A CML-ECA Chaotic Image Encryption System Based on Multi-Source Perturbation Mechanism and Dynamic DNA Encoding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Elementary Cellular Automata (ECA)
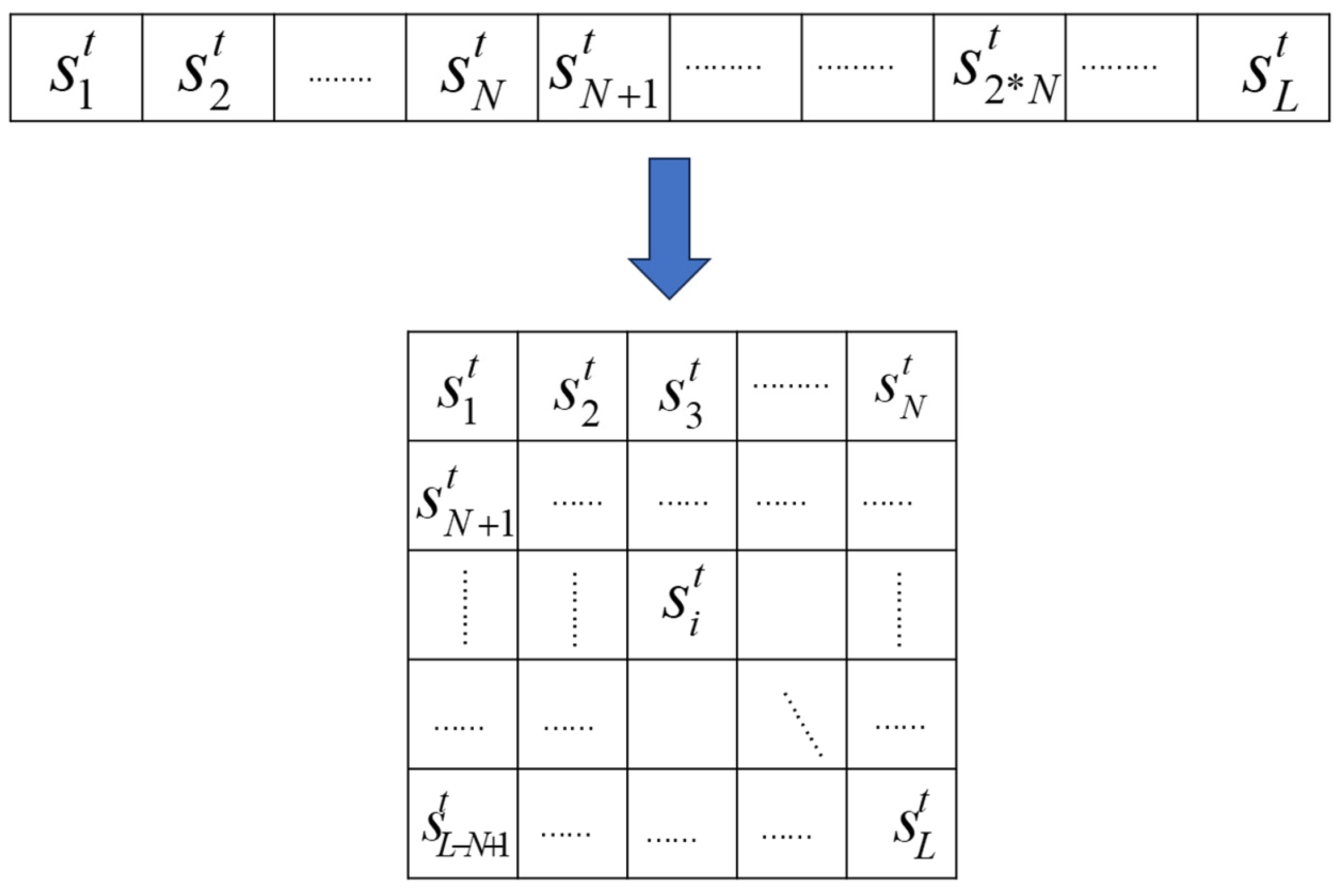
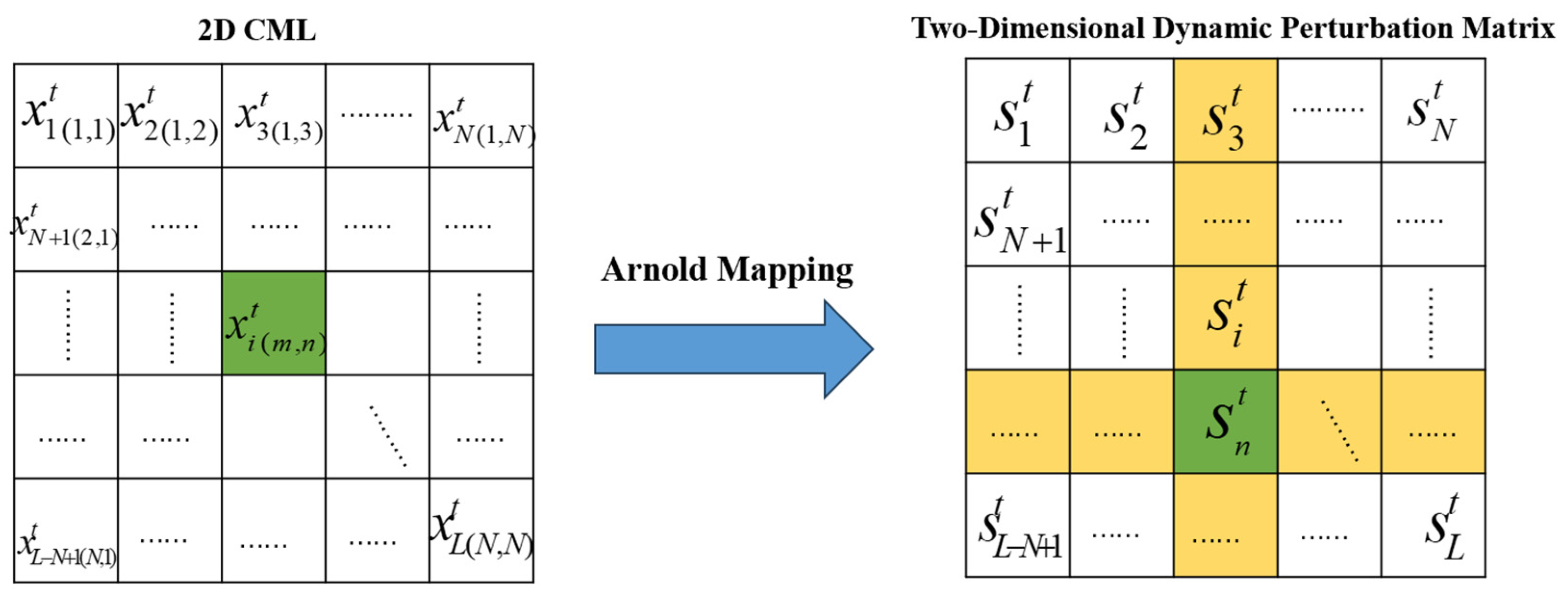
2.2. Two-Dimensional Coupled Map Lattice (2D CML)
3. The Chaotic System Proposed in This Paper
3.1. Introduction to the Proposed System
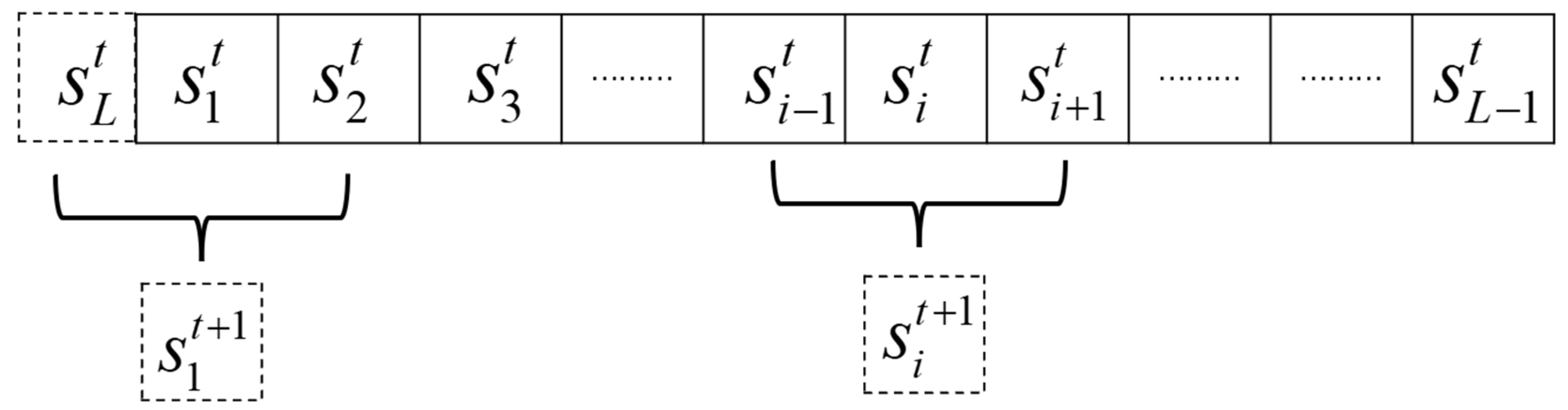
ECA-CML System Details
- a is the number of cells to the left of that have a value of 0,
- b is the number of cells to the right of that have a value of 1.
- c is the number of cells above that have a value of 0,
- d is the number of cells below that have a value of 1.
3.2. Performance Analysis
3.2.1. Bifurcation Diagram
3.2.2. Kolmogorov–Sinai Entropy Analysis
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. The Proposed Image Encryption Algorithm
4.1. Permutation Stage
4.2. Diffusion Stage
4.3. Dynamic DNA Encryption
4.4. Encryption and Decryption Algorithm
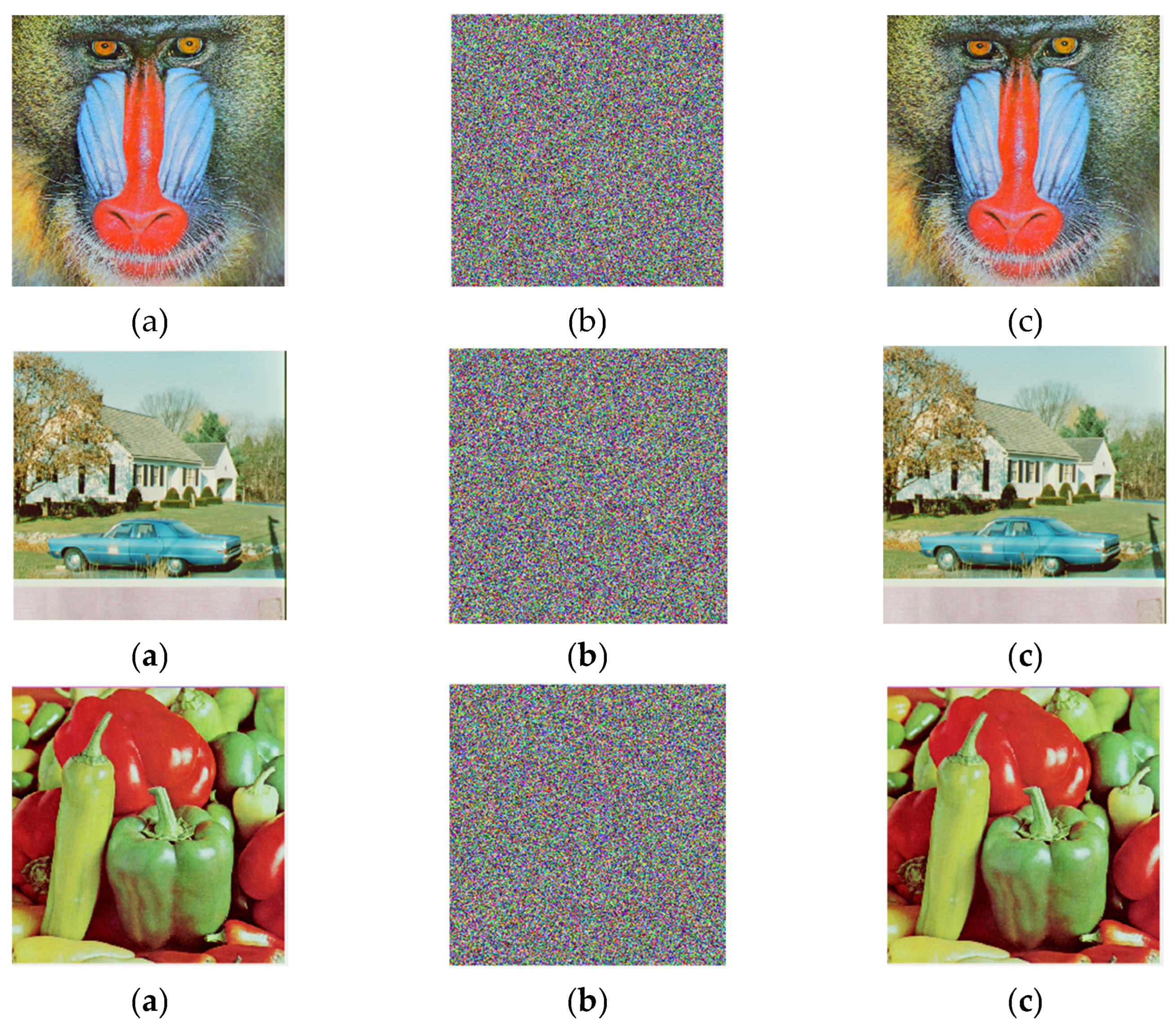
4.5. Experimental Results
5. Performance Analysis of the Encryption System
5.1. Secret Key Sensitivity Analysis
5.2. Histogram Analysis
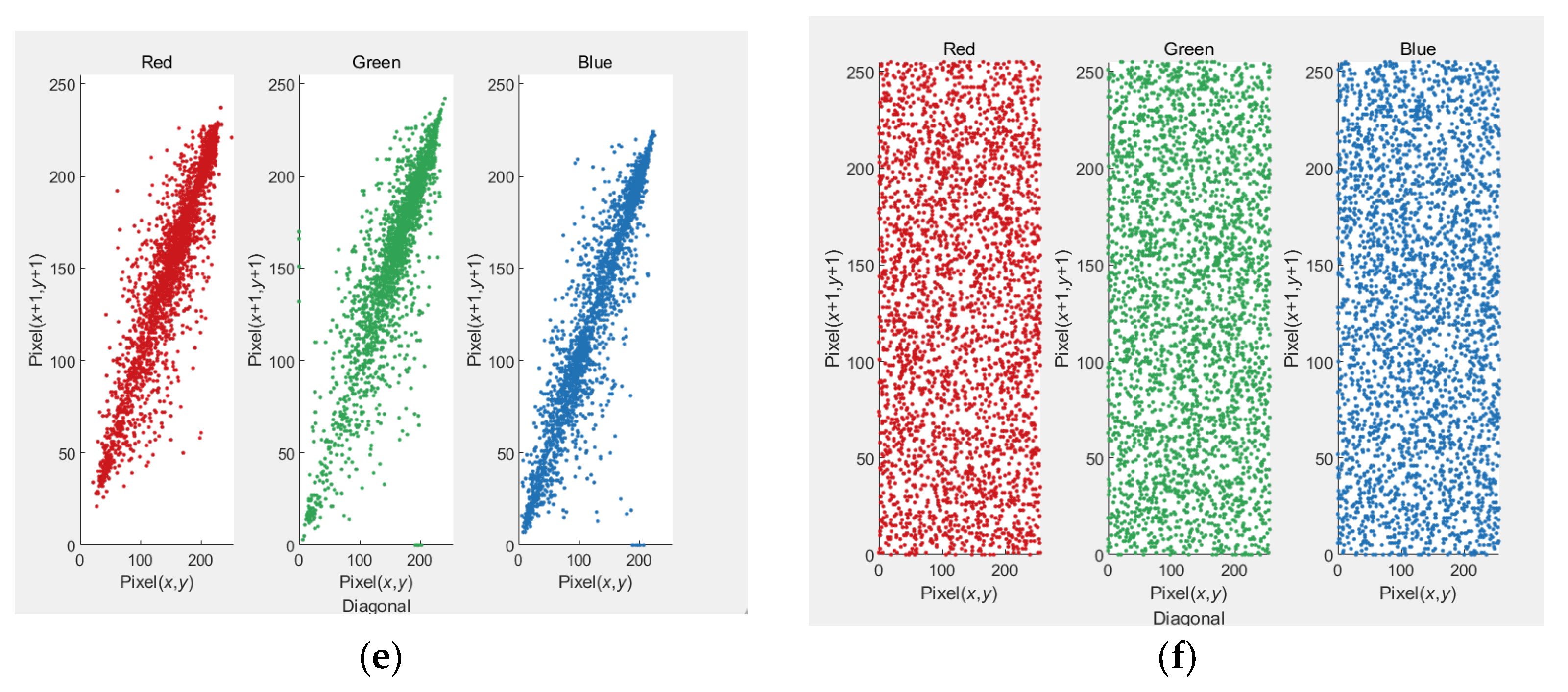
5.3. Correlation Coefficients Analysis
5.4. Information Entropy
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qobbi, Y.; Jarjar, A.; Essaid, M.; Benazzi, A. Image encryption algorithm based on genetic operations and chaotic DNA encoding. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 5823–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qobbi, Y.; Jarjar, A.; Essaid, M.; Benazzi, A. Image encryption algorithm using dynamic permutation and large chaotic S-box. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 18545–18564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Chen, Y.; Broyde, L. A novel chaos-based image encryption algorithm using DNA sequence operations. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 88, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Image encryption using value-differencing transformation and modified ZigZag transformation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 106, 3583–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyat, A.Y.; Hei, R.M.H.; Jahan, M.V. Chaos-based Image Encryption Using a Hybrid Cellular Automata and a DNA Sequence. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Congress on Technology, Communication and Knowledge (ICTCK), Mashhad, Iran, 11–12 November 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Kaslik, E.; Sivasundaram, S. Nonlinear dynamics and chaos in fractional-order neural networks. Neural Netw. 2012, 32, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Wang, J. A novel fractional-order 3-D chaotic system and its application to secure communication based on chaos synchronization. Phys. Scr. 2025, 100, 025243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Liu, S. A compact image encryption system based on Arnold transformation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 2647–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettayeb, M.; Al–Saggaf, U.M.; Djennoune, S. Single channel secure communication scheme based on synchronization of fractional-order chaotic Chua’s systems. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 2018, 40, 3651–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.K.; Srivastava, M.; Das, S. Synchronization of fractional order chaotic systems using active control method. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2012, 45, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Hanif, M.; Abbas, S.; Khan, M.A.; Almotiri, S.H.; Al Ghamdi, M.A. DNA strands level scrambling based color image encryption scheme. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 178167–178182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Mohapatra, R.N.; Agarwal, S.; Sathish, G.; Raw, S.N. A new RGB image encryption using generalized Vigenére-type table over symmetric group associated with virtual planet domain. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 10227–10263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Z.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, T. Medical image encryption algorithm based on a new five-dimensional multi-band multi-wing chaotic system and QR decomposition. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Fast image encryption algorithm based on multi-parameter fractal matrix and MPMCML system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 164, 112742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, X. An image encryption approach based on chaotic maps and genetic operations. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 25613–25633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaissi, S.; Chikouche, N.; Hamza, R. A novel image encryption algorithm based on hybrid chaotic maps using a key image. Optik 2023, 272, 170316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Shang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Y. A novel image encryption algorithm with anti-tampering attack capability. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 189, 115638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Designing a 2D infinite collapse map for image encryption. Signal Process. 2020, 171, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, P. A new full chaos coupled mapping lattice and its application in privacy image encryption. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 2021, 69, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Wu, X.; He, C.; Wang, L.; Cao, C. Improved fractal coding and hyperchaotic system for lossless image compression and encryption. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 113, 12233–12262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.Q.; Wu, G. A color image encryption and decryption scheme based on extended DNA coding and fractional-order 5D hyper-chaotic system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 254, 124413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Hu, Q.; Teng, L.; Su, Y. Unmanned ship image encryption method based on a new four-wing three-dimensional chaotic system and compressed sensing. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 185, 115146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Teng, L.; Zhou, W.; Yan, X.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, S. A new 2D cross hyperchaotic Sine-modulation-Logistic map and its application in bit-level image encryption. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 261, 125328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.; Perumal, R. A novel 2D Hyperchaotic Sine Logistic map based image encryption scheme. J. Opt. 2024, 27, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, J.; Zhong, Y. Multi-image encryption combining four-dimensional chaotic systems and multi-layer embedding. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2024, 233, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Feng, S.; Chen, X. An image encryption scheme using bit-plane cross-diffusion and spatiotemporal chaos system with nonlinear perturbation. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 1223–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Xian, Y. Color image encryption based on cross 2D hyperchaotic map using combined cycle shift scrambling and selecting diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 105, 1859–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, Z. A 4D discrete Hopfield neural network-based image encryption scheme with multiple diffusion modes. Optik 2023, 291, 171387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, K. Novel multiple-image encryption algorithm based on a two-dimensional hyperchaotic modular model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 173, 113630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Liu, T.; Yin, J. An encryption algorithm for color images based on an improved dual-chaotic system combined with DNA encoding. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.G.; Wang, K.S.; Wang, X.Y. Color image dna encryption using NCA map-based CML and one-time keys. Signal Process 2018, 148, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kurths, J.; Kan, H. A robust and lossless dna encryption scheme for color images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 12349–12376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, S.; Vijay, R. A synchronous intertwining logistic map-DNA approach for color image encryption. J Amb Intel Hum Comp 2019, 10, 2277–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveenkumar, P.; Amirtharajan, R.; Thenmozhi, K.; Rayappan, J.B. Fusion of confusion and diffusion: A novel image encryption approach. Telecommun. Syst. 2017, 65, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machkour, M.; Saaidi, A.; Benmaati, M.L. A novel image encryption algorithm based on the two-dimensional logistic map and the latin square image cipher. 3D Res. 2015, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.L.; Gan, Z.H.; Yuan, K.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.-R. An image encryption scheme based on three-dimensional Brownian motion and chaotic system. Chin. Phys. B 2017, 26, 020504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.M.; Said, L.A.; Radwan, A.G.; Madian, A.H.; Abu-Elyazeed, M.F. Generalized double-humped logistic map-based medical image encryption. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 10, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Han, F.; Qian, W.; Yao, Y.-D.; Zhu, Z.-L. Cryptanalysis and improvement in an image encryption scheme using combination of the 1D chaotic map. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 93, 2399–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Zhao, H.; Chai, H. Chaotic image encryption algorithm using wave-line permutation and block diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 83, 2067–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X. An image encryption algorithm based on bit level Brownian motion and new chaotic systems. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y. A plaintext-related image encryption algorithm based on chaos. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 6647–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Neighbor Combinations | 111 | 110 | 101 | 100 | 011 | 010 | 001 | 000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| next state | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Neighbor Combinations | 111 | 110 | 101 | 100 | 011 | 010 | 001 | 000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| next state | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Neighbor Combinations | 111 | 110 | 101 | 100 | 011 | 010 | 001 | 000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| next state | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Binary | Rule1 | Rule2 | Rule3 | Rule4 | Rule5 | Rule6 | Rule7 | Rule9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | A | T | C | G | A | T | C | G |
| 01 | T | C | G | A | G | A | T | C |
| 10 | C | G | A | T | T | C | G | A |
| 11 | G | A | T | C | C | G | A | T |
| Algorithm 1: Image Encryption and Decryption |
| Input: Original image, user key; Output: Encrypted image, decrypted image; 1: [h, w, ~] ← size(img) 2: dw_num ← 64 3: N ← dw_num * dw_num//Calculate the number of pixels per block 4: total_pixels ← h * w//Calculate the total number of pixels in the image 5: iterate_num ← ceil(total_pixels/N)//Calculate the required number of iterations for processing 6: fprintf(‘Chaos iterations set to: % d\n’, iterate_num)//Display the number of iterations 7: key ← Input key 8: hash_bits ← GenerateHashBits(key, 4000)//Generate hash bits from the key 9: Split hash_bits into R, G, B parts 10: Initialize chaotic parameters for each channel//Prepare chaotic parameters for encryption 11: for c ← 1 to 3 do 12: [control_u, initial_LOG, iten_e] ← ExtractParams(r_part)//Extract parameters needed for the chaotic system 13: chaos_params(c)← {control_u, initial_LOG, iten_e}//Store the parameters 14: end for 15: encrypted_img ← zeros(size(img), ‘uint8’)//Initialize the encrypted image matrix 16: shuffle_indices ← Cell array//Prepare a cell array to store shuffle indices(processed X) 17: xor_keys ← Cell array//Prepare a cell array to store XOR keys(processed Y) 18: processed_z_sequences ← Cell array//Prepare a cell array to store processed Z sequences 19: for c ← 1 to 3 do//Encrypt each channel 20: Generate chaotic sequence//Generate the chaotic sequence for the current channel 21: Shuffle pixel positions//Shuffle the positions of pixels in the current channel 22: XOR diffusion//Perform XOR diffusion on the pixel values 23: DNA encoding//Apply DNA encoding to enhance encryption 24: encrypted_img ← Reshape encrypted data//Reshape and store the encrypted data in the encrypted image 25: end for 26: Save encrypted image 27: Read the user input key (key). 28: Use the key to generate hash bits (hash_bits) = GenerateHashBits(key, 4000), generating hash bits of length 4000. 29: Divide the generated hash bits into three parts, corresponding to the red (R), green (G), and blue (B) channels.//Split hash bits into parts for each channel 30: Initialize chaotic parameters for each channel.//Prepare chaotic parameters for decryption 31: for c ← 1 to 3 do 32: [control_u, initial_LOG, iten_e] ← ExtractParams(r_part) 33: chaos_params(c) ← {control_u, initial_LOG, iten_e} 34: end for 35: decrypted_img ← zeros(size(img), ‘uint8’)//Initialize the decrypted image matrix 36: for c ← 1 to 3 do//Decrypt each channel 37: DNA decoding//Reverse DNA encoding to restore pixel values 38: Reverse XOR diffusion//Reverse XOR diffusion to recover original pixel values 39: Restore pixel positions//Restore the original positions of pixels 40: decrypted_img← Reshape decrypted data//Reshape and store the decrypted data in the decrypted image 41: end for |
| Image | UACI | R | G | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baboon | 33.4284% | 33.4543% | 33.4034% | 33.4275% |
| House | 33.4400% | 33.4217% | 33.4576% | 33.4408% |
| Peppers | 33.5341% | 33.5681% | 33.4705% | 33.5637% |
| Image | NPCR | R | G | B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baboon | 99.6078% | 99.6132% | 99.5995% | 99.6109% |
| House | 99.6003% | 99.6147% | 99.5934% | 99.5930% |
| Peppers | 99.6146% | 99.6056% | 99.6235% | 99.6147% |
| Algorithm | NPCR (%) | UACI (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Proposed Algorithm | 99.6078 | 33.4284 |
| Ref. [34] | 99.5819 | 32.0972 |
| Ref. [35] | 99.8000 | 33.3700 |
| Ref. [36] | 99.6200 | 33.4400 |
| Ref. [37] | 75.5000 | 33.4520 |
| Ref. [38] | 99.5980 | 33.1420 |
| Ref. [39] | 99.6150 | 33.4020 |
| Image | Algorithm | Correlation Direction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Vertical | Diagonal | ||
| Baboon | Proposed Algorithm | −0.0023 | 0.0009 | 0.0021 |
| House | Proposed Algorithm | −0.0039 | −0.0036 | 0.0028 |
| Peppers | Proposed Algorithm | −0.0018 | 0.0004 | −0.0032 |
| House | Proposed Algorithm | −0.0007 | −0.0029 | 0.0020 |
| Baboon | Ref. [34] | 0.0030 | −0.0062 | 0.0046 |
| Baboon | Ref. [35] | 0.002181 | 0.001928 | 0.002138 |
| Baboon | Ref. [36] | 0.0057 | 0.00005048 | 0.0024 |
| Baboon | Ref. [40] | 0.0013 | −0.0281 | 0.0128 |
| Baboon | Ref. [41] | −0.0142 | −0.0446 | 0.0106 |
| Image | Algorithm | Correlation Direction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red | Green | Blue | ||
| House | Proposed Algorithm | 7.9895 | 7.9901 | 7.9887 |
| Baboon | Proposed Algorithm | 7.9915 | 7.9913 | 7.9914 |
| Peppers | Proposed Algorithm | 7.9916 | 7.9917 | 7.9914 |
| House | Proposed Algorithm | 7.9915 | 7.9911 | 7.9913 |
| Lena | Ref. [33] | 7.9892 | 7.9898 | 7.9899 |
| Lena | Ref. [34] | 7.9895 | 7.9894 | 7.9894 |
| Lena | Ref. [35] | 7.9758 | 7.9822 | 7.9419 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, B.; Ning, H.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Q.; Li, Z. A CML-ECA Chaotic Image Encryption System Based on Multi-Source Perturbation Mechanism and Dynamic DNA Encoding. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071042
Xie X, Zhang K, Zheng B, Ning H, Zhou Y, Peng Q, Li Z. A CML-ECA Chaotic Image Encryption System Based on Multi-Source Perturbation Mechanism and Dynamic DNA Encoding. Symmetry. 2025; 17(7):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071042
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xin, Kun Zhang, Bing Zheng, Hao Ning, Yu Zhou, Qi Peng, and Zhengyu Li. 2025. "A CML-ECA Chaotic Image Encryption System Based on Multi-Source Perturbation Mechanism and Dynamic DNA Encoding" Symmetry 17, no. 7: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071042
APA StyleXie, X., Zhang, K., Zheng, B., Ning, H., Zhou, Y., Peng, Q., & Li, Z. (2025). A CML-ECA Chaotic Image Encryption System Based on Multi-Source Perturbation Mechanism and Dynamic DNA Encoding. Symmetry, 17(7), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071042





