A DVA-Beam Element for Dynamic Simulation of DVA-Beam System: Modeling, Validation and Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Description and Problem Formulation
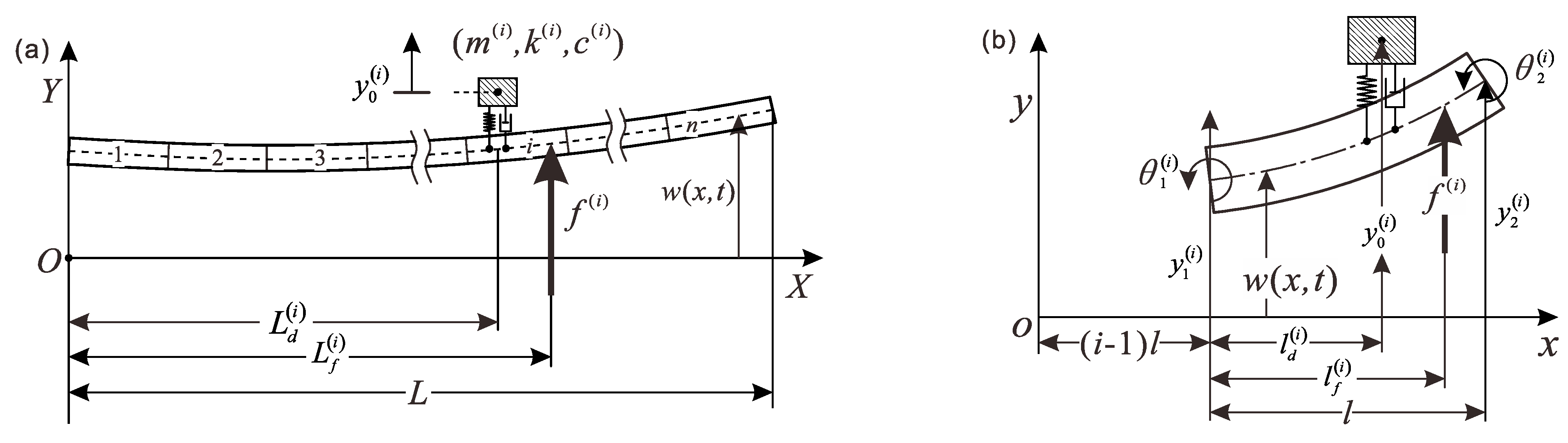
2.1. DVA-Beam Element
2.2. Motion Equations and Assembling
3. DVA Effect Deactivating Method
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Selection of Deactivating Coefficient
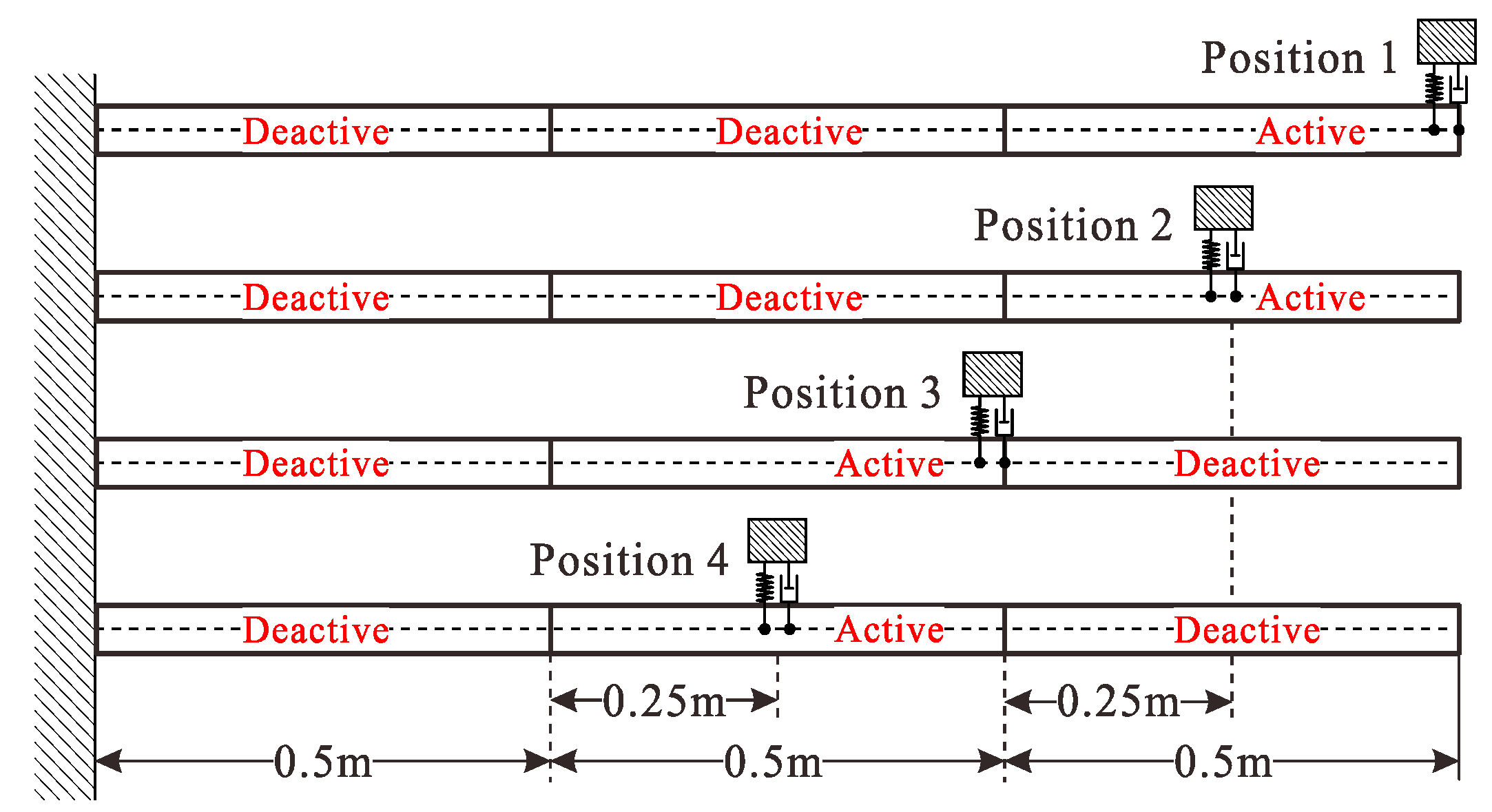
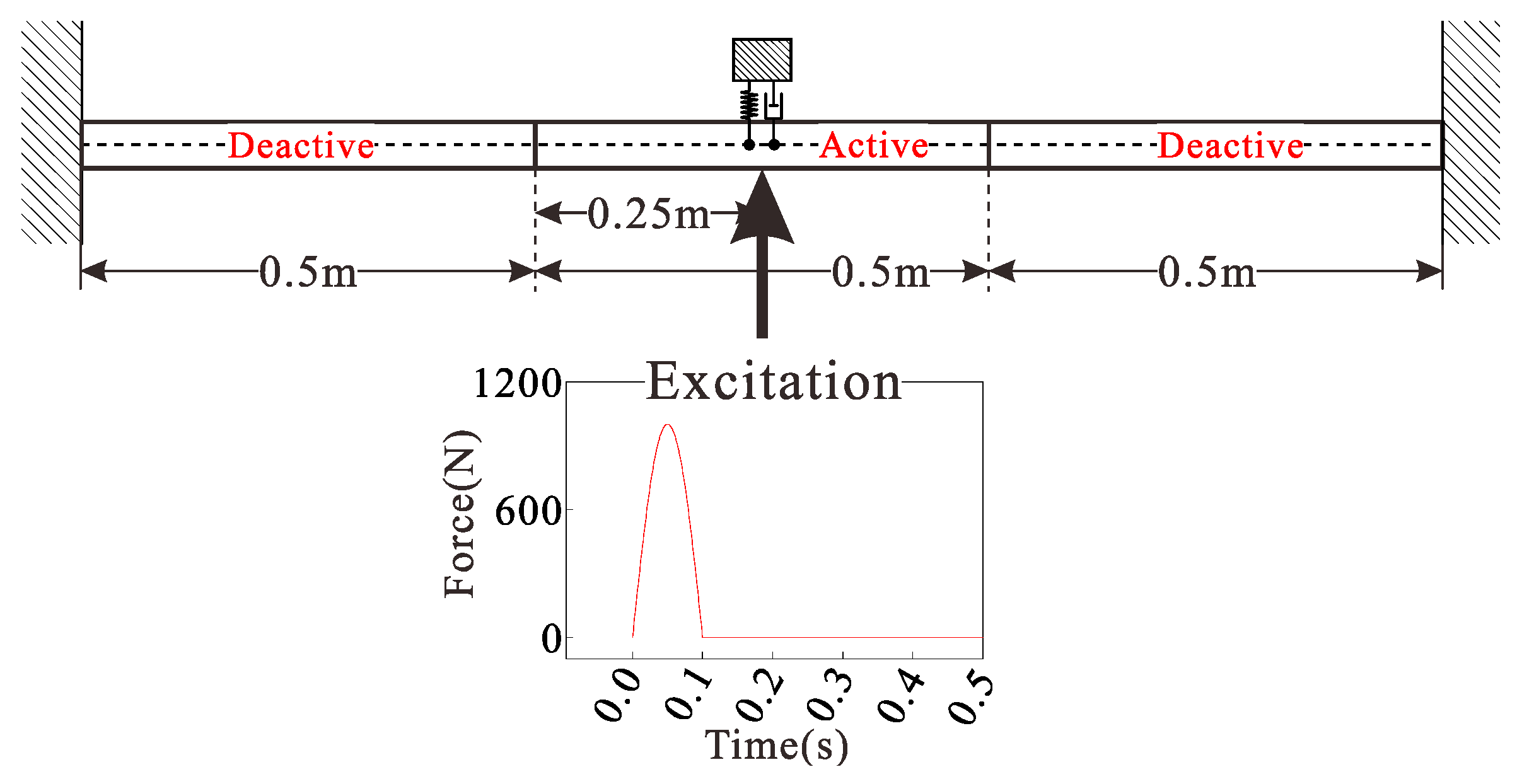
4.2. Validation of the Reliability of the DVA-Beam Element
4.3. Application Examples: DVA Optimal Design
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. MATLAB Code for DVA-Beam Element

References
- Hua, H.L.; Liao, Z.Q.; Guo, H.; Chen, Y.J. Study on launch dynamics and dispersion accuracy of a machine gun system with supporting structures. J. Ordnance Equip. Eng. 2022, 43, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, H.L. Study on the Dynamics of Eccentrically Rotating Beam and Axially Moving Cantilever Beam. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Science & Technology, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Liao, Z.; Song, J. Vibration reduction and firing accuracy improvement by natural frequency optimization of a machine gun system. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 3635–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, X. The self-excited vibrations of an axially retracting cantilever beam using the Galerkin method with fitted polynomial basis functions. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Qiu, M.; Liao, Z. Dynamic analysis of an axially moving beam subject to inner pressure using finite element method. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2017, 31, 2663–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.L.; Liao, Z.Q.; Jiang, C.Y.; Cheng, X. Design and Test of Compact Series Elastic Force Actuator for Grasping Mechanism. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 426–432. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, H.; Liao, Z.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C. A back-drivable linear force actuator for adaptive grasping. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 4213–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Liao, Z.; Zhao, J. Design, Analysis, and Experiment of an Underactuated Robotic Gripper Actuated by Linear Series Elastic Actuator. J. Mech. Robot. 2022, 15, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Liao, Z.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y. A Bezier based state calibrating method for low-cost potentiometer with inherent nonlinearity. Measurement 2021, 178, 109325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Liao, Z.; Chen, Y. A 1-Dof bidirectional graspable finger mechanism for robotic gripper. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 4735–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, F.S.; Pellicano, F.; Masoumi, A. Performances of dynamic vibration absorbers for beams subjected to moving loads. Nonlinear Dyn. 2013, 73, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Liang, B. Space robots with flexible appendages: Dynamic modeling, coupling measurement, and vibration suppression. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 396, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbo, M.; Vera, S.A. Optimization of a Two Degree of Freedom System Acting as a Dynamic Vibration Absorber. J. Vib. Acoust. 2008, 130, 011013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, L.; Anh, N.; Matsuhisa, H. The effective damping approach to design a dynamic vibration absorber using Coriolis force. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.K.; Savage, G.J. Optimal probabilistic design of the dynamic performance of a vibration absorber. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 307, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.; Cheung, Y. Optimal design of a damped dynamic vibration absorber for vibration control of structure excited by ground motion. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.-J.; Brennan, M.J.; Rustighi, E. Comparing the Performance of Optimally Tuned Dynamic Vibration Absorbers with Very Large or Very Small Moment of Inertia. J. Vib. Acoust. 2010, 132, 034501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Wang, S.; Brennan, M.J. Dynamic analysis and optimal design of a passive and an active piezo-electrical dynamic vibration absorber. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 330, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Wang, S.; Brennan, M.J. Optimal and robust modal control of a flexible structure using an active dynamic vibration absorber. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 21010–21011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbo, M. Optimal Parameters and Characteristics of a Three Degree of Freedom Dynamic Vibration Absorber. J. Vib. Acoust. 2012, 134, 021010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D׳amico, R.; Koo, K.; Claeys, C.; Pluymers, B.; Desmet, W. Optimal dynamic vibration absorber design for minimizing the band-averaged input power using the residue theorem. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 338, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asami, T. Optimal Design of Double-Mass Dynamic Vibration Absorbers Arranged in Series or in Parallel. J. Vib. Acoust.-Trans. Asme 2017, 139, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Peng, H.; Li, X.; Yang, S. Analytically optimal parameters of dynamic vibration absorber with negative stiffness. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 85, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, O.; Asami, T. Closed-Form Solutions to the Exact Optimizations of Dynamic Vibration Absorbers (Minimizations of the Maximum Amplitude Magnification Factors). J. Vib. Acoust. 2002, 124, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenk, S. Frequency Analysis of the Tuned Mass Damper. J. Appl. Mech. 2005, 72, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, G.B. Optimum absorber parameters for various combinations of response and excitation parameters. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1982, 10, 381–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilletti, M.; Elliott, S.J.; Rustighi, E. Optimisation of dynamic vibration absorbers to minimise kinetic energy and maximise internal power dissipation. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 4093–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, H. Damping of transient vibration by a dynamic absorber. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. C 1988, 54, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, D.; Crawley, E.; Ward, B. Inertial actuator design for maximum passive and active energy dissipation in flexible space structures. In Proceedings of the 26th Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–17 April 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, F.S.; Pellicano, F. Vibration reduction on beams subjected to moving loads using linear and nonlinear dynamic absorbers. J. Sound Vib. 2009, 325, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, F.S.; Pellicano, F. Vibration reduction of beams under successive traveling loads by means of linear and nonlinear dynamic absorbers. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 2272–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Si, P.; Hua, H.; Li, Z. A DVA-Beam Element for Dynamic Simulation of DVA-Beam System: Modeling, Validation and Application. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14081608
Song J, Si P, Hua H, Li Z. A DVA-Beam Element for Dynamic Simulation of DVA-Beam System: Modeling, Validation and Application. Symmetry. 2022; 14(8):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14081608
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jie, Peng Si, Hongliang Hua, and Zhongxin Li. 2022. "A DVA-Beam Element for Dynamic Simulation of DVA-Beam System: Modeling, Validation and Application" Symmetry 14, no. 8: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14081608
APA StyleSong, J., Si, P., Hua, H., & Li, Z. (2022). A DVA-Beam Element for Dynamic Simulation of DVA-Beam System: Modeling, Validation and Application. Symmetry, 14(8), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14081608





