SAFE-GTA: Semantic Augmentation-Based Multimodal Fake News Detection via Global-Token Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We design a global-token cross-attention mechanism for multimodal representation fusion to effectively capture the correlations between text and image, in which the trainable Query and Key matrices for the two modalities are shared with each other.
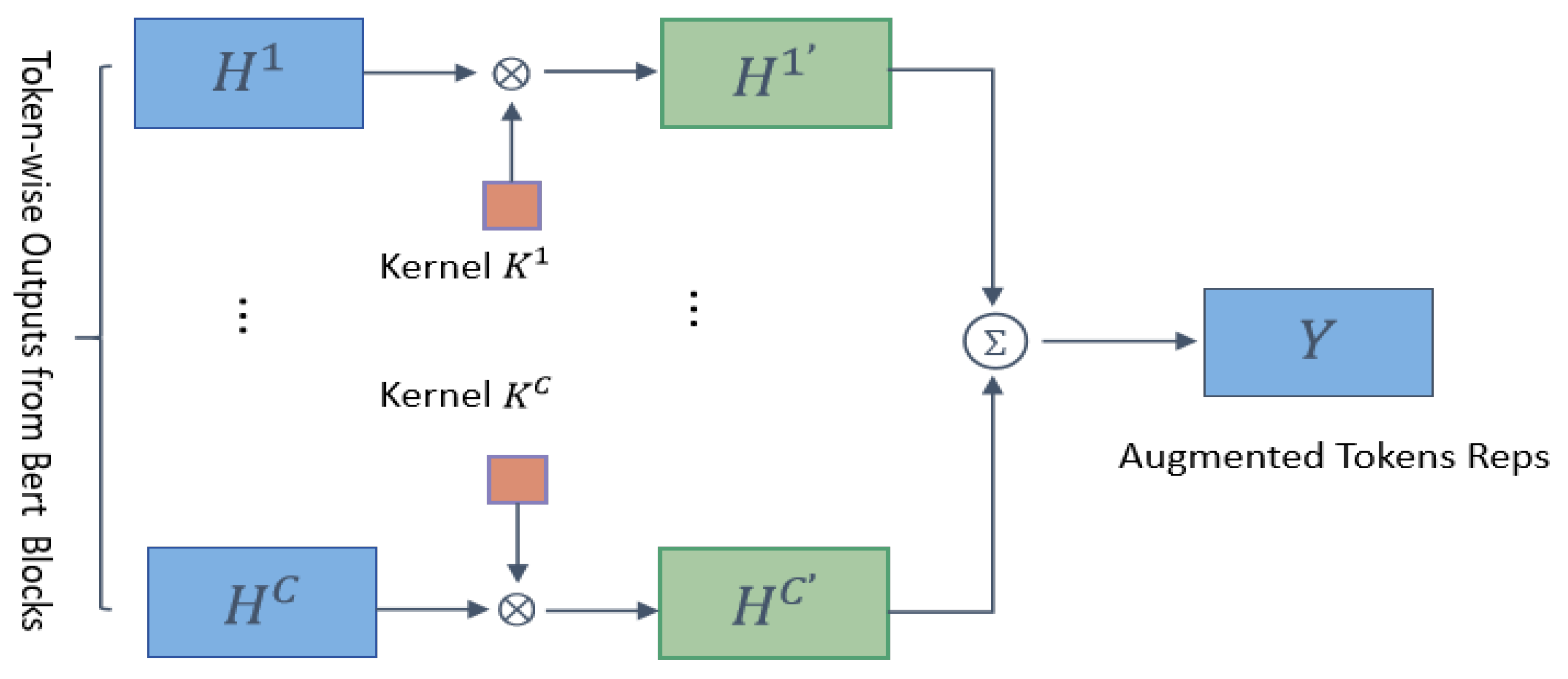
- We manipulate token-level representations yielded from twelve stacked blocks of BERT using a Convolutional Neural Network for semantic augmentation.
- We propose SAFE-GTA, a multimodal fake news detection system implemented based on dual unimodal pre-trained models. Specifically, we adopt BERT for text learning and ViT for image representation.
- We conduct a massive amount of experiments, and the results show that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines by 0.8% in accuracy and 2.2% in F-score on average across three widely adopted datasets.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Unimodal Fake News Detection
2.2. Multimodal Fusion for Fake News Detection
3. The Framework of SAFE-GTA
3.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2. Image and Text Encoders
3.3. Multimodal Information Fusion
3.4. Classification Module
4. Experimental Analysis
4.1. Experiment Platform and Datasets
- PolitiFact is a well-known non-profit fact-checking website that rates the accuracy of claims by officials, pundits, and other public figures. A large number of in-field researchers collect data from the website, aiming to detect unimodal or multimodal misinformation.
- Gossipcop is a resource specifically established for the detection and analysis of fake news, particularly in the context of entertainment news and celebrity gossip. This dataset is key for research and development in the field of misinformation studies, especially with a focus on multimodal data.
- ReCOVery is a specially designed and constructed repository aimed at supporting research efforts in the fight against misinformation related to COVID-19.
4.2. Baselines and Evaluation Metrics
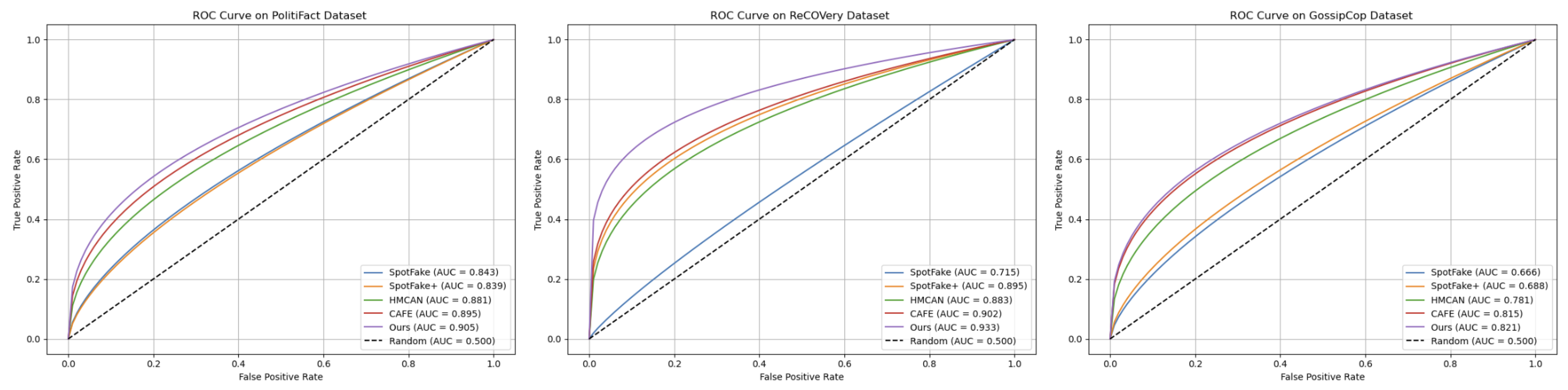
4.3. Effectiveness Evaluation
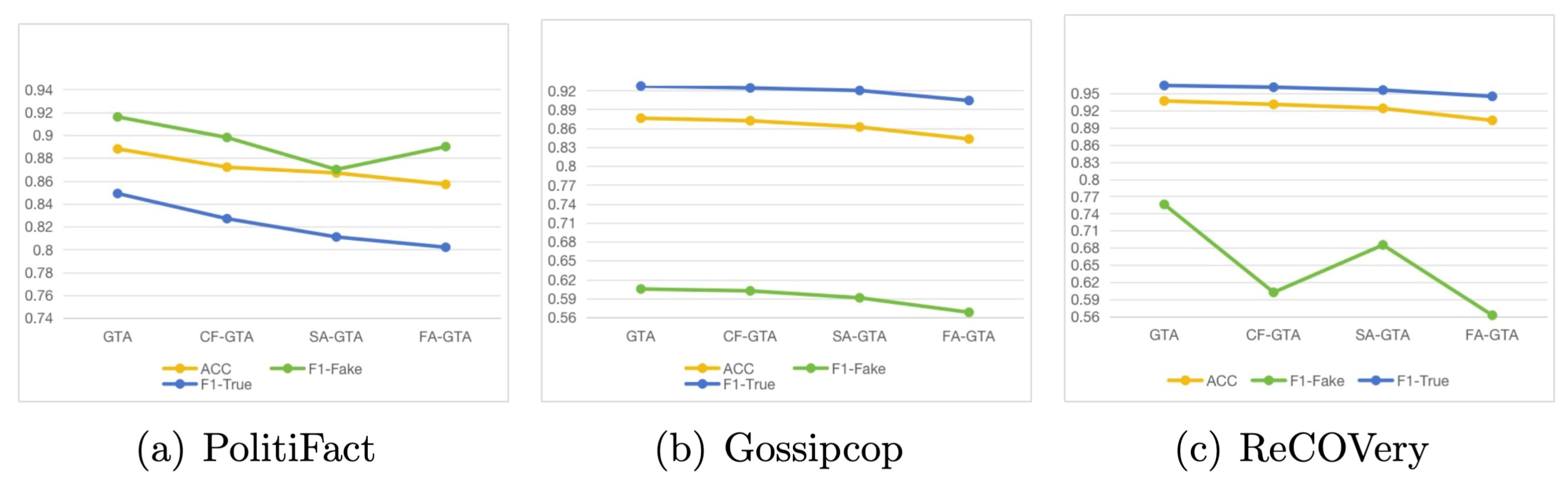
4.4. The Ablation Study
- CF–SAFE: represents the SAFE-GTA model that disables the multimodal information fusion module.
- SA–SAFE: denotes another SAFE-GTA variant that closes the functionality of semantic augmentation.
- FA–SAFE: indicates the SAFE-GTA that shuts down the effects of both information fusion and semantic augmentation.
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grinberg, N.; Joseph, K.; Friedland, L.; Swire-Thompson, B.; Lazer, D. Fake news on Twitter during the 2016 US presidential election. Science 2019, 363, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwa, P.; Sharma, S.; Pykl, S.; Guptha, V.; Kumari, G.; Akhtar, M.S.; Ekbal, A.; Das, A.; Chakraborty, T. Fighting an infodemic: Covid-19 fake news dataset. In Proceedings of the Combating Online Hostile Posts in Regional Languages During Emergency Situation: First International Workshop, CONSTRAINT 2021, Collocated with AAAI 2021, Virtual Event, 8 February 2021. Revised Selected Papers 1; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tenali, N.; Babu, G.R.M. A systematic literature review and future perspectives for handling big data analytics in COVID-19 diagnosis. New Gener. Comput. 2023, 41, 243–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazer, D.M.; Baum, M.A.; Benkler, Y.; Berinsky, A.J.; Greenhill, K.M.; Menczer, F.; Metzger, M.J.; Nyhan, B.; Pennycook, G.; Rothschild, D.; et al. The science of fake news. Science 2018, 359, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.A.; Vilares, D.; Gómez-Rodríguez, C.; Vilares, J. Sentiment analysis for fake news detection. Electronics 2021, 10, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Mahudeswaran, D.; Wang, S.; Lee, D.; Liu, H. Fakenewsnet: A data repository with news content, social context, and spatiotemporal information for studying fake news on social media. Big data 2020, 8, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Zafarani, R.; Liu, H. The role of user profiles for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 27–30 August 2019; pp. 436–439. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Sugiyama, K.; Nakov, P.; Kan, M.Y. Fang: Leveraging social context for fake news detection using graph representation. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Virtual Event, 19–23 October 2020; pp. 1165–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, K.; Mahudeswaran, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Hierarchical propagation networks for fake news detection: Investigation and exploitation. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, Virtual, 8 June 2020; Volume 14, pp. 626–637. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, U.; Pandey, P.; Kumar, S. A transformer-based model for evaluation of information relevance in online social-media: A case study of covid-19 media posts. New Gener. Comput. 2022, 40, 1029–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 5485–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Early detection of rumours on twitter via stance transfer learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Information Retrieval: 42nd European Conference on IR Research, ECIR 2020, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 April 2020, Proceedings, Part I 42; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 575–588. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Yi, P.; Ma, J.; Jiang, H.; Luo, Z.; Shi, S.; Liu, R. Zero-shot rumor detection with propagation structure via prompt learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 5213–5221. [Google Scholar]
- Kaliyar, R.K.; Goswami, A.; Narang, P. FakeBERT: Fake news detection in social media with a BERT-based deep learning approach. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 11765–11788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, X. Multimodal fake news detection via clip-guided learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Brisbane, Australia, 10–14 July 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, F.; Han, J.; Hu, S. Invariant Meets Specific: A Scalable Harmful Memes Detection Framework. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 4788–4797. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, M.D.; Sundar, S.S.; Le, T.; Lee, D. “Fake news” is not simply false information: A concept explication and taxonomy of online content. Am. Behav. Sci. 2021, 65, 180–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Selvaraju, R.; Gotmare, A.; Joty, S.; Xiong, C.; Hoi, S.C.H. Align before fuse: Vision and language representation learning with momentum distillation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (NeurIPS 2021), Vitrual, 6–14 December 2021; pp. 9694–9705. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Shenzhen, China, 26 February–1 March 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12597. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, California, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Przybyła, P.; Soto, A.J. When classification accuracy is not enough: Explaining news credibility assessment. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Goenka, N.; Kalra, S.; Sharma, Y. Fake news detection: Experiments and approaches beyond linguistic features. In Proceedings of the Data Management, Analytics and Innovation: Proceedings of ICDMAI 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 2, pp. 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Sheng, V.S.; Wang, M. A unified perspective for disinformation detection and truth discovery in social sensing: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2021, 55, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, N.; Fenza, G.; Loia, V.; Nota, F.D. Content Based Fake News Detection with machine and deep learning: A systematic review. Neurocomputing 2023, 530, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkina, E.; Hossain, T.; Logan IV, R.L.; Arana-Catania, M.; Procter, R.; Zubiaga, A.; Singh, S.; He, Y.; Liakata, M. Evaluating the generalisability of neural rumour verification models. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahi, A.; Safari, L. Evaluating the effectiveness of publishers’ features in fake news detection on social media. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 2913–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Ding, C. Fake news detection based on news content and social contexts: A transformer-based approach. Int. J. Data Sci. Anal. 2022, 13, 335–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allein, L.; Moens, M.F.; Perrotta, D. Preventing profiling for ethical fake news detection. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, T.; Slimi, H.; Bounhas, I.; Slimani, Y. A hybrid approach for fake news detection in twitter based on user features and graph embedding. In Proceedings of the Distributed Computing and Internet Technology: 16th International Conference, ICDCIT 2020, Bhubaneswar, India, 9–12 January 2020, Proceedings 16; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 266–280. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.Y.; Kung, Y.C.; Leu, F.Y. Predictive intelligence in harmful news identification by BERT-based ensemble learning model with text sentiment analysis. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 102872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvembe, A.M.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Xu, G. Dual emotion based fake news detection: A deep attention-weight update approach. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiang, J.; Wu, X. Prompt-Learning for Short Text Classification. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. (TKDE) 2024, 36, 5328–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Gong, C.; Sharma, K.; Liu, Y. Neural User Response Generator: Fake News Detection with Collective User Intelligence. In Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; Volume 18, pp. 3834–3840. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Cao, J.; Nan, Q.; Shu, K.; Wu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, F. Memory-guided multi-view multi-domain fake news detection. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 35, 7178–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazkova, A.; Glazkov, M.; Trifonov, T. g2tmn at Constraint@AAAI2021: Exploiting CT-BERT and Ensembling Learning for COVID-19 Fake News Detection. In Combating Online Hostile Posts in Regional Languages During Emergency Situation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, J.; Lin, Y.; Luo, S. Towards COVID-19 fake news detection using transformer-based models. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 274, 110642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.; Cao, J.; Yang, T.; Guo, J.; Li, J. Exploiting multi-domain visual information for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Beijing, China, 8–11 November 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 518–527. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tian, Q. Novel visual and statistical image features for microblogs news verification. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2016, 19, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, L.; Wei, L. Detecting fake news by exploring the consistency of multimodal data. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Wu, H.; Sun, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, H. Multimodal fake news detection via progressive fusion networks. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comito, C.; Caroprese, L.; Zumpano, E. Multimodal fake news detection on social media: A survey of deep learning techniques. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2023, 13, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Bu, Y.; Cao, J.; Ji, W.; Shui, R.; Xiao, J.; Wang, D.; Chua, T.S. Fakesv: A multimodal benchmark with rich social context for fake news detection on short video platforms. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 14444–14452. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Shen, C.; Van Den Hengel, A. Wider or deeper: Revisiting the resnet model for visual recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 90, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, F.; Jin, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xun, G.; Jha, K.; Su, L.; Gao, J. Eann: Event adversarial neural networks for multi-modal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Lodon, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 849–857. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Fang, Q.; Xu, C. Hierarchical multi-modal contextual attention network for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 44th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Virtual, 11–15 July 2021; pp. 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Xu, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, S. Cross-modal contrastive learning for multimodal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 5696–5704. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Sui, J.; Lv, Q.; Tun, L.; Shang, L. Cross-modal ambiguity learning for multimodal fake news detection. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022, Virtual Event, Lyon, France, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 2897–2905. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, S.; Shah, R.R.; Chakraborty, T.; Kumaraguru, P.; Satoh, S. Spotfake: A multi-modal framework for fake news detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Fifth International Conference on Multimedia Big Data (BigMM), Singapore, 11–13 September 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, S.; Kabra, A.; Sharma, M.; Shah, R.R.; Chakraborty, T.; Kumaraguru, P. Spotfake+: A multimodal framework for fake news detection via transfer learning (student abstract). In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 13915–13916. [Google Scholar]

| Steps | Modality | Function Call |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Text | BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(“bert-base-uncased”) |
| 2 | Text | tokenizer(raw_text, |
| padding=“max_length”, | ||
| truncation=True, | ||
| max_length=128, | ||
| return_tensors=“pt”) | ||
| 3 | Image | ViTFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained( |
| “google/vit-base-patch16-224”) | ||
| 4 | Image | feature_extractor(raw_image, |
| do_resize=True, | ||
| size=224, | ||
| do_center_crop=True, | ||
| return_tensors=“pt”) |
| Hyperparameters | Setup | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Epochs | 50 | The number of complete passes through the training dataset during model training. |
| Batch Size | 16 | The number of training samples processed simultaneously in one forward/backward pass. |
| Optimizer | Adam | The algorithm used to update model weights based on the computed gradients. |
| Input Size | 768 | The dimensionality of the input features fed into the model. |
| Learning Rate | 3 × 10−5 | The step size in each iteration while moving toward a minimum of the loss function. |
| Weight Decay | 1 × 10−4 | A regularization technique that penalizes large weights to help prevent overfitting. |
| Dropout Rate | 0.4 | The proportion of neurons randomly set to zero during training to improve generalization. |
| Datasets | Real News | Fake News | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Test Set | Training Set | Test Set | |
| PolitiFact | 647 | 75 | 1117 | 121 |
| Gossipcop | 6253 | 767 | 2135 | 166 |
| ReCOVery | 1105 | 123 | 194 | 22 |
| Datasets | Methods | AUC | Accuracy | Real News | Fake News | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ||||
| PolitiFact | Spotfake | 0.843 | 0.796 | 0.804 | 0.884 | 0.843 | 0.777 | 0.653 | 0.711 |
| Spotfake+ | 0.839 | 0.842 | 0.830 | 0.933 | 0.879 | 0.866 | 0.693 | 0.770 | |
| HMCAN | 0.881 | 0.847 | 0.902 | 0.843 | 0.871 | 0.772 | 0.853 | 0.810 | |
| CAFE | 0.895 | 0.882 | 0.865 | 0.958 | 0.909 | 0.919 | 0.760 | 0.832 | |
| SAFE-concat | 0.882 | 0.857 | 0.855 | 0.926 | 0.889 | 0.862 | 0.747 | 0.800 | |
| SAFE-GTA | 0.905 ∗,†,‡ | 0.888 ∗,†,‡ | 0.896 | 0.925 | 0.916 ∗,†,‡ | 0.873 | 0.826 | 0.849 ∗,†,‡ | |
| Gossipcop | Spotfake | 0.715 | 0.869 | 0.714 | 0.227 | 0.344 | 0.876 | 0.983 | 0.927 |
| Spotfake+ | 0.895 | 0.903 | 0.700 | 0.636 | 0.667 | 0.936 | 0.951 | 0.943 | |
| HMCAN | 0.883 | 0.924 | 0.923 | 0.545 | 0.687 | 0.924 | 0.991 | 0.957 | |
| CAFE | 0.902 | 0.903 | 0.900 | 0.409 | 0.563 | 0.903 | 0.991 | 0.945 | |
| SAFE-concat | 0.905 | 0.903 | 0.654 | 0.773 | 0.708 | 0.958 | 0.927 | 0.942 | |
| SAFE-GTA | 0.933 ∗,†,‡ | 0.938 ∗,†,‡ | 0.882 | 0.682 | 0.769 ∗,†,‡ | 0.945 | 0.984 | 0.964 ∗,†,‡ | |
| ReCOVery | Spotfake | 0.666 | 0.869 | 0.714 | 0.227 | 0.344 | 0.876 | 0.983 | 0.927 |
| Spotfake+ | 0.688 | 0.903 | 0.700 | 0.636 | 0.667 | 0.936 | 0.951 | 0.943 | |
| HMCAN | 0.781 | 0.924 | 0.923 | 0.545 | 0.687 | 0.924 | 0.991 | 0.957 | |
| CAFE | 0.815 | 0.903 | 0.900 | 0.409 | 0.563 | 0.903 | 0.991 | 0.945 | |
| SAFE-concat | 0.614 | 0.823 | 0.509 | 0.181 | 0.267 | 0.844 | 0.962 | 0.900 | |
| SAFE-GTA | 0.821 ∗,†,‡ | 0.937 ∗,†,‡ | 0.933 ∗,†,‡ | 0.636 ∗,†,‡ | 0.756 ∗,†,‡ | 0.938 ∗,†,‡ | 0.991 ∗,†,‡ | 0.964 ∗,†,‡ | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y. SAFE-GTA: Semantic Augmentation-Based Multimodal Fake News Detection via Global-Token Attention. Symmetry 2025, 17, 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060961
Zhang L, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Huang Y. SAFE-GTA: Semantic Augmentation-Based Multimodal Fake News Detection via Global-Token Attention. Symmetry. 2025; 17(6):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060961
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Like, Chaowei Zhang, Zewei Zhang, and Yuchao Huang. 2025. "SAFE-GTA: Semantic Augmentation-Based Multimodal Fake News Detection via Global-Token Attention" Symmetry 17, no. 6: 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060961
APA StyleZhang, L., Zhang, C., Zhang, Z., & Huang, Y. (2025). SAFE-GTA: Semantic Augmentation-Based Multimodal Fake News Detection via Global-Token Attention. Symmetry, 17(6), 961. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060961






