Dynamic Behavior of Remolded Saline Soil Under Dual Symmetric Factors: Cyclic Loading and Freeze–Thaw Cycles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Geological Setting for Salinization
2.2. Study Area and Soil Properties
3. Experimental Approaches
3.1. Specimen Preparation
3.2. Dynamic Triaxial Test
4. Experimental Results and Analyses
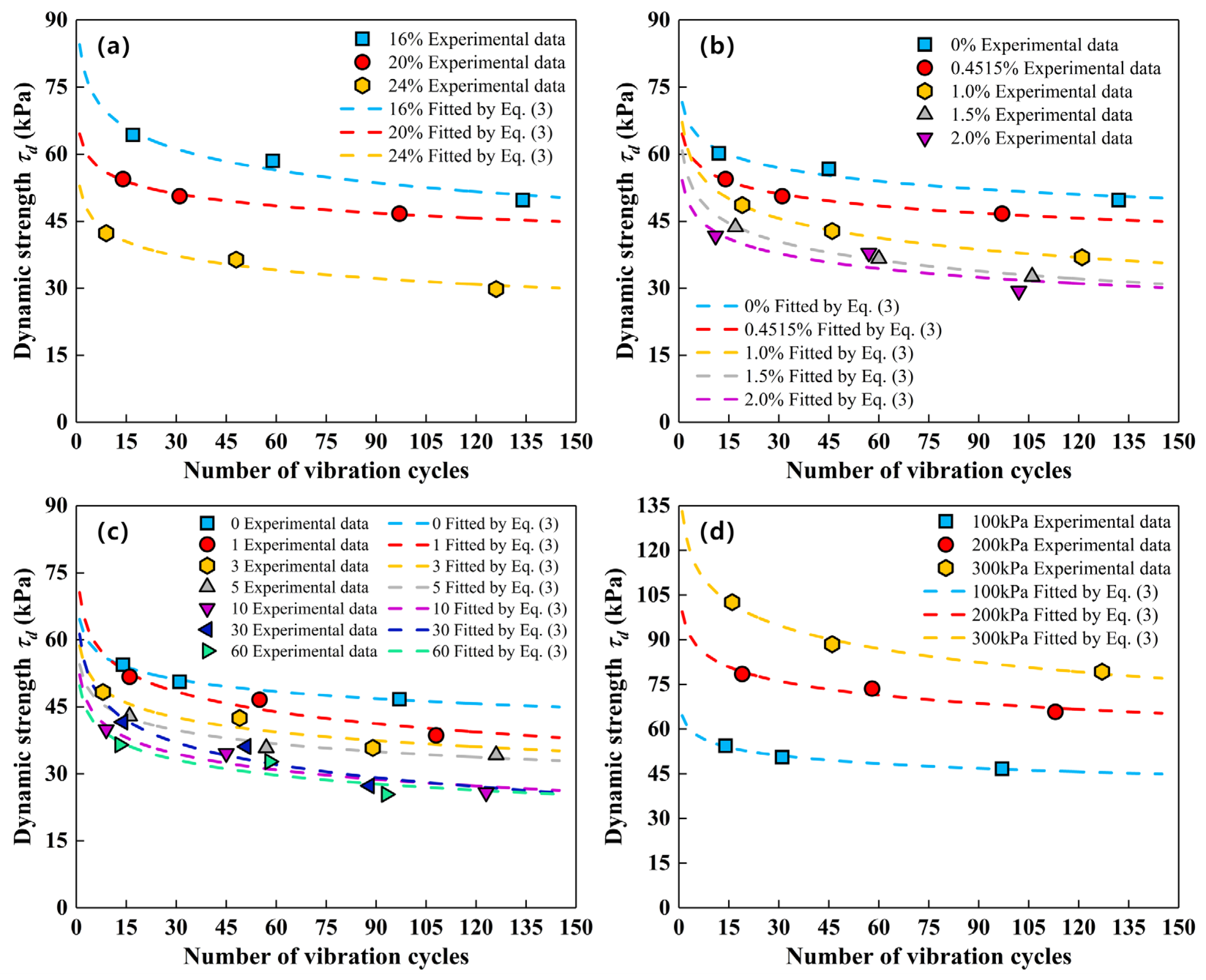
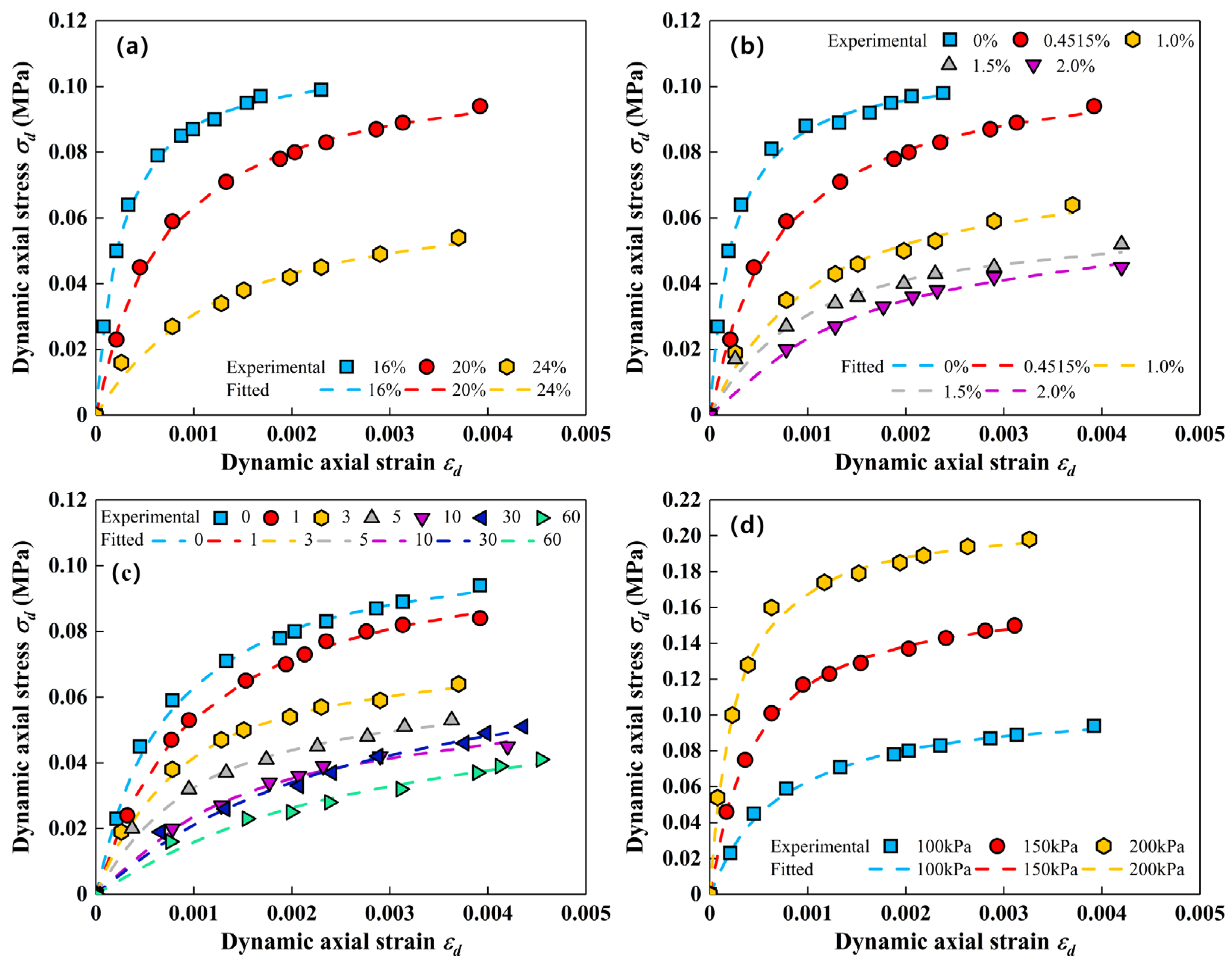
4.1. Dynamic Strength
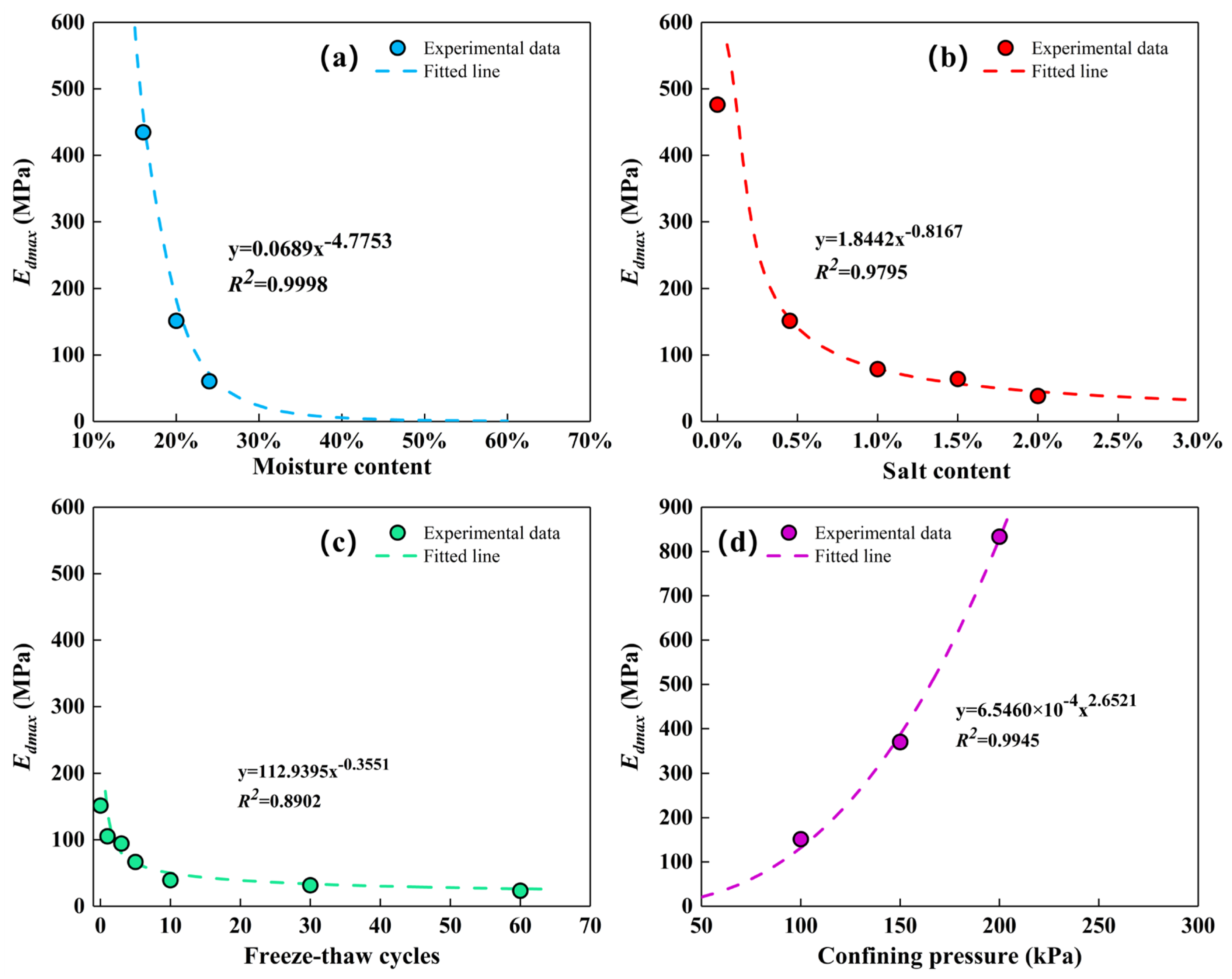
4.2. Dynamic Elastic Modulus
5. Discussion on Factors Affecting Dynamic Behavior
5.1. Moisture Content
5.2. Salt Content
5.3. Freeze–Thaw Cycles
5.4. Confining Pressure
5.5. Practical Insights for Subgrade Performance
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The relationship between the dynamic strength of saline soil and increasing vibration cycles can be well described by logarithmic functions.
- (2)
- With increasing dynamic axial strains, the reductions in real-time dynamic elastic moduli are especially significant when the dynamic axial strains are small (<0.2%), then the dynamic strength and elastic modulus basically begin to stabilize at higher dynamic axial strains (>0.2%).
- (3)
- The dynamic strength and elastic modulus (including the maximum dynamic elastic modulus) both decrease with increasing moisture content, salt content, and freeze–thaw cycle, and increase considerably with increasing confining pressure. In particular, the dispersion of clay particles induced by NaHCO3, the dominant salt in this carbonate saline soil, is identified as the primary mechanism responsible for the observed decrease in dynamic parameters with increasing salt content. Moreover, these dynamic parameters remain almost constant after undergoing five freeze–thaw cycles. The variations in maximum elastic moduli with the above variables can be well expressed by power functions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vlase, S.; Ochsner, A.; Marin, M. Dynamic properties of the structures with three level of symmetry. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 2025, 37, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Yu, Q.; Niu, C.; Sun, D.; Wang, Q. The coupling effects of wet-dry and freeze-thaw cycles on the mechanical properties of saline soil synergistically solidified with sulfur-free lignin, basalt fiber and hydrophobic polymer. Catena 2024, 238, 107832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Q.L.; An, L.S.; Wang, J.H. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of frozen compacted sand subjected to freeze–thaw cycle under multi-stage cyclic loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2015, 76, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, B. Dynamic properties of reclaimed soft soil under the combined frequency cyclic loading. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elif Orakoglu, M.; Liu, J.; Niu, F. Dynamic behavior of fiber-reinforced soil under freeze-thaw cycles. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 101, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qu, S.; Nie, Z.; Zhang, J. Effects of density and moisture variation on dynamic deformation properties of compacted lateritic soil. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5951832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.-Y.; Ling, X.-Z.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Lu, Q.-R.; Chen, S.-J.; Zou, Z.-Y.; Guo, Z.-H. Experimental investigation of the dynamic behavior of frozen clay from the Beiluhe subgrade along the QTR. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 69, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.D.; Li, J.W.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.C. Dynamic characteristics of unsaturated remolded sandy soil through cyclic shear tests. Rock Soil Mech. 2016, 37, 3115–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Liao, H.J.; Wu, J.; Akiro, T. Study of the dynamic shear strength of cohesive soils. Key Eng. Mater. 2003, 243–244, 619–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmohammad Sadeghi, M.; Hassan Beigi, F. Dynamic behavior of reinforced clayey sand under cyclic loading. Geotext. Geomembr. 2014, 42, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, F.; Feng, D.; Tang, K.; Feng, X. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of thawed saturated clay under long-term cyclic loading. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 145, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Xu, X.; Dong, Y.; Li, S. Present situation and prospect of mechanical research on frozen soils in China. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 87, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-D.; Zhu, Z.-W.; Song, S.-C.; Kang, G.-Z.; Ning, J.-G. Dynamic behavior of frozen soil under uniaxial strain and stress conditions. Appl. Math. Mech. 2013, 34, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Kang, G. Dynamic stress–strain behavior of frozen soil: Experiments and modeling. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2014, 106–107, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirar, B.; Maheshwari, B.K. Dynamic properties of soils at large strains in Roorkee region using field and laboratory tests. Indian Geotech. J. 2017, 48, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokusho, T. Cyclic triaxial test of dynamic soil properties for wide strain range. Soils Found. 1980, 20, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Bu, C.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Chen, G. Dynamic characteristics of expanded polystyrene composite soil under traffic loadings considering initial consolidation state. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 102, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, W.; Gabryś, K.; Szymański, A. Effect of time on dynamic shear modulus of selected cohesive soil of one section of express way No. S2 in Warsaw. Acta Geophys. 2015, 63, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.-Z.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, S.-J.; Wang, L.-N.; Gao, X.; Lu, Q.-R. Dynamic elastic modulus for frozen soil from the embankment on Beiluhe Basin along the Qinghai–Tibet Railway. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2009, 57, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, W.; Feng, W.; Xiao, D.; Hou, X. Reconstruction of soil particle composition during freeze-thaw cycling: A review. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrod, K.D. Effects of cyclic freezing and thawing on volume changes and permeabilities of soft fine-gained soils. Can. Geotech. J. 1996, 33, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Optimization of particle size distribution of sulfur-free lignin in enhancing disintegration resistance of saline soil. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 17, 4632–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Code for Investigation of Geotechnical Engineering (GB 50021-2001); China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Carteret, R.d.; Buzzi, O.; Fityus, S.; Liu, X. Effect of Naturally Occurring Salts on Tensile and Shear Strength of Sealed Granular Road Pavements. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 04014010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, G.; Kamai, T.; Chen, W.; Zhang, D.; Yang, J. Undrained shear behavior of loess saturated with different concentrations of sodium chloride solution. Eng. Geol. 2013, 155, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Fang, J. Impact of cooling on shear strength of high salinity soils. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 141, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Lai, Y.; You, Z.; Zhang, M. The phase change process and properties of saline soil during cooling. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 3923–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, M. Study on the freezing temperature of saline soil. Acta Geotech. 2018, 13, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen, E.; Isacsson, U. Soil behavior during freezing and thawing using variable and constant confining pressure triaxial tests. Can. Geotech. J. 2001, 38, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Experimental study of the dynamic behavior of high-grade highway-subgrade soil in a seasonally frozen area. Sci. Cold Arid. Reg. 2017, 9, 289–296. Available online: https://www.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2017&filename=HAQK201703017&uniplatform=OVERSEA&v=QEdZU0RQUjvCmruZZ3DPED0tZuazwLvYkILV2Nk3G4G5BdOAhb9FeSIf9FlZ-egu (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Sun, Z. Extensive reclamation of saline-sodic soils with flue gas desulfurization gypsum on the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Geoderma 2018, 321, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, C.; Wang, Q.; Shen, J.; Han, M.; Xia, W.; Zhou, T.; Yu, Z.; Shan, X. Analysis of the pore structure characteristics of saline soil in the profile within the frozen depth. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2023, 212, 103882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Song, S.; Niu, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Shu, H.; Xia, W.; Wang, Q. Evolution characteristics of microscopic pore structure of saline soil profile in Qian’an country, Northeastern China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.D.; Zhao, W.D.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J. Analysis of the frost heaving characteristics of carbonate-saline soil in western Jilin Province, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 4170–4179. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Peng, W.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Fan, J. Evolution law of the properties of saline soil in western Jilin Province under multi field effect. J. Jilin Univ. (Earth Sci. Ed.) 2017, 47, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ruan, Y.; Chen, Y. Mechanical effect of pre-consolidation pressure of structural behavior soil. Xinan Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao/J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2016, 51, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D2487-11; Standard Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Tian, Y. Experimental study of the dynamic properties of cement- and lime-modified clay soils subjected to freeze–thaw cycles. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Peng, W.; Ma, B.; Yu, Q.; Kasama, K.; Furukawa, Z.; Niu, C.; Wang, Q. Micro-composition evolution of the undisturbed saline soil undergoing different freeze-thaw cycles. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2023, 210, 103825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dang, J.; Yang, X. A Study of the Soil Water Characteristic Curve of Saline Soil. Geotech. Investig. Surv. 2009, 37, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, D. Response of the physical and mechanical parameters of saline soil to changes in salt content and to its microstructure characteristics. J. Qinghai Univ. 2023, 41, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Yao, M.; Sun, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Experimental investigation of the mechanical properties of hydrophobic polymer-modified soil subjected to freeze-thaw cycles. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 3623–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Niu, C.; Leng, G.; Tian, G. Dynamic characteristics of saturated loess under different confining pressures: A microscopic analysis. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2017, 78, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, K. Postcyclic undrained strength for Cohesive Soils. J. Geotech. Eng. 1994, 120, 1961–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Principles and Methods of the Dynamic Triaxial Test; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.-J.; Lai, Y.-M.; Li, S.-Y.; Chang, X.-X. Dynamic strength of frozen soils. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2008, 30, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, B.O.; Drnevich, V.P. Shear modulus and damping in soils: Design equations and curves. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1972, 98, 667–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Wu, S.; Tang, H.; Xin, P.; Liang, C. Dynamics stress–strain behavior of Tianshui soils. Landslides 2016, 14, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shayea, N.A. The combined effect of clay and moisture content on the behavior of remolded unsaturated soils. Eng. Geol. 2001, 62, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppala, A.J.; Pedarla, A.; Pino, A.; Hoyos, L.R. Diffused double-layer swell prediction model to better characterize natural expansive clays. J. Eng. Mech. 2017, 143, 04017069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.S.; Liu, S.Y.; Shen, S.L.; Negami, T. Comparison in undrained shear strength between undisturbed and remolded ariake clays. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2006, 132, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.Q.; Zhong, M.; Wei, C.F.; Zhang, W.H.; Hu, F.N. Shear strength features of soils developed from purple clay rock and containing less than two-millimeter rock fragments. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 1464–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Bora, P.K. Plastic limit, liquid limit and undrained shear strength of soil-reappraisal. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2003, 129, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazavi, M.; Roustaie, M. The influence of freeze–thaw cycles on the unconfined compressive strength of fiber-reinforced clay. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Qu, J.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, X. Effects of freeze-thaw cycles on soil mechanical and physical properties in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Vermeer, P.A.; Cheng, G. A review of the influence of freeze-thaw cycles on soil geotechnical properties. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2006, 17, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Bohra, N.C.; Altschaeffl, A.G.; White, T.D. Resilient modulus of cohesive soils and the effect of freeze–thaw. Can. Geotech. J. 1995, 32, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
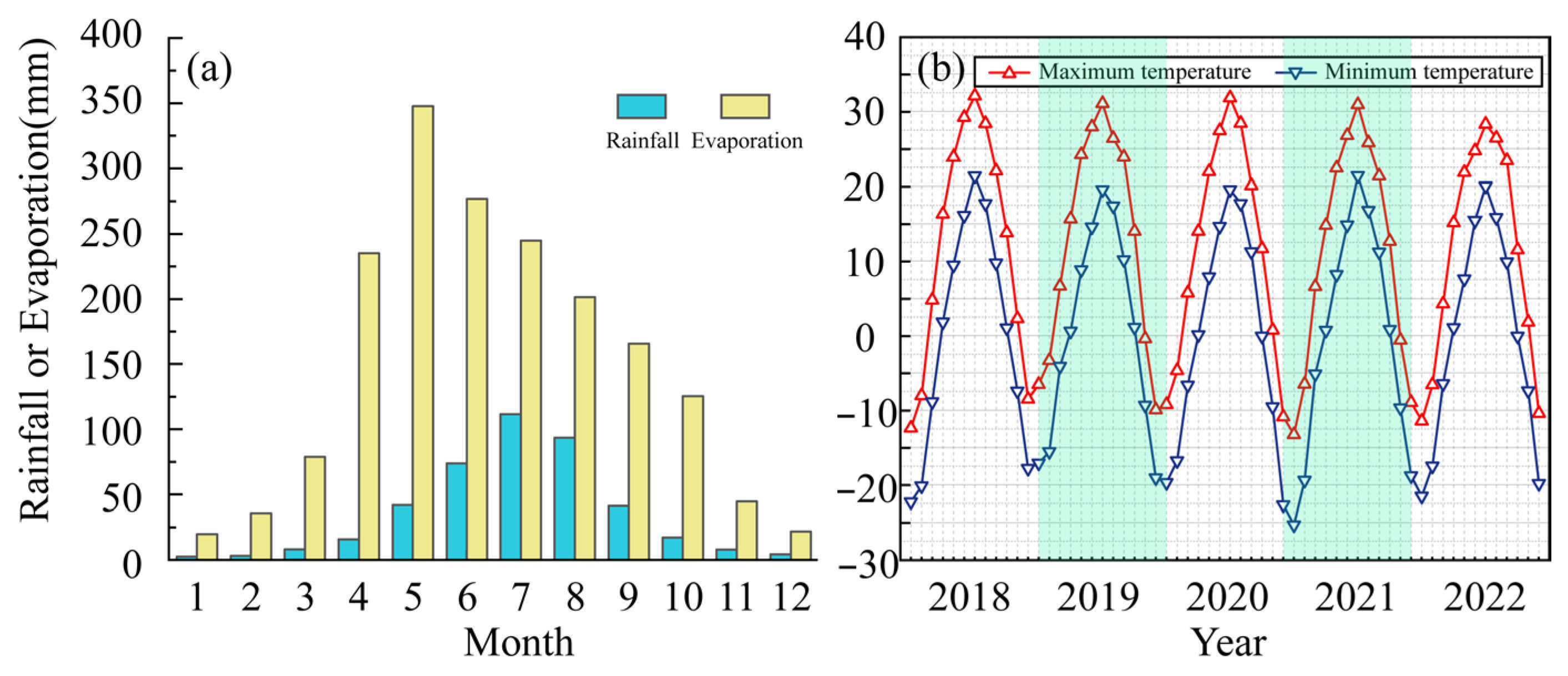
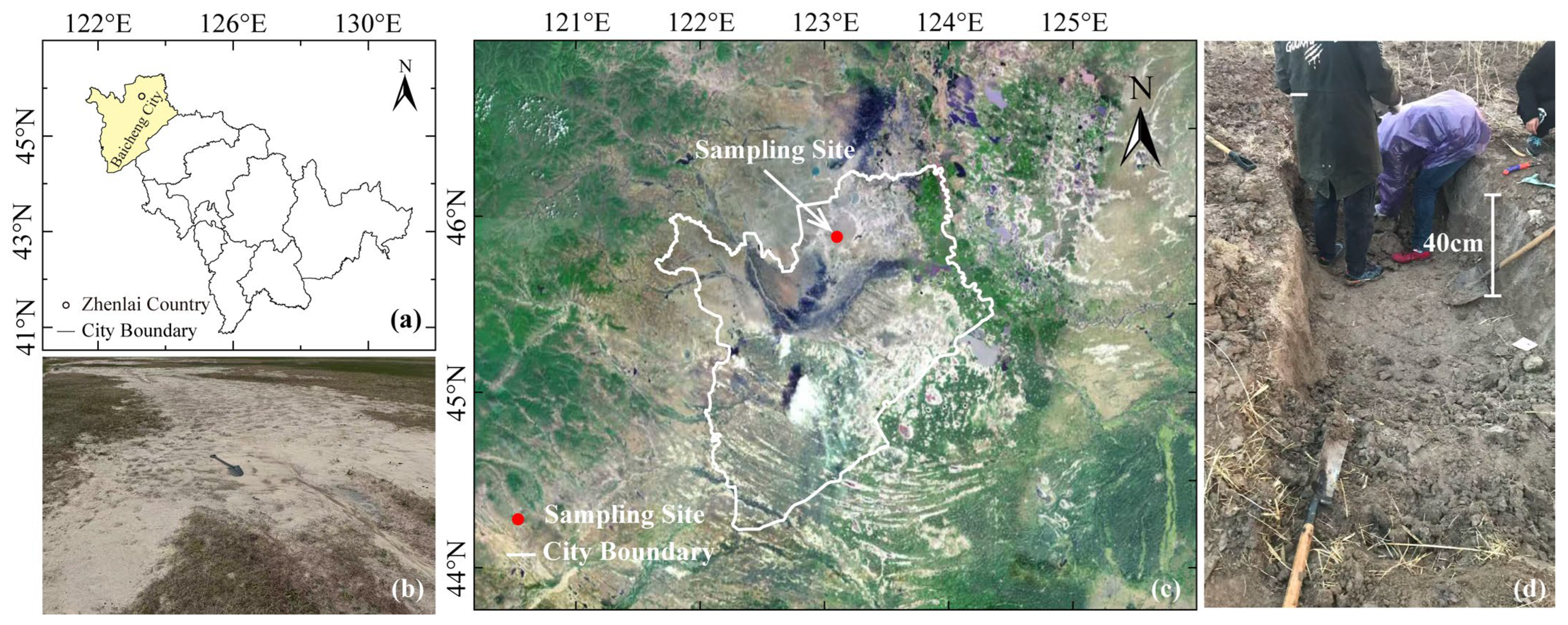
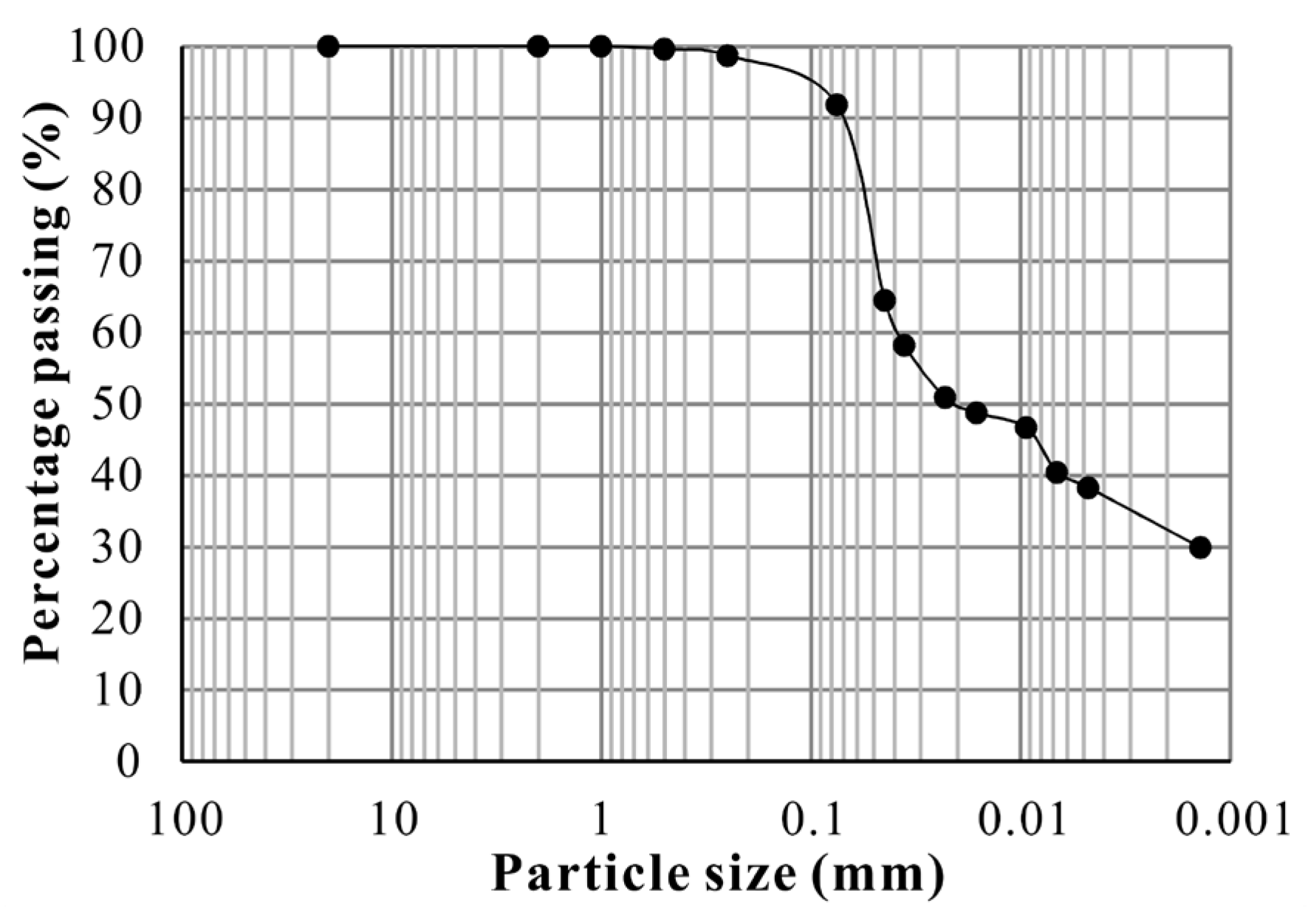


| Soil Type | Plastic Limit (%) | Liquid Limit (%) | Plasticity Index | Optimum Moisture Content (%) | Maximum Dry Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL | 18.5 | 32.4 | 13.9 | 20.0 | 1.74 |
| Clay fraction (<0.005 mm) | Silt fraction (0.005–0.075 mm) | Sand fraction (0.075–2 mm) | |||
| 38.26% | 53.53% | 8.21% | |||
| Item | Total | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | SO42− | HCO3− | CO32− | Cl− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 0.5 | 0.0999 | 0.0012 | 0.0073 | 0.0044 | 0.0089 | 0.1929 | 0 | 0.0141 |
| Group Label | Moisture Content (%) | Salt Content (%) | Freeze–Thaw Cycle | Confining Pressure (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | 16, 20, 24 | 0.5 | 0 | 100 |
| SC | 20 | 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 | 0 | 100 |
| FT | 20 | 0.5 | 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, 30, 60 | 100 |
| CP | 20 | 0.5 | 0 | 100, 150, 200 |
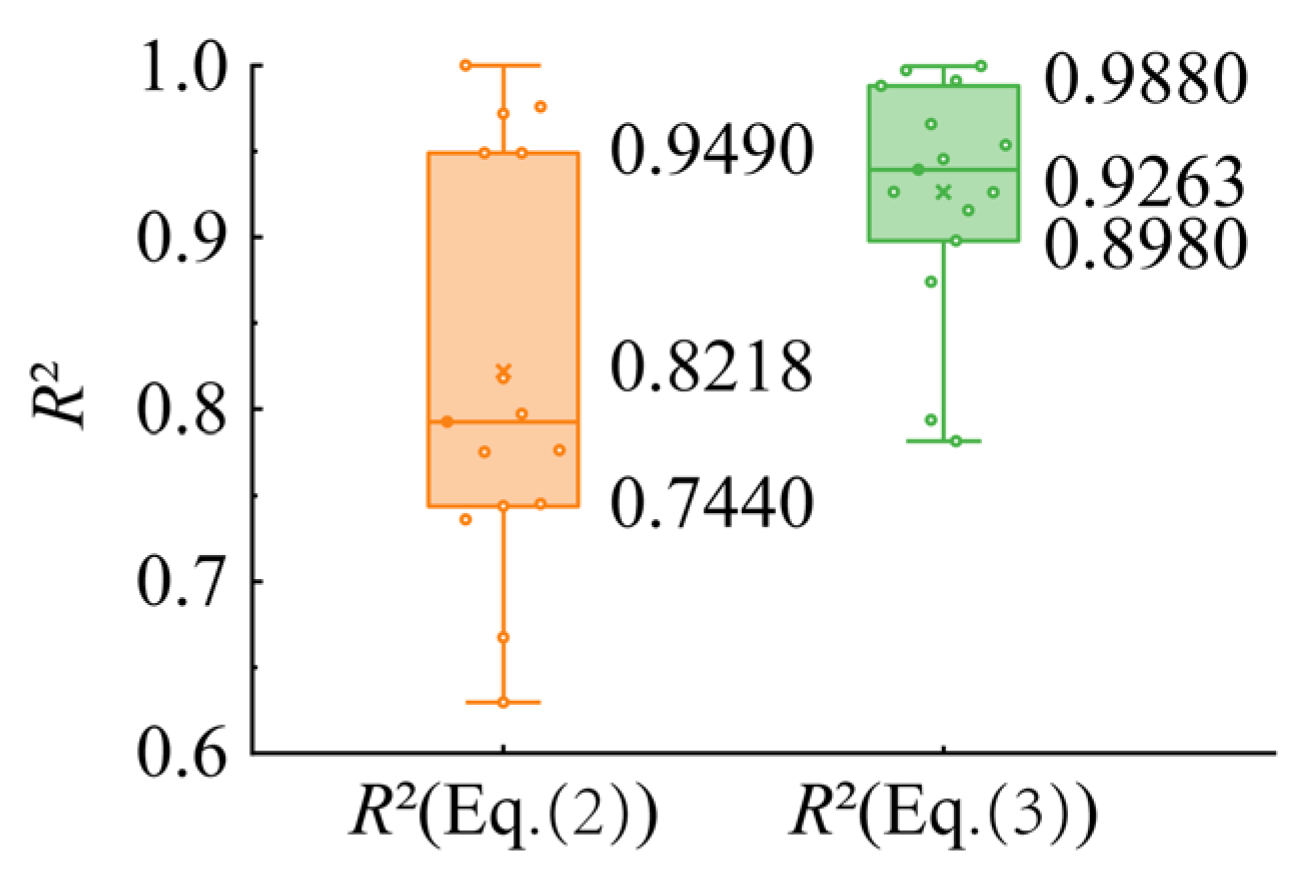
| Moisture Content | Salt Content | Freeze–Thaw Cycle | Confining Pressure | Linear Fitting by Equation (2) | Logarithmic Fitting by Equation (3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | R2 | a′ | b′ | R2 | ||||
| 16% | 0.5% | 0 | 100 kPa | 2.4015 | 0.5084 | 0.7971 | 0.0688 | 0.8456 | 0.9453 |
| 20% | 1.2259 | 0.4591 | 0.9718 | 0.0394 | 0.6455 | 0.9909 | |||
| 24% | 1.0060 | 0.3148 | 0.8178 | 0.0460 | 0.5289 | 0.9657 | |||
| 20% | 0 | 0 | 100 kPa | 1.1476 | 0.5121 | 0.7440 | 0.0431 | 0.7160 | 0.9392 |
| 1.0% | 2.5054 | 0.3587 | 0.9490 | 0.0632 | 0.6712 | 0.9996 | |||
| 1.5% | 2.0532 | 0.3182 | 0.9490 | 0.0599 | 0.6079 | 0.9970 | |||
| 2.0% | 1.1166 | 0.3193 | 0.6297 | 0.0482 | 0.5412 | 0.7817 | |||
| 20% | 0.5% | 1 | 100 kPa | 2.0394 | 0.3952 | 0.7755 | 0.0652 | 0.7056 | 0.9156 |
| 3 | 0.8721 | 0.3765 | 0.7764 | 0.0472 | 0.5867 | 0.8980 | |||
| 5 | 1.5897 | 0.3297 | 0.9999 | 0.0434 | 0.5450 | 0.9535 | |||
| 10 | 1.0944 | 0.2827 | 0.7362 | 0.0520 | 0.5217 | 0.9263 | |||
| 30 | 1.9124 | 0.2847 | 0.7452 | 0.0714 | 0.6130 | 0.8739 | |||
| 60 | 1.2636 | 0.2711 | 0.6675 | 0.0489 | 0.4973 | 0.7935 | |||
| 20% | 0.5% | 0 | 150 kPa | 1.6357 | 0.4413 | 0.7924 | 0.0456 | 0.6626 | 0.9260 |
| 200 kPa | 2.0413 | 0.3880 | 0.9758 | 0.0563 | 0.6655 | 0.9880 | |||
| Moisture Content | Salt Content | Freeze–Thaw Cycle | Confining Pressure | A (MPa−1) | B (MPa−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16% | 0.5% | 0 | 100 kPa | 0.00224 | 9.121 | 0.9994 |
| 20% | 0.00635 | 9.233 | 0.9979 | |||
| 24% | 0.01753 | 14.400 | 0.9910 | |||
| 20% | 0 | 0 | 100 kPa | 0.00203 | 9.422 | 0.9984 |
| 1.0% | 0.01283 | 12.770 | 0.9929 | |||
| 1.5% | 0.01557 | 16.480 | 0.9874 | |||
| 2.0% | 0.02635 | 15.380 | 0.9973 | |||
| 20% | 0.5% | 1 | 100 kPa | 0.00941 | 9.245 | 0.9983 |
| 3 | 0.01045 | 13.070 | 0.9993 | |||
| 5 | 0.01499 | 15.190 | 0.9961 | |||
| 10 | 0.02577 | 15.420 | 0.9957 | |||
| 30 | 0.03360 | 12.350 | 0.9914 | |||
| 60 | 0.04542 | 15.170 | 0.9884 | |||
| 20% | 0.5% | 0 | 150 kPa | 0.00265 | 5.896 | 0.9991 |
| 200 kPa | 0.00114 | 4.748 | 0.9978 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Li, L.; Niu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, W.; Shangguan, Y. Dynamic Behavior of Remolded Saline Soil Under Dual Symmetric Factors: Cyclic Loading and Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101691
Liu J, Wang Q, Yu Q, Li L, Niu C, Zhang Y, Xia W, Shangguan Y. Dynamic Behavior of Remolded Saline Soil Under Dual Symmetric Factors: Cyclic Loading and Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Symmetry. 2025; 17(10):1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101691
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jing, Qing Wang, Qingbo Yu, Laishi Li, Cencen Niu, Yu Zhang, Weitong Xia, and Yuhao Shangguan. 2025. "Dynamic Behavior of Remolded Saline Soil Under Dual Symmetric Factors: Cyclic Loading and Freeze–Thaw Cycles" Symmetry 17, no. 10: 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101691
APA StyleLiu, J., Wang, Q., Yu, Q., Li, L., Niu, C., Zhang, Y., Xia, W., & Shangguan, Y. (2025). Dynamic Behavior of Remolded Saline Soil Under Dual Symmetric Factors: Cyclic Loading and Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Symmetry, 17(10), 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101691







