A Noise Reduction Method for GB-RAR Bridge Monitoring Data Based on CEEMD-WTD and PCA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Principles of the CEEMD Method
2.2. Wavelet Thresholding Denoising
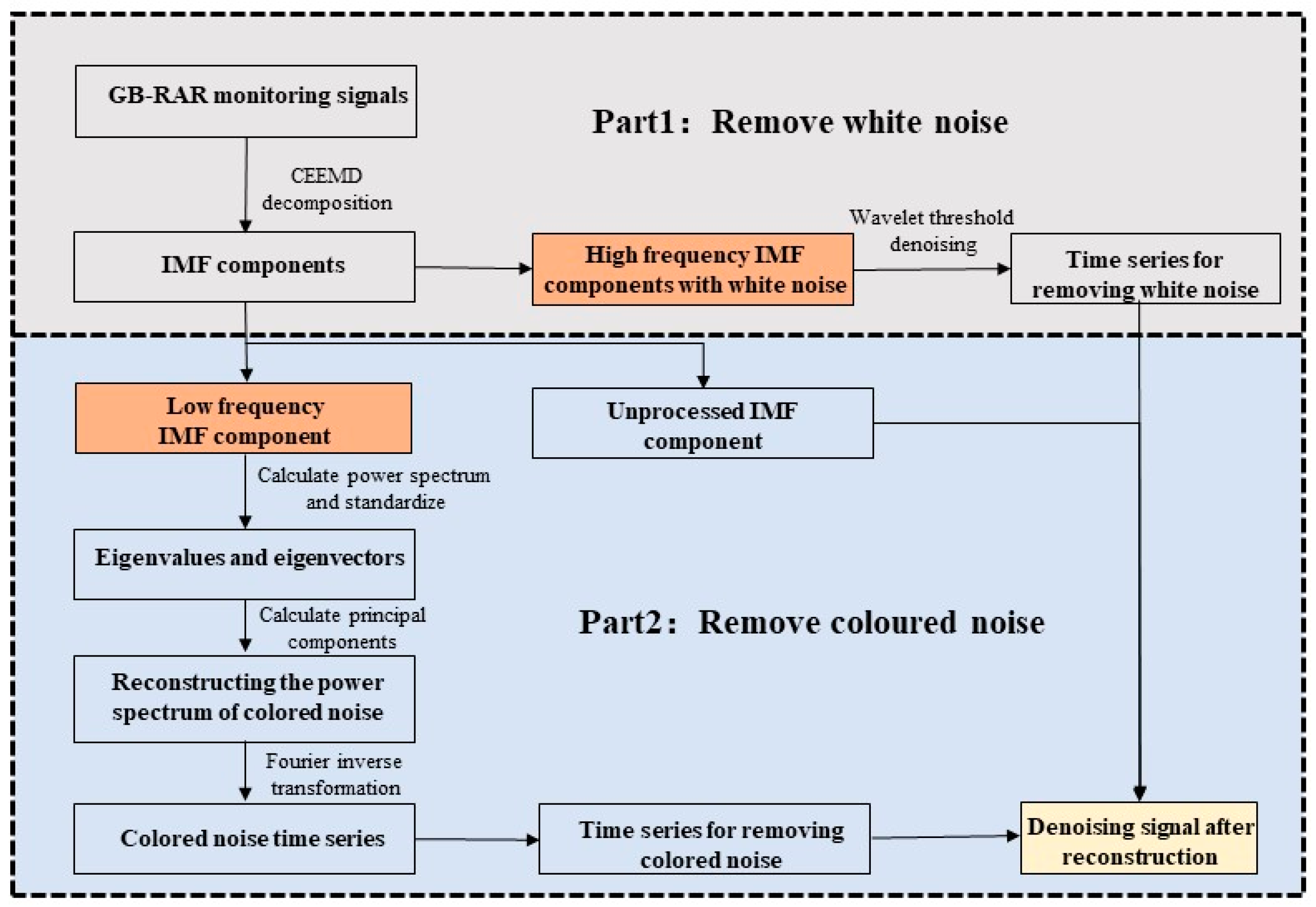
2.3. CEEMD-WTD-Based Denoising Method
2.4. Principal Component Analysis and Data Reconstruction
2.5. Evaluation of Denoising Effect
- (1)
- RMSE
- (2)
- SNR
3. Engineering Examples
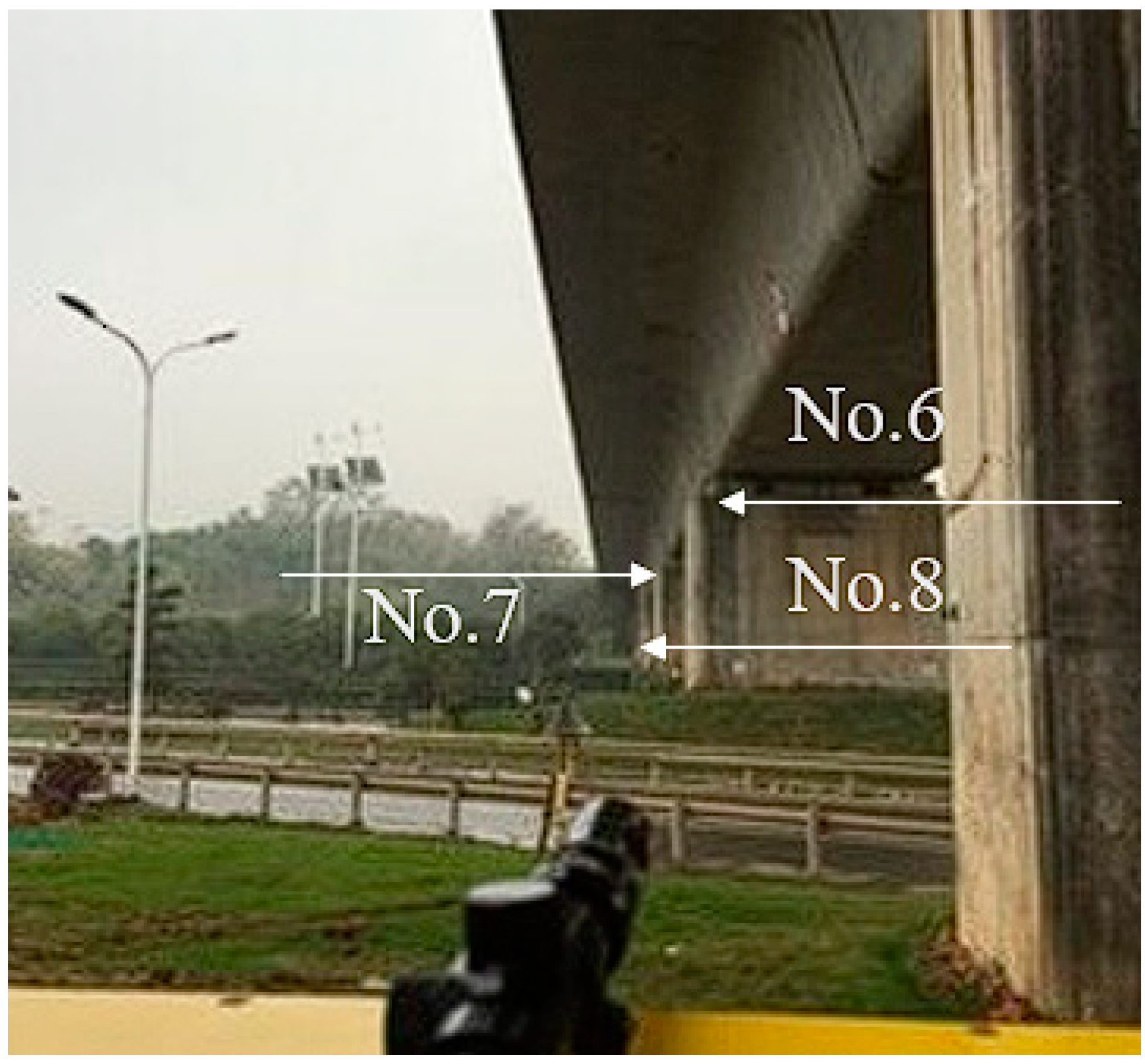
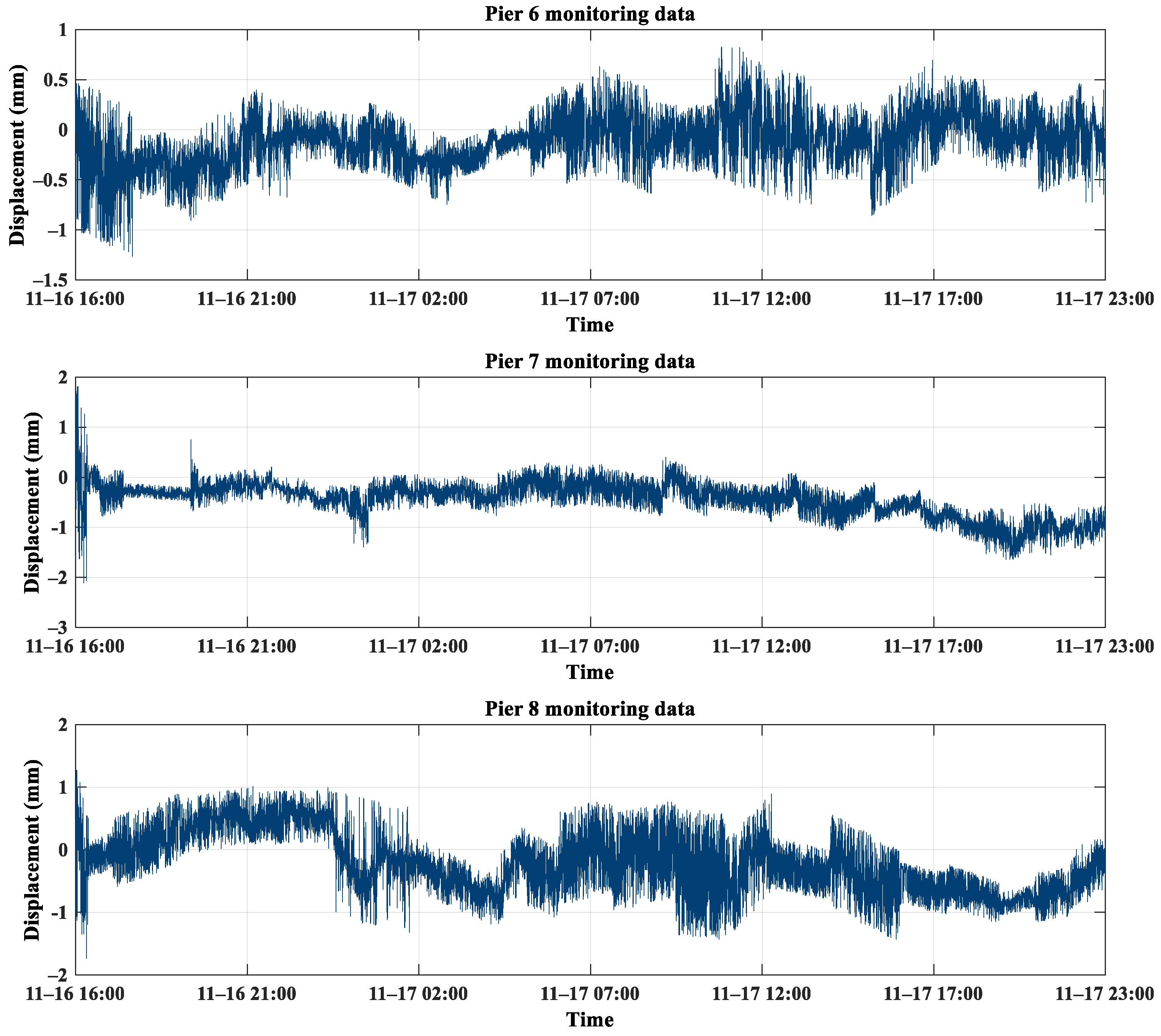
3.1. Objects of Monitoring
3.2. Overview of the Monitoring Program and Measurements
4. Experimental Results
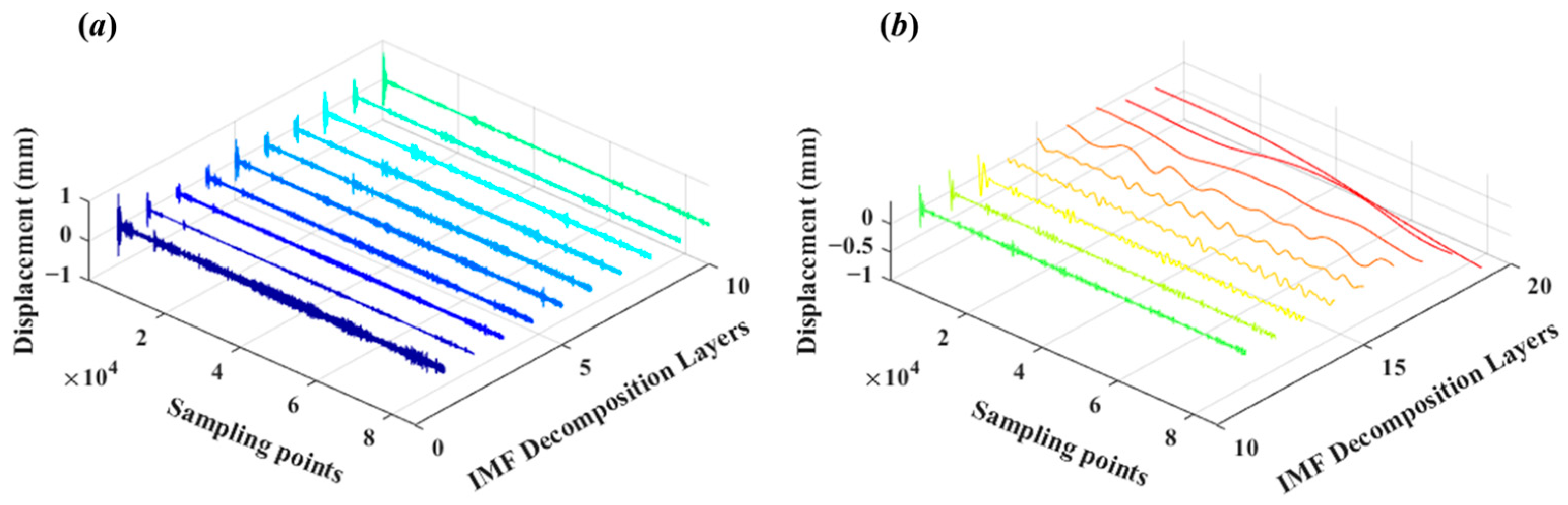
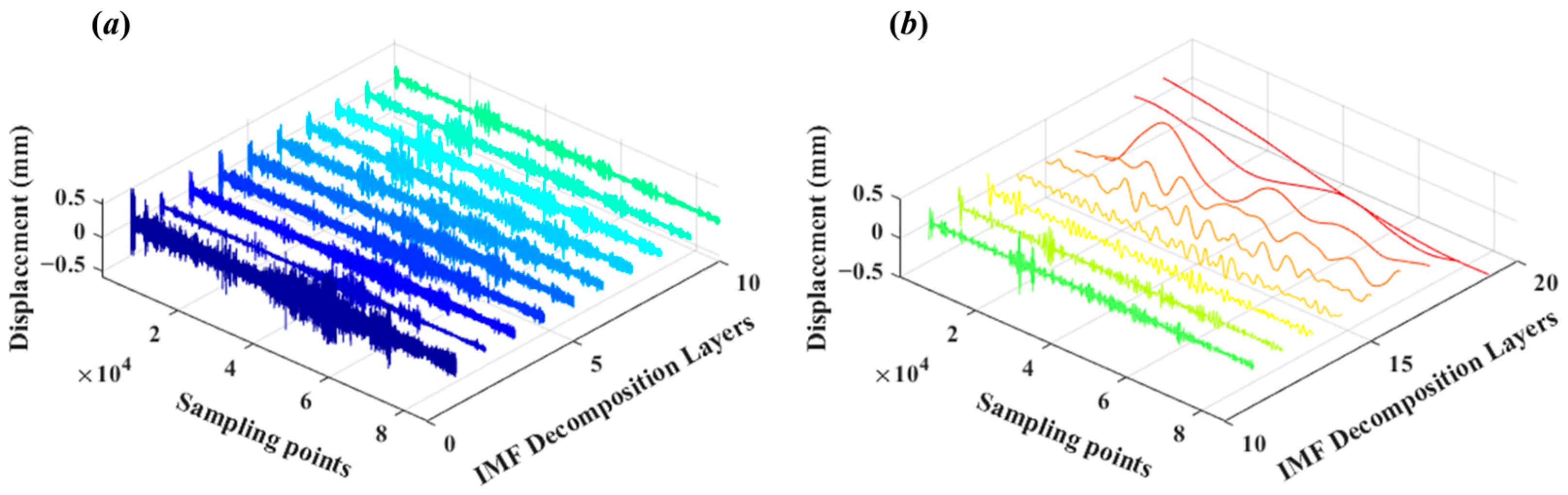
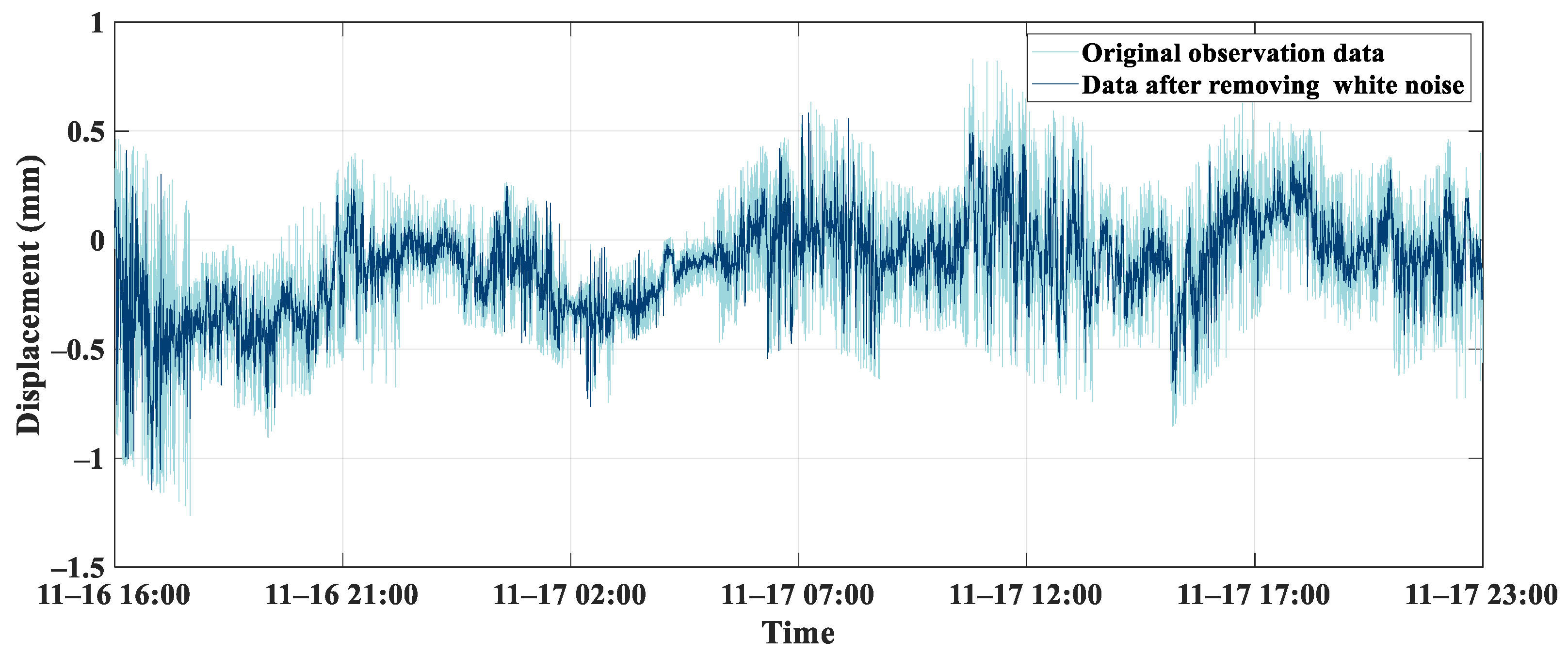
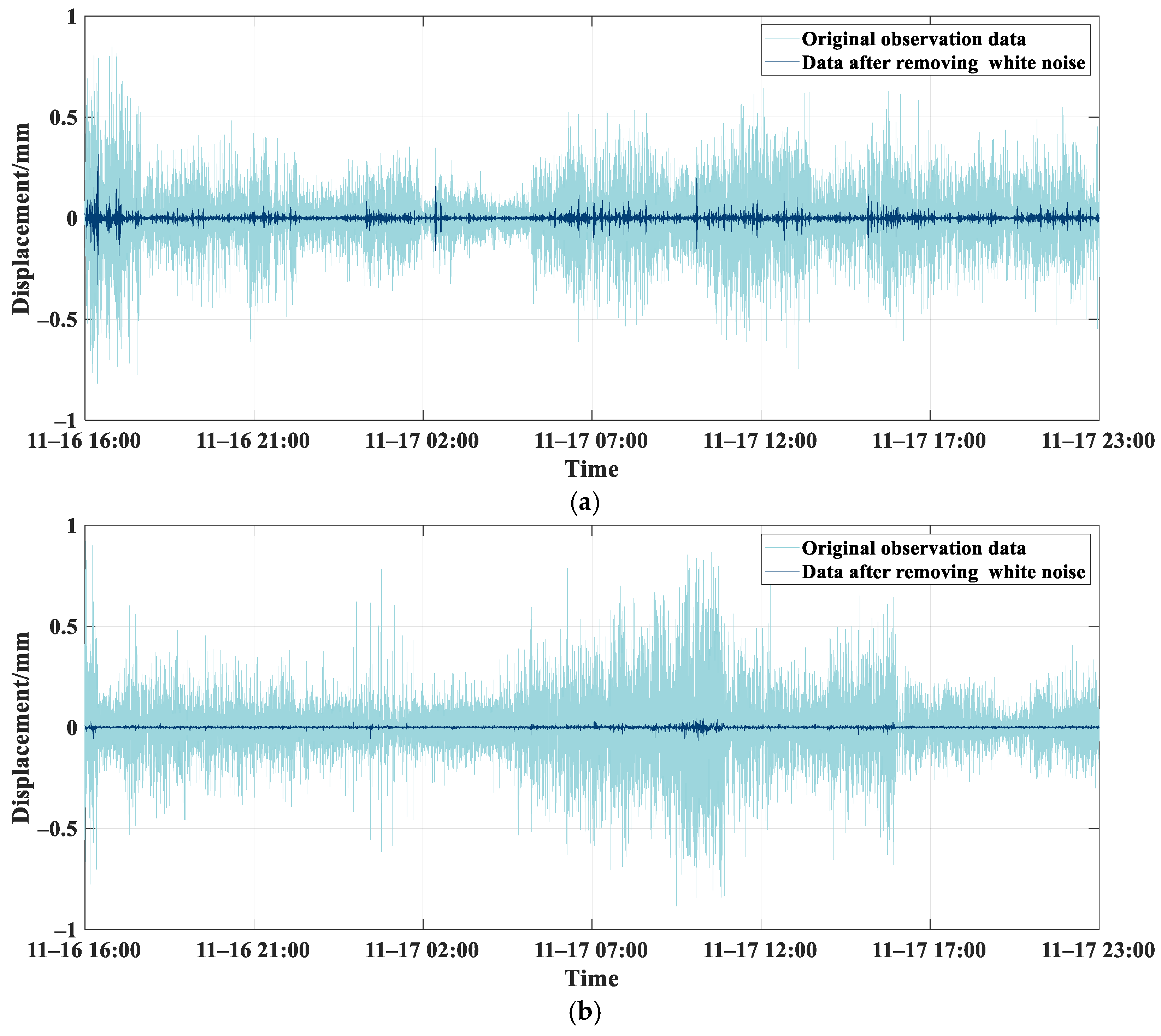
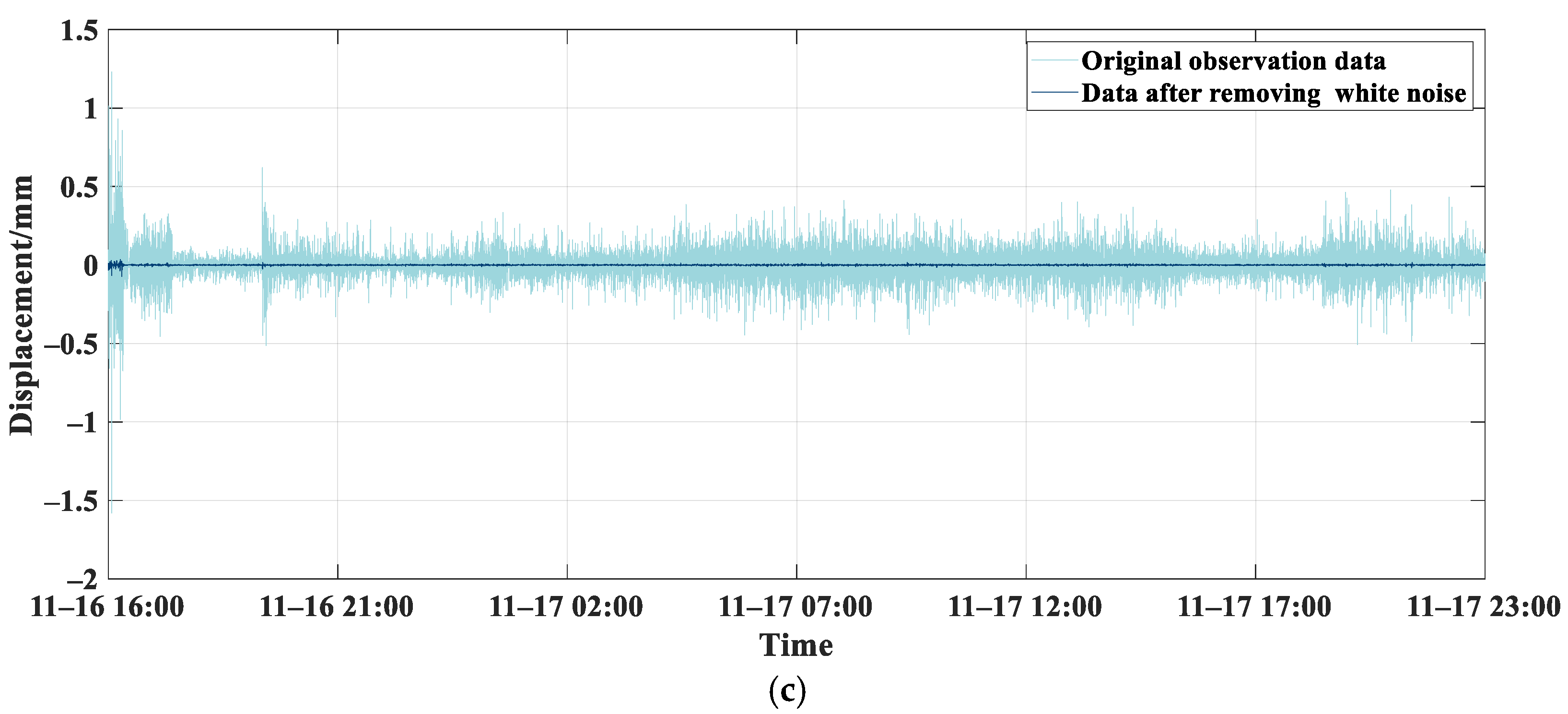
4.1. A Denoising Method Based on CEEMD-WTD
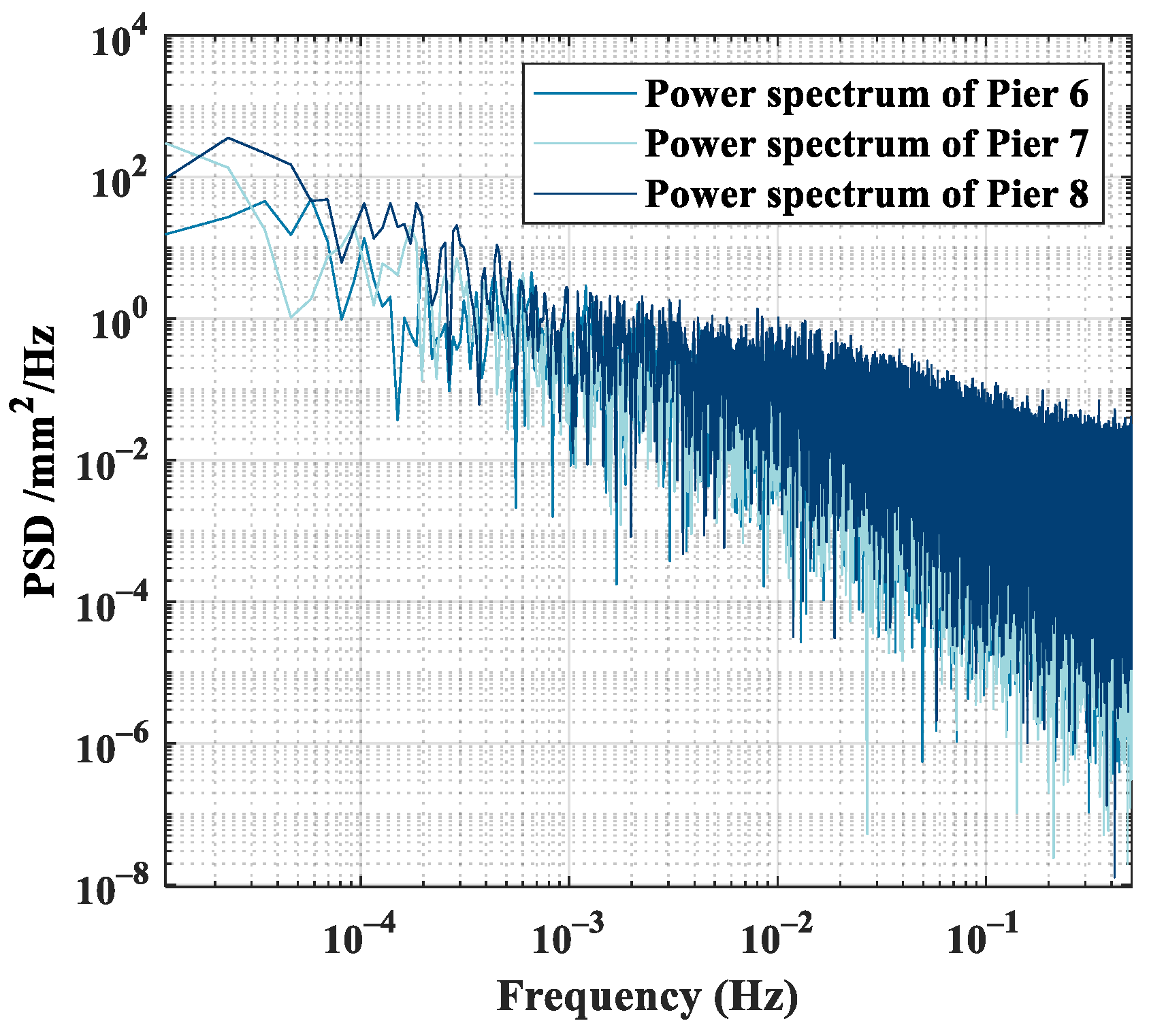
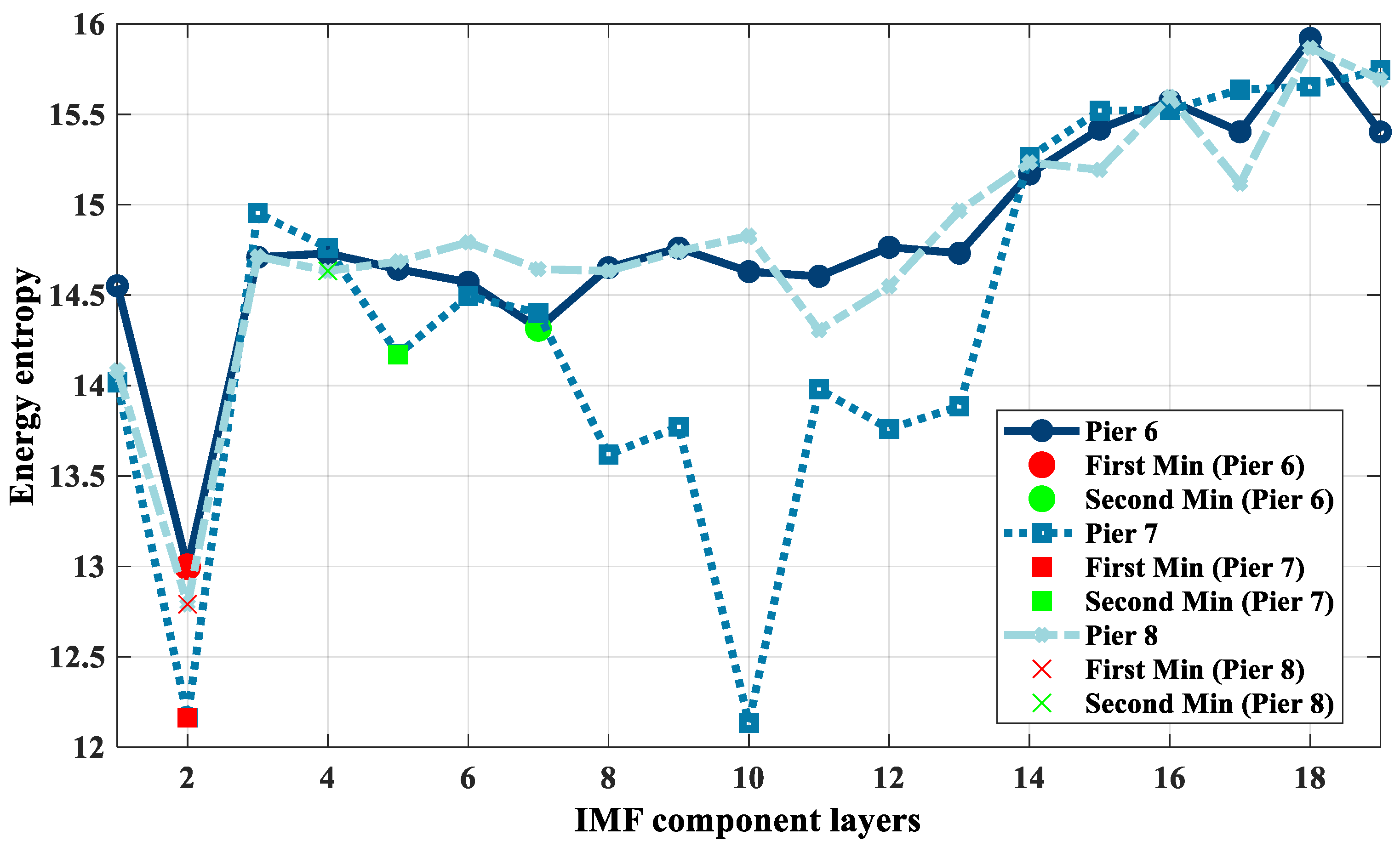
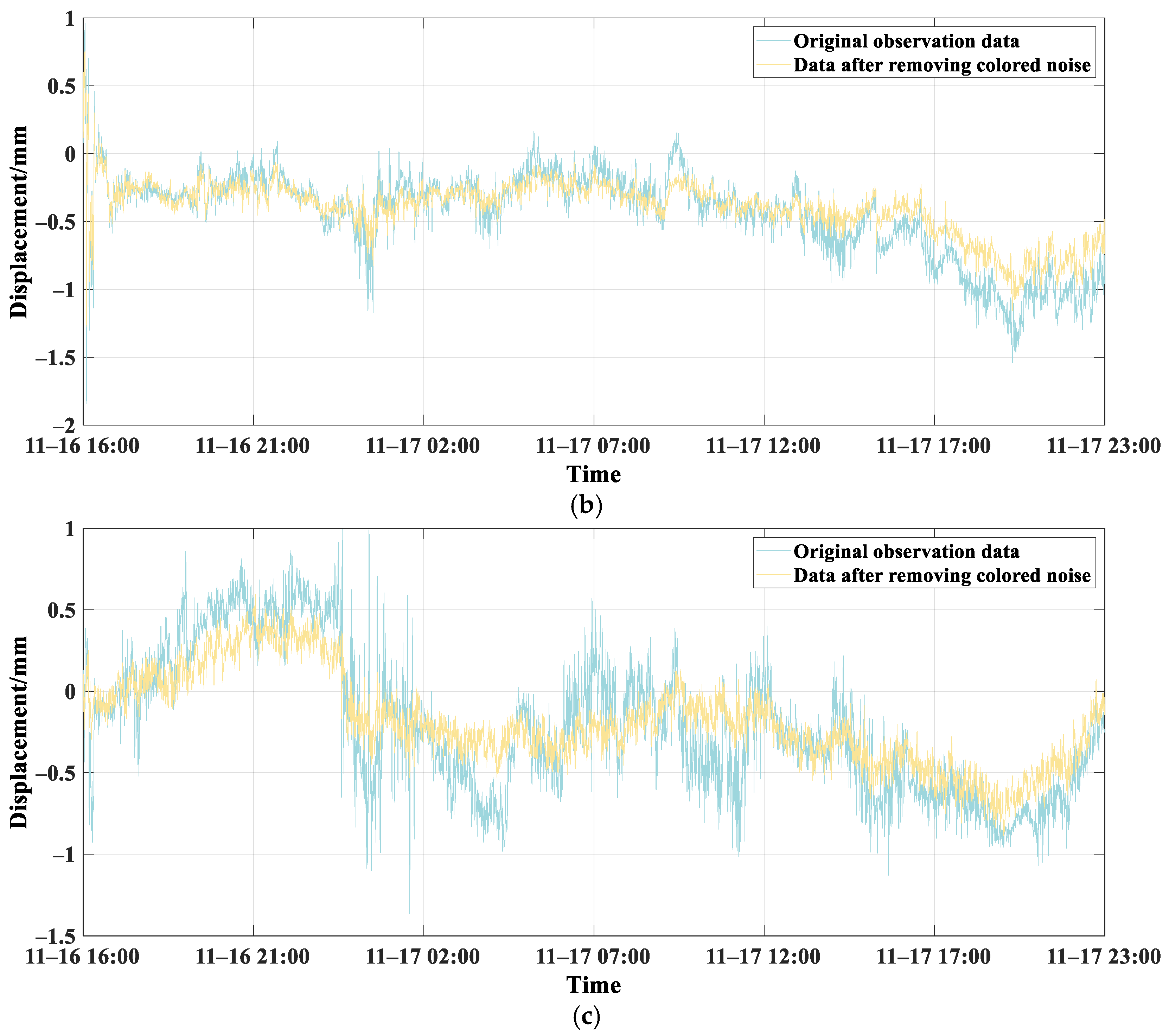
4.2. Coloured Noise Removal Using PCA
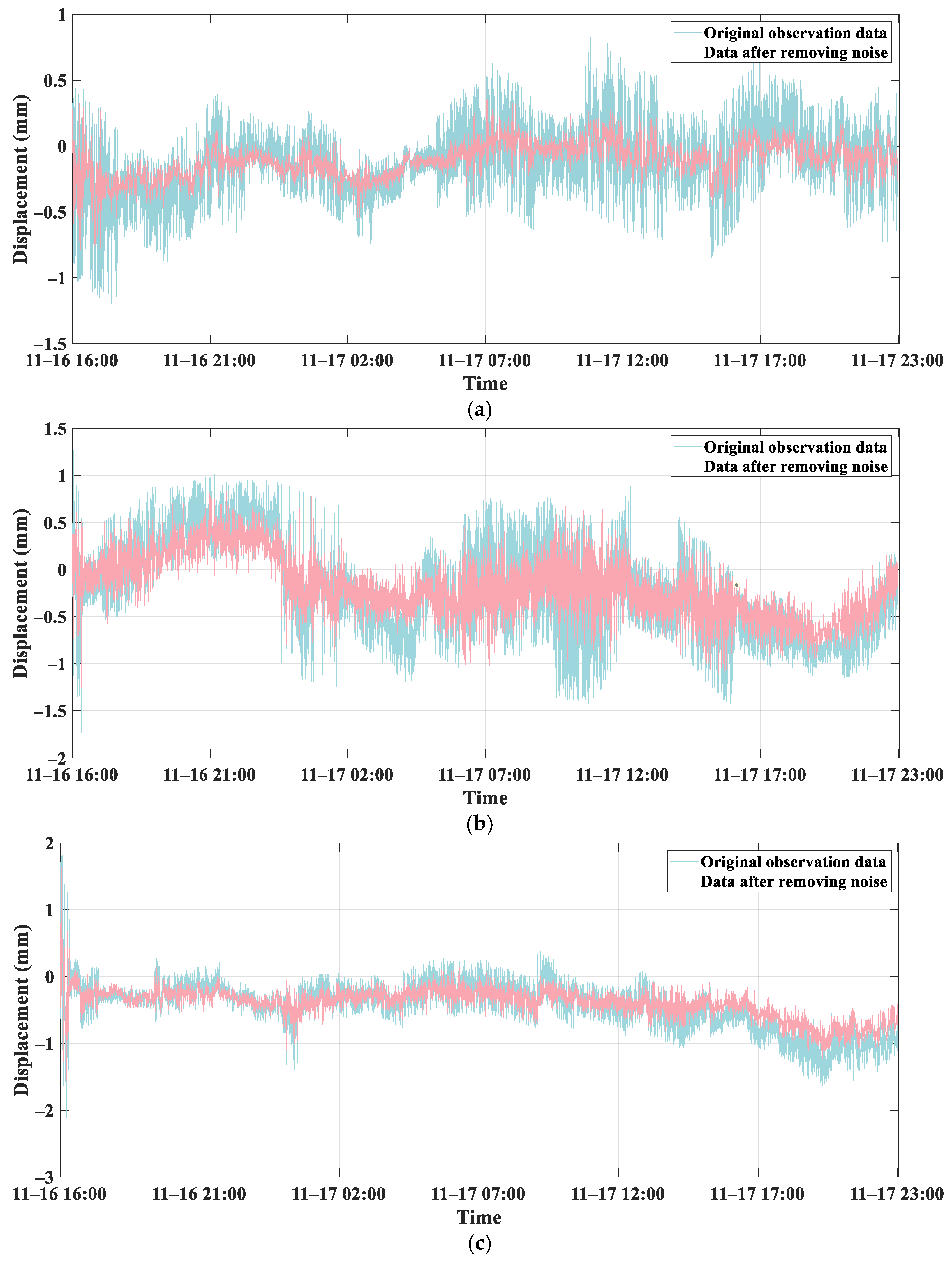
4.3. Comparative Experiment of CEEMD-WTD and PCA Denoising Methods
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The CEEMD-WTD method, compared to WTD, is more proficient at extracting bridge deformation data against a background of white noise. After de-noising, the SNR for the three bridge piers were 8.61 dB, 19.87 dB, and 15.06 dB, respectively, with RMSE of 0.1 mm, 0.06 mm, and 0.09 mm. By harnessing the strengths of both denoising methods, this approach improves the SNR while retaining deformation characteristics, making it apt for bridge monitoring data denoising.
- (2)
- Using the low-frequency IMF component from three concurrently monitored adjacent bridge piers as input data and processing the CEEMD-decomposed power spectrum matrix composed of these components through PCA, we effectively removed the principal components of the coloured noise spectrum. This mitigated the effects of coloured noise and attenuated abrupt local deformation trends, showcasing its efficacy as a denoising method.
- (3)
- Upon employing the combined CEEMD-WTD and PCA method to remove white and coloured noises, the uncertainties for the three piers were 0.129, 0.212, and 0.303, respectively. These were reduced by 43.2%, 35.8%, and 33.1%. The reduction rates are high compared to other denoising methods, indicating that the combined denoising method reduces the effect of noise while retaining the real bridge deformation data.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stiros, S.; Psimoulis, P.; Moschas, F.; Saltogianni, V.; Tsantopoulos, E.; Triantafyllidis, P. Multi-sensor measurement of dynamic deflections and structural health monitoring of flexible and stiff bridges. Bridge Struct. 2019, 15, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, R.; He, Q.; Meng, X. Bridge monitoring using multi-GNSS observations with high cutoff elevations: A case study. Measurement 2021, 168, 108303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, W.; Shu, J. Dynamic monitoring and data analysis of a long-span arch bridge based on high-rate GNSS-RTK measurement combining CF-CEEMD method. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 11, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, M.A.; Gonzalez, D.C.; Minguez, J.; Schumacher, T. A novel laser and video-based displacement transducer to monitor bridge deflections. Sensors 2018, 18, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farneti, E.; Cavalagli, N.; Costantini, M.; Trillo, F.; Minati, F.; Venanzi, I.; Ubertini, F. A method for structural monitoring of multispan bridges using satellite InSAR data with uncertainty quantification and its pre-collapse application to the Albiano-Magra Bridge in Italy. Struct. Health Monit. 2023, 22, 353–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Tong, A.; Wu, W.; Zhu, C. Health monitoring and safety evaluation of bridge dynamic load with a ground-based real aperture radar. Surv. Rev. 2022, 54, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieraccini, M.; Miccinesi, L.; Abdorazzagh Nejad, A.; Naderi Nejad Fard, A. Experimental dynamic impact factor assessment of railway bridges through a radar interferometer. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Wen, X.; Ma, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D. Monitoring and analysis of dynamic characteristics of super high-rise buildings using GB-RAR: A case study of the WGC under construction, China. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Suo, Z.; Tian, F.; Qi, L.; Tao, H.; Li, Z. A novel GB-SAR system based on TD-MIMO for high-precision bridge vibration monitoring. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, R.; Huang, M. Improved data-driven stochastic subspace identification with autocorrelation matrix modal order estimation for bridge modal parameter extraction using GB-SAR Data. Buildings 2022, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Guo, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Hang, C. Dynamic vibration characteristics monitoring of high-rise buildings by interferometric real-aperture radar technique: Laboratory and full-scale tests. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 6423–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuras, P.; Ortyl, Ł.; Owerko, T.; Salamak, M.; Łaziński, P. GB-SAR in the diagnosis of critical city infrastructure—A case study of a load test on the long tram extradosed bridge. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Di, H.; Zhuo, Y.; Jia, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X. Rating for operational performance of high-speed railway bridges based on Ground-based Interferometry Radar. J. China Railw. Soc. 2023, 45, 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; Ma, J.; Shi, A.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. GB-RAR Deformation Information Estimation of High-Speed Railway Bridge in Consideration of the Effects of Colored Noise. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, S.; Fan, K. Differential ground-based radar interferometry for slope and civil structures monitoring: Two case studies of landslide and bridge. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Xiong, H.; Yuan, C.; Kong, Q. A novel deep convolutional image-denoiser network for structural vibration signal denoising. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L. Denoising GPS-Based Structure Monitoring Data Using Hybrid EMD and Wavelet Packet. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 4920809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Sheng, V.S.; Ding, X. An ECG signal de-noising approach based on wavelet energy and sub-band smoothing filter. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Luan, X. Denoising Ocean Turbulence Microstructure Signals for Application in Estimating Turbulence Kinetic Energy Dissipation Rates Based on EMD-PCA. Sensors 2022, 22, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Han, K. Fault feature extraction and diagnosis of rolling bearings based on wavelet thresholding denoising with CEEMDAN energy entropy and PSO-LSSVM. Measurement 2021, 172, 108901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-R.; Shieh, J.-S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaci, S. A new ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) denoising method for seismic signals. Energy Procedia 2016, 97, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Mao, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, C.; Gong, X.; Rao, Z. An EEMD-SVD-LWT algorithm for denoising a lidar signal. Measurement 2021, 168, 108405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Guo, H.; Shang, X. EEMD and multiscale PCA-based signal denoising method and its application to seismic P-phase arrival picking. Sensors 2021, 21, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huimin, C.; Ruimei, Z.; Yanli, H. Improved threshold denoising method based on wavelet transform. Phys. Procedia 2012, 33, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lang, Q.; Jing, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Ai, Q. An improved wavelet threshold denoising method for health monitoring data: A case study of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge immersed tunnel. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REN, A.; XU, K. Time domain signal extraction from GNSS time series with colored noise. Chin. J. Geophys. 2023, 66, 518–529. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, H.A.; Hanif, M.U.; Hassan, M.U.; Shahid, J.M.; Khan, S.A.; Ali, A. Improved damage assessment of bridges using advanced signal processing techniques of CEEMDAN-EWT and Kernal PCA. Eng. Struct. 2025, 329, 119774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, R. ESMD-WSST high-frequency de-noising method for bridge dynamic deflection using GB-SAR. Electronics 2022, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J. BDS/GPS deformation analysis of a long-span cable-stayed bridge based on colored noise filtering. Geod. Geodyn. 2023, 14, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, J. Noise in GPS displacement measurements from Southern California and Southern Nevada. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Fang, R.; Yi, L. Accuracy enhancement of high-rate GNSS positions using a complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition-based multiscale multiway PCA. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 169, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shang, J. Denoising method of steel frame structure settlement data based on CEEMD and improved Wavelet Threshold method. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 42, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Cao, J. Seismic attenuation analysis using ensemble empirical mode decomposition and wavelet transform. Oil Geophys. Prospect. 2016, 51, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, L. GPR signal denoising and target extraction with the CEEMD method. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1615–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; He, X.; Ferreira, V.G. Ocean wave separation using CEEMD-Wavelet in GPS wave measurement. Sensors 2015, 15, 19416–19428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Du, J.; Zhao, D.; Yu, Z. Impact-Type Sunflower Yield Sensor Signal Denoising Method Based on CEEMD-WTD. Agriculture 2023, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing-Yi, L.; Hong, L.; Dong, Y.; Yan-Sheng, Z. A new wavelet threshold function and denoising application. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 3195492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Kang, C.; Li, G.; Li, C. Integration of wavelet denoising and HHT applied to the analysis of bridge dynamic characteristics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG, H.; YE, R.; Du, W. A hybrid denoising method for bridge vibration signal based on EMD and wavelet threshold. Highway 2021, 66, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Fu, Y. Noise analysis of GPS continuous observation stations. J. Earthq. 2007, 29, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, F. CEEMDAN-SG based blast shock wave denoising algorithm research. Foreign Electron. Meas. Technol. 2022, 41, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Peng, D.; Zuo, M.J.; Xia, J.; Qin, Y. Improved Hilbert–Huang transform with soft sifting stopping criterion and its application to fault diagnosis of wheelset bearings. ISA Trans. 2022, 125, 426–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Wavelet | SNR | Wavelet | SNR | Wavelet | SNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| db1 | 7.95 | sym1 | 7.59 | coif1 | 8.19 |
| db2 | 8.17 | sym2 | 8.17 | coif2 | 8.25 |
| b3 | 8.25 | sym3 | 8.25 | coif3 | 8.26 |
| db4 | 8.24 | sym4 | 8.27 | coif4 | 8.26 |
| db5 | 8.27 | sym5 | 8.27 | coif5 | 8.30 |
| db6 | 8.28 | sym6 | 8.28 | ||
| db7 | 8.26 | sym7 | 8.26 | ||
| db8 | 8.29 | sym8 | 8.28 | ||
| db9 | 8.29 | sym9 | 8.30 | ||
| db10 | 8.27 | sym10 | 8.28 |
| Decomposition Layer | SNR | RMSE/mm |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14.02 | 0.05 |
| 2 | 11.36 | 0.07 |
| 3 | 9.66 | 0.08 |
| 4 | 8.30 | 0.10 |
| 5 | 7.24 | 0.11 |
| 6 | 6.44 | 0.12 |
| Denoising Method | Pier | SNR/dB | RMSE/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMD | 6 | 22.38 | 3.37 |
| WTD | 8.3 | 0.10 | |
| CEEMD-WTD | 8.61 | 0.10 | |
| EMD | 7 | 9.94 | 1.74 |
| WTD | 16.67 | 0.08 | |
| CEEMD-WTD | 19.87 | 0.06 | |
| EMD | 8 | 19.96 | 4.99 |
| WTD | 11.17 | 0.15 | |
| CEEMD-WTD | 15.06 | 0.09 |
| Number of Times Each IMF Component Crosses Zero for 19 Layers of IMF | IMF7–IMF8 | IMF8–IMF9 |
|---|---|---|
| slope | −1999 | −1204 |
| First Principal Component | Second Principal Component | Third Principal Component |
|---|---|---|
| 66.9% | 22.4% | 10.7% |
| Pier 6 | Pier 7 | Pier 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before denoising | 0.227 | 0.330 | 0.453 |
| After denoising | 0.129 | 0.212 | 0.303 |
| Pier 6 | Pier 7 | Pier 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Filtering algorithm | Uncertainty reduction rate before and after denoising (%) | Uncertainty reduction rate before and after denoising (%) | Uncertainty reduction rate before and after denoising (%) |
| The combined CEEMD-WTD and PCA method | 43.2 | 35.8 | 33.1 |
| Kalman filtering method | 33.22 | 30.92 | 29.24 |
| Gaussian filtering method | 12.07 | 11.99 | 6.14 |
| Mobile mean filtering method | 13.85 | 7.68 | 5.41 |
| REMD | 26.66 | 34.54 | 29.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Lai, P.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Y.; Shi, A.; Li, X.; Ma, J. A Noise Reduction Method for GB-RAR Bridge Monitoring Data Based on CEEMD-WTD and PCA. Symmetry 2025, 17, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17040588
Zhou L, Lai P, Zhao W, Yang Y, Shi A, Li X, Ma J. A Noise Reduction Method for GB-RAR Bridge Monitoring Data Based on CEEMD-WTD and PCA. Symmetry. 2025; 17(4):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17040588
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Lv, Pengde Lai, Wenyi Zhao, Yanzhao Yang, Anping Shi, Xin Li, and Jun Ma. 2025. "A Noise Reduction Method for GB-RAR Bridge Monitoring Data Based on CEEMD-WTD and PCA" Symmetry 17, no. 4: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17040588
APA StyleZhou, L., Lai, P., Zhao, W., Yang, Y., Shi, A., Li, X., & Ma, J. (2025). A Noise Reduction Method for GB-RAR Bridge Monitoring Data Based on CEEMD-WTD and PCA. Symmetry, 17(4), 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17040588






