Abstract
Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) has been widely applied in many fields due to its advantages of fast convergence speed, simple parameter settings, and easy implementation. However, with the deepening of algorithm research, GWO has also exposed some problems, such as being prone to becoming stuck in local optima and insufficient convergence accuracy. To address the above issues, a double-swarm Grey Wolf Optimizer with covariance and dimension learning (CDL-DGWO) is proposed. In the CDL-DGWO, firstly, chaotic grouping is used to divide the grey wolf population into two sub-swarms, forming a symmetric cooperative search framework, thereby improving the diversity of the population. Meanwhile, covariance and dimension learning strategies are utilized to improve the hunting behavior of grey wolves; the global search capability and the stability of the algorithm are thereby enhanced. Moreover, CDL-DGWO is validated on 23 benchmark problems and the CEC2017 test set. The results indicate that the CDL-DGWO algorithm outperforms swarm intelligence optimization algorithms such as Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Moth Flame Optimization (MFO), and other variants of GWO. Finally, the CDL-DGWO algorithm addresses three engineering design problems that are representative of real-world scenarios. The statistical analysis of the experimental outcomes demonstrates the feasibility and practicality of the proposed methodology.
1. Introduction
Optimization problems are prevalent across diverse real-world applications, such as image segmentation [1], economic load dispatch [2], and feature selection [3]. Traditional optimization methods often fail to solve complex, nonlinear, non-convex, discontinuous, or discrete problems effectively. In contrast, metaheuristic algorithms have gained attention due to their avoidance of unnecessary assumptions and their powerful global search capabilities. Over the past few decades, numerous metaheuristic algorithms have been developed, including Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [4], Grey Wolf Optimizer [5], Moth Flame Optimization (MFO) [6], Slime Mold Algorithm (SMA) [7], Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) [8], Mayfly Algorithm (MA) [9], and Harris Hawks Optimization (HHO) [10].
The Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) is a population-based algorithm that emulates the leadership hierarchy and hunting behavior of grey wolves [5]. In GWO, the population is categorized into alpha, beta, delta, and omega wolves, with the first three leading the optimization process by steering the search direction. GWO is recognized as an effective metaheuristic, with applications across various domains such as fuel cell technology [11], localization technology [12], and robotics [13].
Despite its successful applications across various fields, GWO encounters challenges including reduced population diversity, imbalanced exploration and exploitation, and premature convergence. These limitations are attributed to its dependence on , and wolves for location updates. To overcome these limitations, researchers have conducted extensive studies. In [14,15], GWO is combined with SCA and GSA to create two hybrid algorithms, integrating the strengths of both to enhance search performance. In [16], the GWO is hybridized with the Jaya algorithm to enhance task scheduling in fog computing, improving load balancing, response time, and resource efficiency. In [17], an enhanced GWO incorporating Lévy mutation (LGWO) was introduced, utilizing Lévy mutation and greedy selection strategies to refine the hunting phases. In [18], a modified version of GWO, termed RWGWO, was proposed to enhance its optimization capabilities. In [19], the “survival of the fittest” (SOF) principle and differential evolution (DE) were employed to improve GWO. This approach increases the likelihood of GWO escaping local optima. Ref. [20] introduced an improved GWO variant leveraging information entropy for dynamic position updates and a nonlinear convergence strategy, aiming to balance exploration and exploitation. Ref. [21] introduced a fuzzy strategy Grey Wolf Optimization algorithm, utilizing fuzzy mutation, crossover operators, and a non-inferior selection strategy to refine wolf positions and enhance search accuracy. Ref. [22] introduced DI-GWOCD, a discrete version of the Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer, for effectively detecting communities in complex networks. It enhances community detection through local search strategies and binary distance calculations, demonstrating superior performance over existing algorithms in community quality assessment. However, increasing population diversity in solving practical problems requires further attention. In [23], an Improved Adaptive Grey Wolf Optimization (IAGWO) algorithm was introduced by integrating concepts from Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), using an Inverse Multiquadratic Function (IMF) for inertia weight adjustment, and employing a Sigmoid-based adaptive updating mechanism. Extensive experiments show that IAGWO outperforms the compared algorithms on benchmark test sets and effectively addresses 19 real-world engineering challenges, demonstrating its robustness and broad application potential in optimization problems.
Ref. [24] introduced an Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm with Adaptive Covariance Matrix(ACoM-ABC), which incorporates an adaptive covariance matrix to enhance the performance of the original Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) in addressing problems with high variable correlations. The effectiveness of ACoM-ABC was validated through extensive testing on multiple benchmark platforms. Ref. [25] proposed Cumulative Covariance Matrix Artificial Bee Colony (CCoM-ABC) algorithm accumulates covariance matrix information from each generation to construct an eigen-coordinate system, thereby guiding the search direction. Additionally, it dynamically selects between the eigen-coordinate and natural coordinate systems during the search process to balance exploration and exploitation capabilities, thereby improving performance on non-separable problems. The Covariance Matrix Adapted Grey Wolf Optimizer (CMA-GWO) is an enhanced version of the Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) [26]. It employs a Covariance Matrix Adaptation (CMA) strategy in the initial phase to optimize the initial positions of the prey, thereby augmenting the algorithm’s exploration capability and convergence rate. This research not only provides a novel approach for modeling and optimizing the direct metal deposition additive manufacturing process but also enhances the predictive accuracy and generalization ability of the model through the improved GWO. The I-GWO algorithm effectively balances global and local search capabilities by integrating the Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) with a Dimension Learning-based Hunting (DLH) search strategy [27]. This integration prevents premature convergence to local optima and maintains population diversity. I-GWO demonstrates its potential in solving real-world engineering optimization problems by effectively handling constraints and identifying optimal solutions.
In light of the “No Free Lunch” theorem [28], which posits that no single optimization algorithm can be universally optimal for all problems, this study addresses several issues of the GWO, including insufficient population diversity, premature convergence, and an imbalance between exploitation and exploration. To overcome these challenges, a double-swarm Grey Wolf Optimizer with covariance and dimension learning (CDL-DGWO) is introduced. In CDL-DGWO, chaotic grouping is used to divide the grey wolf population into two sub-swarms, thereby improving the population diversity. Meanwhile, covariance and dimension learning are utilized to improve the hunting behavior of grey wolves, thereby enhancing both global search capability and algorithm stability. In summary, the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- (1)
- Chaotic grouping is utilized to generate two sub-swarms of grey wolves. This strategy can improve population diversity of CDL-DGWO algorithm.
- (2)
- Covariance and dimension learning strategies are utilized to improve the hunting behavior of grey wolves, which can enhance the global search capability and algorithm stability.
- (3)
- The performance of the CDL-DGWO algorithm is validated on 23 benchmark problems and the CEC2017 test suite. The results indicate that the CDL-DGWO outperforms the compared swarm intelligence algorithms such as PSO, MFO, and GWO variants in terms of solving optimal solutions and convergence performance. Additionally, the CDL-DGWO is applied to three engineering design problems, which fully demonstrate the practicality of the proposed methodology.
2. Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO)
The Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) is a metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the leadership and social behavior of grey wolves, designed to simulate predation process [5,29]. This article provides a brief introduction to GWO.
In GWO, the population of wolves is divided into four categories based on their hunting capabilities: , and , and . The , and wolves are considered the leaders and have the best fitness, guiding the rest of the pack in searching for prey. In the context of optimization, the prey represents the optimal solution.
The hunting process of grey wolves is simulated through three main steps: encircling, hunting, and attacking the prey. The mathematical model for encircling prey is given by the following formulas:
Here, t denotes the current iteration count. signifies any grey wolf within the population, while represents the position vector of the prey. and are diagonal coefficient matrices that dictate the search dynamics, and their calculation methods are described in [30]. denotes the distance between the grey wolf and its prey. The notation “” signifies the transformation of each vector element into its absolute value.
The hunting process is led by the , and wolves, with the position update formulas for the other wolves being:
Among them, represents the position of the v-th wolf in the previous iteration. signifies the position of the current solution. Subsequently, other candidate grey wolves randomly adjust their positions near the prey, guided by the optimal information from , and .
Finally, when the prey is cornered, the wolves attack and capture it. This phase in GWO is simulated by updating the position of the wolves when the coefficients and are less than 1, forcing the wolves to converge towards the prey.
The main steps and pseudo-code of GWO are presented as Algorithm 1:
| Algorithm 1: Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO). |
1: Initialize , dimension D, population size N, , ; % and represent the maximum number of function evaluations and the current number of function evaluations respectively. 2: Initialize population of wolves; 3: while 4: Calculate the fitness value of wolves and update ; 5: , and are the first three wolves with the best fitness; 6: for 7: for 8: Updata parameters a, and ; 10: end 11: end 12: end while |
3. Double-Swarm Grey Wolf Optimizer with Covariance and Dimension Learning (CDL-DGWO)
Inspired by previous research on GWO, a double-swarm Grey Wolf Optimizer with covariance and dimension learning (CDL-DGWO) is proposed. In CDL-DGWO, chaotic grouping is used to divide the grey wolf population into two sub-swarms, thereby the diversity of the population is improved. Meanwhile, covariance and dimension learning strategies are utilized to improve the hunting behavior of grey wolves, thereby enhancing the global search capability and algorithm stability. The CDL-DGWO and its pseudocode are described in detail as follows.
3.1. Chaotic Grouping and Dynamic Regrouping
In this section, the entire population is grouped using a chaos grouping mechanism [31]. The mechanism divides the population by generating a set of highly correlated sequences through a chaos function, thereby improving the grouping quality and search performance. The iterative chaos map is used as the chaos function, with the mapping formula as follows:
where b is a constant with range .
The process of chaotic grouping is given in Algorithm 2, where denotes a chaotic sequence.
| Algorithm 2: Chaotic grouping mechanism. |
1: The first chaotic value () is initialized randomly in (0,1); 2: for
3: ; 4: ; 5: end for 6: 7: The grey wolf population is divided into two sub-swarms according to I; |
To strengthen the information exchange between the two sub-swarms in the search process, the two sub-swarms are reorganized every generations. If the value of is too large, timely information exchange between sub-swarms is hindered. Conversely, if the value of is too small, the sub-swarms cannot conduct an adequate search. In the early stage of the search, the sub-swarms should be given sufficient time to search independently. In the later stage of the search, maximizing population diversity enhances the ability of the algorithm to locate the global optimum. This paper employs the following dynamic regrouping mechanism:
where and represent the maximum and minimum interval iterations respectively, and indicates rounding up to the nearest integer.
The choice of dividing the population into two sub-swarms establishes a symmetrical cooperative search architecture, which is based on a balance between algorithmic complexity and performance enhancement. A dual-swarm structure provides a clear and computationally efficient framework for implementing complementary search strategies: one swarm focused on exploration (via covariance learning) and the other on exploitation (via dimension learning). This dichotomy has been effectively demonstrated in other multi-swarm optimizers [32], proving sufficient to introduce beneficial population diversity and mitigate premature convergence.
3.2. Learning Strategies
In GWO, the positions of individual grey wolves are updated through hunting activities. However, the inter-variable interactions are typically not considered, which makes GWO perform poorly in solving complex optimization problems. The update of individual grey wolf positions using a covariance matrix aims to transform the original space into a feature space, thereby enhancing information sharing among variables and improving the algorithm’s overall performance. The detailed explanation is as follows:
The covariance matrices () for the populations of wolves and , and are computed, with the calculation process for detailed below:
where , , , , .
where . The formula for , are as follows:
To rotate the original space into the eigenspace, eigen decomposition is applied to as follows:
where is orthogonal matrices, which is composed of eigenvectors of . is diagonal matrices that composed of eigenvalues of .
Then, the wolf individuals are transformed from the original space to the eigenspace. The conversion formula is as follows:
Since , , , and can be obtained.
In the eigenspace, wolves update their positions with the following form:
Among them, . represents the position of the wolf in the previous iteration in eigenspace. is the position of the current solution, and , and denote the position of the leaders , and .
After the wolves’ positions have been updated, the wolves are transformed from the eigenspace to the original space by the following formula:
While covariance learning enhances global search capability, dimension learning provides local refinement. The combination ensures a balanced approach to optimization.
In GWO, , and guide the other wolves to update their position in each iteration, resulting in strong convergence. Dimension learning involves updating positions based on interactions with different neighbors and randomly selected wolves. The detailed process is as follows [27]:
First, the radius is obtained by calculating the Euclidean distance between the current position and the candidate position :
Then, the neighborhood of is defined using the radius . is the Euclidean distance between and .
Finally, calculate the candidate solution obtained through dimension learning:
where is a random wolf, and is d-th dimension of a random neighbor. The better solution between and is selected as the final candidate for the next iteration.
3.3. Framework of the CDL-DGWO
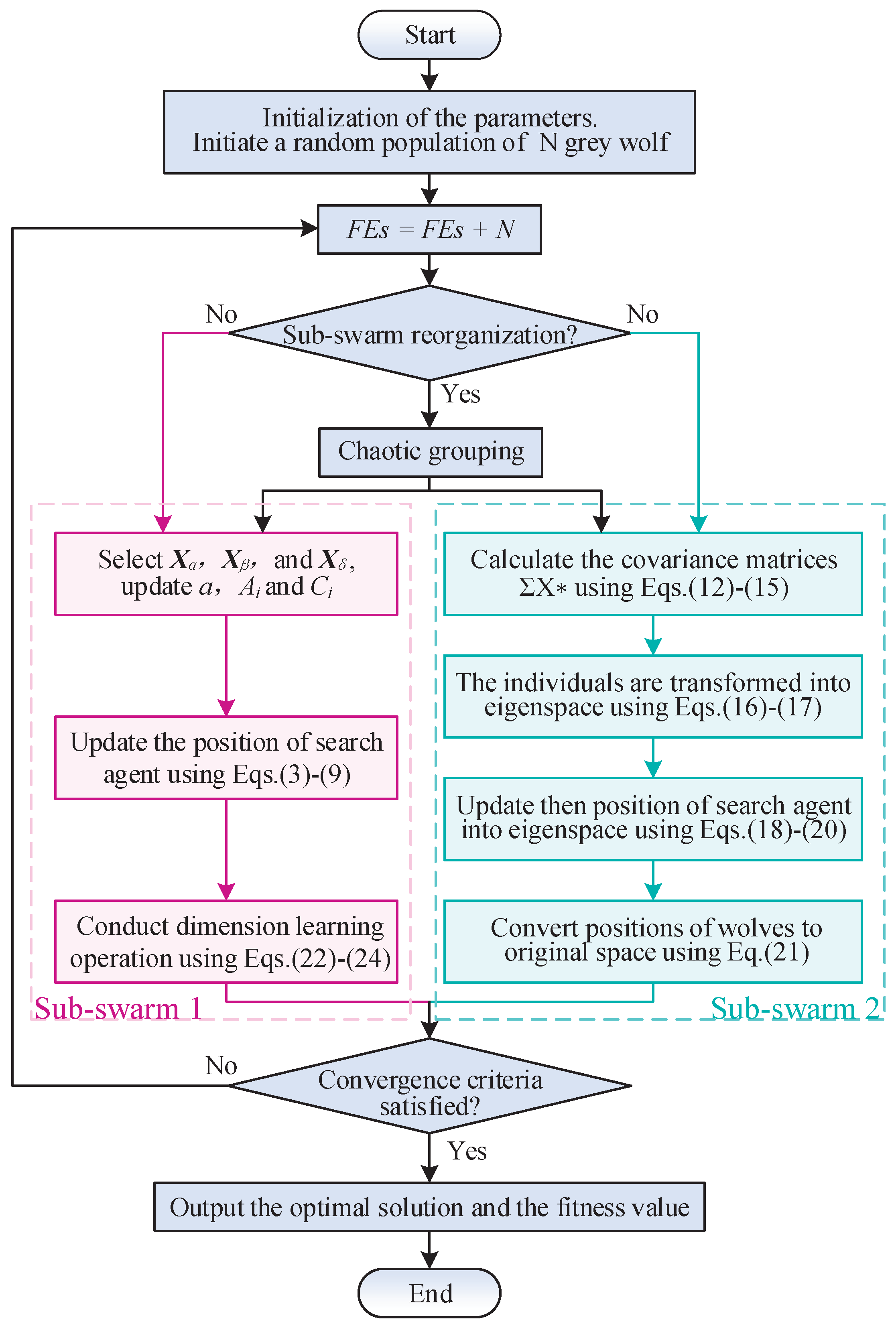
This subsection presents the detailed pseudo-code and a comprehensive flowchart that elucidate the workings of the CDL-DGWO. These are delineated in Algorithm 3 and Figure 1, respectively.
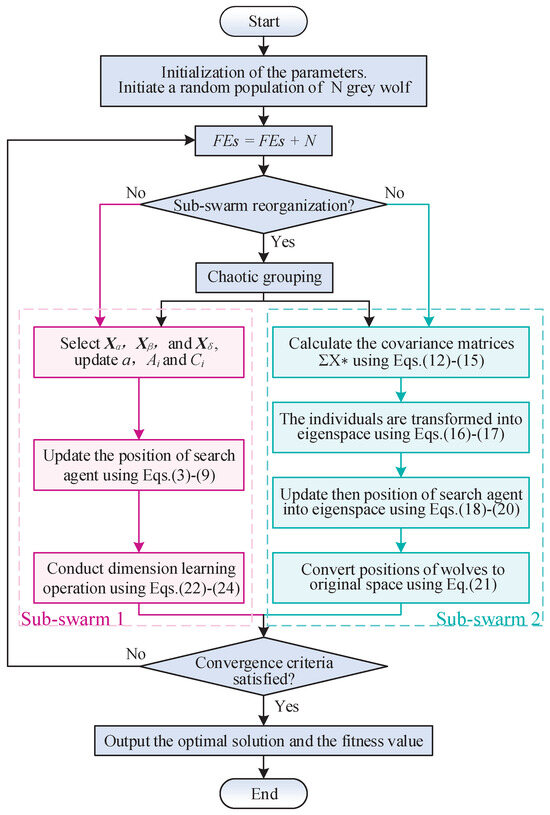
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the CDL-DGWO algorithm.
To ensure clarity and facilitate understanding, the steps of the CDL-DGWO are outlined as follows:
- Step 1:
- Initialize the system parameters, which include population size N, individual dimension d, random parameters a, and , as well as the maximum number of function evaluations () and the current number of function evaluations ().
- Step 2:
- Generate the initial population of wolves randomly within the defined upper and lower bounds of .
- Step 3:
- Divide the population into two sub-swarms using Algorithm 2.
- Step 4:
- Check the stopping criteria: Determine whether or the best fitness value meets the accuracy requirements. If conditions are met, output the position of as the best approximated optimum, otherwise, proceed to step 5.
- Step 5:
- Calculate and sort the fitness of each individual, updating . Select the top three individuals as , and .
- Step 6:
- Step 7:
- For the Sub-swarm 2, introduce a covariance matrix to enhance information sharing among individual variables, thereby improving the overall performance of the algorithm.
- Step 8:
- Perform dynamic regrouping using Equation (11) and Algorithm 2, then return to Step 4.
- Step 9:
- Return the best solution.
| Algorithm 3: Pseudocode of CDL-DGWO. |
1: Initialize , d, N, , ; 2: Initialize population of wolves; 3: The population is divided into 2 sub-swarms by Algorithm 2; 4: while 5: Calculate the fitness value of wolves, ; 6: , and are the first three wolves with the best fitness; %% The Sub-swarm 1 7: for 8: for 9: Updata parameters a, and ; 11: end 12: end %% The Sub-swarm 2 15: is obtained, which is composed of eigenvectors of , based on eigen decomposition relation Equation (16); 16: The individuals of wolves are transformed into eigenspace based on eigenvector using Equation (17); 17: for 18: for 19: Updata parameters a, and ; 21: end 22: end 23: Convert positions of wolves to original space using Equation (21); 24: If mod(t,)==0 25: Regrouping using Algorithm 2; 26: end 27: end while |
3.4. Computational Complexity of the CDL-DGWO
The computational complexity of CDL-DGWO is determined by the original GWO and the hierarchical guidance strategy. The original GWO primarily consists of the following stages: initialization with a complexity of , fitness evaluation with a complexity of , the first three wolfs update with a complexity of , and position update with a complexity of . Based on these stages, the overall complexity of GWO can be expressed as , where N represents the population size, D denotes the dimensionality of the function, and T is the maximum number of iterations.
The computational complexity of CDL-DGWO is primarily determined by the following components per iteration:
- (1)
- Fitness Evaluation: .
- (2)
- Standard GWO Operations (population update, leader selection): .
- (3)
- (4)
- (5)
- Chaotic Grouping: The generation and sorting of chaotic sequences incur , but when amortized over all iterations, this becomes negligible.
Therefore, the complexity per iteration is: + + . Over T iterations, Big O notation ignores constant coefficients and lower-order terms. Therefore, the computational complexity of the CDL-DGWO can be simplified to: .
4. Test Results and Analysis
4.1. Test Suites, Test Methods and Performance Index
To assess the performance of the CDL-DGWO presented in this article, 23 basic functions [33] and the CEC2017 test set [34] are utilized for evaluation. The former includes unimodal, multimodal, and fixed-dimensional multimodal problems. The CEC2017 test suite is characterized by high nonlinearity, multimodality, high dimensionality, and non-convexity. These characteristics pose greater challenges for algorithms in solving problems, as they need to overcome issues such as local optima and curse of dimensionality in the solution space.
Based on the above two test sets, a comprehensive performance evaluation of CDL-DGWO is conducted. Additionally, CDL-DGWO is compared with and validated against other improved GWO and heuristic algorithms. The comparison algorithms include: GWO [5], MIGWO [30], IGWO [19], LGWO [17], HGWOSCA [14], RWGWO [18], EGWO [35], PSOGWO [36], PSO [37], MFO [6], SSA [38], WOA [8], HSCA [39], HCLPSO [40], PSOGSA [41], mSCA [42]. The parameters of comparative algorithms in the experiment are given in Table 1. The parameters listed in Table 1 are defined as follows, adhering to their original sources: , , r, p are uniformly distributed random numbers in [0,1]; a is a control parameter that decreases linearly from 2 to 0; , are acceleration coefficients; w is the inertia weight; b, t are constants specific to MFO; , are control parameters as defined in [41]. All other unspecified parameters follow the standard definitions from the corresponding references.

Table 1.
Parameter settings.
During the experiment, the maximum number of function evaluations () for the two test suites are set at 30,000 and 300,000, respectively. The dimension D of both test suites is set to 30. To ensure a fair comparison of the algorithms’ core search capabilities while maintaining statistical reliability, all algorithms were evaluated using the following procedure: For each test function, an identical set of 30 initial populations was generated. Each algorithm was then independently run 30 times, with each run starting from a corresponding population in this shared set. Different random seeds were employed across these runs to ensure the robustness of results, while the consistent initialization eliminates any performance bias that could arise from specific starting positions. The maximum number of function evaluations () for the 23 benchmark functions is set to 30,000. This value is chosen in accordance with common practices in the metaheuristic optimization literature [33], providing a sufficient budget for algorithms to demonstrate convergence behaviors while maintaining computational tractability for extensive comparative studies involving multiple algorithms and independent runs.
In this paper, Mean, Std, the multiple-problem Wilcoxon test and Friedman test are used to evaluate the performance of CDL-DGWO algorithm. Mean and Std denote the average and standard deviation of 30 independent runs, respectively. the multiple-problem Wilcoxon test is applied to each test set.
4.2. Effects of Proposed Strategies
The proposed CDL-DGWO algorithm builds upon the original GWO and enhances its performance through the introduction of hybrid chaotic grouping and dynamic regrouping. These mechanisms effectively divide the population into two distinct sub-swarms. The first sub-swarm employs a covariance strategy, while the second sub-swarm utilizes a dimension learning strategy. Both strategies are designed to improve the overall performance of the algorithm.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed strategies, a comparative experiment is designed in this section. Specifically, the C-GWO algorithm represents an enhanced variant of the original GWO. In this variant, one sub-swarm incorporates the covariance learning mechanism, whereas the other sub-swarm retains the original GWO update mechanism. Similarly, the D-GWO algorithm is another variant of GWO. Here, one sub-swarm employs the dimension learning strategy, while the other sub-swarm maintains the original GWO update mechanism.
Table 2 illustrates the configuration of these strategies. Within this matrix, the binary indicator “1” signifies that a particular strategy is applied within the algorithm, while “0” indicates that the strategy is not utilized.

Table 2.
Various GWOs with three strategies.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the introduced policies, the performance of four algorithms (GWO, C-GWO, D-GWO, and CDL-DGW) was assessed across 23 benchmark functions. In the simulation tests, the population size was set to 30 for all algorithms, and the stopping criterion was defined as a maximum of 30,000 function evaluations. Each algorithm was independently executed 30 times on each function. The results, including the average values (Mean) and standard deviations (Std) for each algorithm, are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
The test results of 4 algorithms.
The results of the multiple comparisons using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test are presented in Table 4. Additionally, Table 5 displays the Friedman test results for each algorithm across 23 benchmark functions.

Table 4.
Results of multiple-problem Wilcoxon test.

Table 5.
Friedman test results of the 4 algorithms.
Compared to the original GWO, the C-GWO algorithm achieved the smallest values on 14 out of the 23 benchmark functions, including F1 and F3. This demonstrates the effectiveness of the covariance strategy employed by C-GWO. Similarly, D-GWO outperformed GWO on 14 functions, such as F5 and F6, by achieving the smallest values. This highlights the efficacy of the dimension learning strategy utilized by D-GWO. According to the results of the Friedman test, CDL-DGWO, C-GWO, and D-GWO all ranked higher than the original GWO, with CDL-DGWO achieving the highest overall ranking. This indicates that the integration of both covariance and dimension learning strategies in CDL-DGWO yields the best performance.
4.3. Comparisons on Classical Benchmark Problems
This section presents the comparison results between CDL-DGWO and 15 other algorithms. Specifically, Table 6 shows the average and standard deviation of the 16 algorithms after 30 independent runs. Table 7 presents the results of the multiple-problem Wilcoxon test. Table 8 shows the Friedman test results for each algorithm across the benchmark problems.

Table 6.
The test results of 16 algorithms.

Table 7.
Results of multiple-problem Wilcoxon test.

Table 8.
Friedman test results of the 16 algorithms.
The statistical outcomes for “R+” represent a positive rank, indicating the superiority of CDL-DGWO compared to its counterparts. Conversely, “R−” denotes a negative rank, suggesting that CDL-DGWO is worse in performance relative to other algorithms. The “+/−/≈” represent that the CDL-DGWO is significantly better than, worse than, and similar to its compared algorithm on the associated function, respectively. Friedman test is used to provide a ranking of all algorithms on a group of test problems, thereby providing a more transparent assessment of the algorithm’s efficacy. “Ave” represents the average ranking, and “Rank” denotes the final ranking.
At the 0.05 level, when p < 0.05, it indicates that CDL-DGWO is significantly better than the compared algorithm, while p > 0.05 indicates that there is no significant difference in performance between the two compared algorithms.
Regarding the 23 benchmark problems, Table 6 indicates that CDL-DGWO outperforms other algorithms on F1-F4, F7, F9, F10, F11, and F12. CDL-DGWO also exhibits strong competitiveness in the remaining test problems. IGWO demonstrates superior results to other algorithms on problems F5 and F14–F19. SSA outperforms other algorithms on problem F6; WOA does so on F8; HCLPSO does so on F13, F21, and F23. Table 7 reveals no significant difference between CDL-DGWO, IGWO, and HCLPSO for the 23 test problems, but a significant difference when compared to the other 13 algorithms. In addition, Table 8 presents the ranking of 16 algorithms, with an average ranking of 3.2 and a final ranking of 1 for CDL-DGWO.
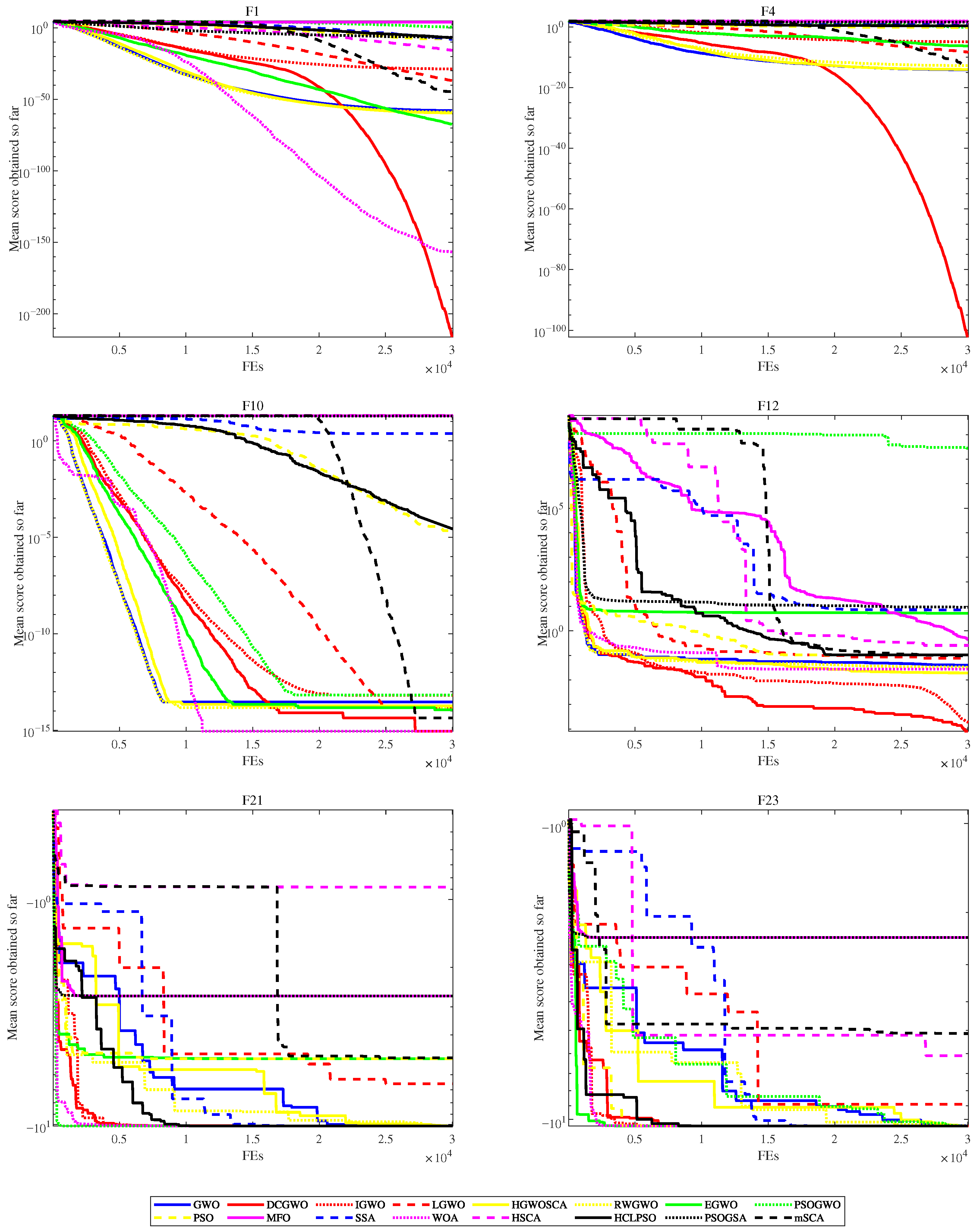
For a more intuitive demonstration of the CDL-DGWO’s performance, convergence curves have been plotted, comparing it with other swarm intelligence algorithms and GWO variants on selected functions. Figure 2 shows the convergence curves of CDL-DGWO for problems F1, F4, F10, F12, F21, and F23. These include problems with single peaks, multiple peaks, and fixed-dimensional multimodal peaks.
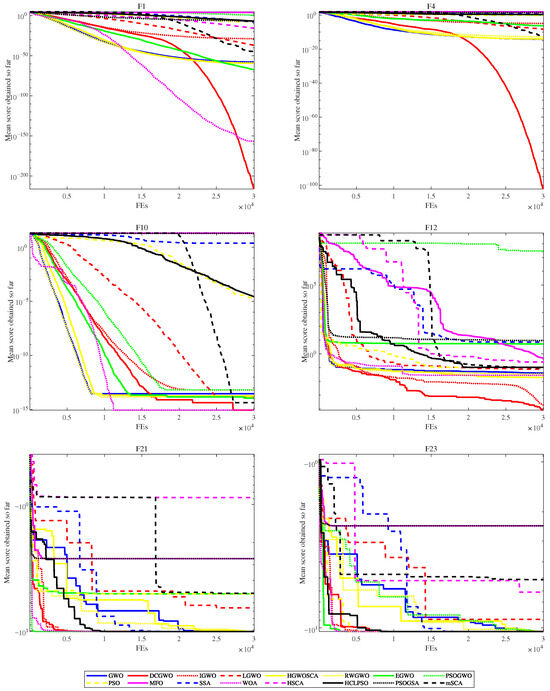
Figure 2.
Convergence curves on 6 functions.
On unimodal functions (F1, F4), CDL-DGWO does not exhibit a superior convergence rate initially but outperforms other algorithms in the later stages, achieving higher precision. For multimodal functions (F10, F12), it demonstrates rapid early convergence, though the pace of improvement slows considerably thereafter. A similar two-phase convergence pattern—characterized by a fast start followed by gradual refinement—is also observed on functions F21 and F23.
To sum up, CDL-DGWO can find competitive solutions to benchmark testing problems. Double swarm technology and dimensional learning can maintain population diversity and enhance the search space exploration efficiency. Covariance strategies can improve information exchange between variables, thereby enhancing the performance of GWO.
4.4. Comparisons on CEC 2017
To further assess the performance of CDL-DGWO, this study analyzes its performance based on the CEC 2017 benchmark and compares it with various algorithms, including GWO, IGWO, LGWO, HGWOSCA, RWGWO, EGWO, PSOGWO, MIGWO, PSO, MFO, SSA, WOA, HSCA, PSOGSA, and mSCA. Table 9 provides the average and standard deviation of 16 algorithms running independently for 30 times. Table 10 presents the results of the multiple-problem Wilcoxon test. Table 11 shows the Friedman test results for each algorithm on CEC 2017. This test assesses the performance of each algorithm across multiple problems, providing a ranking that highlights the overall effectiveness of the CDL-DGWO relative to the other contenders.

Table 9.
Comparisons of CDL-DGWO and other algorithms on CEC 2017.

Table 10.
Results of multiple-problem Wilcoxon test.

Table 11.
Test results of the 16 algorithms.
For CEC2017, it can be seen from Table 9 that CDL-DGWO performs better than other compared algorithms on problems f7, f10, f24, and f26. CDL-DGWO also has strong competitiveness in other test cases. According to Table 10, there is no significant difference between CDL-DGWO, IGWO, SSA, and PSO on the 23 test instances, but a notable difference is observed when compared to the other algorithms. “+” indicates the superiority of CDL-DGWO over the 11 comparative algorithms. In addition, Table 11 presents the rankings for the 16 algorithms, with CDL-DGWO achieving an average ranking of 3.03 and a final ranking of 2. In summary, CDL-DGWO is effective in solving complex optimization problems.
The achievement of near-optimal solutions on several fixed-dimension multimodal functions (e.g., F14–F16) primarily demonstrates CDL-DGWO’s efficacy in locating the global optimum on these specific static benchmarks. To assess the risk of overfitting and generalization capability, the algorithm was further tested on the more complex and modern CEC2017 test suite, which comprises functions characterized by multimodality, asymmetry, noise, and rotation properties, along with intricate variable interactions and noisy fitness landscapes. The competitive performance of CDL-DGWO on CEC2017 (as shown in Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11) suggests that its strengths—maintained population diversity and adaptive search strategies—generalize effectively beyond the simpler classical benchmarks. Furthermore, its success on the diverse set of engineering design problems in Section 5, which involve non-linear constraints and real-world variable dependencies, provides additional evidence of its robustness and general applicability.
4.5. Analysis of Population Diversity in CDL-DGWO
Population diversity reflects the distribution of solutions within a population and can be used to assess the exploration and exploitation capabilities of an algorithm during the iterative process. In this subsection, based on the method described in [43], the population diversity index of CDL-DGWO is calculated and compared with that of the GWO. The calculation method is as follows:
where represents the average value of solutions in the d-th dimension.
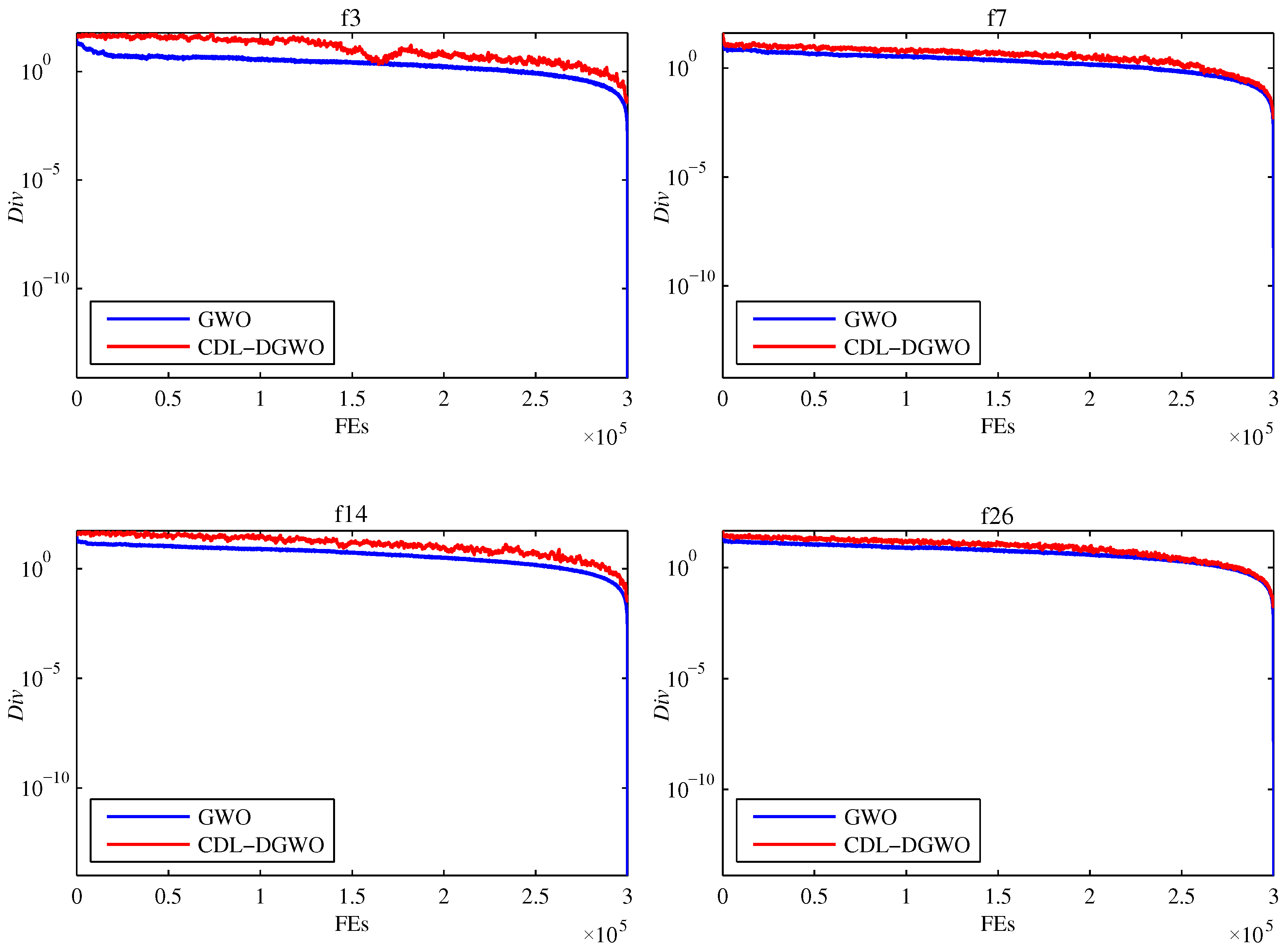
Figure 3 illustrates the dynamic changes in population diversity with respect to the number of function evaluations for the CDL-DGWO and GWO on four typical functions (unimodal function f3, simple multimodal function f7, hybrid function f14, and composite function f26) from the 30-dimensional CEC2017 benchmark test suite. These selected functions represent different types of optimization problems, including unimodal, multimodal, hybrid, and composite functions, and thus can reflect the performance of the algorithms in various scenarios. As observed from the figure, the population diversity of the GWO algorithm remains relatively stable and consistent throughout the search process for all four test functions. This indicates that GWO maintains a relatively stable level of population diversity during the search process. However, this relatively uniform diversity pattern limits the algorithm’s ability to escape local optima in complex optimization problems, revealing its limitations in exploring new solution spaces. Consequently, the global search capability of GWO is somewhat compromised. In contrast, the population diversity of the proposed CDL-DGWO algorithm fluctuates significantly throughout the search process and consistently maintains a higher level of diversity. This dynamic diversity pattern confers several notable advantages. This ability to balance exploration and exploitation significantly enhances the algorithm’s capacity to escape local optima, resulting in stronger adaptability and robustness when tackling complex optimization problems.
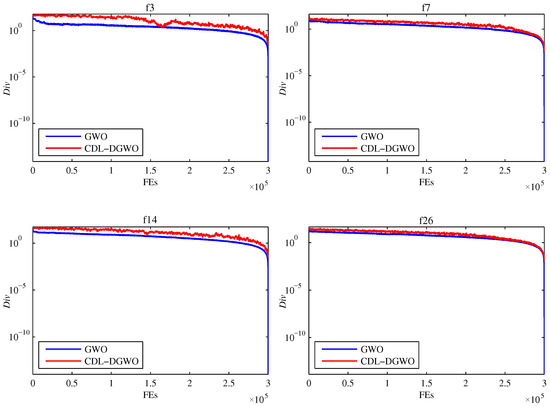
Figure 3.
The population diversity of the GWO and CDL-DGWO.
5. Testing of Engineering Design Problems
This section employs three practical engineering optimization problems to evaluate CDL-DGWO. In the experiment, the maximum number of function evaluations () is set to 15,000, and the population size is set to 30. Each experiment is conducted independently 30 times.
5.1. Constrained Problem
For the constrained problem, the objective function and constraint of this problem are as follows [44]:
For this minimization problem, Table 12 provides comparative results for the constrained problem. It is evident that CDL-DGWO yields the optimal solution. The results in Table 12 demonstrate that CDL-DGWO is competitive for the constrained problem.

Table 12.
Comparison of results on welded beam design problem.
5.2. Tension/Compression Spring Design Problem
For the tension/compression spring design problem, the goal is to achieve the lowest-cost spring by selecting a set of values, as illustrated in Figure 4. This optimization must consider constraints such as shear stress, resonant frequency, and minimum deflection requirements.

Figure 4.
Tension/compression spring design problem.
The objective function and constraint for this problem are as follows [5,45]:
where N represents the number of active coils, D is mean coil diameter, and d is the wire diameter. , , .
Table 13 demonstrates the comparison results of comparison among CDL-DGWO and competitors, CDL-DGWO achieves the best performance. Table 13 provides the statistical results for multiple algorithms in terms of average and standard deviation. It is evident that CDL-DGWO achieves the minimum weight design compared to other optimization algorithms.

Table 13.
Comparison of results on tension/compression spring design.
5.3. Welded Beam Design Problem
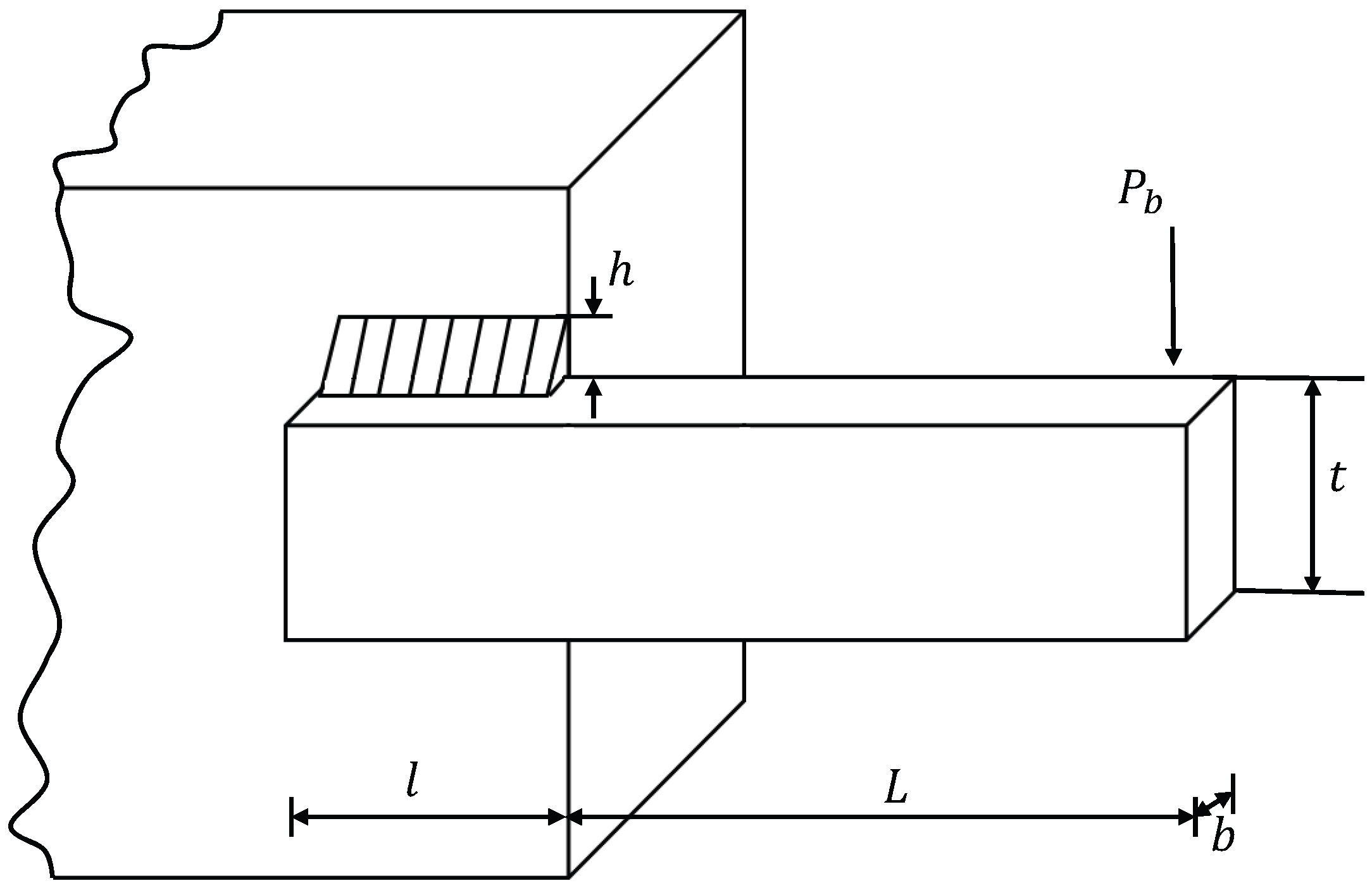
Welded beam design is a standard engineering benchmark problem, as introduced in the literature [5,45]. As shown in Figure 5, the objective is to design a welded beam at the lowest possible manufacturing cost by finding the global optimal solution.
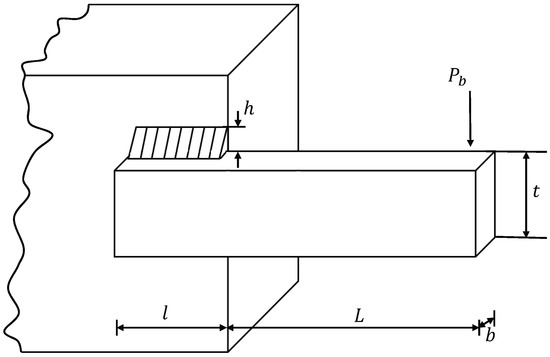
Figure 5.
Welded beam design problem.
The design involves four optimization variables: the weld thickness (h), length of the clamped bar (l), the bar height (t), and thickness of the bar (b). The constraints for the welded beam design include the shear stress () and bending stress () in the beam, buckling load () on the bar, and end deflection () of the beam. Let , the specific mathematical model is described as follows:
Table 14 provides comparative results for the welded beam design problem. It is evident that CDL-DGWO achieved smaller design solutions in terms of both the average and optimal values compared to the other 14 algorithms, and also obtained the smallest standard deviation. The results in Table 14 demonstrate that CDL-DGWO is competitive in solving the welded beam design problem.

Table 14.
Comparison of results on welded beam design problem.
Based on the strong performance of CDL-DGWO demonstrated across 23 benchmark functions, the CEC2017 test suite, and three engineering design problems, the algorithm shows particular promise in complex, real-world optimization scenarios characterized by high dimensionality, non-linearity, and multi-modality. Its enhanced population diversity, achieved through chaotic double-swarm grouping and dynamic regrouping, makes it exceptionally suitable for problems where traditional GWOs are prone to premature convergence. The integration of covariance matrix learning allows CDL-DGWO to effectively handle problems with correlated variables by transforming the search space into an eigenspace, thereby improving information sharing among dimensions. This is especially beneficial in fields such as mechanical design, structural optimization, and energy systems—where design variables often exhibit strong interactions. Furthermore, the dimension learning strategy enhances local exploration, making CDL-DGWO a robust choice for fine-tuning solutions in precision-critical applications like aeronautical engineering, robotics trajectory planning, and embedded system design.
6. Conclusions
In this study, a novel Double-swarm Grey Wolf Optimizer with Covariance and Dimension Learning (CDL-DGWO) has been proposed. This enhancement of the traditional Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) utilizes chaotic grouping to partition the population into two sub-swarms, which has been found to improve population diversity. Furthermore, covariance and dimension learning strategies have been incorporated to refine the hunting behavior of grey wolves, thereby significantly enhancing the global search capability and stability of the algorithm. The performance of CDL-DGWO was evaluated using 23 benchmark problems and the CEC2017 test suite. It was demonstrated that CDL-DGWO surpasses the compared swarm intelligence algorithms such as PSO, MFO, and GWO variants in terms of optimal solution identification and convergence performance. Moreover, according to the results of the Friedman test, CDL-DGWO ranks first compared to the comparison algorithms. The efficacy of CDL-DGWO in addressing real-world challenges was further confirmed through its successful application to three practical engineering design problems. The results indicate that the CDL-DGWO algorithm exhibits significant performance advantages in handling complex engineering design optimization problems, particularly in the search for global optima and the maintenance of algorithmic stability. Future research may focus on further refinements in parameter tuning, multi-group dynamic grouping strategy, integration with other optimization techniques, and testing across a broader range of practical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M. and M.X.; methodology, S.M.; software, S.M.; validation, S.M., M.X. and X.Z.; formal analysis, X.Z.; investigation, X.Y.; resources, M.X.; data curation, X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M.; writing—review and editing, M.X.; visualization, S.M.; supervision, X.Y.; project administration, M.X.; funding acquisition, M.X. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Science Research Project of Hebei Education Department (Grant No. QN2025401), Doctoral Research Startup Fund Project of Tangshan University (Grant No. BC202415) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province under Grant (Grant No. ZR2023QF044).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Nomenclature
| Acronyms and Abbreviations | |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| CDL-DGWO | Double-swarm Grey Wolf Optimizer with Covariance and Dimension Learning |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| MFO | Moth Flame Optimization |
| SMA | Slime Mold Algorithm |
| WOA | Whale Optimization Algorithm |
| MA | Mayfly Algorithm |
| HHO | Harris Hawks Optimization |
| SCA | Sine Cosine Algorithm |
| GSA | Gravitational Search Algorithm |
| LGWO | modified Lévy-embedded Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| RWGWO | Random Walk Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| SOF | Survival Of the Fittest |
| DE | Differential Evolution |
| DI-GWOCD | Discrete version of the Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| IAGWO | Improved multi-strategy adaptive Grey Wolf Optimization |
| IMF | Inverse Multiquadratic Function |
| ACoM-ABC | Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm with Adaptive Covariance Matrix |
| ABC | Artificial Bee Colony |
| CCoM-ABC | Cumulative Covariance Matrix Artificial Bee Colony |
| CMA-GWO | Covariance Matrix Adapted Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| I-GWO | Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| DLH | Dimension Learning-based Hunting |
| MIGWO | Multi-swarm Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| HGWOSCA | Hybrid Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO)–Sine Cosine Algorithm (SCA) |
| EGWO | Enhanced Grey Wolf Optimizer |
| PSOGWO | Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO) |
| SSA | Salp Swarm Algorithm |
| HSCA | Hybrid Sine Cosine Algorithm |
| HCLPSO | Heterogeneous Comprehensive Learning Particle Swarm Optimization |
| PSOGSA | Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)–Gravitational Search Algorithm (GSA) |
| mSCA | self-adaptive Sine Cosine Algorithm |
| CEC | Congress on Evolutionary Computation |
| C-GWO | Double-swarm Grey Wolf Optimizer with Covariance |
| D-GWO | Double-swarm Grey Wolf Optimizer with Dimension Learning |
| Mathematical Symbols | |
| t | Current iteration number |
| T | Maximum number of iterations |
| N | Population size (number of wolves) |
| D | Dimensionality of the problem (number of variables) |
| Position vector of a grey wolf | |
| , , | Position vectors of the alpha, beta, and delta wolves (best solutions) |
| Position vector of the prey | |
| , | Coefficient vectors in GWO |
| a | Control parameter that decreases linearly from 2 to 0 |
| Distance vector between a wolf and the prey | |
| Covariance matrix | |
| Orthogonal matrix of eigenvectors | |
| Diagonal matrix of eigenvalues | |
| Position vector in the eigenspace | |
| Neighborhood radius for dimension learning | |
| Neighborhood of the i-th wolf | |
| Candidate solution from dimension learning | |
| Regrouping interval | |
| , | Maximum and minimum values for calculation |
| Maximum number of function evaluations | |
| Current number of function evaluations | |
| Mean value of all solutions in the d-th dimension | |
| Population diversity index | |
References
- Yu, X.; Wu, X. Ensemble grey wolf Optimizer and its application for image segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, T.C.; Lee, C.C.; Kuo, C.C. A hybrid grey wolf optimization algorithm using robust learning mechanism for large scale economic load dispatch with vale-point effect. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Chen, S.; Xiong, H. A high-dimensional feature selection method based on modified Gray Wolf Optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 135, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, R.; Kennedy, J.; Blackwell, T. Particle swarm optimization: An overview. Swarm Intell. 2007, 1, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 89, 228–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S. Slime mould algorithm: A new method for stochastic optimization. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 111, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, G.; Deng, W.; Luo, Q. Bioinspired bare bones mayfly algorithm for large-scale spherical minimum spanning tree. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 830037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Mafarja, M.; Chen, H. Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.M.; Hasanzadeh, S.; Khatibi, S. Parameter identification of fuel cell using repairable grey wolf optimization algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 147, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.W.; Huang, L.P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, P.; Li, Y. WSN node location based on beetle antennae search to improve the gray wolf algorithm. Wirel. Netw. 2022, 28, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereli, S. A new modified grey wolf optimization algorithm proposal for a fundamental engineering problem in robotics. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 14119–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, S. A novel hybrid GWO-SCA approach for optimization problems. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 1586–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Lin, Q.; Wang, T. A grey wolf optimizer-based chaotic gravitational search algorithm for global optimization. J.·Supercomput. 2023, 79, 2691–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, R.; Vidyarthi, D.P. An ML-based task clustering and placement using hybrid Jaya-gray wolf optimization in fog-cloud ecosystem. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2024, 36, e8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.A.; Pahlavani, P. An efficient modified grey wolf optimizer with Levy flight for optimization tasks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 60, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Deep, K. A novel random walk grey wolf optimizer. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2019, 44, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Li, S.X. An improved grey wolf optimizer based on differential evolution and elimination mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Sun, J.; Chen, C.; Cao, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhou, X.; Tang, N.; Tian, Y. An information entropy-based grey wolf optimizer. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 4669–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Meng, T.; Cao, Y. Fuzzy strategy grey wolf optimizer for complex multimodal optimization problems. Sensors 2022, 22, 6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Moeini, E.; Taghian, S.; Mirjalili, S. Discrete improved grey wolf optimizer for community detection. J. Bionic Eng. 2023, 20, 2331–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xu, J.; Liang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Bao, S.; Tang, L. Improved multi-strategy adaptive Grey Wolf Optimization for practical engineering applications and high-dimensional problem solving. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.D. Artificial bee colony algorithm with adaptive covariance matrix for hearing loss detection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 216, 106792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xia, X.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.D. An artificial bee colony algorithm with a cumulative covariance matrix mechanism and its application in parameter optimization for hearing loss detection models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 229, 120533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.R.; Gupta, D.; Roy, S.S.; Lohar, A.K.; Mandal, N. Covariance matrix adapted grey wolf optimizer tuned eXtreme gradient boost for bi-directional modelling of direct metal deposition process. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 199, 116971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Taghian, S.; Mirjalili, S. An improved grey wolf optimizer for solving engineering problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpert, D.H.; Macready, W.G. No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1997, 1, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Grey wolf optimizer: A review of recent variants and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Z. Multi-swarm improved Grey Wolf Optimizer with double adaptive weights and dimension learning for global optimization problems. Math. Comput. Simul. 2023, 205, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, F. Novel chaotic grouping particle swarm optimization with a dynamic regrouping strategy for solving numerical optimization tasks. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2020, 194, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Peng, H.; Xiao, J.; Wu, Q. Dynamic multi-swarm differential learning particle swarm optimizer. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2018, 39, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, G. Evolutionary programming made faster. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1999, 3, 82–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, N.H.; Ali, M.Z.; Suganthan, P.N. Ensemble sinusoidal differential covariance matrix adaptation with Euclidean neighborhood for solving CEC2017 benchmark problems. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Donostia, Spain, 5–8 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 372–379. [Google Scholar]
- Qais, M.H.; Hasanien, H.M.; Alghuwainem, S. Augmented grey wolf optimizer for grid-connected PMSG-based wind energy conversion systems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 69, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenel, F.A.; Gökçe, F.; Yüksel, A.S.; Yiğit, T. A novel hybrid PSO–GWO algorithm for optimization problems. Eng. Comput. 2019, 35, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Mirjalili, S.M. Salp Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Deep, K. A novel hybrid sine cosine algorithm for global optimization and its application to train multilayer perceptrons. Appl. Intell. 2020, 50, 993–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, N.; Suganthan, P.N. Heterogeneous comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization with enhanced exploration and exploitation. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2015, 24, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Hashim, S.Z.M. A new hybrid PSOGSA algorithm for function optimization. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Computer and Information Application, Tianjin, China, 3–5 December 2010; pp. 374–377. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Deep, K. A hybrid self-adaptive sine cosine algorithm with opposition based learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 119, 210–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Shi, Y.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, R. Population diversity maintenance in brain storm optimization algorithm. J. Artif. Intell. Soft Comput. Res. 2014, 4, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandar, H.; Sadollah, A.; Bahreininejad, A.; Hamdi, M. Water cycle algorithm—A novel metaheuristic optimization method for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Comput. Struct. 2012, 110, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coello, C.A.C. Use of a self-adaptive penalty approach for engineering optimization problems. Comput. Ind. 2000, 41, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).