High-Intensity Harmonic Generation with Energy Tunability Produced by Robust Two-Color Linearly Polarized Laser Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
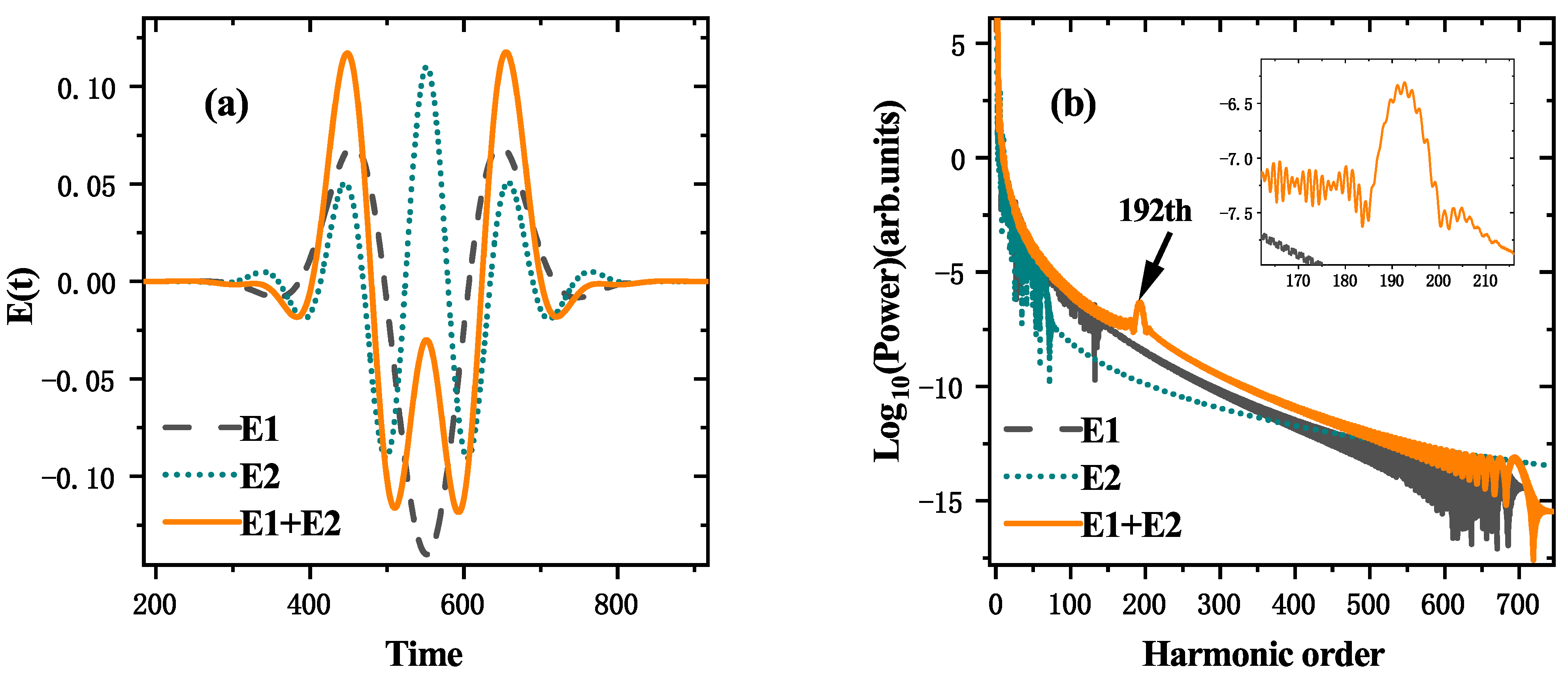
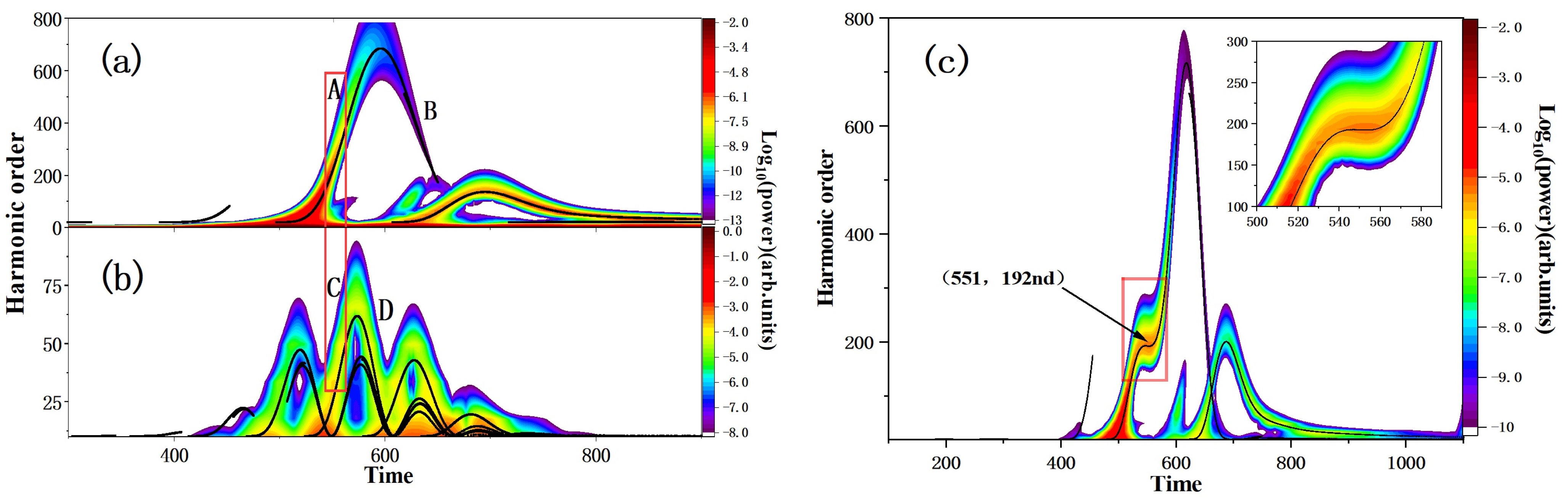
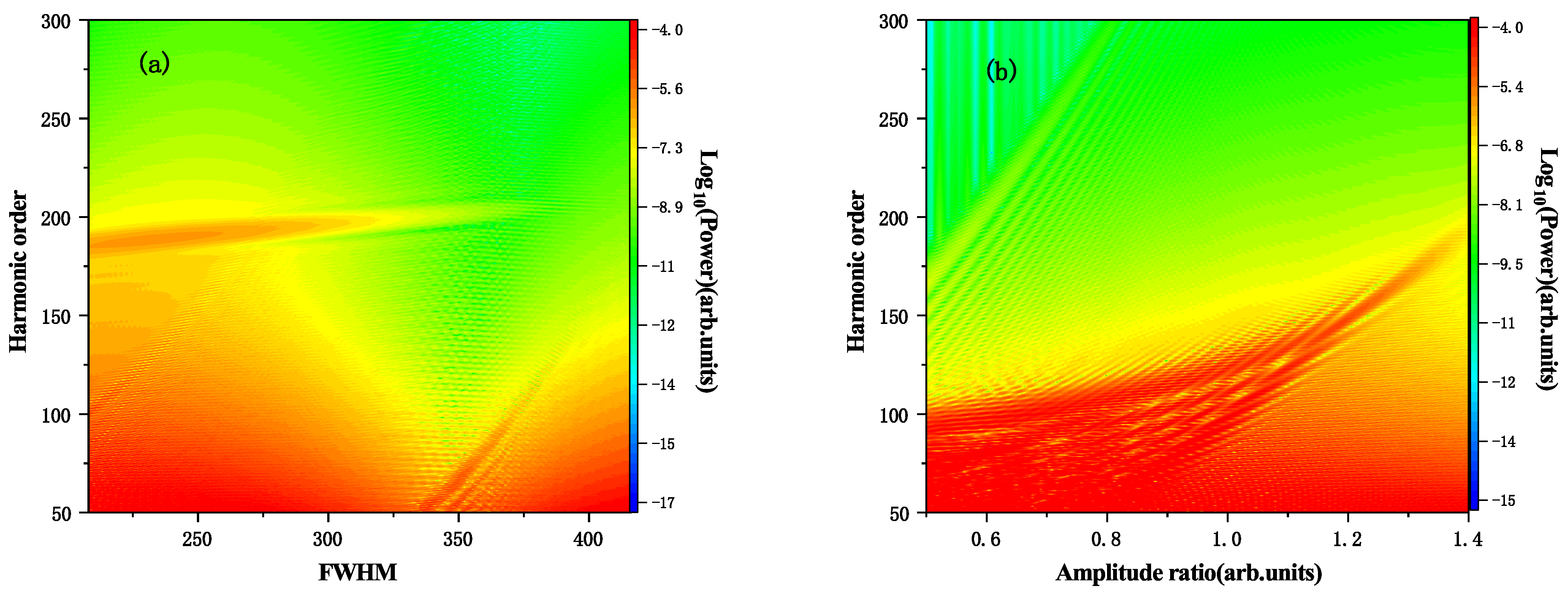
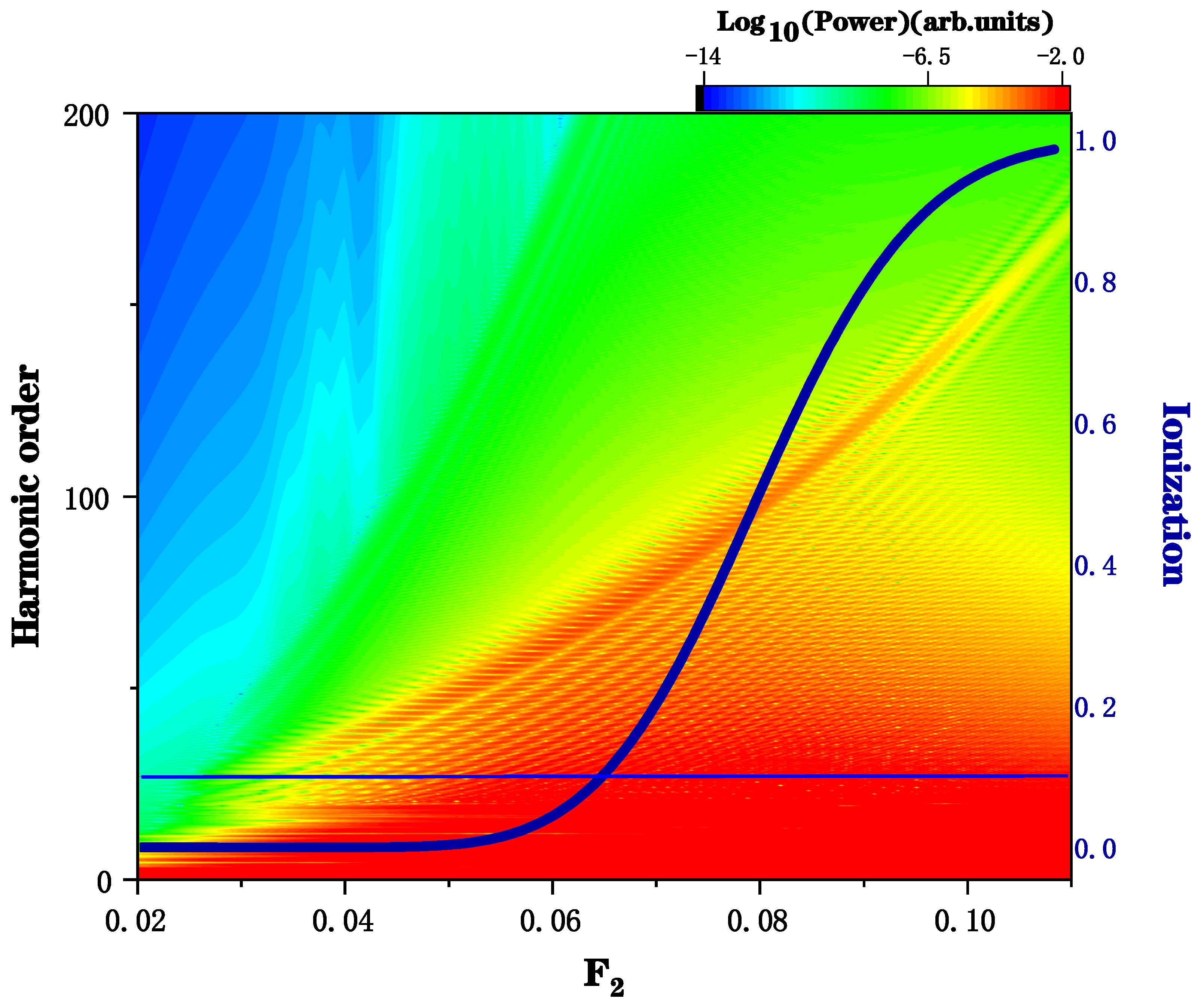
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.C.; Arpin, P.; Popmintchev, T.; Gerrity, M.; Zhang, B.; Seaberg, M.; Popmintchev, D.; Murnane, M.; Kapteyn, H. Bright, coherent, ultrafast soft X-ray harmonics spanning the water window from a tabletop light source. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 173901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausz, F.; Ivanov, M. Attosecond physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2009, 81, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, S.; Khan, S.D.; Wu, Y.; Chini, M.; Chang, Z. Isolated attosecond pulse generation without the need to stabilize the carrier-envelope phase of driving lasers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 093902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Tian, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y. Polarization properties of below-threshold harmonics from aligned molecules H2+ in linearly polarized laser fields. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 18106–18116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staudte, A.; Ruiz, C.; Schöffler, M.; Schössler, S.; Zeidler, D.; Weber, T.; Meckel, M.; Villeneuve, D.; Corkum, P.; Becker, A.; et al. Binary and recoil collisions in strong field double ionization of helium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 263002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudenko, A.; De Jesus, V.; Ergler, T.; Zrost, K.; Feuerstein, B.; Schröter, C.; Moshammer, R.; Ullrich, J. Correlated two-electron momentum spectra for strong-field nonsequential double ionization of He at 800 nm. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 263003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Guo, F.M.; Chen, J.G.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.J. Ionization of an atom with different initial angular momenta in an intense circular polarized laser field. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2020, 53, 235601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.; Bucksbaum, P. Above-threshold double-ionization spectroscopy of argon. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 64, 053405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.L.; Midorikawa, K. Above-threshold double ionization of helium with attosecond intense soft X-ray pulses. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 013407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Wei, S.S.; Guo, F.M.; Zeng, S.L.; Chen, J.G.; Yang, Y.J. Investigation on the influence of atomic potentials on the above threshold ionization. Chin. Phys. B 2014, 23, 053202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niikura, H.; Corkum, P.; Villeneuve, D. Controlling vibrational wave packet motion with intense modulated laser fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 203601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Huo, Y.Q.; Jiang, S.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, J.G. All-optical reconstruction of three-band transition dipole moments by the crystal harmonic spectrum from a two-color laser pulse. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 9971–9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Huillier, A.; Schafer, K.J.; Kulander, K.C. Theoretical aspects of intense field harmonic generation. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1991, 24, 3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopapas, M.; Keitel, C.H.; Knight, P.L. Atomic physics with super-high intensity lasers. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1997, 60, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vampa, G.; McDonald, C.; Orlando, G.; Klug, D.; Corkum, P.; Brabec, T. Theoretical analysis of high-harmonic generation in solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 073901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Guo, F.M.; Li, S.Y.; Chen, J.G.; Yang, Y.J. High-intensity molecular harmonic generation without ionization. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 033203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Li, S.Y.; Ding, D.J.; Chen, J.G.; Guo, F.M.; Yang, Y.J. Ultrashort-attosecond-pulse generation by reducing harmonic chirp with a spatially inhomogeneous electric field. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 92, 033848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odžak, S.; Hasović, E.; Milošević, D.B. High-order harmonic generation in polyatomic molecules induced by a bicircular laser field. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 033419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslar, J.; Telnov, D.A.; Chu, S.I. Generation of circularly polarized XUV and soft-X-ray high-order harmonics by homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecules subject to bichromatic counter-rotating circularly polarized intense laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 063404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslar, J.; Telnov, D.A.; Chu, S.I. Controlling electron quantum paths for generation of circularly polarized high-order harmonics by H 2+ subject to tailored (ω, 2 ω) counter-rotating laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 043419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Xu, Y.; Jia, G.R.; Bian, X.B. Controlling polarization of high-order harmonic generation by molecular alignment in a bicircular laser field. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 033410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liao, Q.; Zhu, X. Polarization control of the high-order harmonics generated from molecules by the carrier envelope phase of few-cycle laser field. Opt. Commun. 2021, 485, 126763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.B.; Bandrauk, A.D. Probing nuclear motion by frequency modulation of molecular high-order harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 193901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Yu, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Lu, R.; Lin, C. Smooth periodic gauge satisfying crystal symmetry and periodicity to study high-harmonic generation in solids. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y. Cooper minimum of high-order harmonic spectra from an MgO crystal in an ultrashort laser pulse. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 101, 033413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Ma, S.Y.; Jiang, S.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.G. All-optical reconstruction of k-dependent transition dipole moment by solid harmonic spectra from ultrashort laser pulses. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 34392–34404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Jiang, S.C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.G.; Yang, Y.J. Effect of interband polarization on a solid’s high-order-harmonic generation just belowthe band gap. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2874–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu-Jun, Y.; Gao, C.; Ji-Gen, C.; Qi-Ren, Z. A time-distinguished analysis of the harmonic structure from a model molecular ion. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2004, 21, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.Z.; Zhao, S.S.; Lan, W.D.; Li, S.Y.; Zhou, S.S.; Chen, J.G.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yang, Y.J. Calculation of high-order harmonic generation of atoms and molecules by combining time series prediction and neural networks. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 35444–35456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J. Review on the Reconstruction of Transition Dipole Moments by Solid Harmonic Spectrum. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; He, L.; Njoroge, S.M.; Wang, D.; Shao, R.; Lan, P.; Lu, P. Generation of Near-Circularly Polarized Attosecond Pulse with Tunable Helicity by Unidirectionally Rotating Laser Field. Ann. Der Phys. 2020, 532, 1900570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, I.N.; Hofmann, C.; Medišauskas, L.; Lewenstein, M.; Ciappina, M.F.; Dixit, G. Controlling polarization of attosecond pulses with plasmonic-enhanced bichromatic counter-rotating circularly polarized fields. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 013104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, R.; Long, H. Near-circularly polarized isolated attosecond pulse generation from coherent superposition state by a circularly polarized laser field. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2019, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, M.; Kienberger, R.; Spielmann, C.; Reider, G.A.; Milosevic, N.; Brabec, T.; Corkum, P.; Heinzmann, U.; Drescher, M.; Krausz, F. Attosecond metrology. Nature 2001, 414, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, G.; Benedetti, E.; Calegari, F.; Vozzi, C.; Avaldi, L.; Flammini, R.; Poletto, L.; Villoresi, P.; Altucci, C.; Velotta, R.; et al. Isolated single-cycle attosecond pulses. Science 2006, 314, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu-Ming, G.; Yu-Jun, Y.; Ming-Xing, J.; Da-Jun, D.; Qi-Ren, Z. A theoretical strategy to generate an isolated 80-attosecond pulse. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2009, 26, 053201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.L.; Miao, X.Y. Generation of linear isolated sub-60 attosecond pulses by combining a circularly polarized pulse with an elliptically polarized pulse. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2015, 32, 043202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, K.; Chew, A.; Cheng, Y.; Cunningham, E.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. 53-attosecond X-ray pulses reach the carbon K-edge. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.S.; Lan, W.D.; Chen, J.G.; Wang, J.; Guo, F.M.; Yang, Y.J. High-order harmonic generation of 1-nonene under linearly polarized laser pulses. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 106, 023510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.S.; Yang, Y.J.; Yang, Y.; Suo, M.Y.; Li, D.Y.; Qiao, Y.; Yuan, H.Y.; Lan, W.D.; Hu, M.H. High-order harmonic generation of the cyclo[18]carbon molecule irradiated by circularly polarized laser pulse. Chin. Phys. B 2023, 32, 013201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, F.; Abdurrouf, A.; Miyazaki, K.; Miyaji, G. Origin of anomalous spectra of dynamic alignments observed in N2 and O2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 143001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Dorfman, K. Detecting electronic coherences by time-domain high-harmonic spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9776–9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Huo, Y.; Liang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, S. Robust retrieval method of crystal transition dipole moments by high-order harmonic spectrum. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 107, 075201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Liang, H.; Peng, L.Y. Laser-Induced Electron Fresnel Diffraction in Tunneling and Over-Barrier Ionization. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2022, 39, 044203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.J.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, J.Y.; Cho, D.J.; Nam, C.H. Highly efficient high-harmonic generation in an orthogonally polarized two-color laser field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 243901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtovaara, L.; Havu, V.; Puska, M. All-electron density functional theory and time-dependent density functional theory with high-order finite elements. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 054103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Astiaso, M.; Silva, R.; Gubaydullin, A.; Rivière, P.; Meier, C.; Martín, F. Enhancing high-order harmonic generation in light molecules by using chirped pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 093003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscam Abbing, S.D.; Campi, F.; Zeltsi, A.; Smorenburg, P.; Kraus, P.M. Divergence and efficiency optimization in polarization-controlled two-color high-harmonic generation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Q.; Peng, Z.; Lang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lü, Z.; Zhao, Z. Decoherence Effects of Terahertz Generation in Solids under Two-Color Femtosecond Laser Fields. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2022, 39, 053301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Wang, G.; Wei, H.; Le, A.T.; Lin, C. Waveforms for optimal sub-keV high-order harmonics with synthesized two-or three-colour laser fields. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.T.; Wu, J.; Xia, C.L.; Liu, X.S. Enhanced high-order harmonics and an isolated short attosecond pulse generated by using a two-color laser and an extreme-ultraviolet attosecond pulse. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 80, 055404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jin, C.; Lin, C.D. Coherent control of high-harmonic generation using waveform-synthesized chirped laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 023416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, L.; Qiao, Y. Selective enhancement of single-order and two-order harmonics from He atom via two-color and three-color laser fields. Chem. Phys. 2019, 527, 110497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.G.; Wang, J.; Guo, F.M.; Yang, Y.J. High-order harmonic generation from H 2+ irradiated by a co-rotating two-color circularly polarized laser field. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 063428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Chen, J.G.; Chi, F.P.; Zhu, Q.R.; Zhang, H.X.; Sun, J.Z. Ultrahigh harmonic generation from an atom with superposition of ground state and highly excited states. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2007, 24, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtovaara, L.; Toivanen, J.; Eloranta, J. Solution of time-independent Schrödinger equation by the imaginary time propagation method. J. Comput. Phys. 2007, 221, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, A.; DeCusatis, C.M.; Das, P.K. Time-Frequency Analysis of Signals. In Wavelets and Subbands: Fundamentals and Applications; Birkhäuser Boston: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 103–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.X.; Wang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, A.H.; Guo, F.M.; Yang, Y.J. Significantly enhanced conversion efficiency of high-order harmonic generation by introducing chirped laser pulses into scheme of spatially inhomogeneous field. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 8768–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.; Calegari, F.; Lucchini, M.; Vozzi, C.; Stagira, S.; Sansone, G.; Nisoli, M. High-energy isolated attosecond pulses generated by above-saturation few-cycle fields. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, W.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, F.; Yang, Y. High-Intensity Harmonic Generation with Energy Tunability Produced by Robust Two-Color Linearly Polarized Laser Fields. Symmetry 2023, 15, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15030580
Lan W, Wang X, Qiao Y, Zhou S, Chen J, Wang J, Guo F, Yang Y. High-Intensity Harmonic Generation with Energy Tunability Produced by Robust Two-Color Linearly Polarized Laser Fields. Symmetry. 2023; 15(3):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15030580
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Wendi, Xinyu Wang, Yue Qiao, Shushan Zhou, Jigen Chen, Jun Wang, Fuming Guo, and Yujun Yang. 2023. "High-Intensity Harmonic Generation with Energy Tunability Produced by Robust Two-Color Linearly Polarized Laser Fields" Symmetry 15, no. 3: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15030580
APA StyleLan, W., Wang, X., Qiao, Y., Zhou, S., Chen, J., Wang, J., Guo, F., & Yang, Y. (2023). High-Intensity Harmonic Generation with Energy Tunability Produced by Robust Two-Color Linearly Polarized Laser Fields. Symmetry, 15(3), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15030580






