LISA-YOLO: A Symmetry-Guided Lightweight Small Object Detection Framework for Thyroid Ultrasound Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
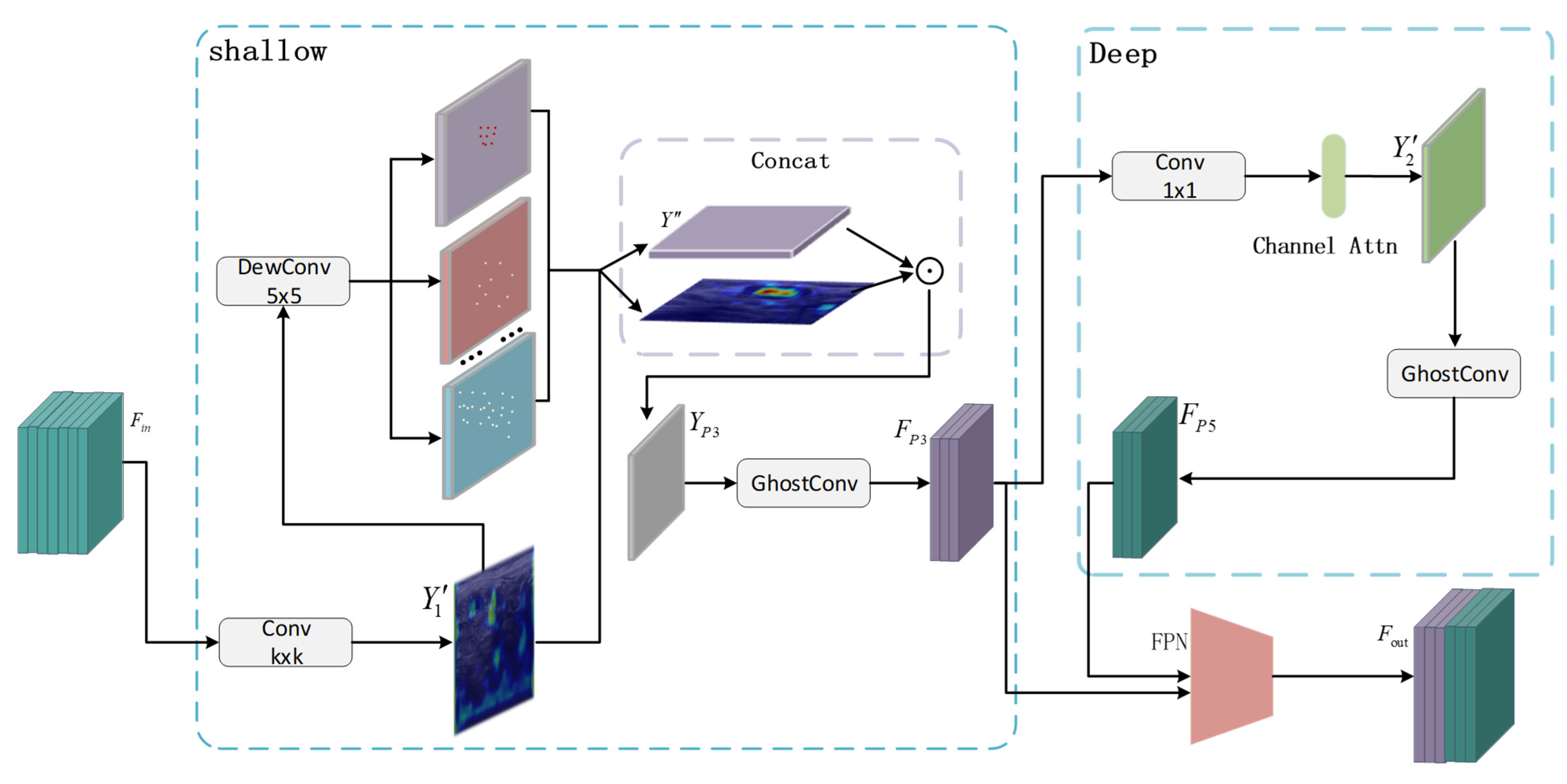
- This paper presents a lightweight dual-path feature extraction mechanism based on the Ghost module (DG-FNet), which enhances feature reuse while maintaining a lightweight architecture. The design incorporates structural symmetry in its dual-branch processing to effectively extract low-level and high-level semantic information in a balanced manner. A progressive feature optimization mechanism iteratively refines tumor features such as texture, shape, and boundaries. Additionally, deformable convolutions are utilized to generate flexible, symmetry-preserving “ghost features,” which protect fine-grained shallow features while reducing redundant deep semantics. This allows for dynamic adjustments of sampling locations to remain consistent with tumor deformations, while also reducing computational complexity and improving processing speed;
- (2)
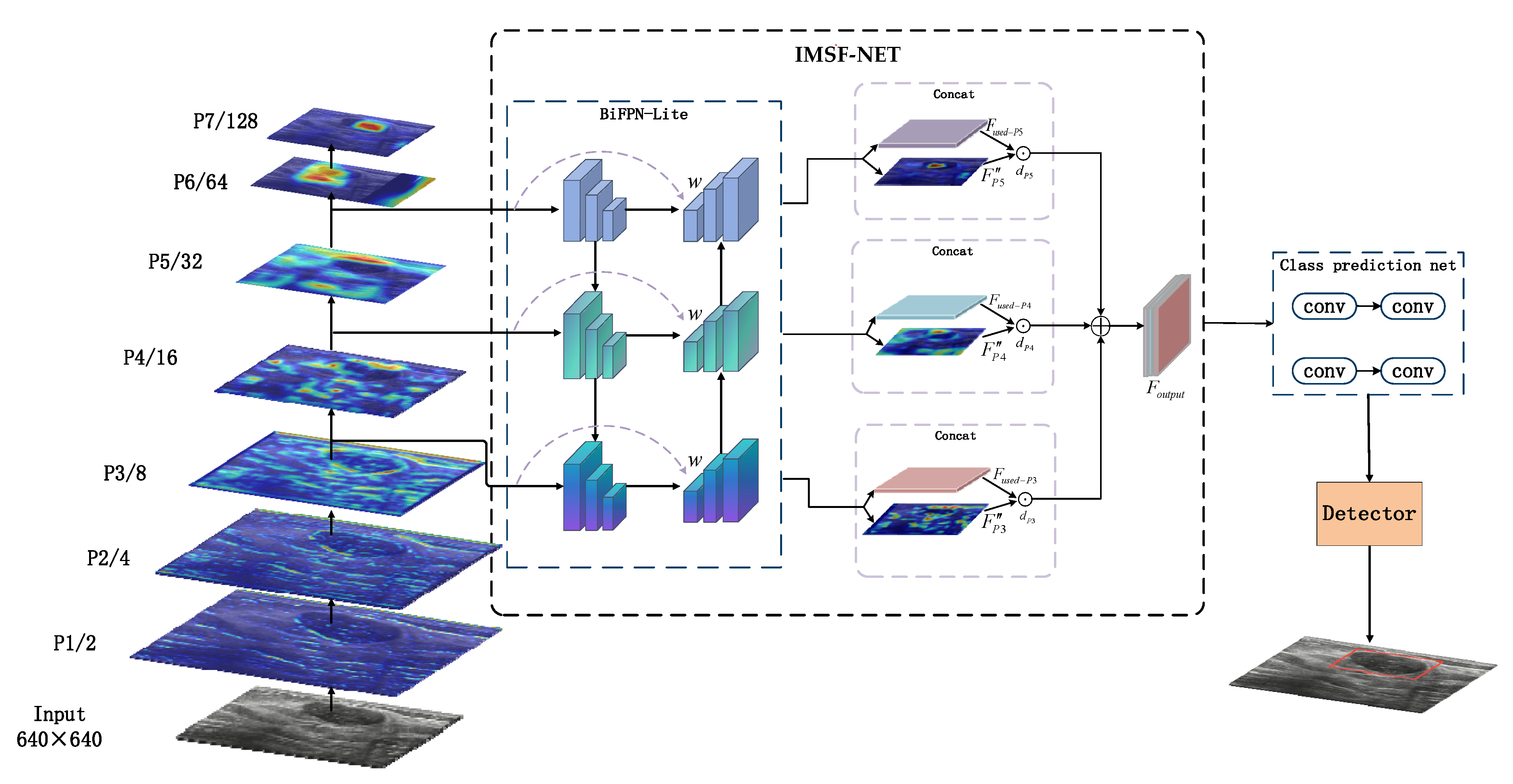
- This paper proposes the IMSF-Net module, an improvement based on the BiFPN architecture, which incorporates a symmetry-aware design in its bidirectional fusion path. Through dynamically weighted multi-scale feature aggregation, this module enhances cross-scale detection sensitivity while maintaining architectural balance. A hierarchical optimization strategy effectively integrates nodule localization and classification tasks. Furthermore, by symmetrically coordinating with YOLOv11’s original C3k2 module, IMSF-Net enhances small object detection performance with only a slight increase in computational cost;
- (3)
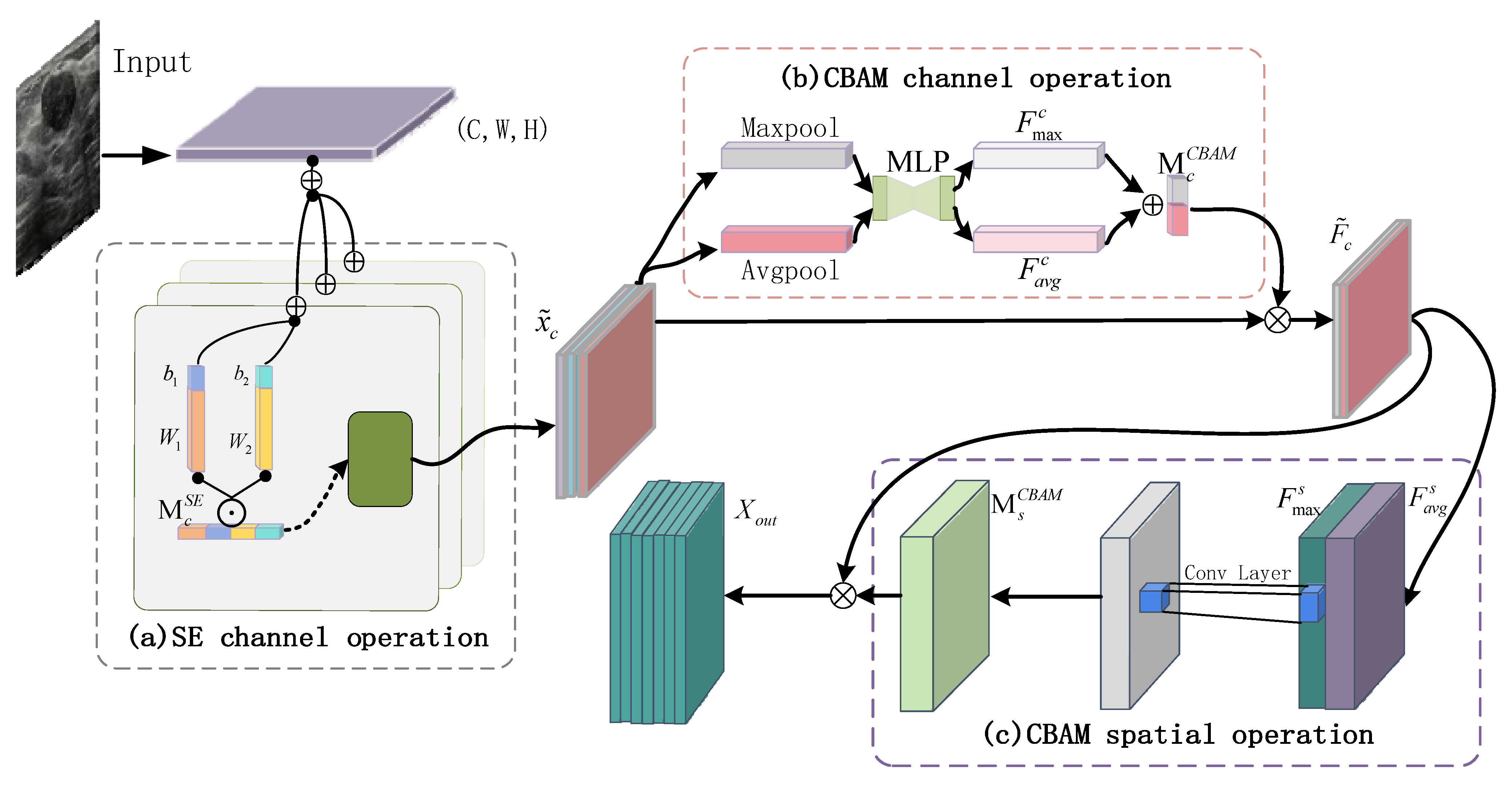
- This paper proposes a collaborative attention mechanism (SAF-Net) that combines channel-wise and spatial feature refinement within a symmetrical dual-branch architecture. Initially, features are filtered through a coarse channel attention process, followed by fine-grained selection of key diagnostic channels. This is subsequently complemented by spatial attention refinement. The collaborative attention structure ensures symmetric calibration of spatial and channel weights, enhancing the model’s focus on the boundaries and echogenic features of thyroid nodules. The guided attention constraint enforces structural coherence, allowing the model to dynamically highlight diagnostically relevant regions and significantly improve small object sensitivity and feature representation quality.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Methods for Diagnosing Thyroid Tumors
2.2. CNN-Based Detection Methods
2.3. YOLO-Based Tumor Detection Methods
3. Methods
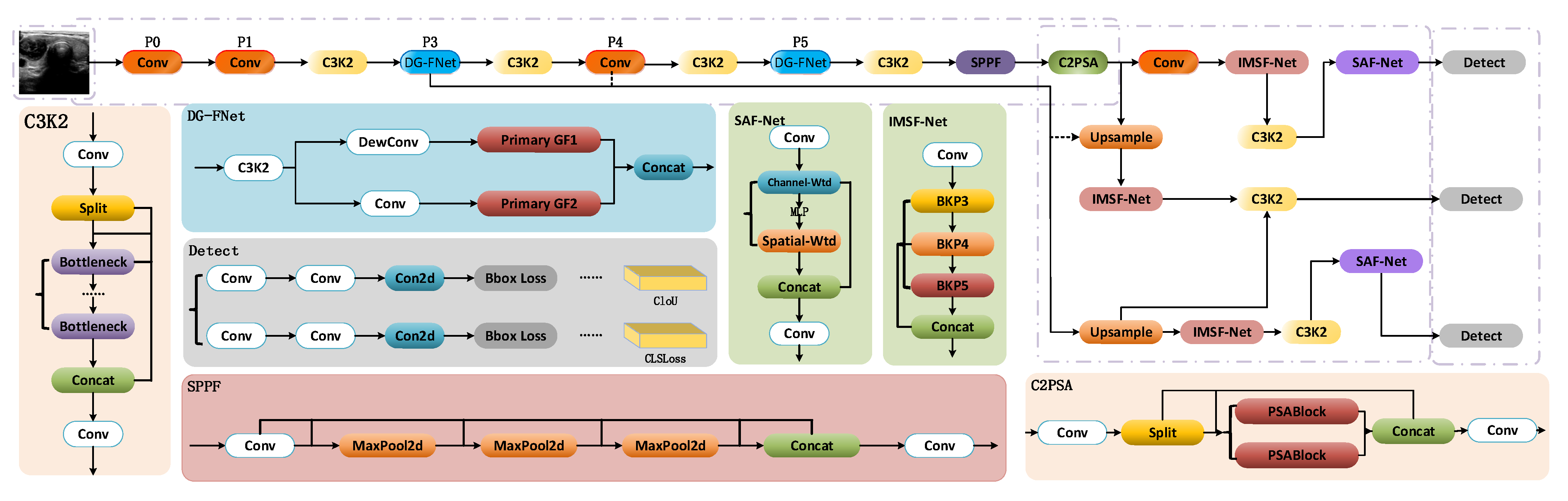
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. DG-FNET Module
3.3. Multi-Scale Feature Fusion IMSF-NET Module
3.4. Collaborative Attention Mechanism SAF-NET Module
4. Experiments and Results
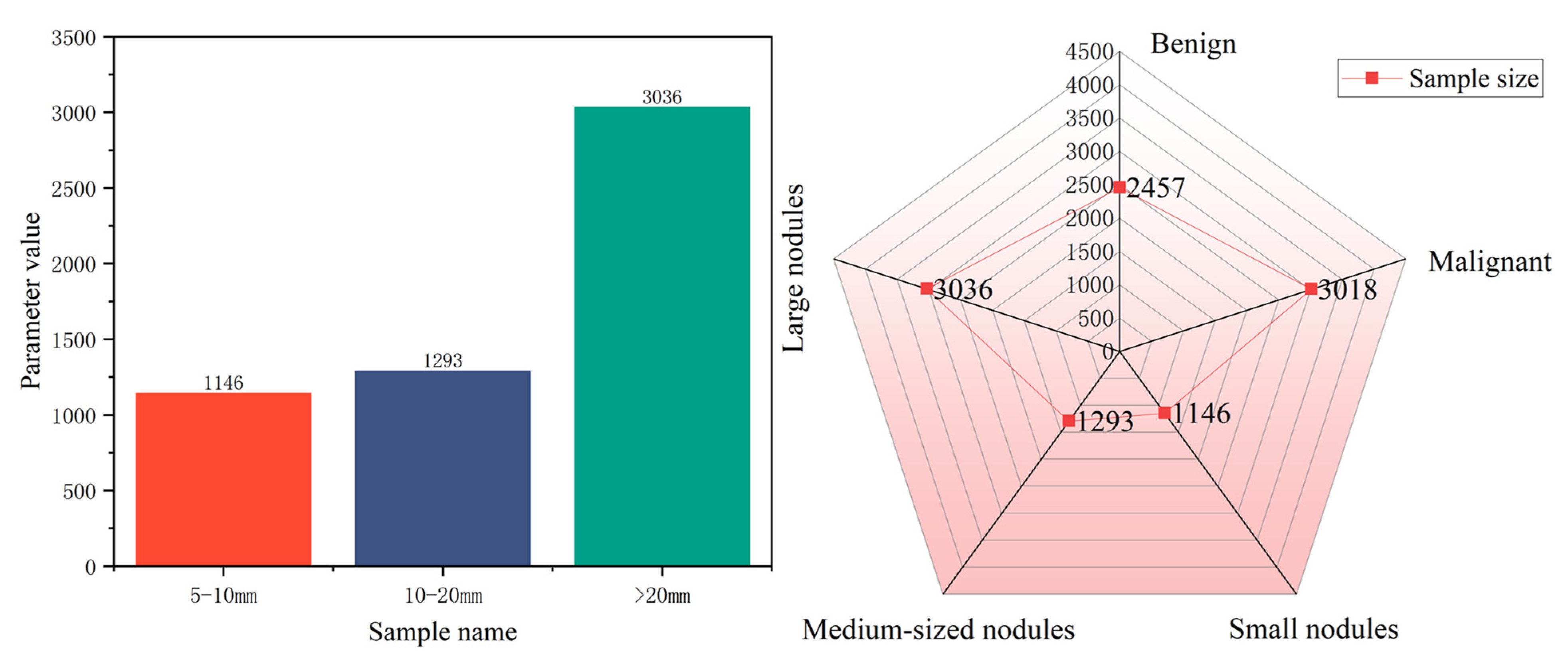
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Method Comparison and Results Analysis
4.4.1. Module Performance Comparison
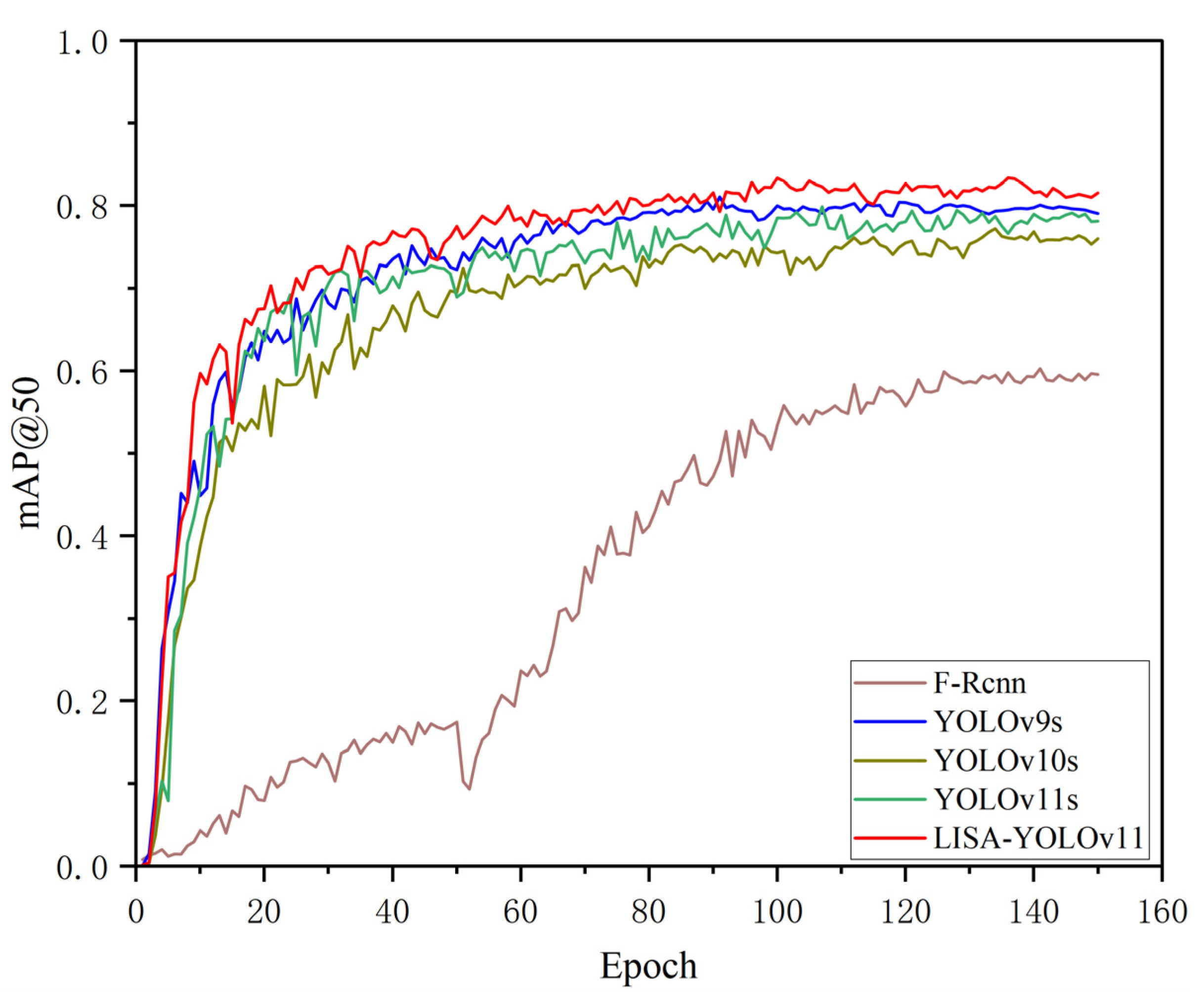
4.4.2. Method Comparison
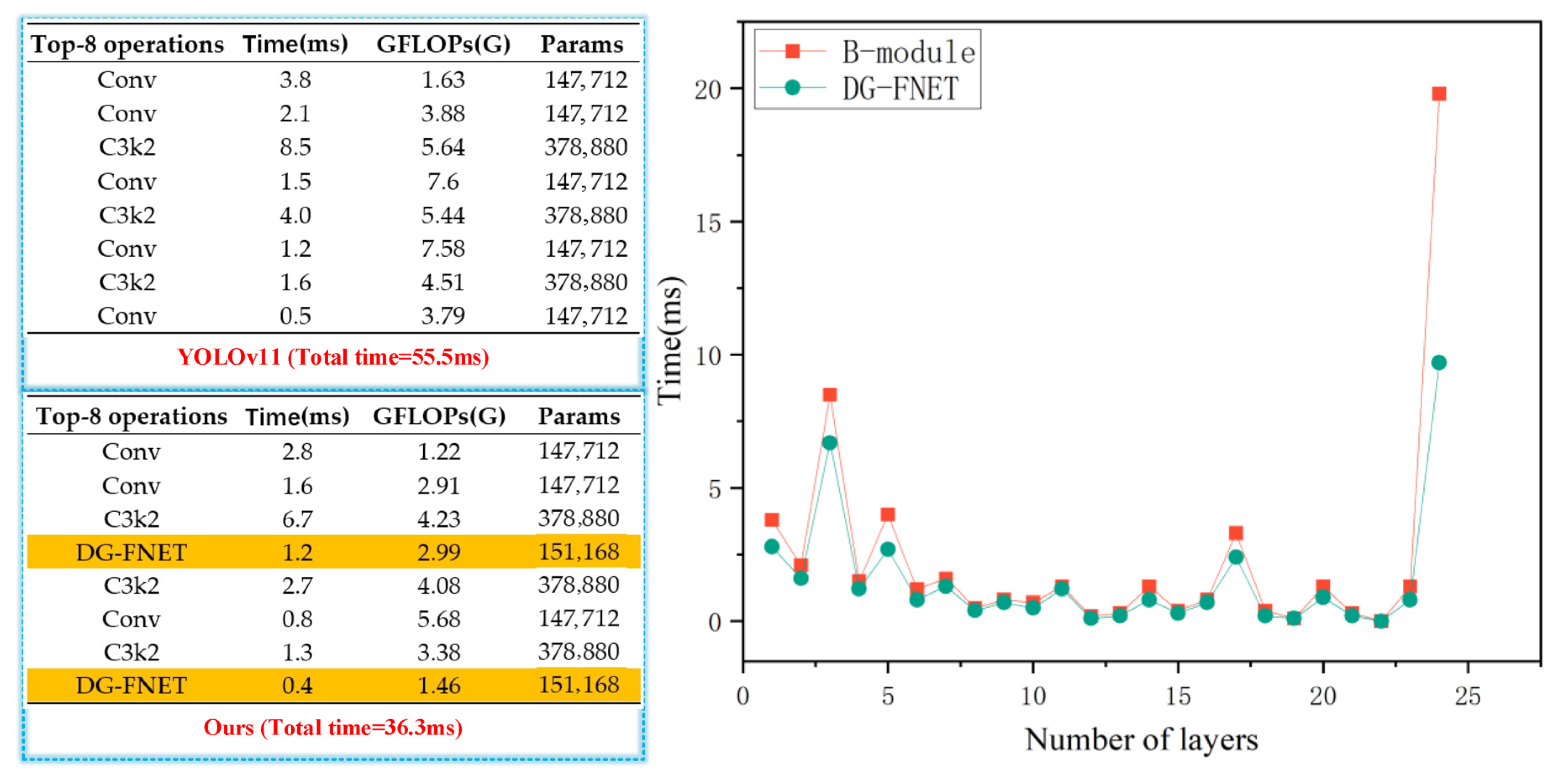
4.4.3. Benchmarking Strategy Across Devices
4.4.4. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Tan, G.; Luo, H.; Chen, Z.; Pu, B.; Li, S.; Li, K. A knowledge-interpretable multi-task learning framework for automated thyroid nodule diagnosis in ultrasound videos. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 91, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, Y.; Bakhshali, M.A.; Dehghani, T.; DanaiAshgzari, M.; Sargolzaei, M.; Eslami, S. Deep learning on ultrasound images of thyroid nodules. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 636–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Xia, J.; Li, R.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Qu, D.; You, J. Automatic thyroid nodule detection in ultrasound imaging with improved yolov5 neural network. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 22662–22670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahdati, S.; Khosravi, B.; Robinson, K.A.; Rouzrokh, P.; Moassefi, M.; Akkus, Z.; Erickson, B.J. A multi-view deep learning model for thyroid nodules detection and characterization in ultrasound imaging. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajilisa, O.A.; Jagathy Raj, V.P.; Sabu, M.K. A deep learning framework for the characterization of thyroid nodules from ultrasound images using improved inception network and multi-level transfer learning. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.-A.; Chen, Y.; Mao, Y.-J.; Cheung, J.C. Enhancing thyroid nodule detection in ultrasound images: A novel yolov8 architecture with a c2fa module and optimized loss functions. Echnologies 2025, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Geng, H.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; An, X.; Cong, Z. Identification of lesion location and discrimination between benign and malignant findings in thyroid ultrasound imaging. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 32118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekong, F.; Yu, Y.; Patamia, R.A.; Feng, X.; Tang, Q.; Mazumder, P.; Cai, J. Bayesian depth-wise convolutional neural network design for brain tumor mri classification. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibas, E.S.; Baloch, Z.W.; Fellegara, G.; LiVolsi, V.A.; Raab, S.S.; Rosai, J.; Diggans, J.; Friedman, L.; Kennedy, G.C.; Kloos, R.T.; et al. A prospective assessment defining the limitations of thyroid nodule pathologic evaluation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Diao, W.; Mu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Jia, Z. Radiomics in differentiated thyroid cancer and nodules: Explorations, application, and limitations. Cancers 2021, 13, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás, G.; Tarabichi, M.; Gacquer, D.; Hébrant, A.; Dom, G.; Dumont, J.E.; Keutgen, X.; Fahey, T.J.; Maenhaut, C.; Detours, V. A general method to derive robust organ-specific gene expression-based differentiation indices: Application to thyroid cancer diagnostic. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4490–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anari, S.; Tataei Sarshar, N.; Mahjoori, N.; Dorosti, S.; Rezaie, A.; Darba, A. Review of deep learning approaches for thyroid cancer diagnosis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xin, X.; Qin, C.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; et al. Diagnosis of thyroid cancer using deep convolutional neural network models applied to sonographic images: A retrospective, multicohort, diagnostic study. Lancet. Oncol. 2019, 20, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Z. A deep learning-based method for detecting and classifying the ultrasound images of suspicious thyroid nodules. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 7959–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wu, T.; Xu, X.; Dai, Q.; Kong, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, W.; Leng, X.; Qiu, W.; et al. Deep learning for the diagnosis of suspicious thyroid nodules based on multimodal ultrasound images. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1012724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, S.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, T.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, A.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, W.; et al. Ultrasound image-based deep learning to assist in diagnosing gross extrathyroidal extension thyroid cancer: A retrospective multicenter study. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Chang, L.; Yu, R.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Yu, M.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y. Thyroid nodules risk stratification through deep learning based on ultrasound images. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 6355–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Cao, H.; Hu, K.; Wang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Gao, J.; Tang, Y. Geometry-aware 3d point cloud learning for precise cutting-point detection in unstructured field environments. J. Field Robot. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummalla, D.K.; Ganesan, S.; Pokhrel, S.; Somasiri, N. Enhanced early detection of thyroid abnormalities using a hybrid deep learning model: A sequential cnn and k-means clustering approach. J. Innov. Image Process. 2024, 6, 244–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Thyroid diagnosis from spect images using convolutional neural network with optimization. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 6212759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etehadtavakol, M.; Etehadtavakol, M.; Ng, E.Y.K. Enhanced thyroid nodule segmentation through u-net and vgg16 fusion with feature engineering: A comprehensive study. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2024, 251, 108209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-J.; Kim, J.-A.; Kim, N.; Hwangbo, Y.; Jeon, H.J.; Lee, D.-H.; Oh, J.E. Red-net: A neural network for 3d thyroid segmentation in chest ct using residual and dilated convolutions for measuring thyroid volume. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 3026–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Jiang, F.; Wei, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, W. Parathyroid gland detection based on multi-scale weighted fusion attention mechanism. Electronics 2025, 14, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussainan, N.F.; Ben Youssef, B.; Ben Ismail, M.M. A deep learning approach for brain tumor firmness detection based on five different yolo versions: YOLOv3–YOLOv7. Computation 2024, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almufareh, M.F.; Imran, M.; Khan, A.; Humayun, M.; Asim, M. Automated brain tumor segmentation and classification in mri using yolo-based deep learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 16189–16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinzi, F.; Insalaco, M.; Orlando, A.; Gaglio, S.; Vitabile, S. A yolo-based model for breast cancer detection in mammograms. Cogn. Comput. 2024, 16, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-T.; Yang, T.-Y.; Han, X.-H.; Piao, J.-C. Thyroid-detr: Thyroid nodule detection model with transformer in ultrasound images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2024, 98, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, S.; Nagaral, M.U. YOLOv8 based an automated segmentation and classification of thyroid nodules using usg images. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Innovation and Novelty in Engineering and Technology (INNOVA), Vijayapura, India, 20–21 December 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabri, H.; Fathallah, W.; Hamroun, M.; Othman, S.B.; Bellali, H.; Sakli, H.; Abdelkrim, M.N. Ai-enhanced thyroid detection using yolo to empower healthcare professionals. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Workshop on Mechatronic Systems Supervision (IW_MSS), Hammamet, Tunisia, 2–5 November 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Qiu, Y.; Han, L.; Liao, G.; Zhuang, Y.; Ma, B.; Luo, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, K. A lightweight network for automatic thyroid nodules location and recognition with high speed and accuracy in ultrasound images. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2022, 30, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
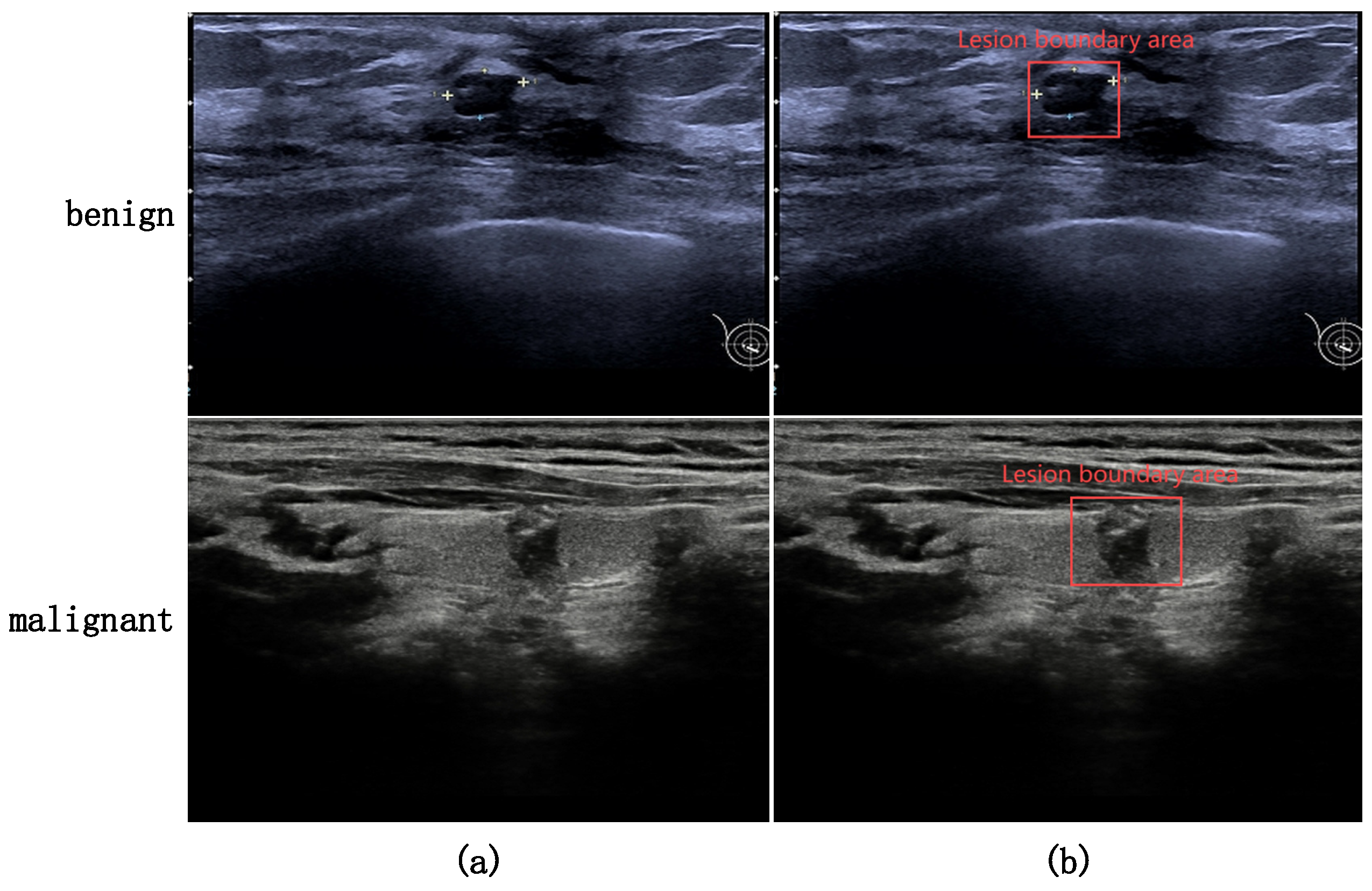

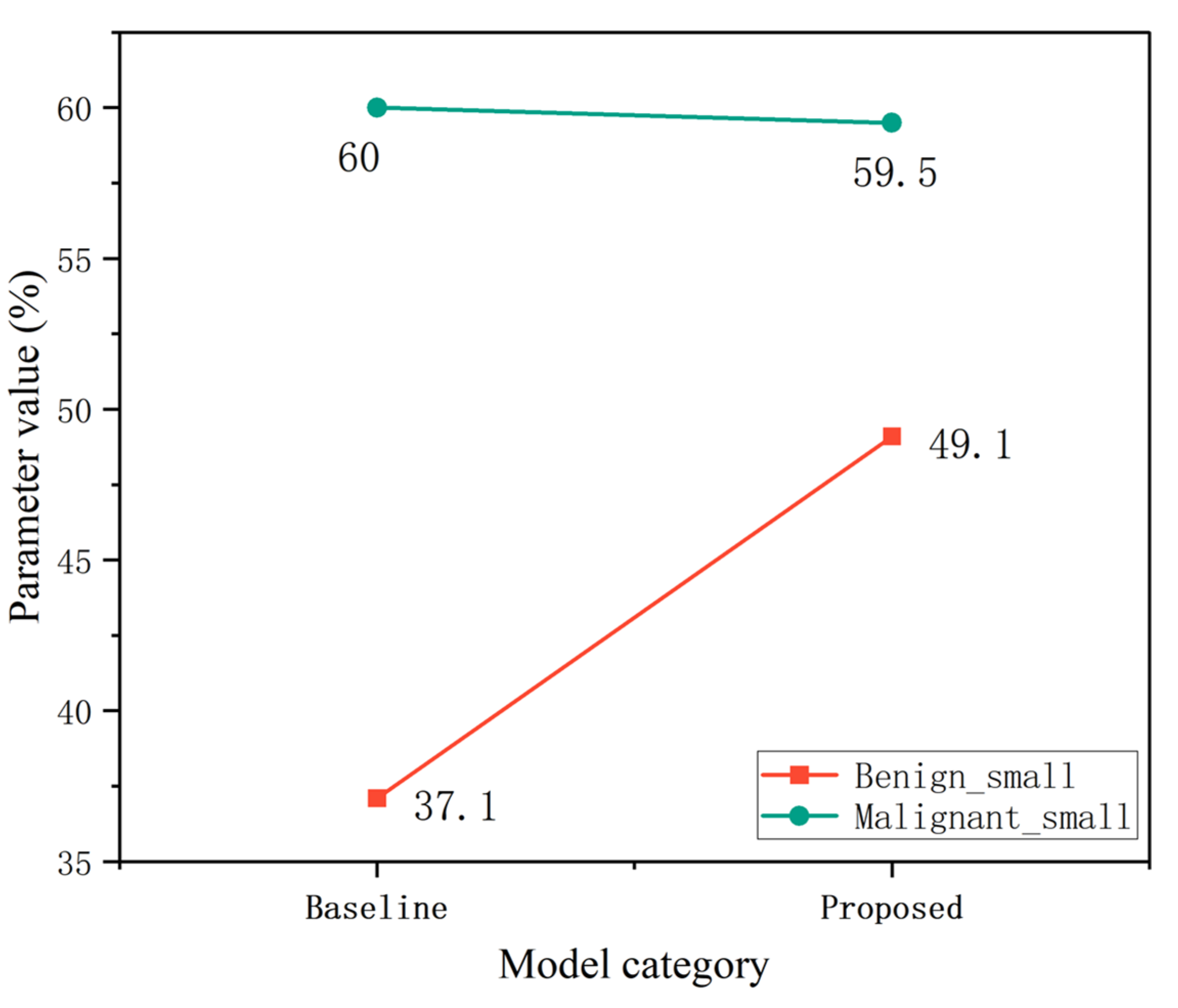
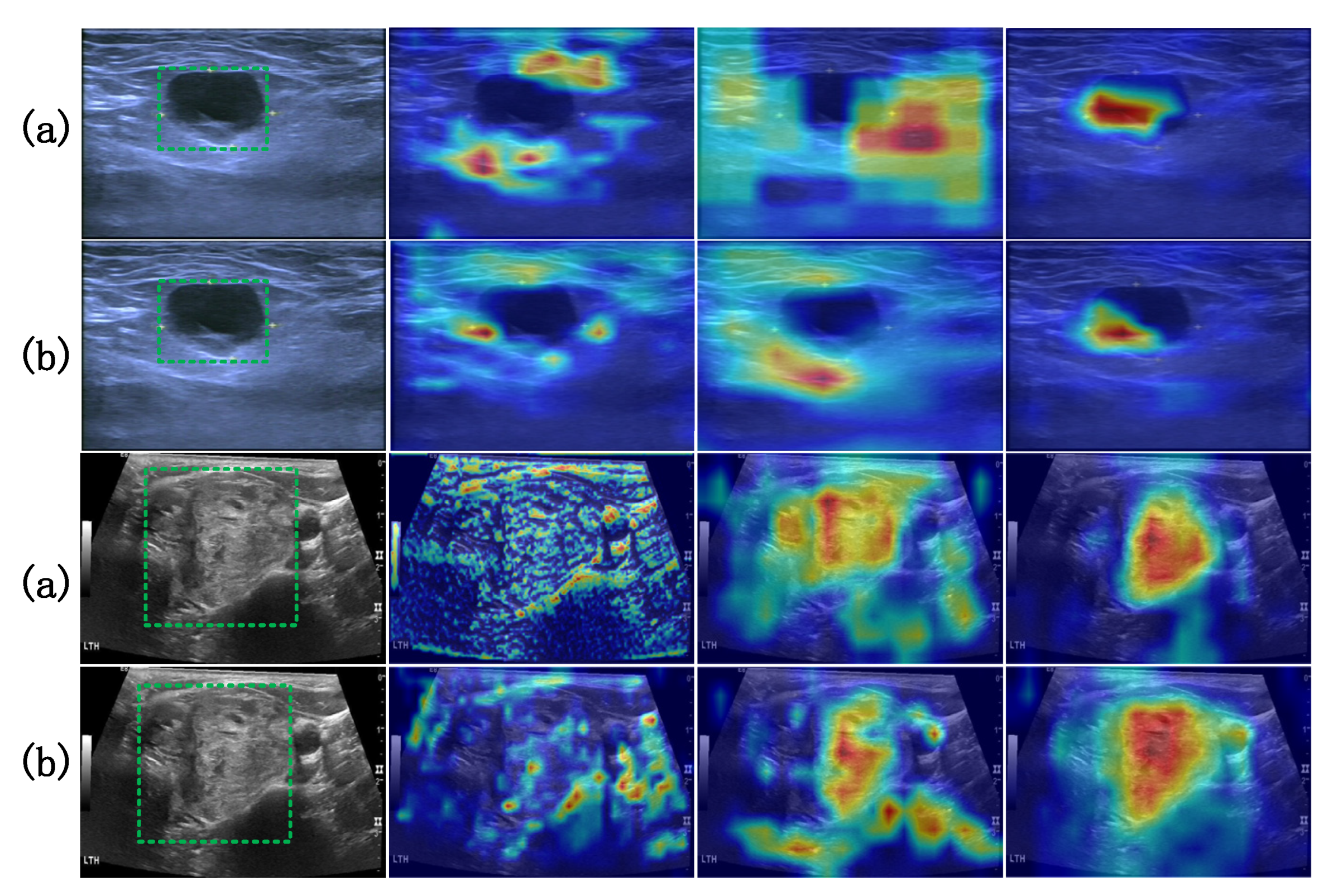
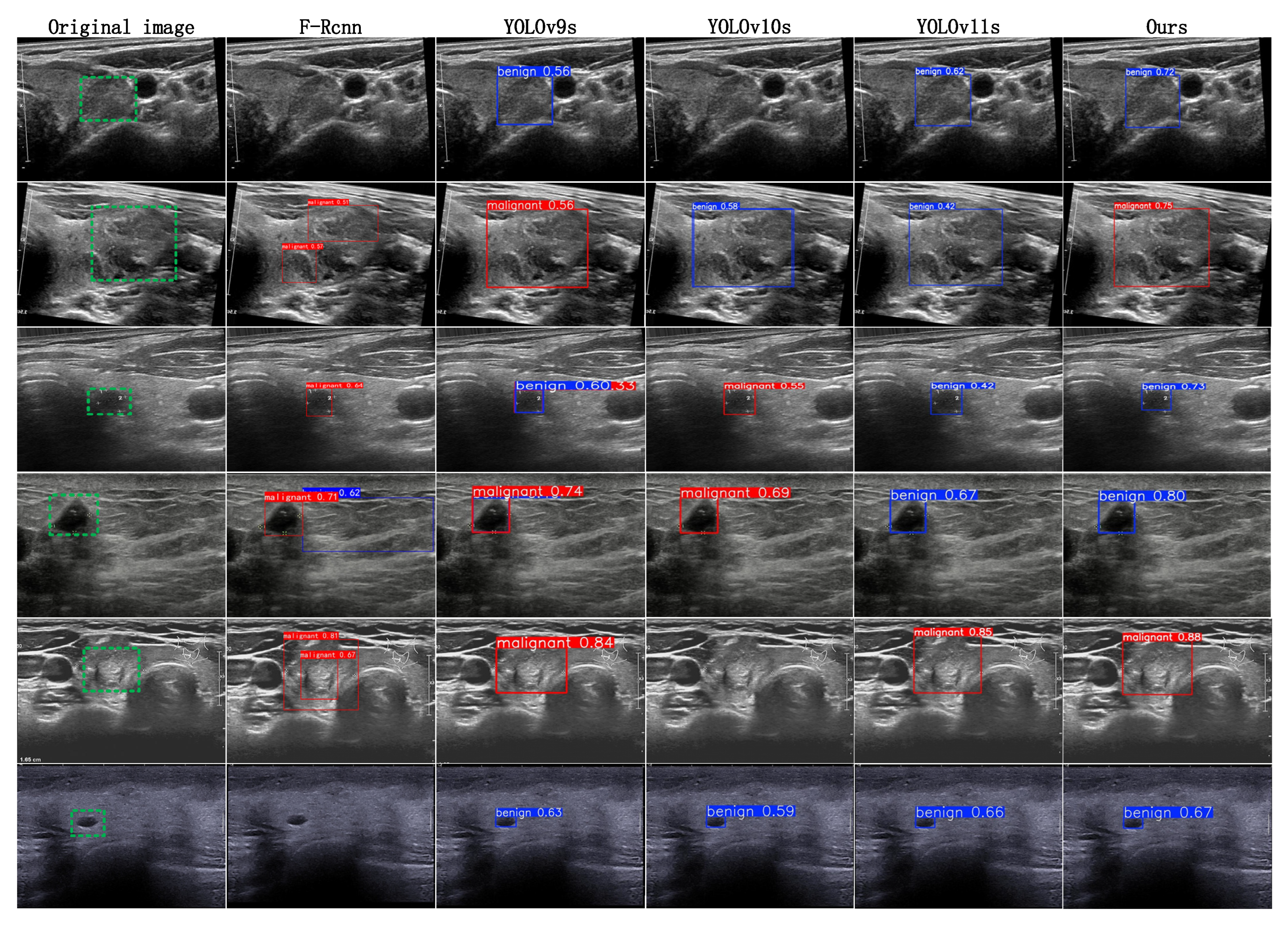

| Category | Baseline AP (%) | Proposed AP (%) | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign small | 69.1 | 69.3 | +0.2 |
| Malignant small | 76.8 | 80.4 | +3.6 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | mAP@50 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs (G) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster-Rcnn | 54.9 | 57.2 | 56.0 | 60.3 | 41.8 | — | 17.1 |
| YOLOv9s | 74.5 | 75.4 | 74.9 | 80.3 | 25.3 | 263.9 | 25.4 |
| YOLOv10s | 74.4 | 72.2 | 73.2 | 76.8 | 8.1 | 21.6 | 23.1 |
| YOLOv11s | 75.1 | 74.3 | 74.6 | 78.9 | 2.5 | 6.1 | 26.6 |
| Ours | 75.6 | 78.2 | 76.9 | 83.4 | 2.6 | 5.8 | 35.6 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | mAP@50 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs (G) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster-Rcnn | 52.2 | 54.4 | 53.2 | 58.34 | 41.8 | — | 17.1 |
| YOLOv9s | 74.7 | 71.5 | 73.1 | 79.7 | 25.3 | 263.9 | 25.4 |
| YOLOv10s | 75.8 | 68.5 | 71.9 | 75.7 | 8.1 | 21.6 | 23.1 |
| YOLOv11s | 77.5 | 74.1 | 75.7 | 77.8 | 2.5 | 6.1 | 26.6 |
| Ours | 74.3 | 76.0 | 75.2 | 81.6 | 2.6 | 5.8 | 35.6 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | mAP@50 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs (G) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster-Rcnn | 56.9 | 59.3 | 58.1 | 61.9 | 41.8 | — | 17.1 |
| YOLOv9s | 74.4 | 79.4 | 76.8 | 80.9 | 25.3 | 263.9 | 25.4 |
| YOLOv10s | 72.9 | 75.8 | 74.3 | 77.9 | 8.1 | 21.6 | 23.1 |
| YOLOv11s | 72.8 | 74.5 | 73.6 | 80.1 | 2.5 | 6.1 | 26.6 |
| Ours | 76.9 | 80.4 | 78.6 | 85.2 | 2.6 | 5.8 | 35.6 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | mAP@50 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs (G) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster-Rcnn | 62.6 | 69.8 | 66.0 | 75.7 | 41.8 | — | 21.9 |
| YOLOv9s | 82.5 | 85.3 | 83.8 | 89.9 | 25.3 | 263.9 | 31.6 |
| YOLOv10s | 88.9 | 89.7 | 89.2 | 94.5 | 8.1 | 21.6 | 32.4 |
| YOLOv11s | 87.4 | 87.2 | 87.3 | 93.1 | 2.5 | 6.1 | 32.9 |
| Ours | 91.7 | 90.5 | 91.1 | 94.9 | 2.6 | 5.8 | 38.9 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | mAP@50 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs (G) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster-Rcnn | 60.5 | 69.8 | 64.8 | 74.6 | 41.8 | — | 21.9 |
| YOLOv9s | 79.8 | 81.5 | 80.6 | 79.7 | 25.3 | 263.9 | 31.6 |
| YOLOv10s | 88.6 | 86.6 | 87.5 | 93.3 | 8.1 | 21.6 | 32.4 |
| YOLOv11s | 86.2 | 84.3 | 85.2 | 92.4 | 2.5 | 6.1 | 32.9 |
| Ours | 92.4 | 86.8 | 89.5 | 94.0 | 2.6 | 5.8 | 38.9 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | mAP@50 (%) | Param (M) | GFLOPs (G) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster-Rcnn | 64.5 | 69.5 | 66.9 | 76.3 | 41.8 | — | 21.9 |
| YOLOv9s | 85.2 | 89.1 | 87.1 | 91.8 | 25.3 | 263.9 | 31.6 |
| YOLOv10s | 89.2 | 92.9 | 91.0 | 95.7 | 8.1 | 21.6 | 32.4 |
| YOLOv11s | 88.7 | 90.0 | 89.3 | 93.9 | 2.5 | 6.1 | 32.9 |
| Ours | 90.9 | 94.1 | 92.5 | 95.8 | 2.6 | 5.8 | 38.9 |
| Device Type | Processor Model | GPU Model | RAM (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | Intel Core i7-14650HX (13th Gen, 16 cores, Raptor Lake-HX) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti Laptop GPU (16 GB, Ampere) | 32 |
| Model B | Intel Core i7-12850HX (12th Gen, 16 cores, Alder Lake-HX) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 Laptop GPU (8 GB, Ada Lovelace) | 32 |
| Model C | Intel Core i7-12700H (12th Gen, 14 cores, Alder Lake-H) | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Laptop GPU (6 GB, Ampere) | 16 |
| Method | RAM Cost (CPU) | RAM Cost (GPU) | FPS | Time Cost (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 5577.31 MB | 392.81 | 21.6 | 10.04 |
| Model B | 5753.80 | 500.29 | 18.8 | 13.07 |
| Model C | 6290.94 | 1270.17 | 17.5 | 13.23 |
| Experimental Programmes | A | B | C | F1 (%) | mAP@50 (%) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv11 | 74.6 | 78.9 | 26.6 | |||
| 1 | √ | 75.5 (+0.9) | 81.6 (+2.7) | 27.6 (+1.0) | ||
| 2 | √ | 75.8 (+1.2) | 81.7 (+2.8) | 27.4 (+0.8) | ||
| 3 | √ | 74.7 (+0.1) | 81.3 (+2.4) | 29.2 (+2.6) | ||
| 4 | √ | √ | 75.7 (+1.1) | 81.9 (+3.0) | 28.3 (+1.7) | |
| 5 | √ | √ | 76.2 (+1.6) | 82.8 (+3.9) | 31.2 (+4.6) | |
| 6 | √ | √ | 75.9 (+1.3) | 81.7 (+2.8) | 32.8 (+6.2) | |
| Ours | √ | √ | √ | 76.9 (+2.3) | 83.4 (+4.5) | 35.6 (+9.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, G.; Gu, G.; Liu, W.; Fu, H. LISA-YOLO: A Symmetry-Guided Lightweight Small Object Detection Framework for Thyroid Ultrasound Images. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081249
Fu G, Gu G, Liu W, Fu H. LISA-YOLO: A Symmetry-Guided Lightweight Small Object Detection Framework for Thyroid Ultrasound Images. Symmetry. 2025; 17(8):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081249
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Guoqing, Guanghua Gu, Wen Liu, and Hao Fu. 2025. "LISA-YOLO: A Symmetry-Guided Lightweight Small Object Detection Framework for Thyroid Ultrasound Images" Symmetry 17, no. 8: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081249
APA StyleFu, G., Gu, G., Liu, W., & Fu, H. (2025). LISA-YOLO: A Symmetry-Guided Lightweight Small Object Detection Framework for Thyroid Ultrasound Images. Symmetry, 17(8), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17081249





