A Class of Discrete Memristor Chaotic Maps Based on the Internal Perturbation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of a Memristor Model with Internal Perturbation
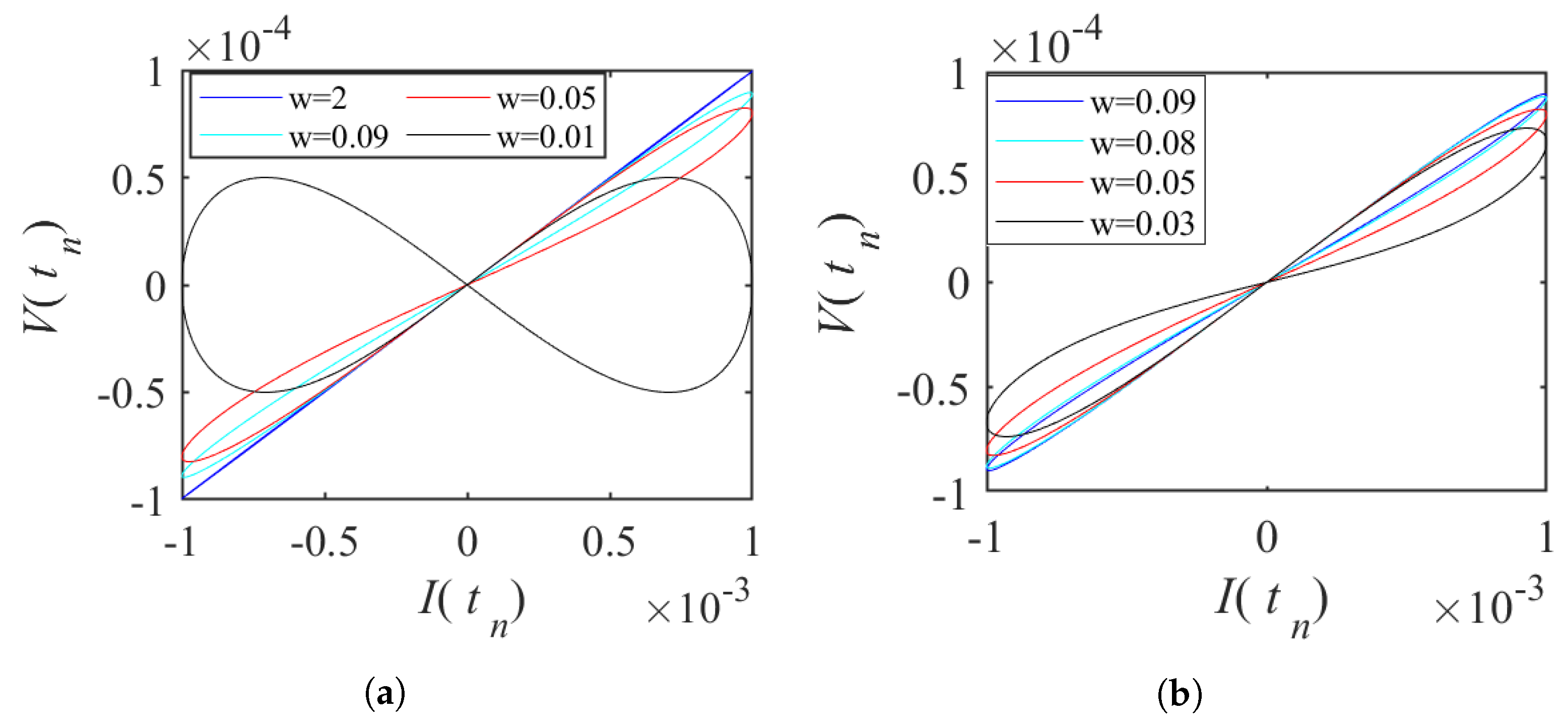
2.1. The Discrete Memristor
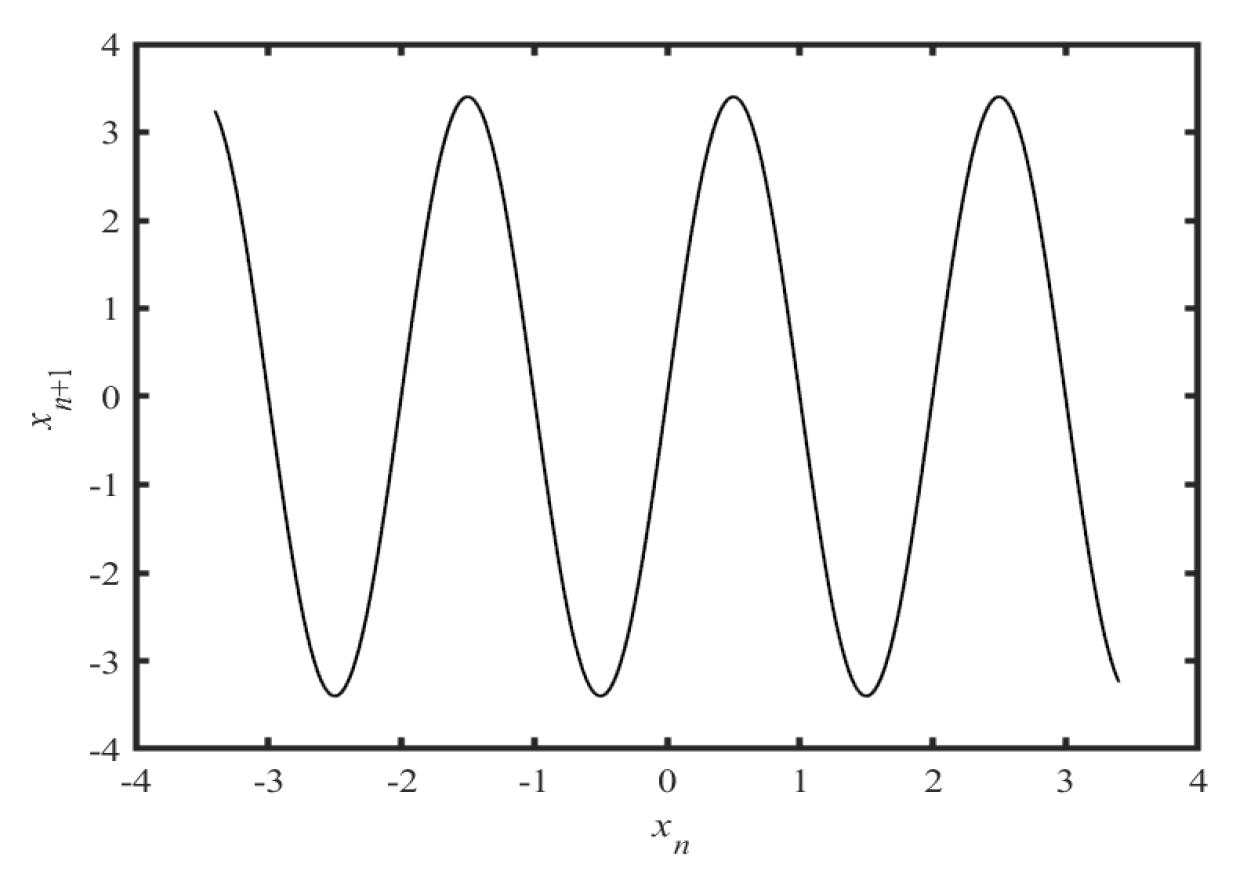
2.2. The Sine Map
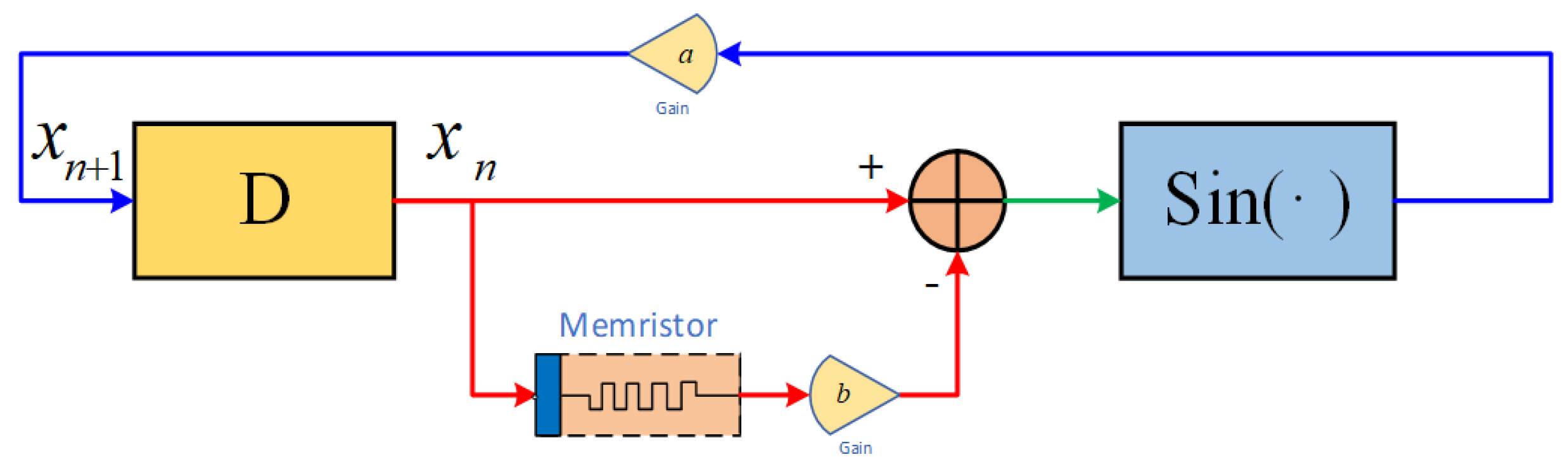
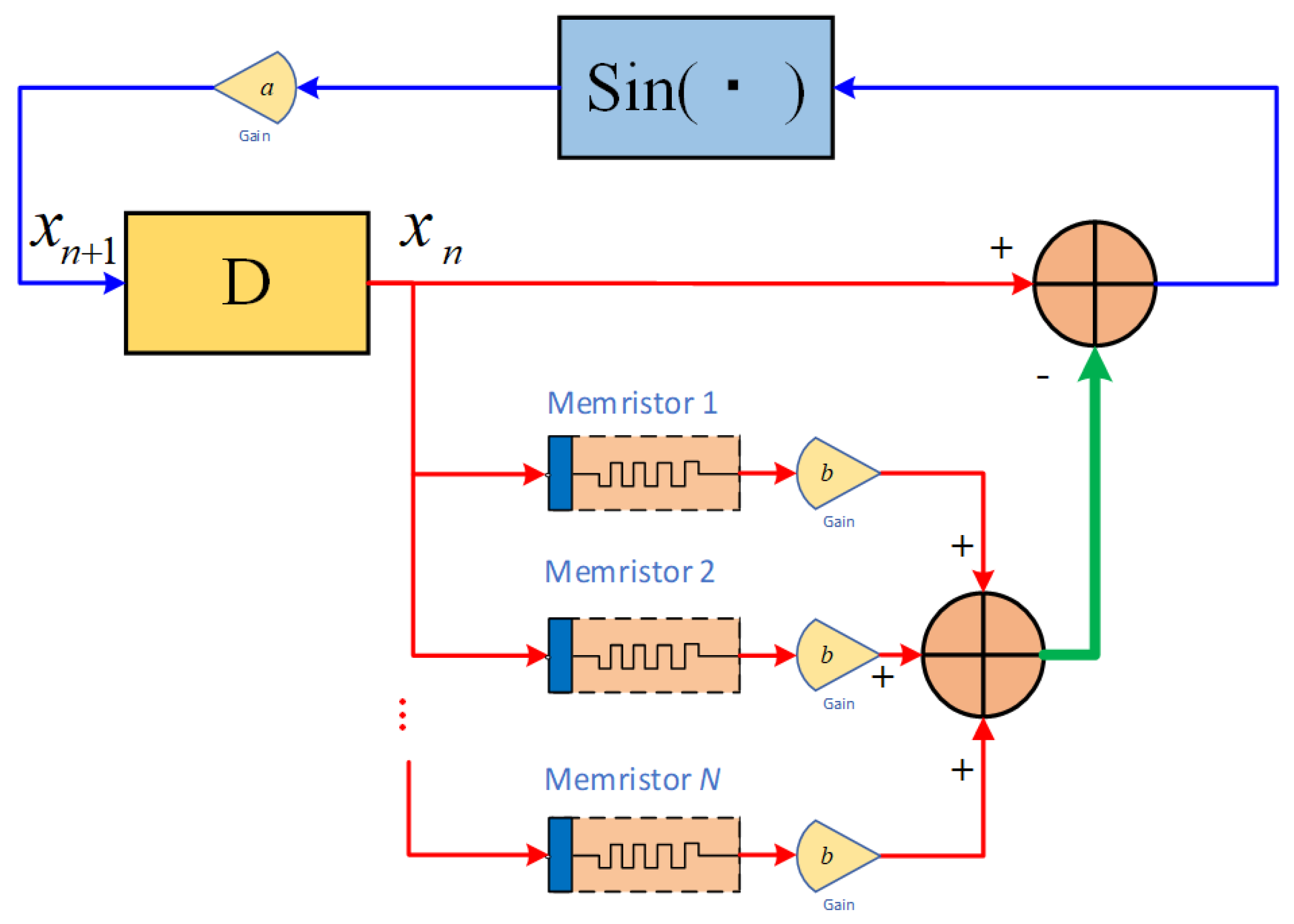
2.3. Chaotic Maps with Discrete Memristor Perturbations
3. Dynamics of the Sine Map with Single Internal Perturbation
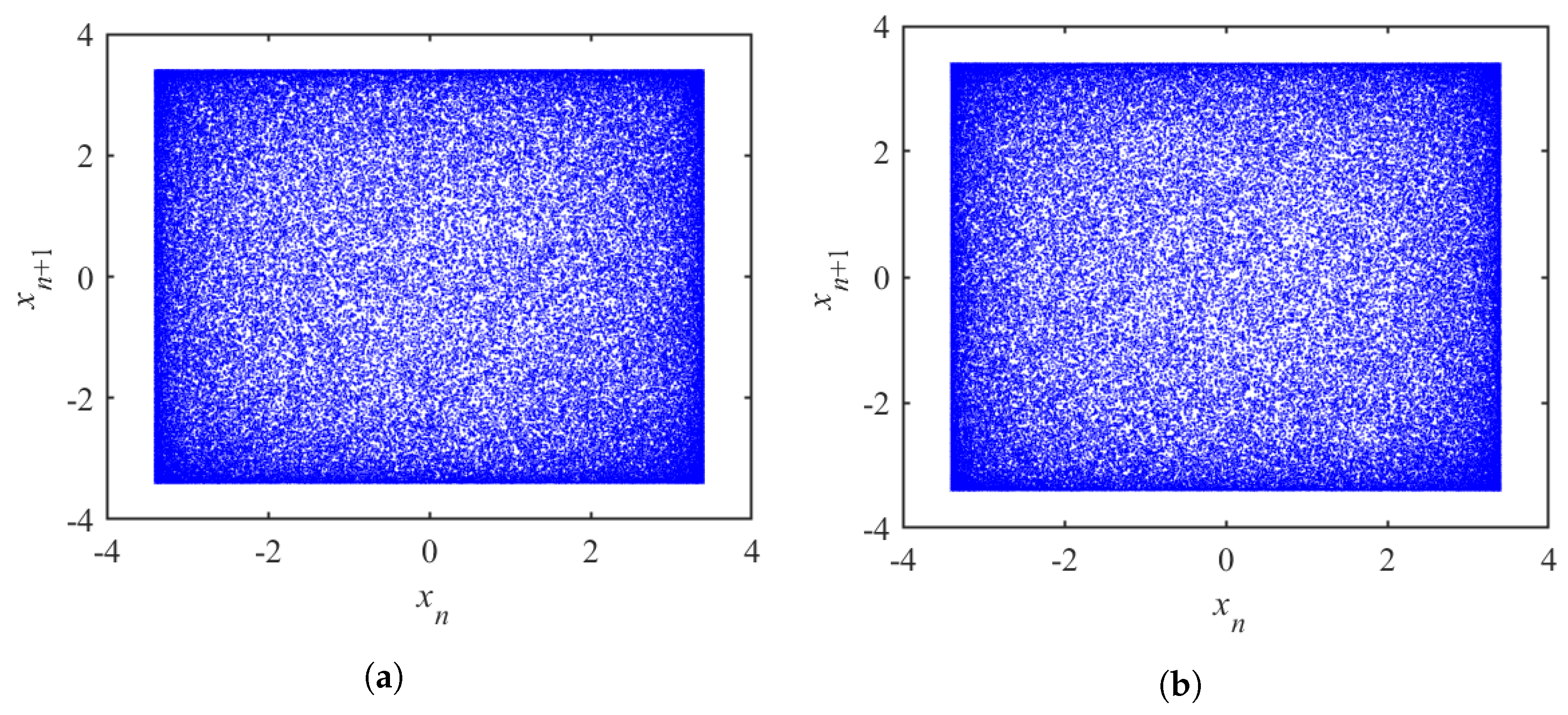
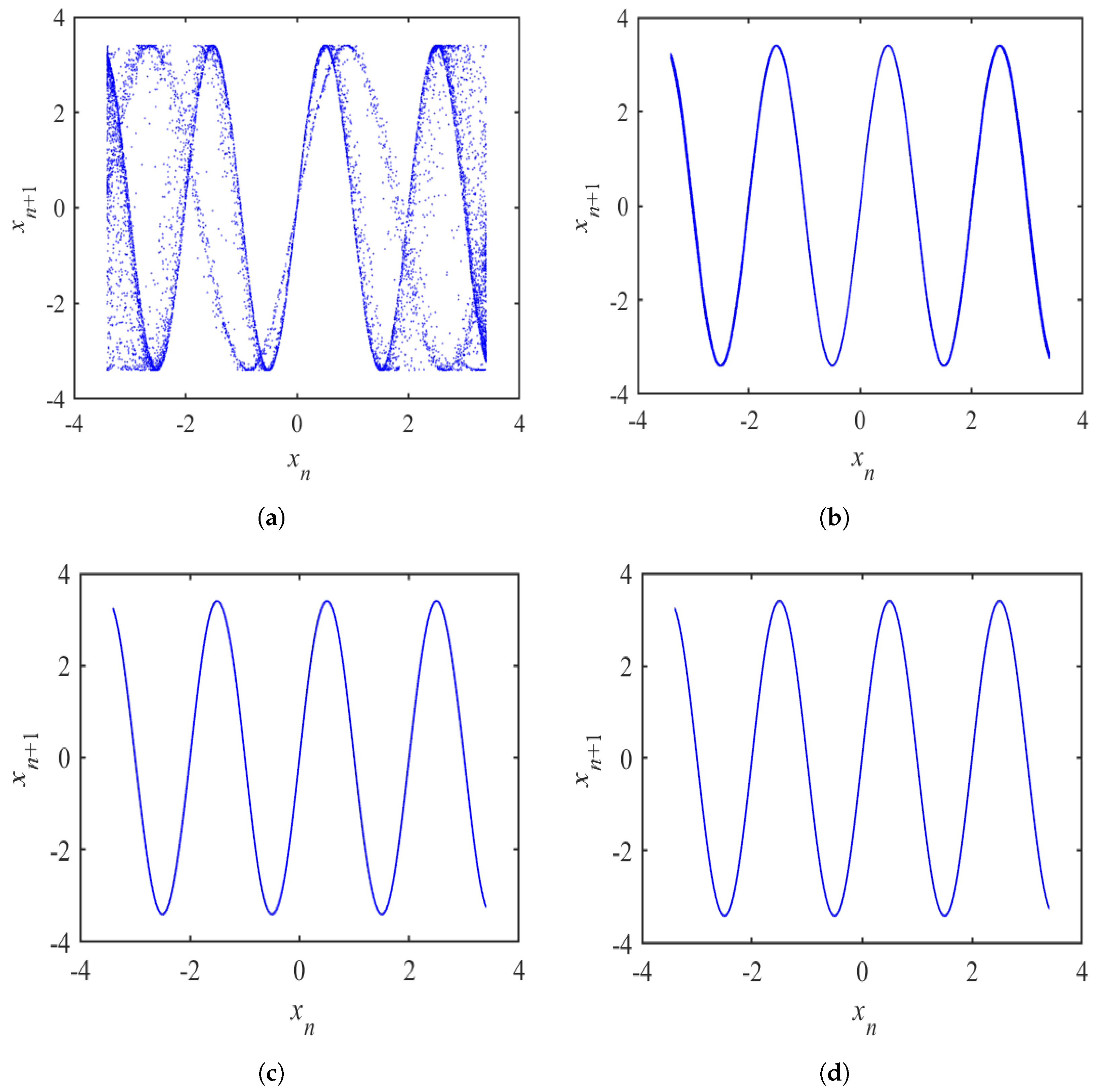
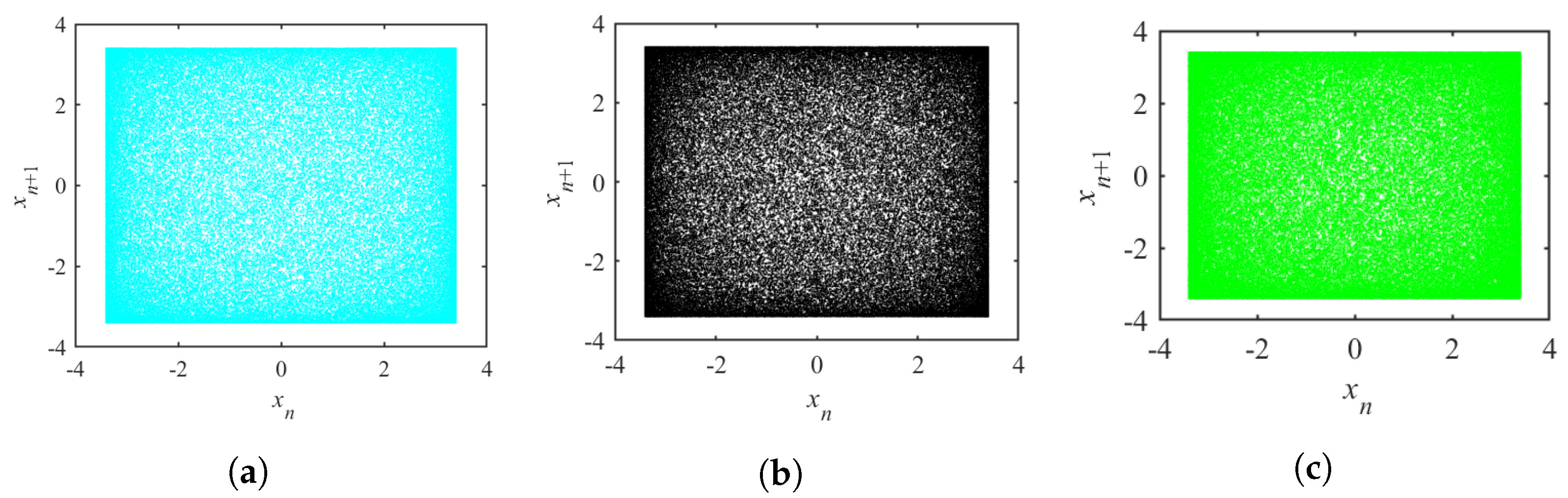
3.1. Chaotic Attractor of a Single Perturbation Model
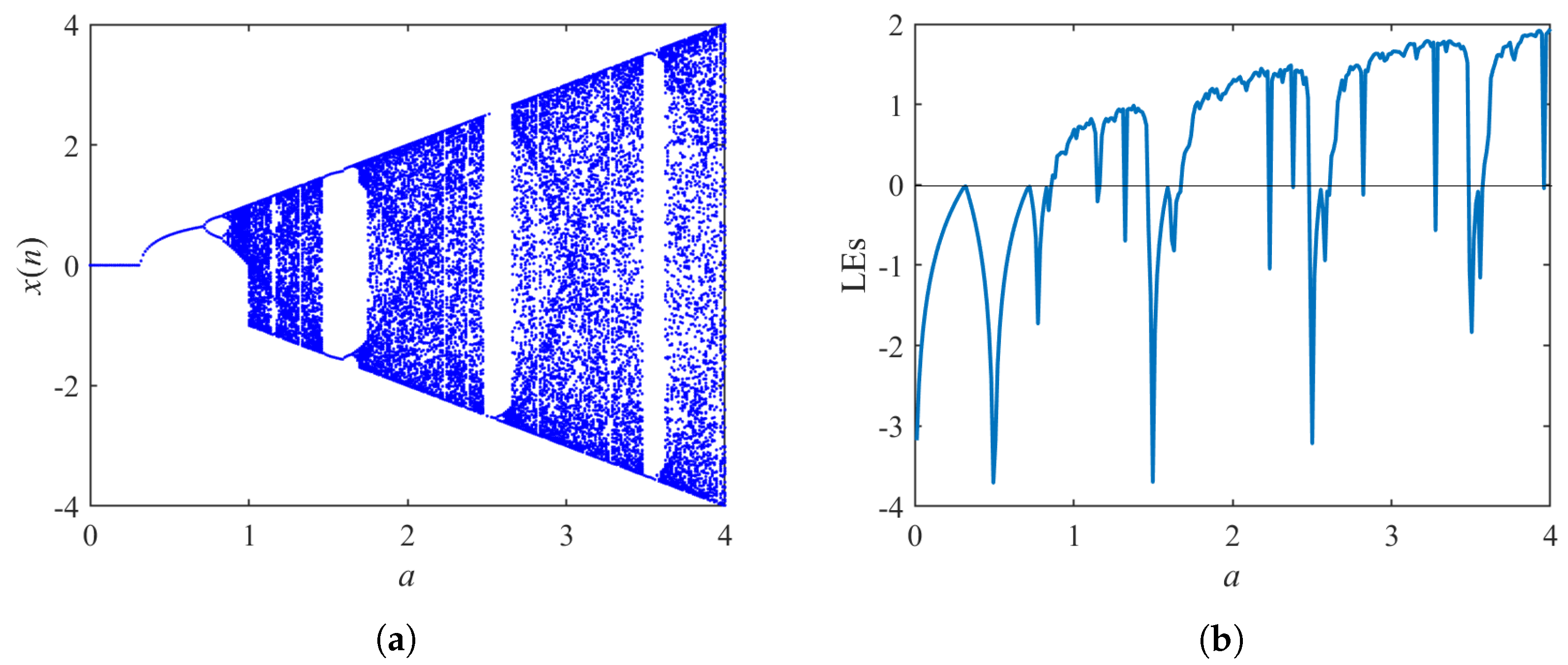
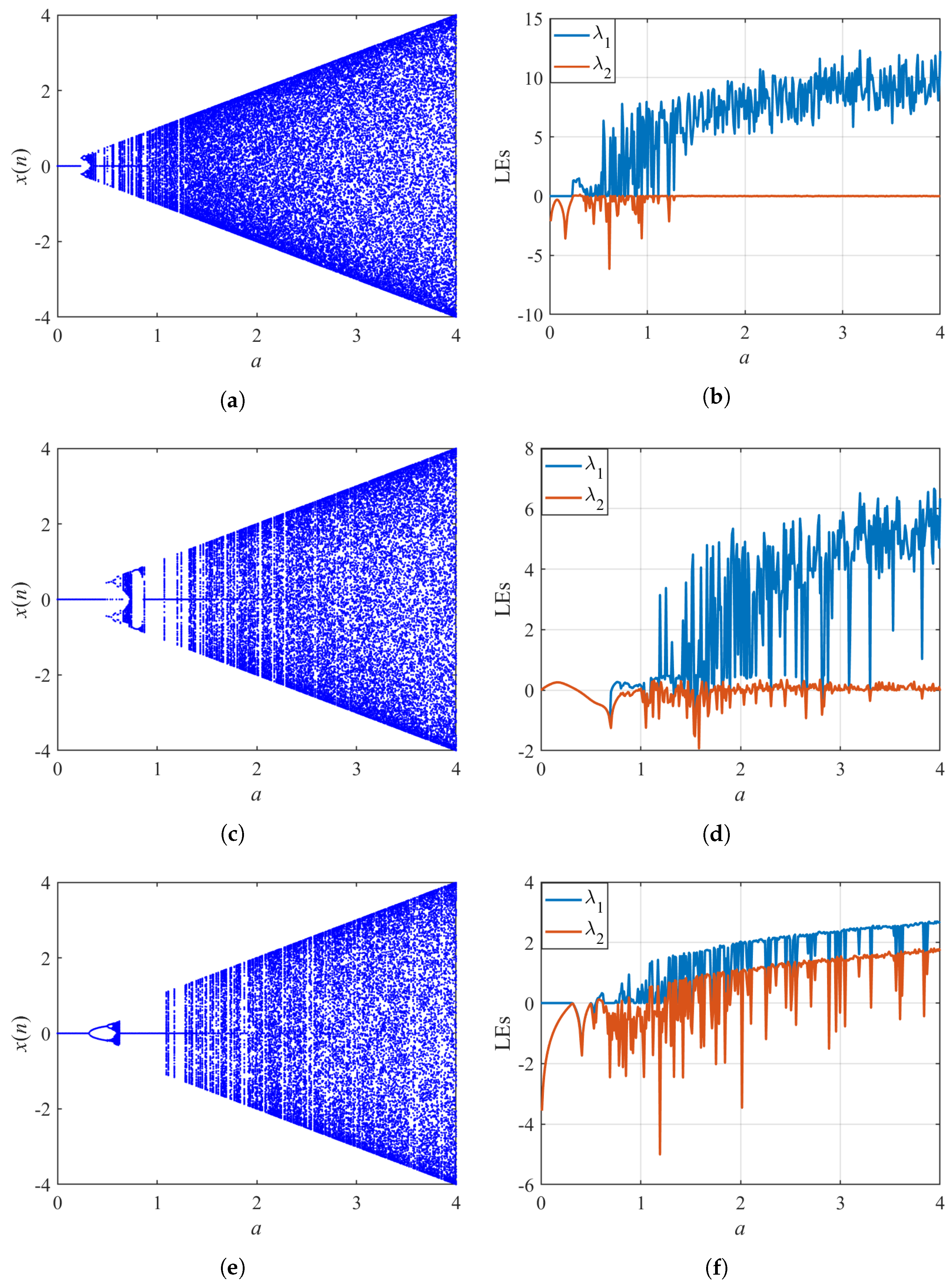
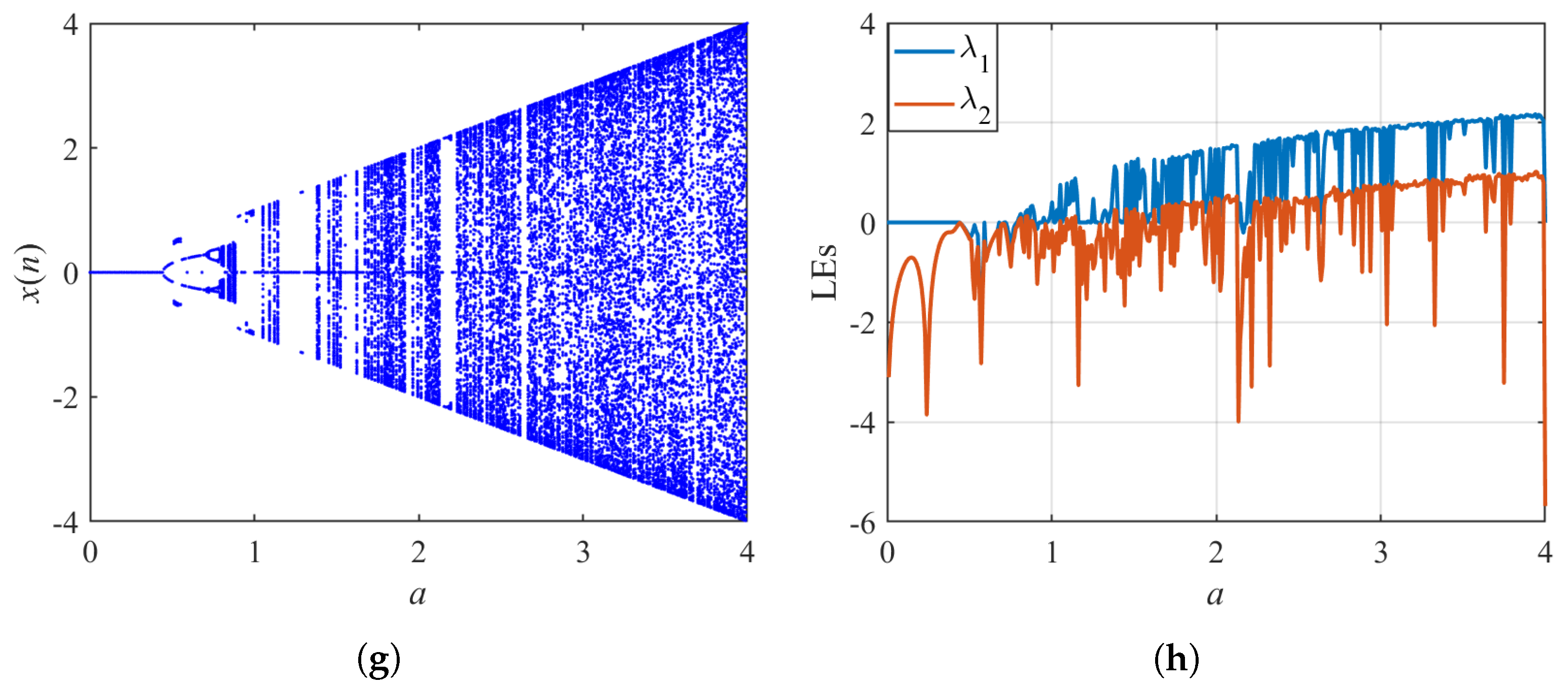
3.2. Bifurcation and LE of a Single Perturbation Model
4. Dynamics of Sine Map with Multi-Internal Perturbation
4.1. Chaotic Attractor of Multi-Internal Perturbation
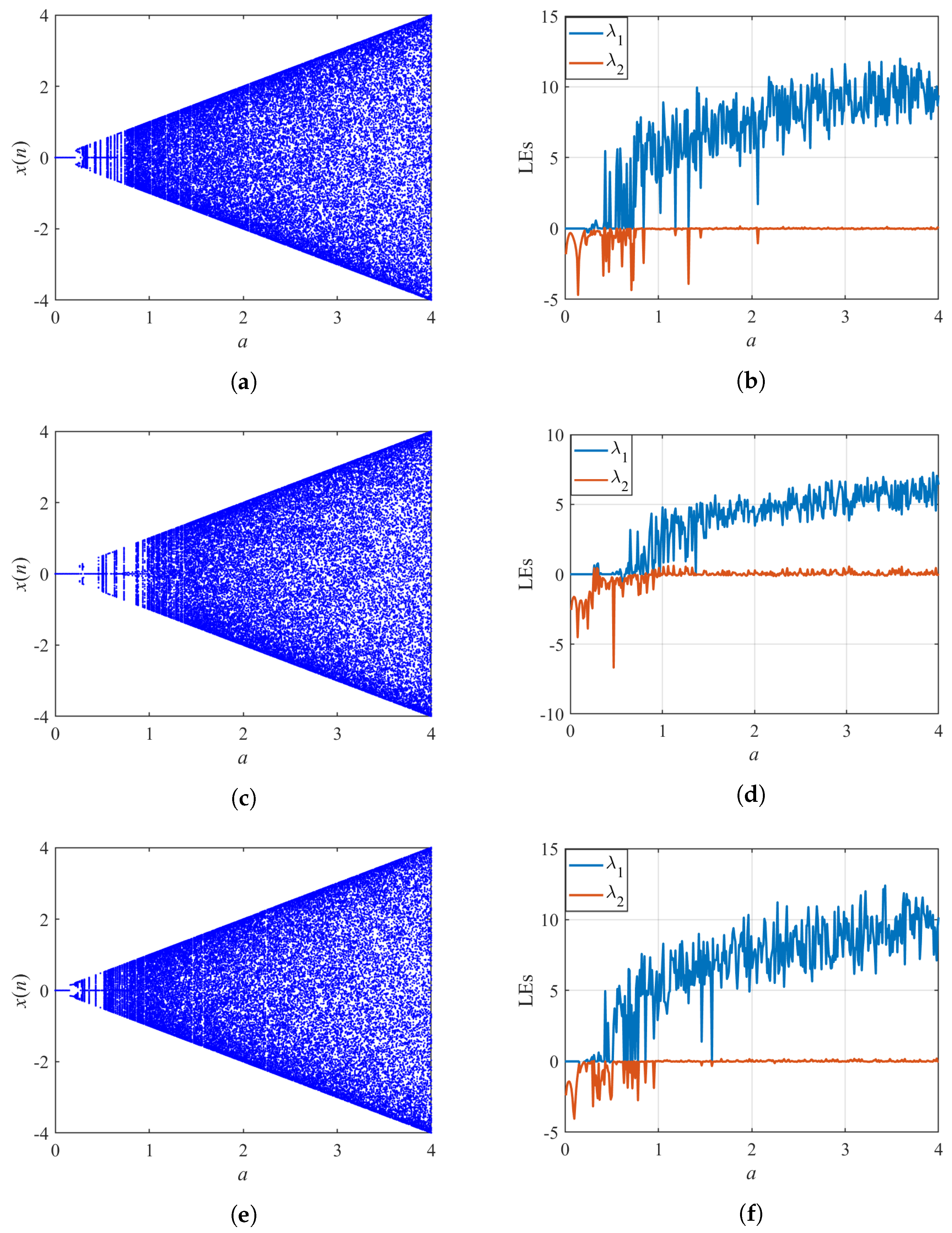
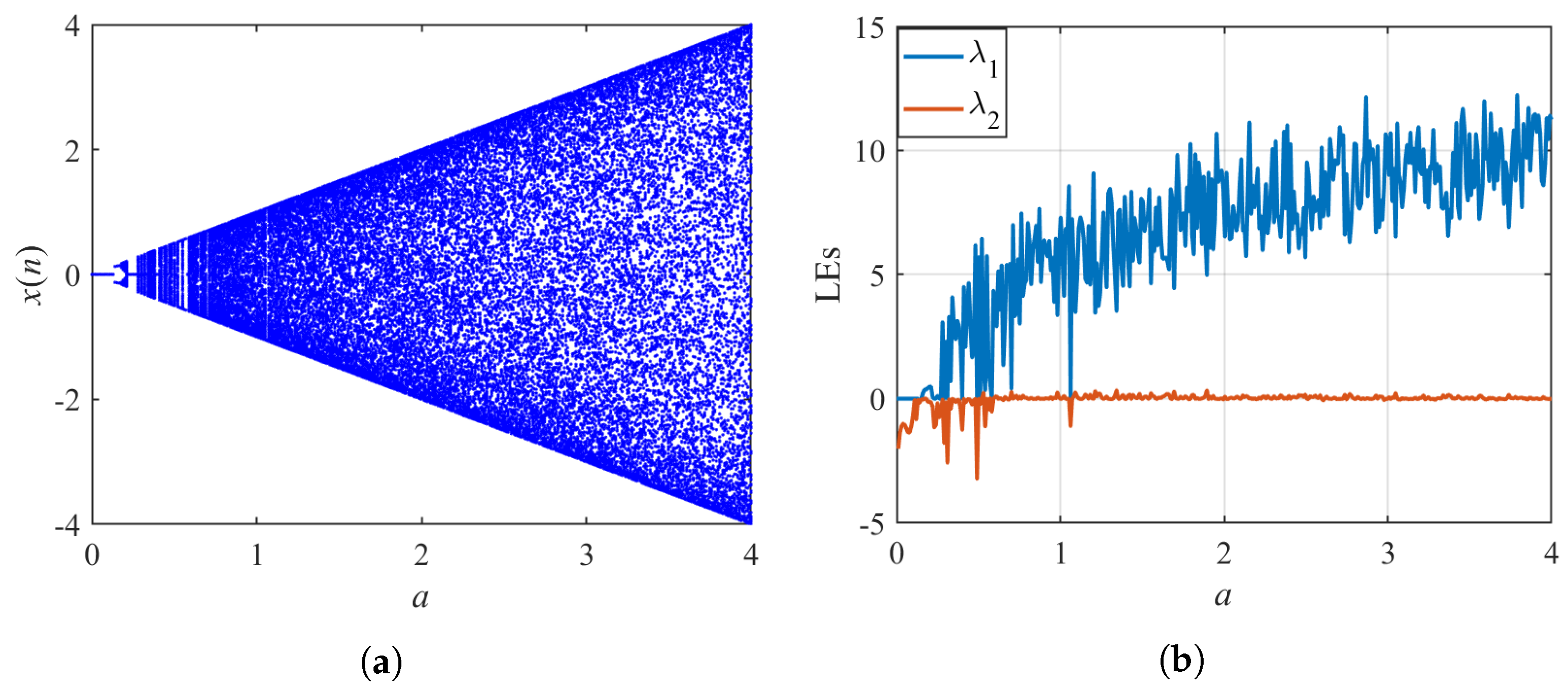
4.2. Bifurcation and LE of Multi-Internal Perturbations
5. Pseudo-Random Sequence Generator
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chua, L. Memristor–the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.; Kang, S. Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Chua, L. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.P.; Sah, M.P.; Kim, H.; Chua, L. Three fingerprints of memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 3008–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, N.; Li, D.; Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, W. Analog switching and artificial synaptic behavior of Ag/SiOx: Ag/TiOx/p++-Si memristor device. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Xia, Y.; Bai, Y.; Cao, J.; Gu, L. Fixed-time synchronization of the impulsive memristor-based neural networks. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2019, 77, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Hong, Q.; Deng, Q.; Chen, H. Memristor-based neural network circuit with weighted sum simultaneous perturbation training and its applications. Neurocomputing 2021, 462, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Hu, X.; Dong, Z.; Wang, L.; Mazumder, P. Memristor-based cellular nonlinear/neural network: Design, analysis, and applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 26, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamani, G.; Rajan, G.S.; Zhu, Q. Exponential state estimation for memristor-based discrete-time BAM neural networks with additive delay components. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 50, 4281–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Choi, H.; Park, S.; Sah, M.P.; Kim, H.; Chua, L. A memristor emulator as a replacement of a real memristor. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rziga, F.O.; Mbarek, K.; Ghedira, S.; Besbes, K. An efficient Verilog-A memristor model implementation: Simulation and application. J. Comput. Electron. 2019, 18, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Deng, C.; Pan, S.; Zhou, N. Image compression-encryption algorithms by combining hyper-chaotic system with discrete fractional random transform. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 103, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M. DNA encoding for RGB image encryption with memristor based neuron model and chaos phenomenon. Microelectron. J. 2020, 104, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Qu, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiong, Z. Synchronization, circuit and secure communication implementation of a memristor-based hyperchaotic system using single input controller. Chin. J. Phys. 2021, 71, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldarola, F.; Pantano, P.; Bilotta, E. Computation of supertrack functions for Chua’s oscillator and for Chua’s circuit with memristor. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numerical Simul. 2021, 94, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi, M.; Forti, M.; Storace, M. Stability analysis of the synchronous solution in arrays of memristive Chua’s circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2023, 70, 1694–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, N.; Mokaev, T.; Ponomarenko, V.; Seleznev, E.; Stankevich, N.; Chua, L. Hidden attractors in Chua circuit: Mathematical theory meets physical experiments. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 5859–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; He, P.; Li, G.; Xu, X.; Zhong, H. Multi-directional annular multi-wing chaotic system based on Julia fractals. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 165, 112799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, E.; Sun, X.; Song, Z. Multi-scroll fractional-order chaotic system and finite-time synchronization. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 025203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, H.; Huang, L.; Zang, H. Multistability dynamics analysis and digital circuit implementation of entanglement-chaos symmetrical memristive system. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, X.; Zhong, H. A image encryption algorithm based on coexisting multi-attractors in a spherical chaotic system. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 32005–32031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Li, G. Multi-image encryption algorithm based on wavelet transform and 3D shuffling scrambling. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 24757–24776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Ji, M.; Wang, L.; Duan, S. Memristor-based chaotic system with abundant dynamical behaviors and its application. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, A.X.; Zhu, B.D.; Wang, G.Y. Complex dynamic behaviors in hyperbolic-type memristor-based cellular neural network. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 020502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, G.; Iu, H.H.C.; Yu, S.; Yuan, F. A memristor–meminductor-based chaotic system with abundant dynamical behaviors. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 96, 765–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Dong, W.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Ding, Q. Discrete-time memristor model for enhancing chaotic complexity and application in secure communication. Entropy 2022, 24, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, B. Two-memristor-based chaotic system and its extreme multistability reconstitution via dimensionality reduction analysis. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 127, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, F.; Ren, G.; Tang, J. A class of initials-dependent dynamical systems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 298, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Iu, H.H.; Wang, C. Tri-valued memristor-based hyper-chaotic system with hidden and coexistent attractors. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 159, 112177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Sun, K.; Peng, Y.; Wang, L. Modeling of discrete fracmemristor and its application. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 015010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; He, S.; Sun, K. A higher dimensional chaotic map with discrete memristor. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 129, 153539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; He, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, K. A novel discrete memristive chaotic map. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Mou, J.; Xiong, L.; Han, X.; Yan, H.; Cao, Y. Hyperchaotic maps of a discrete memristor coupled to trigonometric function. Phys. Scr. 2021, 96, 125242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; He, S.; Sun, K. Chaos in the discrete memristor-based system with fractional-order difference. Results Phys. 2021, 24, 104106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhong, H.; Xu, W.; Xu, X. Two modified chaotic maps based on discrete memristor model. Symmetry 2022, 14, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mou, J.; Lu, J.; Banerjee, S.; Cao, Y. A discrete memristor coupled two-dimensional generalized square hyperchaotic maps. Fractals 2023, 11, 2340136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Mou, J.; Banerjee, S.; Zhang, Y. A hyperchaotic map with a new discrete memristor model: Design, dynamical analysis, implementation and application. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 167, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; He, S.; Sun, K.; Wang, H. A novel hyperchaotic map with sine chaotification and discrete memristor. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 120501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y. Sine chaotification model for enhancing chaos and its hardware implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, W. The fractional difference form of the sine chaotification model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 137, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Rajagopal, K.; He, S.; Jafari, S.; Sun, K. Chaotification of Sine-series maps based on the internal perturbation model. Results Phys. 2021, 31, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadoss, J.; Ouannas, A.; Tamba, V.K.; Grassi, G.; Momani, S.; Pham, V.T. Constructing non-fixed-point maps with memristors. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Hua, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Bao, B. Discrete memristor hyperchaotic maps. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2022, 68, 4534–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Bao, B. Parallel bi-memristor hyperchaotic map with extreme multistability. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2022, 160, 112273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhan, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, K.; Peng, Y. Discrete memristor and discrete memristive systems. Entropy 2022, 24, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Model | Memristor | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Q-DM | |
| Model 2 | A-DM | |
| Model 3 | S-DM | |
| Model 4 | E-DM |
| Model | Memristor | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Model 5 | Q-DM &A-DM | |
| Model 6 | E-DM& A-DM | |
| Model 7 | Q-DM& E-DM | |
| Model 8 | Q-DM, E-DM&A-DM |
| No. | Test Index | Number of Test | p Value a | Proportion | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Frequency | 1 | 0.304126 | 0.99 | pass |
| 2 | Block frequency | 1 | 0.032923 | 1 | Pass |
| 3 | Cumulative sums | 2 | 0.514124 | 0.98 | Pass |
| 4 | Runs | 1 | 0.798139 | 1 | Pass |
| 5 | Longest test | 1 | 0.779188 | 0.98 | Pass |
| 6 | Rank | 1 | 0.759756 | 1 | Pass |
| 7 | FFT | 1 | 0.383827 | 1 | Pass |
| 8 | Non-overlapping template | 148 | 0.401199 | 0.99 | Pass |
| 9 | Overlapping template | 1 | 0.455937 | 1 | Pass |
| 10 | Universal | 1 | 0.554420 | 0.98 | Pass |
| 11 | Approximate entropy | 1 | 0.236810 | 1 | Pass |
| 12 | Random excursions | 8 | 0.455937 | 0.98 | Pass |
| 13 | Random excursion variant | 18 | 0.534146 | 0.99 | Pass |
| 14 | Serial | 2 | 0.494392 | 0.99 | Pass |
| 15 | Linear complexity | 1 | 0.115387 | 0.98 | Pass |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yihyis, W.A.; He, S.; Tang, Z.; Wang, H. A Class of Discrete Memristor Chaotic Maps Based on the Internal Perturbation. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15081574
Yihyis WA, He S, Tang Z, Wang H. A Class of Discrete Memristor Chaotic Maps Based on the Internal Perturbation. Symmetry. 2023; 15(8):1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15081574
Chicago/Turabian StyleYihyis, Worke Adugna, Shaobo He, Zhouqing Tang, and Huihai Wang. 2023. "A Class of Discrete Memristor Chaotic Maps Based on the Internal Perturbation" Symmetry 15, no. 8: 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15081574
APA StyleYihyis, W. A., He, S., Tang, Z., & Wang, H. (2023). A Class of Discrete Memristor Chaotic Maps Based on the Internal Perturbation. Symmetry, 15(8), 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15081574







