Robust Filtered-x LMS Algorithm Based on Adjustable Softsign Framework for Active Impulsive Noise Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
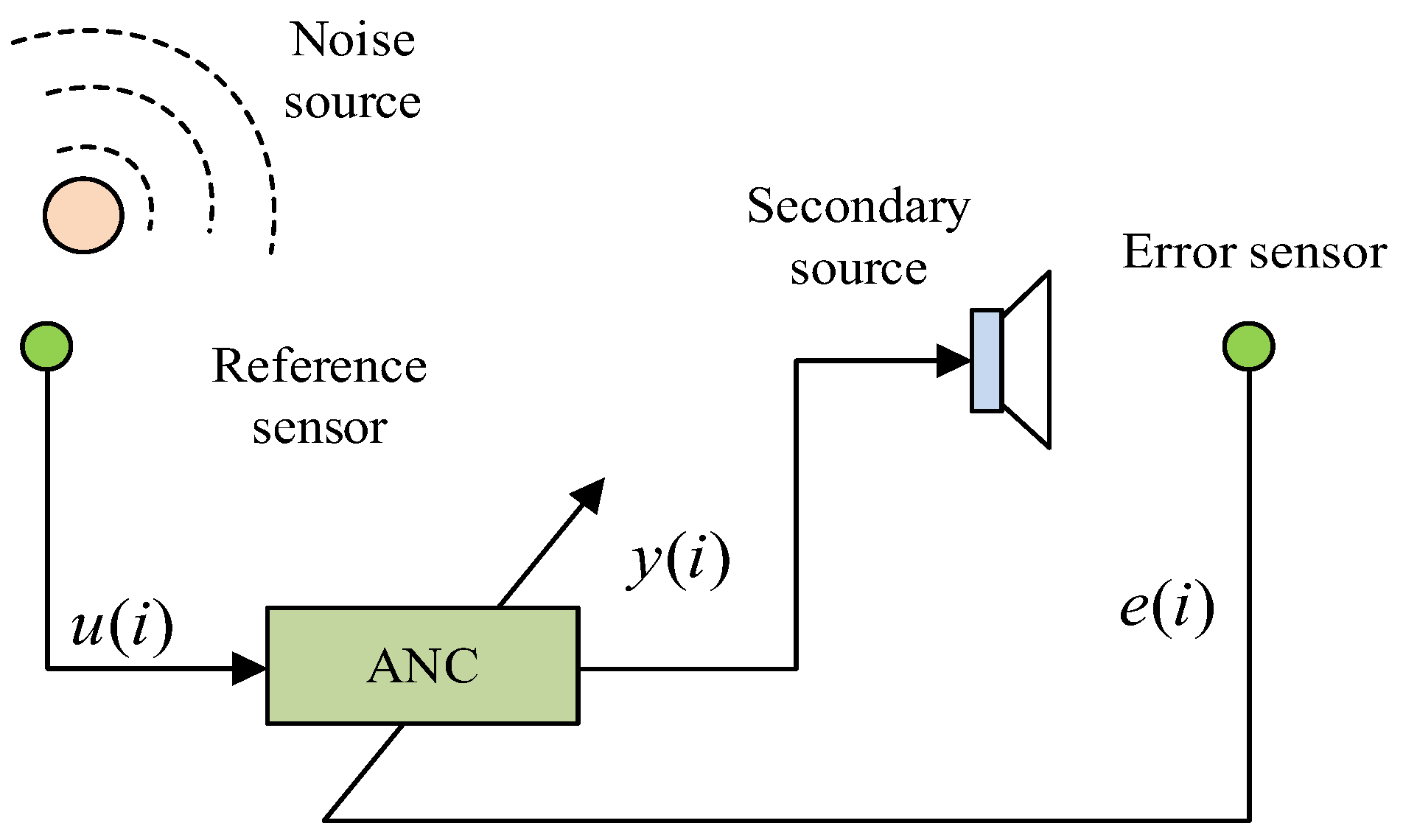
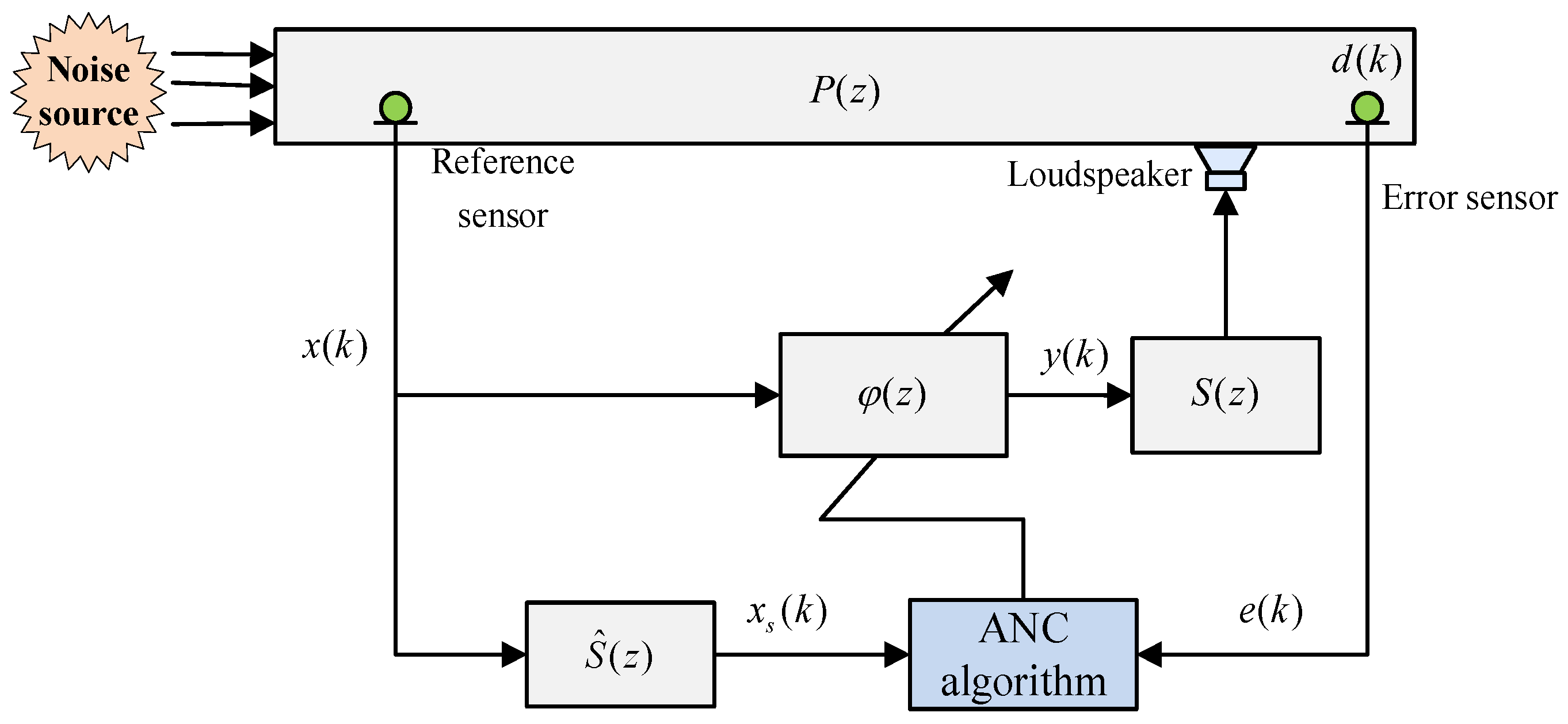
2. Feedforward ANC System Model
3. Proposed Algorithms
3.1. Robust Cost Function Framework
3.2. The Proposed Softsign-FxLMS (SFxLMS) Algorithm
3.3. The Proposed Variable λ-Parameter SFxLMS (VSFxLMS) Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Proposed VSFxLMS Algorithm |
| Initializations: |
| Parameters: , , , , , |
| Adaptive process: for k = 0, 1, 2, … end |
4. Performance Analysis
4.1. Stability Analysis
4.2. Computational Complexity
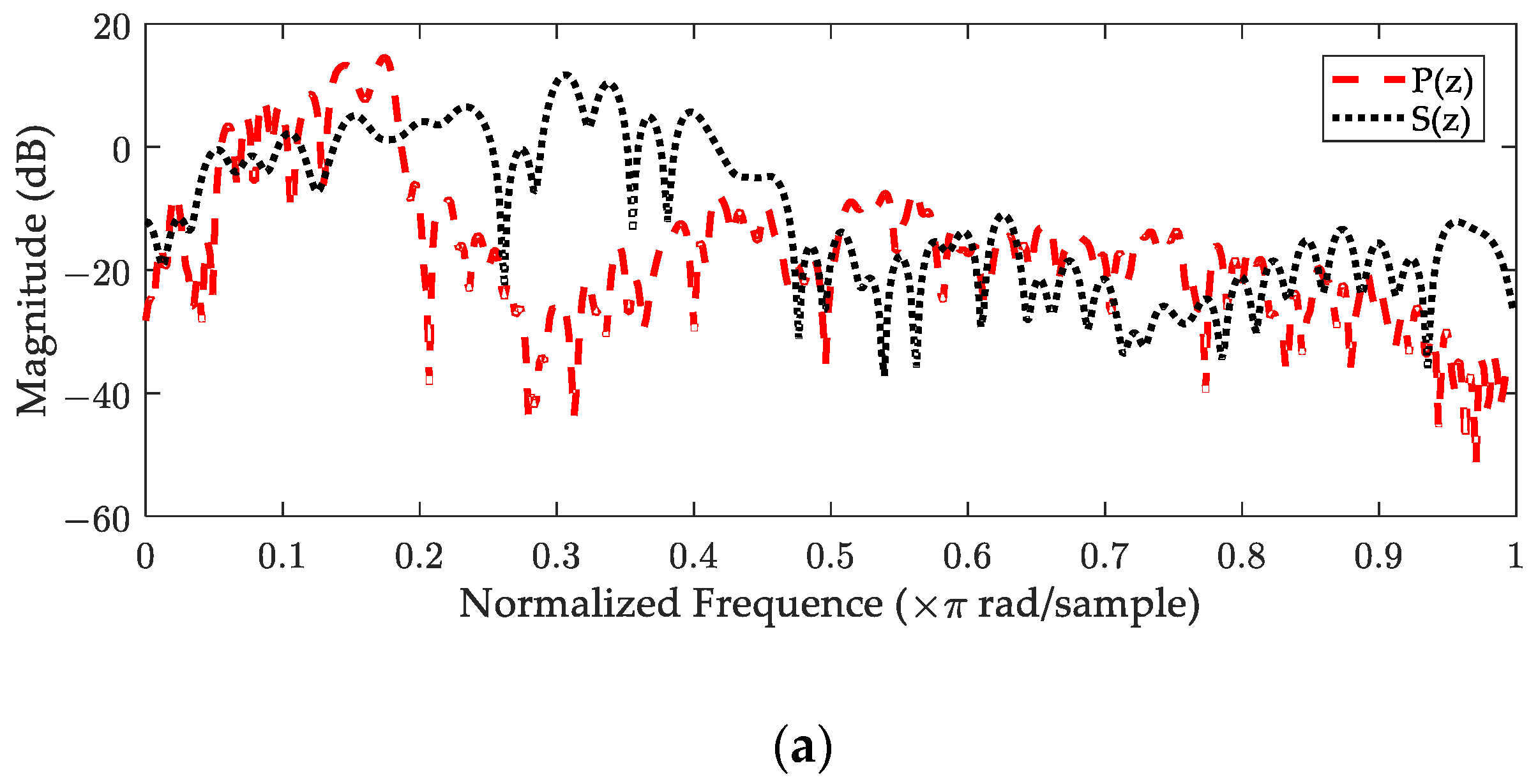
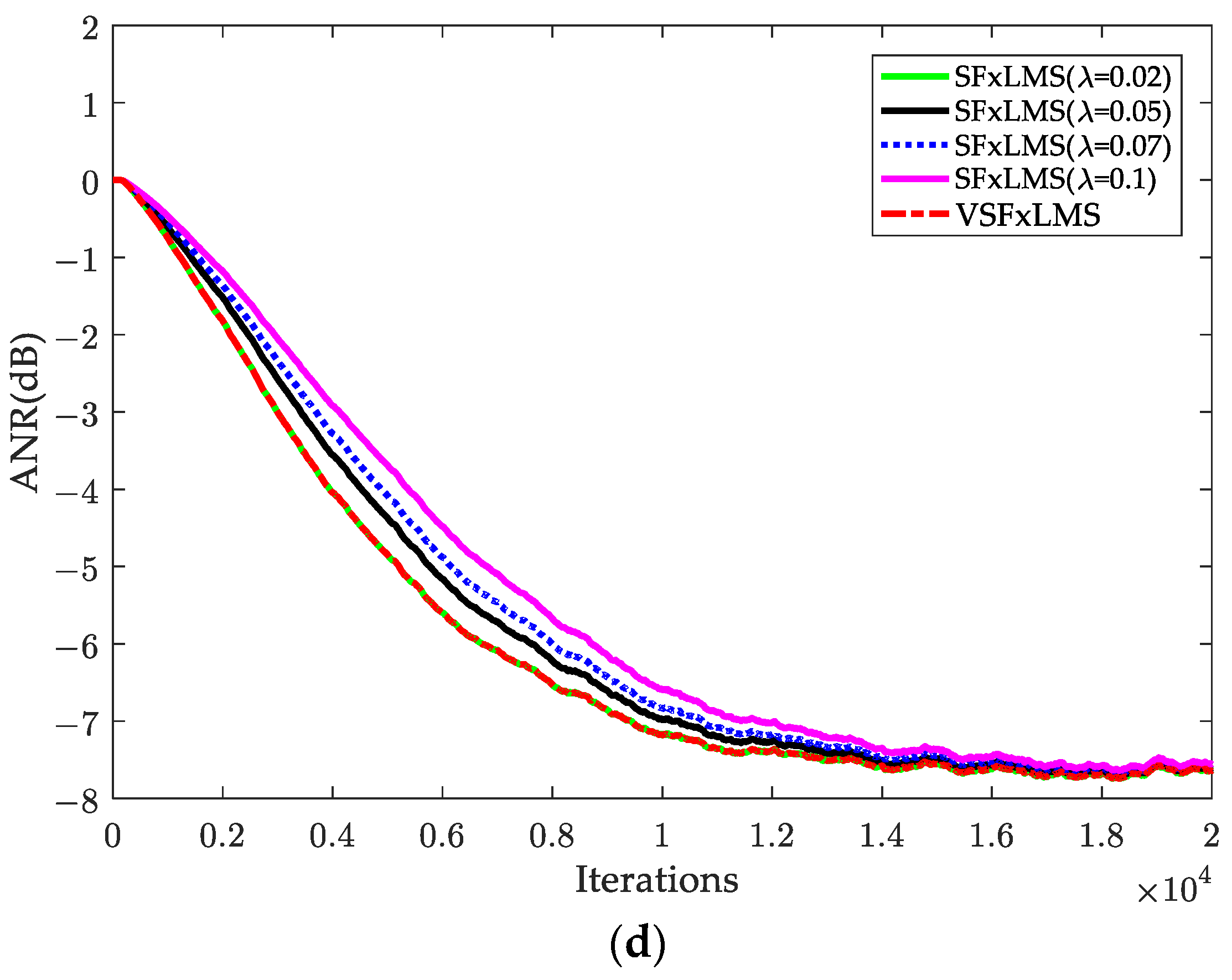
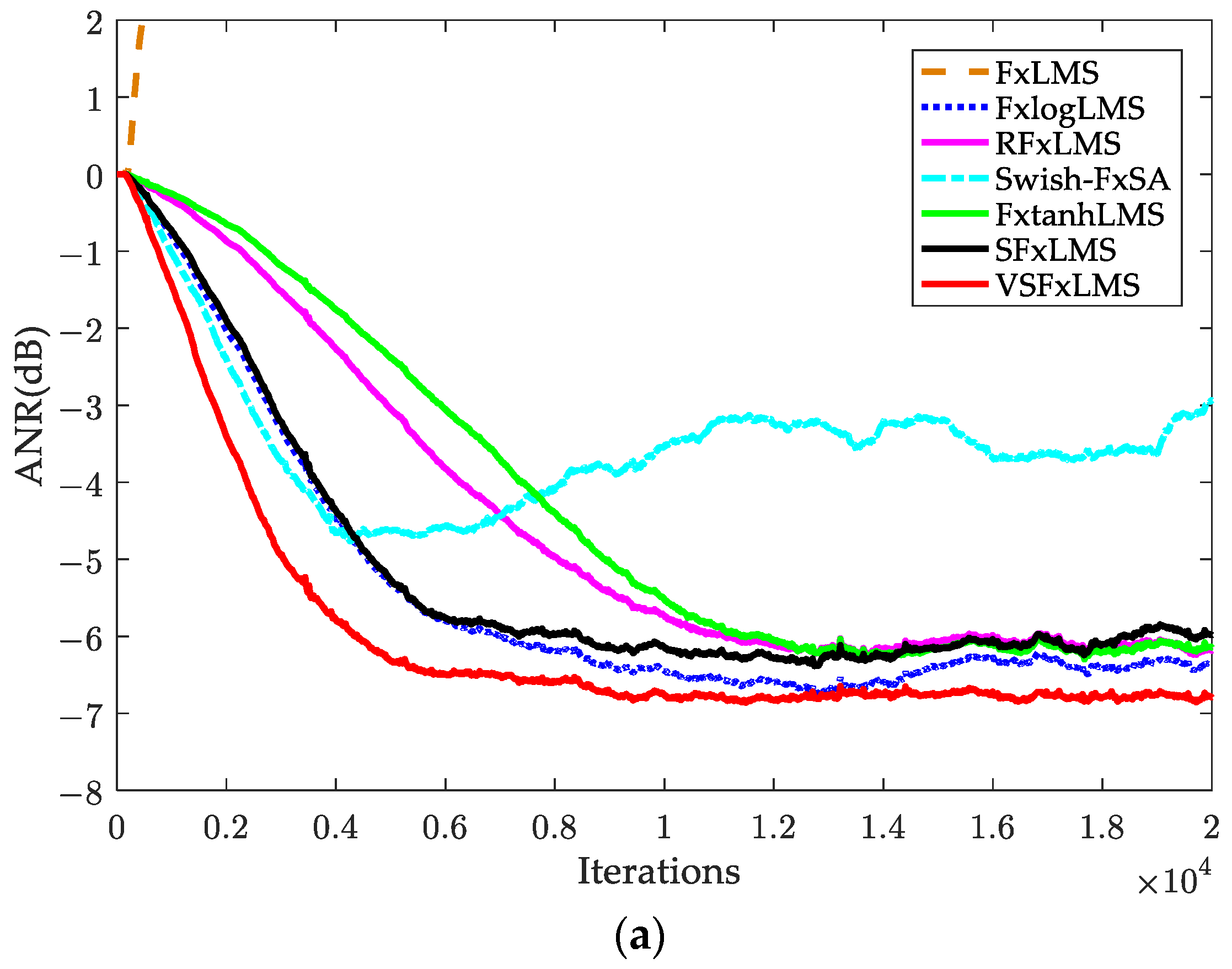
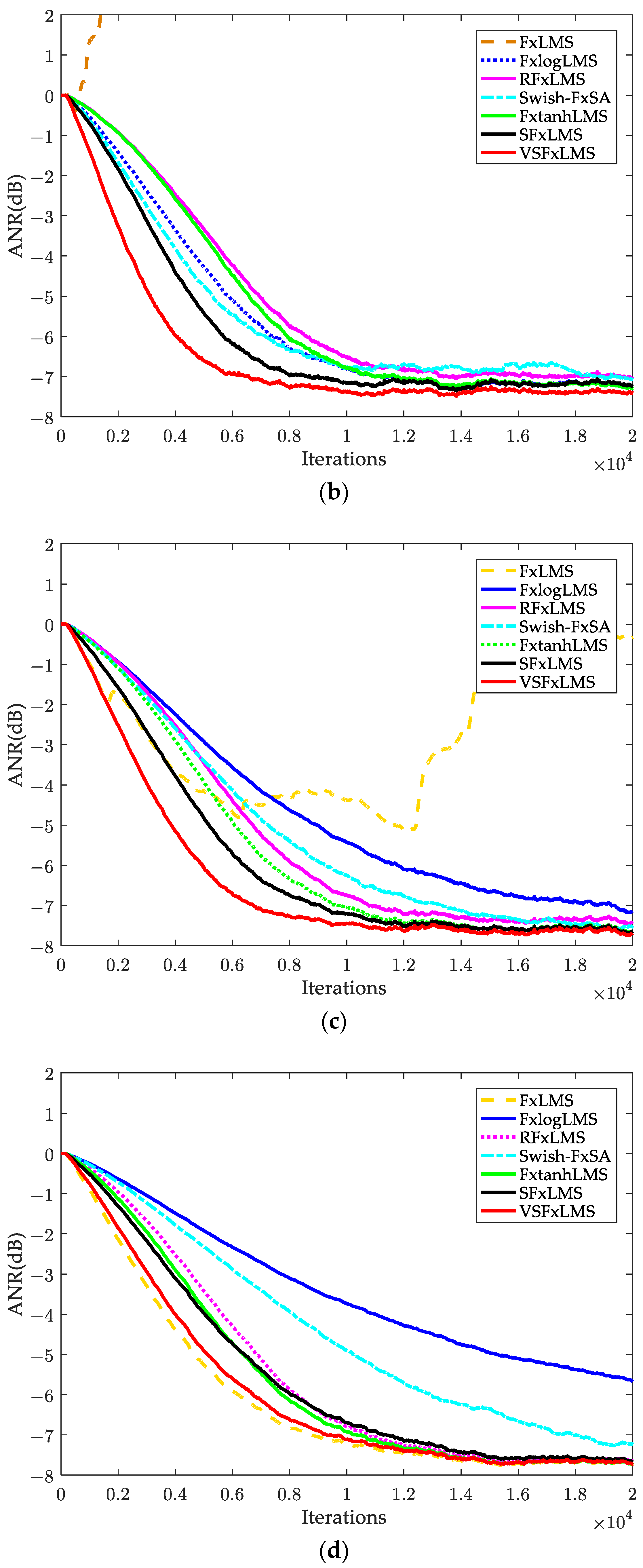
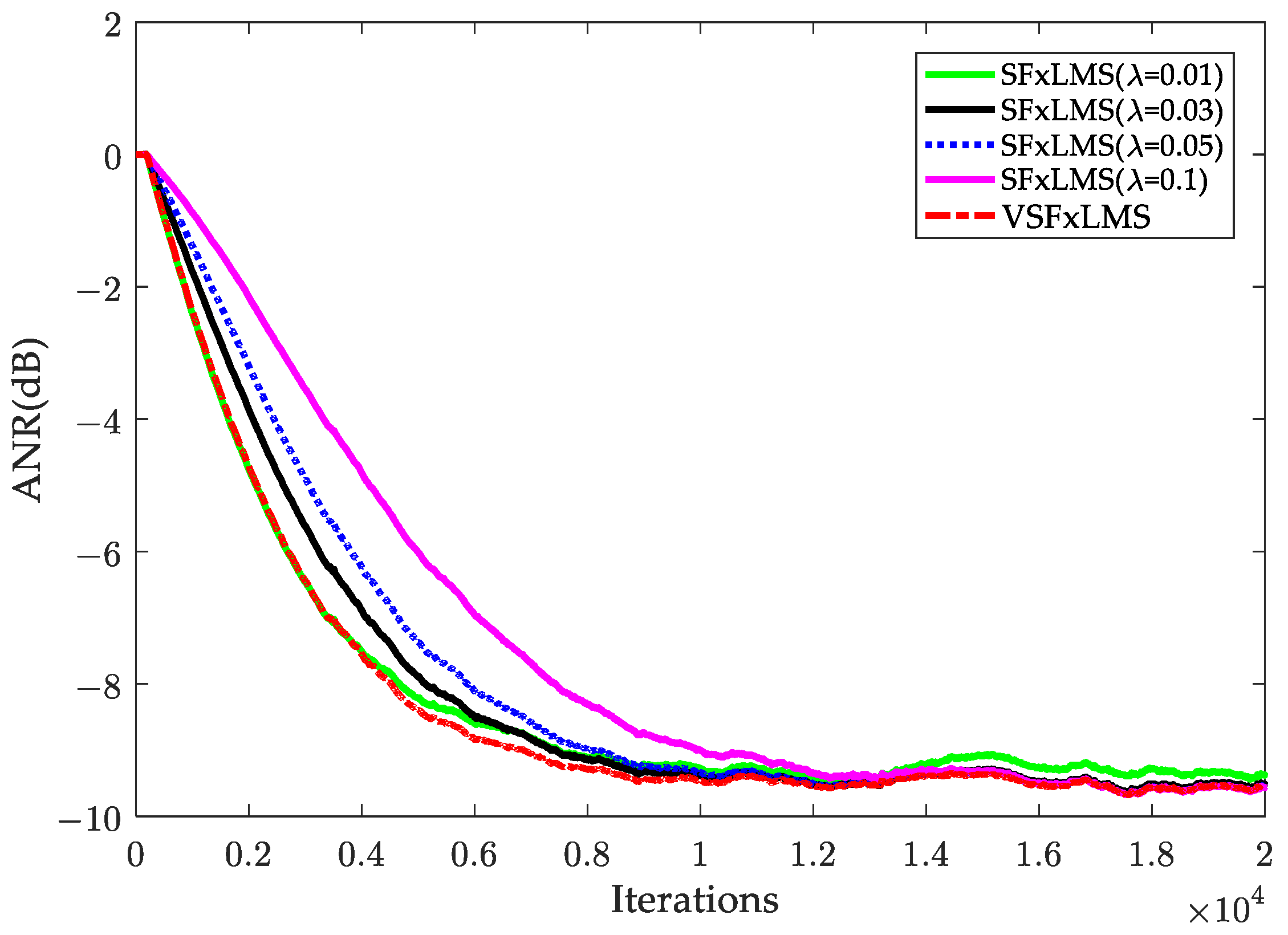
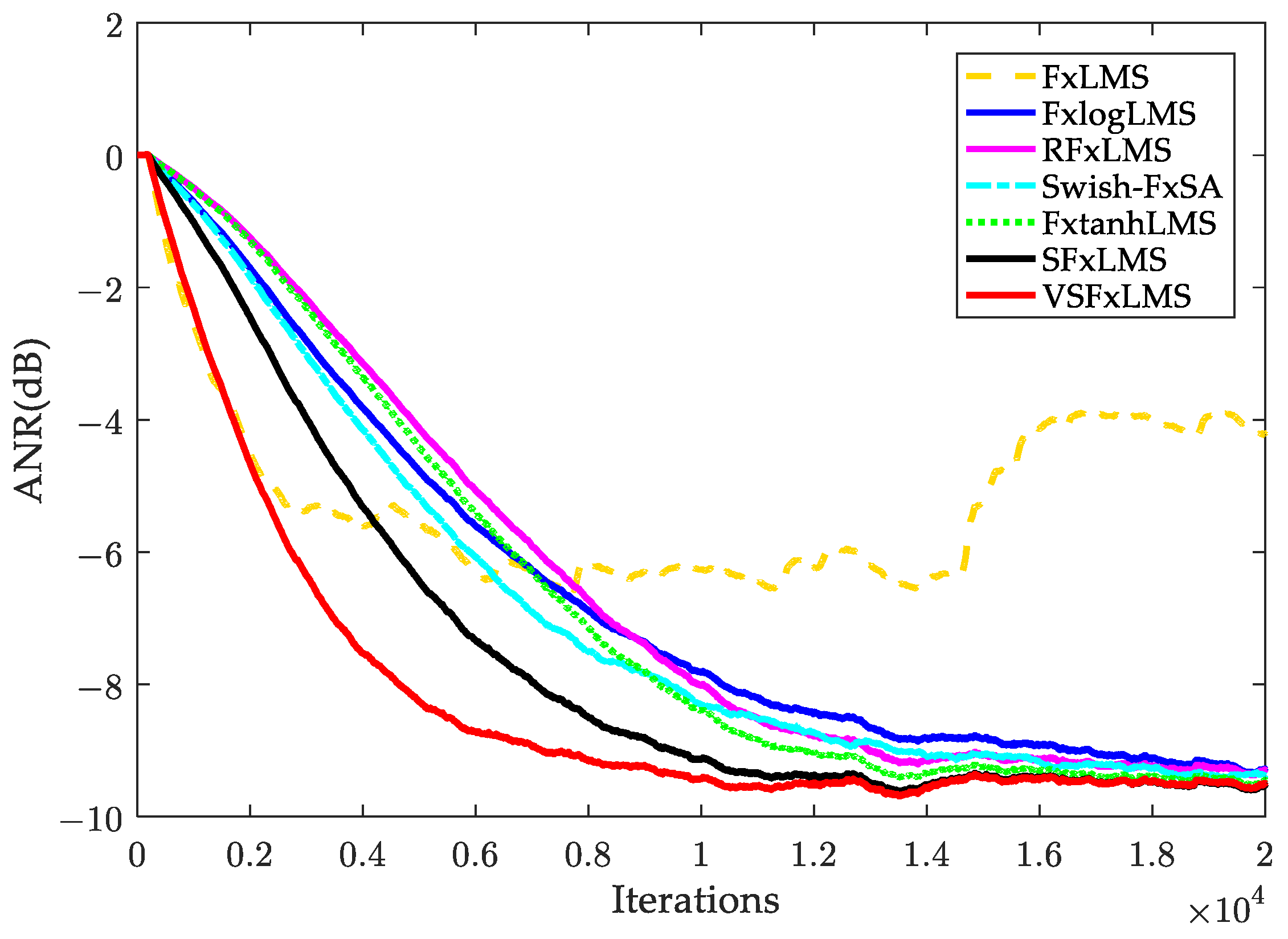
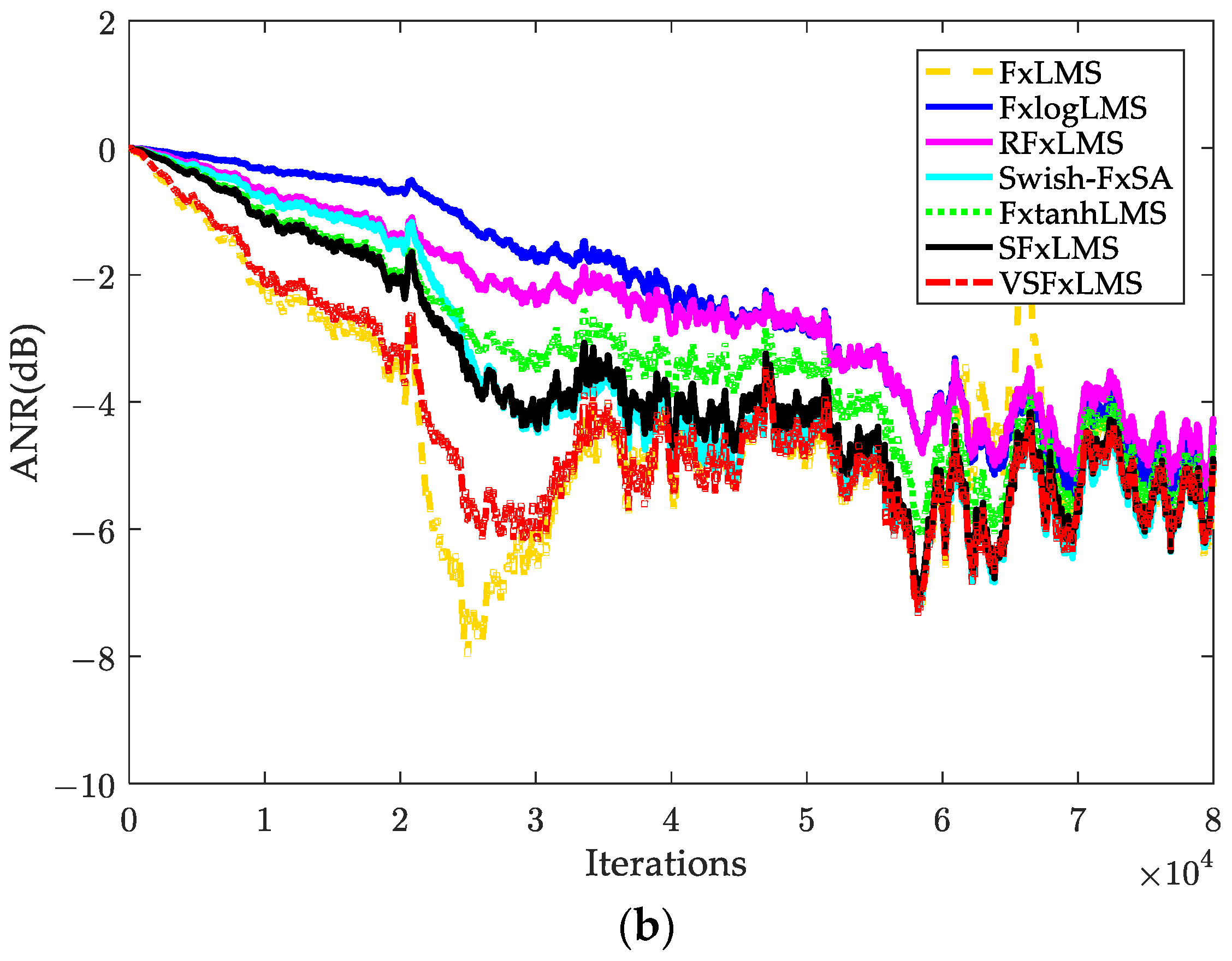
5. Computer Simulations
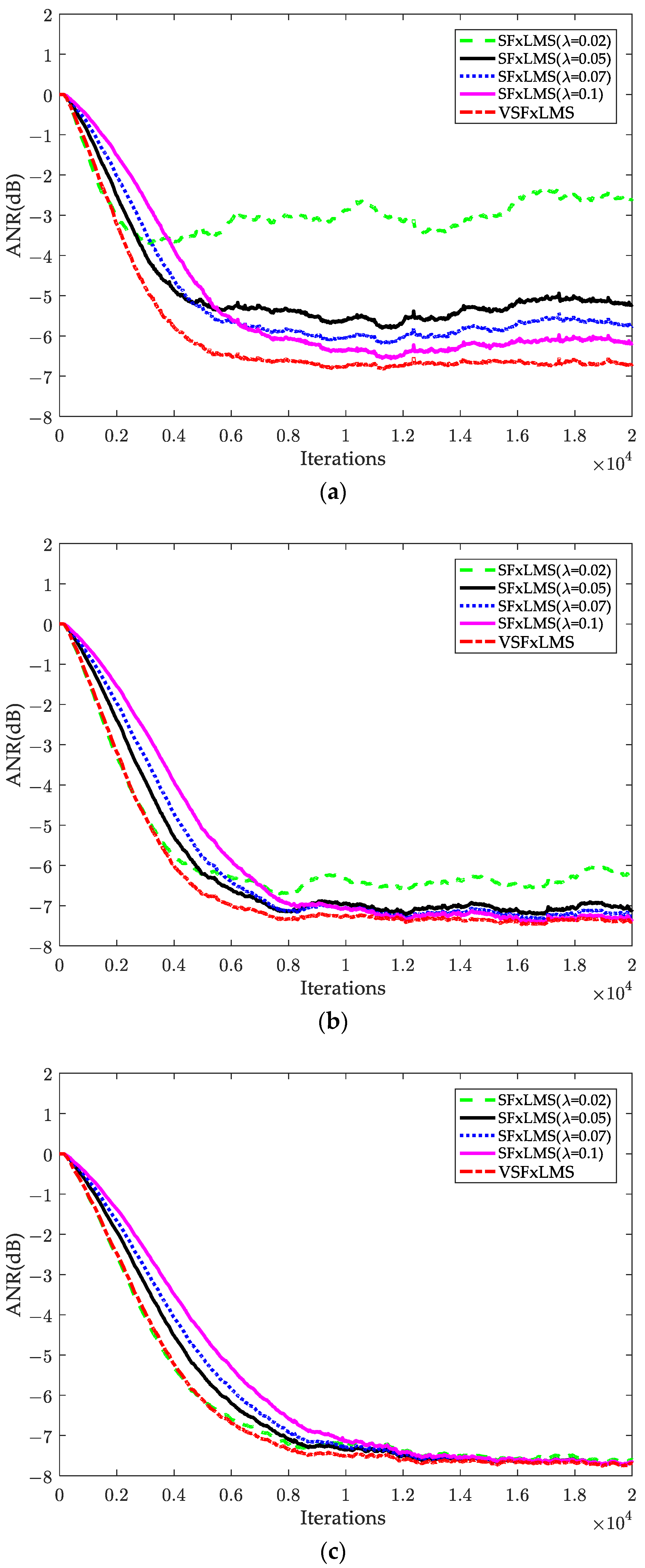
5.1. Impulsive Noise
5.2. Sinusoidal Impulsive Noise
5.3. Real Audio: Traction Substation Noise
5.4. Verification of Tracking Capability
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, K.L.; Zhao, H.R.; Pu, Y.F.; Lu, L. Nonlinear active noise control with tap-decomposed robust volterra filter. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 206, 110887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, T.; Chandra, M.; Kar, A.; Swamy, M.N.S. Design and analysis of an improved hybrid active noise control system. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 127, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, T.; Chandra, M.; Kar, A. Performance evaluation of hybrid active noise control system with online secondary path modeling. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 133, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carini, A.; Malatini, S. Optimal variable step-size NLMS algorithms with auxiliary noise power scheduling for feedforward active noise control. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2008, 16, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lin, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S. Error reused filtered-X least mean square algorithm for active noise control. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2023, 32, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Ou, S.; Cai, Z.; Gao, Y. Posterior error energy minimization based combined FXNLMS and FXLMS algorithm for active noise control. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 30754–30764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, T.; Chandra, M.; Kar, A.; Swamy, M.N.S. A new adaptive control strategy for hybrid narrowband active noise control systems in a multi-noise environment. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 146, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A. An intelligent momentum perturbed variable step-size adaptive algorithm for fast converging HNANC systems. Digit. Signal Process. 2024, 145, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ma, L.; Khorasani, K. A new hybrid active noise control system with input-power-controlled online secondary-path modeling. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2024, 32, 3157–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Zhang, M.; Ser, W. A weight-constrained FxLMS algorithm for feedforward active noise control systems. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2002, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T.; Mitsuhashi, W. Improving performance of FxLMS algorithm for active noise control of impulsive noise. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 327, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; He, H.; Qiu, X. An active impulsive noise control algorithm with logarithmic transformation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2011, 19, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.V.; Panda, G. A robust filtered-s LMS algorithm for nonlinear active noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 73, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y. Active control of impulsive noise with symmetric α-stable distribution based on an improved step-size normalized adaptive algorithm. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 56–57, 320–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Li, M.; Lim, T.C. Enhanced filtered-x least mean M-estimate algorithm for active impulsive noise control. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 90, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Padhi, T.; Majhi, B.; Swamy, M.N.S. Analysing the impact of system dimension on the performance of a variable-tap-length adaptive algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 150, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Shoba, S.; Burra, S.; Goel, P.; Kumar, S.; Vasundhara, V.; Sooraksa, P. Adaptive tap-length based sub-band mean M-estimate filtering for active noise cancellation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2024, 43, 5912–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Jiang, J. Active control of impulsive noise using a nonlinear companding function. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 58–59, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T. Binormalized data-reusing adaptive filtering algorithm for active control of impulsive sources. Digit. Signal Process. 2016, 49, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T.; Mitsuhashi, W. A modified normalized FxLMS algorithm for active control of impulsive noise. In Proceedings of the 2010 18th European Signal Processing Conference, Aalborg, Denmark, 23–27 August 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Shen, L.; Chen, B. An efficient parameter optimization of maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, N.C.; Patel, K.; George, N.V. Robust active noise control: An information theoretic learning approach. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 117, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Mirza, A.; Khan, Q.U.; Sheikh, S.A. Improving performance of FxRLS algorithm for active noise control of impulsive noise. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 116, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.; Zeb, A.; Umair, M.Y.; Ilyas, D.; Sheikh, S.A. Less complex solutions for active noise control of impulsive noise. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2020, 102, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, F.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y. An enhanced normalized step-size algorithm based on adjustable nonlinear transformation function for active control of impulsive noise. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 176, 107853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.R.; Yu, C.H.; Tsao, H.W. Affine-projection-like maximum correntropy criteria algorithm for robust active noise control. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2022, 30, 2255–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, X.; Chen, B. Robust generalized maximum correntropy criterion algorithms for active noise control. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Ge, P.; Cao, Y. Active control of impulsive noise based on a modified convex combination algorithm. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 186, 108438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z. An enhanced impulse noise control algorithm using a novel nonlinear function. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 42, 6524–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.; Afzal, F.; Zeb, A.; Wakeel, A.; Qureshi, W.S.; Akgul, A. New FxLMAT-based algorithms for active control of impulsive noise. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 81279–81288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jin, G.; Liu, H.; Li, J. Active impulsive noise control algorithm based on adjustable hyperbolic tangent function. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 42, 5559–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranthi, R.; Vasundhara; Kar, A.; Christensen, M.G. A family of Swish diffusion strategy based adaptive algorithms for distributed active noise control. IEEE Open J. Signal Process. 2024, 5, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannadi, P.; Kourehli, S.S.; Mirjalili, S. The application of PSO in structural damage detection: An analysis of the previously released publications (2005–2020). Frat. Integrità Strutt. 2022, 16, 460–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, N.K.; Das, D.P.; Panda, G. Particle swarm optimization based active noise control algorithm without secondary path identification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2011, 61, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, X. Interpolated individual weighting subband Volterra filter for nonlinear active noise control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 70, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gu, F.; Liang, C.; Meng, H.; Wu, K.; Zhou, Z. Review on active noise control technology for α-stable distribution impulsive noise. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 41, 956–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Algorithms | Multiplications/Divisions | Additions/Subtractions |
|---|---|---|
| FxLMS | ||
| FxlogLMS | ||
| RFxLMS | ||
| Swish-FxSA | ||
| FxtanhLMS | ||
| SFxLMS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, P.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, S.; Chen, G. Robust Filtered-x LMS Algorithm Based on Adjustable Softsign Framework for Active Impulsive Noise Control. Symmetry 2025, 17, 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101592
Song P, Zhao H, Zhu Y, Lv S, Chen G. Robust Filtered-x LMS Algorithm Based on Adjustable Softsign Framework for Active Impulsive Noise Control. Symmetry. 2025; 17(10):1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101592
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Pucha, Haiquan Zhao, Yingying Zhu, Shaohui Lv, and Gang Chen. 2025. "Robust Filtered-x LMS Algorithm Based on Adjustable Softsign Framework for Active Impulsive Noise Control" Symmetry 17, no. 10: 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101592
APA StyleSong, P., Zhao, H., Zhu, Y., Lv, S., & Chen, G. (2025). Robust Filtered-x LMS Algorithm Based on Adjustable Softsign Framework for Active Impulsive Noise Control. Symmetry, 17(10), 1592. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17101592







