An Approximate Belief Rule Base Student Examination Passing Prediction Method Based on Adaptive Reference Point Selection Using Symmetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Description
3. Construction of the EPP Model Based on ABRB-A
3.1. Theoretical Basis and Advantages of Model Design
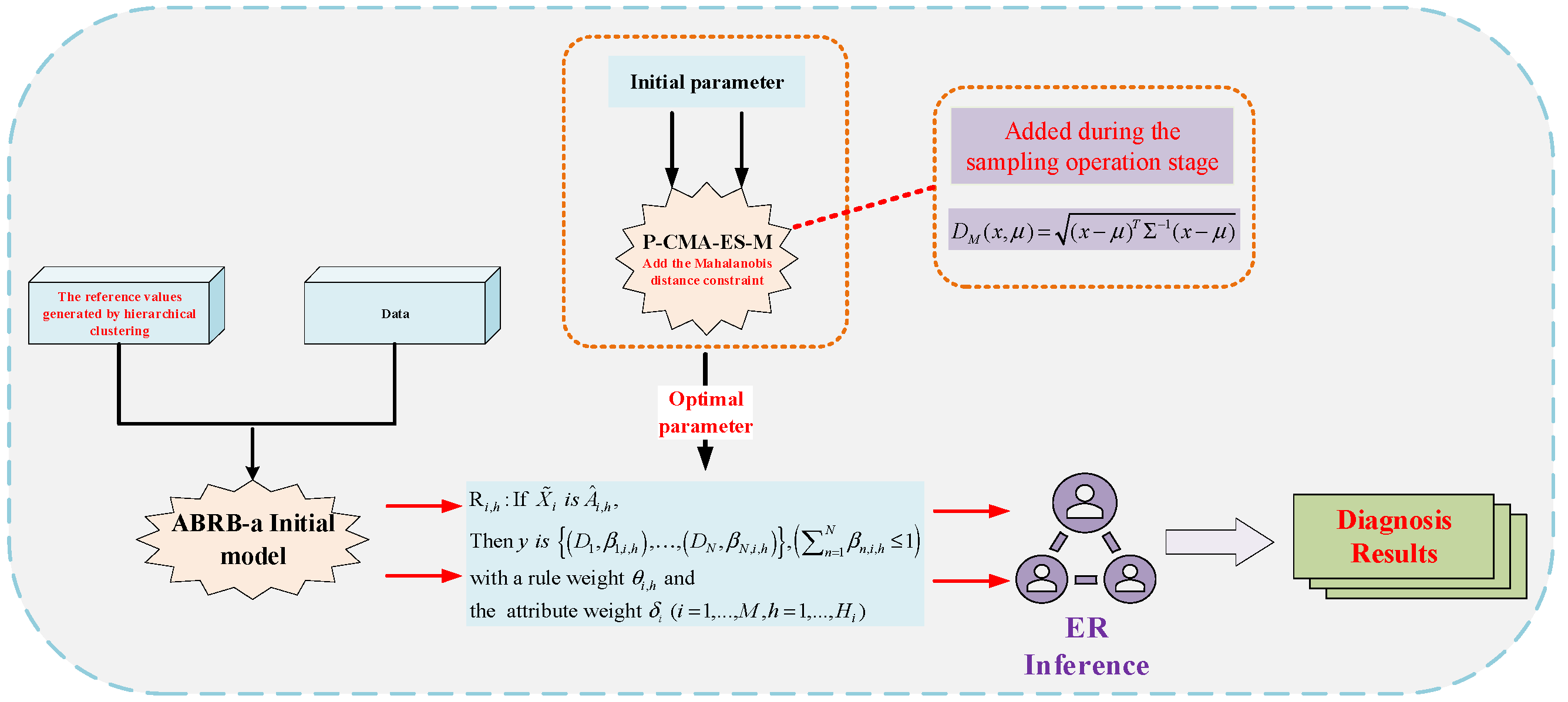
3.2. Construction Process of the Model
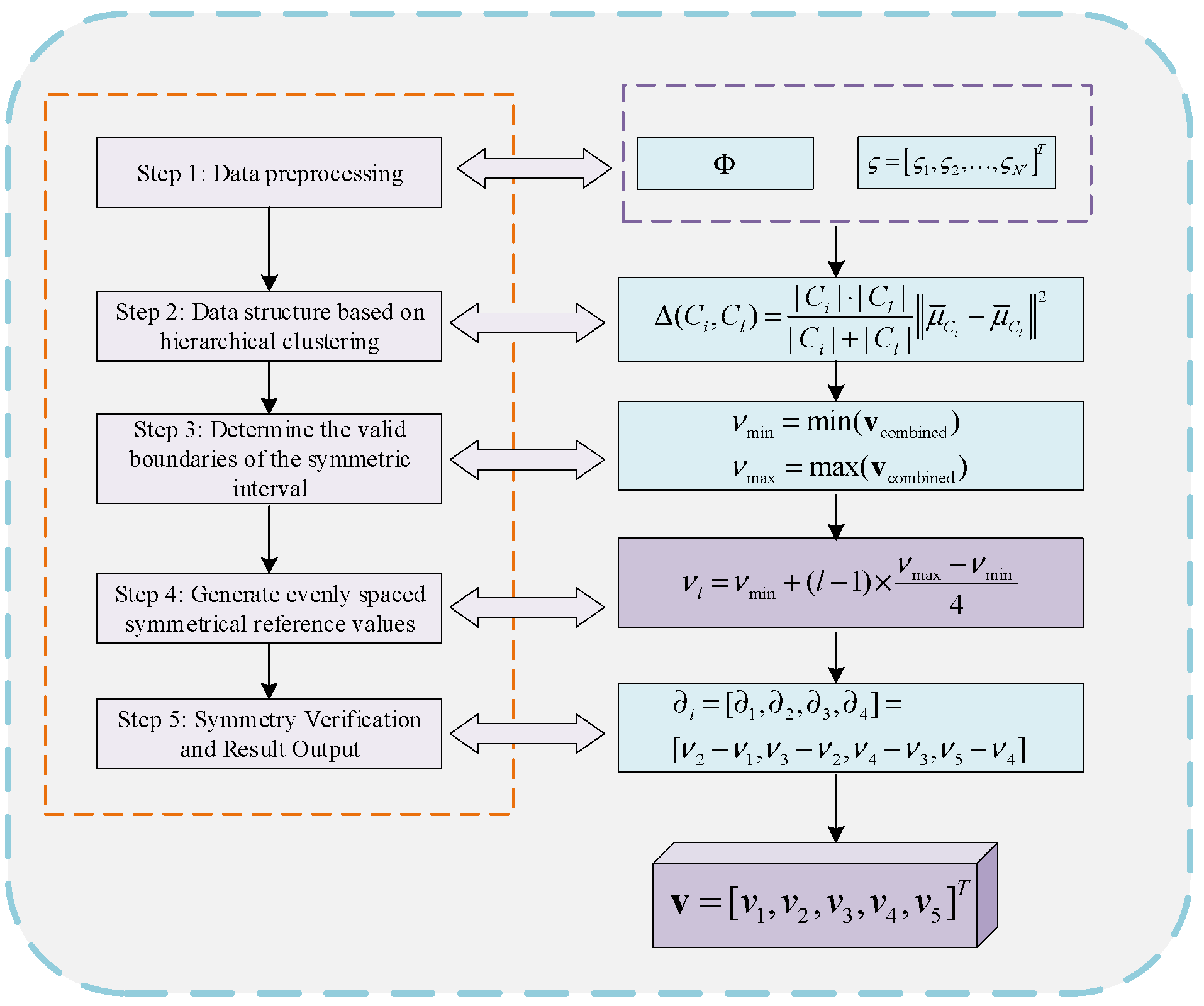
3.3. Adaptive Construction Method for Reference Points in Hierarchical Clustering
3.3.1. Introduction to Hierarchical Clustering
3.3.2. Operating Procedure
3.4. Reasoning Process of the ABRB-A Model
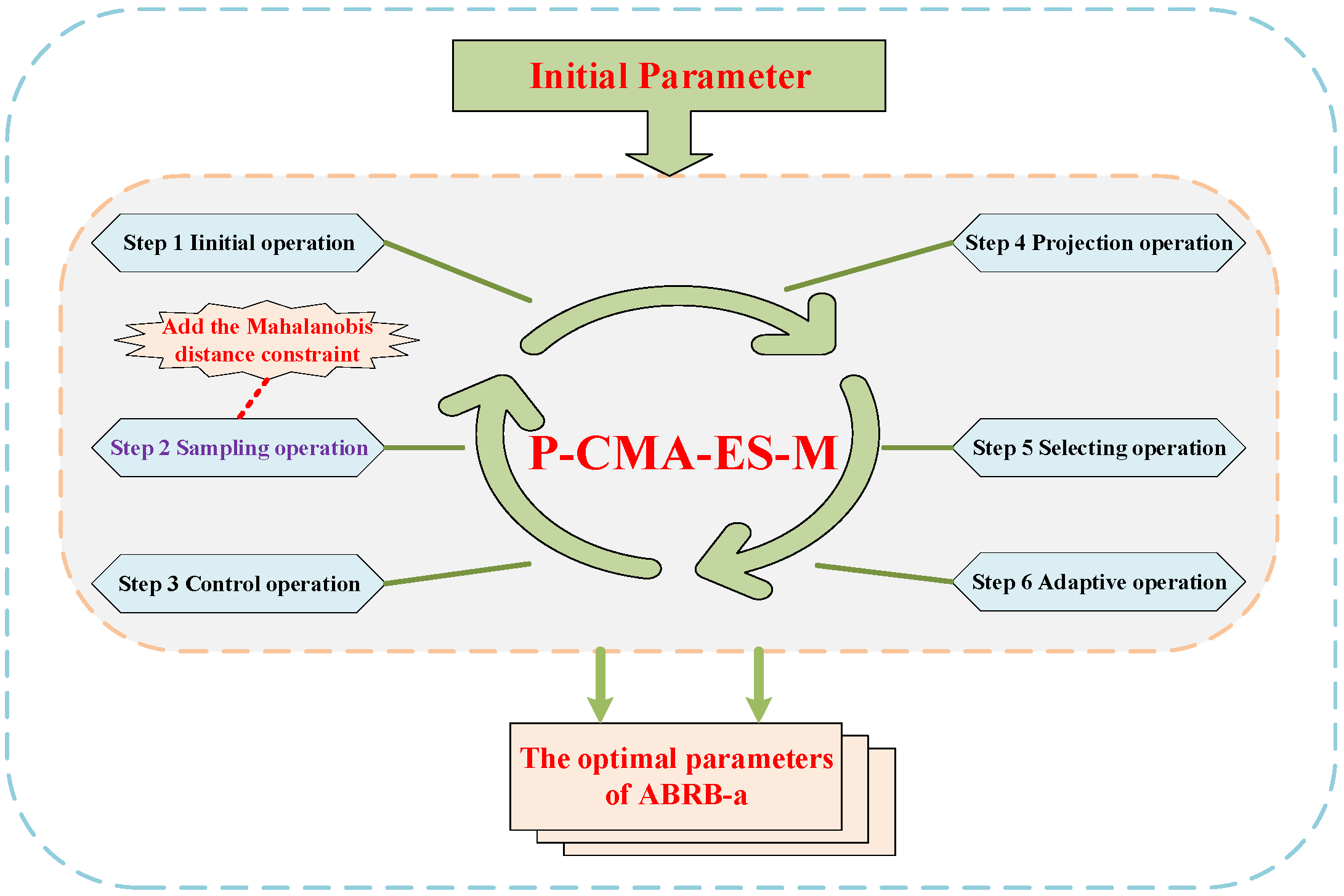
3.5. Optimization Process of the ABRB-A Model
3.6. Analysis Related to Algorithms
3.6.1. ABRB-A Student Exam Pass Prediction Pseudo-Code
| Algorithm 1 Pseudocode for ABRB-a Student Examination Passing Prediction Model |
| //Step 1: Build the ABRB-a Model Initialize the ABRB-a model with expert-defined belief rules Initialize input attribute set based on feature selection results Ensure linear growth of rules to avoid combinatorial explosion //Step 2: Adaptive Reference Point Generation For each input attribute: Apply hierarchical clustering algorithm to analyze data distribution Automatically generate symmetric reference points Validate the symmetry of generated reference points //Step 3: Evidence Reasoning Process For each input data instance: Calculate matching degree between input and reference points Determine rule activation weights based on matching results Execute evidence reasoning for rule fusion Output belief distribution for pass/fail prediction //Step 4: Model Parameter Optimization Initialize model parameters with expert knowledge Apply P-CMA-ES-M algorithm with Mahalanobis distance constraints Optimize belief degrees, rule weights, and attribute weights Ensure parameters satisfy interpretability constraints //Step 5: Model Evaluation Input test dataset to the optimized ABRB-a model For each test instance: Calculate expected utility value for pass/fail prediction Compare predicted results with actual labels Evaluate model performance using accuracy and other metrics //Output the final prediction results and model performance End |
3.6.2. Complexity Analysis
4. Case Study
4.1. Background Description
4.2. ABRB-A Model Setup
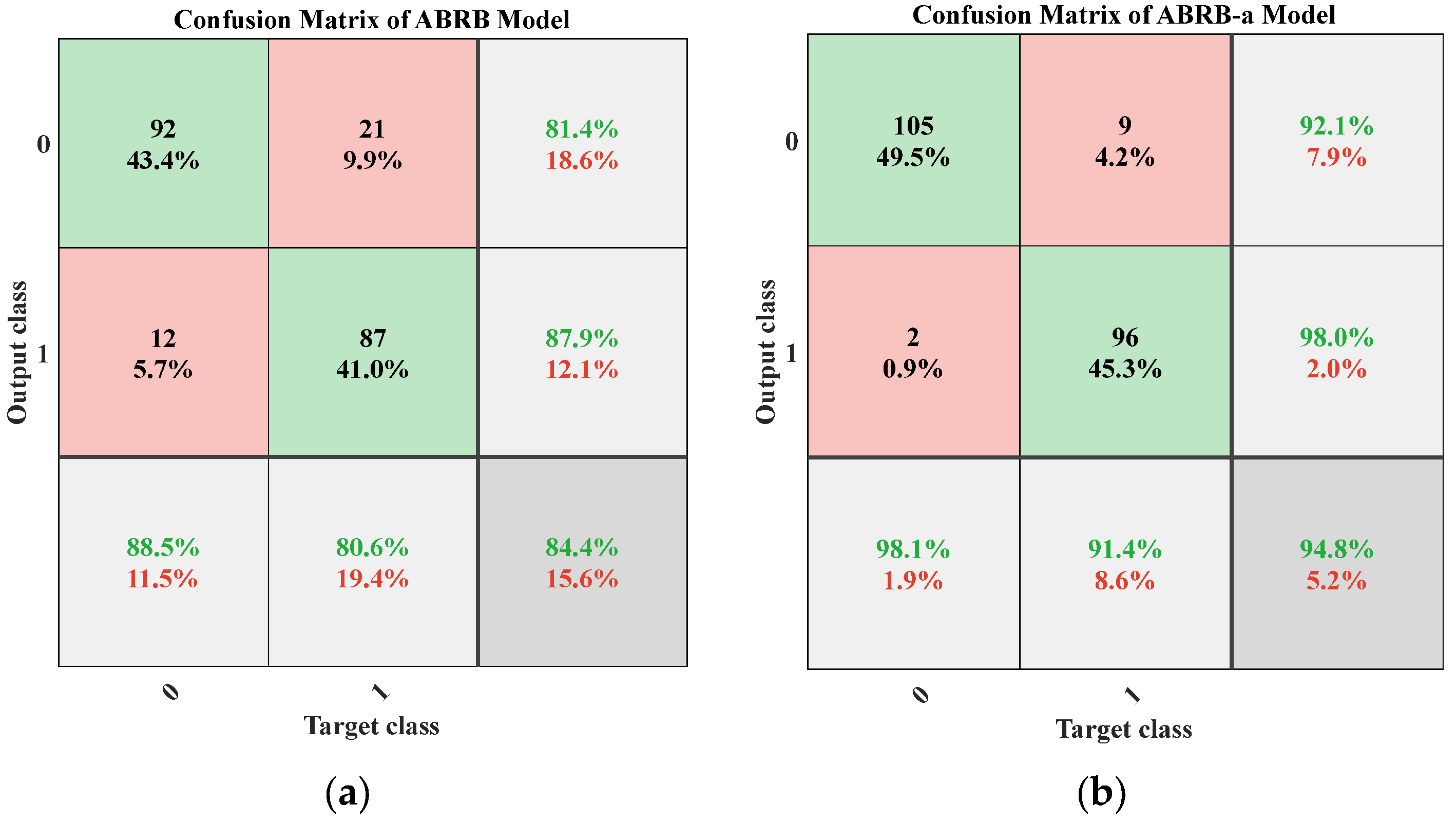
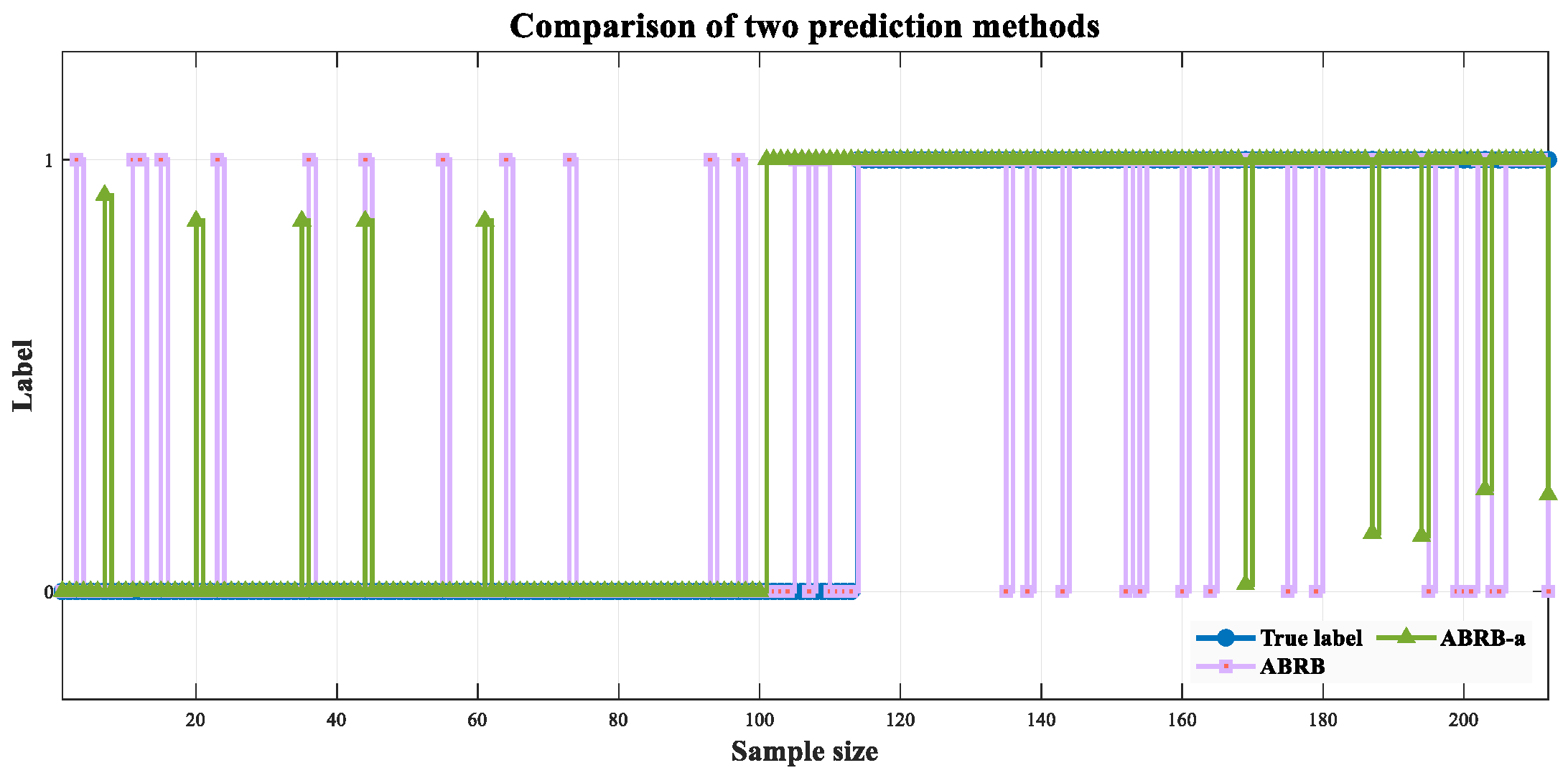
4.3. Experimental Result Analysis
4.4. Comparative Experiment
4.4.1. Core Evaluation Criteria
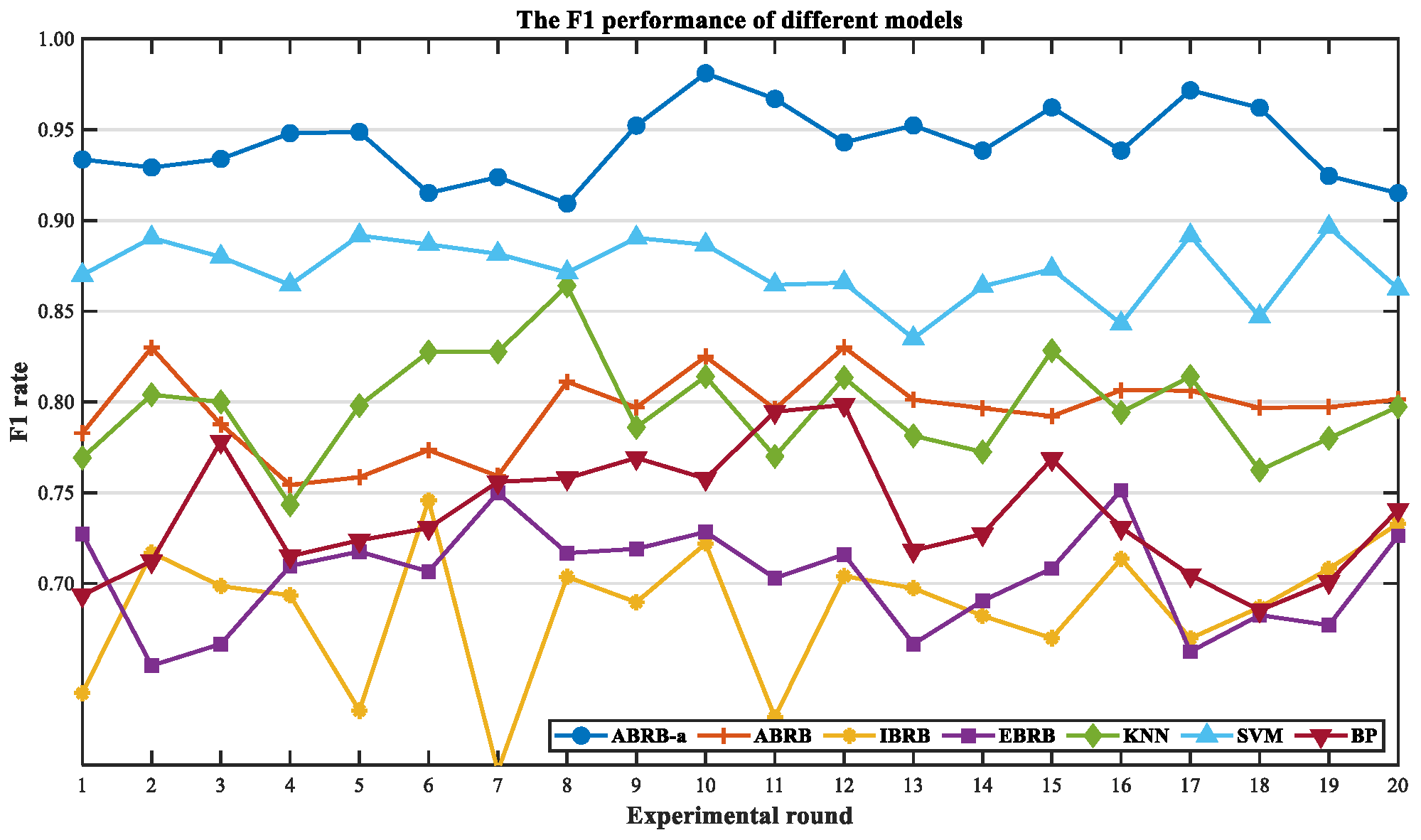
4.4.2. Model Prediction Performance Analysis
4.4.3. Multi-Dimensional Comparison Verification
4.5. Generalization Verification
4.6. Experimental Summary
5. Conclusions
6. The Meaning of the Letters
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| NO | Notation | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The initial parameters of the model | |
| 2 | The data mining process | |
| 3 | The educational data | |
| 4 | The Data Mining Parameters | |
| 5 | The optimization parameters of the model | |
| 6 | The model optimization process | |
| 7 | The parameters of P-CMA-ES-M | |
| 8 | The prediction result of the model | |
| 9 | The input feature set | |
| 10 | The total number of input attributes | |
| 11 | The total number of the rules | |
| 11 | The nonlinear functional relationship between the system characteristics and the predicted value | |
| 12 | The belief rule | |
| 13 | The reference value of | |
| 14 | The belief degree of | |
| 15 | The result belief degree | |
| 16 | The rule weight of | |
| 17 | The attribute weight of the premise | |
| 18 | type matrix | |
| 19 | The quantity of the dataset | |
| 20 | A data vector representing the observed values of all samples for the feature | |
| 21 | The specific sample observation values at the and positions within vector | |
| 22 | The cluster and the | |
| 23 | The number of clusters | |
| 24 | The arithmetic mean of the sample value within the cluster | |
| 25 | The sum of squared within-cluster variances caused by merging clusters and | |
| 26 | The center of the cluster | |
| 27 | A comprehensive vector consisting of the global minimum value | |
| 28 | The difference vector | |
| 29 | The most symmetrical set of reference values | |
| 30 | A constant value between two adjacent reference values | |
| 31 | The normalization weight of the attributes | |
| 32 | The matching degree of the rule | |
| 33 | The number of all rules | |
| 34 | The rule activation weights | |
| 35 | An intermediate variable | |
| 36 | The set of belief distributions | |
| 37 | The input vector of the actual system | |
| 38 | The utility function | |
| 39 | The prediction accuracy of the model | |
| 40 | The current number of iterations | |
| 41 | The covariance matrix | |
| 42 | The population size | |
| 43 | The offspring population size | |
| 44 | The initial step size | |
| 45 | The mean of the optimal whole in the generation | |
| 46 | The parameter set | |
| 47 | The population generated in the generation | |
| 48 | A normal distribution | |
| 49 | The mahalanobis distance | |
| 50 | The distance range | |
| 51 | The generation of reasonable belief distribution | |
| 52 | The parameter vector | |
| 53 | The number of parameters | |
| 54 | The number of equation constraints contained in the constraints | |
| 55 | The weighting factor | |
| 56 | An intermediate variable | |
| 57 | The learning rate | |
| 58 | The evolution path of the covariance matrix path | |
| 59 | The backward time horizon of the evolution path | |
| 60 | The damping coefficient | |
| 61 | The expected value of the Euclidean norm | |
| 62 | The identity matrix | |
| 63 | The parameters of the conjugate evolution path | |
| 64 | The number of samples that produce correct output results | |
| 65 | The total number of evaluated samples | |
| 66 | The true positive | |
| 67 | The false negative | |
| 68 | The number of samples | |
| 69 | The true value | |
| 70 | The predicted value |
References
- Al-Shehri, H.; Al-Qarni, A.; Al-Saati, L.; Batoaq, A.; Badukhen, H.; Alrashed, S.; Alhiyafi, J.; Olatunji, S.O. Student performance prediction using support vector machine and k-nearest neighbor. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 30th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Windsor, ON, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kabakchieva, D. Student performance prediction by using data mining classification algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Manag. Res. 2012, 1, 686–690. [Google Scholar]
- Raftopoulos, G.; Davrazos, G.; Kotsiantis, S. Fair and Transparent Student Admission Prediction Using Machine Learning Models. Algorithms 2024, 17, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, N.T.; Ha, N.T.; Trung, N.N.; Binh, V.T.; Hang, N.T.; Binh, V.T. Comparing the Effectiveness of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models in Student Credit Scoring: A Case Study in Vietnam. Risks 2025, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukaras, C.; Hatzikraniotis, E.; Mitsiaki, M.; Koukaras, P.; Tjortjis, C.; Stavrinides, S.G. Revolutionising Educational Management with AI and Wireless Networks: A Framework for Smart Resource Allocation and Decision-Making. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Vizitei, E.; Ganapathi, V. GritNet: Student performance prediction with deep learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.07405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, C.M. Using technology and assessment to personalize instruction: Preventing reading problems. Prev. Sci. 2019, 20, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, A.; Miller, H.; Clarke, D.D. Identifying barriers to help-seeking: A qualitative analysis of students’ preparedness to seek help from tutors. Br. J. Guid. Couns. 1998, 26, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Hu, P.; Chu, S.-C.; Pan, J.-S. Multi-objective gray wolf optimizer with cost-sensitive feature selection for Predicting students’ Academic performance in college english. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalawi, A.; Soh, B.; Li, A.; Samra, H. Predictive Models for Educational Purposes: A Systematic Review. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Mai, N.T.; Liu, W. Adaptive Knowledge Assessment via Symmetric Hierarchical Bayesian Neural Networks with Graph Symmetry-Aware Concept Dependencies. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triveni, G.R.; Danish, F.; Albalawi, O. Advancing Survey Sampling Efficiency under Stratified Random Sampling and Post-Stratification: Leveraging Symmetry for Enhanced Estimation Accuracy in the Prediction of Exam Scores. Symmetry 2024, 16, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, B. Academic achievement prediction in higher education through interpretable modeling. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abromavičius, V.; Serackis, A.; Katkevičius, A.; Kazlauskas, M.; Sledevič, T. Prediction of exam scores using a multi-sensor approach for wearable exam stress dataset with uniform preprocessing. Technol. Health Care 2023, 31, 2499–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khairy, D.; Alharbi, N.; Amasha, M.A.; Areed, M.F.; Alkhalaf, S.; Abougalala, R.A. Prediction of student exam performance using data mining classification algorithms. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 21621–21645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isinkaye, F.O.; Folajimi, Y.O.; Ojokoh, B.A. Recommendation systems: Principles, methods and evaluation. Egypt. Inform. J. 2015, 16, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Medo, M.; Yeung, C.H.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Zhang, Z.-K.; Zhou, T. Recommender systems. Phys. Rep. 2012, 519, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saganowski, S. Bringing emotion recognition out of the lab into real life: Recent advances in sensors and machine learning. Electronics 2022, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-B.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Sii, H.-S.; Wang, H.-W. Belief rule-base inference methodology using the evidential reasoning approach-RIMER. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.—Part A Syst. Hum. 2006, 36, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhou, Z.; Han, X.; Feng, Z. A Text-Oriented Fault Diagnosis Method for Electromechanical Device Based on Belief Rule Base. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Qian, G.; He, W.; Zhou, G. A liquid launch vehicle safety assessment model based on semi-quantitative interval belief rule base. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, H.; He, W. Learning Emotion assessment method based on belief rule base and evidential reasoning. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.S. Modular System Design and Evaluation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gligorea, I.; Yaseen, M.U.; Cioca, M.; Gorski, H.; Oancea, R. An interpretable framework for an efficient analysis of students’ academic performance. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascharka, D.; Tran, P.; Soklaski, R.; Majumdar, A. Transparency by design: Closing the gap between performance and interpretability in visual reasoning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4942–4950. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Yang, R.; He, W.; Zhu, H.J. A novel belief rule base expert system with interval-valued references. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, X.; Xi, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.J. Comprehensive survey on hierarchical clustering algorithms and the recent developments. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 8219–8264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F.; Contreras, P.J. Algorithms for hierarchical clustering: An overview, II. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2017, 7, e1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, I.S.; Mallela, S.; Kumar, R. Enhanced word clustering for hierarchical text classification. In Proceedings of the Eighth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 23–26 June 2002; pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, N.; Callan, J.; Krishnan, R.; Duncan, G.; Padman, R. Incremental hierarchical clustering of text documents. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Arlington, VA, USA, 6 November 2006; pp. 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, S.; Long, P.M. Performance guarantees for hierarchical clustering. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2005, 70, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, H.; Pandey, A.C.; Saraswat, M.; Kumar, S.; Pal, R.; Modwel, G. A comprehensive survey of image segmentation: Clustering methods, performance parameters, and benchmark datasets. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 35001–35026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, L.-H.; Fu, Y.-G.; Chang, L.-L.; Chin, K.-S. Dynamic rule adjustment approach for optimizing belief rule-base expert system. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 96, 40–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.-L.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.-B.; Liu, G.-P.; Wang, J.; Jenkinson, I.; Ren, J. Inference and learning methodology of belief-rule-based expert system for pipeline leak detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2007, 32, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, Z.-g.; Qian, B.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.-W. BRB prediction with customized attributes weights and tradeoff analysis for concurrent fault diagnosis. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 15, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, C.; He, W.; Tang, S. On the interpretability of belief rule-based expert systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 3489–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, W.; Zhou, G.; Li, H.; Cao, Y. A new interpretable behavior prediction method based on belief rule base with rule reliability measurement. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 256, 110712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

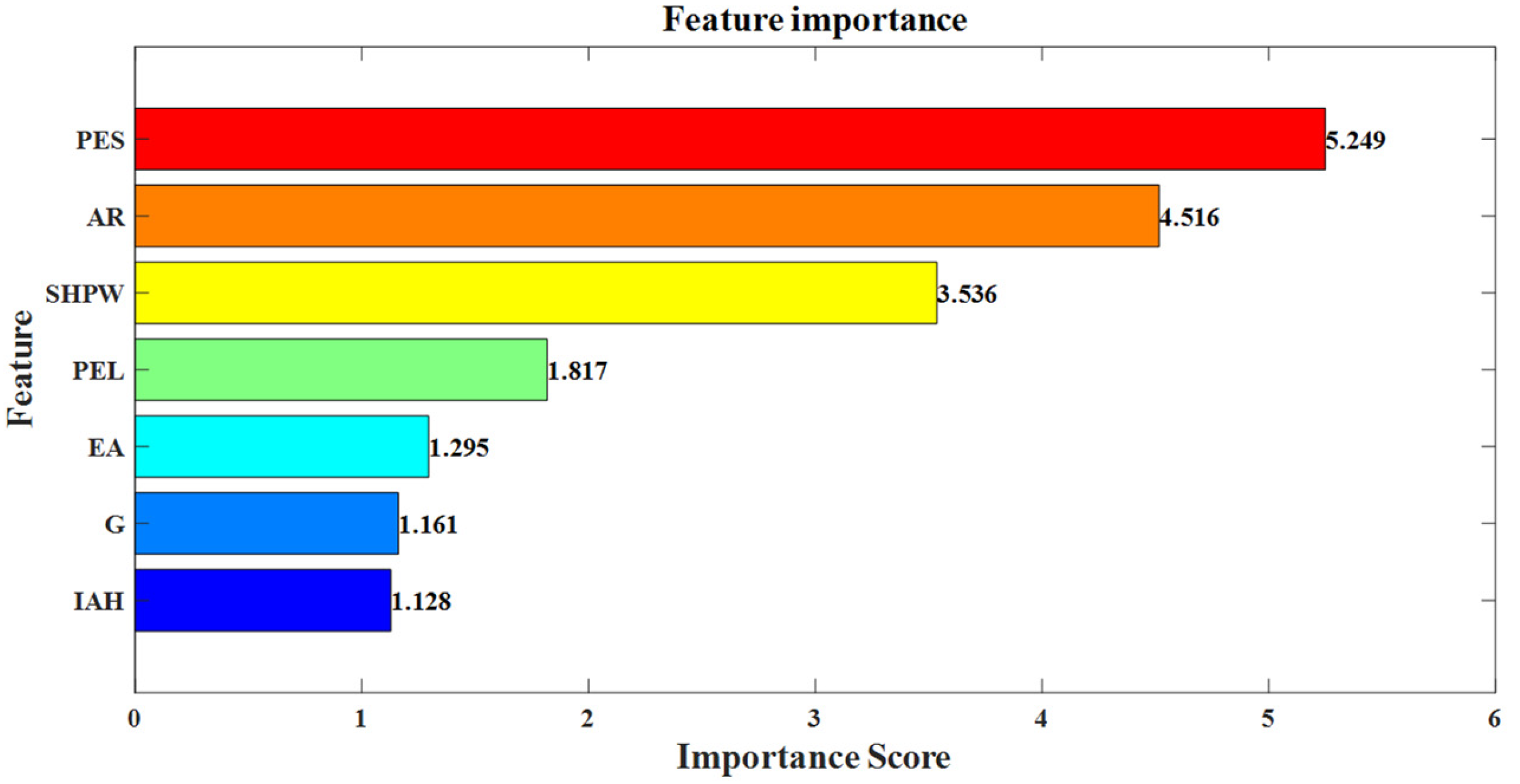
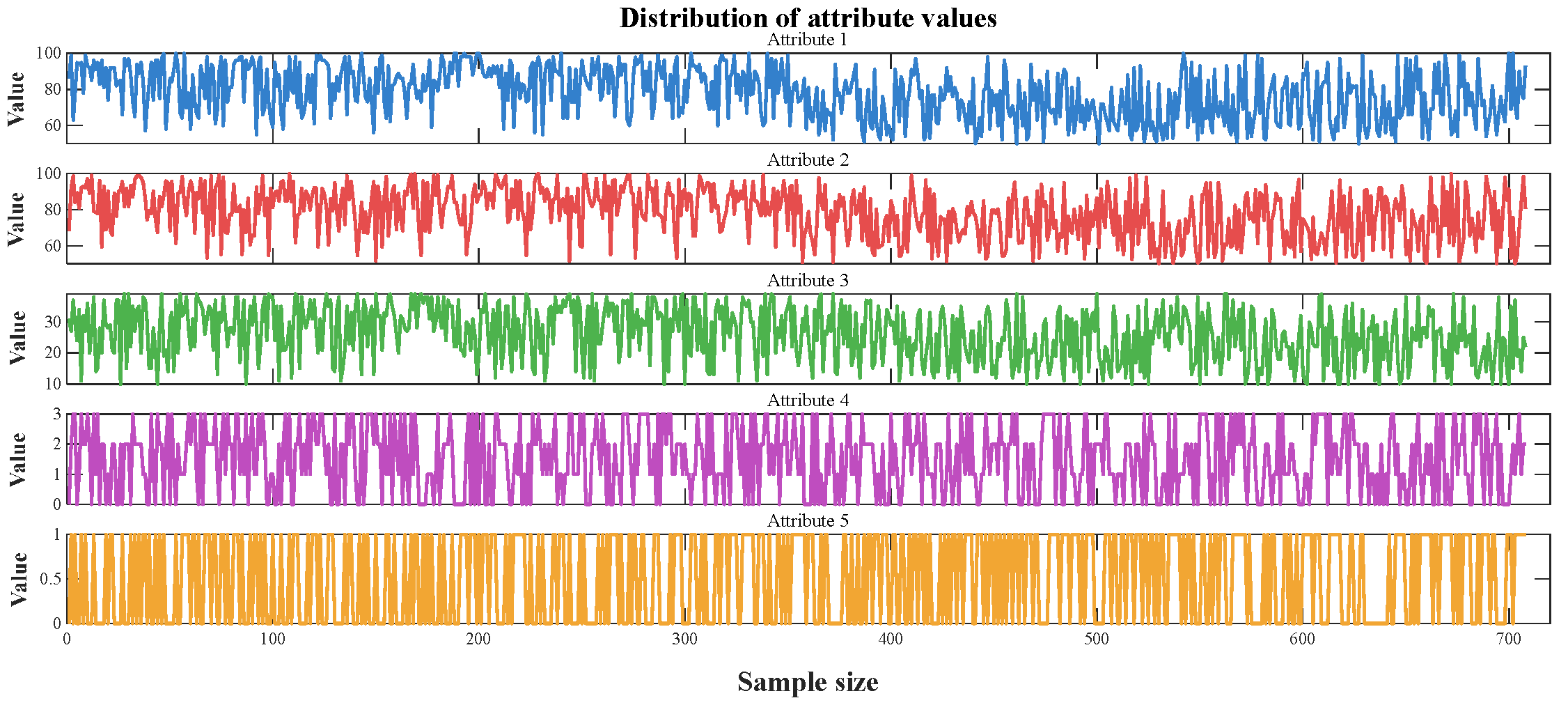
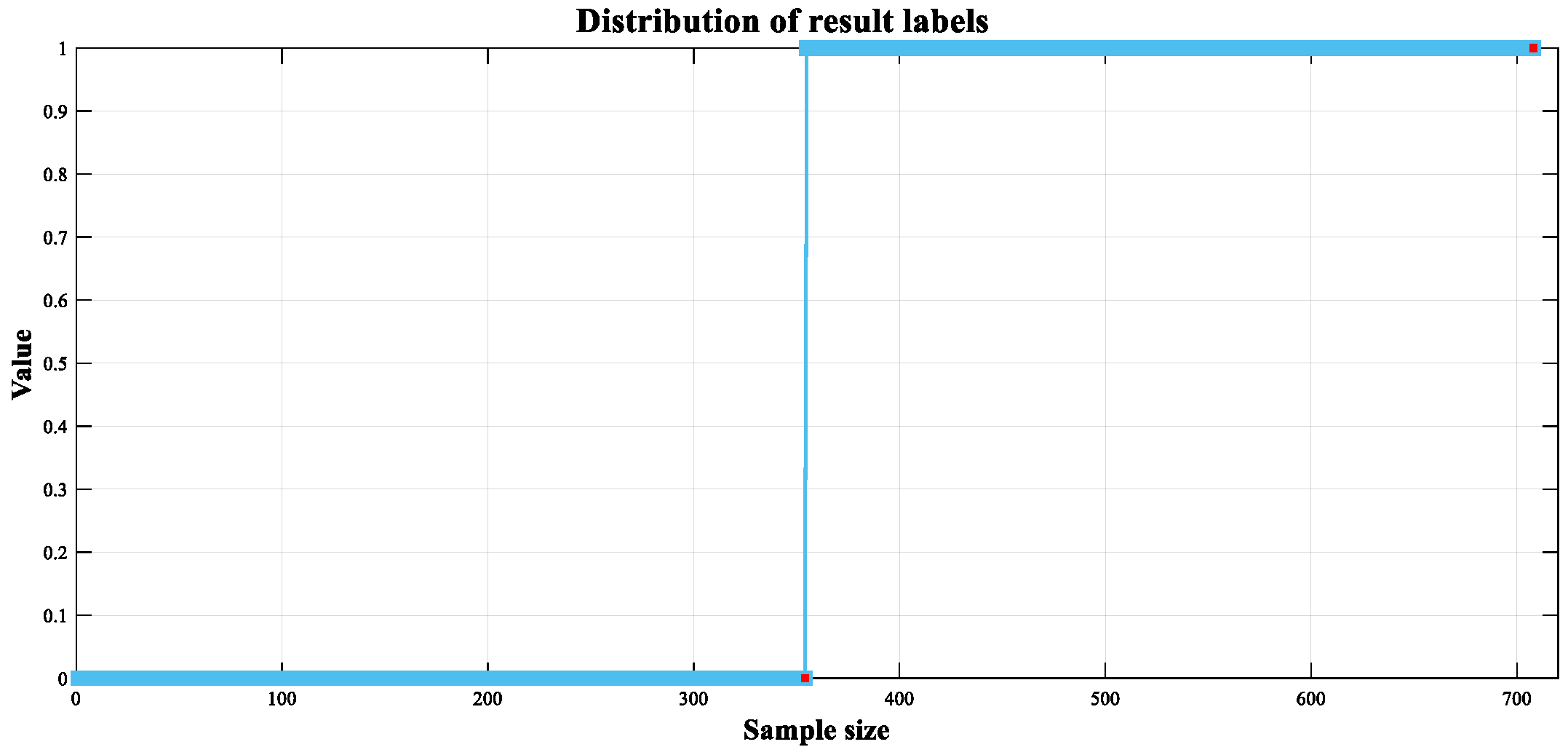
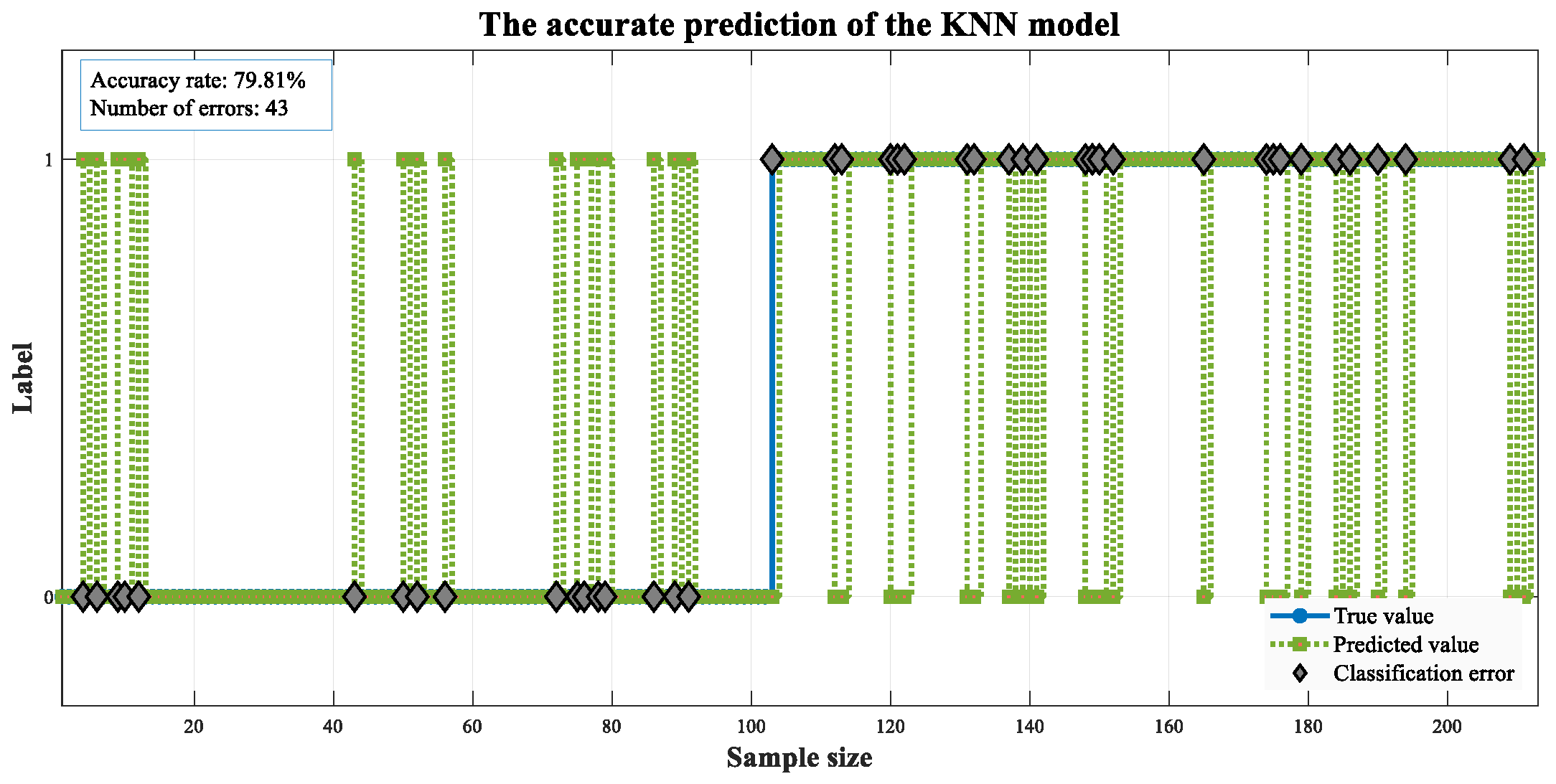
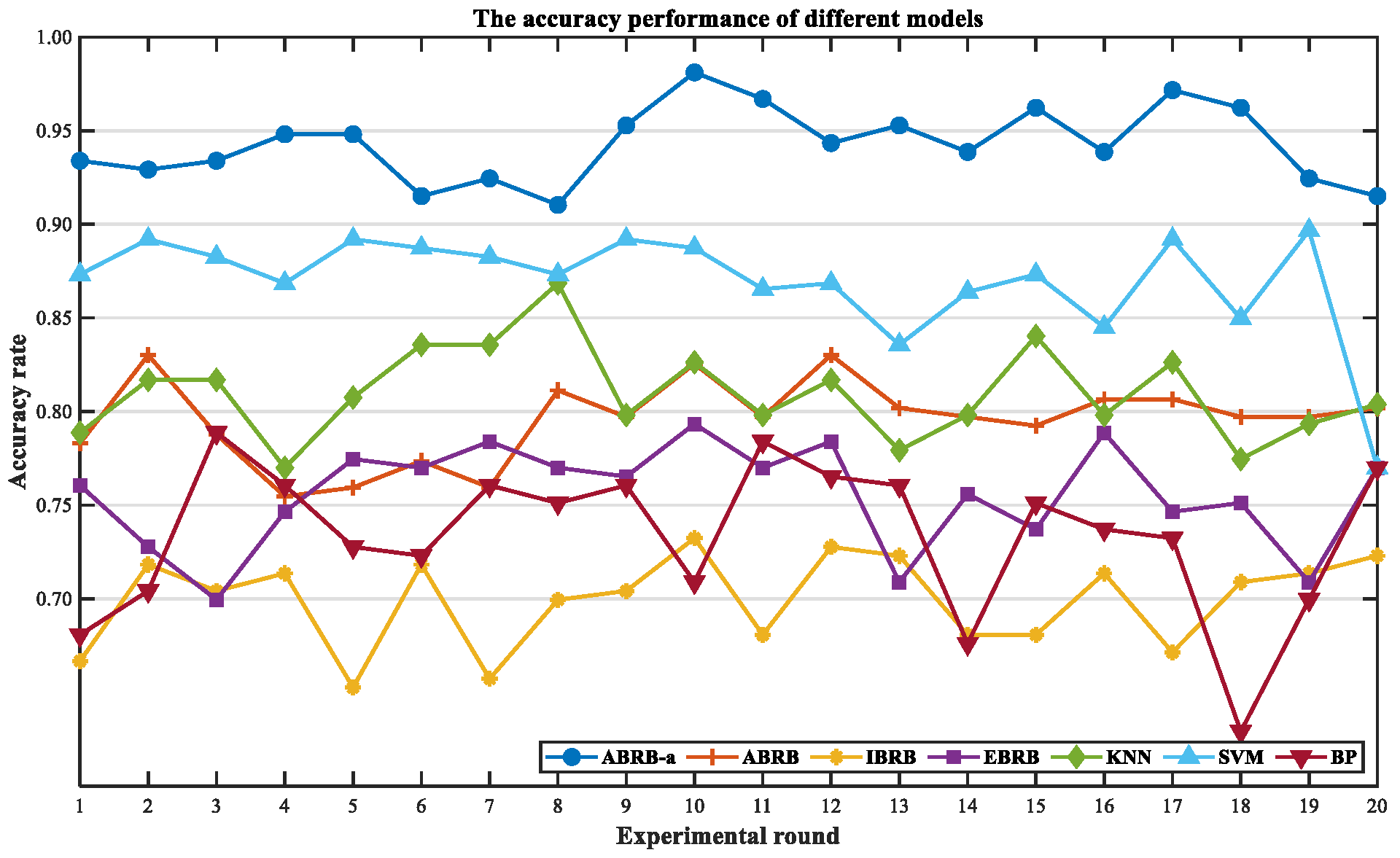
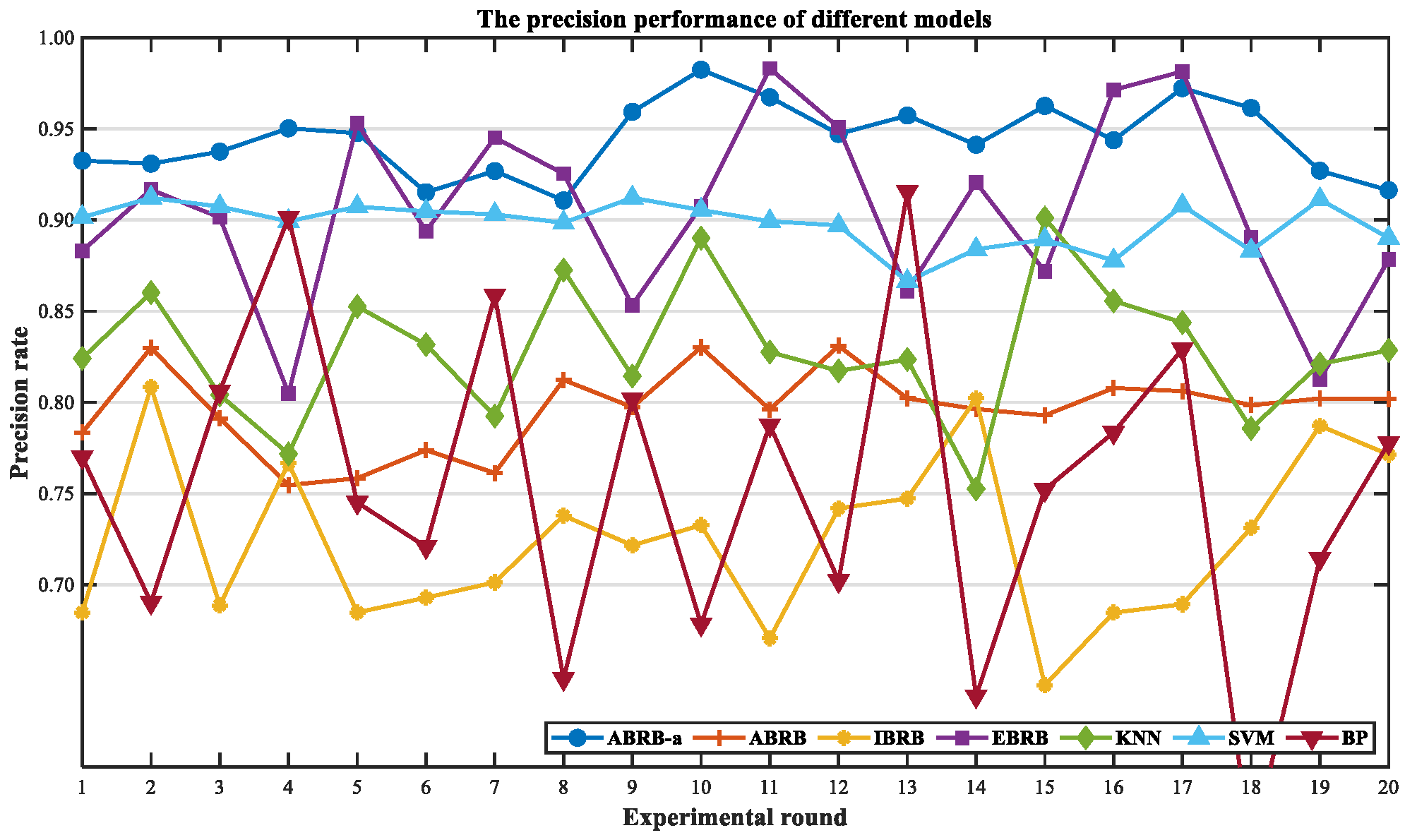
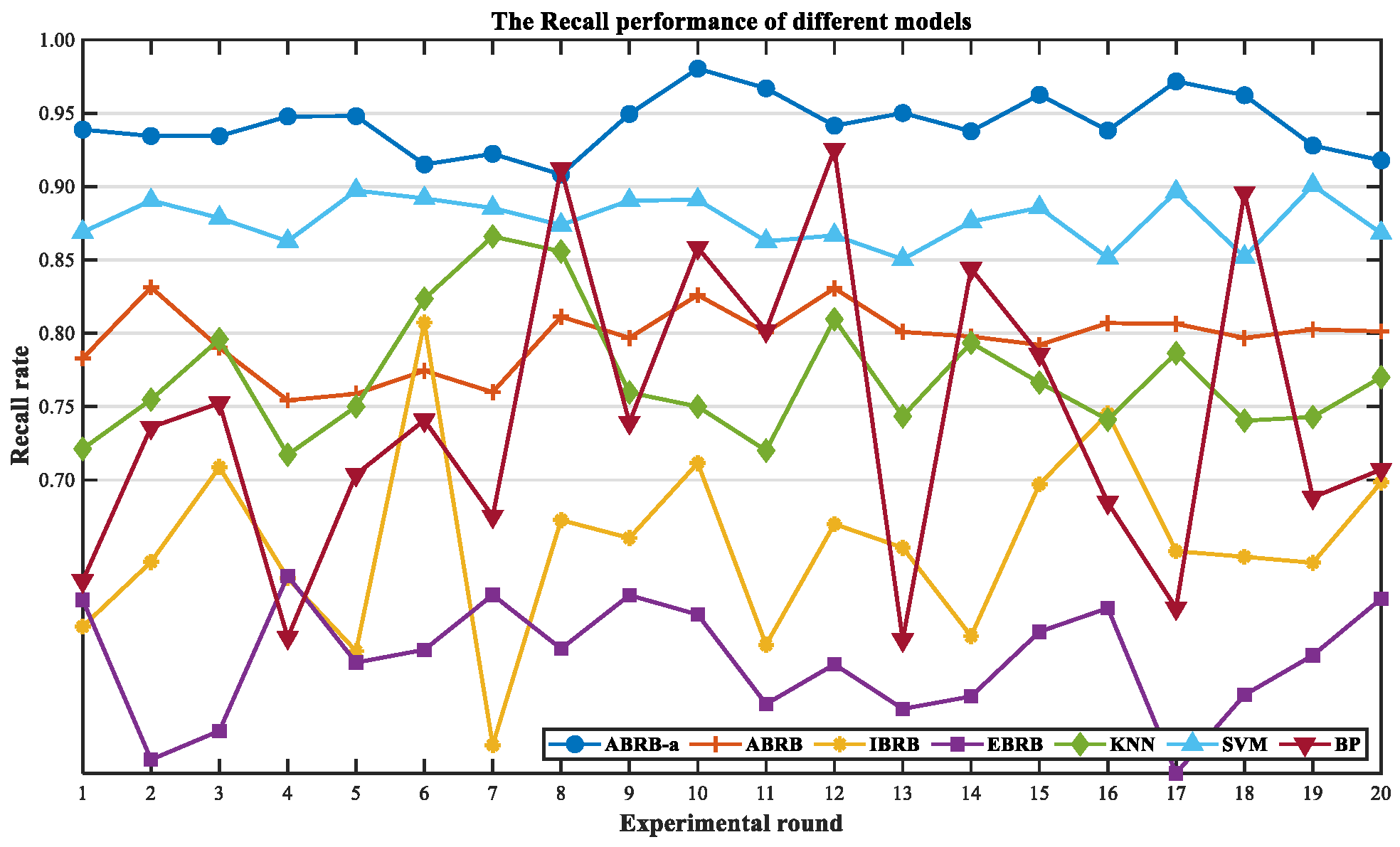
| Symbol Representation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| X1 | Past Exam Scores (PES) |
| X2 | Attendance Rate (AR) |
| X3 | Study Hours Per Week (SHPW) |
| X4 | Parental Education Level (PEL) |
| X5 | Extracurricular Activities (EA) |
| Attribute | Attribute | VL | L | M | H | VH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 1 | 10 | 17.25 | 24.5 | 31.75 | 39 |
| X2 | 1 | 50.117 | 62.5796 | 75.0423 | 87.505 | 99.9677 |
| X3 | 1 | 50 | 62.5 | 75 | 87.5 | 100 |
| X4 | 1 | 0 | 0.75 | 1.5 | 2.25 | 3 |
| X5 | 1 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 1 |
| Symbol Representation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Pass(P) |
| 1 | Fail(F) |
| NO | Attributes | Rule Weights | Reference Values | Output Belief Degree {P, F} |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PES = 1 | 1 | VL | {0.6,0.4} |
| 2 | 1 | L | {0.1,0.9} | |
| 3 | 1 | M | {0.8,0.2} | |
| 4 | 1 | H | {0.3,0.7} | |
| 5 | 1 | VH | {0.15,0.85} | |
| 6 | AR = 1 | 1 | VL | {0.25,0.75} |
| 7 | 1 | L | {0.45,0.55} | |
| 8 | 1 | M | {0.34,0.66} | |
| 9 | 1 | H | {0.85,0.15} | |
| 10 | 1 | VH | {0.95,0.05} | |
| 11 | SHPW = 1 | 1 | VL | {0.33,0.67} |
| 12 | 1 | L | {1,0} | |
| 13 | 1 | M | {0.55,0.45} | |
| 14 | 1 | H | {0.15,0.85} | |
| 15 | 1 | VH | {0,1} | |
| 16 | PEL = 1 | 1 | VL | {0.2,0.8} |
| 17 | 1 | L | {0.7,0.3} | |
| 18 | 1 | M | {0,1} | |
| 19 | 1 | H | {1,0} | |
| 20 | 1 | VH | {0.9,0.1} | |
| 21 | EA = 1 | 1 | VL | {0.25,0.75} |
| 22 | 1 | L | {0.85,0.15} | |
| 23 | 1 | M | {1,0} | |
| 24 | 1 | H | {0.1,0.9} | |
| 25 | 1 | VH | {0,1} |
| NO | Attributes | Rule Weights | Reference Values | Output Belief Degree {P, F} |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PES = 0.8698 | 0.4041 | VL | {0.03,0.97} |
| 2 | 0.3041 | L | {0.02,0.98} | |
| 3 | 0.2029 | M | {0.1,0.9} | |
| 4 | 0 | H | {0.84,0.16} | |
| 5 | 0.5407 | VH | {0.01,0.99} | |
| 6 | AR = 0.2544 | 0.4793 | VL | {0.03,0.97} |
| 7 | 0.3358 | L | {0,1} | |
| 8 | 0.0226 | M | {0.34,0.66} | |
| 9 | 0.1463 | H | {0.97,0.03} | |
| 10 | SHPW = 0.9559 | 0.8662 | VH | {1,0} |
| 11 | 0.9691 | VL | {0.01,0.99} | |
| 12 | 0.3046 | L | {0.02,0.98} | |
| 13 | 0 | M | {0.08,0.92} | |
| 14 | 0.3008 | H | {1,0} | |
| 15 | 0.9205 | VH | {1,0} | |
| 16 | PEL = 0.4761 | 0.0293 | VL | {0.2,0.8} |
| 17 | 0.0158 | L | {0.23,0.77} | |
| 18 | 0.1409 | M | {0.01,0.99} | |
| 19 | 0.0728 | H | {0.92,0.08} | |
| 20 | 0.0077 | VH | {0.77,0.23} | |
| 21 | EA = 0.5652 | 0.1603 | VL | {0,1} |
| 22 | 0.0747 | L | {0.4,0.6} | |
| 23 | 0.3699 | M | {0.53,0.47} | |
| 24 | 0.4480 | H | {0.58,0.42} | |
| 25 | 0.0313 | VH | {0.87,0.13} |
| Models | Parameter Settings |
|---|---|
| ABRB-a & BRBs | BRBs use the same parameter settings as ABRB-a |
| KNN | Number of nearest neighbors = 200; Weight function = ‘uniform’; Weight function = ‘uniform’; Parameter in distance measurement = 2 |
| SVM | Regularization parameter = 5; Kernel function type= ‘rbf’; Coefficient of kernel function = ‘auto’; Constant term in kernel function = 0 |
| BP | Number of neurons in hidden layers= [10, 2]; Activation function= ‘tansig’; Learning rate update strategy = ‘constant’; Maximum number of iterations = 10; |
| Data Partitioning | Method | mAccuracy (%) | mPrecision (%) | mRecall (%) | mF1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training:Testing 7:3 | ABRB-a | 94.27 | 94.45 | 94.28 | 94.25 |
| ABRB | 79.55 | 79.64 | 79.61 | 79.52 | |
| IBRB | 69.95 | 72.45 | 65.64 | 68.64 | |
| EBRB | 75.44 | 90.40 | 57.57 | 70.19 | |
| KNN | 81.00 | 82.86 | 77.04 | 79.74 | |
| SVM | 87.44 | 89.79 | 97.7 | 87.28 | |
| BP | 73.36 | 75.38 | 74.39 | 73.82 |
| Data Partitioning | Method | mAccuracy (%) | mPrecision (%) | mRecall (%) | mF1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training:Testing 6:4 | ABRB-a | 93.64 | 93.79 | 93.63 | 93.63 |
| ABRB | 78.98 | 79.12 | 79.07 | 78.93 | |
| IBRB | 69.37 | 63.31 | 81.06 | 71.1 | |
| EBRB | 73.24 | 89.16 | 52.48 | 66.07 | |
| KNN | 78.16 | 84.62 | 70.21 | 76.74 | |
| SVM | 86.61 | 89.45 | 86.06 | 86.23 | |
| BP | 70.42 | 77.69 | 68.24 | 72.66 |
| Data Partitioning | Method | mAccuracy (%) | mPrecision (%) | mRecall (%) | mF1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training:Testing 8:2 | ABRB-a | 94.72 | 94.82 | 94.67 | 94.68 |
| ABRB | 78.08 | 78.03 | 78.04 | 77.90 | |
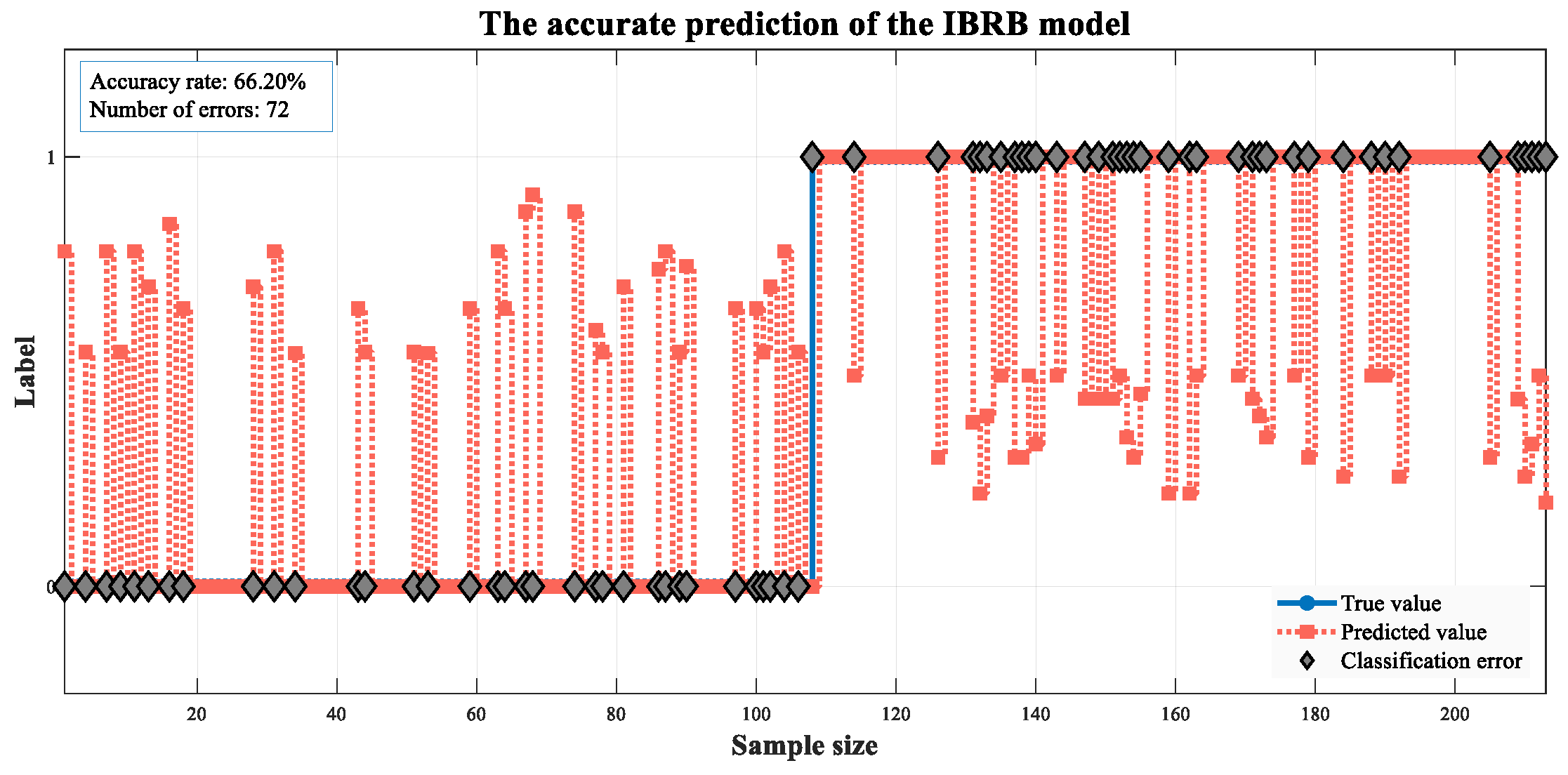
| IBRB | 71.13 | 71.21 | 68.12 | 69.63 | |
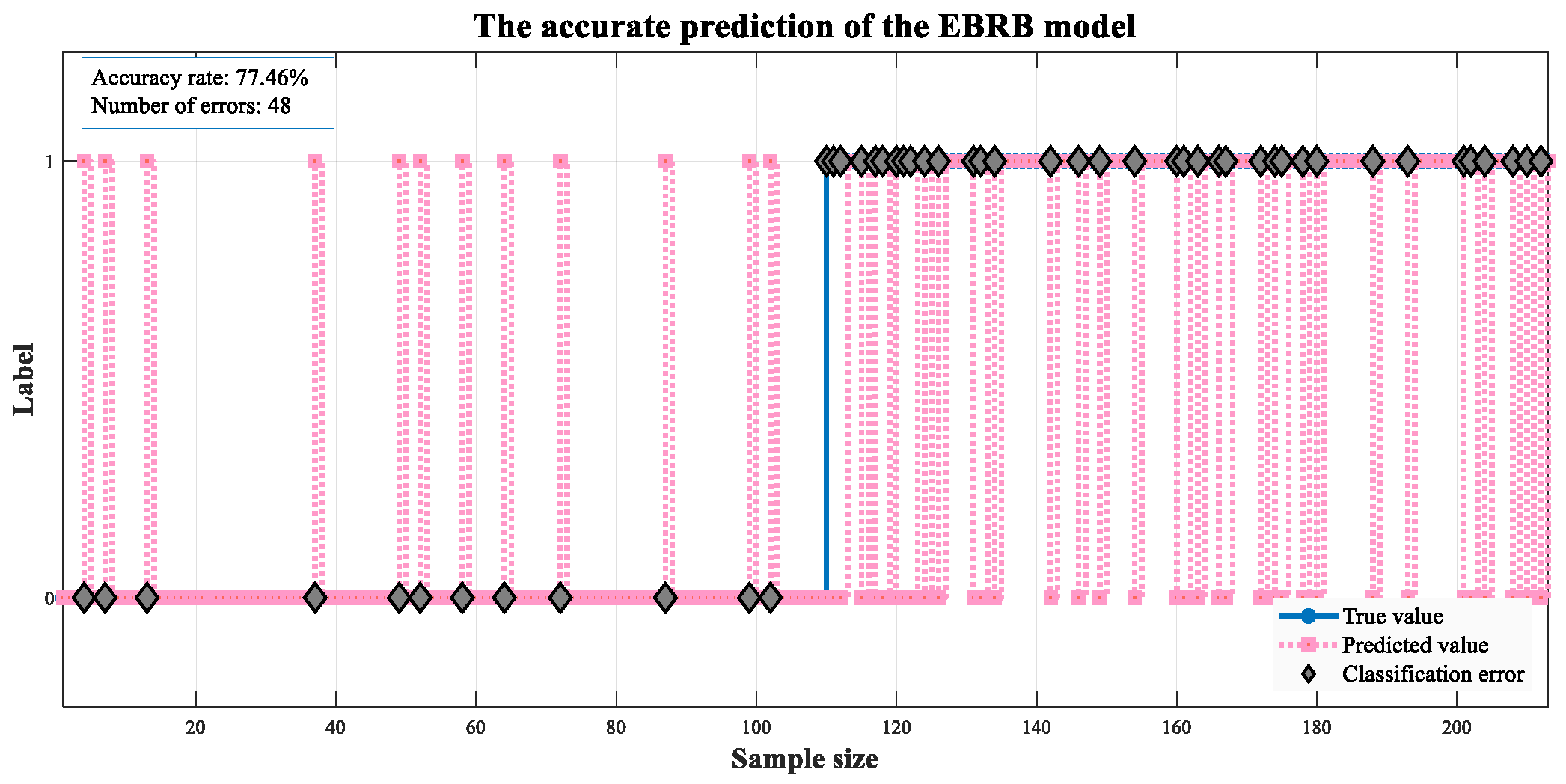
| EBRB | 77.46 | 97.87 | 59.74 | 74.19 | |
| KNN | 83.80 | 76.12 | 80.95 | 78.46 | |
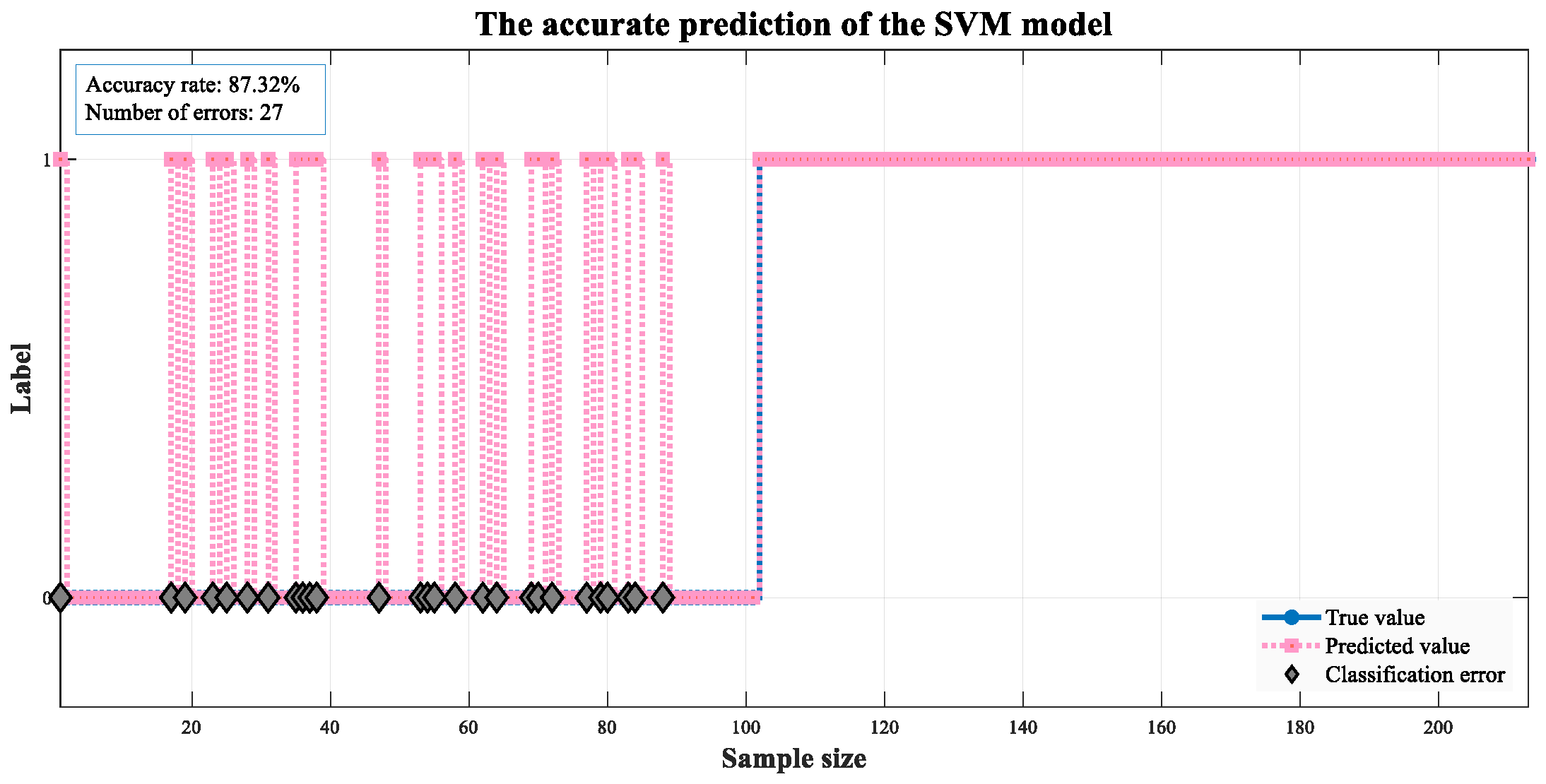
| SVM | 91.54 | 93.04 | 92.57 | 92.24 | |
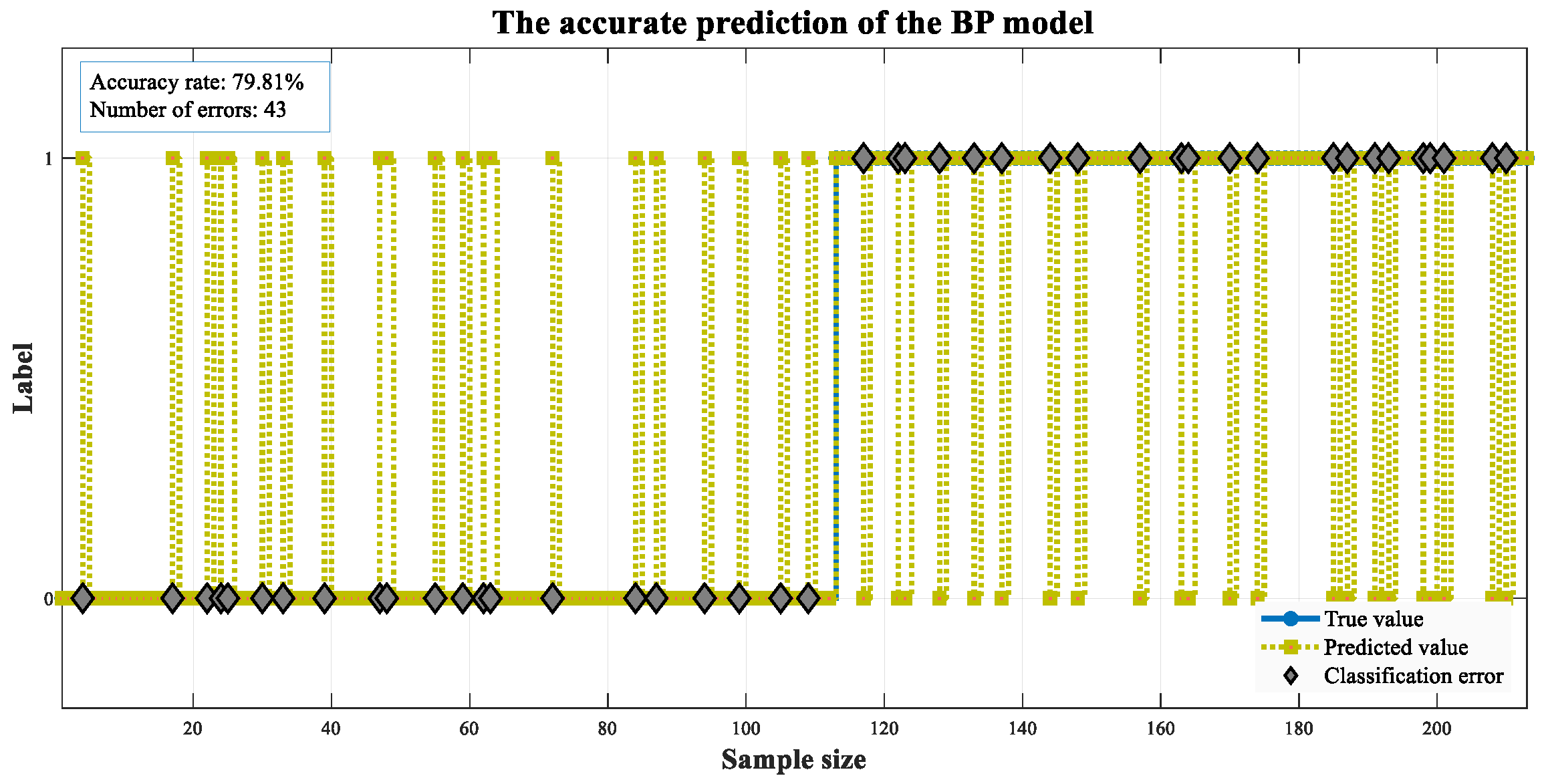
| BP | 80.28 | 82.26 | 70.83 | 76.12 |
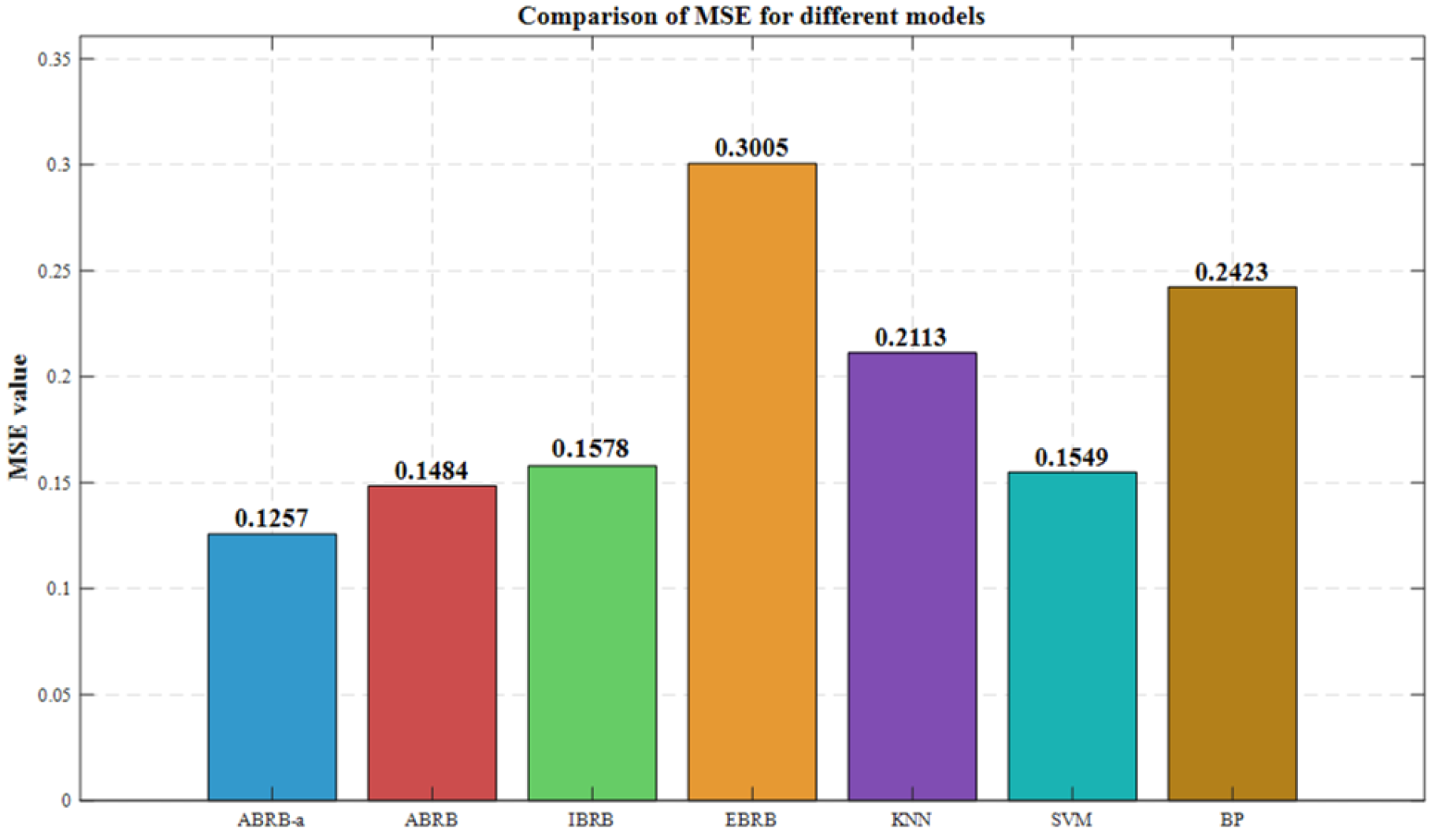
| Distance Constraint | MSE |
|---|---|
| Mahalanobis | 0.1257 |
| Euclidean | 0.1855 |
| Data Types | mAccuracy (%) | mPrecision (%) | mRecall (%) | mF1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw data | 94.27 | 94.45 | 94.28 | 94.25 |
| P = 0.5 | 92.3 | 92.52 | 92.28 | 92.25 |
| P = 0.7 | 88.68 | 88.08 | 88.02 | 87.73 |
| Method | mAccuracy (%) | mPrecision (%) | mRecall (%) | mF1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABRB-a | 95 | 96.16 | 94.66 | 94.65 |
| ABRB | 83.78 | 85.91 | 84.51 | 83.23 |
| IBRB | 74.76 | 74.09 | 60.85 | 61.21 |
| EBRB | 70.94 | 78.44 | 80.07 | 79.01 |
| KNN | 69.72 | 55.5 | 53.32 | 53.78 |
| SVM | 64.04 | 51.90 | 41.96 | 43.92 |
| BP | 73.05 | 56.19 | 53.64 | 52.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Li, K.; Zhu, H.; Yang, C.; Han, J. An Approximate Belief Rule Base Student Examination Passing Prediction Method Based on Adaptive Reference Point Selection Using Symmetry. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101687
Li J, Li K, Zhu H, Yang C, Han J. An Approximate Belief Rule Base Student Examination Passing Prediction Method Based on Adaptive Reference Point Selection Using Symmetry. Symmetry. 2025; 17(10):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101687
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jingying, Kangle Li, Hailong Zhu, Cuiping Yang, and Jinsong Han. 2025. "An Approximate Belief Rule Base Student Examination Passing Prediction Method Based on Adaptive Reference Point Selection Using Symmetry" Symmetry 17, no. 10: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101687
APA StyleLi, J., Li, K., Zhu, H., Yang, C., & Han, J. (2025). An Approximate Belief Rule Base Student Examination Passing Prediction Method Based on Adaptive Reference Point Selection Using Symmetry. Symmetry, 17(10), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101687






