Symmetric Model for Predicting Homography Matrix Between Courts in Co-Directional Multi-Frame Sequence
Abstract
1. Introduction
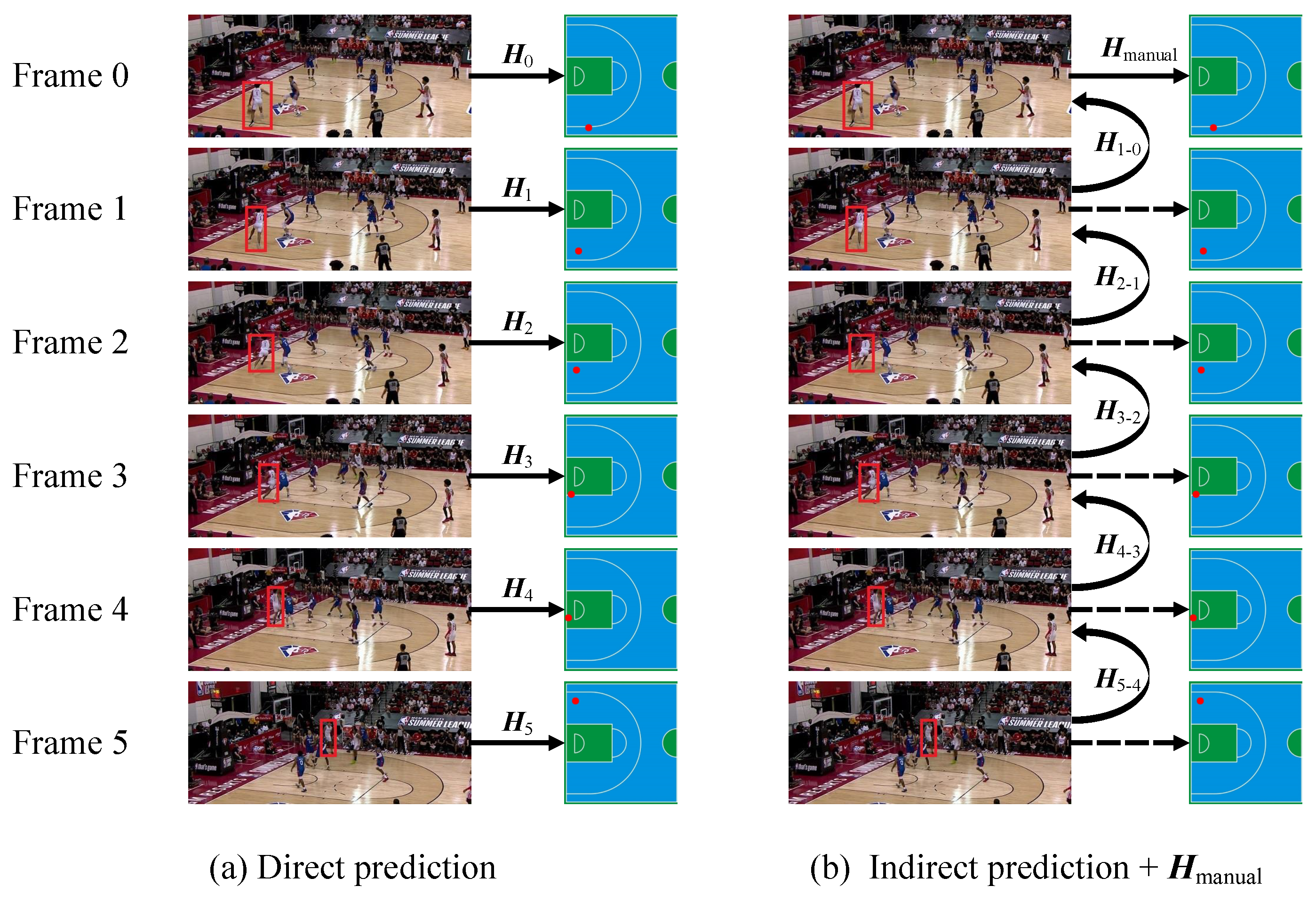
- The model exploits the mutual invertibility property of bidirectional homography transformation matrices for paired images, enhancing the accuracy of homography transformation even in scenarios with certain content changes.
- By leveraging matrix decomposition, the proposed method requires homography matrix annotation only for the initial and final frames, thereby reducing the data annotation workload.
- The proposed strategy of selecting four pairs of keypoints effectively trains the symmetric bidirectional stacked neural network by using a continuous frame sequence as input.
2. Related Work
3. Methods
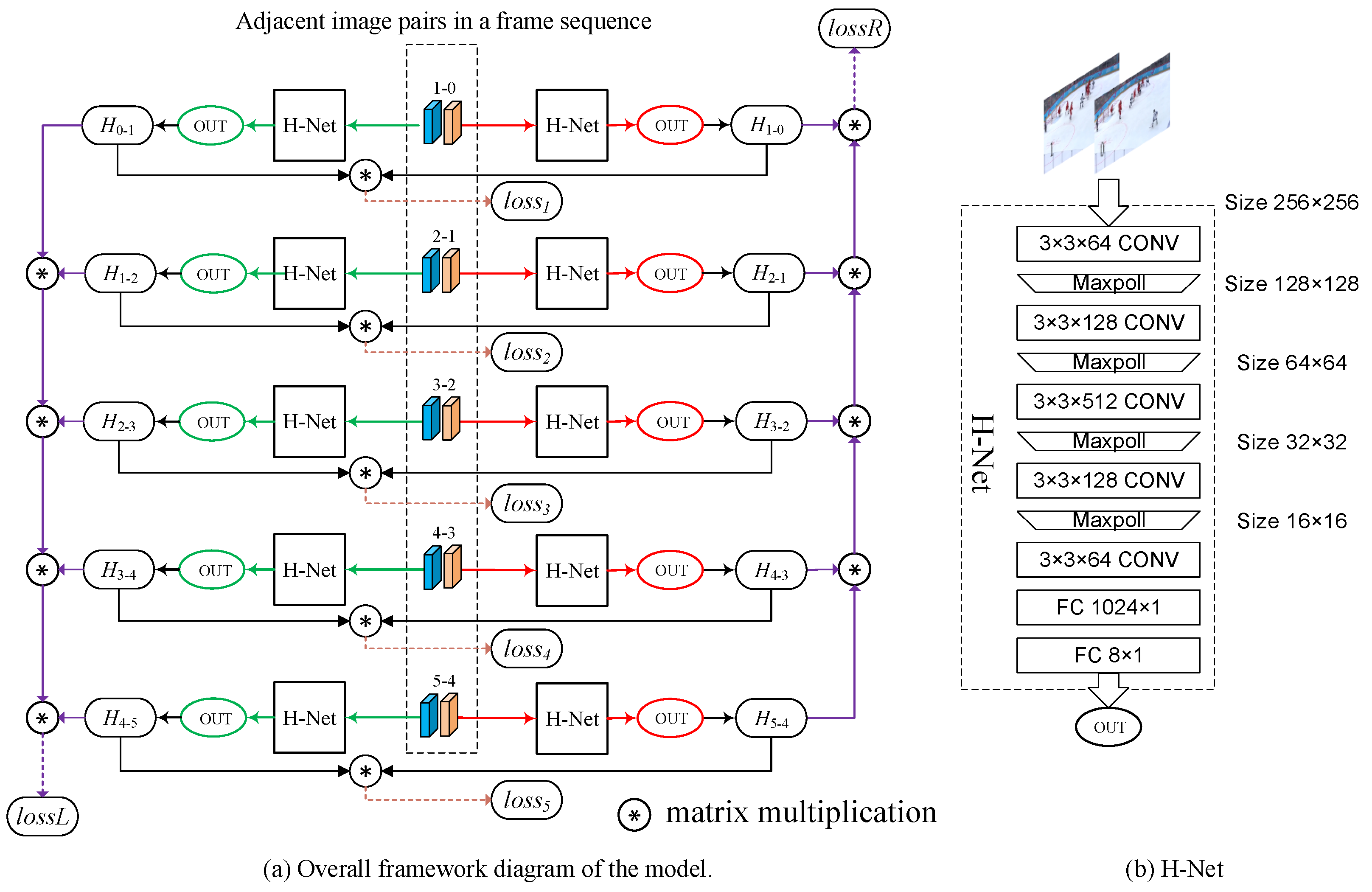
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. Decomposability of Homography Matrix
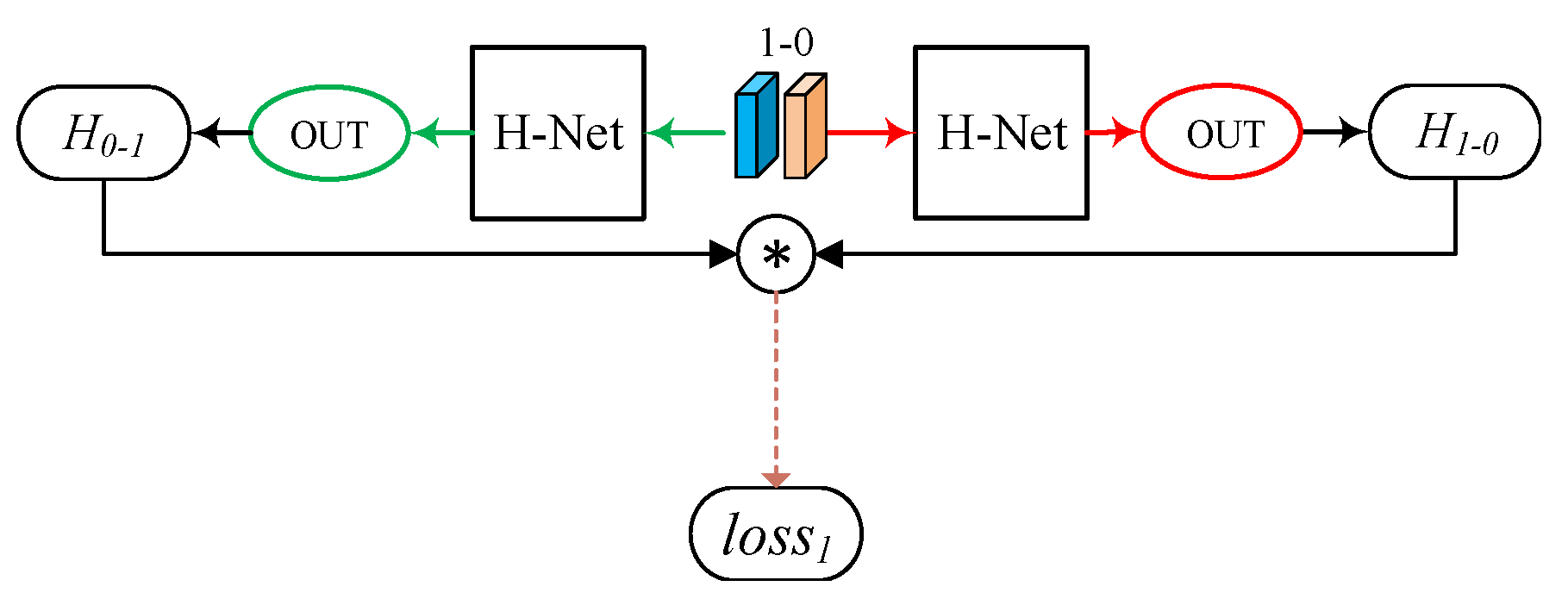
3.3. Mutual Invertibility of Bidirectional Homography Matrices
3.4. Key Point Selection Strategy
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Experimental Environment and Dataset
4.2. Pre-Training of the Stacked Unit Network
4.3. Performance Metrics
5. Results and Discussion
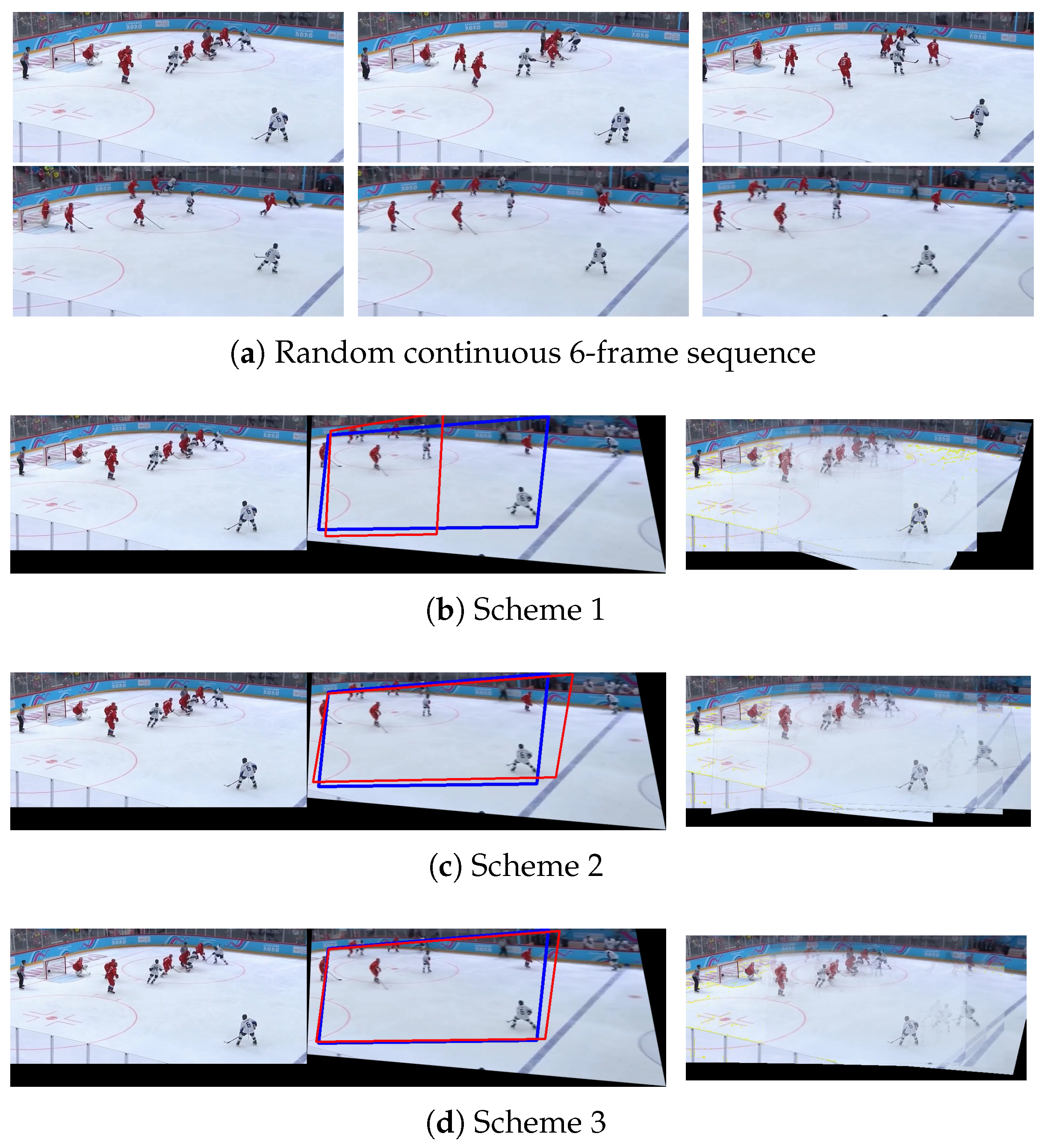
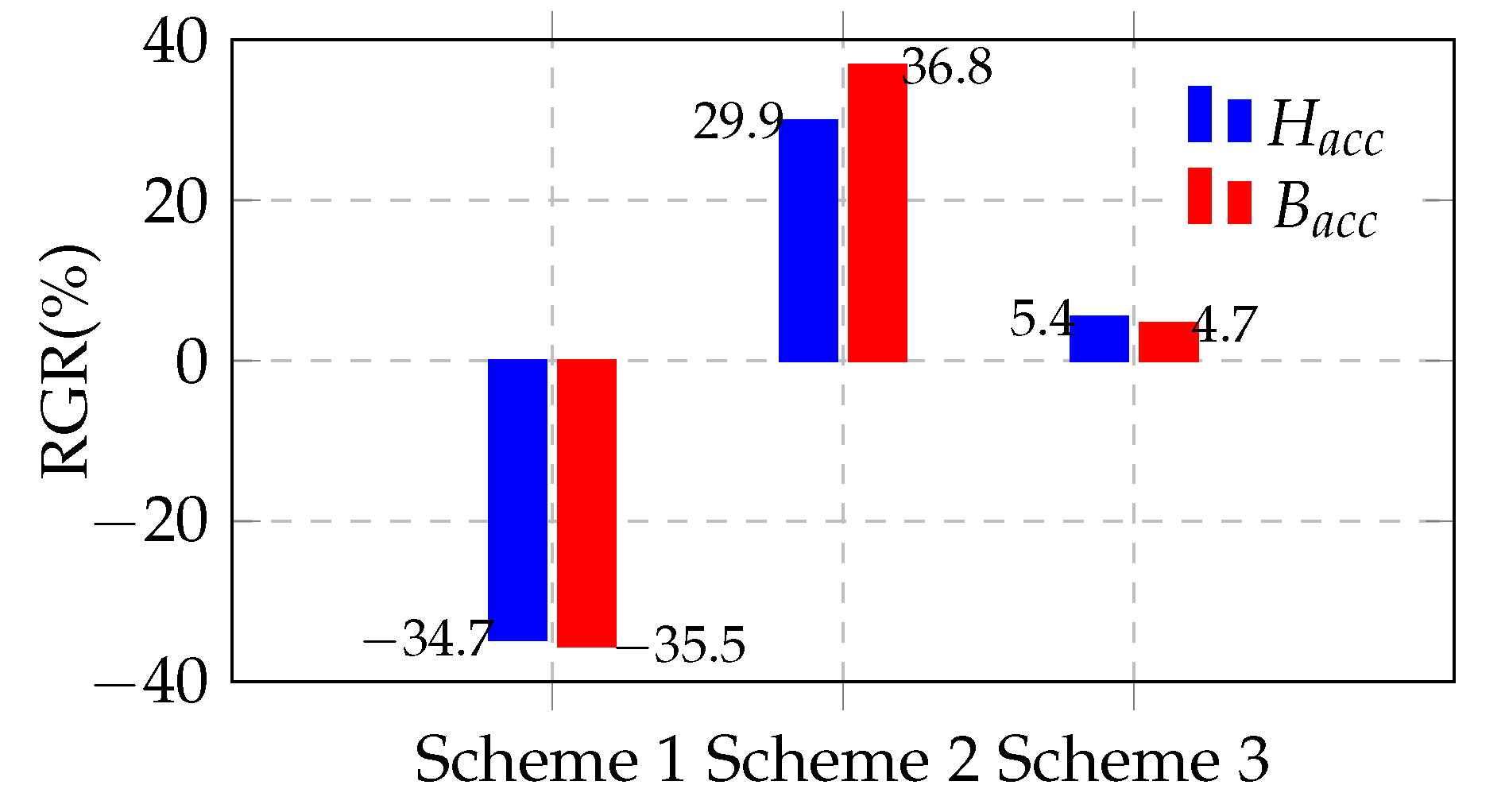
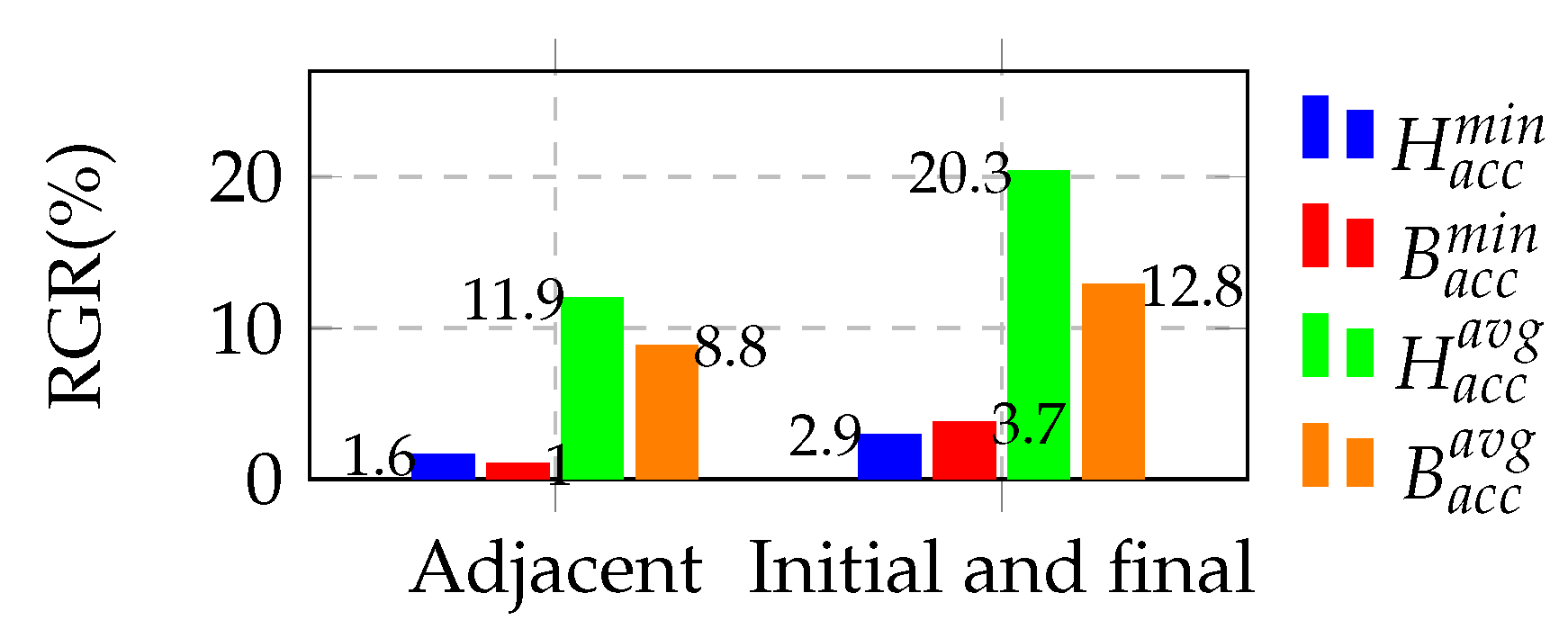
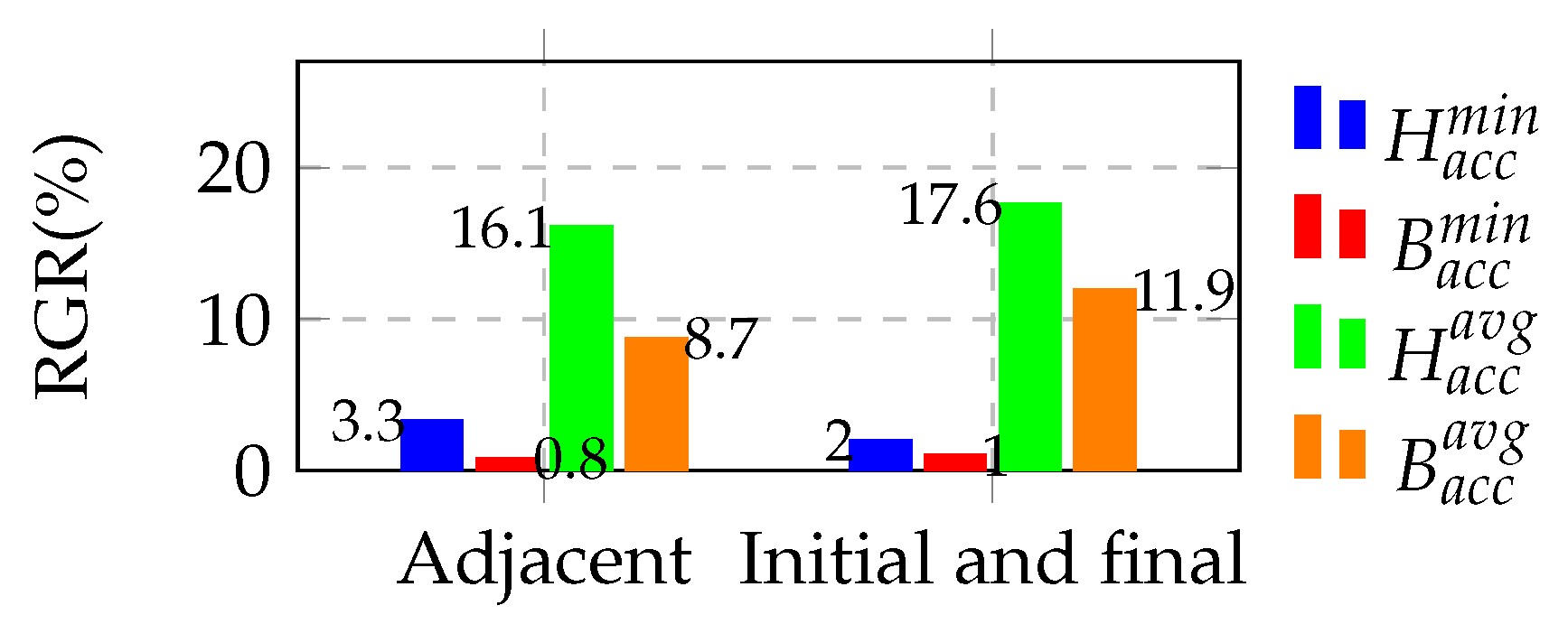
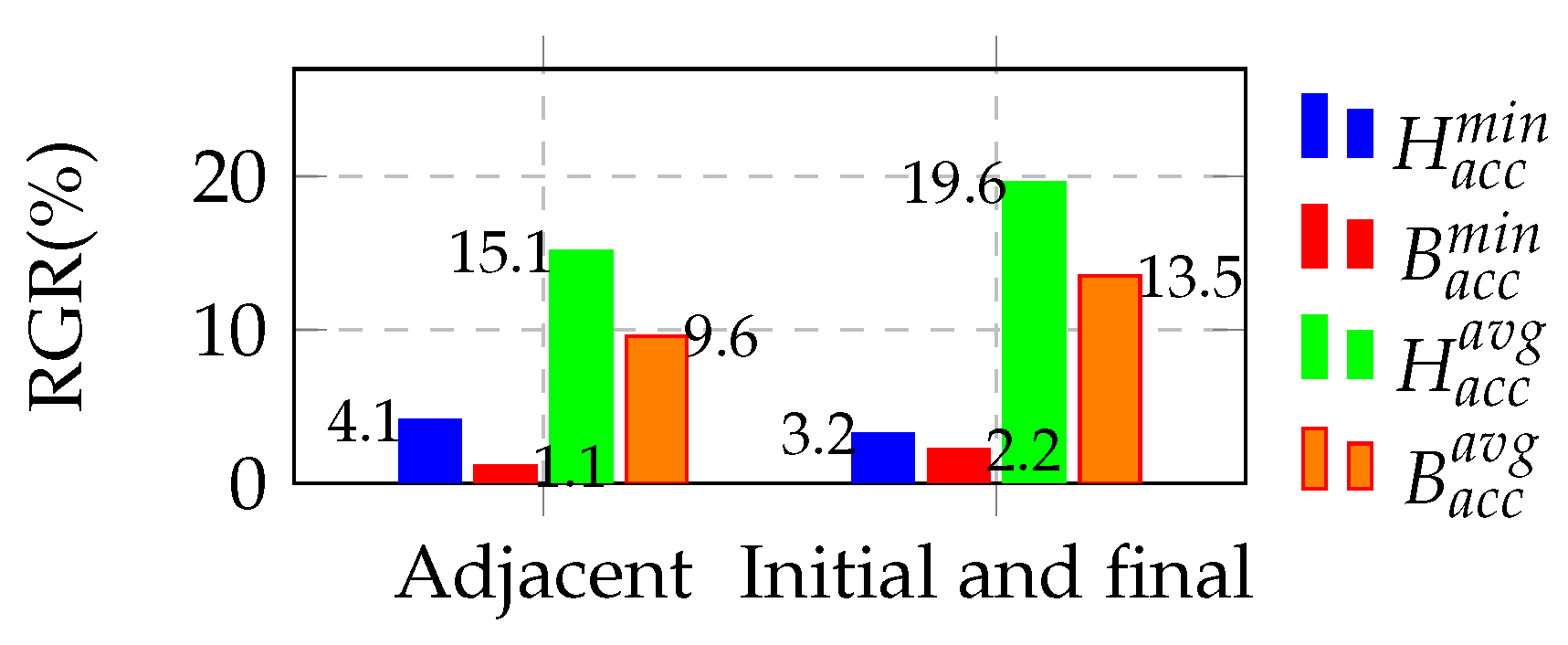
5.1. Stacking Quantity Selection Experiment
5.2. Ablation Experiment
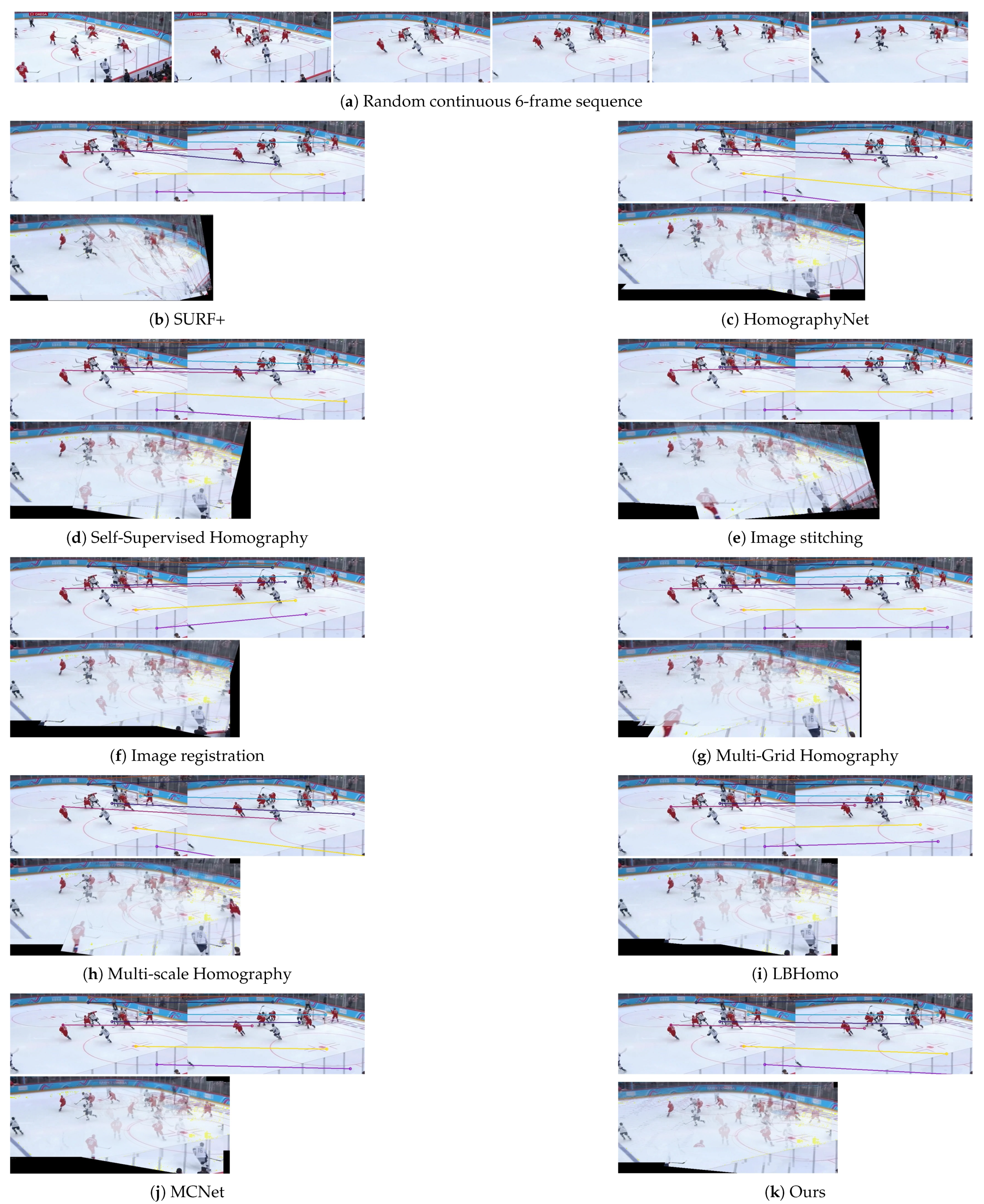
5.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Agapito, L.; Hayman, E.; Reid, I. Self-Calibration of Rotating and Zooming Cameras. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2001, 45, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Da, F. Calibration refinement for a fringe projection profilometry system based on plane homography. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 140, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yao, C.; Feng, B.; Dai, F. Image stitching via deep homography estimation. Neurocomputing 2021, 450, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Lin, C.; Liao, K.; Zhao, Y. Learning edge-preserved image stitching from multi-scale deep homography. Neurocomputing 2022, 491, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.; Gong, H.; Fisher, R. Color Homography: Theory and Applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Spatiotemporally Enhanced Photometric Loss for Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, J.; Tardos, J. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chin, T.; Suter, D. Simultaneously Fitting and Segmenting Multiple-Structure Data with Outliers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1177–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Chang, C.; Ai, Y. A New Accurate and Fast Homography Computation Algorithm for Sports and Traffic Video Analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 2993–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ye, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Jia, L.; Luo, K.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Content-Aware Unsupervised Deep Homography Estimation and its Extensions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 2849–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murino, V.; Castellani, U.; Etrari, A.; Fusiello, A. Registration of very time-distant aerial images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Rochester, NY, USA, 22–25 September 2002; pp. 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, J.; Shashua, A. Multiple View Geometry of General Algebraic Curves. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 56, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P. How the Hough transform was invented [DSP History]. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2009, 26, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Chang, M.; Wu, J.; Chi, L. Robust Camera Calibration and Player Tracking in Broadcast Basketball Video. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2011, 13, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battikh, T.; Jabri, I. Camera calibration using court models for real-time augmenting soccer scenes. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2011, 51, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sang, H. Robust image mosaicing of soccer videos using self-calibration and line tracking. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2001, 4, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Pan, X.; Cheng, J.; Song, J. Deep Image Registration With Depth-Aware Homography Estimation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeTone, D.; Malisiewicz, T.; Rabinovich, A. Deep image homography estimation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.03798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derpanis, K. The Harris Corner Detector; York University: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Sukthankar, R. PCA-SIFT: A more distinctive representation for local image descriptors. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004; p. 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikainen, M.; Maenpaa, T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van, G.L. Surf: Speeded up robust features. Lecture notes in computer science. In Proceeding of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; pp. 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Kubota, A.; Kawakita, K.; Nonaka, K.; Sankoh, H.; Naito, S. Fast camera self-calibration for synthesizing Free Viewpoint soccer Video. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–9 March 2017; pp. 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Lakemond, R.; Denman, S.; Sridharan, S.; Fookes, C.; Morgan, S. Calibrating Cameras in Poor-Conditioned Pitch-Based Sports Games. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 6–11 June 2018; pp. 1902–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorgpour, A.; Fotouhi, M.; Kasaei, S. Robust homography optimization in soccer scenes. In Proceedings of the 2015 23rd Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering, Tehran, Iran, 10–14 May 2015; pp. 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Y.; Ait-Aider, O. Rolling Shutter Homography and its Applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2780–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Bai, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Deep homography estimation with pairwise invertibility constraint. In Proceedings of the Structural, Syntactic, and Statistical Pattern Recognition: Joint IAPR International Workshop, Beijing, China, 17–19 August 2018; pp. 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czolbe, S.; Krause, O.; Feragen, A. DeepSim: Semantic similarity metrics for learned image registration. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.05735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassab, V.; Maanicshah, K.; Bouguila, N.; Green, P. REP-Model: A deep learning framework for replacing ad billboards in soccer videos. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), Naples, Italy, 29 November–1 December 2020; pp. 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Cabello, M.; Garcia-Gonzalez, J.; Luque-Baena, R.; Thurnhofer-Hemsi, K.; Lopez-Rubio, E. Adaptive estimation of optimal color transformations for deep convolutional network based homography estimation. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 3106–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Du, Y.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, J.; Yang, J. A Novel Region-Based Image Registration Method for Multisource Remote Sensing Images Via CNN. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; You, Z.; An, P.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y. Efficient and robust homography estimation using compressed convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the Digital TV and Multimedia Communication: 15th International Forum, Shanghai, China, 20–21 September 2018; pp. 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Robinson, D.; Vidal, R.; Kneip, L.; Tsakiris, M. Robust Homography Estimation via Dual Principal Component Pursuit. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6079–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Li, H. FM-Net: Deep Learning Network for the Fundamental Matrix Estimation from Biplanar Radiographs. Comput. Meth. Programs Biomed. 2022, 220, 106782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Chen, S.W.; Shivakumar, S.S.; Taylor, C.J. Unsupervised deep homography: A fast and robust homography estimation model. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Self-Supervised deep homography estimation with invertibility constraints. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 128, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koguciuk, D.; Arani, E.; Zonooz, B. Perceptual loss for robust unsupervised homography estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Online, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 4274–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Han, S.; Liu, S. Semi-supervised deep large-baseline homography estimation with progressive equivalence constraint. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; pp. 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youku. Available online: https://v.youku.com/video?spm=a2hkm.8166622.PhoneSokuUgc_1.dscreenshot&&vid=XNTEzNjY3NzU4MA==&playMode=pugv&frommaciku=1 (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Tencent Video. Available online: https://v.qq.com/x/cover/mzc00200q077ncj/m0046rerfdq.html (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Youku. Available online: https://v.youku.com/video?spm=a2hkm.8166622.PhoneSokuUgc_1.dscreenshot&&vid=XNDA1NDc1NDA1Mg==&playMode=pugv&frommaciku=1 (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Huang, C.W.; Cheng, J.C.; Pan, X. Pixel-wise visible image registration based on deep neural network. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2022, 48, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Fang, J.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, X. Registration method for power equipment infrared and visible images based on contour feature. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2022, 41, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Yap, P.; Shen, D. Deformable Image Registration Using a Cue-Aware Deep Regression Network. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 1900–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Yang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Hu, X. Rapid multimodality registration based on MM-SURF. Neurocomputing 2014, 131, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Lin, C.; Liao, K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y. Depth-Aware Multi-Grid Deep Homography Estimation With Contextual Correlation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 4460–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, K.; Sun, S.; He, C. Multi-scale homography estimation based on dual feature aggregation transformer. IET Image Process. 2023, 17, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cao, S.Y.; Hu, J.; Zuo, S.; Yu, B.; Ying, J. MCNet: Rethinking the core ingredients for accurate and efficient homography estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 25932–25941. [Google Scholar]
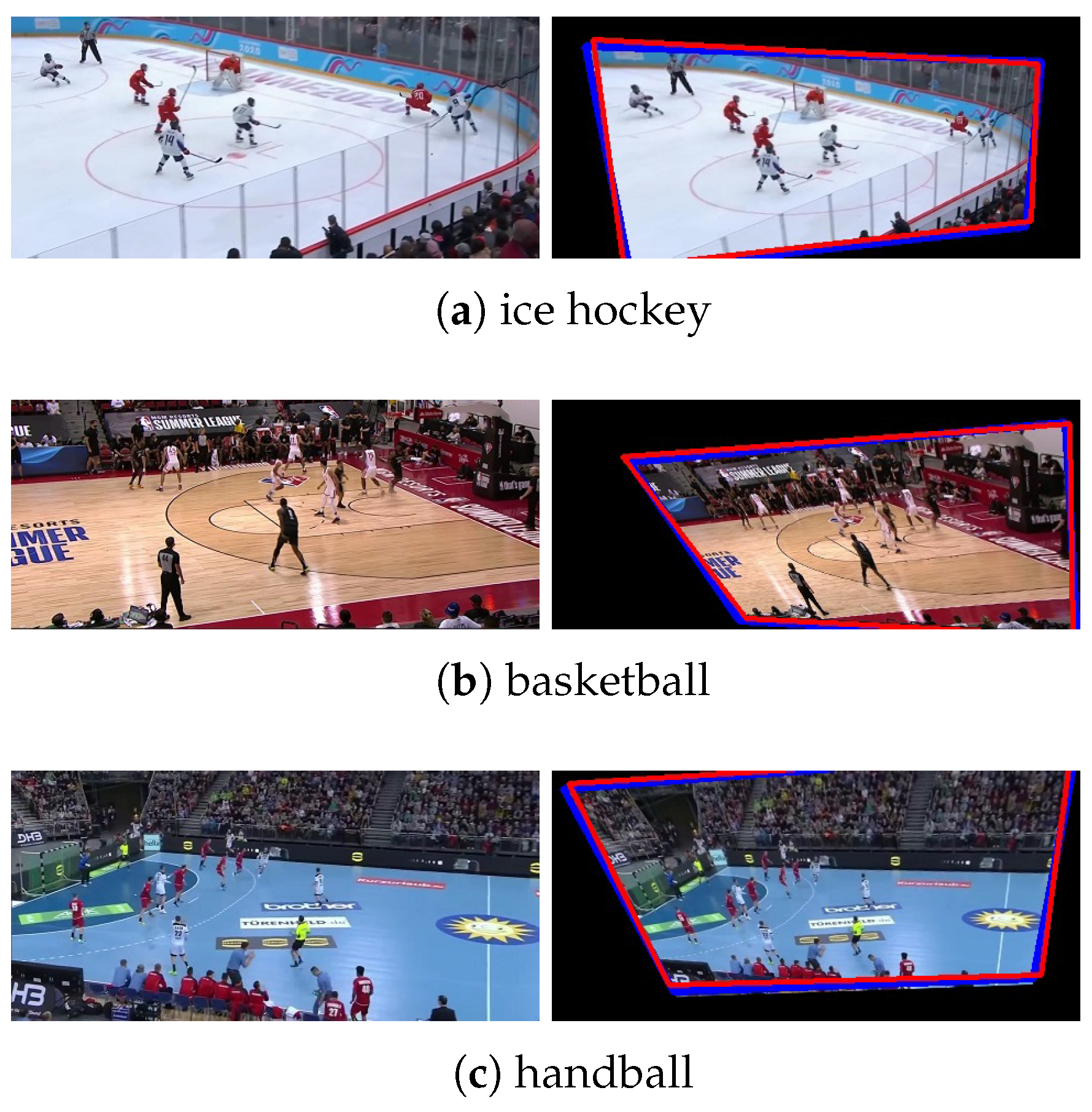
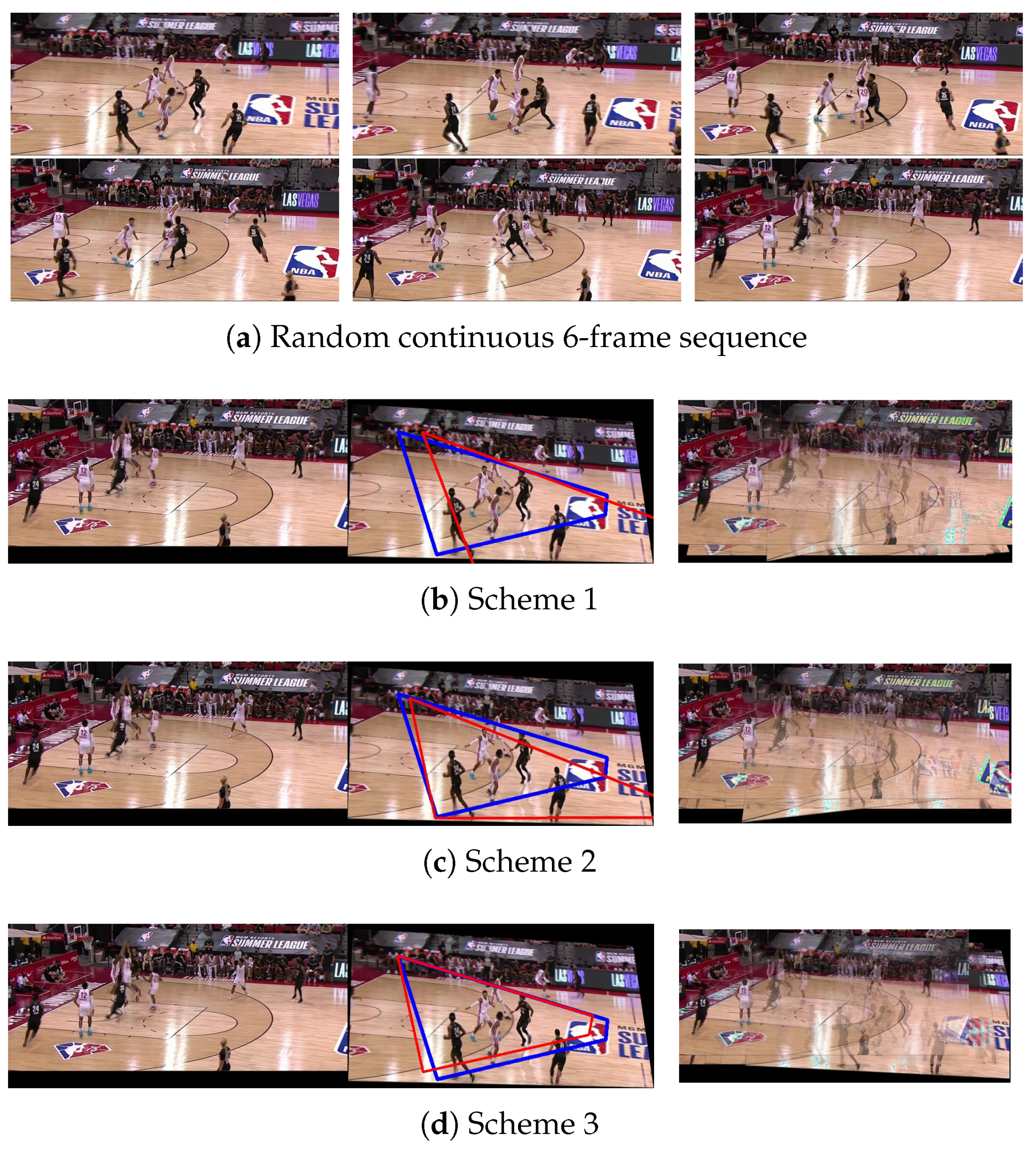
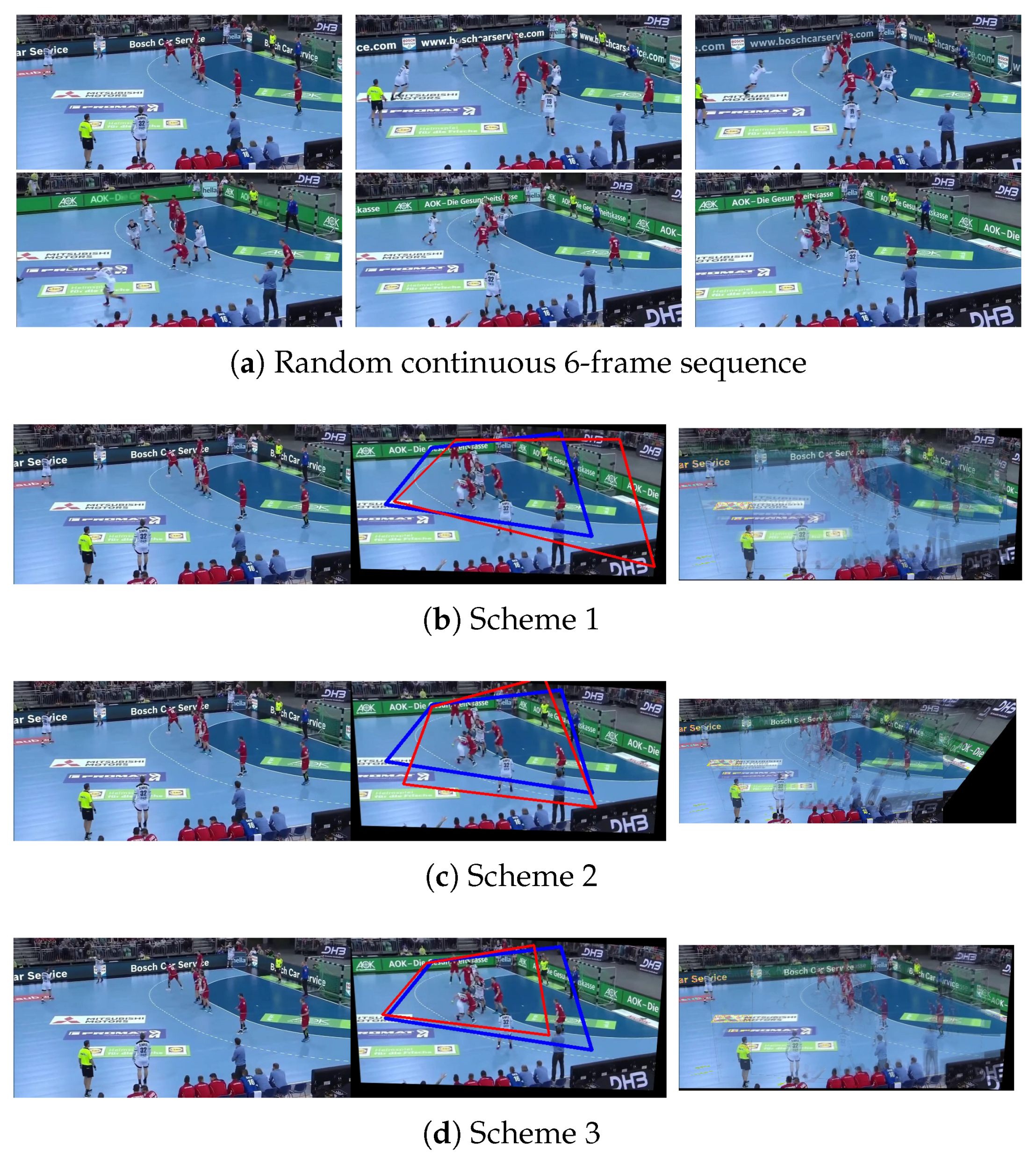






| Quantity | Parameters | Time (ms) | Proportion of Labels (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 67 M | 31.3 | 50 | 88.2 | 90.4 |
| 3 | 84 M | 47.8 | 33.3 | 86.6 | 88.5 |
| 4 | 100 M | 64.6 | 25 | 84.9 | 86.3 |
| 5 | 117 M | 80.4 | 20 | 83.8 | 85.7 |
| 6 | 134 M | 96.1 | 16.7 | 71.4 | 74.6 |
| 7 | 151 M | 112.5 | 14.3 | 48.7 | 55.3 |
| Scheme | Ice Hockey | Basketball | Handball | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | 52.3 | 63.5 | 47.7 | 58.0 | 58.1 | 67.3 |
| Scheme 2 | 35.7 | 39.6 | 30.5 | 33.8 | 43.8 | 49.7 |
| Scheme 3 | 76.4 | 80.4 | 77.6 | 81.8 | 80.7 | 83.5 |
| Scheme | Ice Hockey | Basketball | Handball | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | 34.1 | 41.6 | 31.1 | 36.4 | 38.0 | 43.7 |
| Scheme 2 | 48.2 | 53.3 | 42.5 | 55.1 | 51.4 | 58.6 |
| Scheme 3 | 82.4 | 85.8 | 80.2 | 83.9 | 84.3 | 87.1 |
| Methods | Ice Hockey | Basketball | Handball | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SURF+ [47] | 71.5 | 77.3 | 73.0 | 78.6 | 70.9 | 74.5 |
| HomographyNet [18] | 51.4 | 62.3 | 48.6 | 60.5 | 54.9 | 65.2 |
| Self-Supervised Homography [38] | 70.7 | 74.2 | 64.4 | 76.1 | 73.6 | 77.4 |
| Image stitching [3] | 74.0 | 78.5 | 74.7 | 81.1 | 76.5 | 82.6 |
| Image registration [44,45] | 72.6 | 77.8 | 73.2 | 80.4 | 71.8 | 79.7 |
| Multi-Grid Homography [48] | 74.3 | 79.6 | 71.6 | 79.5 | 74.3 | 81.8 |
| Multi-scale Homography [49] | 53.6 | 61.4 | 50.6 | 61.8 | 58.4 | 62.7 |
| LBHomo [40] | 75.2 | 79.1 | 75.1 | 80.2 | 77.5 | 82.3 |
| MCNet [50] | 71.3 | 74.9 | 70.5 | 78.7 | 73.2 | 79.4 |
| Ours | 76.4 | 80.4 | 77.6 | 81.8 | 80.7 | 83.5 |
| Methods | Ice Hockey | Basketball | Handball | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SURF+ [47] | 65.5 | 73.8 | 68.9 | 77.1 | 66.4 | 78.4 |
| HomographyNet [18] | 54.0 | 67.5 | 59.7 | 67.1 | 56.8 | 66.2 |
| Self-Supervised Homography [38] | 63.4 | 73.5 | 60.5 | 68.3 | 69.1 | 71.4 |
| Image stitching [3] | 74.4 | 80.3 | 76.6 | 82.5 | 78.2 | 84.8 |
| Image registration [44,45] | 69.2 | 79.4 | 61.5 | 68.7 | 74.5 | 75.3 |
| Multi-Grid Homography [48] | 78.5 | 81.9 | 72.3 | 83.1 | 81.7 | 85.2 |
| Multi-scale Homography [49] | 57.8 | 64.5 | 60.2 | 65.7 | 50.1 | 62.3 |
| LBHomo [40] | 80.1 | 82.7 | 78.6 | 82.4 | 81.3 | 84.5 |
| MCNet [50] | 73.8 | 80.8 | 75.5 | 79.6 | 76.4 | 82.6 |
| Ours | 82.4 | 85.8 | 80.2 | 83.9 | 84.3 | 87.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Luo, J.; Liang, X. Symmetric Model for Predicting Homography Matrix Between Courts in Co-Directional Multi-Frame Sequence. Symmetry 2025, 17, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060832
Zhang P, Luo J, Liang X. Symmetric Model for Predicting Homography Matrix Between Courts in Co-Directional Multi-Frame Sequence. Symmetry. 2025; 17(6):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060832
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Pan, Jiangtao Luo, and Xupeng Liang. 2025. "Symmetric Model for Predicting Homography Matrix Between Courts in Co-Directional Multi-Frame Sequence" Symmetry 17, no. 6: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060832
APA StyleZhang, P., Luo, J., & Liang, X. (2025). Symmetric Model for Predicting Homography Matrix Between Courts in Co-Directional Multi-Frame Sequence. Symmetry, 17(6), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17060832







