Abstract
In this study, a facile strategy of regulated self-assembly synthesis of Mn-MIL-100, using sodium acetate (CH3COONa) as a mono-dentate ligand capping agent (CA), was proposed. The as-prepared product is denoted Mn-MIL-100-CA. The coordination modulation of CH3COONa, led by its interference in the connectivity and symmetry of the metal centers and organic nodes, plays a vital role in the synthesis process. The crystallinity, morphology, topology, and properties of such MOF products were improved, since the self-assembly process of Mn-MIL-100-CA was promoted and regulated effectively. The materials were systematically characterized via XRD, SEM, N2 isotherms, XPS, and TGA in terms of crystallization behavior, morphology, topology, chemical composition, and thermal and water stability. The ability of Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-CA to remove methylene blue (MB) from an aqueous solution was investigated using a UV–vis spectrophotometer. The results indicate that with the addition of a molar ratio of 50% CH3COONa, Mn-MIL-100-CA particles developed a regularly symmetrical morphology, i.e., ‘spherical pyramid-like structure’ crystals with a dimension of 2~5 μm. Their specific surface area and pore volume increased by 59.2% and 56.7%, respectively. The increased proportion of Mn3+ implies reduced crystal defects and improved crystal structural order and integrity, and therefore an enhanced water stability. Mn-MIL-100-CA exhibited excellent adsorption performance towards MB from aqueous solution. The equilibrium adsorption value was as high as 1079.9 mg/g, which is 44.7% higher than that of Mn-MIL-100 without the addition of CA. The good adsorption capacity and excellent water stability mean that Mn-MIL-100-CA has great potential for the practical removal of MB dye pollutants from water.
1. Introduction
Rapid economic growth has been witnessed in the last few decades. However, enormous development has prompted various crises in the world. One of the most severe problems, for example, is water pollution in the vicinity of factories and communities [1,2]. Efficient adsorption of contaminates is one of the most widely recognized and used environmental control approaches, and significant achievements have also been made in chemistry and engineering applications in related fields in recent years [3,4,5,6]. Various solid porous materials have been employed as an absorbent to remove pollutants from wastewater, including fruit peel [7], zeolite [8] or activated carbon [9], graphene oxide [10], polymeric resins [11], clay [12], and metal organic frameworks (MOFs) [13]. Among these, MOFs were found to possess a high removal efficiency in wastewater treatment [14]. Recently, MOFs, such as the emerging and promising materials fabricated through the self-assembly of metal ions and organic ligands [15,16], have attracted significant interest. The main advantages of such coordinated network structures are their high surface area, tunability, and uniformity [17,18]. Among the large variety of MOFs, a remarkable number of compounds known as M(iii)-MIL-100 (M(iii) designate the trivalent metal ion that forms a cluster including V3+ [19], Cr3+ [20], Fe3+ [21], Al3+ [22], Sc3+ [23] and Mn3+ [24]; these compounds exhibit permanent porosity with high specific surface areas and pore volumes, and possess outstanding thermal as well as chemical stability. Such unique inherent properties make MIL-100 a very good candidate for potential applications as a water adsorbent [25,26].
However, MOFs synthesized via conventional methods often require critical conditions, i.e., high temperature, tens of hours of reaction time, and sometimes, special reagents (HF, or HNO3 et al.), which could lead to massive energy consumption and environmental pollution that severely harms human health [27,28]. Besides, due to their unique growth mechanisms, it is difficult to control the properties of MOFs, in terms of size, shape, pore parameters, and stability [29], using traditional synthesis methods. Therefore, an innovative synthesis method that promotes the self-assembly of MOFs in order to control their properties is urgently needed.
Control of crystallization behavior, morphology, and topology such as the pore structure and dimensions of MOFs may result in exceptional performances in all practical applications [18,30]. Helge et al. reported the synthesis of a Mn-based analogue of the MIL-100-framework through a methanolic solvothermal process [24]. They found that the process could be completed within a very short reaction time (~2 h), at 125 °C and without using any strong acids. Apart from the synthesis of MOFs, the main drawbacks of the majority of MOFs include (i) their low crystallinity with poor crystal shape [31,32]; and (ii) their stability in methanol and ethanol, but significant decreases in crystallinity in water or open air [33,34,35]. Thanks to the impressive findings of Hermes et al. in a previous study [36], it was reported that MOFs’ performances, including their pore properties, crystal size, shape, and crystallinity can be significantly improved by introducing mono-dentate ligand salts as capping agents (CA) during the synthesis [27]. As a result, the nucleation and crystal growth processes can be controlled by the reaction time, temperature, solvent, and pH of the solution. Therefore, the influence of capping agents on MOFs is quite pronounced [30].
Based on the above consideration, in the present work, we propose a novel strategy of the regulated self-assembly synthesis of Mn-MIL-100, using sodium acetate (CH3COONa) as a capping agent. The Mn-MIL product named Mn-MIL-100-CA was designed to remove methylene blue (MB) pollutants from aqueous solution. In particular, the effects of the addition of CH3COONa on microstructure, morphology, topology, chemical composition, thermal and water stability, and the MB adsorption performance of Mn-MIL-100-CA have been investigated. It was believed that crystal nucleation and growth during the self-assembly synthesis of Mn-MIL-100-CA can be effectively promoted and regulated. Additionally, it was speculated that the topology of Mn-MIL-100-CA can be optimized by regulating the connectivity and the symmetry of the metal ions (or metal clusters) and organic nodes after introducing CA [37,38], since the connectivity and site symmetry of a node are probably the most important factors affecting the net topology of MOFs. Consequently, the as-prepared Mn-MIL-100-CA may demonstrate outstanding adsorption performance in removing MB from aqueous solution [39].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All chemicals were of analytical grade and used as received without any further purification. Among them, 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid (BTC), methylene blue (MB), methanol, and ethanol were provided by Aladdin (China). Mn(NO3)2 solution was supplied by Sigma Aldrich (America).
2.2. Synthesis of Mn-MIL-100
In a typical experiment, 420 mg of BTC (2 mmol) was dissolved in 35 mL of methanol under ultrasonic conditions. After 10 min, 0.520 mL (2.2 mmol) of 50 wt% Mn(NO3)2 solution was quickly added to the solution. After being kept in the same conditions for an extra 10 min, the solution was transferred to a 50 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave and then heated at 125 °C for 2 h, followed by cooling down to room temperature and washing with methanol and ethanol. The brown sediments obtained were centrifuged (8000 rpm; 8 min) then dried in a vacuum oven at room temperature for 24 h and weighed, yielding ~0.65 g of products from a 50 mL autoclave.
2.3. Synthesis of Mn-MIL-100-CA
The steps followed are quite similar to those followed in the synthesis of Mn-MIL-100. The only difference is that BTC and Mn(NO3)2 were mixed into 20 mL methanol, and a different mass of CH3COONa was added into a 15 mL methanol solution, making sure the molar ratio of CH3COONa/BTC was 10%, 30%, 50%, 70% and 100%, respectively. Then, two solutions were mixed under ultrasound for 10 min and poured into a 50 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave. The synthesis parameter details are given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Synthesis parameters of MOFs samples with various CA concentrations.
2.4. General Characterization
The prepared Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-CA were characterized systematically to observe their structure, morphology and topology. The synthesized samples were analyzed with powder X-ray diffraction (XRD, Cu Kα D8 Advance, Bruker, Germany) to study their structural features. The morphological properties of these MOFs were studied using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, S-4800, Hitachi, Japan). The thermal stability of these MOFs was investigated on a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA, TGA/DSC1, Mettler Toledo, Switzerland) in a temperature range of 25–600 °C at a heating rate of 5 °C min−1 under argon atmosphere. The composition and chemical status of the prepared samples was determined via X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, PHI5000 Versa Probe II). Furthermore, nitrogen sorption isotherms at 77 K were evaluated using an automatic gas adsorption apparatus (BelSorp Max), and the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method was applied to calculate the specific surface area.
2.5. Adsorption Performance Evaluation
The adsorption performance of the Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-CA was evaluated using a UV-vis analysis technique. The adsorption capability of the material was defined by the amount of MB absorbed by the Mn-MIL-100 sample synthesized with or without CA. The MB was dissolved into deionized water to prepare a 50 mg/L aqueous solution. Prior to the experiment, Mn-MIL-100 was dried in vacuum at room temperature for a day. The adsorption process was conducted by adding 5 mg of dried MOFs sample to the MB solution under stirring. At different time intervals, 2 mL of the above MB solution was removed and consequently centrifuged to determine the concentration of upper clear MB solution, using its adsorption band at ~664 nm, in the spectrum obtained on a Scinco S-4100 spectrophotometer. Such a procedure was repeated until the concentration of the obtained upper MB solution remained intact. The final concentration was deemed the equilibrium adsorption concentration of the MOF sample. In order to facilitate the calculation of the MB concentration, the relationship between adsorption peaks and the corresponding MB concentration was found, and the relevant linear fitting equation was also obtained accordingly. (Figure 1)
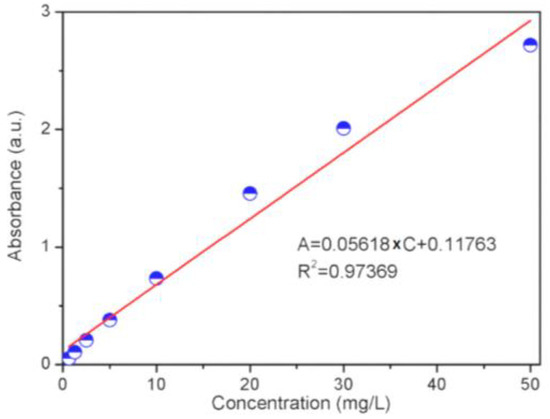
Figure 1.
Curve fitting between the absorbance (a.u.) and concentration (mg/L) of the UV-vis spectrum.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Properties
The XRD patterns of the prepared Mn-MIL-100 synthesized with or without CA are illustrated in Figure 2. The diffraction peaks of all samples match well with the standard pattern [24,40,41]. Strong peak intensities of both Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-CA indicate high crystallinity, while the most substantial diffraction peaks of Mn-MIL-100-CA are stronger than those of Mn-MIL-100. Such phenomena may happen for two reasons: firstly, the solvent molecules occluded inside the pores are different [42]; secondly, the coordination modulation regulation of the CA, possibly led by its interference in the connectivity and symmetry of the metal centers and organic nodes, is able to regulate the nucleation and crystal growth rate of Mn-MIL-100, and thereby improve its crystallinity [36].
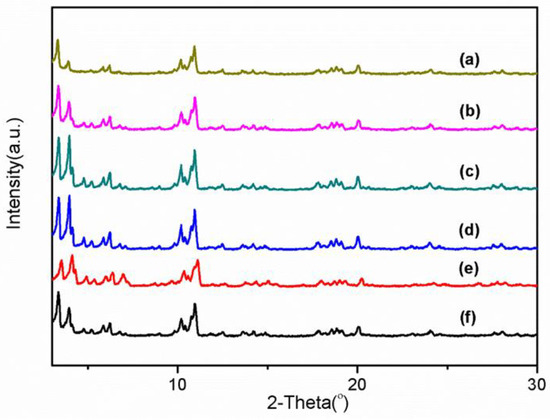
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of Mn-MIL-100 synthesized with or without CA. (a–f) show when the n(CA)/n(BTC) of the Mn-MOFs is 0, 10%, 30%, 50%, 70%, and 100%, respectively.
Morphological characterizations of Mn-MIL-100 synthesized with or without CA were performed on an FE-SEM and are shown in Figure 3. The influence of CA on the morphology of Mn-MIL-100 can be concluded based on comparisons of these SEM micrographs. Figure 3a shows that the Mn-MIL-100 particles had relatively irregular shapes with a random size distribution, and by adding the CA in various dosages, such a phenomenon was improved to a certain extent. When the molar ratio of CA was less than 30%, the regulating effect of CA on the crystal growth of Mn-MIL-100-CA was relatively weak. Consequently, the most synthesized products possessed a particle size larger than 10 μm, as shown in Figure 3b,c. The most obvious crystal growth-regulating effect of the CA was witnessed when the molar ratio of CA reached 50% (Figure 3d). As the amount of added CA increases, it coordinates with more metal centers during the MOF’s construction, and this may have a certain impact on the crystal growth’s orientation. Hence, the product shows a regular “spherical pyramid-like structure” morphology with a relatively uniform particle size ranging from 2 to 5 μm. However, further increasing the CA contents did not prompt any improvement in the morphology. In contrast, deterioration in both particle shape and distribution uniformity can be observed in Figure 3e,f. Such a trend was possibly prompted by the incomplete formation of the Mn-MIL-100 primary skeleton structure, since adding excessive CA forces means that more metal centers are involved in the reaction with the mono-dentate ligand, i.e., with the CA instead of the skeleton ligand.
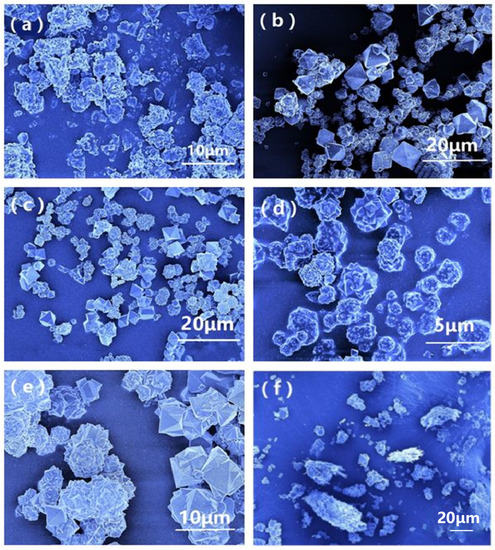
Figure 3.
SEM images of Mn-MIL-100 (a) and Mn-MIL-100-CA with a CA molar ratio of 10% (b), 30% (c), 50% (d), 70% (e), and 100% (f).
In order to gain a better understanding of the formation mechanism of the ‘spherical pyramid-like structure’ of Mn-MIL-100-CA, microstructures of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA prepared over various durations were observed using FE-SEM. The self-assembly process of crystal growth was tracked and analyzed. Figure 4a shows that the Mn-MIL-100-50%CA synthesized in 60 min mainly has an octahedral geometry with a nanoscale (~60 nm) particle size. As the number of nanograins increased, the crystal growth followed the Oswald ripening mechanism, whereby large crystals grow by swallowing small ones [43]. When the synthesis time extended to 80 min, the crystal rapidly grew to ~1 μm in dimension. At this moment, the octahedral morphological features of crystals remained intact, although the overall appearance became a combination of several regular octahedra, as shown in Figure 4b. In addition, a great deal of nanograins can be observed on the surface along the (111) crystal plan of the Mn-MIL-100-CA octahedron. Such ultrafine grains became new nucleation sites, which promoted crystal growth along the surface or edges of the (111) crystal plan. The crystal size reached ~2 μm after 90 min of synthesis, while the crystal morphology was irregular, as it was still in a growth transition state (Figure 4c). To minimize the surface free energy, the crystal tended to grow into a spherical-like shape with a diameter of approximate ~3 μm when the synthesis time reached 100 min, as illustrated in Figure 4d. Irregular octahedrons with teeming edges and corners can be found on the crystal surface. Figure 4e shows that a typical pyramid-like structure formed on the surface, with the crystallization degree increasing after 120 min of synthesis. Eventually, the crystal particles showed more regularly symmetrical morphological features. Further extending the synthesis time to 150 min provided no apparent improvement in the overall morphology of the crystals (Figure 4f).
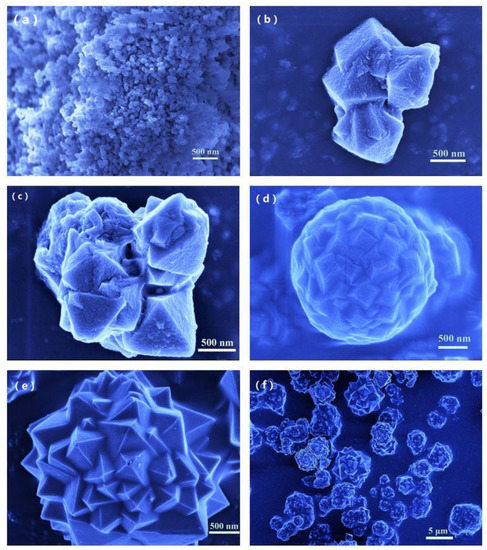
Figure 4.
Crystal growth process of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA, (a) 60 min, (b) 80 min, (c) 90 min, (d) 100 min, (e) 120 min, and (f) 150 min.
3.2. Isotherms Study
As shown in Figure 5a, the sorption isotherm is a type-I isotherm for both Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-CA, according to IUPAC classification. This both suggests and confirms that they feature a microporous topology. The sorption isotherm cure of Mn-MIL-100 shows a relatively slow increasing trend between p/p0 ~ 0.01 and 0.18 that indicates the characteristic of large pores, which can be attributed to the larger cages of the MIL-100 frameworks [44]. Moreover, a capillary condensation step can be observed in the isotherms. This may result from primary mesopore cages (p/p0 = 0.40 to 0.70), and interchannel mesopores may result from structural defects (p/p0 = 0.90 to 0.99) [45]. By comparison, the N2 adsorption value of the Mn-MIL-100-50%CA was significantly increased after introducing CA. Such a phenomenon implies that both specific surface area and topology, such as the pore structure and dimensions of Mn-MIL-100, can be greatly affected by the addition of CA.
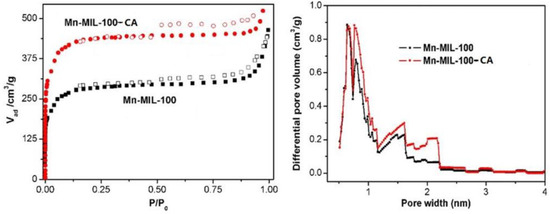
Figure 5.
N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms (a) and HK-model pore distribution (b) of Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-CA.
The BET analysis data of the synthesized MOFs are given in Table 2. The influences of CA on the specific surface area and pore structure of the MOF products can observed in the following three aspects. (i) Specific surface area (BET): the specific area of the Mn-MIL-100-CA increases with the amount of CA added, that is, until it reaches a maximum value of 1671.3 m2/g when the dosage of CA is 1.0 mmol; this represents an improvement of 59.2% compared to the Mn-MIL-100 sample (1050.1 m2/g). The specific surface area decreases as the added amount of CA increases. (ii) Pore size distribution: the average pore size of Mn-MIL-100-CA reduces after adding the CA, although the impact degree varies. (iii) Total pore volume: the influences of CA on the pore volume of MOF products are similar to the observations made with BET; they exhibit the varying trends of increasing first and then decreasing. The pore volume increased from 0.67 m3/g to a maximum of 1.05 m3/g (an improvement of 56.7%) when the specific surface area of the Mn-MIL-100-50%CA sample reached a maximum. In addition, it can be concluded that the pore number per unit mass of the Mn-MIL-100-CA samples significantly increased according to the variation trend of the average pore diameter and total pore volume. This indicates that addition of CA in the synthesis of Mn-MIL-100 can stabilize the internal pore structure and reduce the formation of crystal defects. This implies that addition of CA may improve the order and stability of the second building units (SUBs) of Mn-MIL-100, and thereby exert a regulation effect on the self-assembly of Mn-MIL-100. Such topology effects are also verified by the HK-model pore distribution results shown in Figure 5b. Mn-MIL-100-50%CA has a relatively higher quantity of micropores, especially the proportion of these pores with diameter of 1–2 nm, compared to the Mn-MIL-100. This is likely due to the fact that the mono-dentate ligand capping agent could coordinate with the metal centers originally linked to the carboxylic acid group of the multi-dentate ligand, i.e., BTC, during the Mn-MIL-100 construction process. Such a consequence was thought to be similar to results of the ‘partial truncation’ strategy [46] used in reduced-symmetry ligand design for gaining MOFs with versatile topologies. Since the CAs interfere in the connectivity and symmetry of the SUBs, a greater number of cages with different geometries and relatively small dimensions can eventually be formed.

Table 2.
BET surface, mean pore diameter, and pore volume of samples.
3.3. Surface Components
Mn-MIL-100 synthesized with or without CA was investigated using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) for determining the effect of CA on the surface chemical components of these MOFs. The relevant results are given in Figure 6 and Table 3. By performing peak-fitting deconvolution, the C1s peak could be separated into two peaks near 284.7 eV and 288.7 eV, which are attributed to the carbon bond in the benzene ring and the C=O in carboxylic acid, respectively [47], as shown in Figure 6a. For the O1s spectra in Figure 6b, three peaks located at 530.0 eV, 531.7 eV and 533.1 eV were assigned to the O atom in the carbonyl group, the O atom in carboxylic acid, and the adsorption of oxygen or water, respectively [48]. In Figure 6c, the Mn2p peaks could be deconvoluted to two peaks. The peaks at 642.3 eV and 645.1 eV represent Mn3+ and Mn4+, respectively [49].
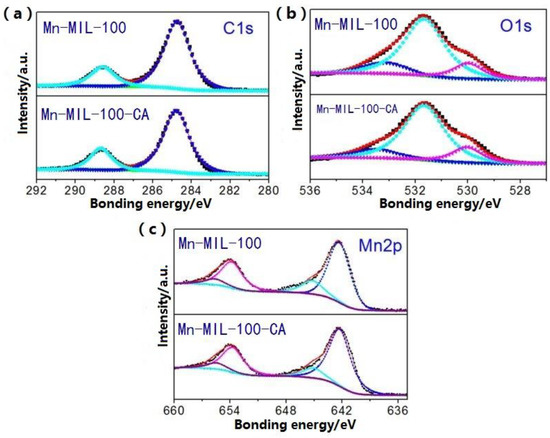
Figure 6.
XPS spectra peak-fitting curves of (a) C1s, (b) O1s, and (c) Mn2p.

Table 3.
XPS analysis data of Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-50%CA.
It can be observed from Table 3 that obvious chemical variations occurred on the surface of Mn-MIL-100-CA. The carbon atom ratio of Mn-MIL100-50%CA is 53.4%, which represents an increase of 4.2% compared to that of Mn-MIL-100 (49.2%), whilst the oxygen and manganese atom ratios reduced from 37.4% to 34.4%, and from 13.1% to 11.8%, respectively. Interestingly, the increased value of C atom content is approximately level with the total decreased value of O and Mn atoms. Moreover, the addition of CA also had great influence on the valence state of the metal atoms within the MOFs. Without adding any CA, the Mn3+ proportion of the pristine Mn-MIL-100 is 80.4%. By comparison, the Mn3+ proportion of the Mn-MIL-100-CA synthesized with the involvement of 50% CA actually increased by 5.2%. Usually, the Mn element in the defect-free ordered Mn-MIL-100 exists in the form of trivalent metal ions. In other words, the larger the proportion of Mn3+ in Mn-MIL-100, the more ordered the structure, and the smaller the number of defects. Such findings verified the positive effect of CA addition on the structural stability of Mn-MIL-100-CA.
3.4. Thermal and Water Stability
Thermogravimetric analysis is a useful tool for studying the thermal stability of a sample. Mn-MIL-100 showed an outstanding thermal stability up to 450 °C in an argon atmosphere, as given in Figure 7. Three different stages of weight loss between 25 °C and 600 °C can be observed in the TGA curves of all the MOF products. The first weight loss from 25 to 120 °C corresponds to removal of the methanol (or ethanol) and water remains inside the pores. The second weight loss from 120 to 240 °C may be caused by the residual acid attached to the metal sites [24]. The final weight loss above 450 °C is attributed to the breakdown of the MOFs, which resulted from the disintegration of organic ligands followed by the formation of metal oxide residuals [50]. By comparing the TGA curves of Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-50%CA, it can be noted that the latter shows a remarkable improvement of ~20 °C in its decomposition temperature. In addition, with the increase in the CA dosage, the residual mass after absolute decomposition showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. The residual mass of Mn-MIL-100 was 38.2% of the initial mass of the sample, while that of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA reached a peak value of 46.2%, which was 8% higher than the former. Such an increase implies that the Mn element per unit mass in the Mn-MIL-100-CA crystal structure is higher. In other words, it reflects that Mn-MIL-100-CA has better structural stability due to the reduction of its defects.
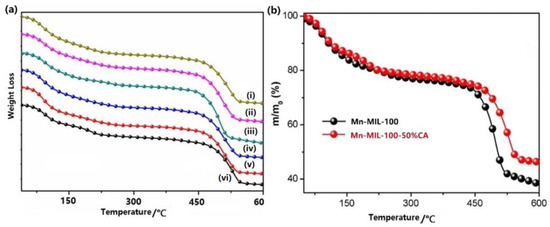
Figure 7.
(a) TGA curves of Mn-MIL-100 with a CA molar ratio of 0 (i), 10% (ii), 30% (iii), 50% (iv), 70% (v), and 100% (vi), and (b) TGA curves comparisons between Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-50%CA.
The water stability of MOFs is one of most decisive factors in their adsorption performance in practice. In order to examine water stability, a 24 h water soaking experiment was carried out on both Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-50%CA. Before and after the water soaking experiment, XRD and BET analyses were conducted on both MOFs, and the relevant results are presented in Figure 8 and Table 4.
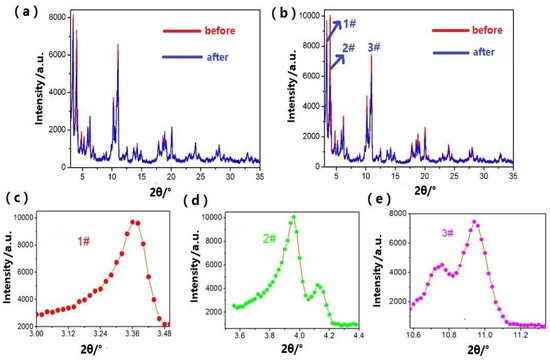
Figure 8.
XRD patterns of MOFs before and after the water soaking: (a) Mn-MIL-100, (b) Mn-MIL-100-50%CA, and (c–e) corresponding to 1#, 2#, and 3# peak of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA, respectively.

Table 4.
XRD peak area and BET data of the MOFs before and after water soaking.
The peak area in an XRD pattern can be used to characterize the structural features of the inner pores and crystallinity of MOFs [51], which is a primary measure of the structural integrity of these materials. The greater the structural integrity of the MOFs after exposure to the medium, the more stable they are in such a medium, and the larger the corresponding XRD peak area. From Table 4, it can be seen that prior to the water soaking experiment, the three main XRD peak areas of Mn-MIL-100-50%AC are relatively higher than those of Mn-MIL-100. This indicates that the addition of CA can improve the crystallinity of the Mn-MIL-100-CA product. After water soaking, the 2# peak areas of both samples become very close, since they are mainly affected by the guest molecules in the MOFs’ structures. Meanwhile, the 1# and 3# XRD peak areas of Mn-MIL-100-after reduce by 10.8% and 32.8%, respectively; these are much higher than the reduction rates of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA-after, i.e., 6.1% and 13.8%. Meanwhile, the specific surface area of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA-after only reduced by 9.4%, and remained 1514.2 m2/g. In contrast, the Mn-MIL-100-after showed a significant decrease of 22.4% in its specific surface area, which reduced to 812.8 m2/g. Therefore, the addition of CA can provide Mn-MIL-100-CA with a remarkable improvement in its water stability, which has important significance for its application in engineering.
3.5. Adsorption Ability with Regard to MB
The synthesized materials were used for MB dye removal from aqueous solution in order to evaluate their adsorption performance. MB is a typical cationic dye with dimensions of 1.43 nm × 0.61 nm × 0.4 nm [52].
The adsorbed quantities (qt) of MB dyes are related to time t, and can be defined as follows:
where qt is the amount (mg/g) of MB adsorbed on MOFs at time t, and Ct and C0, respectively, represent the MB concentration (mg/L) at time t and the initial concentration of MB. V is the total volume (L) of the MB dye solution, and M is the mass of the absorbent. Moreover, qe and Ce correspond to qt and Ct at equilibrium, respectively.
As shown in Figure 9a,b, the MB adsorption capacity of Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-50%CA increased rapidly at the initial stage, then gradually slowed down as the time increased, and finally approached adsorption equilibrium. This implies that the adsorption rate of the material was relatively higher at the beginning, then began to decrease until the adsorption equilibrium was established after 120 min. Meanwhile, at absorption equilibrium, Mn-MIL-100-50%CA shows a weaker absorbance compared with Mn-MIL-100, as observed from the UV-visible spectra given in Figure 9c. This indicates that less MB remained in the solution after adsorption, and Mn-MIL-100-50%CA absorbed the majority of the MB dye (and therefore possess the greater MB adsorption capability). Figure 9d shows that the equilibrium adsorption values of the MOFs first show an increasing then a decreasing trend as the CA content increases. The equilibrium adsorption value of Mn-MIL-100 with no CA addition was 742.8 mg/g. When the molar ratio of CA became 50%, the equilibrium adsorption value of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA increased by 44.7%, and reached a maximum of 1074.9 mg/g. However, upon further increasing the CA content, the adsorption performance of the material deteriorated. Such phenomena are in good accordance with previous findings regarding the trends of CA’s influence on microstructure, morphology and pore topology. The coordination modulation of CA and its regulation of the nucleation and crystal growth of Mn-MIL-100-CA gradually increase as the amount of added CA increases, and reach a maximum when the molar ratio of CA is 50%. At this point, the crystallinity, morphology regularity, and dimension uniformity of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA was obviously improved, and the product developed into a regularly symmetrical morphological appearance, i.e., ‘spherical pyramid-like structure’ crystals with a dimension of 2~5 μm. Mn-MIL-100-50%CA also shows a relatively higher quantity of micropores, especially the proportion of these pores with diameter of 1–2 nm. Its specific surface area and pore volume increased by 59.2% and 56.7%, respectively. Moreover, increasing the Mn3+ proportion of the surface chemical composition caused a reduction in crystal defects; improved crystal structural order and integrity of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA was achieved, and this served to enhance water stability. Hence, stronger water stability combined with enhanced specific surface area and pore topology mean Mn-MIL-100-CA has an outstanding adsorption performance with MB.
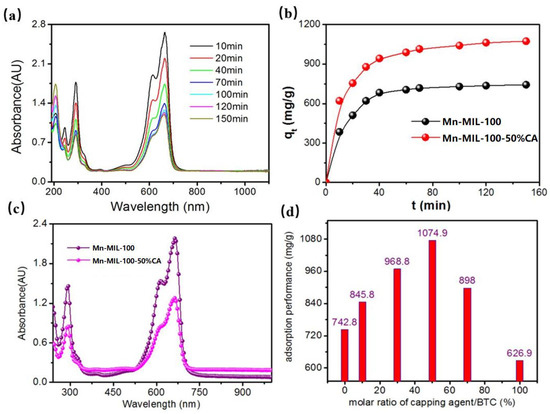
Figure 9.
(a) UV-vis spectra of Mn-MIL-100-50%CA during its adsorption process with MB; (b) adsorption kinetics curves of Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-50%CA; (c) UV-vis spectra of Mn-MIL-100 and Mn-MIL-100-50%CA at adsorption equilibrium; (d) equilibrium adsorption values of Mn-MIL-100-CA with different amounts of added CA.
The adsorption performance of Mn-MIL-100-CA was significantly improved compared with Mn-MIL-100. This can mainly be attributed to the following three aspects. First, the introduction of CA greatly improved the specific surface area and topology features of Mn-MIL-100-CA, which provided a basic guarantee for MB adsorption. Secondly, the coordination modulation of CA, led by its interference the connectivity and symmetry of the SUBs, plays a vital role in the synthesis process, to a certain extent. According to the results of a previous analysis, it is known that introduction of CA can effectively reduce crystal defects and improve the crystal structural order and integrity of Mn-MIL-100-CA, thereby enhancing its water stability. Last but not least, the ‘spherical pyramid-like structure’ morphological feature of Mn-MIL-100-CA can notably prevent powder aggregation in order to facilitate the formation of a suspension in the solution, so that the outstanding adsorption performance towards MB can be achieved eventually.
4. Conclusions
In summary, in this study, Mn-MIL-100-CA was successfully designed and synthesized by introducing CH3COONa as a mono-dentate ligand CA to regulate crystal nucleation and growth. Specifically, the coordination modulation of CH3COONa, led by its interference in the connectivity and symmetry of the SUBs, plays a vital role in the synthesis process. The microstructure, morphology, and topology of the MOF product were greatly improved, since the self-assembly process of Mn-MIL-100-CA was promoted and regulated effectively. The results reveal that with the addition of a molar ratio of 50% CH3COONa, Mn-MIL-100-CA particles developed into a regular symmetrical morphological appearance, i.e., ‘spherical pyramid-like structure’ crystals with a dimension of 2~5 μm. Their specific surface area and pore volume were increased by 59.2% and 56.7%, respectively. Meanwhile, the chemical composition of the surface and the valence state of the metal atoms were also modified. The proportion of Mn3+ increased by 5.2%, which effectively reduced the crystal defects and improved the crystal structural order and integrity of Mn-MIL-100-CA, thereby enhancing its water stability. Hence, the as-prepared Mn-MIL-100-50%CA exhibited excellent adsorption performance when removing MB from aqueous solution. Its equilibrium adsorption value is as high, at 1079.9 mg/g, which is 44.7% higher than that of Mn-MIL-100 without the addition of CA. Mn-MIL-100-CA’s good adsorption capacity and excellent water stability means it has great potential for the practical removal of MB dye pollutants from water.
Author Contributions
G.S. conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, original writing, funding acquisition; C.S. investigation, formal analysis, data curation, original draft preparation; D.B. methodology, editing and reviewing; Q.L. methodology, supervision, funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Shenzhen Science and Technology Program JCYJ20180306174102763, JSGG20201102172801004 and WDZC2020821100123001.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Primack, R.B.; Morrison, R.A. Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 401–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Deng, B.W.; Yu, L.Z.; Cui, E.B.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, W. Degradation of azo dyes Congo red by MnBi alloy powders: Performance, kinetics and mechanism. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 251, 123096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.D.; Li, Z.L.; Cheng, B.W.; Zhuang, X.P.; Lin, T. Hierarchical porous metal organic framework aerogel for highly efficient CO2 adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.; Reimus, P.; Ma, F.N.; Soltanian, M.R.; Xing, B.S.; Zang, J.Z.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Z.X. Plutonium reactive transport in fractured granite: Multi-species experiments and simulations. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.S.; Huang, X.F.; Wu, Q.F.; Li, M.; Xie, Q.L.; Liu, Z.W.; Zou, X.M. Adsorption of sulfonamides on polyamide microplastics in an aqueous solution: Behavior, structural effects, and its mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Dai, L.Y.; Yao, J.C.; Guo, T.J.; Hrynsphan, D.; Tatsiana, S.; Chen, J. Enhanced adsorption and reduction performance of nitrate by Fe–Pd–Fe3O4 embedded multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Nayak, A. Cadmium removal and recovery from aqueous solutions by novel adsorbents prepared from orange peel and Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 180, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solińska, A.; Bajda, T. Modified zeolite as a sorbent for removal of contaminants from wet flue gas desulphurization wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.Z.; Song, G.L.; Tang, G.Y. A facile modification method of activated carbon by spark discharge of atmospheric pressure plasma jets to improve its adsorption performance of methylene blue. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 354, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbe-Ek, J.; Andrade-Martínez, J.; Gómez, R.; Rodríguez-González, V. A functional assembly of SiO2 nanospheres/graphene oxide composites. Mater. Lett. 2015, 142, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, L.C.D.S.; Aguiar, M.R.M.P.; D’Elia, P.; Ferreira, L.O.; Wang, S.H. Comparative adsorptive removal of biperidene and sibutramine chlorhydrates from methanolic solutions by using active coal, clay and polymeric resins. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3395–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuabonah, E.I.; Günter, C.; Weber, J.; Lubahn, S.; Taubert, A. Hybrid clay: A new highly efficient adsorbent for water treatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Shan, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.T.; Kong, Q.Q.; Pang, H. Application of metal organic framework in wastewater treatment. Green Energ. Environ. 2022, 8, 698–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Agboola, O.S.; Ogunmodede, J.; Araoye, A.O.; Bello, O.S. Metal-organic frameworks as adsorbents for sequestering organic pollutants from wastewater. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 253, 123246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Li, A.H.L.; Yaghi, O.M. Highly porous and stable metal-organic frameworks: structure design and sorption properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Chen, B.L.; Reineke, T.M.; Li, H.L.; Eddaoudi, M.; Moler, D.B.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Assembly of metal−organic frameworks from large organic and inorganic secondary building units: new examples and simplifying principles for complex structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8239–8247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J.; Rosi, N.; Vodak, D.; Wachter, J.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in methane storage. Science 2002, 295, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.L.; Chen, K.J.; Xing, H.B.; Yang, Q.W.; Krishna, R.; Bao, Z.B.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Dong, X.L.; Han, Y.; et al. Pore chemistry and size control in hybrid porous materials for acetylene capture from ethylene. Science 2016, 353, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, A.; Leclerc, H.; Devic, T.; Serre, C.; Margiolaki, I.; Mahjoubi, F.; Lee, J.S.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; Chang, J.S. MIL-100(V)—A mesoporous vanadium metal organic framework with accessible metal sites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 157, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferey, G.; Serre, C.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Millange, F.; Surble, S.; Dutour, J.; Margiolaki, I. A hybrid solid with giant pores prepared by a combination of targeted chemistry, simulation, and powder diffraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 6296–6301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, P.; Surble, S.; Serre, C.; Hong, D.Y.; Seo, Y.K.; Chang, J.S.; Greneche, J.M.; Margiolaki, I.; Ferey, G. Synthesis and catalytic properties of MIL-100(Fe), an iron(iii) carboxylate with large pores. Chem. Commun. 2007, 27, 2820–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkringer, C.; Popov, D.; Loiseau, T.; Fe’rey, G.; Burghammer, M.; Riekel, C.; Haouas, M.; Taulelle, F. Synthesis, single-crystal X-ray microdiffraction, and NMR characterizations of the giant pore metal-organic framework aluminum trimesate MIL-100. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 5695–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, J.P.S.; Miller, S.R.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Seymour, V.R.; Ashbrook, S.E.; Wright, P.A. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption properties of microporous scandium carboxylates with rigid and flexible frameworks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 142, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinsch, H.; Stock, N. Formation and characterization of Mn-MIL-100. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2013, 15, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.K.; Yoon, J.W.; Lee, J.S.; Hwang, Y.K.; Jun, C.H.; Chang, J.S.; Wuttke, S.; Bazin, P.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M.; et al. Energy-efficient dehumidification over hierachically porous metal–organic frameworks as advanced water adsorbents. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremias, F.; Khutia, A.; Henninger, S.K.; Janiak, C. MIL-100(Al, Fe) as water adsorbents for heat transformation purposes—A promising application. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 10148–10151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.L.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Qiu, S.L.; Lercher, J.A.; Zhang, H.J. Coordination modulation induced synthesis of nanoscale Eu1-xTbx-metal-organic frameworks for luminescent thin films. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4190–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendon, C.H.; Tiana, D.; Fontecave, M.; Sanchez, C.; D’Arras, L.; Sassoye, C.; Rozes, L.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Walsh, A. Engineering the optical response of the titanium-MIL-125 metal–organic framework through ligand functionalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10942–10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Wang, K.Y.; Powell, J.; Zhou, H.C. Controllable synthesis of metal-organic frameworks and their hierarchical assemblies. Matter 2019, 1, 801–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunzen, H.; Grzywa, M.; Hambach, M.; Spirkl, S.; Volkmer, D. From micro to nano: A toolbox for tuning crystal size and morphology of benzotriazolate-based metal–organic frameworks. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 3190–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.D. A general and efficient approach for tuning the crystal morphology of classical MOFs. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Kim, T.; Choi, S.; Oh, M. Improvement in crystallinity and porosity of poorly crystalline metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) through their induced growth on a well-crystalline MOF Template. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 9048–9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.P.; Yang, J.M.; Kang, Y.S.; Guo, F.; Sun, W.Y. Facile water-stability evaluation of metal–organic frameworks and the property of selective removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8753–8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, T. Water stable MOFs as emerging class of porous materials for potential environmental applications. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.L.; Cai, X.C.; Jiang, H.L. Improving MOF stability: Approaches and applications. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes, S.; Witte, T.; Hikov, T.; Zacher, D.; Bahnmuller, S.; Langstein, G.; Huber, K.; Fischer, R.A. Trapping metal-organic framework nanocrystals: an in-situ time-resolved light scattering study on the crystal growth of MOF-5 in solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5324–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Deconstructing the crystal structures of metal-organic frameworks and related materials into their underlying nets. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 675–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Timmons, D.J.; Yuan, D.Q.; Zhou, H.C. Tuning the topology and functionality of Metal−Organic Frameworks by ligand design. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Liu, X.F.; Lah, M.S. Topology analysis of metal–organic frameworks based on metal–organic polyhedra as secondary or tertiary building units. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 336–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.; Mu, M.M.; Liu, Q.L.; Ji, N.; Song, C.F.; Ma, D.G. Mn-MIL-100 heterogeneous catalyst for the selective oxidative cleavage of alkenes to aldehydes. Catal. Commun. 2018, 103, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Zhao, Q.D.; Li, X.Y. Synthesis of bimetallic MOFs MIL-100 (Fe-Mn) as an efficient catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Q.; Zhang, A.F.; Hou, K.K.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.X.; Song, C.S.; Zhang, G.L.; Guo, X.W. Size- and morphology-controlled NH2-MIL-53(Al) prepared in DMF–water mixed solvents. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 13698–13705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voorhees, P.W. The theory of Ostwald ripening. J. Stat. Phys. 1985, 38, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, S.; Frank, H.; Michael, F.; Lorenz, K.; Viola, D.; Matthias, T.; Christian, S.; Gérard, F.; Norbert, S. Giant pores in a chromium 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylate open-framework structure with MIL-101 topology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 3791–3794. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Che, R.C.; Chen, G.; Fan, J.W.; Sun, Z.K.; Wu, Z.X.; Wang, M.H.; Li, B.; Wei, J.; Wei, Y.; et al. Radially oriented mesoporous TiO2 microspheres with single-crystal–like anatase walls for high-efficiency optoelectronic devices. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.R.; Verdegaal, W.M.; Liu, T.F.; Zhou, H.C. Isostructural metal-organic frameworks assembled from functionalized diisophthalate ligands through a ligand-truncation strategy. Chem.—A Euro. J. 2013, 19, 5637–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzyk, A.P.; Rychlicki, G. The influence of activated carbon surface chemical composition on the adsorption of acetaminophen (paracetamol) in vitro: The temperature dependence of adsorption at the neutral pH. Colloids Surf. A 2000, 163, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Xu, J.; Dai, E.B.; Qiu, J.J.; Yi, L. Synthesis and properties of ferrocene confined within UiO-67 MOFs. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 264, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Yang, G.L.; Li, P.L.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, P.Y. Promotion of formaldehyde oxidation over Ag catalyst by Fe doped MnOx support at room temperature. Catal. Today 2016, 277, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Li, H.G.; Hou, F.L.; Yang, Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, N.; Wang, Y.X.; Cui, L.F. Synthesis of highly efficient Mn2O3 catalysts for CO oxidation derived from Mn-MIL-100. App. Sur. Sci. 2017, 411, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canivet, J.; Fateeva, A.; Guo, Y.M.; Coasne, B.; Farrusseng, D. Water adsorption in MOFs: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5594–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelekani, C.; Snoeyink, V.L. Competitive adsorption between atrazine and methylene blue on activated carbon: The importance of pore size distribution. Carbon 2000, 38, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).