An Advanced Adaptive Group Learning Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This research utilizes the Latin hypercube sampling and reverse learning mechanisms for population initialization, ensuring that the initial population is evenly distributed across the search space. This approach yields a more advantageous initial population, enhancing the probability of the algorithm finding the global optimal solution during the search process, preventing premature convergence, and improving algorithm stability.
- A new golden sine perturbation coefficient is proposed and applied to the linearly decreasing inertia weight, allowing the algorithm to adaptively explore the search space more effectively during different search phases and enhancing the convergence speed of the algorithm.
- A staged group learning mechanism is proposed. In each iteration, the population is randomly divided into groups to establish a group learning approach, with the number of group members adapting to changes at different stages of the iteration. The velocity update formula is improved, enhancing the diversity of population learning and increasing the algorithm’s global search capability.
- An adaptive Gaussian perturbation strategy is proposed to apply adaptive perturbations to different particle velocities in the group, facilitating particles to escape local optima and more effectively balancing the algorithm’s exploration and exploitation capabilities.
2. Basic Concepts
2.1. Classic PSO
2.2. Latin Hypercube Sampling
- Determine the number of sample points N;
- Interval partitioning: Divide the cumulative distribution of the variable in the interval (0, 1) into N non-overlapping sub-intervals, ensuring that each interval contains an equal amount of probability mass;
- Sample extraction: Randomly select one sample point independently from each partitioned interval to obtain N different sample points. This ensures that different sample points for the same variable do not fall within the same interval, avoiding overlap and ensuring the diversity and representativeness of the samples.
2.3. Opposition-Based Learning
2.4. Double-Faced Mirror Theory Boundary Optimization
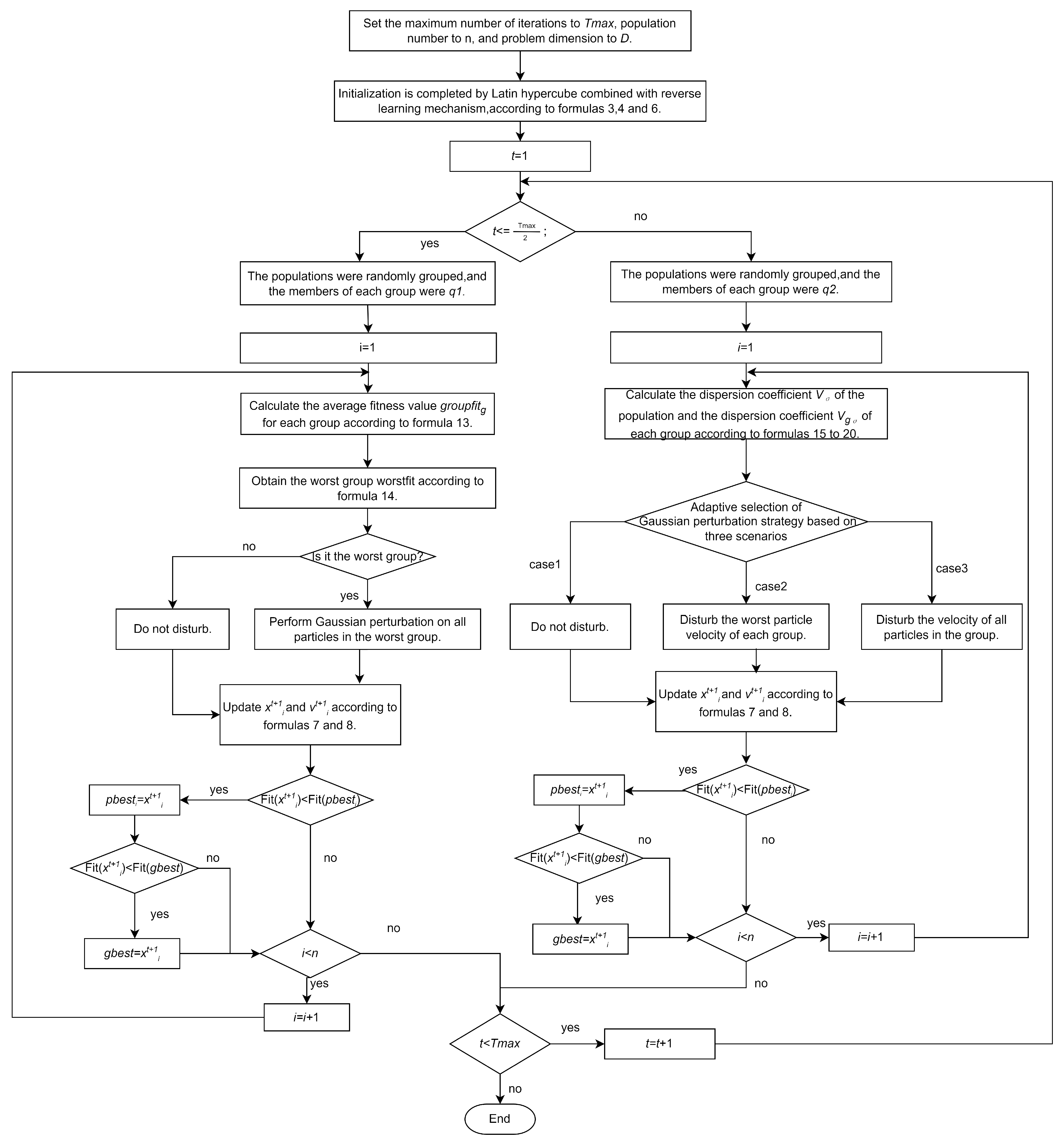
3. Group Learning Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
3.1. Population Initialization
3.2. Stochastic Group Learning Mechanism
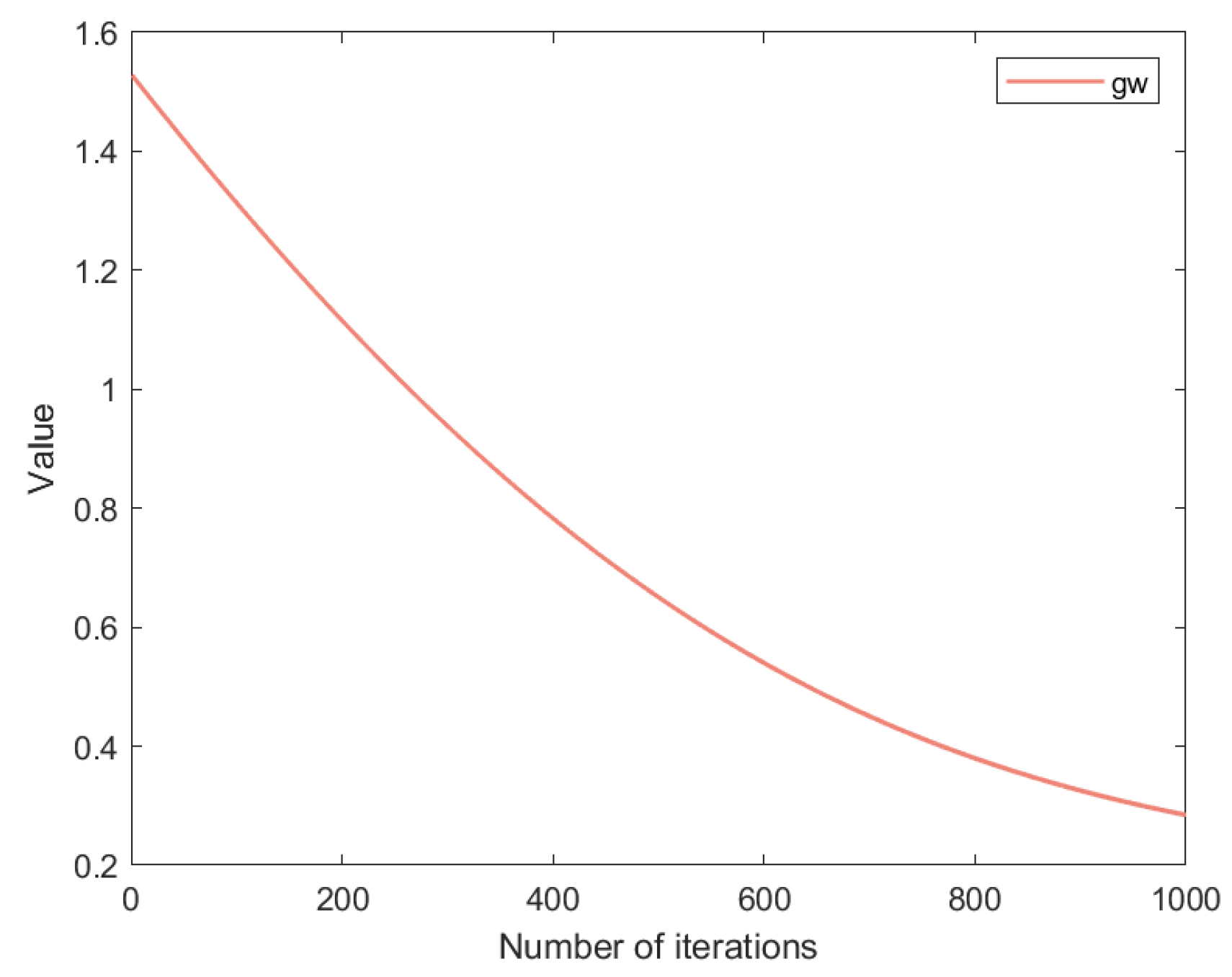
3.3. Particle Renewal Based on Gold Disturbance Coefficient
3.4. Adaptive Gaussian Perturbation Strategy
| Algorithm 1 GLPSO |
|
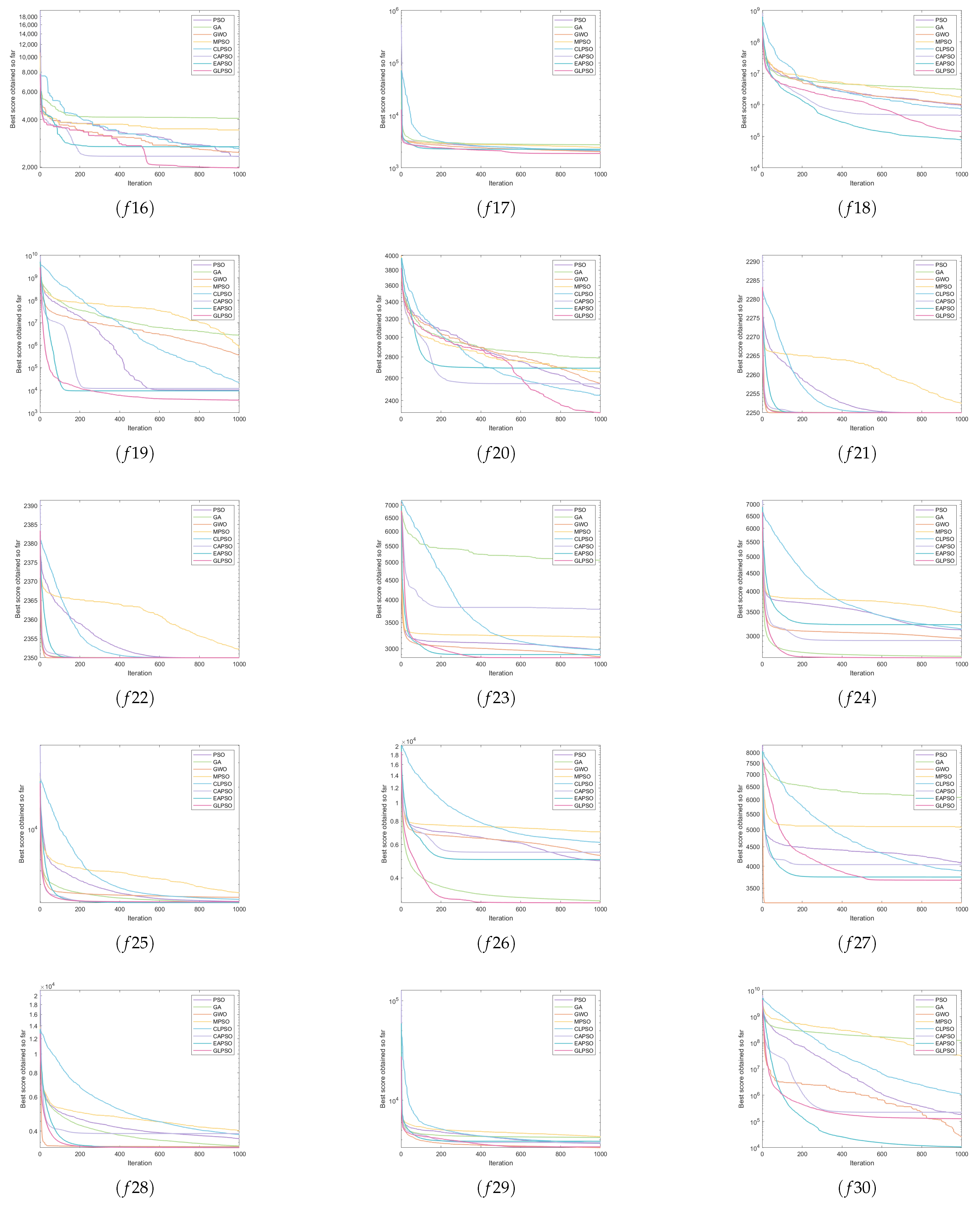
4. Experimental Results and Discussions
4.1. Experiment Setup
4.2. Empirical Analysis and Discussion
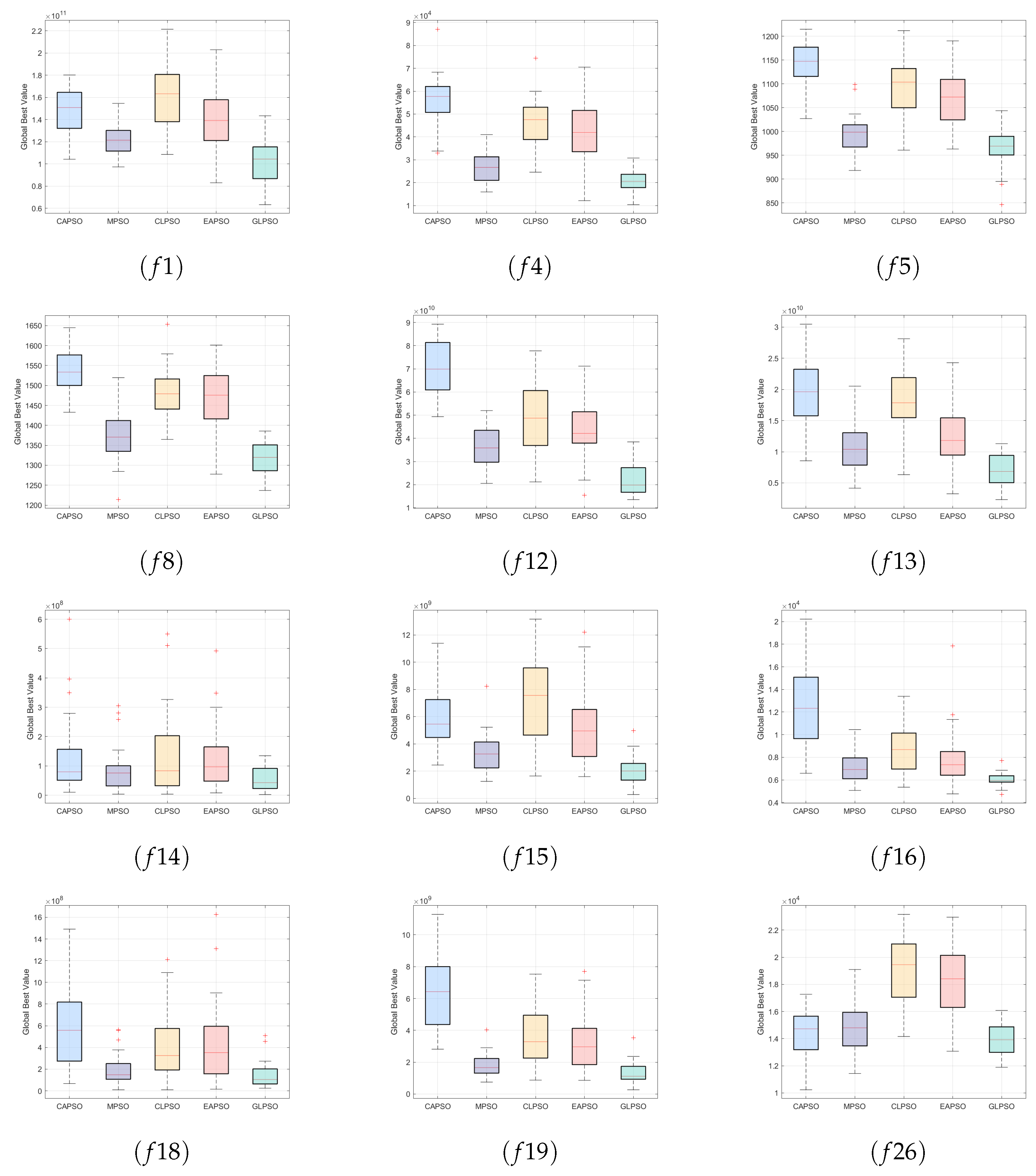
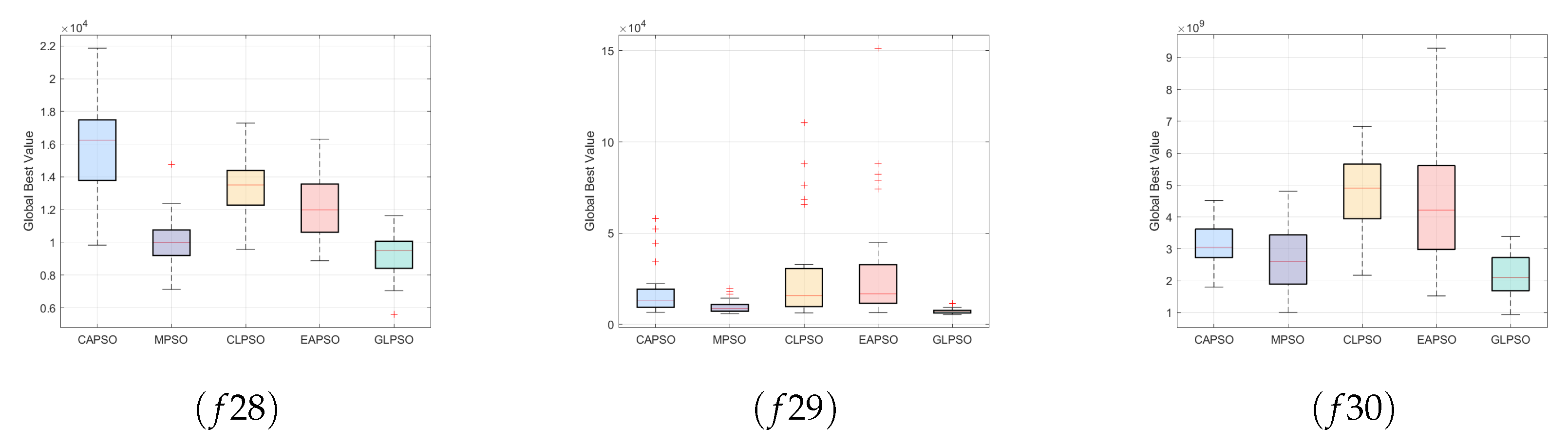
5. Performance Analysis
5.1. Ablation Study Analysis
5.2. Complexity Analysis
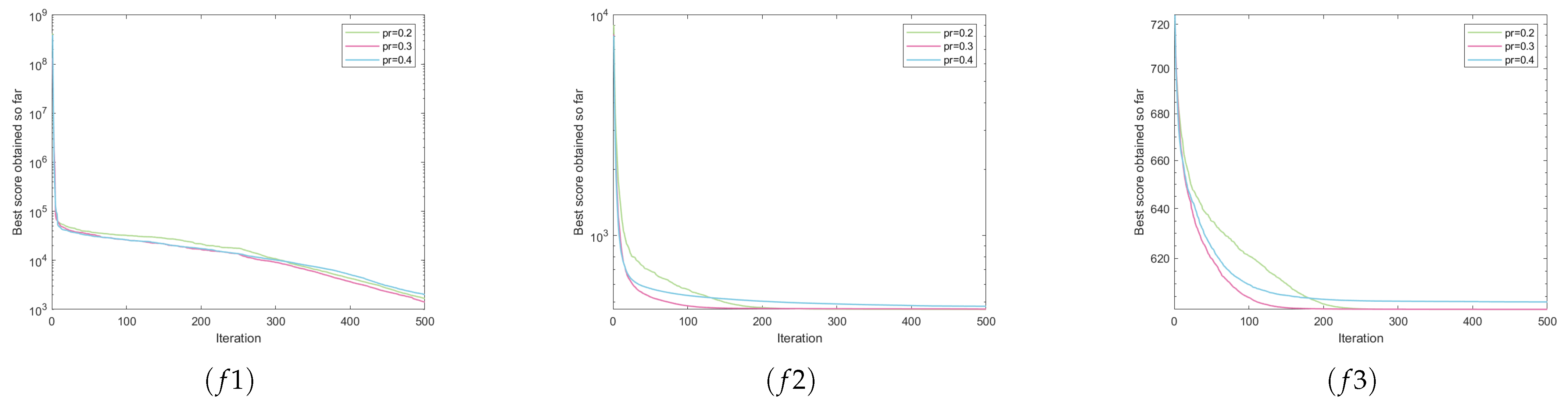
5.3. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
6. Application to Engineering Problems
6.1. Tension/Compression Spring Design
6.2. Weight Minimization of a Speed Reducer
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, B.; Wang, Z.; Zou, L. On global smooth path planning for mobile robots using a novel multimodal delayed PSO algorithm. Cogn. Comput. 2017, 9, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J. Multi-objective optimization of energy consumption in crude oil pipeline transportation system operation based on exergy loss analysis. Neurocomputing 2019, 332, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorpade, S.N.; Zennaro, M.; Chaudhari, B.S.; Saeed, R.A.; Alhumyani, H.; Abdel-Khalek, S. A novel enhanced quantum PSO for optimal network configuration in heterogeneous industrial IoT. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 134022–134036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, V.; Biswas, B.; Shukla, K.K. A novel multiobjective gdwcn-pso algorithm and its application to medical data security. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. (TOIT) 2021, 21, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, D.; Khare, P.; Srivastava, V.K. PBNHWA: NIfTI image watermarking with aid of PSO and BO in wavelet domain with its authentication for telemedicine applications. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, Online First. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Jiang, Y.S.; Gong, Y.J.; Zhan, Z.H.; Zhang, J. A discrete multiobjective particle swarm optimizer for automated assembly of parallel cognitive diagnosis tests. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 49, 2792–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, N.; Hone, K.; Liu, X. A novel sigmoid-function-based adaptive weighted particle swarm optimizer. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 51, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Zhan, Z.H.; Lin, Y.; Yu, W.J.; Wang, H.; Kwong, S.; Zhang, J. Automatic niching differential evolution with contour prediction approach for multimodal optimization problems. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2019, 24, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagireddy, V.; Parwekar, P.; Mishra, T.K. Velocity adaptation based PSO for localization in wireless sensor networks. Evol. Intell. 2021, 14, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, F. Short-term load forecasting based on PSO-KFCM daily load curve clustering and CNN-LSTM model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 50344–50357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihu, N.; Kumam, P.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Babando, H.A. A sufficient descent hybrid conjugate gradient method without line search consideration and application. Eng. Comput. 2024, 41, 1203–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; She, Q.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Lin, Z. Newton design: Designing CNNs with the family of Newton’s methods. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2023, 66, 162101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M. An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mandic, D.P. A generalized normalized gradient descent algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2004, 11, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Birattari, M.; Stutzle, T. Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2007, 1, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November—1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liang, P.; Sun, B.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y. Reinforcement learning-based particle swarm optimization with neighborhood differential mutation strategy. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2023, 78, 101274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.J.; Qin, A.K.; Suganthan, P.N.; Baskar, S. Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2006, 10, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Kennedy, J.; Neves, J. The fully informed particle swarm: Simpler, maybe better. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2004, 8, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.Y.; Suganthan, P.N.; Das, S. A distance-based locally informed particle swarm model for multimodal optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2012, 17, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Xu, L.; Goodman, E.D. A neighbor-based learning particle swarm optimizer with short-term and long-term memory for dynamic optimization problems. Inf. Sci. 2018, 453, 463–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.R.; Cui, J.C.; Lu, Z.D.; Liu, D.Y.; Deng, Y.J. A hierarchical simple particle swarm optimization with mean dimensional information. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 76, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Tian, F.; Meng, X. A fitness landscape ruggedness multiobjective differential evolution algorithm with a reinforcement learning strategy. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 96, 106693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Elite archives-driven particle swarm optimization for large scale numerical optimization and its engineering applications. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2023, 76, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, A. A particle swarm optimization algorithm for mixed-variable optimization problems. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2021, 60, 100808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Q. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization with dynamic population size. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2023, 10, 446–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y. Path planning for intelligent robot based on switching local evolutionary PSO algorithm. Assem. Autom. 2016, 36, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nama, S.; Saha, A.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Gandomi, A.H.; Abualigah, L. Boosting particle swarm optimization by backtracking search algorithm for optimization problems. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2023, 79, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Jena, P.K. Multi-robot path planning using improved particle swarm optimization algorithm through novel evolutionary operators. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 92, 106312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.W.; Tu, L.P. A modified particle swarm optimization using adaptive strategy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 152, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, J.; Deng, W.; Hu, Z. Pyramid particle swarm optimization with novel strategies of competition and cooperation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 121, 108731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Mao, G.; Liang, Y. PSO-sono: A novel PSO variant for single-objective numerical optimization. Inf. Sci. 2022, 586, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, D. Elite-ordinary synergistic particle swarm optimization. Inf. Sci. 2022, 609, 1567–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, R.; Hou, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z. A data-driven motor optimization method based on support vector regression—Multi-objective, multivariate, and with a limited sample size. Electronics 2024, 13, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Yang, M. Enhanced artificial ecosystem-based optimization for global optimization and constrained engineering problems. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 10053–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhu, Y. A hybrid butterfly and Newton–Raphson swarm intelligence algorithm based on opposition-based learning. Clust. Comput. 2024, 27, 14469–14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansuri, M.A.K.; Yusupov, Z.; Rahebi, J.; Ghadami, R. Parameter Estimation of PV Solar Cells and Modules Using Deep Learning-Based White Shark Optimizer Algorithm. Symmetry 2025, 17, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Li, K.S.; Tao, X.Z.; Gu, F.H. An improved MOEA/D algorithm with an adaptive evolutionary strategy. Inf. Sci. 2020, 539, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Eberhart, R. A modified particle swarm optimizer. In 1998 IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Proceedings; IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence (Cat. No. 98TH8360); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Mallipeddi, R.; Suganthan, P.N. Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for the CEC 2017 Competition on Constrained Real-Parameter Optimization; Technical Report; National University of Defense Technology: Changsha, China; Kyungpook National University: Daegu, Republic of Korea; Nanyang Technological University: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Chen, N.; Chang, L.; Ni, Y.; Kumar, S.S.; Zhang, P. CAPSO: Chaos adaptive particle swarm optimization algorithm. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 29393–29405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Price, K.V.; Mohamed, A.W.; Hadi, A.A.; Suganthan, P.N. Problem Definitions and Evaluation Criteria for the 2022 Special Session and Competition on Single Objective Bound Constrained Numerical Optimization; Technical Report; Nanyang Technological University: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Wu, G.; Ali, M.Z.; Mallipeddi, R.; Suganthan, P.N.; Das, S. A test-suite of non-convex constrained optimization problems from the real-world and some baseline results. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2020, 56, 100693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandomi, A.H.; Yang, X.S.; Alavi, A.H. Mixed variable structural optimization using firefly algorithm. Comput. Struct. 2011, 89, 2325–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.C.; Xu, X.W.; Yang, S.Y.; Pan, J.S. Parallel fish migration optimization with compact technology based on memory principle for wireless sensor networks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 241, 108124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyyedabbasi, A.; Kiani, F. Sand Cat swarm optimization: A nature-inspired algorithm to solve global optimization problems. Eng. Comput. 2023, 39, 2627–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, N.; Ansari, M.M. Golden jackal optimization: A novel nature-inspired optimizer for engineering applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 198, 116924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Li, G.; Meng, Z. Beluga whale optimization: A novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 251, 109215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, T.; Ma, S.; Chen, M. Dandelion Optimizer: A nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for engineering applications. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, C.L.; Kamboj, V.K.; Bath, S.K.; Tripathi, S.L.; Khatri, M.; Sehgal, S. A boosted chimp optimizer for numerical and engineering design optimization challenges. Eng. Comput. 2023, 39, 2463–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, B.; Prakash, R.; Vimal, V.; Liang, G.; Chen, H. Improved salp swarm algorithm with mutation schemes for solving global optimization and engineering problems. Eng. Comput. 2022, 38, 3927–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Diabat, A.; Altalhi, M.; Elaziz, M.A. Improved gradual change-based Harris Hawks optimization for real-world engineering design problems. Eng. Comput. 2023, 39, 1843–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, L.; Meng, Q. An intensify atom search optimization for engineering design problems. Appl. Math. Model. 2021, 89, 837–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Yousri, D.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Ewees, A.A.; Al-Qaness, M.A.; Gandomi, A.H. Aquila optimizer: A novel meta-heuristic optimization algorithm. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 157, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






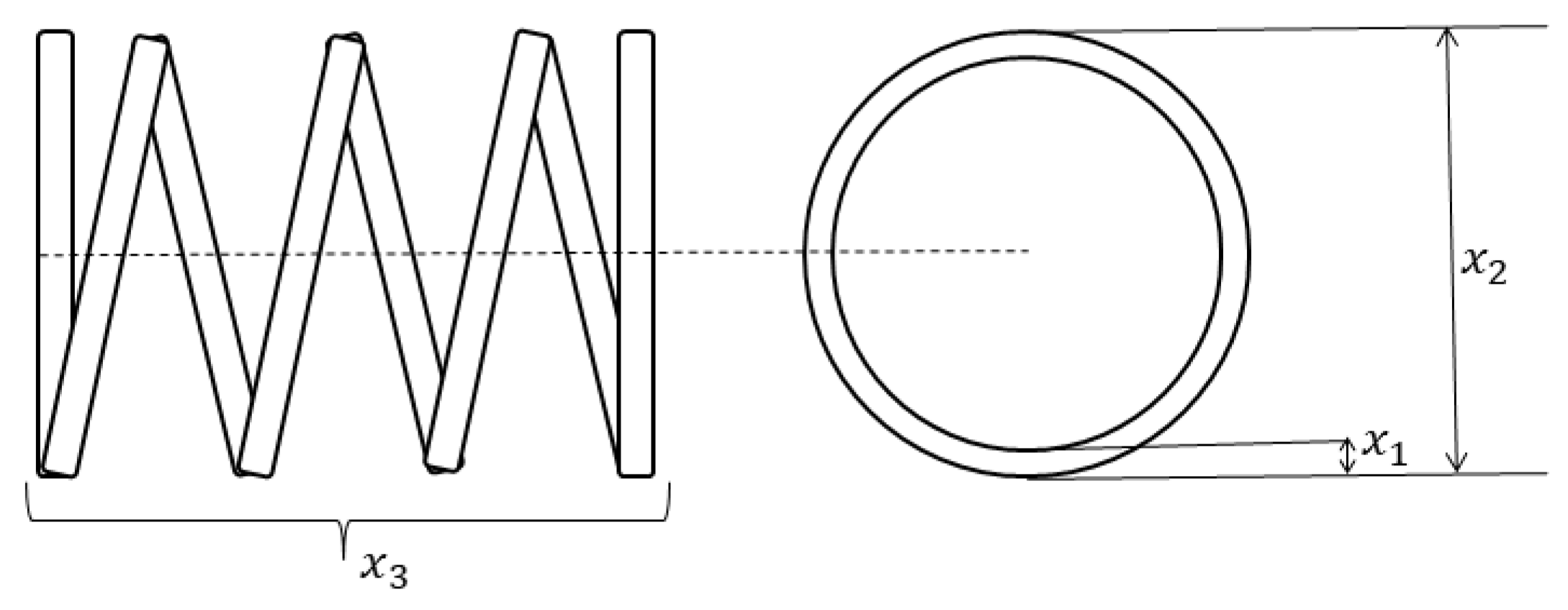
| No. | Functions | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Unimodal Functions | 1 | Shifted and Rotated Bent Cigar Function | 100 |
| 2 | Shifted and Rotated Sum of Different Power Function * | 200 | |
| 3 | Shifted and Rotated Zakharo Function | 300 | |
| Simple Multimodal Functions | 4 | Shifted and Rotated Rosenbrock’s Function | 400 |
| 5 | Shifted and Rotated Rastrigin’s Function | 500 | |
| 6 | Shifted and Rotated Expanded Scaffer’s F6 Function | 600 | |
| 7 | Shifted and Rotated Lunacek Bi_Rastrigin Function | 700 | |
| 8 | Shifted and Rotated Non-Continuous Rastrigin’s Function | 800 | |
| 9 | Shifted and Rotated Levy Function | 900 | |
| 10 | Shifted and Rotated Schwefel’s Function | 1000 | |
| Hybrid Functions | 11 | Hybrid Function 1 (N = 3) | 1100 |
| 12 | Hybrid Function 2 (N = 3) | 1200 | |
| 13 | Hybrid Function 3 (N = 3) | 1300 | |
| 14 | Hybrid Function 4 (N = 4) | 1400 | |
| 15 | Hybrid Function 5 (N = 4) | 1500 | |
| 16 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 4) | 1600 | |
| 17 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 5) | 1700 | |
| 18 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 5) | 1800 | |
| 19 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 5) | 1900 | |
| 20 | Hybrid Function 6 (N = 6) | 2000 | |
| Composition Functions | 21 | Composition Function 1 (N = 3) | 2100 |
| 22 | Composition Function 2 (N = 3) | 2200 | |
| 23 | Composition Function 3 (N = 4) | 2300 | |
| 24 | Composition Function 4 (N = 4) | 2400 | |
| 25 | Composition Function 5 (N = 5) | 2500 | |
| 26 | Composition Function 6 (N = 5) | 2600 | |
| 27 | Composition Function 7 (N = 6) | 2700 | |
| 28 | Composition Function 8 (N = 6) | 2800 | |
| 29 | Composition Function 9 (N = 3) | 2900 | |
| 30 | Composition Function 10 (N = 3) | 3000 | |
| Search Range: | |||
| Algorithm | Year | Default Parameter Settings |
|---|---|---|
| PSO [40] | 1998 | D, , , , . |
| GA [13] | 1998 | D, . |
| CLPSO [19] | 2006 | D, , , , , . |
| GWO [16] | 2014 | D, . |
| MPSO [30] | 2020 | D, , , , . |
| CAPSO [42] | 2022 | D, , , , , , . |
| EAPSO [25] | 2023 | D, . |
| GLPSO | Presented | D, , , , , , . |
| PSO | GA | GWO | MPSO | CLPSO | CAPSO | EAPSO | GLPSO | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | |||||||||
| f1 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 2 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f2 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f3 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 6 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 2 | 3 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f4 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f5 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 2 | 7 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f6 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 2 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f7 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f8 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 2 | 8 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f9 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 2 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 4 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f10 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 7 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f11 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 2 | 8 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f12 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f13 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 1 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f14 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f15 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f16 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f17 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f18 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f19 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f20 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f21 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 7 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f22 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 7 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 4 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f23 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 6 | 8 | 3 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f24 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f25 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 1 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 4 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f26 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f27 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 6 | 8 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f28 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f29 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 7 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f30 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 3 | |
| total rank | 103 | 209 | 127 | 201 | 146 | 152 | 89 | 53 | |
| final rank | 3 | 8 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 1 | |
| PSO | GA | GWO | MPSO | CLPSO | CAPSO | EAPSO | GLPSO | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | |||||||||
| f1 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f2 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f3 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 7 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f4 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f5 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f6 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 5 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f7 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f8 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f9 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f10 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 6 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f11 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f12 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 3 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f13 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f14 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 2 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f15 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 1 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 4 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f16 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f17 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f18 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f19 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f20 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 6 | 7 | 3 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f21 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f22 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f23 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 4 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f24 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 7 | 2 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f25 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f26 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 7 | 2 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 1 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f27 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 6 | 8 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 4 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f28 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 7 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 2 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f29 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 5 | 7 | 2 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 6 | 3 | |
| mean | |||||||||
| f30 | std | ||||||||
| rank | 4 | 7 | 5 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 2 | |
| total rank | 130 | 211 | 139 | 202 | 83 | 158 | 97 | 60 | |
| final rank | 4 | 8 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 1 | |
| Algorithm | The Optimal Variable | Optimal Weight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | 0.052410681 | 0.374327572 | 10.32660253 | 0.012674616 |
| PCFMO | 0.052405 | 0.37416 | 10.338 | 0.012867 |
| SCSO | 0.0500 | 0.3175 | 14.0200 | 0.012717 |
| GJO | 0.0515793 | 0.354055 | 11.4484 | 0.01266752 |
| BWO | 0.0517 | 0.3568 | 11.3132 | 0.012703 |
| DO | 0.051215 | 0.345416 | 11.983708 | 0.012669 |
| ICHIMP-SHO | 0.051324 | 0.347614 | 11.86041 | 0.0126915 |
| EAPSO | 0.0515219 | 0.3527102 | 11.527838 | 0.012666 |
| GLPSO | 0.0514355 | 0.350633 | 11.6596 | 0.012671 |
| Algorithm | The Optimal Variable | Optimal Weight | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSSA | 3.500957 | 0.70 | 17.00 | 7.331317 | 7.806692 | 3.351851 | 5.28669 | 2997.5658 |
| ASO | 3.50000 | 0.70 | 17.0755 | 7.3000 | 8.1198 | 3.4366 | 5.2935 | 3051.31905 |
| HHSC | 3.50379 | 0.70 | 17.00 | 7.3 | 7.7294014 | 3.356511 | 5.28669 | 2997.89844 |
| AO | 3.5021 | 0.70 | 17.00 | 7.3099 | 7.7476 | 3.3641 | 5.2994 | 3007.7328 |
| GLPSO | 3.50402 | 0.700099 | 17.012 | 7.37466 | 7.80098 | 3.36426 | 5.28804 | 3005.4617 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X. An Advanced Adaptive Group Learning Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry 2025, 17, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050667
Han J, Chen Y, Huang X. An Advanced Adaptive Group Learning Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry. 2025; 17(5):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050667
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jialing, Yuyu Chen, and Xiaoqing Huang. 2025. "An Advanced Adaptive Group Learning Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm" Symmetry 17, no. 5: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050667
APA StyleHan, J., Chen, Y., & Huang, X. (2025). An Advanced Adaptive Group Learning Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Symmetry, 17(5), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17050667







