Temporal-Aware and Intent Contrastive Learning for Sequential Recommendation
Abstract
1. Introduction
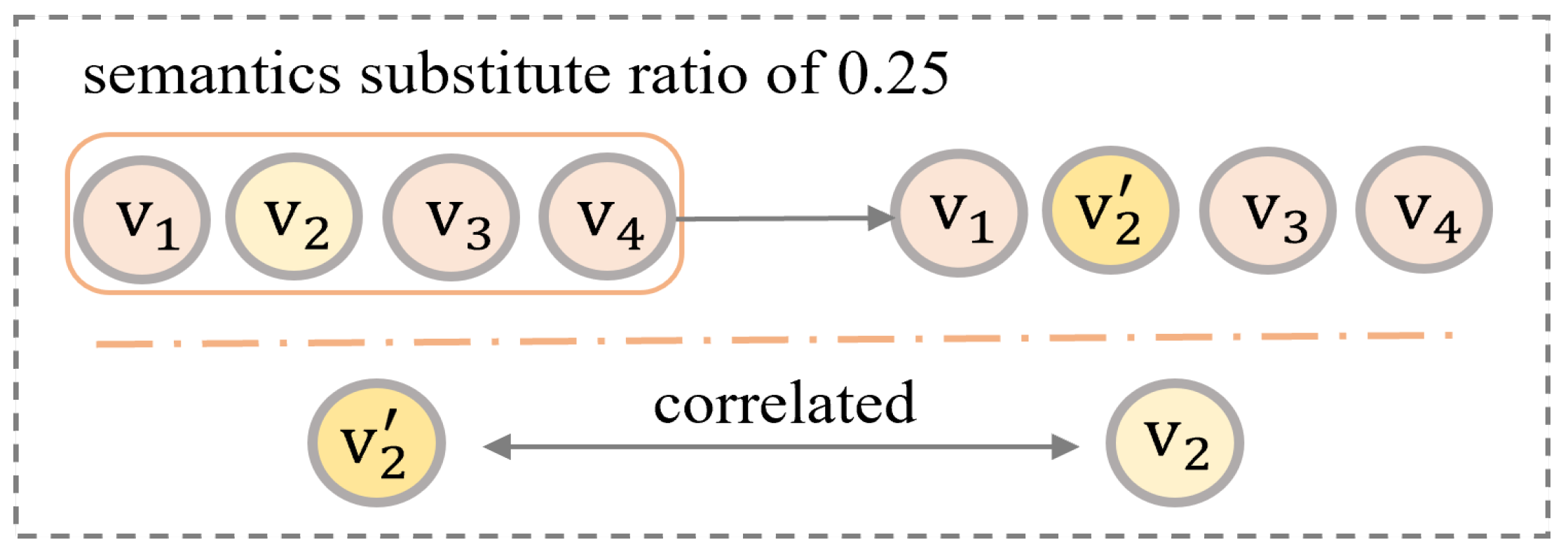
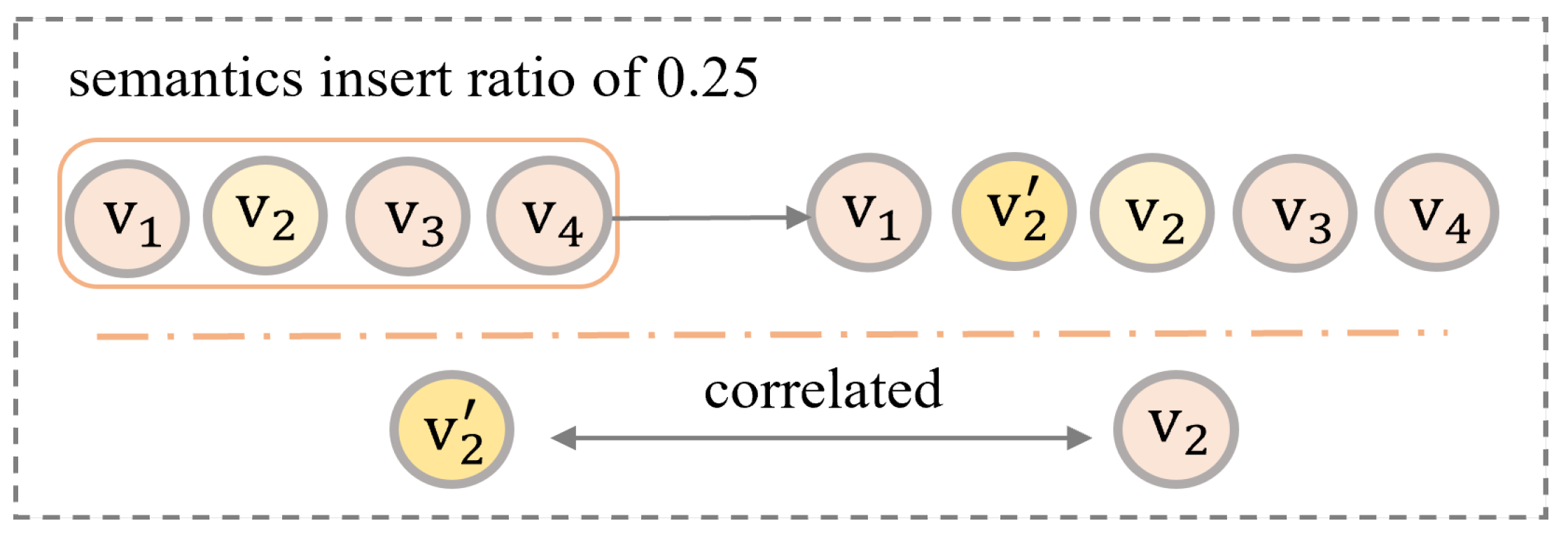
- In terms of data augmentation, a semantic enhancement module based on user preferences is designed to improve existing random augmentation methods. On one hand, two semantic augmentation operators—semantic replacement and semantic insertion—are proposed. By incorporating user rating factors during augmented view construction, these operators generate enhanced sequences that better align with user preferences. On the other hand, a hyperparameter is introduced to dynamically distinguish between long and short sequences, controlling the supplemental intensity of additional self-supervised signals to the original user interaction sequence. This effectively mitigates sequence length skewness, thereby improving the confidence of positive sample pairs.
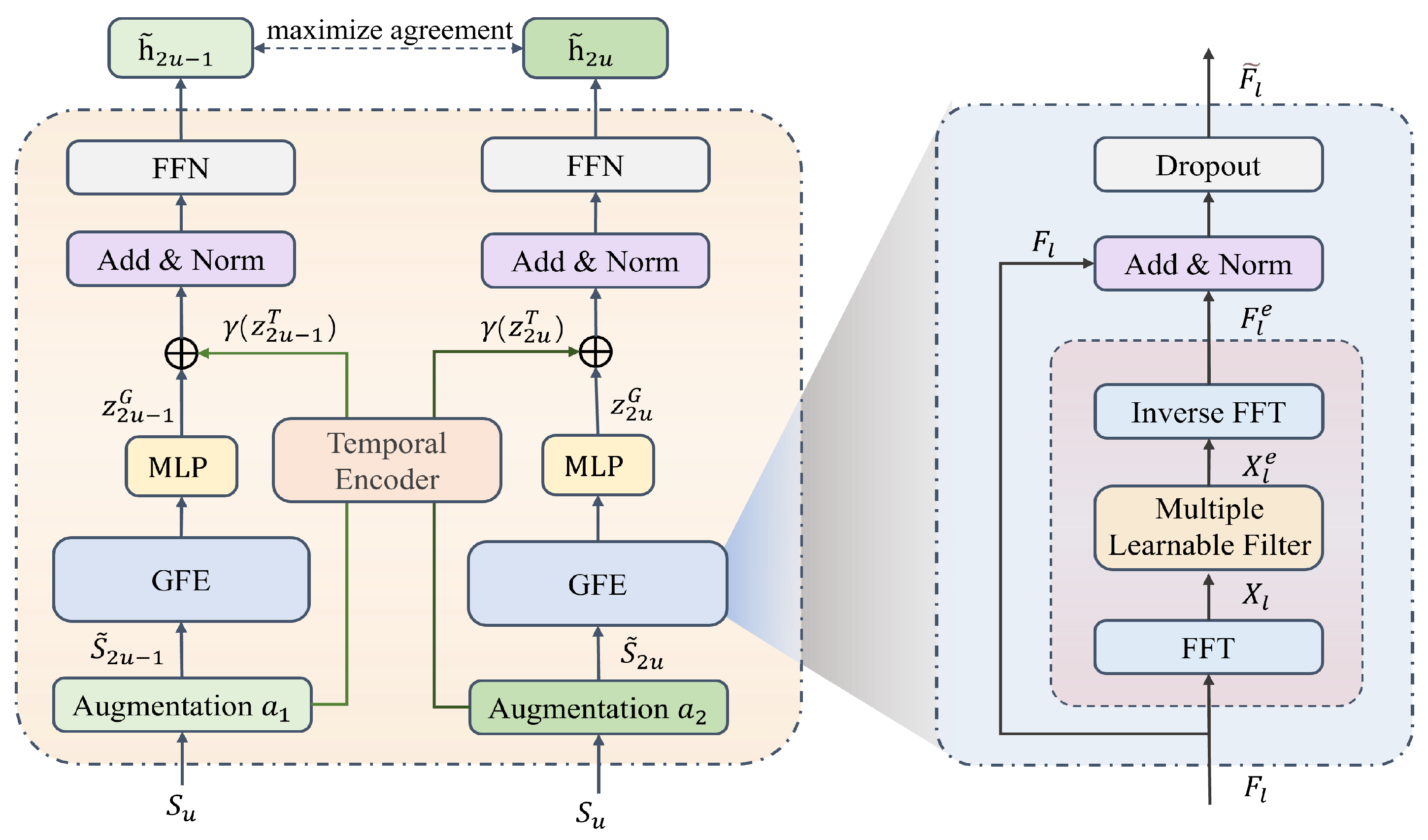
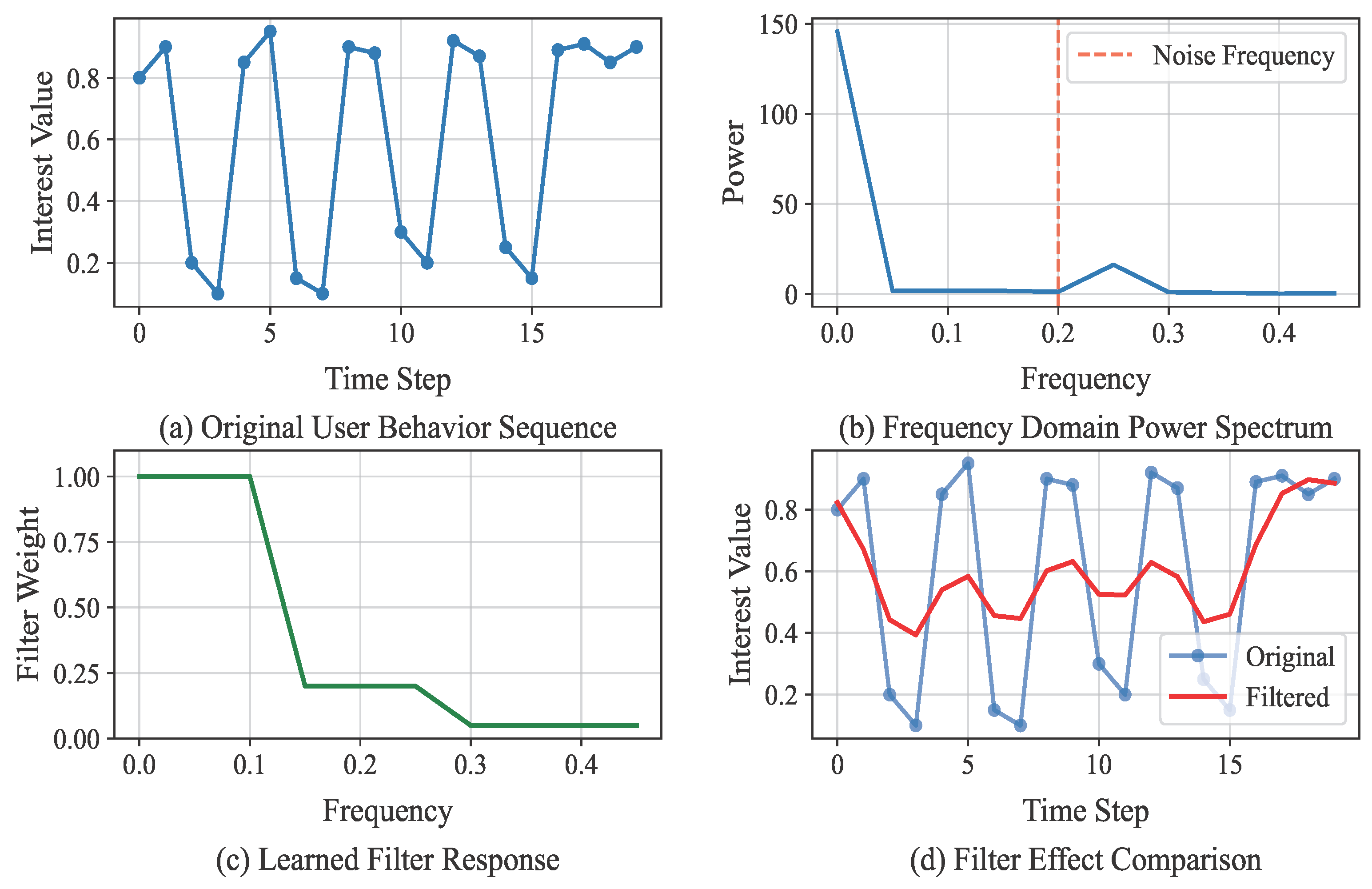
- For sequence modeling, a model-enhanced temporal-aware network is constructed to replace the original Transformer architecture. First, a frequency filter is introduced to adaptively attenuate noisy information in the frequency domain, capturing global features and long-term dependencies in user behavior. Second, an auxiliary temporal dependency modeling encoder is introduced to mitigate the embedding collapse problem caused by using a single sequence encoder, while simultaneously capturing short-term interest dynamics in user behavior. The complementary enhancement between the two modules enables the fusion of diverse temporal dependencies from multiple perspectives, thereby strengthening the temporal perception capability for both long- and short-term user behavior patterns under global patterns.
2. Task Definition
2.1. Problem Formulation
2.2. Sequential Recommendation Task
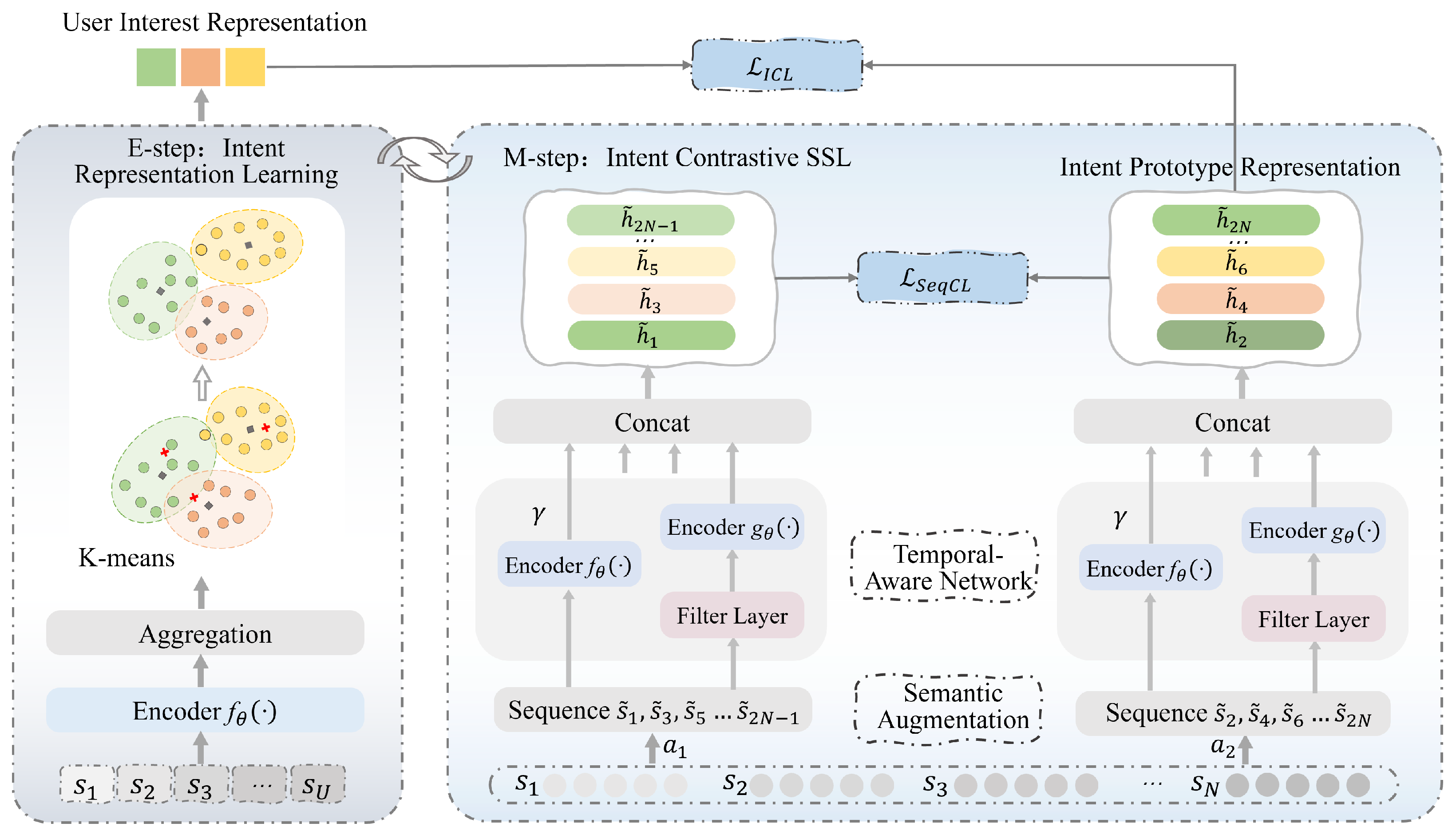
3. The Proposed Model
3.1. Semantic Enhancement Module
3.1.1. Random Augmentation Operators
3.1.2. Semantic Augmentation Operators
3.1.3. Semantic Enhancement Strategy
3.1.4. Contrastive Learning
3.2. Temporal-Aware Network
3.2.1. Global Feature Extraction
3.2.2. Temporal Dependency Modeling
3.3. Intent Contrastive Learning
3.4. Multi-Task Training
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Baseline Methods
- Non-sequential models: BPR-MF [36] employs matrix factorization to represent users and items as low-dimensional vectors, optimizing these vectors to maximally capture preference relationships between users and items.
- Standard sequential models: GRU4Rec [9] is a prevalent RNN variant designed to address the vanishing gradient problem in traditional RNNs when processing long sequences. SASRec [12] employs the self-attention mechanism from Transformer models as its core approach to effectively capture sequential dependencies in users’ historical behaviors.
- Sequential models with additional SSL: BERT4Rec [13] adopts a bidirectional self-attention mechanism by reformulating the next-item prediction task as a Cloze task, enabling the model to simultaneously capture relationships between items and their contexts. CL4SRec [18] integrates contrastive SSL with Transformer-based sequential recommendation models, enhancing the model’s generalization capability through augmentation operators such as cropping, masking, and reordering.
- Sequential models considering latent Intents: DSSRec [25] employs a seq2seq architecture to process user behavior sequences while performing optimization in latent space. ICLRec [27] utilizes contrastive learning to capture latent intents in user sequences, introducing intent variables into the sequential recommendation model through clustering. IOCRec [28] applies contrastive learning by selecting users’ primary intents for denoising, thereby creating high-quality intent views. ELCRec [30] integrates behavior representation learning into an end-to-end clustering framework, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the model.
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Overall Performance Comparison
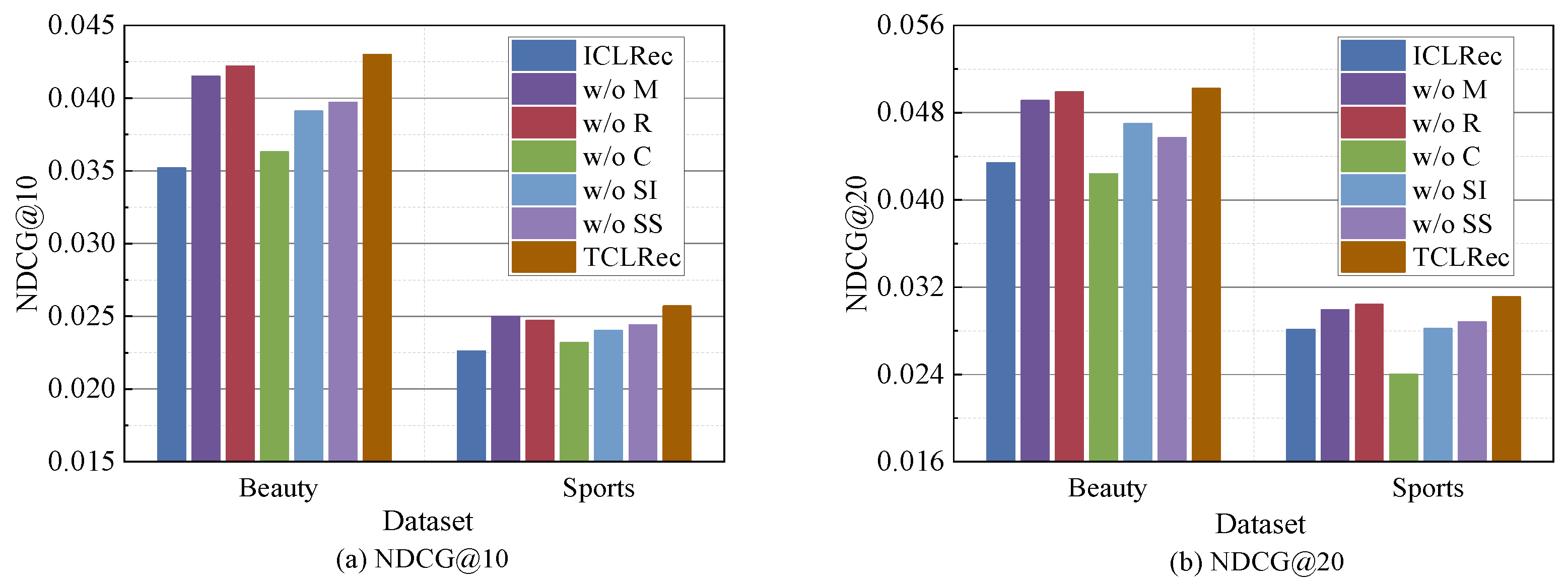
4.5. Ablation Study of TCLRec
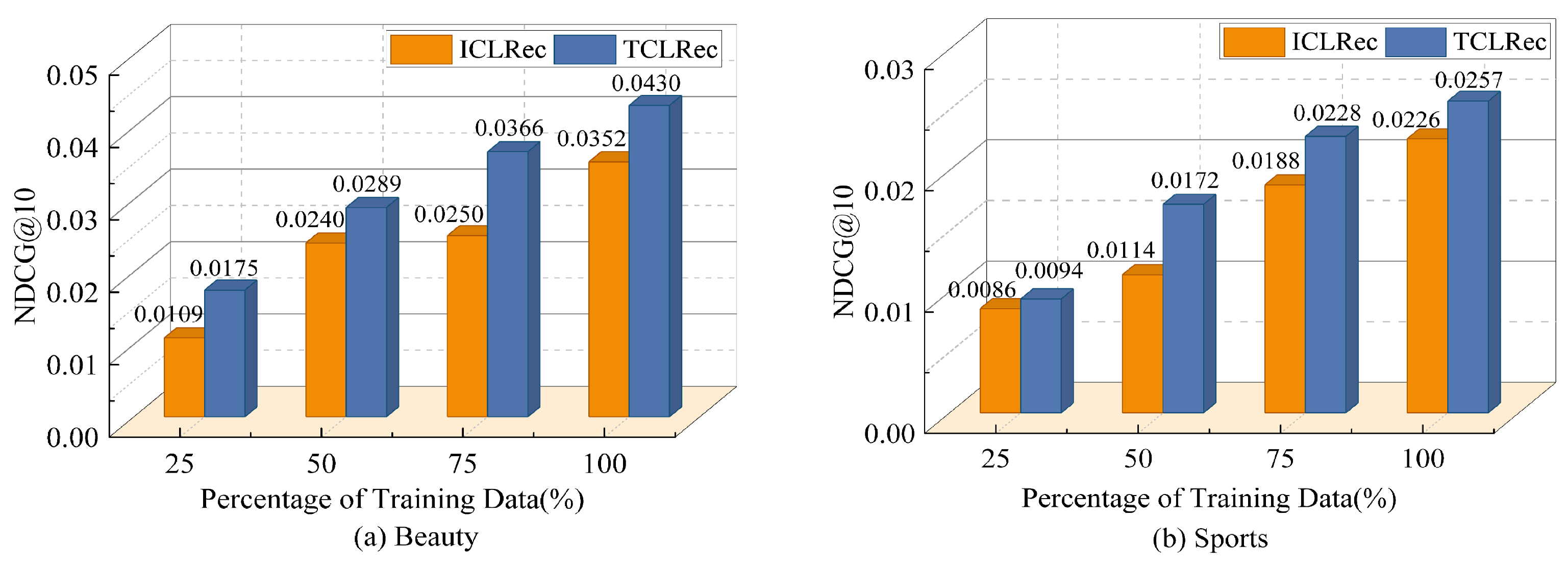
4.6. Effectiveness of Data Augmentation
4.7. Augmentation Analysis
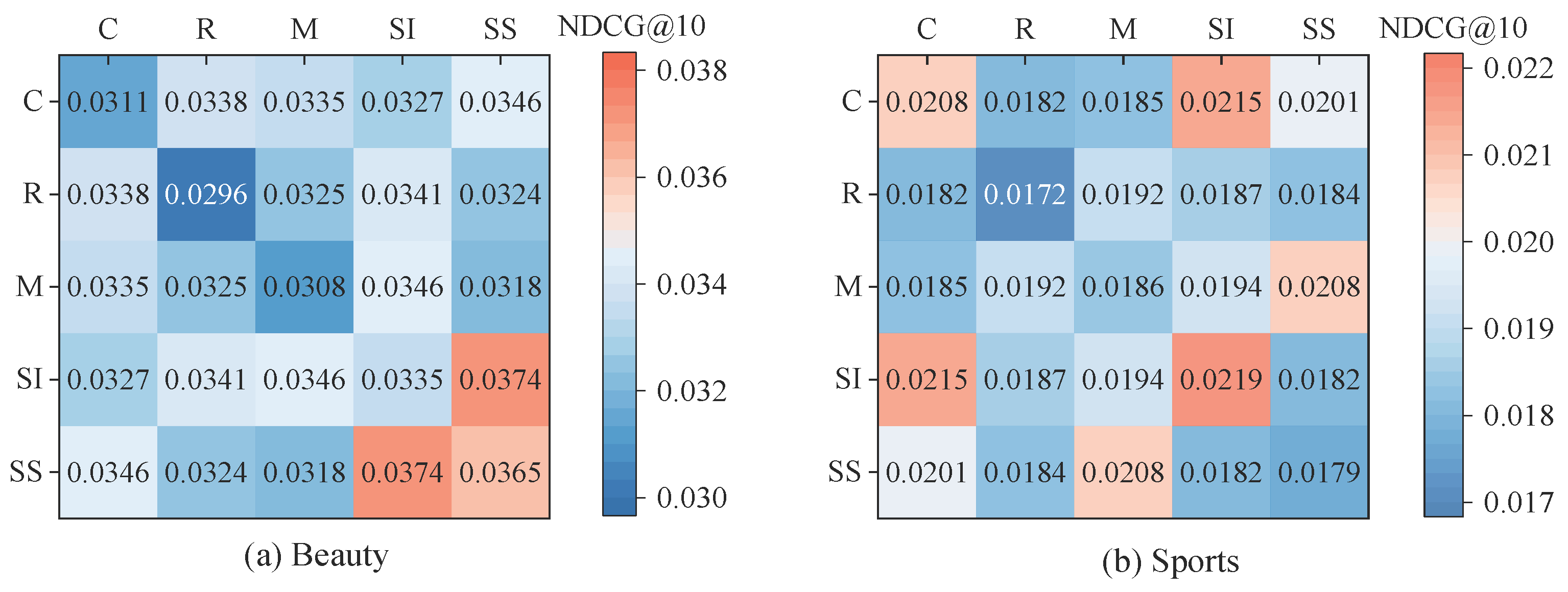
4.7.1. Leave-One-Out Comparison
4.7.2. Pairwise Comparison
4.7.3. Augmentation Set for Short Sequences
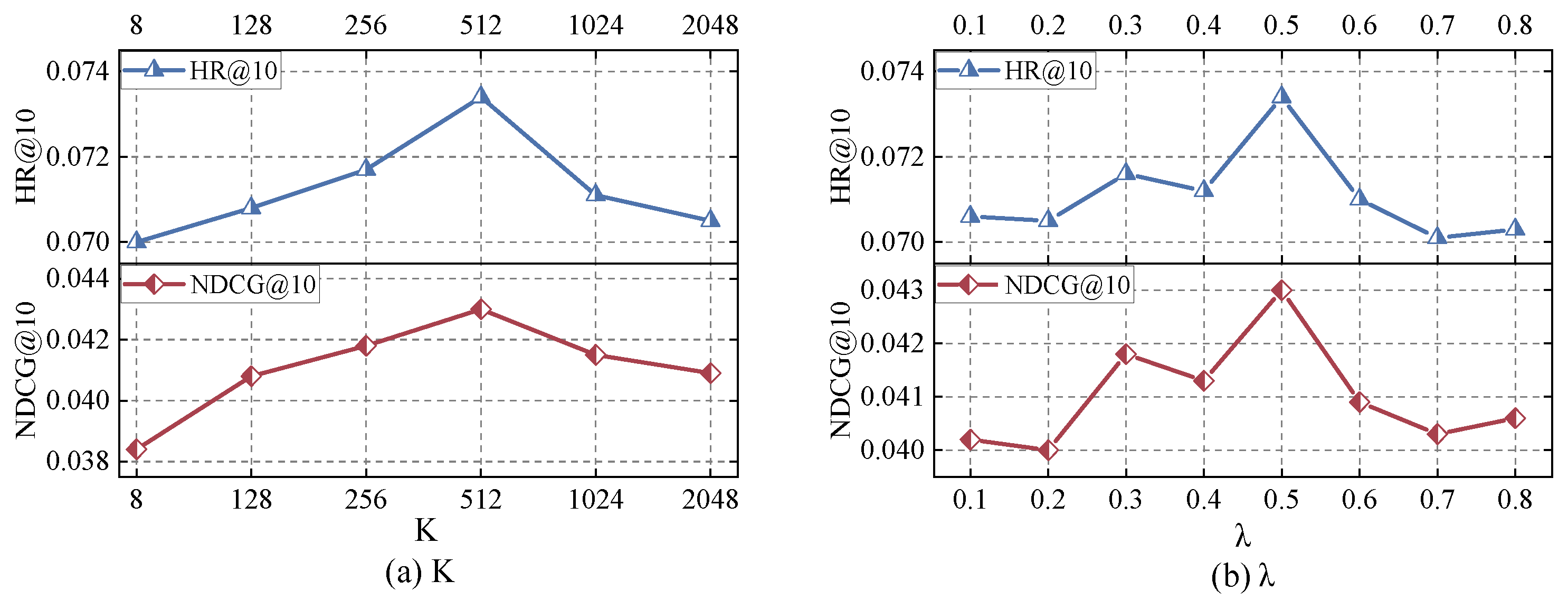
4.8. Parametric Analysis
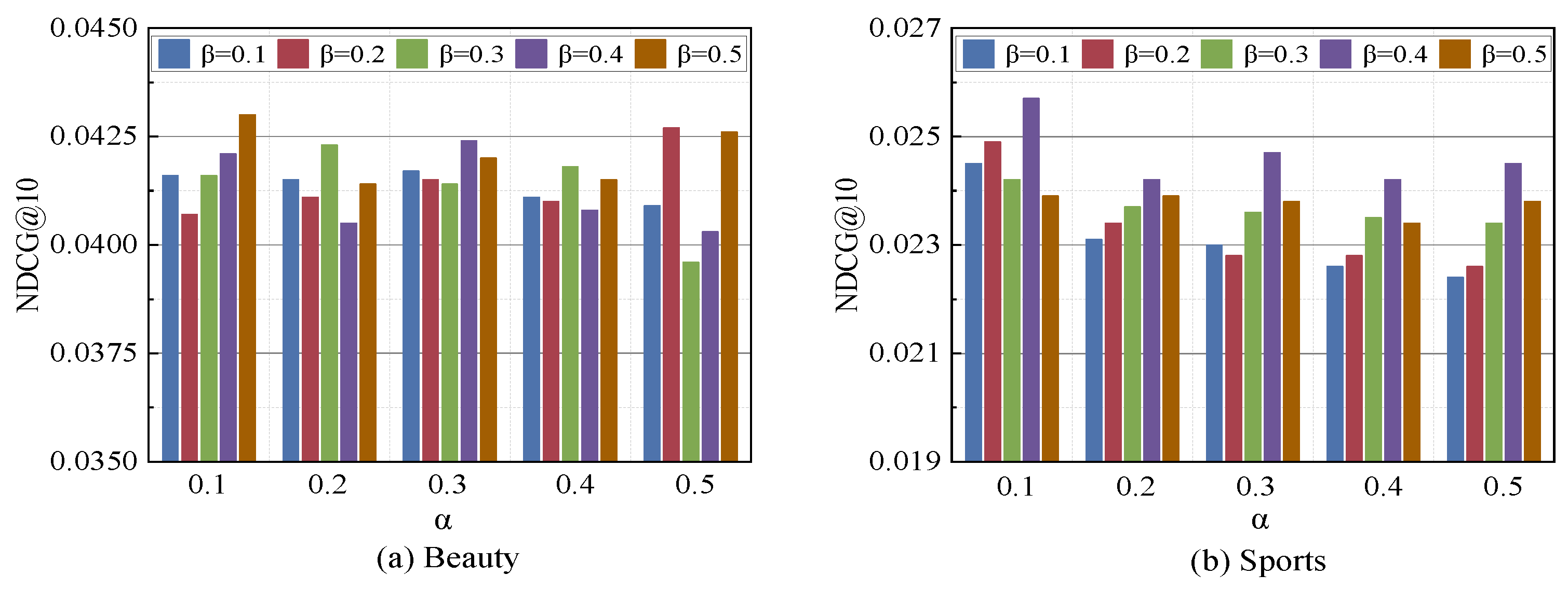
4.8.1. Performance Impact of Semantic Augmentation Ratios
4.8.2. Performance Impact of Long-Short Sequence Threshold
4.8.3. Performance Impact of Intent Contrastive Learning Parameter Settings
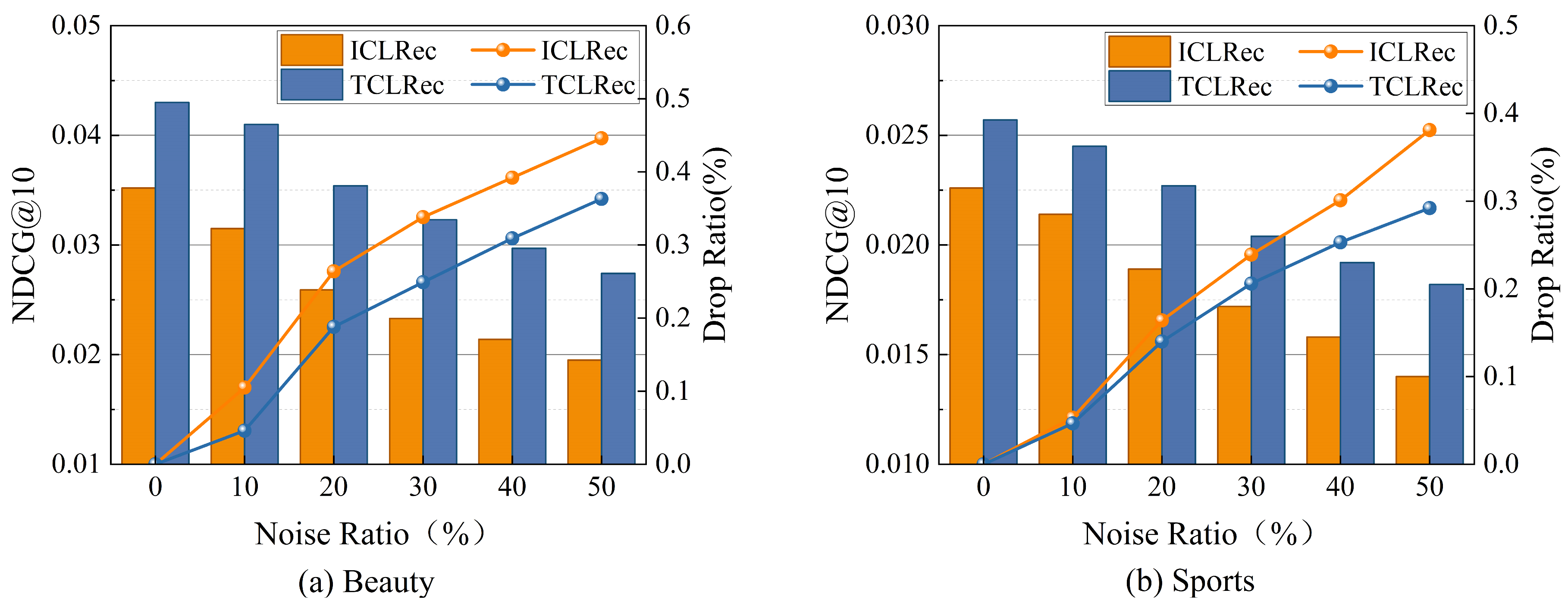
4.9. Robustness Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, C.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z. Matrix factorization recommendation algorithm based on attention interaction. Symmetry 2024, 16, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Wang, M.; Peng, J.; Shen, D. Differential Weighting and Flexible Residual GCN-Based Contrastive Learning for Recommendation. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Chen, C.; Lin, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Zheng, X. Personalized Behavior-Aware Transformer for Multi-Behavior Sequential Recommendation. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 6321–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Li, D.; Gu, H.; Lu, T.; Zhang, P.; Shang, L.; Gu, N. Oracle-guided Dynamic User Preference Modeling for Sequential Recommendation. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Hannover, Germany, 10–14 March 2025; pp. 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; McAuley, J. Fusing similarity models with markov chains for sparse sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), Barcelona, Spain, 12–15 December 2016; pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidasi, B.; Tikk, D. General factorization framework for context-aware recommendations. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2016, 30, 342–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Yin, H.; Nguyen, Q.V.H.; Peng, W.C.; Li, X.; Zhou, X. Sequence-aware factorization machines for temporal predictive analytics. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 36th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Dallas, TX, USA, 20–24 April 2020; pp. 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Ahmed, A.; Beutel, A.; Smola, A.J.; Jing, H. Recurrent recommender networks. In Proceedings of the Tenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Cambridge, UK, 6–10 February 2017; pp. 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidasi, B.; Karatzoglou, A.; Baltrunas, L.; Tikk, D. Session-based recommendations with recurrent neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damak, K.; Khenissi, S.; Nasraoui, O. Debiasing the cloze task in sequential recommendation with bidirectional transformers. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 August 2022; pp. 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Shi, H.; Zhao, P.; Wang, D.; Sheng, V.S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, L. Contrastive learning with bidirectional transformers for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivic, P.; Vazquez, H.; Sánchez, J. Scaling Sequential Recommendation Models with Transformers. In Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Pei, C.; Lin, X.; Ou, W.; Jiang, P. BERT4Rec: Sequential recommendation with bidirectional encoder representations from transformer. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Beijing, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Gao, C.; He, X.; Jin, D.; Li, Y. Multi-behavior recommendation with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Virtual Event, 25–30 July 2020; pp. 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y.; Dai, P.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Pei, J.; Bo, L. Knowledge-enhanced hierarchical graph transformer network for multi-behavior recommendation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 19–21 May 2021; Volume 35, pp. 4486–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yu, H.; Zhao, W.X.; Wen, J.R. Filter-enhanced MLP is all you need for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference, Lyon, France, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 2388–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wen, J.R. S3-rec: Self-supervised learning for sequential recommendation with mutual information maximization. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Virtual Event, 19–23 October 2020; pp. 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Sun, F.; Liu, Z.; Wu, S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Ding, B.; Cui, B. Contrastive learning for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 38th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 9–12 May 2022; pp. 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, P.S.; McAuley, J.; Xiong, C. Contrastive self-supervised sequential recommendation with robust augmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.06479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Huang, Z.; Yin, H.; Wang, Z. Contrastive learning for representation degeneration problem in sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Virtual Event, 21–25 February 2022; pp. 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lim, E.P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, T. Explanation guided contrastive learning for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Atlanta, GA, USA, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 2017–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yue, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J. Unbiased and Robust: External Attention-enhanced Graph Contrastive Learning for Cross-domain Sequential Recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Shanghai, China, 1–4 December 2023; pp. 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Yao, L. Dual contrastive transformer for hierarchical preference modeling in sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 46th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Taipei, Taiwan, 23–27 July 2023; pp. 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, P.; Fang, J.; Zhuang, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, V. Meta-optimized contrastive learning for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 46th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Taipei, Taiwan, 23–27 July 2023; pp. 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, H.; Cui, P.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W. Disentangled self-supervision in sequential recommenders. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Virtual Event, 6–10 July 2020; pp. 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yao, J.; Liu, N.; Zhou, J.; Yang, H.; Hu, X. Sparse-interest network for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Virtual, 8–12 March 2021; pp. 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; McAuley, J.; Xiong, C. Intent contrastive learning for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference, Lyon, France, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, A.; Zhao, M.; Yu, J.; Zhu, K.; Jin, D.; Yu, M.; Yu, R. Multi-intention oriented contrastive learning for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Singapore, 27 February–3 March 2023; pp. 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, P.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, F.; Sheng, V.S. Intent contrastive learning with cross subsequences for sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Merida, Mexico, 4–8 March 2024; pp. 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Xia, J.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhong, W. End-to-end learnable clustering for intent learning in recommendation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 5913–5949. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, Y.L.; Xie, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, S. Is contrastive learning necessary? a study of data augmentation vs contrastive learning in sequential recommendation. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2024, Singapore, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 3854–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S. Sequential recommendation with multiple contrast signals. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2023, 41, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Huang, F.; Kim, S. TransGNN: Harnessing the collaborative power of transformers and graph neural networks for recommender systems. In Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, M.; Yu, P.S.; Xiong, C. Improving contrastive learning with model augmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.15508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, J.; Targett, C.; Shi, Q.; Van Den Hengel, A. Image-based recommendations on styles and substitutes. In Proceedings of the 38th international ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 9–13 August 2015; pp. 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendle, S.; Freudenthaler, C.; Gantner, Z.; Schmidt-Thieme, L. BPR: Bayesian personalized ranking from implicit feedback. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1205.2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, T.T.; Pfister, F.M.; Pichler, D.; Endo, S.; Lang, M.; Hirche, S.; Fietzek, U.; Kulić, D. Data augmentation of wearable sensor data for parkinson’s disease monitoring using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Glasgow, UK, 13–17 November 2017; pp. 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Sun, L.; Yang, F.; Song, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, H. Time series data augmentation for deep learning: A survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zou, G.; Zhou, P.; Yirui, W.; Chen, Z.; Su, H.; Wang, H.; Gong, Z. Sparse enhanced network: An adversarial generation method for robust augmentation in sequential recommendation. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2024, 38, 8283–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Users | Items | Interactions | Avg. Length | Sparsity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beauty | 22,363 | 12,101 | 198,502 | 8.9 | 99.73 |
| Sports | 35,598 | 18,357 | 296,337 | 8.3 | 99.95 |
| LastFM | 1090 | 3646 | 52,551 | 48.2 | 98.68 |
| Dataset | Metric | BPR-MF | GRU4Rec | SASRec | Bert4Rec | CL4SRec | DSSRec | ICLRec | IOCRec | ELCRec | TCLRec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beauty | HR@5 | 0.0178 | 0.0180 | 0.0377 | 0.0360 | 0.0401 | 0.0408 | 0.0428 | 0.0427 | 0.0478 | 0.0514 |
| HR@10 | 0.0296 | 0.0284 | 0.0624 | 0.0601 | 0.0642 | 0.0616 | 0.0668 | 0.0676 | 0.0712 | 0.0734 | |
| HR@20 | 0.0474 | 0.0478 | 0.0894 | 0.0984 | 0.0974 | 0.0894 | 0.0993 | 0.1005 | 0.0994 | 0.1019 | |
| NDCG@5 | 0.0109 | 0.0116 | 0.0241 | 0.0216 | 0.0268 | 0.0263 | 0.0269 | 0.0276 | 0.0308 | 0.0359 | |
| NDCG@10 | 0.0147 | 0.0150 | 0.0342 | 0.0300 | 0.0345 | 0.0329 | 0.0352 | 0.0357 | 0.0387 | 0.0430 | |
| NDCG@20 | 0.0192 | 0.0186 | 0.0386 | 0.0391 | 0.0428 | 0.0399 | 0.0434 | 0.0440 | 0.0462 | 0.0502 | |
| Sports | HR@5 | 0.0123 | 0.0162 | 0.0214 | 0.0217 | 0.0231 | 0.0209 | 0.0264 | 0.0258 | 0.0265 | 0.0306 |
| HR@10 | 0.0215 | 0.0258 | 0.0333 | 0.0359 | 0.0369 | 0.0328 | 0.0419 | 0.0412 | 0.0410 | 0.0459 | |
| HR@20 | 0.0369 | 0.0421 | 0.0500 | 0.0604 | 0.0557 | 0.0499 | 0.0637 | 0.0624 | 0.0634 | 0.0674 | |
| NDCG@5 | 0.0076 | 0.0103 | 0.0144 | 0.0143 | 0.0146 | 0.0139 | 0.0176 | 0.0169 | 0.0177 | 0.0209 | |
| NDCG@10 | 0.0105 | 0.0142 | 0.0177 | 0.0190 | 0.0191 | 0.0178 | 0.0226 | 0.0219 | 0.0224 | 0.0257 | |
| NDCG@20 | 0.0144 | 0.0186 | 0.0218 | 0.0251 | 0.0238 | 0.0221 | 0.0281 | 0.0272 | 0.0280 | 0.0311 | |
| LastFM | HR@5 | 0.0191 | 0.0239 | 0.0346 | 0.0376 | 0.0312 | 0.0379 | 0.0303 | 0.0441 | 0.0266 | 0.0460 |
| HR@10 | 0.0365 | 0.0358 | 0.0543 | 0.0581 | 0.0143 | 0.0588 | 0.0468 | 0.0608 | 0.0339 | 0.0649 | |
| HR@20 | 0.0541 | 0.0495 | 0.0771 | 0.0862 | 0.0798 | 0.0869 | 0.0688 | 0.0964 | 0.0514 | 0.1016 | |
| NDCG@5 | 0.0144 | 0.0155 | 0.0250 | 0.0263 | 0.0213 | 0.0269 | 0.0193 | 0.0318 | 0.0185 | 0.0344 | |
| NDCG@10 | 0.0188 | 0.0194 | 0.0315 | 0.0332 | 0.0253 | 0.0338 | 0.0246 | 0.0362 | 0.0208 | 0.0409 | |
| NDCG@20 | 0.0246 | 0.0228 | 0.0374 | 0.0400 | 0.0343 | 0.0401 | 0.0300 | 0.0484 | 0.0252 | 0.0498 |
| Dataset | Metric | ICLRec | TCLRec-1 | TCLRec-2 | TCLRec-3 | TCLRec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beauty | HR@5 | 0.0428 | 0.0495 | 0.0479 | 0.0487 | 0.0514 |
| HR@10 | 0.0668 | 0.0723 | 0.0717 | 0.0719 | 0.0734 | |
| HR@20 | 0.0993 | 0.1008 | 0.0922 | 0.1001 | 0.1019 | |
| NDCG@5 | 0.0269 | 0.0336 | 0.0322 | 0.0326 | 0.0359 | |
| NDCG@10 | 0.0352 | 0.0407 | 0.0398 | 0.0392 | 0.0430 | |
| NDCG@20 | 0.0434 | 0.0483 | 0.0475 | 0.0491 | 0.0502 | |
| Sports | HR@5 | 0.0264 | 0.0270 | 0.0269 | 0.0279 | 0.0306 |
| HR@10 | 0.0419 | 0.0430 | 0.0428 | 0.0435 | 0.0459 | |
| HR@20 | 0.0637 | 0.0644 | 0.0635 | 0.0656 | 0.0674 | |
| NDCG@5 | 0.0176 | 0.0181 | 0.0182 | 0.0187 | 0.0209 | |
| NDCG@10 | 0.0226 | 0.0232 | 0.0233 | 0.0240 | 0.0257 | |
| NDCG@20 | 0.0281 | 0.0286 | 0.0285 | 0.0294 | 0.0311 | |
| LastFM | HR@5 | 0.0303 | 0.0420 | 0.0403 | 0.0411 | 0.0460 |
| HR@10 | 0.0468 | 0.0584 | 0.0550 | 0.0575 | 0.0649 | |
| HR@20 | 0.0688 | 0.0805 | 0.0806 | 0.0805 | 0.1016 | |
| NDCG@5 | 0.0193 | 0.0274 | 0.0250 | 0.0275 | 0.0344 | |
| NDCG@10 | 0.0246 | 0.0336 | 0.0276 | 0.0322 | 0.0409 | |
| NDCG@20 | 0.0300 | 0.0458 | 0.0410 | 0.0432 | 0.0498 |
| Dataset | Metrics | TCLRec-RPT | TCLRec-Flip | TCLRec-FDA | TCLRec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beauty | HR@5 | 0.0310 | 0.0430 | 0.0444 | 0.0514 |
| HR@10 | 0.0473 | 0.0645 | 0.0652 | 0.0734 | |
| HR@20 | 0.0691 | 0.0927 | 0.0908 | 0.1019 | |
| NDCG@5 | 0.0205 | 0.0283 | 0.0299 | 0.0359 | |
| NDCG@10 | 0.0258 | 0.0352 | 0.0266 | 0.0430 | |
| NDCG@20 | 0.0312 | 0.0423 | 0.0431 | 0.0502 | |
| Sports | HR@5 | 0.0128 | 0.0196 | 0.0210 | 0.0306 |
| HR@10 | 0.0197 | 0.0314 | 0.0314 | 0.0459 | |
| HR@20 | 0.0329 | 0.0469 | 0.0467 | 0.0674 | |
| NDCG@5 | 0.0081 | 0.0132 | 0.0136 | 0.0209 | |
| NDCG@10 | 0.0103 | 0.0170 | 0.0314 | 0.0257 | |
| NDCG@20 | 0.0137 | 0.0209 | 0.0208 | 0.0311 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Sheng, T.; Wang, A. Temporal-Aware and Intent Contrastive Learning for Sequential Recommendation. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101634
Zhang Y, Fan Y, Sheng T, Wang A. Temporal-Aware and Intent Contrastive Learning for Sequential Recommendation. Symmetry. 2025; 17(10):1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101634
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuan, Yaqin Fan, Tiantian Sheng, and Aoshuang Wang. 2025. "Temporal-Aware and Intent Contrastive Learning for Sequential Recommendation" Symmetry 17, no. 10: 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101634
APA StyleZhang, Y., Fan, Y., Sheng, T., & Wang, A. (2025). Temporal-Aware and Intent Contrastive Learning for Sequential Recommendation. Symmetry, 17(10), 1634. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101634






