A General Model Construction and Operating State Determination Method for Harmonic Source Loads
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Model of Harmonic Source Load
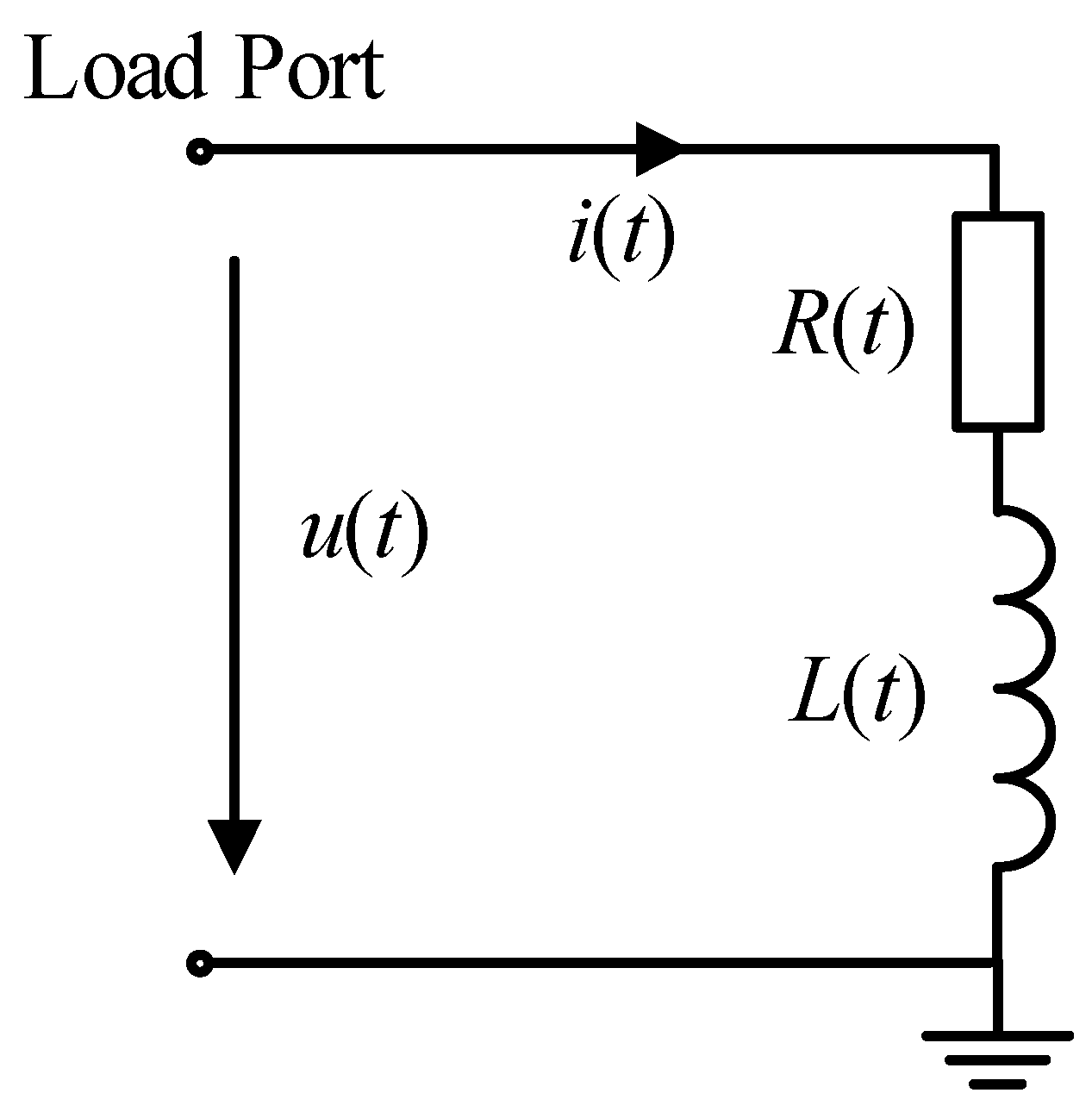
2.1. Basic Principle of Load Equivalent Impedance Parameters
2.2. Model Parameter Solution
3. Operation State Identification of Harmonic Source Loads
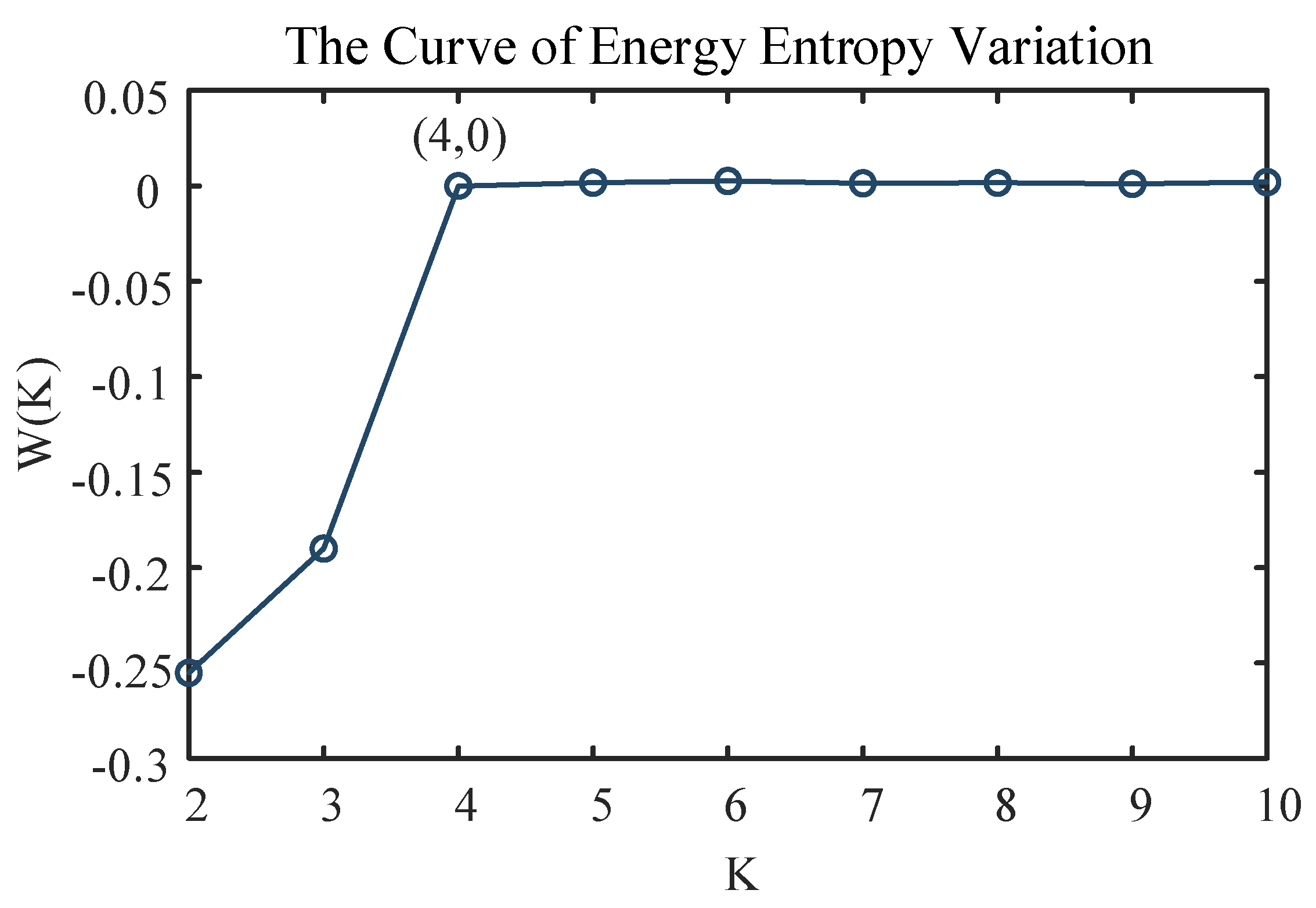
3.1. Variational Mode Decomposition
3.2. DBSCAN
3.3. Operation State Recognition Process
- Data Collection and Annotation
- 2.
- Sliding Window Preprocessing
- 3.
- Variational Mode Decomposition
- 4.
- Feature Extraction
- 5.
- Clustering Analysis
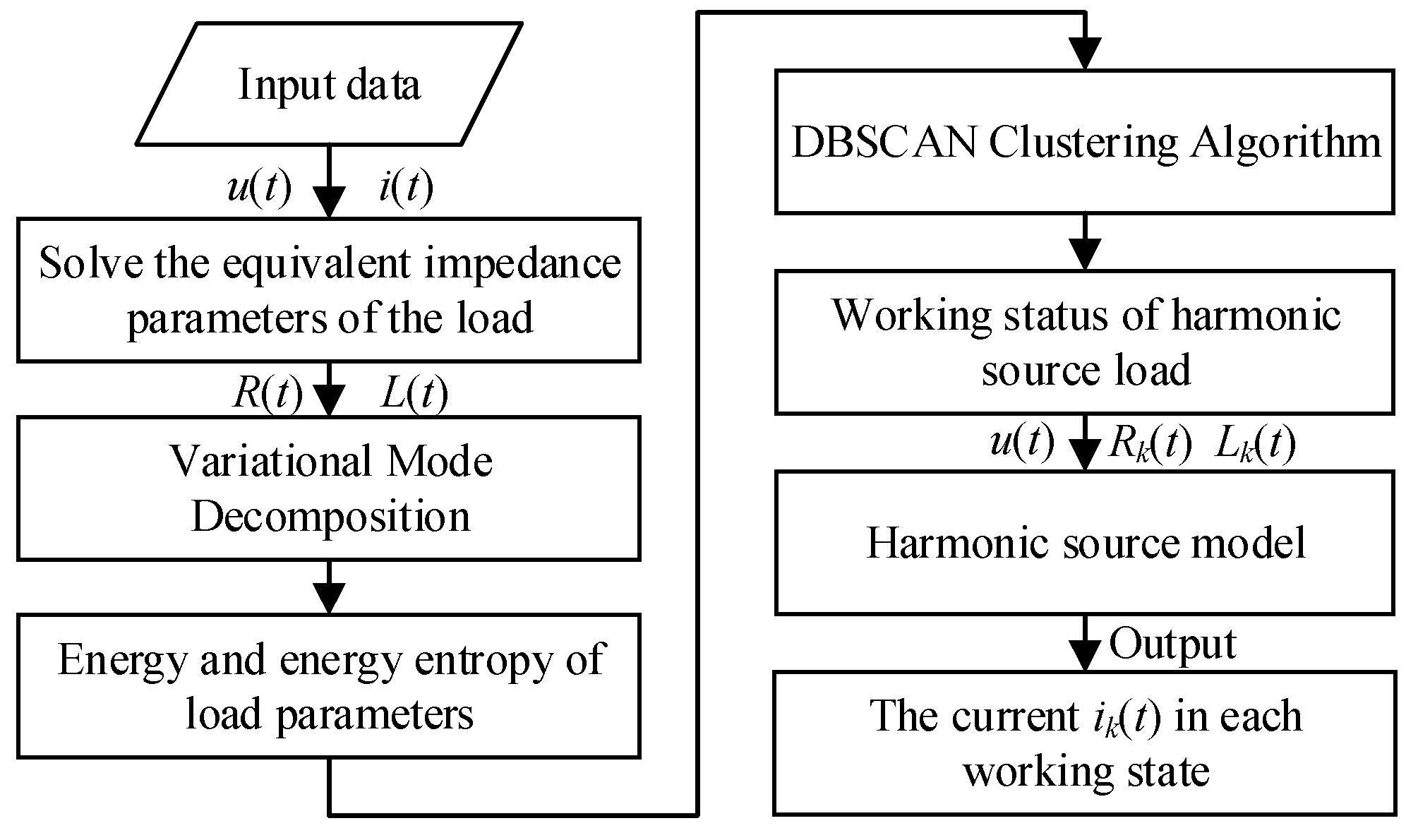
4. The Overall Modeling Process of the Model
5. Case Studies
5.1. Evaluation Indicators
5.2. Validation with Simulation Data
5.3. Verification with Measured Data
5.3.1. Effectiveness Verification of Operating State Identification
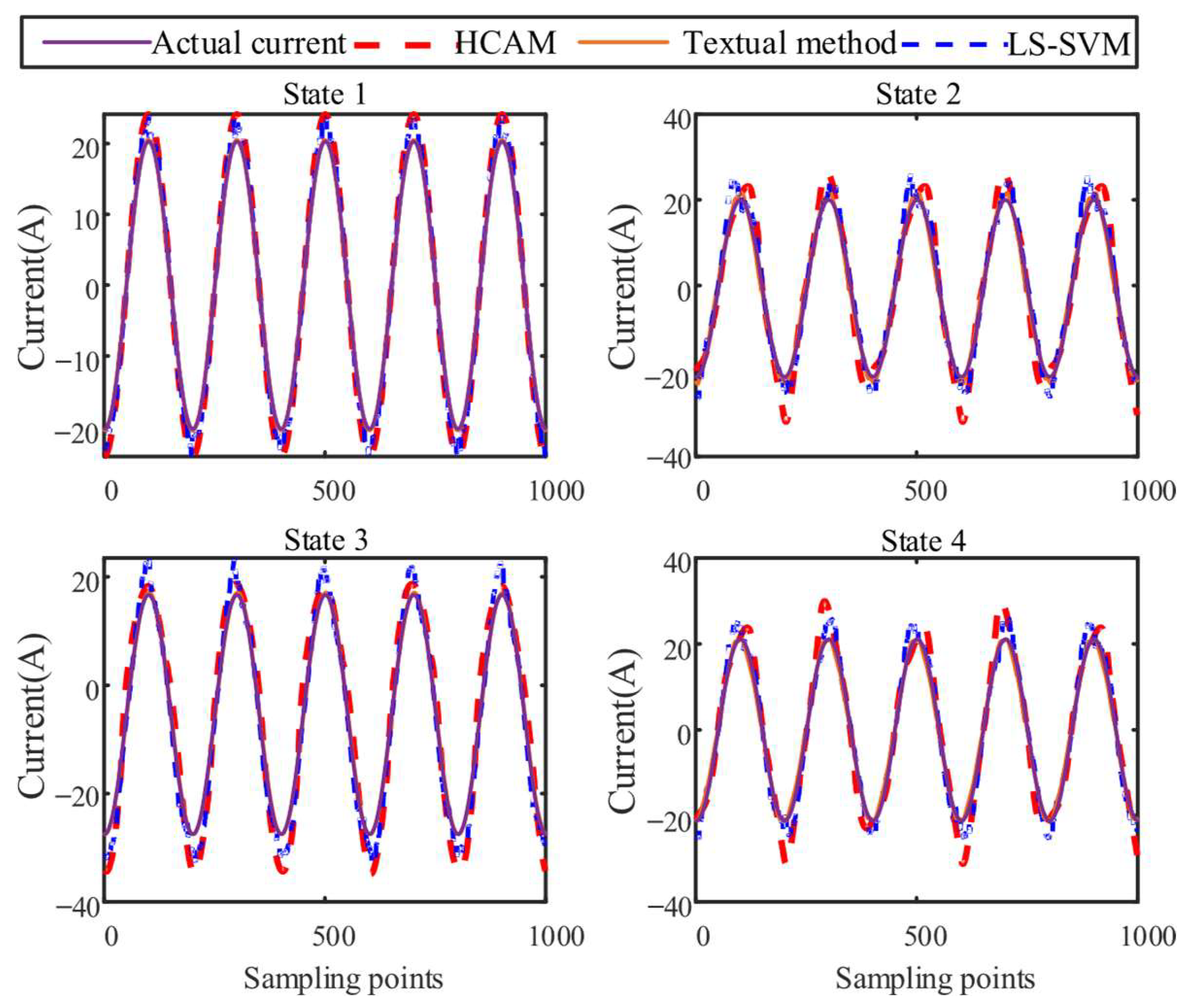
5.3.2. Model Validity Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Yong, J.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Wong, D. Characteristics of harmonic distortions in residential distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2017, 32, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, F.; Mao, H.; Ruan, Y.; Zhang, W. Modeling and analysis of harmonic interaction between multiple grid-connected inverters and power grid. Proc. CSEE 2013, 33, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, K.; Li, K.-J.; Zhang, Y. Probabilistic harmonic forecasting of the distribution system considering time-varying uncertainties of the distributed energy resources and electrical loads. Appl. Energy 2023, 329, 120298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, X.; Yao, W.; Wang, H.; Tang, Z. Unbalanced responsibility division considering renewable energy integration. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14, 6000–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, E. Time-varying parameter model of AC arc furnace for power quality prediction and analysis. Electr. Technol. 2016, 17, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, J. A new chaotic model of AC arc furnace for power quality research. Proc. CSEE 2008, 28, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, P.; Wang, W. Modeling and analysis of harmonic current in middle-frequency band in DFIG based wind turbines. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2018, 42, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, M.A.; Usaola, J. A new balanced harmonic load flow including nonlinear loads modeled with RBF networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2004, 19, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Milanović, J.V. Equivalent modelling of wind farms for probabilistic harmonic propagation studies. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marulanda-Durango, J.; Escobar-Mejía, A.; Alzate-Gómez, A.; Álvarez-López, M. A support vector ma-chine-based method for parameter estimation of an electric arc furnace model. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 196, 107228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, X. Combining transfer learning and constrained long short-term memory for power generation fore casting of newly-constructed photovoltaic plants. Renew. Energy 2022, 185, 1062–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Cheng, H.; Ge, N.; Huang, G. Generalized growing and pruning rbf neural network based harmonic source modeling. Proc. CSEE 2005, 25, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J. Harmonic source modeling based on generalized regression neural network. Adv. Technol. Electr. Eng. Energy 2012, 31, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, P.; Liu, X. Application of least squares support vector machine to harmonic sources modeling based on genetic algorithm. Power Syst. Prot. Control. 2011, 39, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Shao, Z.; Lin, F.; Lin, C. General and uncertain harmonic source model based on Gaussian process regression. Proc. CSEE 2021, 42, 992–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Lin, K.; Chen, J.; Pan, X. Typical modes analysis of harmonic customers based on the interval arithmetic. J. Electr. Power Sci. Technol. 2018, 33, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Yin, W.; Hu, W.; Tao, S. Prediction of power harmonic monitoring data based on LSTM algorithm. Power Capacit. React. Power Compens. 2019, 40, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Fang, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, J. Analysis and prediction of power quality trend of electrified railway. Comput. Digit. Eng. 2019, 47, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Strbac, G.; Kang, C. Using Bayesian deep learning to capture uncertainty for residential net load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zang, T.; Fu, L.; Zheng, Z. Adaptive method for dynamic harmonic state estimation in power system based on feature extraction of harmonic source. Power Syst. Technol. 2018, 42, 2612–2619. [Google Scholar]
- Fauri, M. Harmonic modelling of non-linear load by means of crossed frequency admittance matrix. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1997, 12, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, B.; Lin, C. Industrial Harmonic Source Load Classification Recognition Method Based on Blind Source Separation. Proc. CSEE 2024, 44, 3850–3862. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.; Cai, M.; Luo, J.; Zhu, B.; Tan, T. Harmonic Source Localization Method for Nonlinear Loads Based on Singular Value Decomposition. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2012, 36, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, K.; Shen, C.; Liang, S.; Huang, X. Outlier issues in harmonic source location based on parameter identification method. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Boston, MA, USA, 17–21 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, J.R. L-moments: Analysis and Estimation of Distributions using Linear Combinations of Order Statistics. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1990, 52, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Z.; Li, K.Q.; Wang, J.Q. A curving ACC system with coordination control of longitudinal car-following and lateral stability. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2012, 50, 1085–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Lei, A. Complex Signal Harmonic Source Modeling Method Based on Multivariate Gaussian Process Regression and DBSCAN Algorithm. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A.B.; Yong, J.; Xu, W. Measurement-based approach for constructing harmonic models of electronic home appliances. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2010, 4, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, P.; Liu, X.; Zheng, L. Harmonic source modeling based on least squares support vector machine. Electr. Energy Manag. Technol. 2010, 4, 58–62. [Google Scholar]


| State | Title 2 | Title 3 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | R | 15 Ω |
| L | 0.01 H | |
| 2 | R | 200 Hz 10 to 20 Ω sine waves |
| L | 50 Hz 0.01 to 0.02 H square wave | |
| 3 | R | 50 Hz 10 to 20 Ω square waves |
| L | 200 Hz 0.01 to 0.02 H sine waves | |
| 4 | R | 200 Hz 10 to 20 Ω sine waves |
| L | 200 Hz 0.01 to 0.02 H sine waves |
| Method | RMSE | Error Increase Compared to Z-Score |
|---|---|---|
| Z-score | 3.3601 | - |
| IQR | 3.8927 | 013.7% |
| Working State | State 1 | State 2 | State 3 | State 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nwro | 0 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.04 |
| nmiss | 0 | 0 | 0.17 | 0.2 |
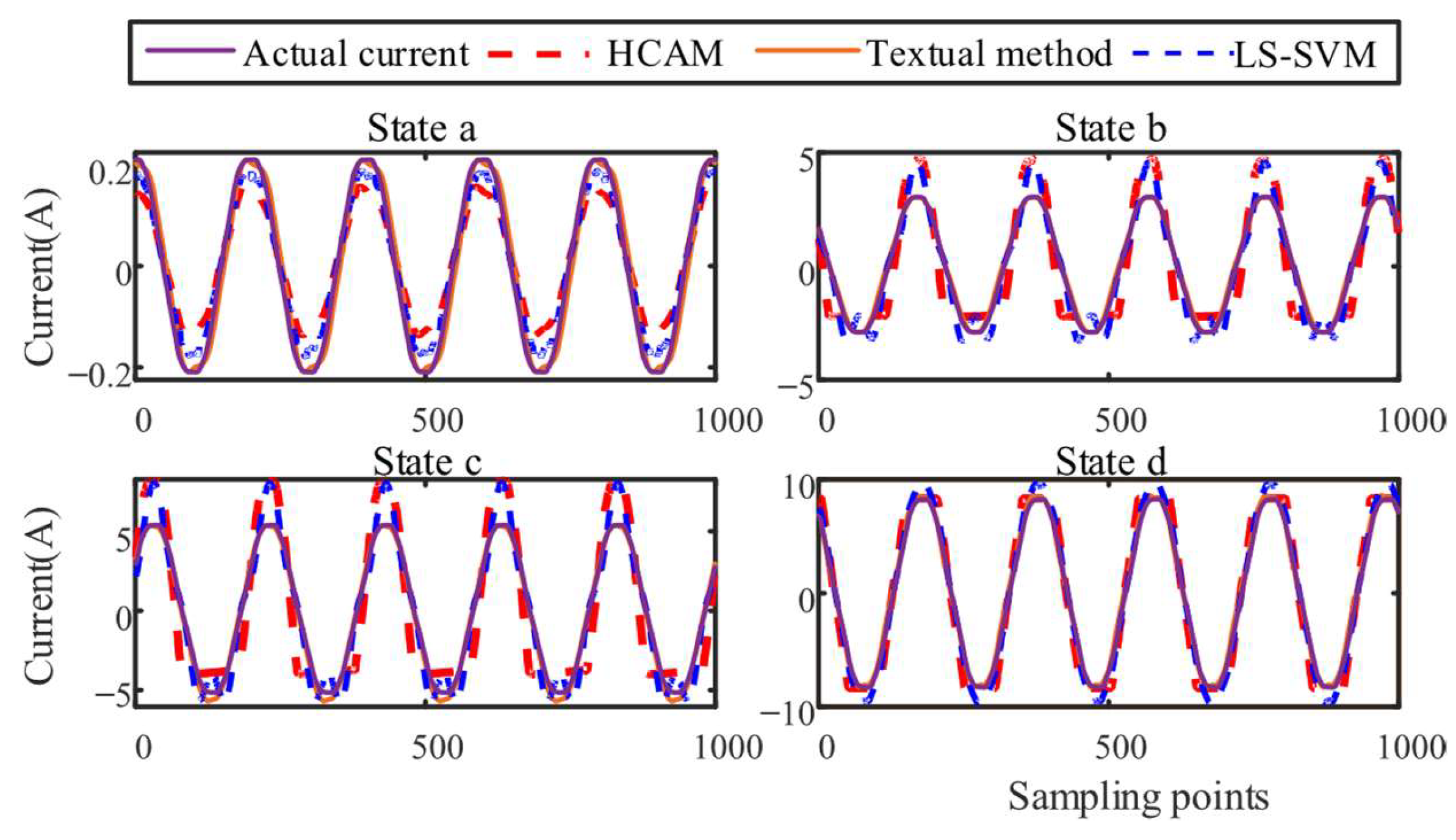
| State | Indicator | Proposed Method | HCAM | LS-SVM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MAE | 0.7366 | 2.3041 | 4.8973 |
| RMSE | 0.8226 | 2.5591 | 5.4191 | |
| R2 | 0.9977 | 0.9775 | 0.8991 | |
| 2 | MAE | 2.6163 | 2.8782 | 5.2376 |
| RMSE | 3.2128 | 3.7058 | 6.1614 | |
| R2 | 0.9666 | 0.9557 | 0.8774 | |
| 3 | MAE | 2.8253 | 3.2998 | 5.86 |
| RMSE | 3.3601 | 3.778 | 7.0667 | |
| R2 | 0.9686 | 0.9603 | 0.8611 | |
| 4 | MAE | 2.9031 | 2.6387 | 5.5608 |
| RMSE | 3.795 | 3.387 | 6.3409 | |
| R2 | 0.9554 | 0.9645 | 0.8756 |
| Working State | Hai | Fan | Mic | Lap |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nwro | 0 | 0 | 1.9 | 3.1 |
| nmiss | 0 | 0 | 2.4 | 2.3 |
| Working State | Textual Method | HCAM | LS-SVM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | MAE | RMSE | |
| Fan a | 0.1725 | 0.2006 | 0.2221 | 0.2446 | 0.2187 | 0.2630 |
| Fan b | 0.7786 | 0.9597 | 0.9881 | 1.1127 | 0.9436 | 1.0974 |
| Fan c | 1.3676 | 1.6761 | 1.7281 | 1.9522 | 1.6567 | 1.9258 |
| Fan d | 0.9248 | 1.1199 | 0.7836 | 0.9001 | 0.9114 | 1.1799 |
| Hai a | 0.0135 | 0.0162 | 0.0263 | 0.0297 | 0.0139 | 0.0163 |
| Hai b | 0.0258 | 0.0285 | 0.0258 | 0.0289 | 0.0174 | 0.0195 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Z.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, Y. A General Model Construction and Operating State Determination Method for Harmonic Source Loads. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071123
Zheng Z, Kang Y, Zhang Y. A General Model Construction and Operating State Determination Method for Harmonic Source Loads. Symmetry. 2025; 17(7):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071123
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Zonghua, Yanyi Kang, and Yi Zhang. 2025. "A General Model Construction and Operating State Determination Method for Harmonic Source Loads" Symmetry 17, no. 7: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071123
APA StyleZheng, Z., Kang, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2025). A General Model Construction and Operating State Determination Method for Harmonic Source Loads. Symmetry, 17(7), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071123







