Analysis of the Multi-Objective Control Sequence Optimization Problem in Bivariate Fertilizer Applicators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. CSO Background and MOP Formulation
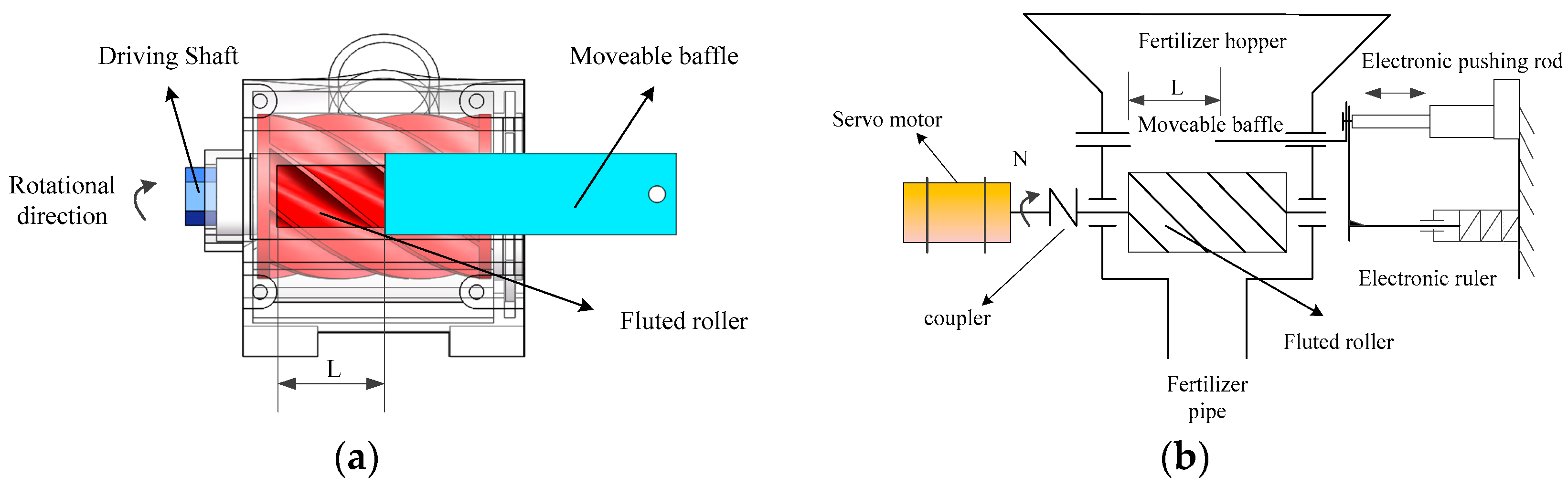
3.1. Working Principle of BFA and Data Preparation
3.1.1. Working Principle
3.1.2. Data Preparation
3.2. COS Problem Description and MOP Formulation
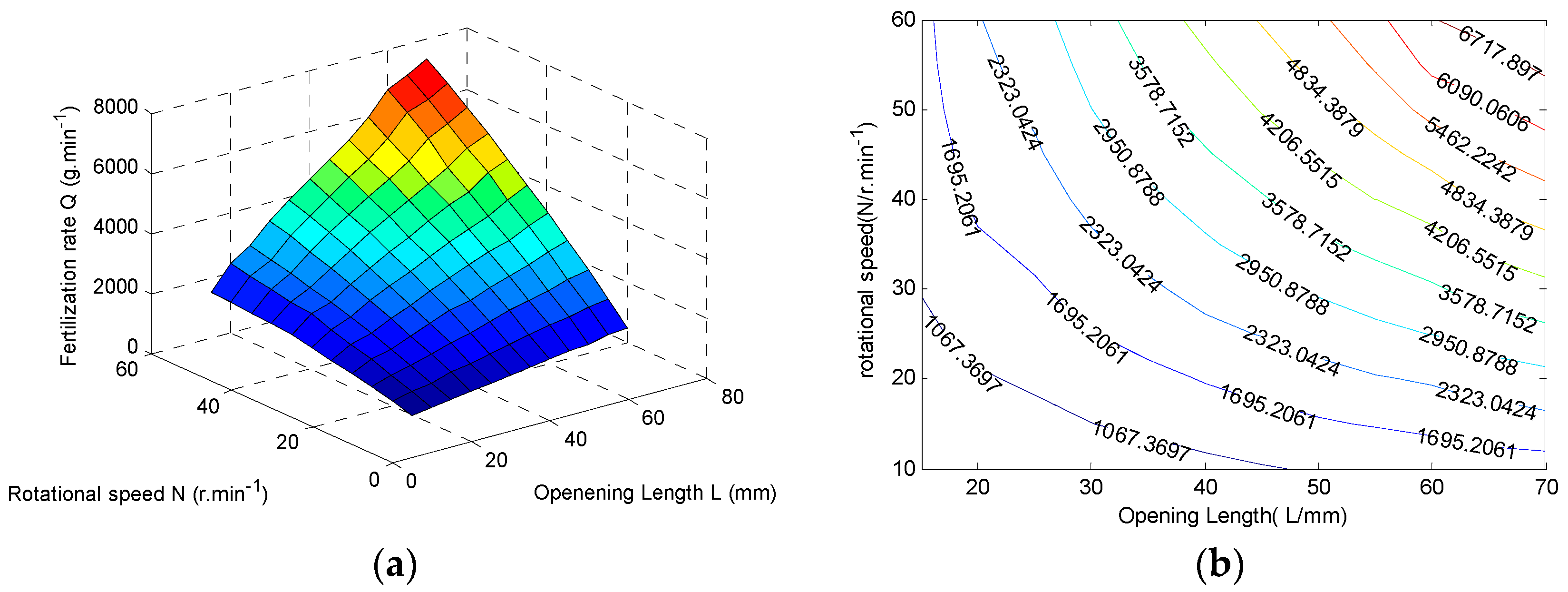
3.2.1. Accuracy Objective Function
3.2.2. Uniformity Objective Function
3.2.3. Adjustment Rapidity Function
4. Evolutionary Multi-Objective Algorithms
4.1. Approaches of Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization
4.1.1. NSGN-III
4.1.2. MOEA/DD
4.1.3. Ar-MOEA
4.2. Performance Metrics for CSO Problem
4.2.1. Hypervolume (HV)
4.2.2. Spacing (SP)
4.2.3. Running Time (RT)
5. Computational Experiments
5.1. Experimental Design
5.2. Parameter Settings
5.3. Evaluation Criteria
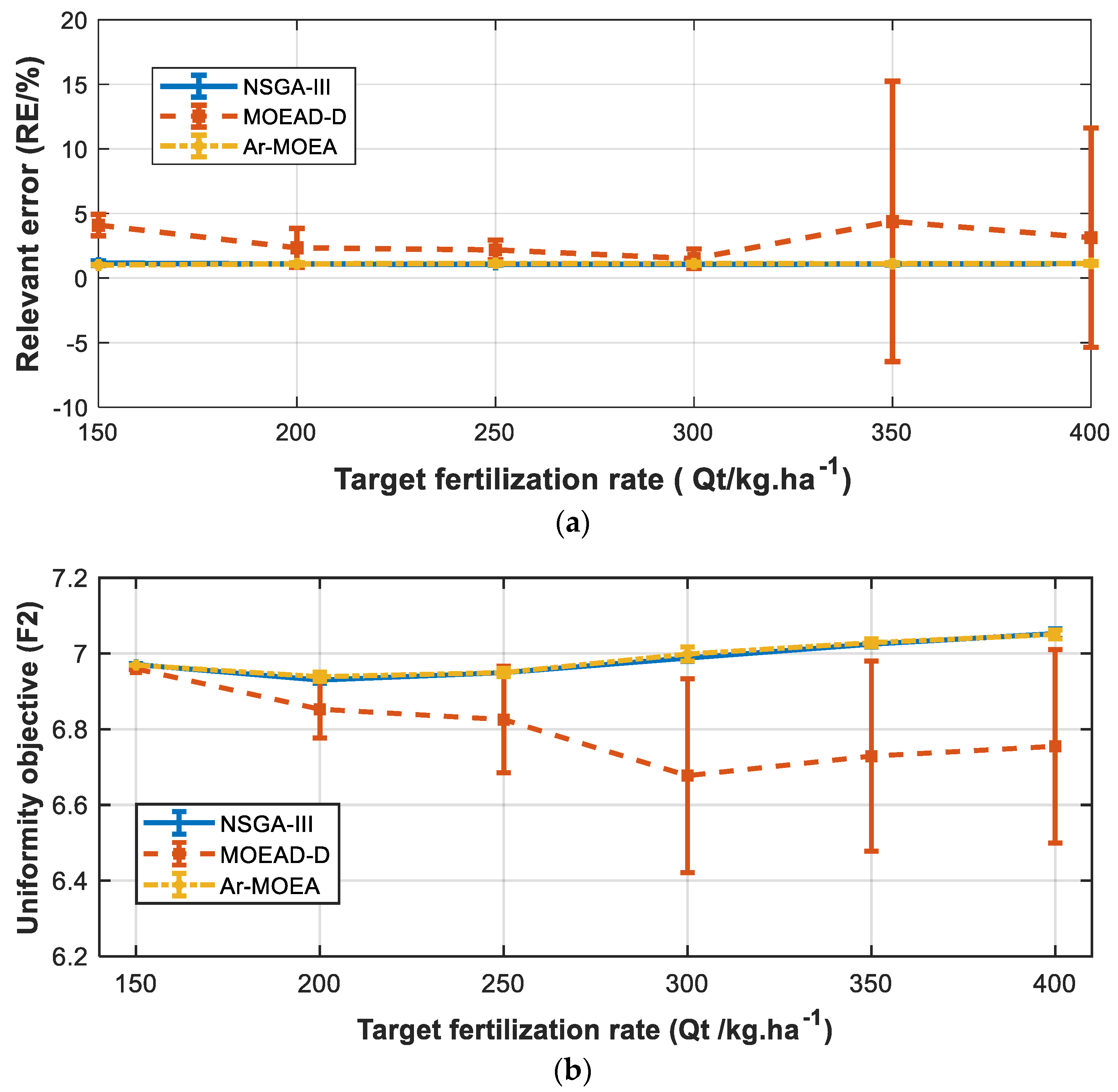
5.3.1. Criteria for the Performance of the MOEAs
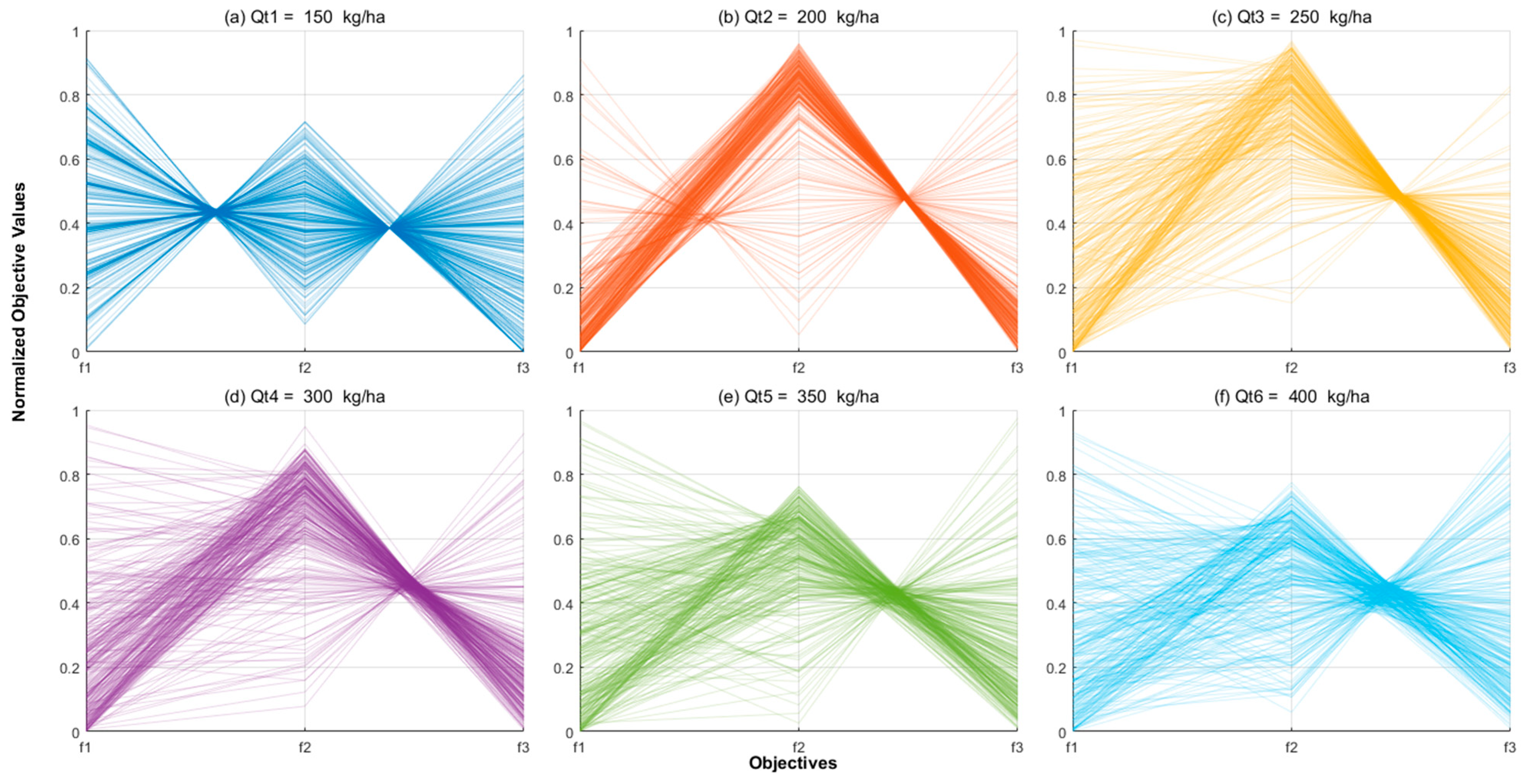
5.3.2. Criteria for the Conflict Analysis Between Different Objectives
5.3.3. Criteria for the Performance of Optimized Control Sequence on Three Objectives
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Performance Comparison of MOEAs
6.2. Analysis of the Conflict Between Different Objects
6.3. Performance on CSO-MOP
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beneduzzi, H.M.; de Souza, E.G.; Moreira, W.K.O.; Sobjak, R.; Bazzi, C.L.; Rodrigues, M. Fertilizer Recommendation Methods for Precision Agriculture—A Systematic Literature Study. Eng. Agric. 2022, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gaadi, K.A.; Tola, E.K.; Alameen, A.A.; Madugundu, R.; Marey, S.A.; Zeyada, A.M.; Edrris, M.K. Control and Monitoring Systems Used in Variable Rate Application of Solid Fertilizers: A Review. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramod Pawase, P.; Madhukar Nalawade, S.; Balasaheb Bhanage, G.; Ashok Walunj, A.; Bhaskar Kadam, P.; Durgude, A.G.; Patil, M.R. Variable Rate Fertilizer Application Technology for Nutrient Management: A Review. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2023, 16, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, W. Variable-Rate Control System for UAV-Based Granular Fertilizer Spreader. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameen, A.A.; Al-Gaadi, K.A.; Tola, E.K. Development and Performance Evaluation of a Control System for Variable Rate Granular Fertilizer Application. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 160, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; He, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, J.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Kang, J. A Fixed-Amount and Variable-Rate Fertilizer Applicator Based on Pulse Width Modulation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 148, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhai, C.; Dou, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, C. Design and Test on Variable Rate Fertilization System Supporting Seeding and Fertilizing Monitoring. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yuan, J.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.; Gu, Y. ARM and DSP-Based Bivariable Fertilizing Control System Design and Implementation. J. Agric. Mach. 2010, 2, 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Luo, C.; Hu, H.; Huang, J. MOEA/D-DE Based Bivariate Control Sequence Optimization of a Variable-Rate Fertilizer Applicator. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 167, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.R.; Mouazen, A.M.; De Ketelaere, B.; Ramon, H.; De Baerdemaeker, J. On-the-Go Variable-Rate Phosphorus Fertilisation Based on a Visible and near-Infrared Soil Sensor. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 99, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y. A Study on the Time Lag and Compensation of a Variable-Rate Fertilizer Applicator. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2021, 37, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelladurai, S.J.S.; Murugan, K.; Ray, A.P.; Upadhyaya, M.; Narasimharaj, V.; Gnanasekaran, S. Optimization of Process Parameters Using Response Surface Methodology: A Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 37, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, C.L.; Li, Y.M.; Zeng, Q.; Zha, X.F. Gaussian Processes Based Bivariate Control Parameters Optimization of Variable-Rate Granular Fertilizer Applicator. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 70, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Tian, M.; Li, J. Control System of Liquid Fertilizer Variable-Rate Fertilization Based on Beetle Antennae Search Algorithm. Processes 2022, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z. An Improved Multi-Objective Optimization Decision Method Using NSGA-III for a Bivariate Precision Fertilizer Applicator. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Y. Design and Experiment of Optimization Control System for Variable Fertilization in Winter Wheat Field Based on Fuzzy PID. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Xu, T.; Song, L.; Wang, R.; Wei, Y. Variable Rate Fertilization System with Adjustable Active Feed-Roll Length. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, G. Effects of Control Sequence Optimisation on the Performance of Bivariate Fertiliser Applicator. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, G.; Der, O. Multi-Objective Optimization of Process Parameters for Laser Cutting Polyethylene Using Fuzzy AHP-Based MCDM Methods. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2025, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.; Anac, S. Multi-Objective Planning Model for Large Scale Irrigation Systems: Method and Application. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3173–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Song, Q.; Chen, S.Y. Multiobjective Fireworks Optimization for Variable-Rate Fertilization in Oil Crop Production. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2013, 13, 4253–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Jain, H. An Evolutionary Many-Objective Optimization Algorithm Using Reference-Point-Based Nondominated Sorting Approach, Part I: Solving Problems with Box Constraints. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2014, 18, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H. MOEA/D: A Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm Based on Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2007, 11, 712–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Bai, J.; He, H.; Peng, J.; Tang, D. Ar-MOEA: A Novel Preference-Based Dominance Relation for Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza-Gutierrez, J.M.; Gomez-Pulido, J.A. Assuming Multiobjective Metaheuristics to Solve a Three-Objective Optimisation Problem for Relay Node Deployment in Wireless Sensor Networks. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2015, 30, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, A.; Srinivasan, D.; Sanyal, K.; Ghosh, A. A Survey of Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithms Based on Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2017, 21, 440–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ding, O.; Qu, R.; Li, K. Hybrid Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithms Based on Decomposition for Wireless Sensor Network Coverage Optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2018, 68, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, R.; Zhang, T.; Ishibuchi, H. Evolutionary Many-Objective Optimization: A Comparative Study of the State-of-The-Art. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 26194–26214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Guan, Z.; Yue, L.; Mumtaz, J.; Liang, J. Modeling and Optimization for Multi-Objective Nonidentical Parallel Machinging Line Scheduling with a Jumping Process Operation Constraint. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Deb, K.; Zhang, Q.; Kwong, S. An Evolutionary Many-Objective Optimization Algorithm Based on Dominance and Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2015, 19, 694–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Y. Integrated Scheduling of Picking and Distribution of Fresh Agricultural Products for Community Supported Agriculture Mode. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Hu, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. Influence of Control Sequence of Spiral Fluted Roller Fertilizer Distributer on Fertilization Performance. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaço, A.F.; de Andrade Rosa, H.J.; Molin, J.P. A Model to Analyze As-Applied Reports from Variable Rate Applications. Precis. Agric. 2014, 15, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ong, Y.S.; Zhang, J.; Feng, L. Consistencies and Contradictions of Performance Metrics in Multiobjective Optimization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 2391–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. Novel Performance Metrics for Robust Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithms. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2015, 21, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Zhao, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. 3-D Deployment Optimization for Heterogeneous Wireless Directional Sensor Networks on Smart City. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Li, X. An Improved NSGA-III Algorithm Based on Distance Dominance Relation for Many-Objective Optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 117738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusar, T.; Filipic, B. Visualization of Pareto Front Approximations in Evolutionary Multiobjective Optimization: A Critical Review and the Prosection Method. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2015, 19, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapotecas-Martínez, S.; Coello Coello, C.A.; Aguirre, H.E.; Tanaka, K. A Review of Features and Limitations of Existing Scalable Multiobjective Test Suites. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 23, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Study | Method | Objectives | Key Findings | Limitations Addressed in This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yuan et al. (2010) [13] | Weighted sum GA | Accuracy, adjustment, rapidity | Achieved 5% RE reduction; runtime < 10 s | Single-objective focus; ignored uniformity |
| Zhang et al. (2019) [9] | MOEA/D-DE | Accuracy, uniformity, rapidity | Identified Pareto solutions; 2.26% RE and 0.33% CV improvement | No field tests |
| Dang et al. (2022) [15] | NSGA-III | Accuracy, uniformity, rapidity, breakage | Taking breakage into account | High computational cost |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Target fertilization rate (Qt) | [150,200,250,300,350,400] | kg/ha |
| Range of the active feed-roll length (L) | [15,70] | mm |
| Range of the rotational speed of driving shaft (N) | [10,60] | r/min |
| Previous adjustment sequence (S0) | [35,0]T | [mm, r/min]T |
| Allowance error (ε) | 0.01 | - |
| Unit adjusting time (Tadj) | [0.15,0.025]T | [s/mm, s/(r/min)]T |
| MOP | NSGA-III | MOEAD/D | AR-MOEA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qt/Kg.ha−1 | HV | SP | RT/s | HV | SP | RT/s | HV | SP | RT/s |
| 150 | 1.64 ± 3.56 × 10−2 | 7.52 × 10−1 ± 1.98 × 10−2 | 5.57 × 10 ± 5.71 | 1.67 ± 1.04 × 10−3 | 1.14 ± 1.94 × 10−3 | 1.84 × 10 ± 7.97 × 10−2 | 1.64 ± 7.58 × 10−5 | 7.21× 10−1 ± 9.82 × 10−3 | 8.76 × 10 ± 3.86 |
| 200 | 8.24 × 10−1 ± 5.14 × 10−2 | 1.32 ± 1.01 × 10−1 | 8.13 × 10 ± 8.85 | 8.19 × 10−1 ± 1.31 × 10−3 | 1.05 ± 4.21 × 10−3 | 1.94 × 10 ± 5.79 | 7.91 × 10 ± 1.01 × 10−3 | 7.46 ± 2.23 × 10−2 | 8.09 × 10 ± 4.01 |
| 250 | 1.30 ± 1.89 × 10−1 | 7.90 × 10−1 ± 4.37 × 10−2 | 1.25 × 102 ± 8.79 | 1.15 ± 1.57 × 10−2 | 1.08 ± 4.90 × 10−3 | 1.93 × 10 ± 5.08 × 10−1 | 1.07 ± 1.29 × 10−2 | 7.27 × 10−1 ± 1.16 × 10−2 | 7.74 × 10 ± 2.51 |
| 300 | 2.21 ± 4.64 × 10−2 | 8.95 × 10−1 ± 6.30 × 10−2 | 1.45 × 102 ± 8.26 | 2.09 ± 1.75 × 10−2 | 1.14 ± 4.45 × 10−3 | 1.86 × 10 ± 6.89 × 10−2 | 1.78 ± 2.30 × 10−2 | 7.13 × 10−1 ± 4.05 × 10−3 | 8.25 × 10 ± 3.06 |
| 350 | 2.02 ± 4.50 × 10−2 | 7.67 × 10−1 ± 2.42 × 10−2 | 1.64 × 102 ± 1.92 × 10 | 1.09 ± 3.08 × 10−2 | 1.12 ± 7.61 × 10−3 | 1.87 × 10 ± 3.97 × 10−1 | 1.64 ± 3.68 × 10−2 | 7.08 × 10−1 ± 6.87 × 10−3 | 8.53 × 10 ± 2.93 |
| 400 | 1.94 ± 6.02 × 10−2 | 7.70 × 10−1 ± 2.84 × 10−2 | 1.71 × 102 ± 5.34 | 1.85 ± 3.43 × 10−2 | 1.11 ± 6.67 × 10−3 | 1.83 × 10 ± 5.75 × 10−2 | 1.63 ± 2.93 × 10−2 | 6.97 × 10−1 ± 3.51 × 10−3 | 8.46 × 10 ± 2.78 |
| MOP | NSGA-III | MOEAD/D | AR-MOEA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qt/Kg.ha−1 | RE/% | F2 | F3 | RE/% | F2 | F3 | RE/% | F2 | F3 |
| 150 | 1.15 ± 1.76 × 10−1 | 6.97 ± 2.32 × 10−3 | 5.11 × 10−1 ± 1.24 × 10−2 | 4.10 ± 0.83× 10−1 | 6.95 ± 2.33 × 10−3 | 3.99 × 10−1 ± 2.60 × 10−2 | 1.01 ± 1.33 × 10−2 | 6.97 ± 1.25 × 10−2 | 3.18 × 10−1 ± 2.16 × 10−2 |
| 200 | 1.09 ± 7.06 × 10−2 | 6.93 ± 3.56 × 10−2 | 3.12 × 10−1 ± 9.28 × 10−3 | 2.34 ± 1.50 × 10−2 | 6.85 ± 7.61 × 10−2 | 9.95 × 10−1 ± 6.55 × 10−1 | 1.10 ± 9.08 × 10−2 | 6.94 ± 1.25 × 10−2 | 3.18 × 10−1 ± 2.16 × 10−2 |
| 250 | 1.07 ± 4.92 × 10−2 | 6.95 ± 4.41 × 10−3 | 3.69 × 10−1 ± 7.40 × 10−3 | 2.18 ± 7.61 × 10−1 | 6.83 ± 1.41 × 10−1 | 1.46 ± 1.35 | 1.13 ± 1.02 × 10−1 | 6.95 ± 1.06 × 10−2 | 3.89 × 10−1 ± 1.95 × 10−2 |
| 300 | 1.07 ± 7.45 × 10−2 | 6.99 ± 4.41 × 10−3 | 4.57 × 10−1 ± 2.14 × 10−2 | 1.50 ± 7.53 × 10−1 | 6.67 ± 2.56 × 10−1 | 3.30 ± 2.38 | 1.11 ± 1.09 × 10−1 | 6.70 ± 1.84 × 10−2 | 4.55 × 10−1± 1.00 × 10−2 |
| 350 | 1.08 ± 8.02 × 10−2 | 7.02 ± 7.88 × 10−3 | 5.46 × 10−1 ± 1.93 × 10−2 | 4.38 ± 1.09 × 10 | 6.73 ± 2.51 × 10−1 | 2.98 ± 2.32 | 1.11 ± 8.07 × 10−2 | 7.29 ± 1.01 × 10−2 | 5.47 × 10−1 ± 1.60 × 10−2 |
| 400 | 1.11 ± 1.08 × 10−3 | 7.05 ± 1.29 × 10−2 | 5.87 × 10−1 ± 1.40 × 10−2 | 3.12 ± 8.49 × 10−2 | 6.76 ± 2.55 × 10−1 | 2.92 ± 2.29 | 1.14 ± 1.35 × 10−1 | 7.05 ± 1.21 × 10−2 | 5.93 × 10−1 ± 2.09 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhuang, Q.; Liu, G. Analysis of the Multi-Objective Control Sequence Optimization Problem in Bivariate Fertilizer Applicators. Symmetry 2025, 17, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060926
Zhang J, Zhuang Q, Liu G. Analysis of the Multi-Objective Control Sequence Optimization Problem in Bivariate Fertilizer Applicators. Symmetry. 2025; 17(6):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060926
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiqin, Qibin Zhuang, and Gang Liu. 2025. "Analysis of the Multi-Objective Control Sequence Optimization Problem in Bivariate Fertilizer Applicators" Symmetry 17, no. 6: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060926
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhuang, Q., & Liu, G. (2025). Analysis of the Multi-Objective Control Sequence Optimization Problem in Bivariate Fertilizer Applicators. Symmetry, 17(6), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060926







