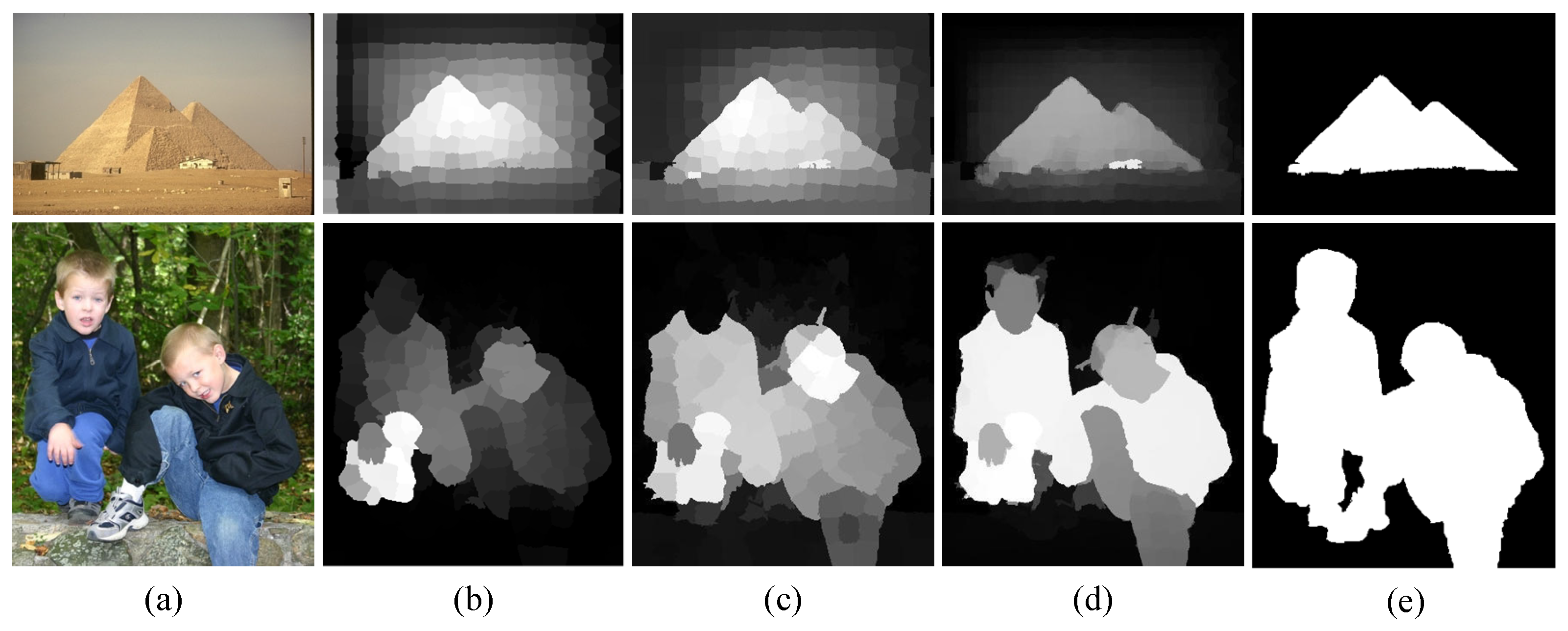
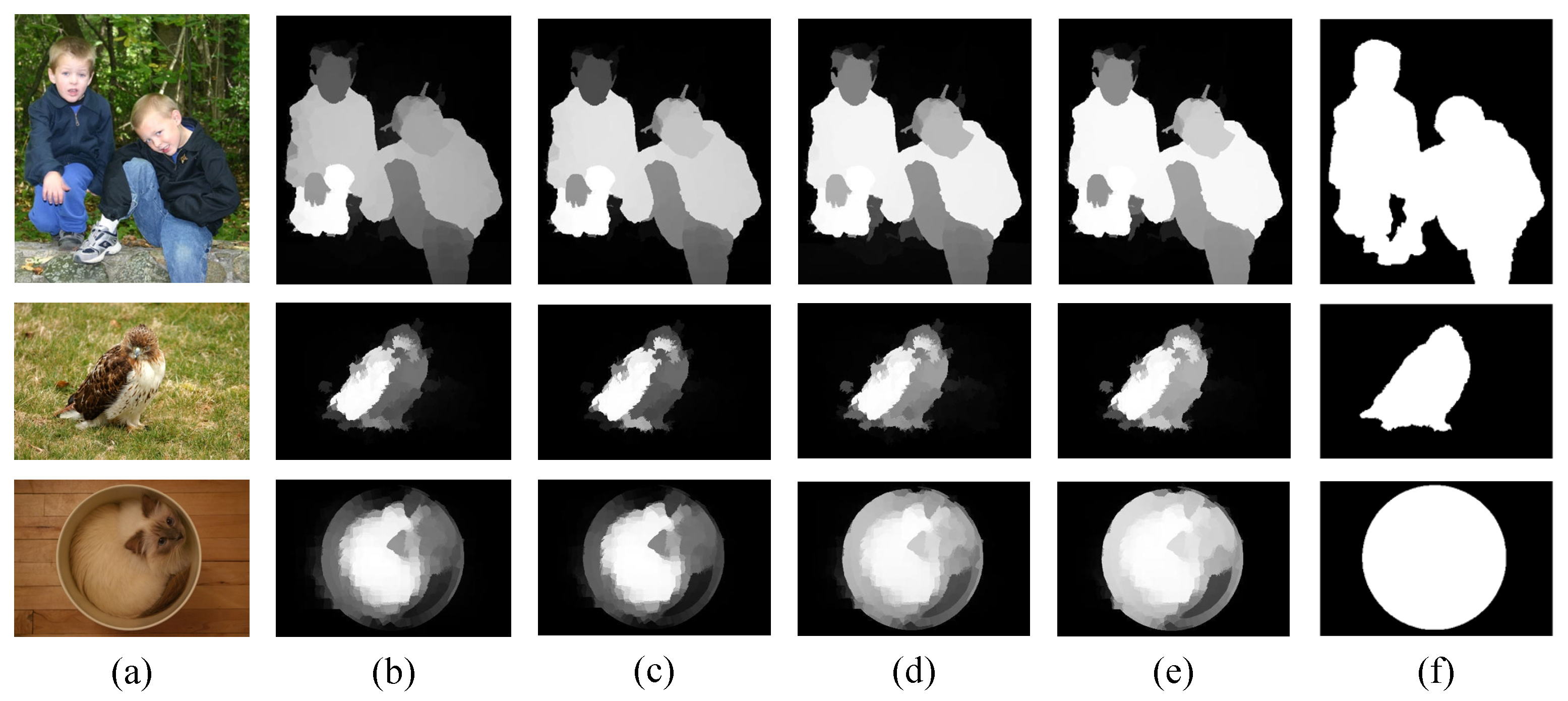





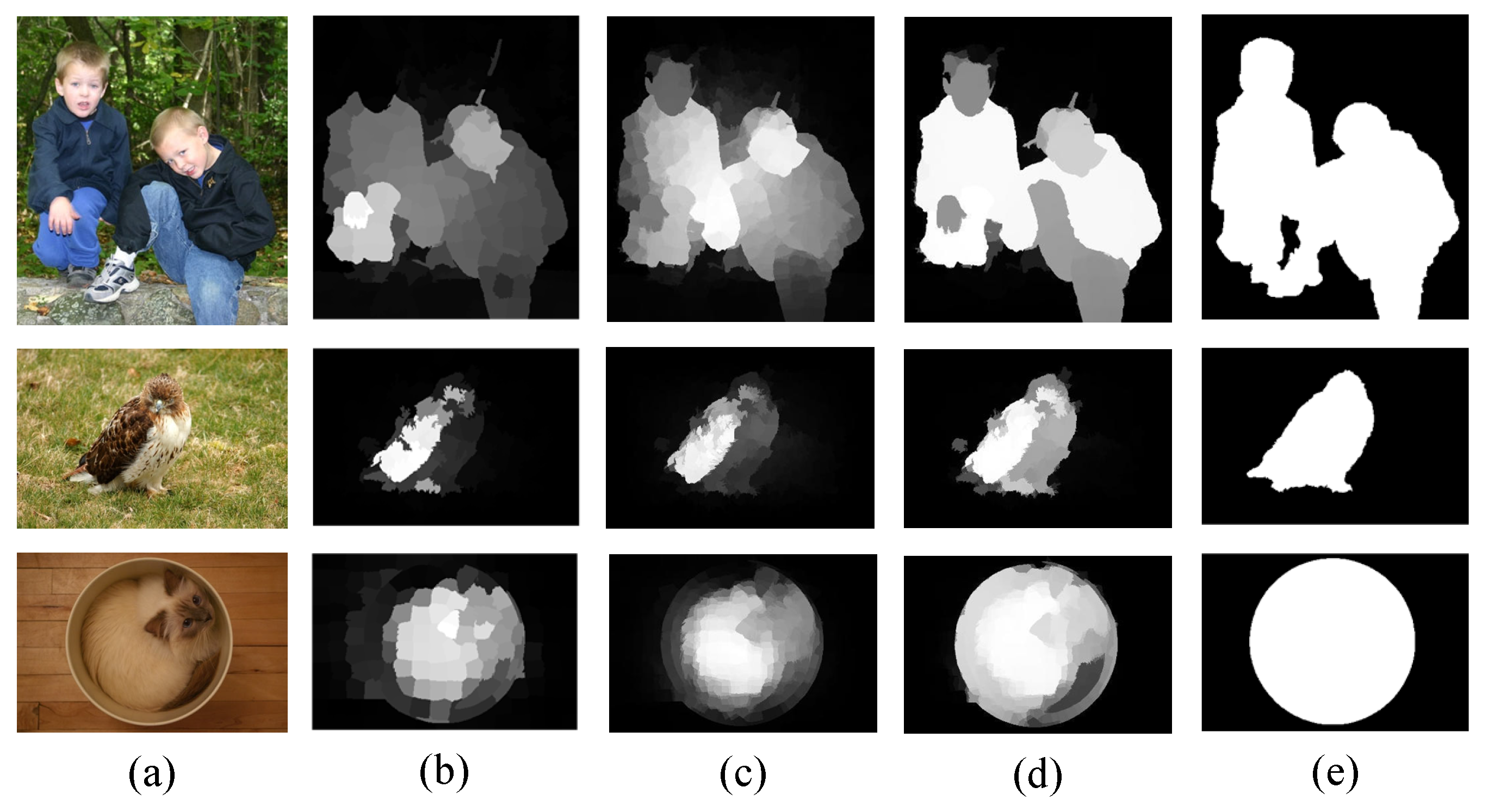


| Types | Feature Descriptions | Dim |
|---|---|---|
| Color features | The average RGB values of each superpixel | 3 |
| The average LAB values of each superpixel | 3 | |
| The average HSV values of each superpixel | 3 | |
| Texture features | The Gabor features of each superpixel [42] | 36 |
| The steerable pyramids features of each superpixel [42] | 12 | |
| The average LBP features of each superpixel | 1 | |
| The QWLD features of each superpixel [43] | 1 | |
| Saliency priors | The warm color prior map [44] | 1 |
| The SR prior map [8] | 1 | |
| The dark channel prior maps [45] | 3 |
| Methods | S-Measure ↑ | E-Measure ↑ | F-Measure ↑ | MAE ↓ | AUC ↑ | OR ↑ | WF ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRFI | 0.752 | 0.816 | 0.733 | 0.164 | 0.833 | 0.584 | 0.542 |
| GMR | 0.689 | 0.774 | 0.689 | 0.189 | 0.790 | 0.520 | 0.493 |
| RBD | 0.689 | 0.787 | 0.676 | 0.189 | 0.781 | 0.525 | 0.513 |
| BSCA | 0.725 | 0.797 | 0.702 | 0.182 | 0.815 | 0.549 | 0.513 |
| SMD | 0.734 | 0.800 | 0.712 | 0.173 | 0.811 | 0.560 | 0.537 |
| 2LSG | 0.702 | 0.786 | 0.703 | 0.181 | 0.795 | 0.541 | 0.510 |
| RCRR | 0.694 | 0.781 | 0.693 | 0.184 | 0.793 | 0.529 | 0.498 |
| WMR | 0.698 | 0.779 | 0.684 | 0.191 | 0.798 | 0.527 | 0.497 |
| AME | 0.775 | 0.824 | 0.789 | 0.168 | 0.832 | 0.628 | 0.586 |
| HCA | 0.707 | 0.825 | 0.778 | 0.119 | 0.781 | 0.616 | 0.674 |
| Ours | 0.756 | 0.821 | 0.756 | 0.145 | 0.816 | 0.614 | 0.603 |
| Methods | S-Measure ↑ | E-Measure ↑ | F-Measure ↑ | MAE ↓ | AUC ↑ | OR ↑ | WF ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRFI | 0.625 | 0.714 | 0.626 | 0.226 | 0.752 | 0.437 | 0.438 |
| GMR | 0.589 | 0.676 | 0.577 | 0.259 | 0.714 | 0.384 | 0.405 |
| RBD | 0.589 | 0.700 | 0.596 | 0.229 | 0.706 | 0.406 | 0.428 |
| BSCA | 0.622 | 0.692 | 0.582 | 0.252 | 0.738 | 0.396 | 0.432 |
| SMD | 0.632 | 0.702 | 0.606 | 0.234 | 0.732 | 0.378 | 0.411 |
| 2LSG | 0.591 | 0.670 | 0.606 | 0.254 | 0.702 | 0.378 | 0.420 |
| RCRR | 0.590 | 0.672 | 0.574 | 0.256 | 0.714 | 0.529 | 0.498 |
| WMR | 0.591 | 0.672 | 0.558 | 0.266 | 0.717 | 0.356 | 0.409 |
| AME | 0.633 | 0.704 | 0.677 | 0.229 | 0.752 | 0.454 | 0.490 |
| HCA | 0.639 | 0.702 | 0.634 | 0.203 | 0.694 | 0.435 | 0.537 |
| Ours | 0.642 | 0.716 | 0.637 | 0.219 | 0.732 | 0.454 | 0.491 |
| Methods | S-Measure ↑ | E-Measure ↑ | F-Measure ↑ | MAE ↓ | AUC ↑ | OR ↑ | WF ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRFI | 0.696 | 0.738 | 0.623 | 0.155 | 0.857 | 0.451 | 0.408 |
| GMR | 0.645 | 0.723 | 0.527 | 0.197 | 0.781 | 0.419 | 0.379 |
| RBD | 0.681 | 0.720 | 0.528 | 0.144 | 0.814 | 0.432 | 0.428 |
| BSCA | 0.652 | 0.706 | 0.567 | 0.191 | 0.808 | 0.409 | 0.392 |
| SMD | 0.680 | 0.728 | 0.572 | 0.166 | 0.809 | 0.440 | 0.424 |
| 2LSG | 0.664 | 0.741 | 0.573 | 0.177 | 0.795 | 0.494 | 0.406 |
| RCRR | 0.649 | 0.720 | 0.527 | 0.182 | 0.779 | 0.421 | 0.384 |
| AME | 0.613 | 0.713 | 0.692 | 0.271 | 0.841 | 0.425 | 0.283 |
| HCA | 0.671 | 0.701 | 0.539 | 0.156 | 0.776 | 0.438 | 0.475 |
| Ours | 0.704 | 0.753 | 0.589 | 0.144 | 0.815 | 0.491 | 0.464 |
| Methods | S-Measure ↑ | E-Measure ↑ | F-Measure ↑ | MAE ↓ | AUC ↑ | OR ↑ | WF ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRFI | 0.735 | 0.831 | 0.738 | 0.148 | 0.849 | 0.571 | 0.498 |
| GMR | 0.674 | 0.792 | 0.661 | 0.175 | 0.794 | 0.501 | 0.456 |
| RBD | 0.707 | 0.812 | 0.677 | 0.143 | 0.810 | 0.538 | 0.516 |
| BSCA | 0.700 | 0.794 | 0.649 | 0.176 | 0.821 | 0.509 | 0.464 |
| SMD | 0.726 | 0.815 | 0.689 | 0.157 | 0.825 | 0.549 | 0.512 |
| 2LSG | 0.692 | 0.807 | 0.663 | 0.166 | 0.808 | 0.539 | 0.479 |
| RCRR | 0.679 | 0.794 | 0.664 | 0.171 | 0.797 | 0.507 | 0.459 |
| AME | 0.765 | 0.860 | 0.772 | 0.137 | 0.845 | 0.636 | 0.573 |
| HCA | 0.743 | 0.824 | 0.740 | 0.113 | 0.786 | 0.581 | 0.628 |
| Ours | 0.745 | 0.829 | 0.725 | 0.132 | 0.826 | 0.592 | 0.567 |
| Methods | S-Measure ↑ | E-Measure ↑ | F-Measure ↑ | MAE ↓ | AUC ↑ | OR ↑ | WF ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRFI | 0.766 | 0.810 | 0.731 | 0.130 | 0.828 | 0.613 | 0.637 |
| GMR | 0.688 | 0.807 | 0.727 | 0.184 | 0.728 | 0.541 | 0.570 |
| RBD | 0.751 | 0.830 | 0.780 | 0.130 | 0.776 | 0.598 | 0.641 |
| BSCA | 0.716 | 0.791 | 0.704 | 0.159 | 0.772 | 0.539 | 0.540 |
| SMD | 0.753 | 0.832 | 0.755 | 0.131 | 0.776 | 0.588 | 0.636 |
| 2LSG | 0.707 | 0.817 | 0.747 | 0.161 | 0.744 | 0.579 | 0.591 |
| RCRR | 0.692 | 0.798 | 0.727 | 0.160 | 0.733 | 0.542 | 0.576 |
| WMR | 0.707 | 0.798 | 0.704 | 0.153 | 0.741 | 0.539 | 0.577 |
| AME | 0.701 | 0.765 | 0.698 | 0.156 | 0.745 | 0.507 | 0.548 |
| Ours | 0.746 | 0.834 | 0.763 | 0.136 | 0.770 | 0.608 | 0.637 |
| Methods | S-Measure ↑ | E-Measure ↑ | F-Measure ↑ | MAE ↓ | AUC ↑ | OR ↑ | WF ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMR | 0.689 | 0.774 | 0.689 | 0.189 | 0.790 | 0.520 | 0.493 |
| Ours by | 0.697 | 0.771 | 0.671 | 0.192 | 0.803 | 0.524 | 0.497 |
| Ours | 0.756 | 0.821 | 0.756 | 0.145 | 0.816 | 0.614 | 0.603 |
| Methods | S-Measure ↑ | E-Measure ↑ | F-Measure ↑ | MAE ↓ | AUC ↑ | OR ↑ | WF ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1 of ours with | 0.744 | 0.814 | 0.748 | 0.162 | 0.828 | 0.608 | 0.559 |
| Stage 2 of ours with | 0.756 | 0.821 | 0.756 | 0.145 | 0.816 | 0.614 | 0.603 |
| Stage 1 of ours without | 0.729 | 0.807 | 0.739 | 0.164 | 0.821 | 0.593 | 0.549 |
| Stage 2 of ours without | 0.733 | 0.803 | 0.737 | 0.150 | 0.804 | 0.593 | 0.586 |
| Superpixels | F-Measure ↑ | MAE ↓ | AUC ↑ | OR ↑ | WF ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 200 | 0.677 | 0.148 | 0.782 | 0.579 | 0.591 |
| N = 300 | 0.677 | 0.144 | 0.805 | 0.605 | 0.602 |
| N = 400 | 0.660 | 0.146 | 0.817 | 0.617 | 0.603 |
| N = 500 | 0.673 | 0.150 | 0.824 | 0.613 | 0.594 |
| Methods | GMR | BSCA | DRFI | AME | HCA | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Runtime(s) | 0.21 | 0.29 | 2.93 | 5.11 | 1.59 | 2.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, F. Multi-Scale Pure Graphs with Multi-View Subspace Clustering for Salient Object Detection. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081262
Wang M, Yang H, Zhang Y, Wang W, Wang F. Multi-Scale Pure Graphs with Multi-View Subspace Clustering for Salient Object Detection. Symmetry. 2025; 17(8):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081262
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mingxian, Hongwei Yang, Yi Zhang, Wenjie Wang, and Fan Wang. 2025. "Multi-Scale Pure Graphs with Multi-View Subspace Clustering for Salient Object Detection" Symmetry 17, no. 8: 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081262
APA StyleWang, M., Yang, H., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., & Wang, F. (2025). Multi-Scale Pure Graphs with Multi-View Subspace Clustering for Salient Object Detection. Symmetry, 17(8), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081262






