Revisiting the Poincaré and Little Groups with Physical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Lorentz Group
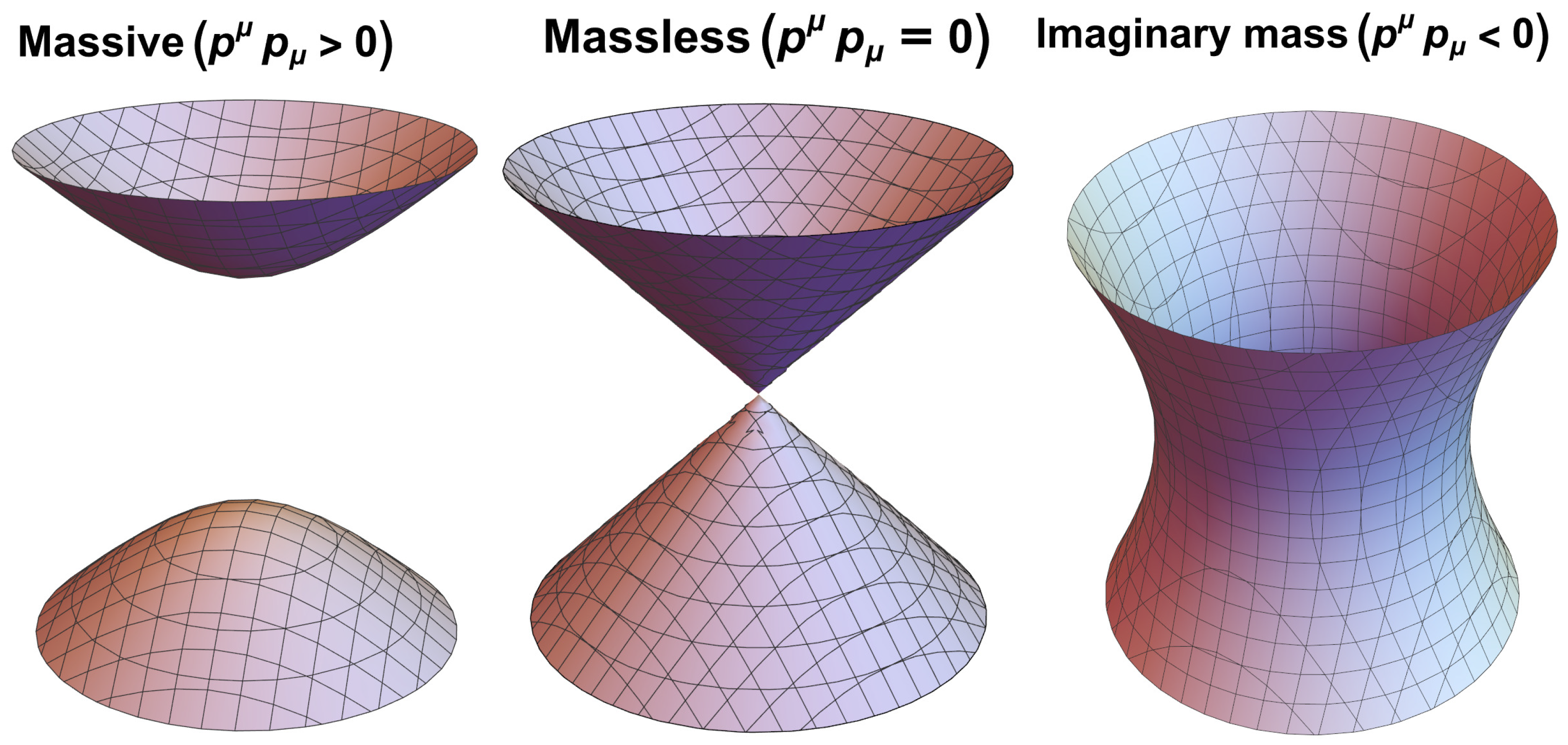
Orbits of the Lorentz Group
- (a)
- For time-like , we have . The little group is, thus, the rotation group.
- (b)
- For light-like , this four-vector is invariant under rotations around the z-axis.
- (c)
- For, again, light-like , the rotation matrix is the same.
- (d)
- For space-like , this four-vector remains invariant under rotations around the z-axis and boosts along either the x- or y-axis. Together, these form the three-dimensional Lorentz group , satisfying the required condition.
- (e)
- For , the entire Lorentz group leaves this zero momentum invariant, where the origin is the orbit.
3. The Covering Group of the Lorentz Group: SL(2, c)
4. Subgroups of the Lorentz Group
The Squeeze-Rotation and the Shear-Squeeze Representations of the Sp(2) Group
5. Poincaré Group and Wigner’s Little Groups
5.1. Poincaré Group
5.2. Wigner’s Little Groups
5.3. Wigner Four-Momentum-Matrices
6. Examples
6.1. Applications to Quantum Mechanics: Lorentz-Covariant Harmonic Oscillators and Entangled Excited States
6.1.1. Lorentz-Covariant Harmonic Oscillators
6.1.2. Entangled Excited States
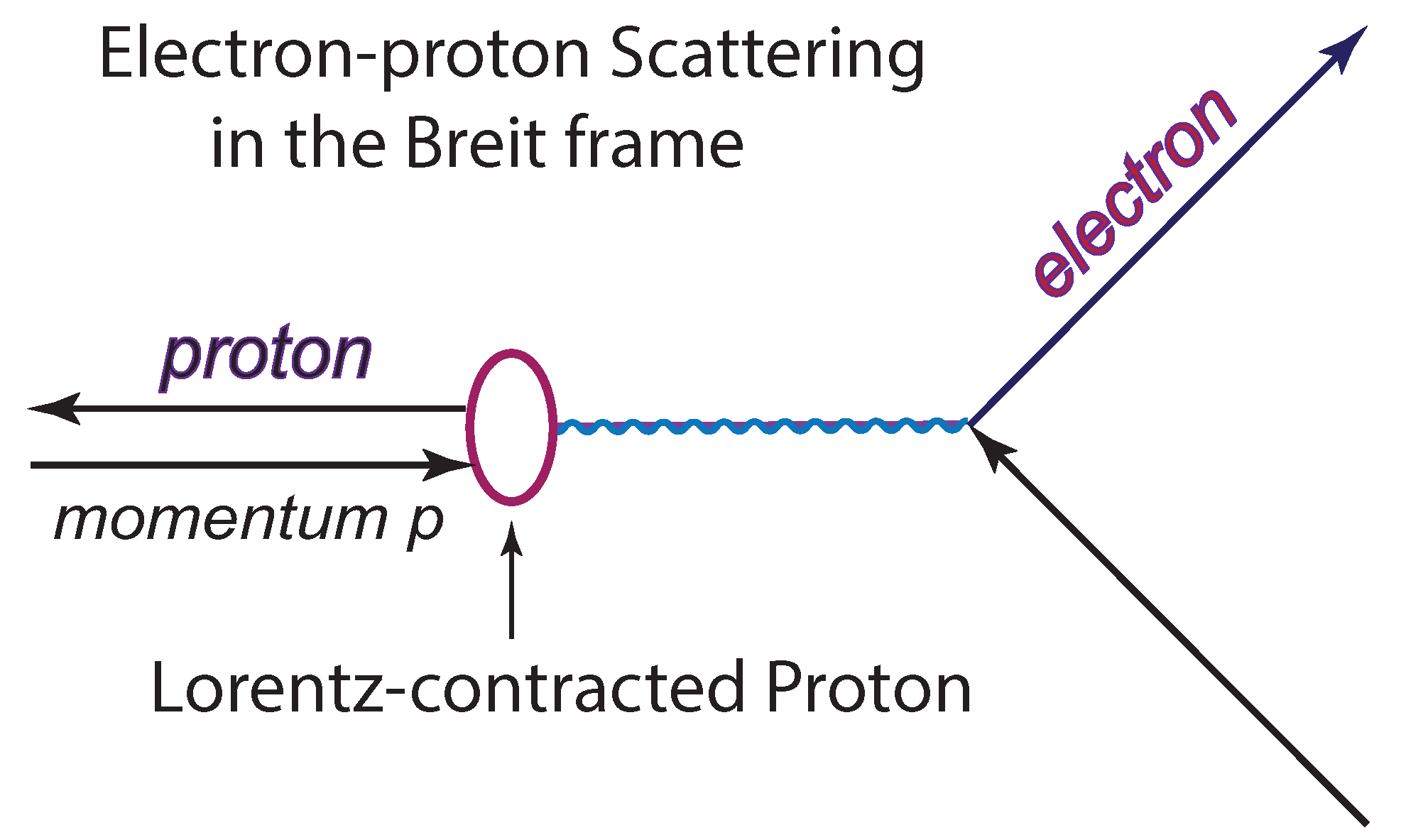
6.2. Applications to High Energy Physics: Proton Form Factor and Feynman’s Parton Model
6.2.1. The Proton Form Factor
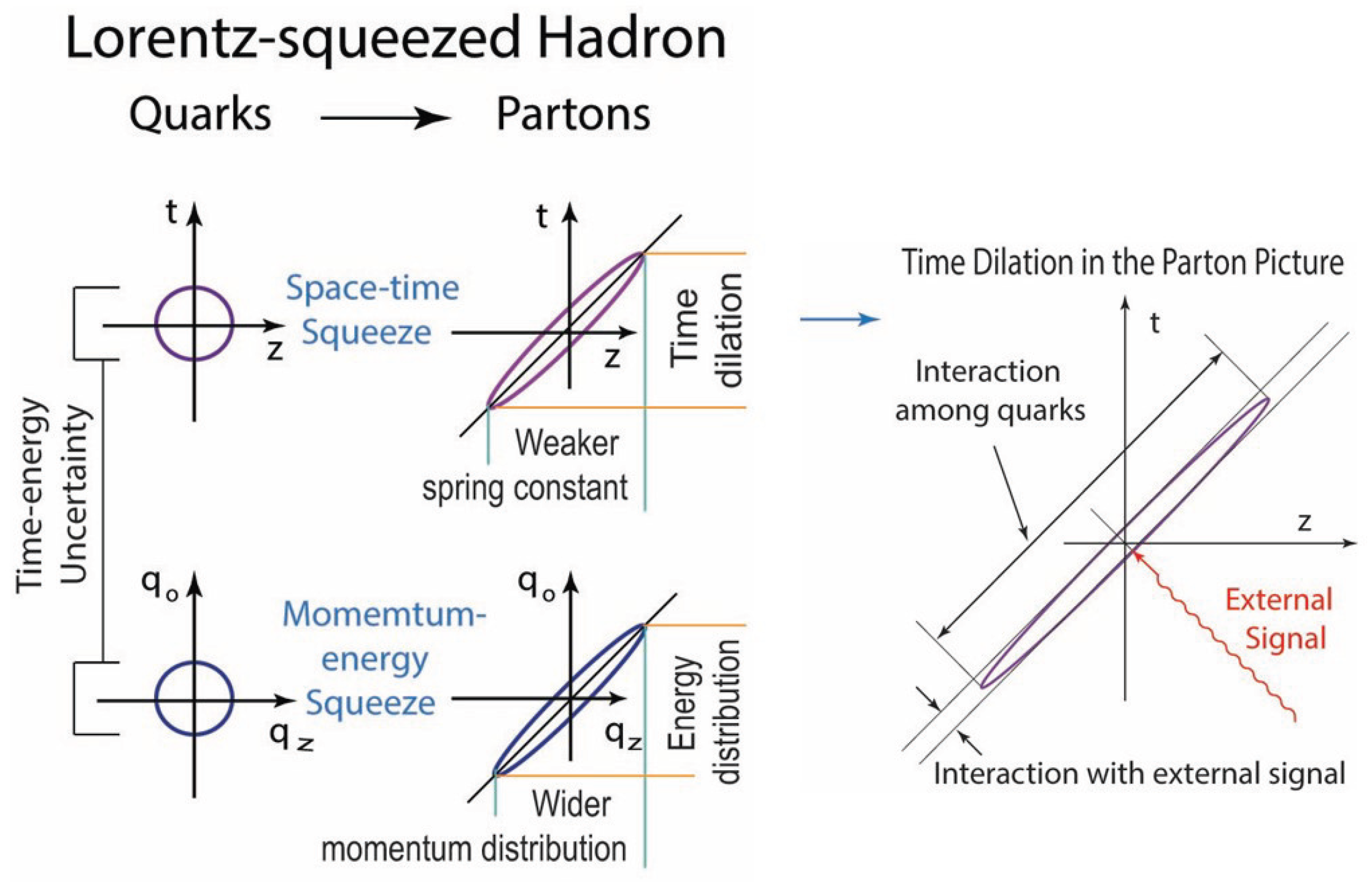
6.2.2. The Parton Picture
- (a)
- The picture is only valid if the hadrons are moving at close to light speed.
- (b)
- The partons behave as independent free particles, and the interaction time of the quarks becomes dilated between the quarks.
- (c)
- The hadron appears to have a widespread momentum distribution of partons.
- (d)
- The parton number appears to be much greater than that of quarks or even infinite.
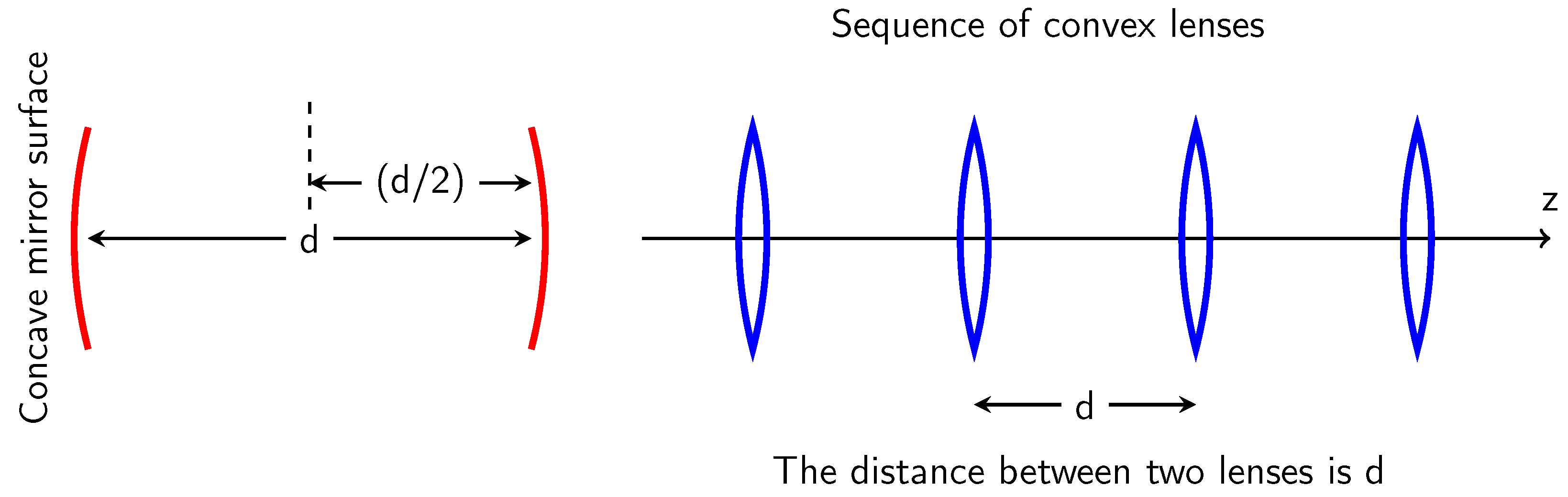
6.3. Application to Classical Optics: Laser Cavity
6.4. Applications to Quantum Optics: Shear States
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Exponentiation | Two-by-Two | Four-by-Four |
|---|---|---|
References
- Dirac, P.A.M. Forms of Relativistic Dynamics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1949, 21, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigner, E.P. On Unitary Representations of the Inhomogeneous Lorentz Group. Ann. Math. 1939, 40, 149–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigner, E.P. Group Theory: And Its Application to the Quantum Mechanics of Atomic Spectra; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1959; (Originally published as: Gruppentheorie und ihre Anwendung auf die Quantenmechanik der Atomspektren; Springer: Braunscheig, Germany, 1931). [Google Scholar]
- Hofstadter, R.; McAllister, R.W. Electron Scattering from the Proton. Phys. Rev. 1955, 98, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gell-Mann, M. The Eightfold Way: A Theory of Strong Interaction Symmetry; CTSL-20; California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1961; Volume TID-12608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gell-Mann, M. Symmetries of Baryons and Mesons. Phys. Rev. 1962, 125, 1067–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gell-Mann, M. A Schematic Model of Baryons and Mesons. Phys. Lett. 1964, 8, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, F.R. Special Relativity and Quantum Mechanics; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Wigner, E. Über nicht kombinierende Terme in der neueren Quantentheorie. II. Teil. Z. Für Phys. 1927, 40, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyl, H. The Theory of Groups and Quantum Mechanics; Nachdr. ed.; Dover Books on Mathematics; Dover Publ: Mineola, NY, USA, 2009. Originally published 1931. [Google Scholar]
- O’Raifeartaigh, L. Group Structure of Gauge Theories; Transferred to Digital Print ed.; Cambridge Monographs on Mathematical Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Başkal, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Theory and Applications of the Poincaré Group, 2nd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Physical principles in quantum field theory and in covariant harmonic oscillator formalism. Found. Phys. 1981, 11, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Wigner, E.P. Space–time geometry of relativistic particles. J. Math. Phys. 1990, 31, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Saxcé, G. Link between Lie Group Statistical Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Continua. Entropy 2016, 18, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Hermann, S.; Sammüller, F.; Schmidt, M. Gauge Invariance of Equilibrium Statistical Mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 133, 217101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, R. Lie Groups, Lie Algebras, and Some of Their Applications; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 2005; (Originally published: John Wiley and Sons; New York, NY, USA, 1974). [Google Scholar]
- Carmeli, M.; Malin, S. Representations of the Rotation and Lorentz Groups: An Introduction; Lecture Notes in Pure and Applied Mathematics; No. 16; M. Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann, V.; Wigner, E.P. Group Theorectical Discussion of Relatistic Wave Equations. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1948, 34, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirac, P.A.M. Application of Quaternions to Lorentz Transformations. Proc. R. Ir. Academy. Sect. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1945, 50, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Naimark, M. Linear Representation of the Lorentz Group. Usp. Mat. Nauk 1954, 9, 19–93, (Naimark M A 1957 Linear Representation of the Lorentz Group Am. Math. Soc. Transl. Ser. 2 6 379–458 Engl. transl.; Naimark M A Linear Representations of the Lorentz Group International Series of Monographs in Pure and Appliead Mathematics vol 63, First Edition 1964, reprinted 2014, series editor: Farahat, H. K., Oxford UK: Pergamon, Engl. transl.). [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, F.R.; Branscomb, E. Wigner’s Analysis of the Unitary Representations of the Poincaré Group; U.S. Atomic Energy Commission: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1965.
- Brice, S.; Marshak, M.; Zeller, G. The XXIX International Conference on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics. In Proceedings of the ICNP XXIX 2020, Avaiable Online Only, Chicago, IL, USA, 22 June–2 July 2020. Held as Online only Conference by Fermilab. [Google Scholar]
- Janner, A.; Janssen, T. Electromagnetic compensating gauge transformations. Physica 1971, 53, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, G. Possibility of Faster-Than-Light Particles. Phys. Rev. 1967, 159, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dam, H.; Ng, Y.J.; Biedenharn, L.C. A comment on fermionic tachyons and poincaré representations. Phys. Lett. B 1985, 158, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barci, D.G.; Bollini, C.G.; Rocca, M. Quantization of a six-dimensional Wess-Zumino model. Il Nuovo Cimento A 1995, 108, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkal, S.; Kim, Y.; Noz, M. Mathematical Devices for Optical Sciences; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; OCLC: 1034620988. [Google Scholar]
- Gürsey, F.; Orfanidis, S. Extended hadrons, scaling variables and the poincaré group. Il Nuovo Cimento A 1972, 11, 225–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Physical basis for minimal time-energy uncertainty relation. Found. Phys. 1979, 9, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukawa, H. Structure and Mass Spectrum of Elementary Particles. I. General Considerations. Phys. Rev. 1953, 91, 415–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P.; Kislinger, M.; Ravndal, F. Current Matrix Elements from a Relativistic Quark Model. Phys. Rev. D 1971, 3, 2706–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S.; Ishida, M.; Oda, M. Spin-Independent Confining Force and a Boosted LS-Coupling Scheme for Covariant Description of Hadron World. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1995, 93, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Maeda, T.; Yamada, K.; Oda, M.; Ishida, S. Radiative decays of charmed mesons in the covariant oscillator quark model. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 2012, 225–227, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bars, I. Relativistic harmonic oscillator revisited. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başkal, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Entangled Harmonic Oscillators and Space-Time Entanglement. Symmetry 2016, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, D.F.; Milburn, G.J. Quantum Optics, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro, A.; Olivares, S.; Paris, M.G.A. Gaussian States in Quantum Information; Napoli Series on Physics and Astrophysics; Bibliopolis: Napoles, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Adesso, G.; Ragy, S.; Lee, A.R. Continuous Variable Quantum Information: Gaussian States and Beyond. Open Syst. Inf. Dyn. 2014, 21, 1440001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedbrook, C.; Pirandola, S.; García-Patrón, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Ralph, T.C.; Shapiro, J.H.; Lloyd, S. Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 621–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P. Very High–Energy Collisions of Hadrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1969, 23, 1415–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P. The Behavior of Hadron Collisions at Extreme Energies. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on High Energy Collisions, Stony Brook, NY, USA, 5–6 September 1969; pp. 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Markov, M. On dynamically deformable form factors in the theory of elementary particles. Il Nuovo Cimento 1956, 3, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzburg, V.L.; Man’ko, V.I. Relativistic oscillator models of elementary particles. Nucl. Phys. 1965, 74, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Namiki, M. Nucleon Electromagnetic Form Factors at High Momentum Transfers in an Extended Particle Model Based on the Quark Model. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1970, 43, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, A.L.; Pagnamenta, A. Wave Functions and Form Factors for Relativistic Composite Particles. I. Phys. Rev. D 1970, 2, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Lorentz Harmonics, Squeeze Harmonics, and Their Physical Applications. Symmetry 2011, 3, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussar, P.E. Valons and harmonic oscillators. Phys. Rev. D 1981, 23, 2781–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Coupled oscillators, entangled oscillators, and Lorentz–covariant harmonic oscillators. J. Opt. B Quantum Semiclassical Opt. 2005, 7, S458–S467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Covariant harmonic oscillators and the parton picture. Phys. Rev. D 1977, 15, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorken, J.D.; Paschos, E.A. Inelastic Electron–Proton and γ-Proton Scattering and the Structure of the Nucleon. Phys. Rev. 1969, 185, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariv, A. Quantum Electronics, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989. (Originally published 1975). [Google Scholar]
- Haus, H.A. Waves and Fields in Optoelectronics; Prentice-Hall Series in Solid State Physical Electronics; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Siegman, A.E. Lasers; University Science Books: Mill Valley, CA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, J.; Latimer, I. Lasers: Theory and Practice; Prentice-Hall International Series in Optoelectronics; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, B.E.A.; Teich, M.C. Fundamentals of Photonics, 2nd ed.; Wiley Series in Pure and Applied Optics, Wiley Interscience; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. (Originaly published 1991). [Google Scholar]
- Başkal, S.; Kim, Y.S. Lorentz group in ray and polarization optics. In Mathematical Optics: Classical, Quantum and Computational Methods; Lakshminarayanan, V., Calvo, M.L., Alieva, T., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 303–349. [Google Scholar]
- Başkal, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Wigner’s Space-Time Symmetries Based on the Two-by-Two Matrices of the Damped Harmonic Oscillators and the Poincaré Sphere. Symmetry 2014, 6, 473–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, P.D.; Ficek, Z. (Eds.) Quantum Squeezing; Number 27 in Springer Series on Atomic, Optical, and Plasma Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann, A.W. Image rotation, Wigner rotation, and the fractional Fourier transform. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1993, 10, 2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Chen, K.; Venegas-Andraca, S.E.; Zhao, J. Quantum image rotation by an arbitrary angle. Quantum Inf. Process. 2017, 16, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Phase Space Picture of Quantum Mechanics: Group Theoretical Approach; Number 40 in Lecture Notes in Physics Series; World Scientific Publishing Co.: Singapore; Hackensack, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Klauder, J.R.; Sudarshan, E.C.G. Fundamentals of Quantum Optics; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 2006; Originally Published: W.A. Benjamin: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Peskin, M.E.; Schroeder, D.V. An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory; The Advanced Book Program; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Başkal, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Einstein’s E = mc2 Derivable from Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Relations. Quantum Rep. 2019, 1, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
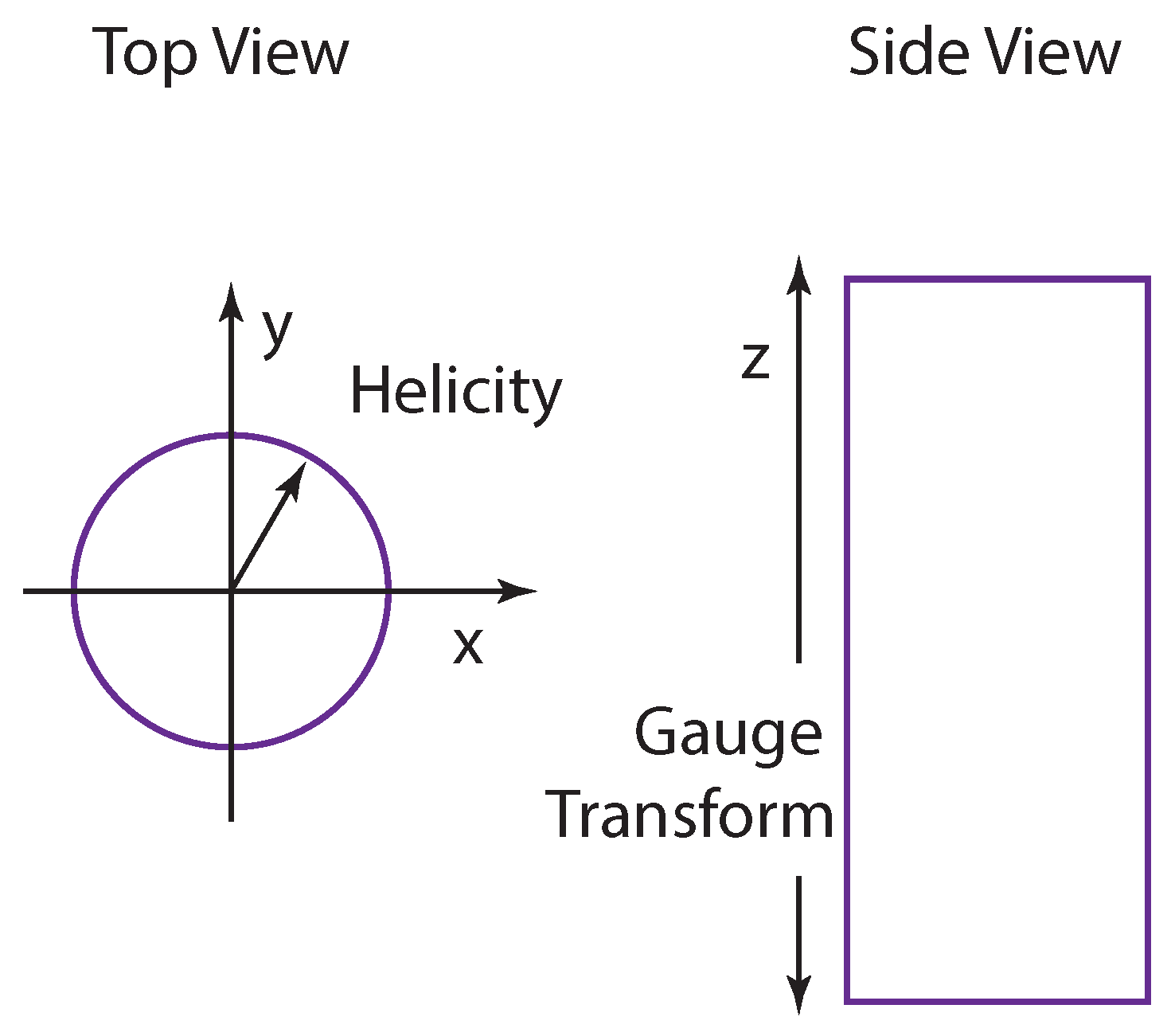
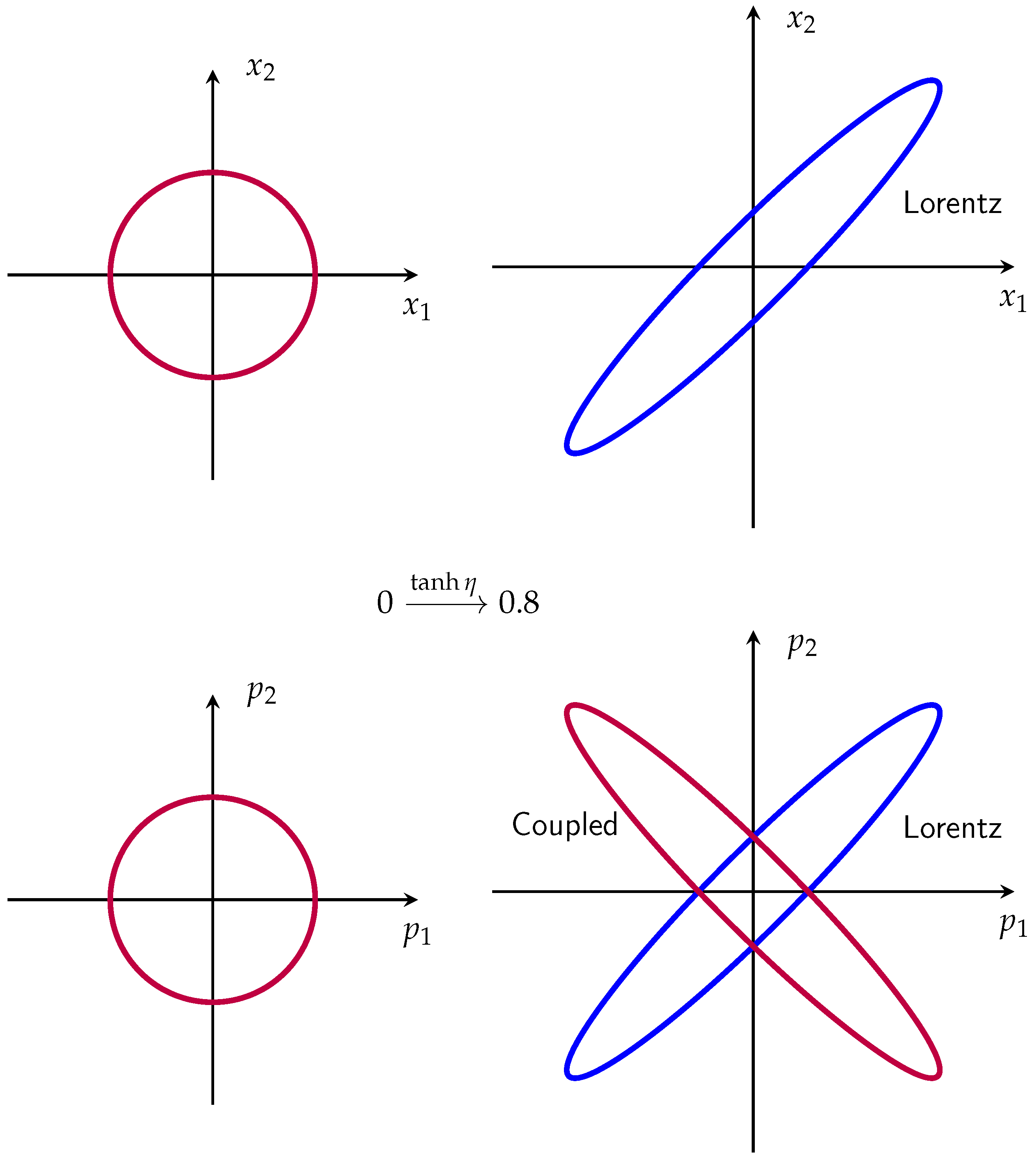

| Particle Mass | Wigner Four-Vector | Wigner Transformation Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Massive | ||
| Massless | ||
| Imaginary-mass |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Başkal, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Noz, M.E. Revisiting the Poincaré and Little Groups with Physical Applications. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071003
Başkal S, Kim YS, Noz ME. Revisiting the Poincaré and Little Groups with Physical Applications. Symmetry. 2025; 17(7):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071003
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaşkal, Sibel, Young S. Kim, and Marilyn E. Noz. 2025. "Revisiting the Poincaré and Little Groups with Physical Applications" Symmetry 17, no. 7: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071003
APA StyleBaşkal, S., Kim, Y. S., & Noz, M. E. (2025). Revisiting the Poincaré and Little Groups with Physical Applications. Symmetry, 17(7), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17071003







