Abstract
An analytical exploration of the phase decoherence equation of two qubits interacting with a coherent field with dipole–dipole interaction is introduced. The study examines the tradeoff relationships between intrinsic concurrence and first-order coherence in the qubits–cavity system while considering the impacts of decoherence and the interactions among the qubits. We affirm that the relationship between intrinsic concurrence and first-order coherence is valid. Additionally, we demonstrate that the minimum limit of intrinsic concurrence is universally applicable, although the upper limit is typically not. These connections in Heisenberg models can provide a means by which to investigate how quantum resources are allocated in spins, potentially leading to future applications in quantum information processing. It is partially but not completely possible to control the tradeoff relations between intrinsic concurrence and first-order coherence of the two-qubit cavity system; this control might involve actions that influence the system and are reflected in intrinsic concurrence and first-order coherence.
1. Introduction
In quantum mechanics, tradeoffs and symmetry are deeply interconnected. The preservation of symmetry in a system often constrains its evolution or measurement outcomes, as symmetry dictates certain conserved quantities such as energy or momentum and limits how the system can evolve over time. However, new tradeoffs emerge when symmetry is broken, such as in phase transitions or spontaneous symmetry breaking. These can involve competing physical properties, where optimizing one aspect of the system, such as coherence or entanglement, may require compromising others, such as stability or precision. Thus, the interplay between symmetry and tradeoffs shapes the behavior and measurement possibilities of quantum systems.
In quantum information processing and quantum communication, the relationship between coherence and entanglement plays a pivotal role. Investigating the tradeoff between intrinsic concurrence and first-order coherence in a two-qubit cavity system that considers qubit–dipole coupling and decoherence effects can provide valuable insights into the fundamental limits of quantum information protocols and help in the development of more robust quantum technologies. In quantum mechanics, entanglement and coherence are two fundamental features of quantum states that are crucial for quantum information processing, communication, and computation. Although they are related in some ways, they represent distinct properties of a quantum system [1,2]. For pure two-qubit systems, there is indeed a complementary relationship between first-order coherence () and concurrence (C). While high coherence typically indicates a less entangled state, high entanglement often leads to a reduction in coherence [3,4]. Intrinsic concurrence () is a critical measure for understanding the relationship between entanglement and coherence in two-qubit mixed states. Unlike standard concurrence, which is limited to pure states, extends the concept of entanglement to mixed states and shows the same complementary relationship with first-order coherence () that we see in pure states [5].
Furthermore, the authors of [6] have endeavored to connect IC and agreement through an inequality relationship without providing a strict mathematical demonstration. They assert that this is true for any generic two-qubit quantum system. Spin chains are robust and adaptable systems, and have gained considerable attention in quantum computing and quantum simulation because of their integrability, scalability, and diverse physical behavior. They serve as an ideal platform for studying entanglement, quantum correlations, and quantum phase transitions, offering great potential for building the next generation of quantum computers. As experimental techniques continue to improve and as new models for quantum error correction and fault tolerance are developed, spin chains are expected to play a central role in the development of scalable and practical quantum computing systems [7,8,9,10,11,12]. In [13], the authors studied the dynamics of quantum systems, focusing on how various Hamiltonians impact entanglement and coherence in multi-qubit states. They also examined engineering techniques that could enhance the efficiency and reliability of structural systems by using advanced materials and design principles. Furthermore, their research explored the statistical mechanics of complex systems, revealing insights into collective behavior and phase transitions in non-equilibrium environments as well as the relationship between classical and quantum mechanics in chaotic systems, particularly with regard to the influence of quantum correlations on information transfer in quantum cryptography. By discussing specific experimental systems such as superconducting qubits and trapped ions, their study provides concrete examples of how theoretical concepts such as coherence and entanglement are realized in practice. These systems demonstrate the practical challenges and innovations in manipulating quantum states and illustrate the implications of quantum dynamics in real-world applications. Highlighting such experimental platforms allows for a deeper understanding of the interplay between theory and experiment, enriching the overall discourse on quantum technologies [14].
Indeed, spin chains have become a crucial element in quantum mechanics, particularly for exploring quantum coherence and correlations. The Heisenberg model, which describes the interaction between spins in a quantum system, plays a significant role in this context [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Spin chain models provide fertile ground for studying quantum resources such as entanglement and coherence. The spin correlations within the chain can lead to powerful quantum phenomena that are central to advancing quantum technologies. These systems are also crucial for understanding the interplay between quantum mechanical effects, many-body physics, and computational resources in quantum information science [27,28,29,30]. The two-qubit Heisenberg XYZ model represents one of the simplest yet most versatile spin chains, and has recently inspired the research community to quickly embrace the Heisenberg XYZ example [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. The dissipative two-qubit Heisenberg XYZ model under the Dzyaloshinsky–Moriya interaction is a rich system for studying the effects of anisotropic spin interactions, relativistic corrections, and environmental dissipation on quantum correlations. All of this earlier research has motivated us to examine the tradeoff relationships for this model. Additionally, we investigate whether the suggested inequality relation is valid for this system and evaluate the tradeoff relationship to gain insights into the shared behavior of entanglement and coherence over time for different system parameters, such as the purity of the initially formed state, dipole–dipole interaction, quantity of photons, and attenuation parameter.
We organize the rest of this research paper in the following manner: in Section 2, we discuss the physical framework and its resolution, then provide a brief introduction to C, , and ; in Section 3, we examine the tradeoff relationships between and along with the inequality relationship between IC and C; in Section 4, we employ the Heisenberg XYZ model to explore the tradeoff relationships between C and ; finally, in Section 5, we showcase our results and findings before ultimately concluding the paper.
2. The Physical Model and Its Solution
We consider a model consisting of two qubits interacting resonantly with a coherent field, with dipole–dipole interaction taking place through via two-photon transitions. This model highlights the implications of photon interactions with two-level systems, emphasizing the differences between one-photon and two-photon cases. While one-photon processes allow for straightforward excitations and generation of entanglement, two-photon interactions lead to more complex dynamics that can be leveraged for enhanced control, nonlinearity, and robustness in quantum information applications. In the rotating-wave approximation, the Hamiltonian of the system is provided by
where denotes the annihilation (creation) operator of the resonant single-mode field, is atomic transition frequency and cavity frequency, is the coupling constant between qubits and cavity, the raising and lowering operators of the qubit i are and , respectively, and is the qubit dipole–dipole coupling constant. Here, only the pure phase decoherence mechanism is considered. In this situation, the master equation governing the time evolution for the system is provided by [31,32]
where is the phase decoherence parameter. The formal solution of the Equation (2) is provided by [33,34]
where and where is the density operator of the initial system. Analysis is confined to a four-dimensional subspace characterized by the most pertinent states. We believe that this approach provides a meaningful representation of the system’s behavior under the studied conditions. In the space states , the used eigenstates of the Hamiltonian (1) are provided by
where the coefficients satisfy the condition of the following eigenvalue problem: . Here, are the corresponding eigenvalues:
where and . The explicit expression of the density matrix is provided by
where is the initial state of the entire system, i.e., the single-mode cavity field initially prepared in the coherent state,
while the two qubits are started in the pure excited state . This density matrix can be used to perform detailed study on the evolution of some measures of mixture and entanglement in the partitions of two dipole-coupled qubits interacting with a coherent cavity under decoherence effect.
3. Quantifiers of Tradeoff Relations of Quantum Information Resource
Here, we briefly review the concepts of first-order coherence (FOC), concurrence (C), and intrinsic concurrence (IC) in order to explore the dynamics of the tradeoff relations between the entanglement and coherence of the generated two-spin qubit states under intrinsic decoherence, spin–orbit interaction, and external magnetic field.
- Intrinsic ConcurrenceThe behaviors of the entanglement between the generated two spin qubit states are explored using the concurrence [35], provided bywhere denotes the roots of the eigenvalues (organized in descending order, ) of the non-Hermitian matrix depending on the spin-flipped density matrix :The initial pure two-spin qubit state has , growing to a maximal state if and to a partially two-spin qubit state if . With the intrinsic concurrence [5] defined as above, for a two-qubit state , the intrinsic concurrence is defined asFor a pure two-qubit state, the concurrence and intrinsic concurrence have the following dynamics. Due to [5], where are the eigenvalues of the the non-Hermitian matrix , the two-qubit concurrence is the lower bound of the intrinsic concurrence. This means that the dynamics of the two-spin Heisenberg qubit concurrence and the intrinsic concurrence allows the following inequality:
- First-Order Coherence (FOC)The first-order coherence can be used to measure the generated coherence of a spin k-qubit state with the reduced density matrix , where and . The FOC of a k-qubit state is defined asHence, considering all k-qubits independently, the first-order coherence measure of the whole two-qubit system can be provided by [36]where the two-qubit first-order coherence satisfies .
- For a general two-qubit state such as , the complementary relation between the intrinsic concurrence and first-order coherence is introduced as follows:This means that for a closed two-qubit system there is a mutual transformation relationship between its first-order and intrinsic concurrence, while for an open two-qubit system the tradeoff relations between the two-qubit nonlocal correlation and the first-order coherence depends on the purity degree of the whole two-qubit system, which is measured by the whole linear entropy equaling to .
4. Two-Spin Heisenberg XYZ-Qubits Dynamics
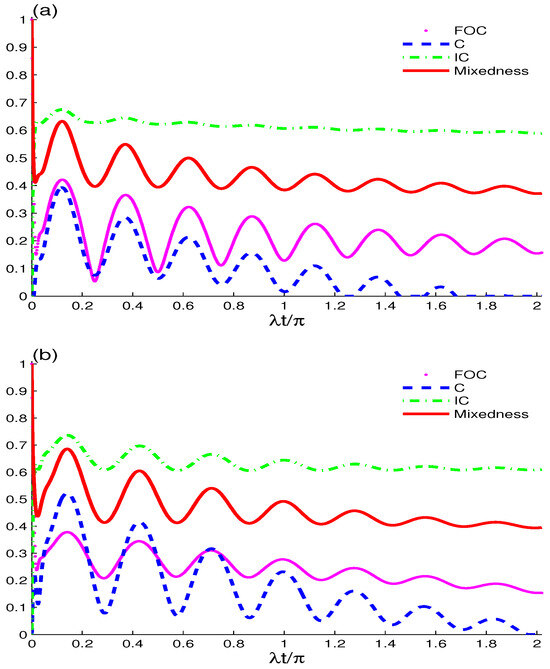
Figure 1 shows the generation of the concurrence (C) and intrinsic concurrence () under the intrinsic decoherence effect along with the degradation of the first-order coherence () in two-qubit states due to atom–cavity interactions without atom–atom interactions. For this, the two atoms are initially considered in the pure upper states , where the initial density matrix has no entanglement, i.e., the concurrence and intrinsic concurrence start with zero values () and the considered quantifiers have maximal coherence () and purity (). Below, we show the FOC, C, and IC dynamics and total mixedness of two non-interacting qubits starting with pure state inside a coherent field cavity with photons under different decoherence effects : (a) shows , (b) shows , and (c) shows .
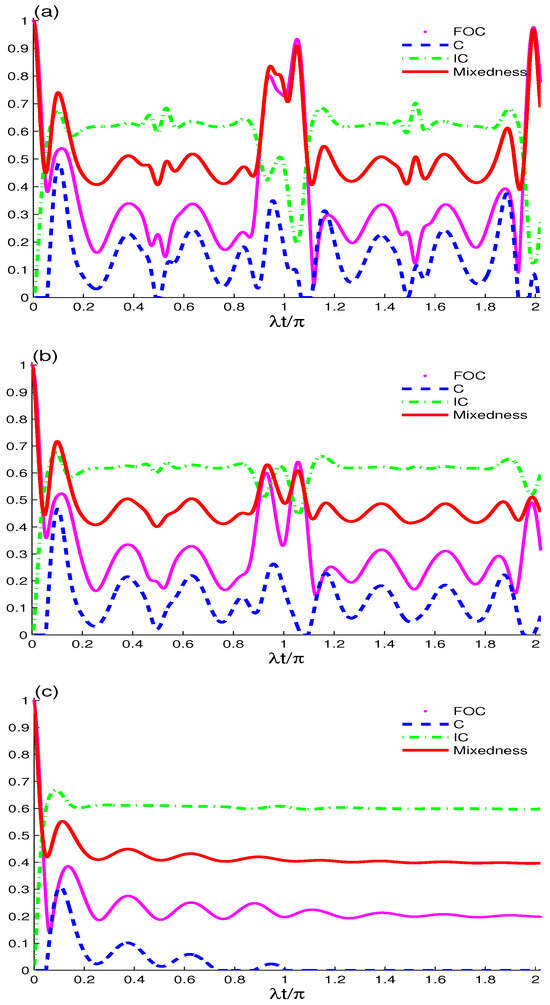
Figure 1.
Dynamics of FOC, C, IC, and total mixedness of two non-interacting qubits starting with pure state inside a coherent field cavity with photons under different decoherence effects : (a) , (b) , and (c) .
By comparing Figure 1 and Figure 2a it can be seen that the evolution of , C, , and total mixedness follows roughly the same quantitative behavior, with different amplitude values for each. Based on the context, these terms might refer to measures of concentration, distribution, or diversity in a system. To better clarify this, we can expand on the potential interpretation. In Figure 2a, there is doubling of the oscillation periods in the interval with momentum and interference from oscillations, whereas the total mixedness (indicated by the red line) represents the upper bound of . It can be observed that for the most part the total mixedness and are above the ; however, in some places the green plot outperforms the red plot, indicating that instead of . Therefore, we can conclude that while the lower bound of stated in Equation (9) is universally true, the upper bound is generally not (see Figure 1 and Figure 2a). Next, we can investigate the effect of the phase decoherence for this bound. Figure 1 and Figure 2b show the plots for these functions when . Again, we can see that for some specific intervals. Therefore, it can be confirmed that the hypothesized upper bound of is not always met. Here, we notice that the maximum values of and C decrease with the entry of gamma, while the values of and remain unchanged. Figure 1 and Figure 2c show the coherent and evenly coherent states with the development of time and increase in the value of the gamma decay. It can be noticed that the amplitude values of , and are confined between , , and , while C turns to zero when . Thus, it can be concluded that the gamma decay effect leads to . After a certain is reached, the concurrence vanishes; however, the FOC, IC, and total mixedness still exist.
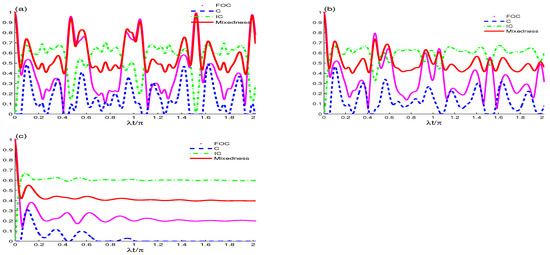
Figure 2.
Same as Figure 1 except that the two non-interacting qubits are inside a cavity filled by an evenly coherent field.
We now examine the impact of the qubit dipole–dipole coupling constant interaction on the previously discussed quantifiers as well as the accompanying complementary tradeoff relationship. Figure 3 and Figure 4 demonstrate the collective decoherence-free dynamics for each of , C, , and total mixedness as functions of t for different fixed values of and with interacting qubits . In Figure 3 and Figure 4a, where , It can be concluded that the evolution of the initial state for , C, , and total mixedness retains separability at for all ensuing instances of . As a result, dipole–dipole interaction takes place. Furthermore, our findings show that increasing the strength of the interaction results in the creation of entanglement. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that the behaviors of entanglement (captured by C), coherence (captured by ), intrinsic concurrence (captured by IC), and total mixedness are constant at any moment regardless of the intensity of the interaction. This suggests that the interaction cannot induce or enhance either coherence or entanglement in this scenario. In Figure 3 and Figure 4b, where , it is evident that the interaction creates an additional wiggling or ripple effect, influencing not only C but also , , and . We also note that, as expected, increasing leads to a decrease in the maximum values for all measures. A similar pattern is evident for in Figure 3 and Figure 4c, except that now entanglement (represented by C) and coherence (represented by ) are mostly zero. Although the interaction cannot increase the maximum value of entanglement, it decreases the minimum value of concurrence. Therefore, it can be said that the presence of dipole–dipole interactions can be used to entangle qubits. By controlling the dipole–dipole coupling strength and phase decoherence parameter , it is possible to generate entangled states, which are the foundation of many quantum algorithms and protocols. We anticipate that as the value of the interaction increases, C will attempt to replicate the changes observed in C as the value of rises, albeit not perfectly. Furthermore, an increase in the interaction leads to a rise in the average oscillation frequency of , C, C, and overall mixedness. In order to study this system more deeply and incorporate the concept of tradeoffs, we now investigate the effect of increasing the number of photons with the absence in the decoherence effect , as shown in Figure 5a,b. It can be observed that C and behave identically and that increasing the value of the interaction significantly increases the oscillation frequency. Generally speaking, given that the initial state is an entangled one, we can assert that an increase in the number of photon interactions leads to a rise in the oscillation frequencies of , C, and . Furthermore, it is evident that the lower bound of , as outlined in Equation (9), is upheld effectively. Figure 6a,b shows the result of increasing the dipole–dipole coupling in a two-qubit cavity system to . As can be seen, this increase causes a significant change in the maximum values of all measures (, C, , and total mixedness), resulting in a significant decrease. Additionally, even in the case of non-zero decoherence, when including the lower bound of IC as provided in Equation (9), the tradeoff relation is preserved entirely strictly. At , the and C have the same values because the initialized state is maximally entangled (as shown in Figure 7a,b with ). On the other hand, decoherence alters and gradually lowers their values. Likewise, with greater values of , the entanglement survival time before the full entanglement death is reduced. Lastly, Equation (12), which is a recently proposed conservation relation, represents the tradeoff relation between and . There is an inherent tradeoff between entanglement (concurrence) and coherence in the system; in this case, while strong coupling to the cavity field can enhance entanglement (concurrence), this can lead to increased decoherence due to coupling with the environment (see Figure 7a,b). As decoherence increases, the system loses both its coherence and entanglement. Thus, the system may experience a reduction in concurrence as decoherence rates increase. Conversely, in a system with low coupling to the field (or low decoherence), the qubits can maintain higher coherence and entanglement. However, without sufficient coupling, the entanglement between the qubits may be weak, leading to lower concurrence.
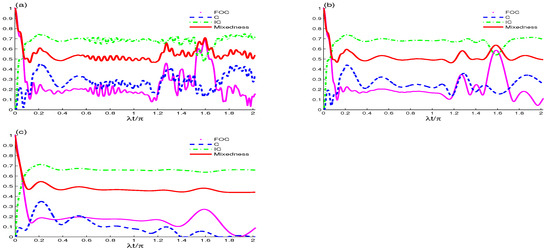
Figure 3.
Same as Figure 1 except for two interacting qubits . (a) , (b) , and (c) .
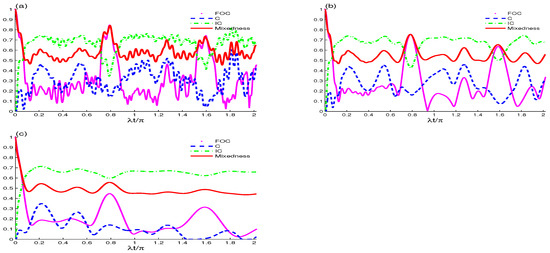
Figure 4.
Same as Figure 2, except for two non-interacting qubits .
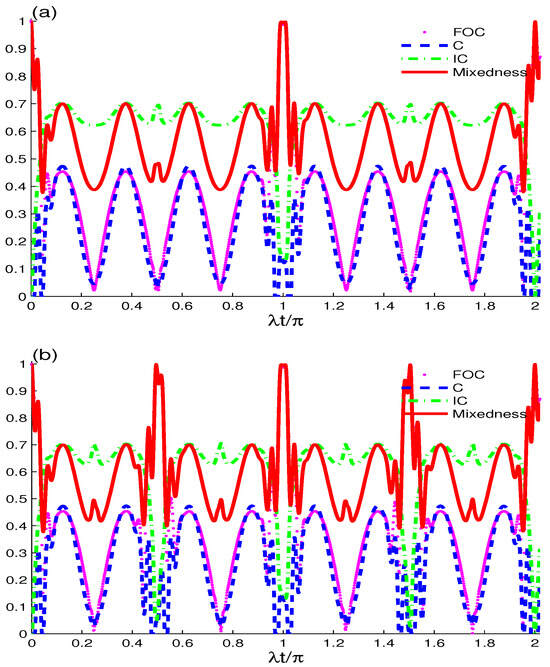
Figure 5.
Dynamics of FOC, C, IC, and total mixedness for two non-interacting qubits starting with pure state , photons, and absence of the decoherence effect inside (a) a coherent field cavity and (b) an evenly coherent field cavity.
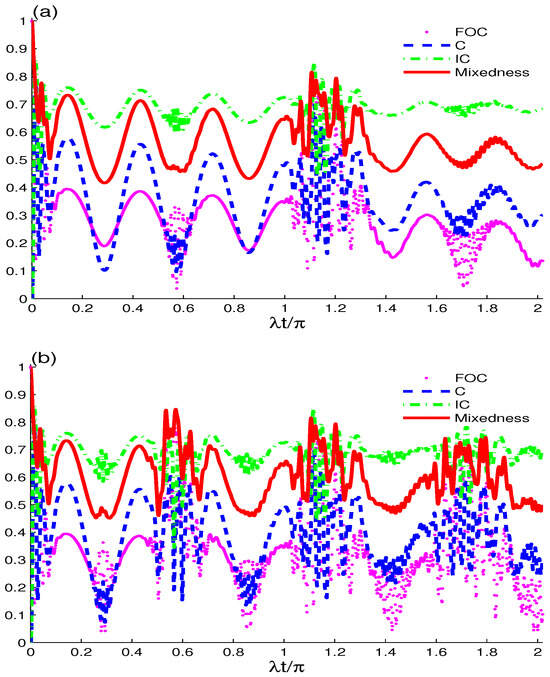
Figure 6.
Same as Figure 5, except for two interacting qubits .
The damped oscillatory behavior in the dynamics of concurrence and first-order coherence arises from the interplay between coherent quantum interactions and weak decoherence when the phase decoherence parameter is small. In a system of coupled two-level atoms interacting with a cavity field, coherence from atomic state superpositions leads to Rabi-like oscillations. Despite small indicating weak decoherence, which typically suggests monotonic damping, the strong coupling allows significant oscillations to persist, resulting in a damped oscillatory pattern instead of simple exponential decay. This behavior reflects the interplay of preserved coherence and the gradual influence of decoherence, resulting in a complex dynamic that illustrates the resilience of quantum correlations amid environmental interactions.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have investigated the situation of two dipole-coupled qubits interacting with a coherent cavity field in the presence of phase decoherence. The inherent relations between , C, , and total mixedness can help us to better understand how quantum resources are distributed and how entanglement and coherence affect each other. The universal tradeoff between these measures underlines a fundamental aspect of quantum systems, making the study of their relations essential for advancing both theoretical and practical applications in quantum technology. This provides strong motivation to study and analytically explore the master equation for this physical model. In particular, one of our strongest interests in this paper has been to study the dynamics of , C, , and total mixedness for two interacting qubits starting in a pure state inside a coherent field cavity and under decoherence effects. The tradeoff relation, which is universal for any arbitrary two-qubit states, indicates that mixedness and decrease as the level of increases (and vice versa) when the coherence effect is absent or weak. However, this does not occur with increasing decay or when dipole–dipole interaction occurs, as the amplitude of becomes higher than those of mixedness and with the development of time. By controlling the dipole–dipole coupling strength and the phase decoherence parameter , it is possible to generate entangled states, which are the foundation of many quantum algorithms and protocols. The increase in the number of interacting photons is responsible for increasing the oscillation frequency of , C, and , provided that the initially established state is the entangled state. There is an inherent tradeoff between entanglement (concurrence) and coherence in the system; in this case, strong coupling to the cavity field can enhance entanglement (concurrence), but this can also lead to increased decoherence due to coupling with the environment. By studying the measures of , C, , and total mixedness as well as the effects of dipole–dipole interaction, decoherence, and the number of photons, it is possible to partially but not completely control the tradeoff relations between intrinsic concurrence and first-order coherence of a two-qubit cavity system. Understanding these phenomena requires rigorous analysis of specific quantum states and their dynamics, challenging existing models and prompting the need for more robust frameworks in real-world applications of quantum mechanics. This control might involve actions that influence the system and that are reflected in the measures of , C, , and total mixedness. We checked the validity of the tradeoff relation between and and the inequality relation between IC and C, confirming that the tradeoff relation between and holds tightly in the given model, that is, . However, the upper bound of the inequality between and C, i.e., , generally does not hold. Therefore, the dynamics exhibit damped oscillations, revealing the intricate balance between coherence and decoherence in quantum systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H. and A.-B.A.M.; methodology, H.A.H., D.B. and A.A.; validation, M.H., H.A.H. and D.B.; formal analysis, S.M.E.-D.; investigation, M.H., A.-B.A.M. and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H. and A.-B.A.M.; writing—review and editing, D.B., A.A. and S.M.E.-D.; supervision, M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I.L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.-L.; Hu, X.Y.; Wang, J.C.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Fan, H. Quantum coherence and geometric quantum discord. Phys. Rep. 2018, 762–764, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.-D.; Song, X.-K.; Fan, X.-G.; Ye, L.; Wang, D. Complementary relations of entanglement, coherence, steering, and Bell nonlocality inequality violation in three-qubit states. Phys. Rev. A 2023, 107, 052403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.-D.; Wei, G.-B.; Song, X.-K.; Wang, D.; Ye, L. Unification of coherence and quantum correlations in tripartite systems. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 106, 042415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-G.; Sun, W.-Y.; Ding, Z.-Y.; Ming, F.; Yang, H.; Wang, D.; Ye, L. Universal complementarity between coherence and intrinsic concurrence for two-qubit states. New J. Phys. 2019, 21, 093053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.-L.; Wang, D.; Fan, X.-G.; Ming, F.; Ye, L. Mutual restriction between concurrence and intrinsic concurrence for arbitrary two-qubit states. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2020, 37, 110302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, F.; Levy, J.; Loss, D. Quantum computing with spin cluster qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 047901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, T.-C. Simulating largesize quantum spin chains on cloud-based superconducting quantum computers. Phys. Rev. Res. 2023, 5, 013183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boixo, S.; Rnnow, T.F.; Isakov, S.V.; Wang, Z.; Wecker, D.; Lidar, D.A.; Martinis, J.M.; Troyer, M. Evidence for quantum annealing with more than one hundred qubits. Nat. Phys. 2014, 10, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.; Sato, Y.; Berkley, A.J.; Reis, M.; Altomare, F.; Amin, M.; Boothby, K.; Bunyk, P.; Deng, C.; Enderud, C.; et al. Phase transitions in a programmable quantum spin glass simulator. Science 2018, 361, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuhn, H.; Barredo, D.; Ravets, S.; De Leseleuc, D.; Macri, T.; Lahaye, T.; Browaeys, A. Tunable two dimensional arrays of single Rydberg atoms for realizing quantum ising models. Nature 2016, 534, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Keever, C.M.; Coopmans, L.; Lubasch, M.; Benedetti, M. Realization of quantum signal processing on a noisy quantum computer. npj Quantum Inf. 2023, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.-B.A.; Rmili, H.; Omri, M.; Abdel-Aty, A.H. Two-qubit quantum nonlocality dynamics induced by interacting of two coupled superconducting flux qubits with a resonator under intrinsic decoherence. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 77, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, S.S.J.; Turner, J.S.E.F.; Kjaergaard, M.; Hartmann, J.I.A.M.H.; Gambetta, J.M. Controlled Environment for Superconducting Qubits and Implementation of Quantum Logic Gates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2022, 128, 150501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmak, A. Entanglement of the isingheisenberg diamond spin-cluster in evolution. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2023, 56, 165302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, G.; Yi, S.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, M. Relationship between quantum-memoryassisted entropic uncertainty and steered quantum coherence in a two-qubit x state. Quantum Inf. Process. 2023, 22, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, M.; Kang, G.; Li, X. Quantum-memory-assisted entropic uncertainty in twoqubit Heisenberg XYZ chain with Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions and effects of intrinsic decoherence. Quantum Inf. Process. 2018, 17, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurischev, M.A. On the quantum correlations in two-qubit XYZ spin chains with Dzyaloshinsky Moriya and Kaplan-Shekhtman-Entin-Wohlman-Aharony interactions. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D. Thermal entanglement and thermal discord in two-qubit Heisenberg XYZ chain with Dzyaloshinskii Moriya interactions. Quantum Inf. Process. 2019, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, F.M.; Alsahli, A.M.; Mohamed, A.-B.A.; Rahman, A.U. Control of quantum-memory induced by generated thermal XYZ-Heisenberg entanglement: y-component DM interaction. Ann. Phys. 2023, 535, 2300094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurischev, M.A.; Haddadi, S. Local quantum Fisher information and local quantum uncertainty for general X states. Phys. Lett. A 2023, 476, 128868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabdallah, F.; El Anouz, K.; Rahman, A.U.; Daoud, M.; El Allati, A.; Haddadi, S. Witnessing quantum correlations in a hybrid qubit-qutrit system under intrinsic decoherence. Fortschritte Phys. 2023, 71, 2300032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidan, N.; Rahman, A.U.; Haddadi, S.; Czerwinski, A.; Haseli, S. Local quantum uncertainty and quantum interferometric power in an anisotropic two-qubit system. Universe 2023, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.-B.A.; Khedr, A.N.; Haddadi, S.; Rahman, A.U.; Tammam, M.; Pourkarimi, M.R. Intrinsic decoherence effects on nonclassical correlations in a symmetric spin orbit model. Results Phys. 2022, 39, 105693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, M.; Mohamed, A.-B.A.; Haddadi, S.; Khedif, Y.; Pourkarimi, M.R.; Daoud, M. Bell nonlocality, entanglement, and entropic uncertainty in a Heisenberg model under intrinsic decoherence: DM and KSEA interplay effects. Appl. Phys. B 2022, 128, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacchino, F.; Chiesa, A.; Carretta, S.; Gerace, D. Quantum computers as universal quantum simulators: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2020, 3, 1900052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y. Error-mitigated deepcircuit quantum simulation of open systems: Steady state and relaxation rate problems. Phys. Rev. Res. 2022, 4, 043140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbeigi, F.; Karimi, M.; Karimipour, V. Simulating of X-states and the two-qubit XYZ Heisenberg system on IBM quantum computer. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 025101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J. Qubits on programmable geometries with a trapped-ion quantum processor. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.10179. [Google Scholar]
- Vandersypen, L.M.; Eriksson, M.A. Quantum computing with semiconductor spins. Phys. Today 2019, 72, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.W. Quantum Noise; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Milburn, G.J. Intrinsic decoherence in quantum mechanics. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 44, 5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Cessa, H.; Buzek, V.; Kim, M.S.; Knight, P.L. Intrinsic decoherence in the atom-field interaction. Phys. Rev. A 1993, 48, 3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.-B.; Zou, X.-B. Dynamic algebraic approach to the system of a three-level atom in the Λ configuration. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 60, 4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootters, W.K. Entanglement of Formation of an Arbitrary State of Two Qubits. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svozilík, J.; Vallés, A.; Peřina, J.; Torres, J.P. Revealing Hidden Coherence in Partially Coherent Light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 220501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).