PMSM Speed Control Based on Improved Adaptive Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Fractional-Order Disturbance Observer (FOSMDO): merges fractional calculus and sliding mode estimation for fast, accurate disturbance tracking, particularly against periodic load torques;
- (2)
- Adaptive Variable Exponential Reaching Law: employs a novel adaptive approach to reduce chattering and accelerate sliding mode convergence;
- (3)
- Integrated Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Observer: utilizes the estimated disturbance to compensate the q-axis current, further enhancing the system’s anti-disturbance capability.
2. PMSM Mathematical Model
- (1)
- Three-phase symmetrical stator winding distribution with ideal electromagnetic characteristics;
- (2)
- Neglect of magnetic saturation effects and iron core losses;
- (3)
- Insensitivity of permanent magnet flux linkage (ψf) to temperature variations;
- (4)
- Exclusion of high-frequency parasitic effects and eddy current losses.
- iα, iβ: Stator current components in α-β frame
- uα, uβ: Stator voltage components in α-β frame
- id, iq: Stator current components in d-q frame
- ud, uq: Stator voltage components in d-q frame
- eα, eβ: Back-EMF components
- Rs: Stator resistance (Ω)
- Ls: Stator winding inductance (H)
- ψf: Permanent magnet flux linkage (Wb)
- p: polar number
- ωr: mechanical angular velocity (rad/s)
- ωe: electrical angular velocity (rad/s)
- Te: electromagnetic torque (N·m)
- TL: load torque (N·m)
- J: Moment of inertia (kg·m2)
3. Design of Speed Controller
3.1. Fractional Order Controller Theory
3.2. Design of a New Adaptive Approach Law
- (1)
- The power term (0 < μ < 1) in enhances the approach force when moving away.
- (2)
- The term E represents the Euclidean distance in the state space between the equilibrium point and the current position.
- (3)
- Switching Gain Adaptation Law
- (4)
- Power gain adaptation law :
3.3. Design of Fractional Sliding Mode Speed Controller
4. Design of Fractional Sliding Mode Observer
5. Simulation Verification
5.1. Performance Test of Fractional Sliding Mode Observer
5.2. Controller Performance Testing
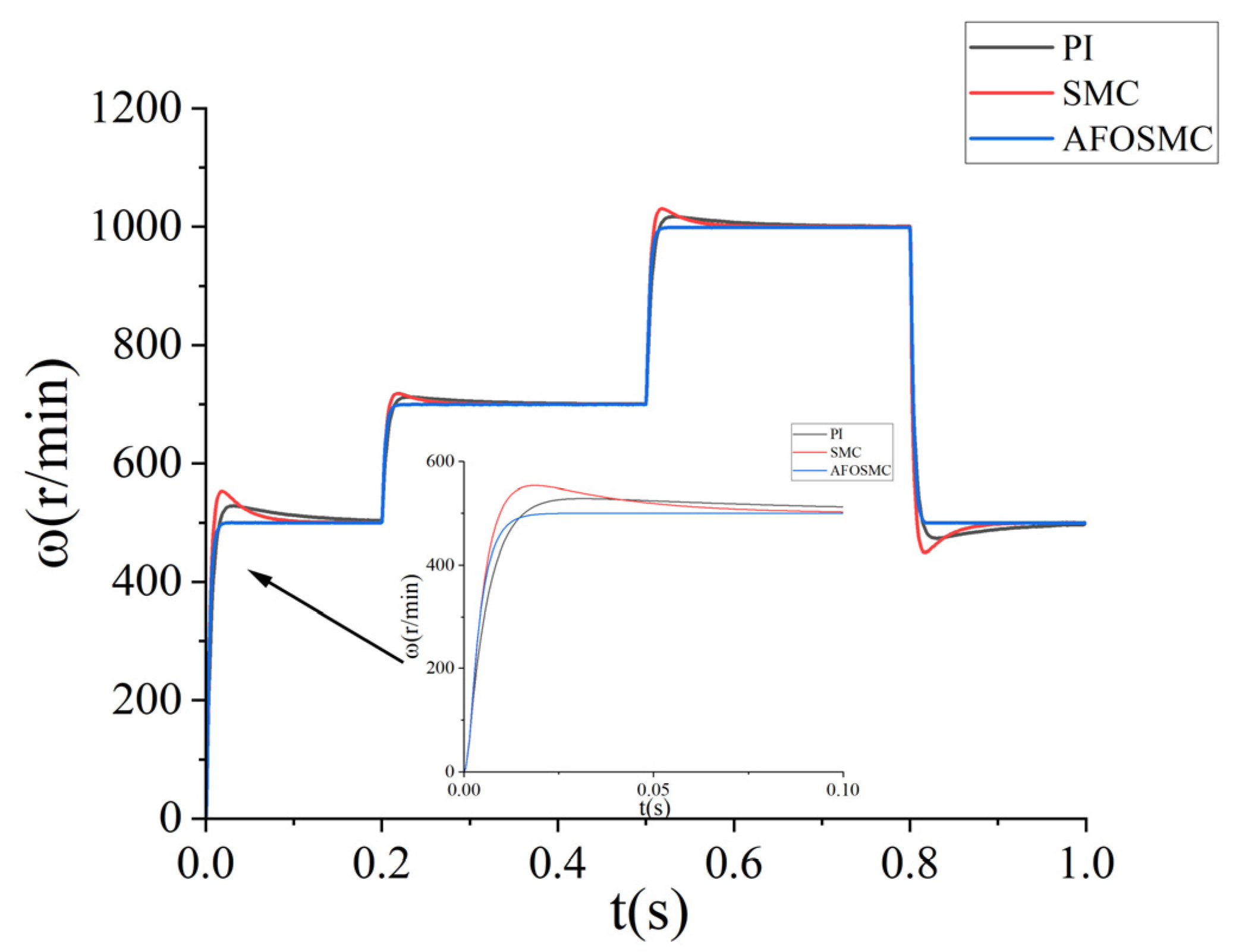
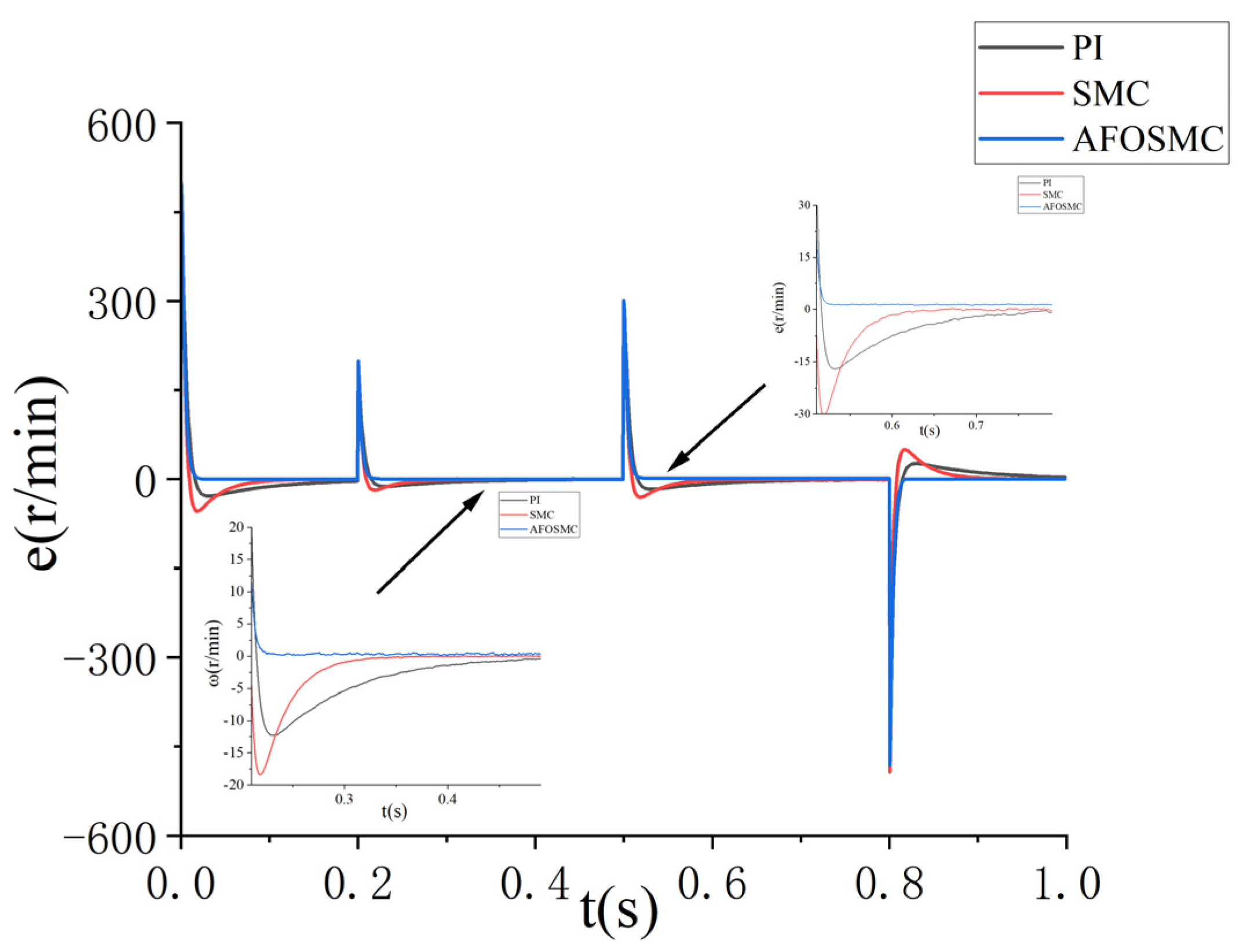
5.2.1. No-Load Start Transmission
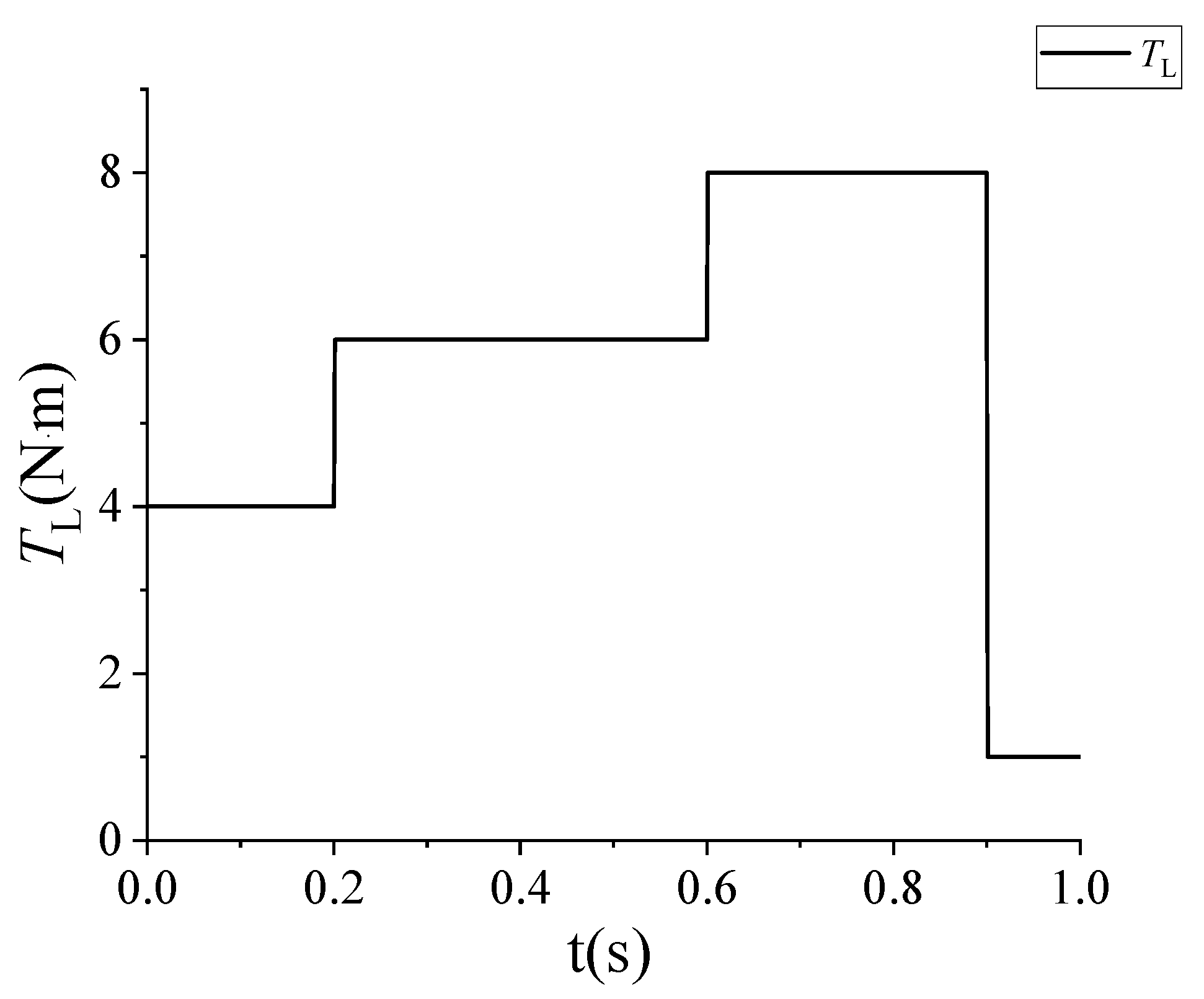
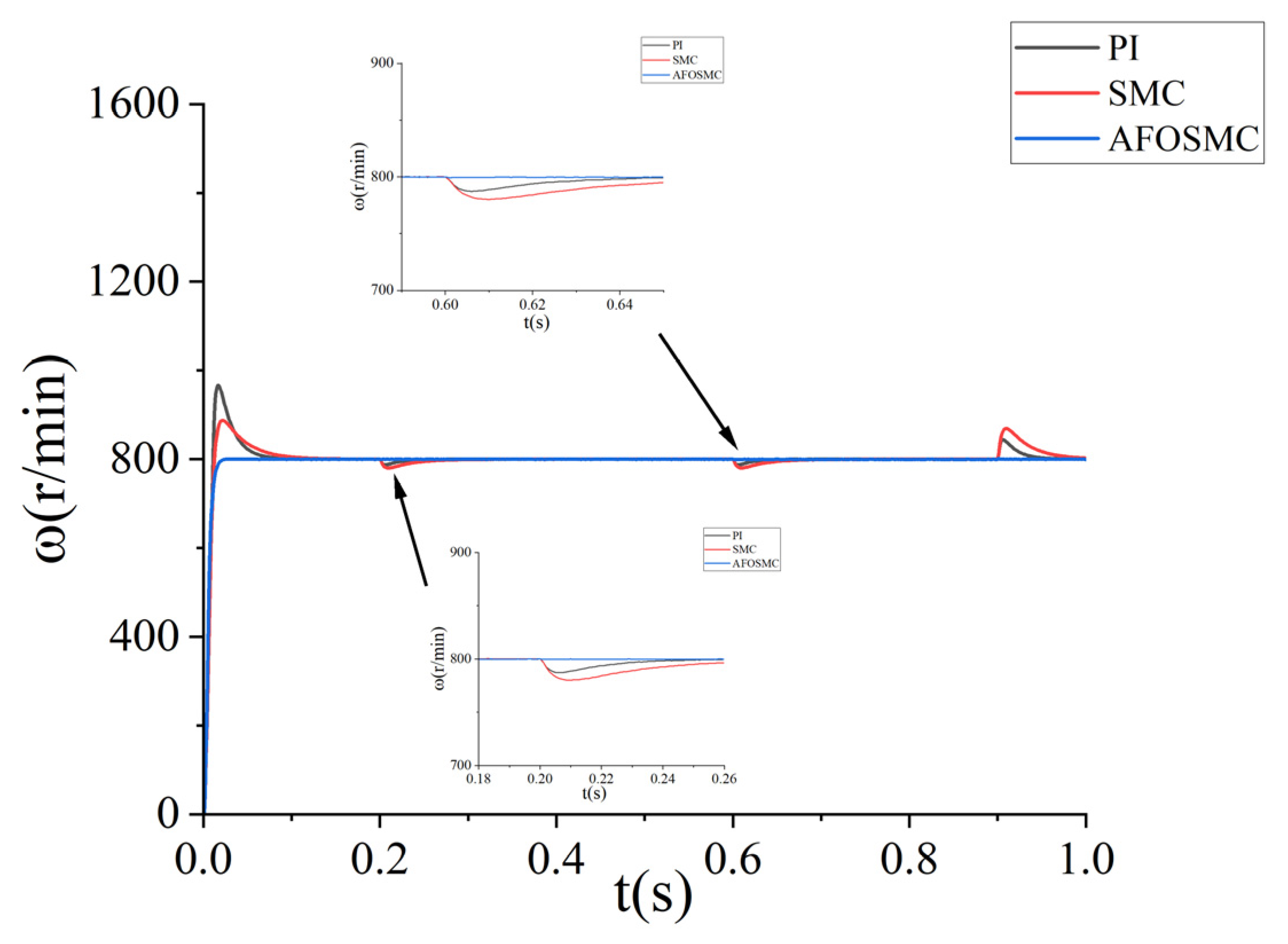
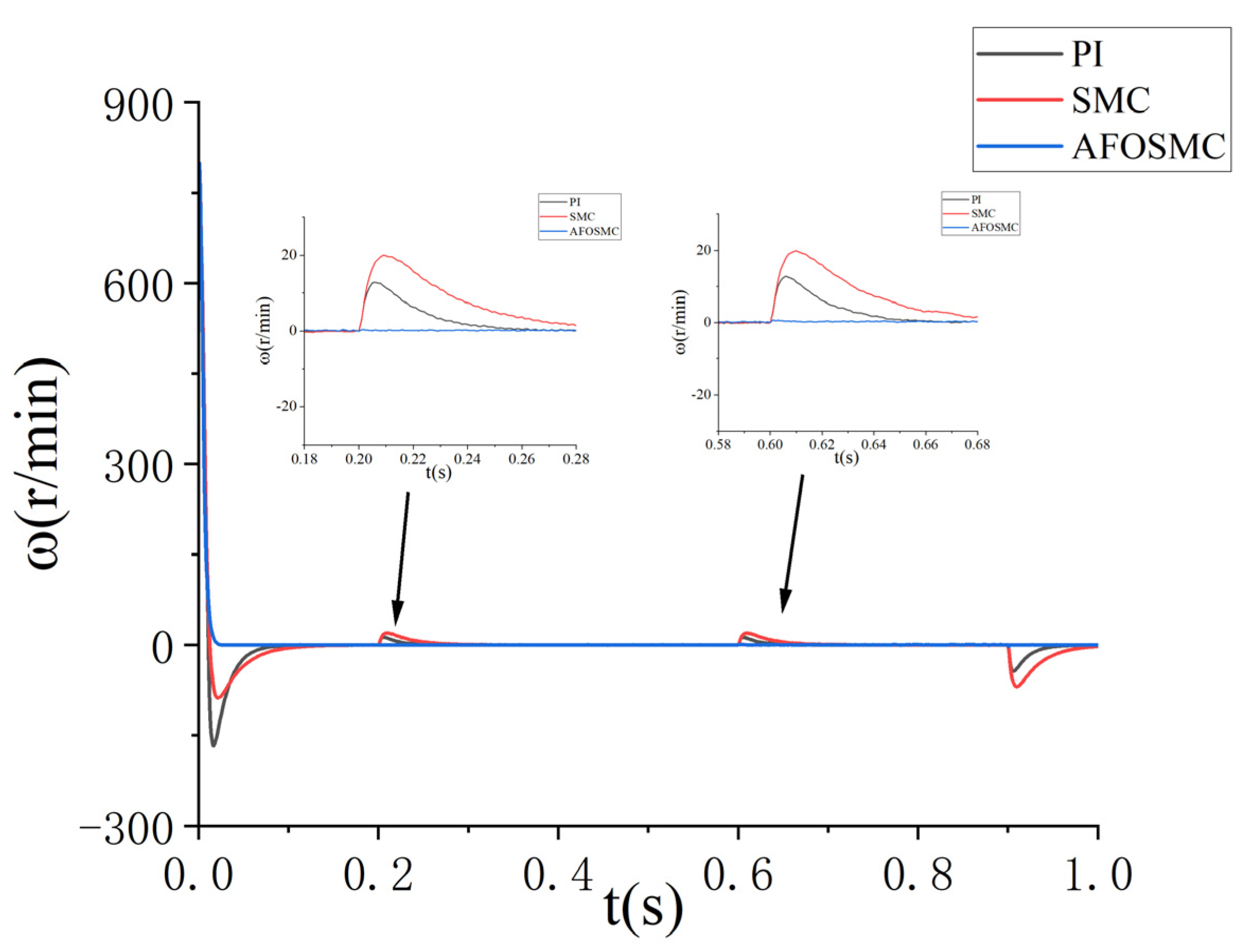
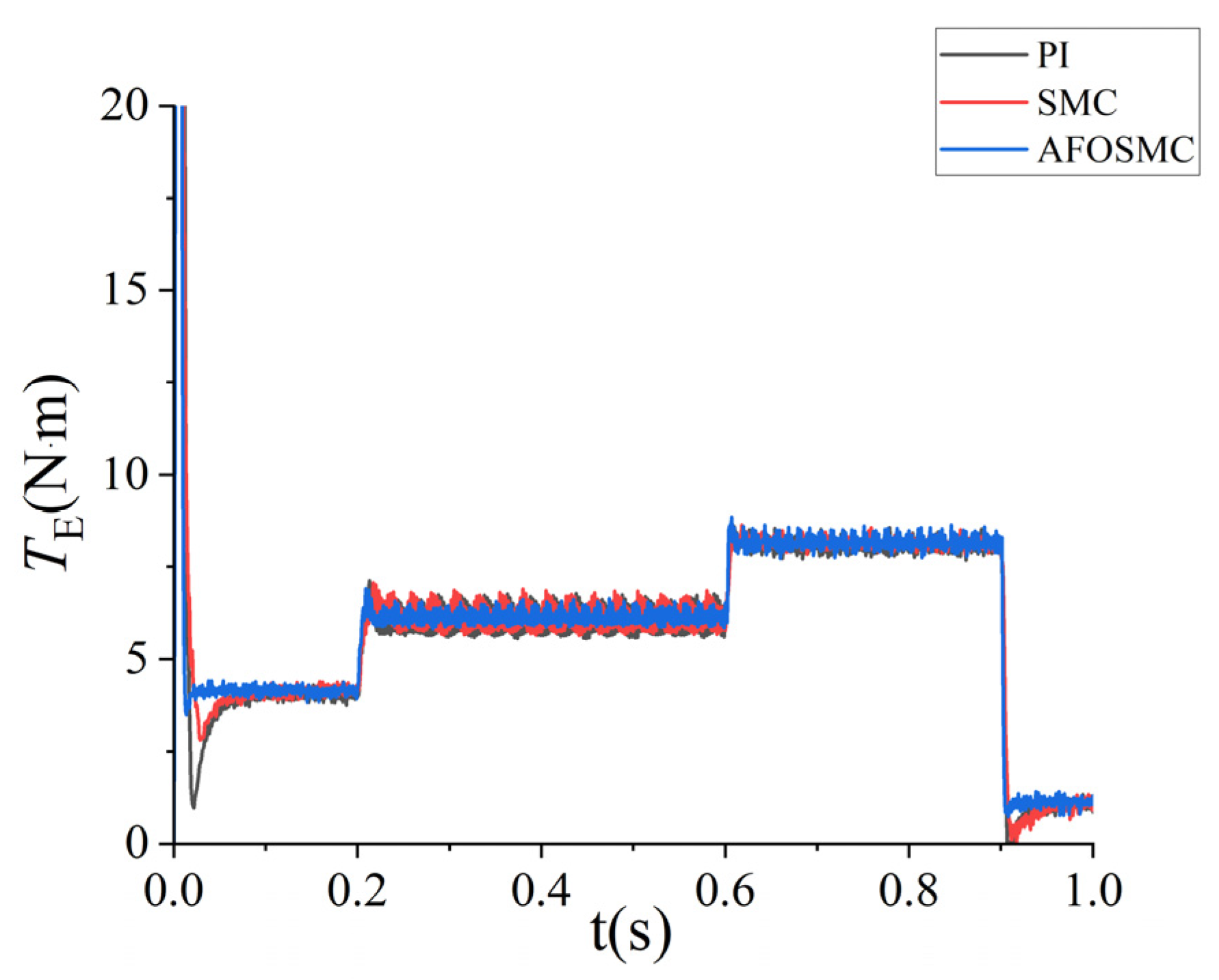
5.2.2. System Response to Sudden Load Changes
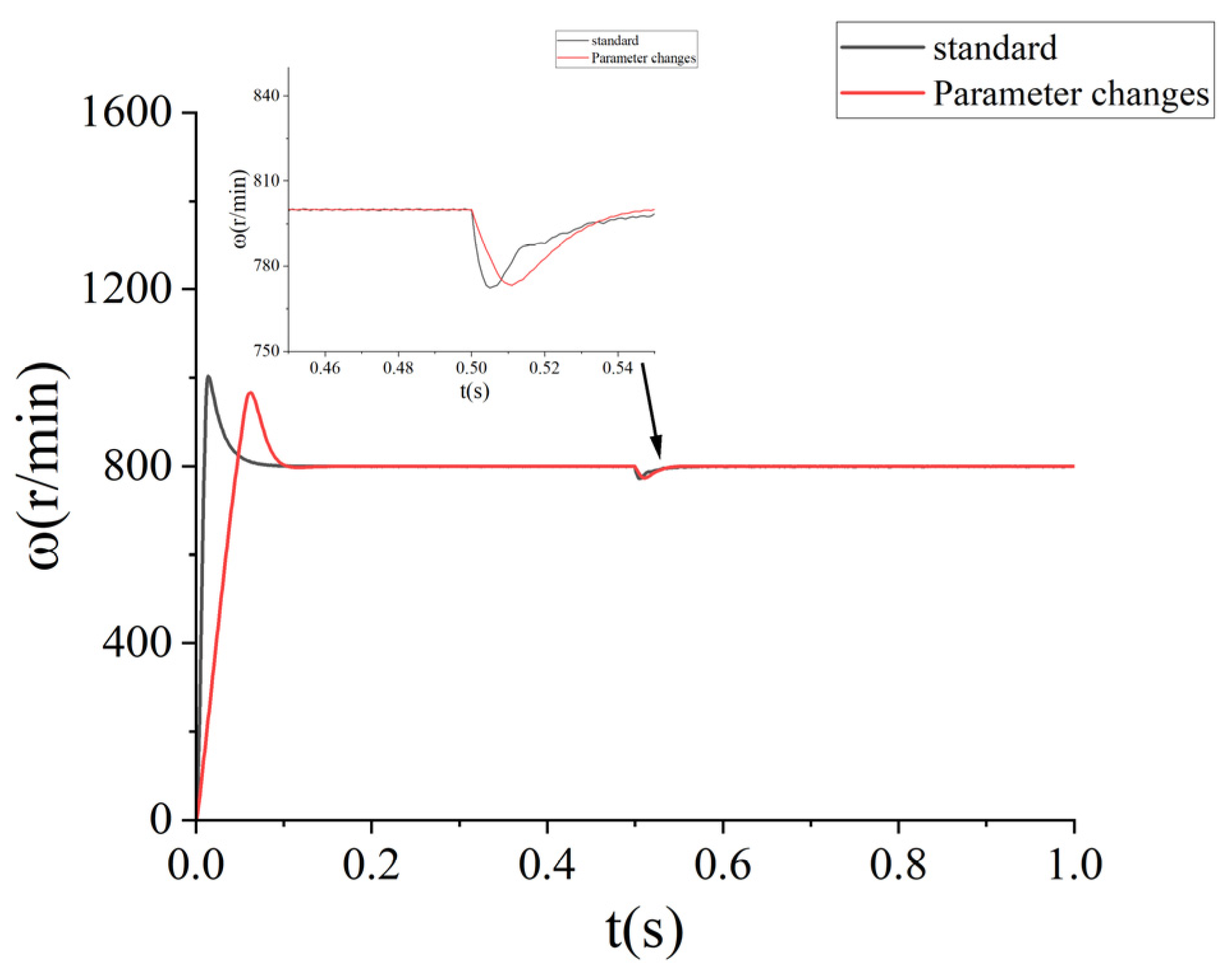
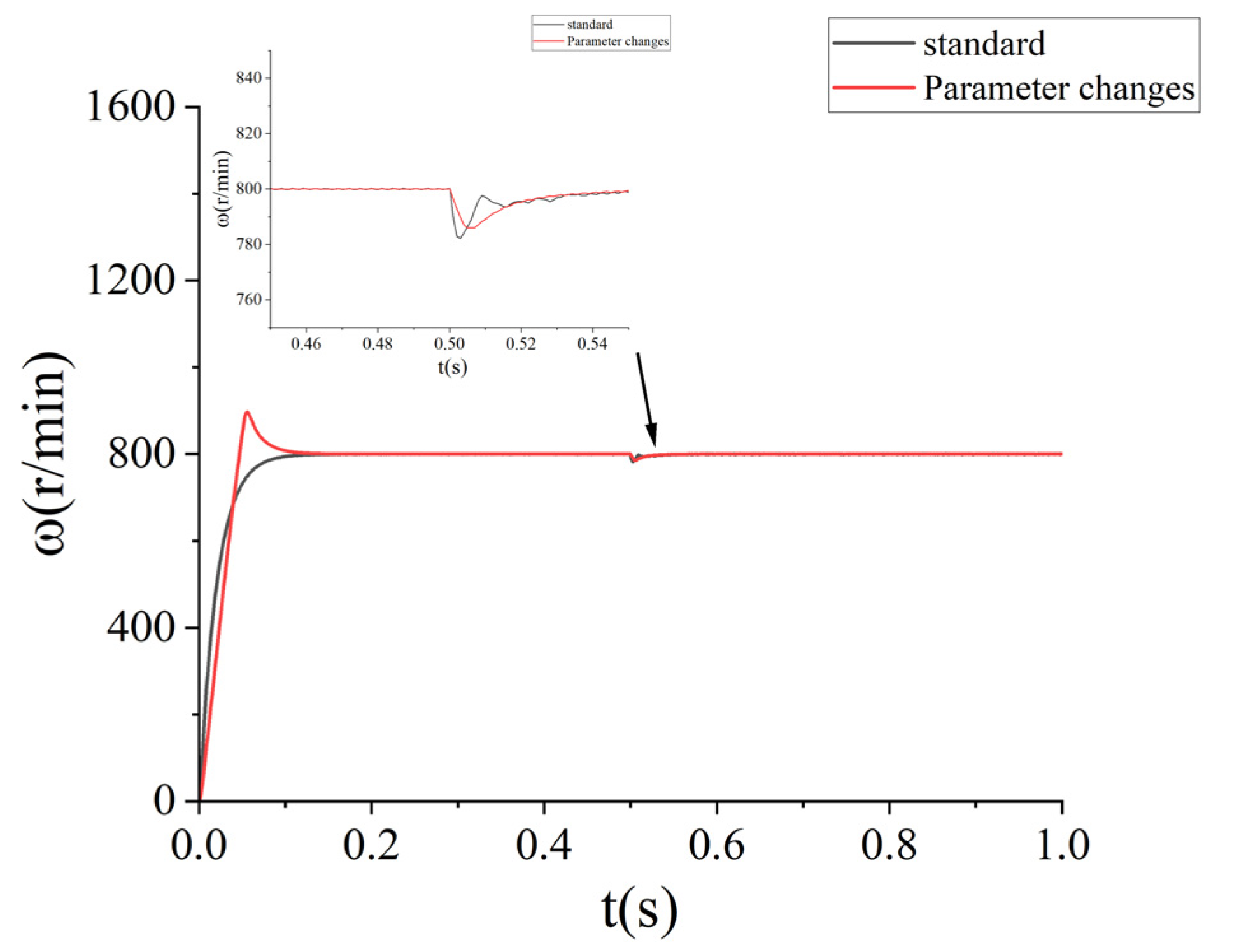
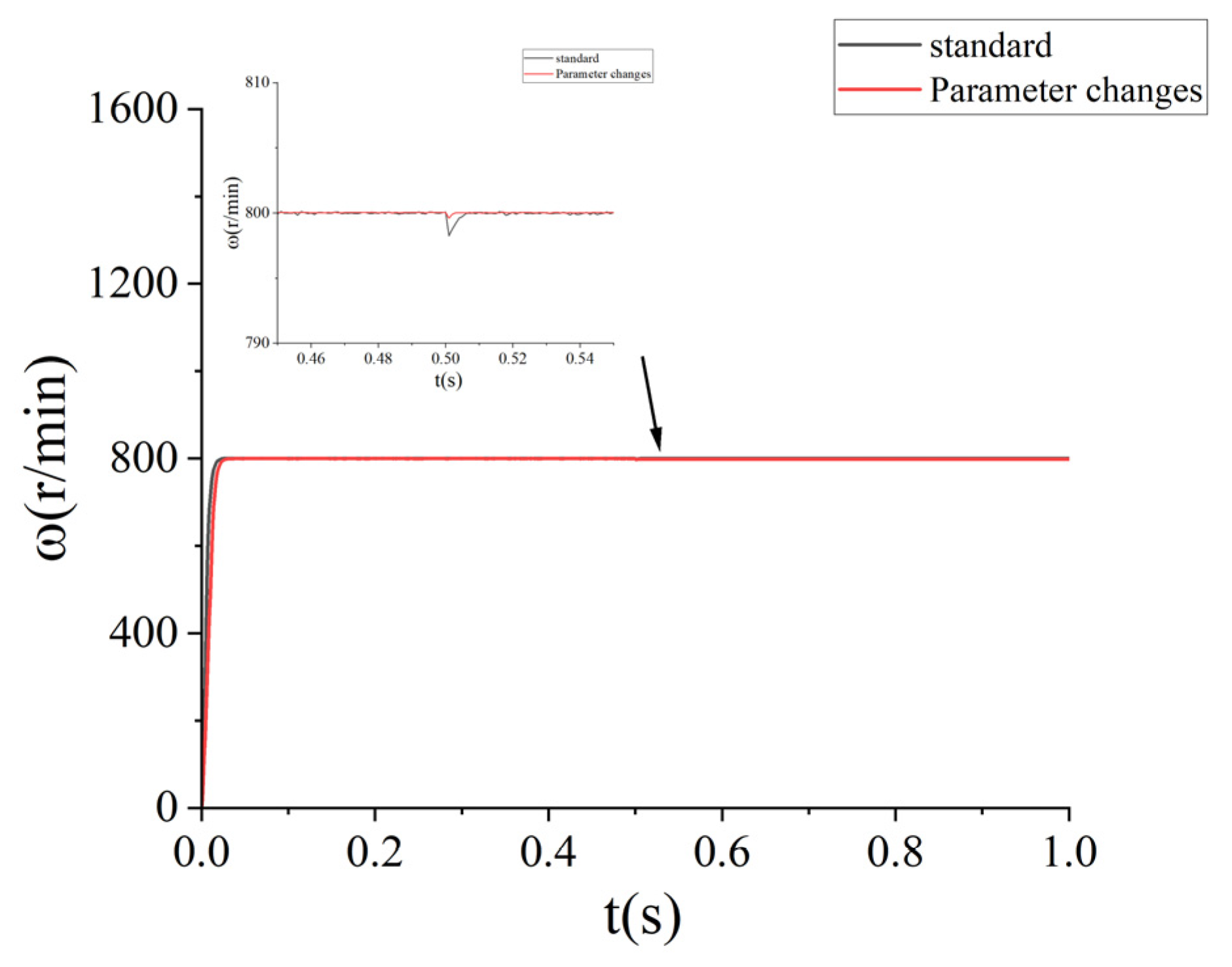
5.3. Parameter Change Test
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, X.; Yao, L.; Han, P.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, J. Active damping control based bus voltage resonance suppression in electrolytic capacitorless PMSM application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2853, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Peng, F.; Huang, Y. A novel energy balance control method for a modular multilevel converter in a high-speed PMSM drive application. Energies 2023, 16, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, M.; Hendershot, J.; Pillay, P. Design of a spoke type PMSM with SMC stator core for traction applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 59, 1418–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Deng, Y.; Qiao, T.; Fei, Q.; Li, H. Gaussian process-based parameter identification and model current predictive control strategy of PMSM. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2023, 31, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, L.; Xue, M.; Liu, T. A full-domain fluidic-thermal approach for a high-speed PMSM considering the bearing components. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2022, 16, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakatsanis, T.S. Overview of IoT security challenges and sensors specifications in PMSM for elevator applications. Machines 2024, 12, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, E.T.; Arabul, F.K. Effects of air gap eccentricity on different rotor structures for PMSM in electric vehicles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, P.K.; Subramaniam, U.; Almakhles, D.J. Laboratory implementation of direct torque controller based speed loop pseudo derivative feedforward controller for PMSM drive. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2024, 8, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Shi, P.; Mei, Y.; Zheng, K.; Qiu, T. Sensorless control of a PMSM based on an RBF neural network-optimized ADRC and SGH-CKF-STF algorithm. Meas. Control 2024, 57, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Meng, B.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, S.; Ding, B.; Feng, G. Dual position offset injection based multi-parameter decoupled estimation of PMSM considering signal injection induced inductance variation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 6913–6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cai, H. Multi-objective tree-structured parzen estimator optimized Res-Net for ITSC fault diagnosis of PMSM. IEEE Access, 2024; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Majumder, M.G.; Rajashekara, K.; Reddy, S.R.P. Parameter estimation for sensorless position control of PMSM drives with long cables in subsea applications. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2023, 12, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowron, M. Analysis of PMSM short-circuit detection systems using transfer learning of deep convolutional networks. Power Electron. Drives 2024, 9, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y. Periodic adaptive learning control of PMSM servo system with LuGre model-based friction compensation. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 167, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojabadi, H.; Ghribi, M. MRAS-based adaptive speed estimator in PMSM drives. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control, Istanbul, Turkey, 27–29 March 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Y. Current optimization-based control of dual three-phase PMSM for low-frequency temperature swing reduction. Def. Technol. 2024, 34, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Q. Analysis of bending and torsional modal of PMSM rotor systems for EV. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2782, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F. Research and simulation of high-efficiency disturbance rejection speed control strategy for PMSM. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2803, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ajmeri, M.; Singh, A.K.; Mandal, R.K. Novel high-gain boost converter with experimentally validated ADRC control technique for renewable energy applications. Electr. Eng. 2025, 107, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, F.B. Linear ADRC is equivalent to PID with set-point weighting and measurement filter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J.; Lin, W.; Zeng, P.; Li, H.; Shao, M. A ripple suppression of sensorless FOC of PMSM electrical drive system based on MRAS. Results Eng. 2023, 20, 101427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J. Design and simulation of the fuzzy PID control system for PMSM. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2820, 012097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, C.; Fan, S. Multimode model predictive control for PMSM drive system. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrific. 2023, 9, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Wheeler, P. Speed-current single-loop control of PMSM based on model-assisted cascaded extended state observer and sliding mode control. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2024, 52, 3558–3583. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska, K.; Dybkowski, M. Experimental analysis of the current sensor fault detection mechanism based on neural networks in the PMSM drive system. Electronics 2023, 12, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X. A study on the characteristics of schizophrenia patients with violent crimes based on clinical, prefrontal functional connectivity, and polygenic risk scores. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2025, 28, i225–i226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Chung, Y.; Hu, M.; You, K. Adaptive quick sliding mode reaching law and disturbance observer for robust PMSM control systems. Actuators 2024, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Xie, E. Noncascade Structure Equivalent SMC for PMSM Driving Based on Improved ESO. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40 Pt 1, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, Y.; Meşe, E.; Ayaz, M. Comparison study on SMC and grain-oriented laminated steel core for small-size axial flux permanent-magnet synchronous machines. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xiao, X.; Yang, J.; Tao, T.; Mei, X. A novel sliding mode control with MRAS inertia identification for permanent magnet synchronous motors. Meas. Control 2024, 57, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Cao, Y.; He, Z.; Wu, Q.; Ma, J.; Qiu, B.; Luo, C. Research on fractional-order sliding mode PMSM speed regulation based on load observer. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2024, 19, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwerger, T.; Mercorelli, P. Optimal control strategies for PMSM with a decoupling super twisting SMC and inductance estimation in the presence of saturation. J. Frankl. Inst. 2024, 361, 106934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, G.; Ouyang, H.; Mei, L. An Adaptive Super Twisting Nonlinear Fractional Order PID Sliding Mode Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Speed Regulation System Based on Extended State Observer. IEEE Access 2022, 8, 53498–53510. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Zheng, W.X.; Niu, Y. Self-triggered sliding mode control for networked PMSM speed regulation system: A PSO-optimized super-twisting algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-F.; Feng, Y.; Yu, J.-Y.; Tang, J.-W.; Zhang, L. Fractional order second-order sliding mode MRASO for SPMSM. Meas. Control. 2024, 57, 863–870. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, R.; Lin, M.; Guo, F. Fractional order sliding mode control for permanent magnet synchronous motor speed servo system via an improved disturbance observer. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Pan, H.H. Model-free double fractional-order integral sliding mode control for permanent magnet synchronous motor based electric mopeds drive system. IEICE Electron. Express 2023, 20, 20230178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, W.; Yin, C.; Cheng, Q. Fractional-Order Sliding-Mode Control and Radial Basis Function Neural Network Adaptive Damping Passivity-Based Control with Application to Modular Multilevel Converters. Energies 2024, 17, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaddy, A.; Labbadi, M.; Elyaalaoui, K.; Bouzi, M. Fixed-Time Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control for UAVs under External Disturbances. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Agashe, S. Review of fractional PID controller. Mechatronics 2016, 38, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Homaifa, A. Discrete-time variable structure control systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1995, 42, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

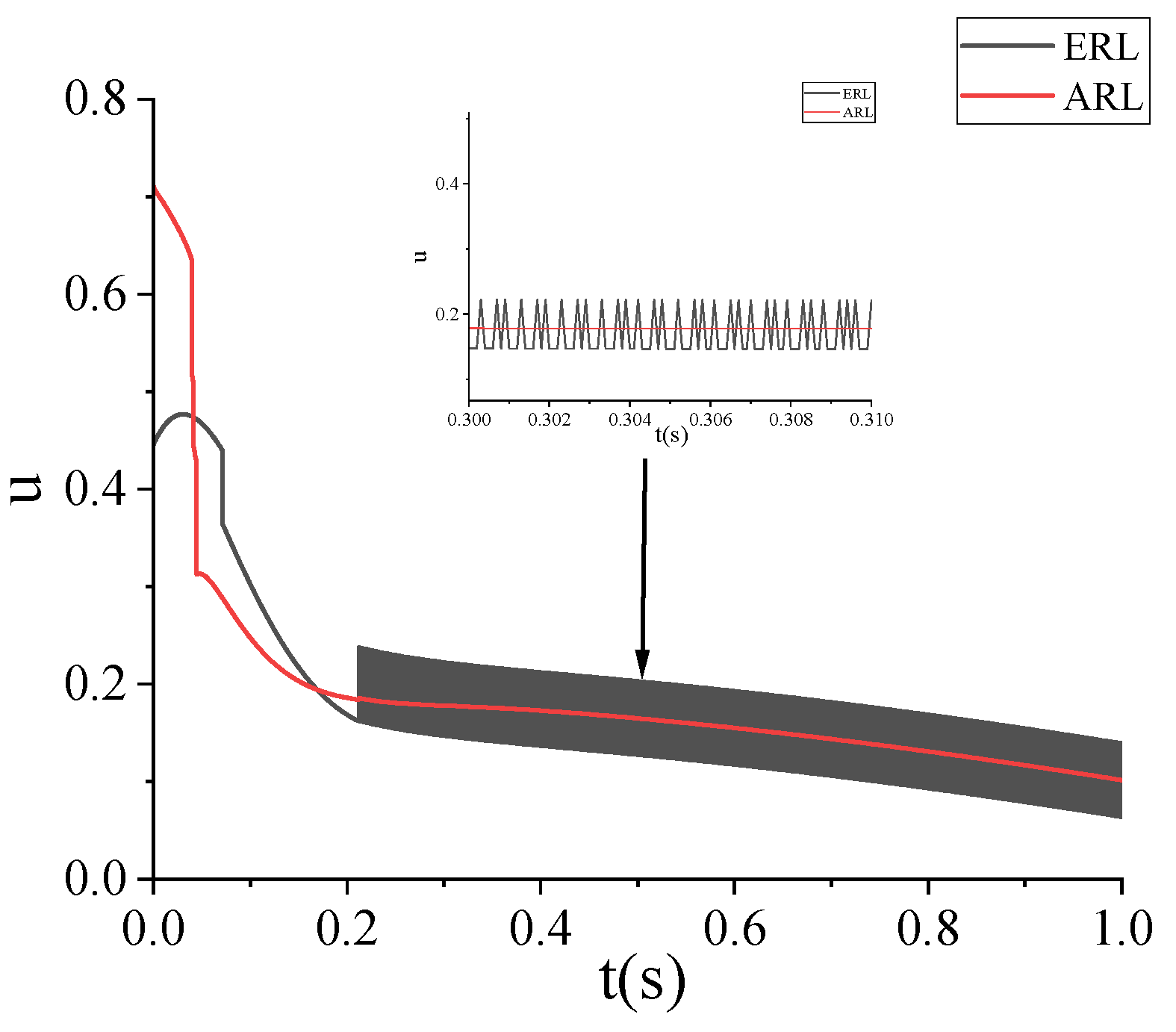
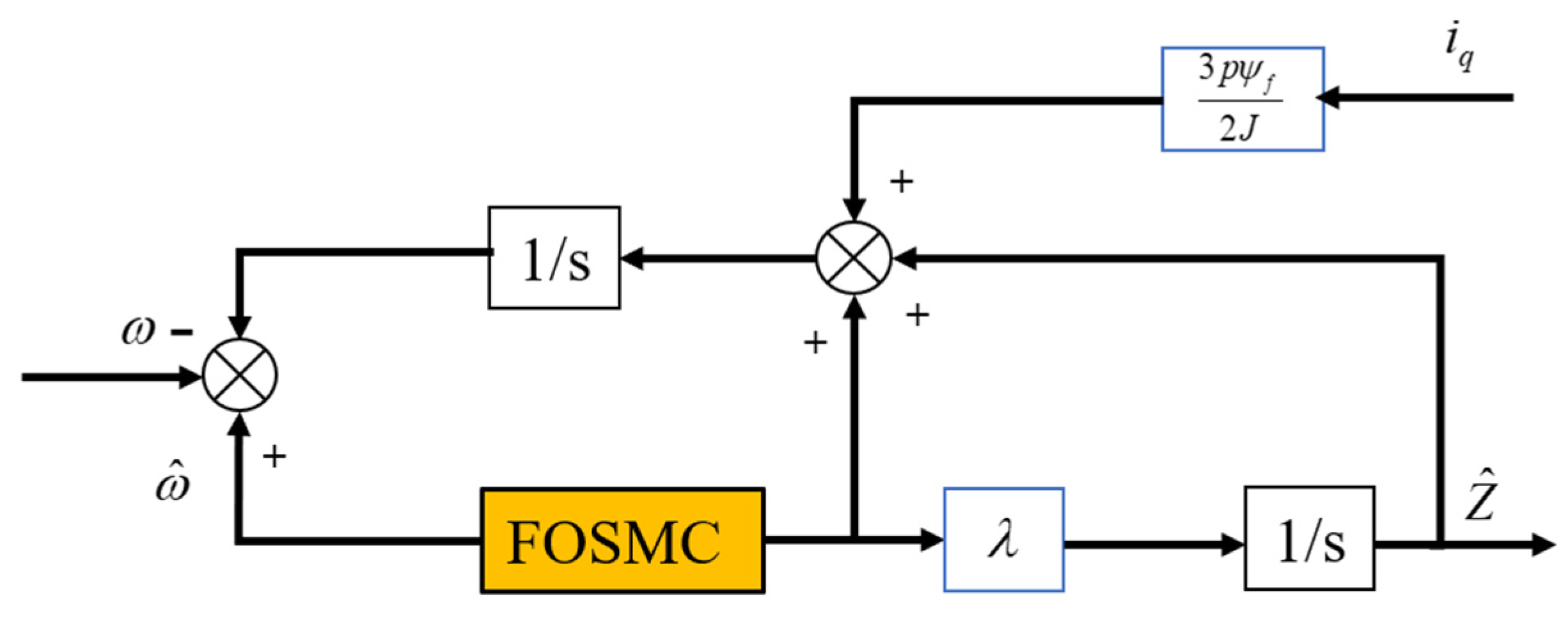
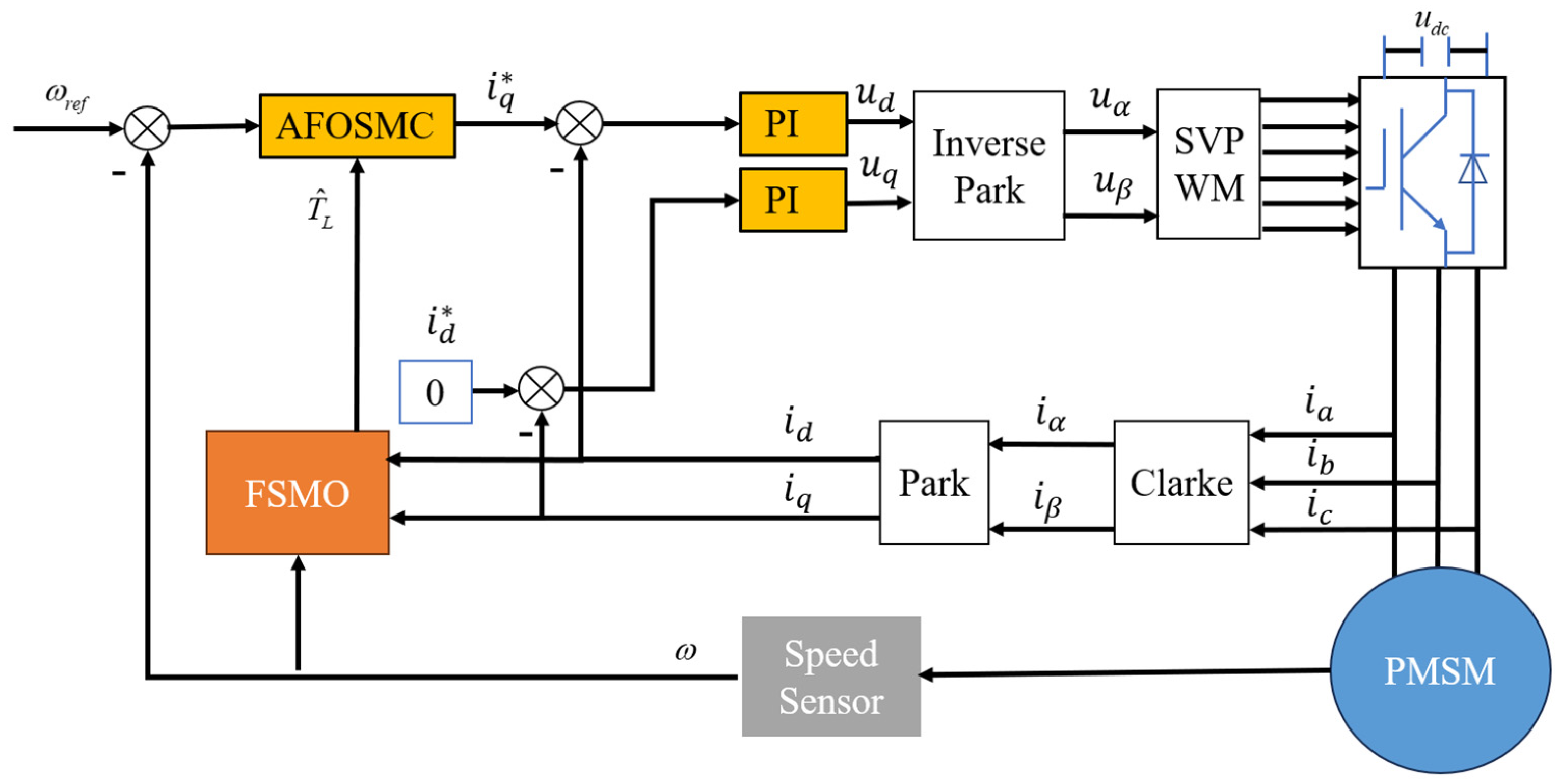
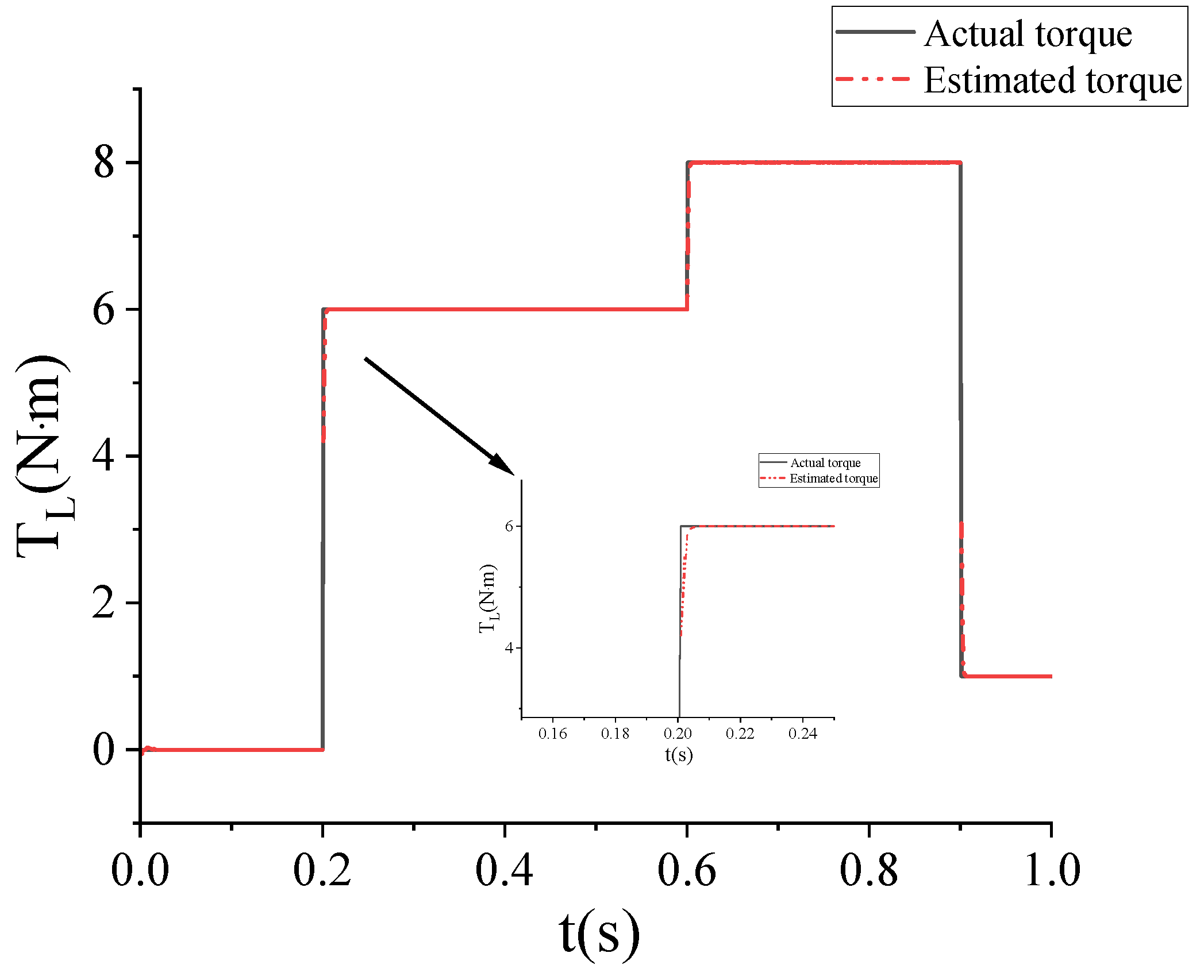
| ERL | ARL |
|---|---|
| ɛ = 5 | η1 = 0.5 |
| k = 15 | δ = 0.1 |
| — | η2 = 0.7, ζ = 1 |
| — | A = 0.6 |
| — | k1 = 1, μ = 0.6 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Pole-pairs | 4 |
| Stator resistance | 2.875 Ω |
| Stator inductance | 8.5 × 10−3 H |
| Permanent magnet flux link | 0.175 Wb |
| Inertia | 0.0003 kg·m2 |
| Viscous friction coefficient | 0 N·m·s |
| Performance Index | PI | SMC | AFOSMC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Settling time/ms | 150 | 110 | 20 |
| Overshoot ratio/% | 5.6 | 10 | 0.15 |
| Steady-state error/r | 3 | 1.1 | 0.13 |
| Performance Index | PI | SMC | AFOSMC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Settling time/ms | 98 | 103 | 20 |
| Overshoot ratio/% | 20.75 | 10.37 | 0.02 |
| Steady-state error/r | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.16 |
| Performance Index | PI | SMC | AFOSMC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Settling time/ms | 109 | 106 | 27 |
| Overshoot ratio/% | 20.75 | 12 | 0.125 |
| Steady-state error/r | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Method | Control Method | Disturbance Observer | Adaptive Mechanism | Fractional-Order | Novel Reaching Law | Chattering Suppression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI | PI | No | No | No | N/A | No |
| SMC | Integer-order SMC | Optional | No | No | Exponential | Limited |
| Super Twisting SMC | STW SMC | Yes | Parameter Tuning | No | Super-Twisting | Yes |
| FOSMC | Fractional-Order SMC | Yes | Some | Yes | Stand/Modified | Yes |
| Proposed | Adaptive FOSMC (AFOSMC) | Fractional SMC | Fully Adaptive | Yes | Novel AVERL | Excellent |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, F.; Chien, Y.-R. PMSM Speed Control Based on Improved Adaptive Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control. Symmetry 2025, 17, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050736
Bian F, Chien Y-R. PMSM Speed Control Based on Improved Adaptive Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control. Symmetry. 2025; 17(5):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050736
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Fengshuo, and Ying-Ren Chien. 2025. "PMSM Speed Control Based on Improved Adaptive Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control" Symmetry 17, no. 5: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050736
APA StyleBian, F., & Chien, Y.-R. (2025). PMSM Speed Control Based on Improved Adaptive Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control. Symmetry, 17(5), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050736






