A Stochastic Discrete Empirical Interpolation Approach for Parameterized Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. The Linear Approximation Space
2.2. Empirical Interpolation Method (EIM)
3. Discrete Empirical Interpolation Method and Its Stochastic Version
3.1. Discrete Empirical Interpolation Method (DEIM)
| Algorithm 1 Discrete empirical interpolation method (DEIM) [6] |
| Input: A candidate sample set and a target function . |
| 1: Initialize and orthonormalize as . |
| 2: Initialize . |
| 3: Initialize and . |
| 4: while do |
| 5: Compute the error for , . |
| 6: Let . |
| 7: Compute through orthonormalizing with by (18). |
| 8: Solve the equation for . |
| 9: Compute the residual . |
| 10: Select the interpolation index as . |
| 11: Update and . |
| 12: end while |
| Output: The matrix of basis functions and the matrix of interpolation points . |
3.2. Stochastic Discrete Empirical Interpolation Method (SDEIM)
| Algorithm 2 Stochastic discrete empirical interpolation method (SDEIM) |
| Input: A constant number N and a target function . |
| 1: Sample randomly. |
| 2: Evaluate the target function and initialize . |
| 3: Initialize . |
| 4: Initialize and . |
| 5: Initialize the counting index . |
| 6: while (if , it means that in verifying stage) do |
| 7: Sample randomly. |
| 8: if error then |
| 9: Set counting index . |
| 10: Compute through orthonormalizing with the by (18). |
| 11: Solve for . |
| 12: Compute the residual . |
| 13: Select the interpolation index as . |
| 14: Update and . |
| 15: else |
| 16: Update . |
| 17: end if |
| 18: end while |
| Output: The matrix of basis functions and the matrix of interpolation points . |
3.3. Performance and Complexity of SDEIM
4. Numerical Experiments
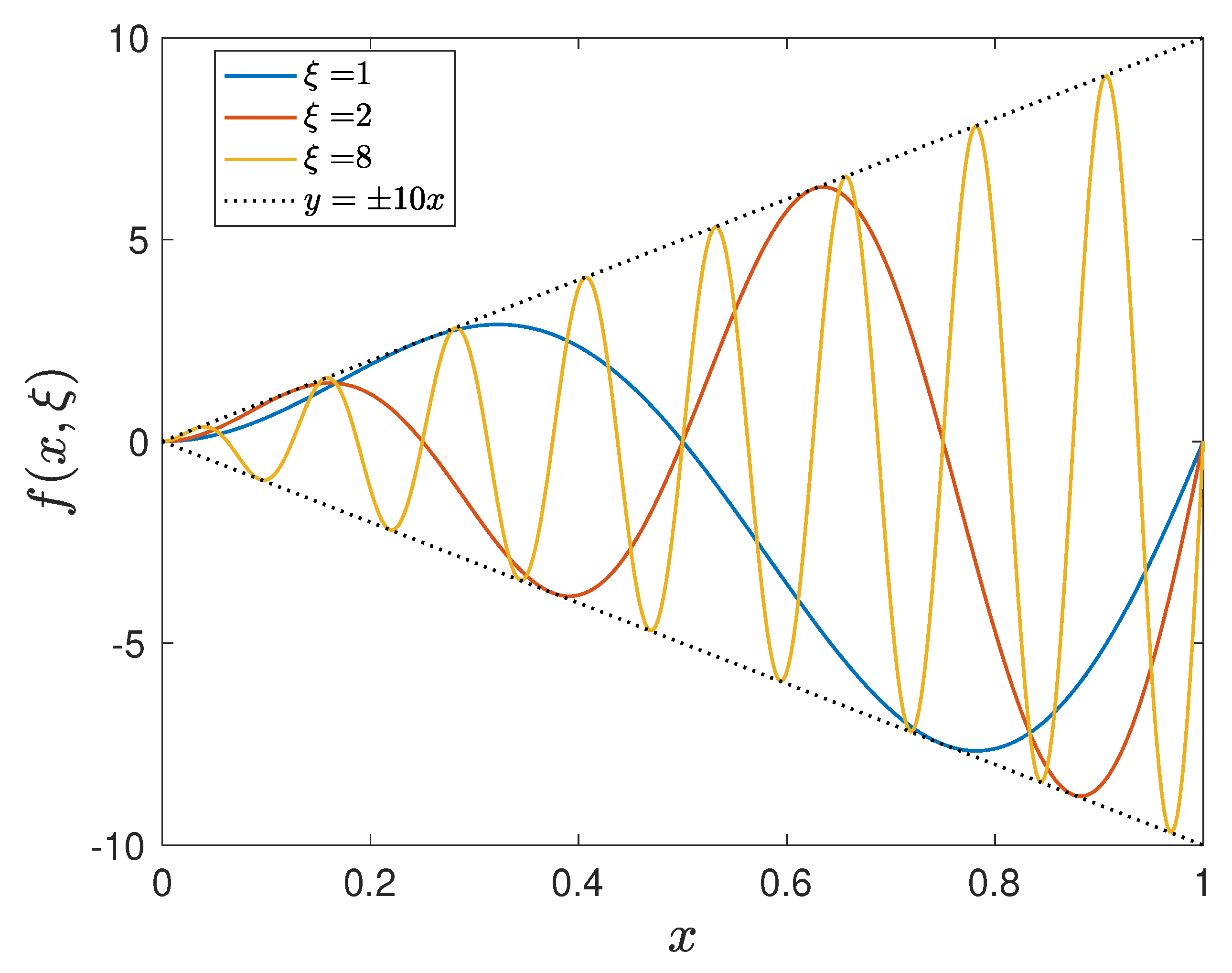
4.1. A Nonlinear Parameterized Function with Spatial Points in One Dimension
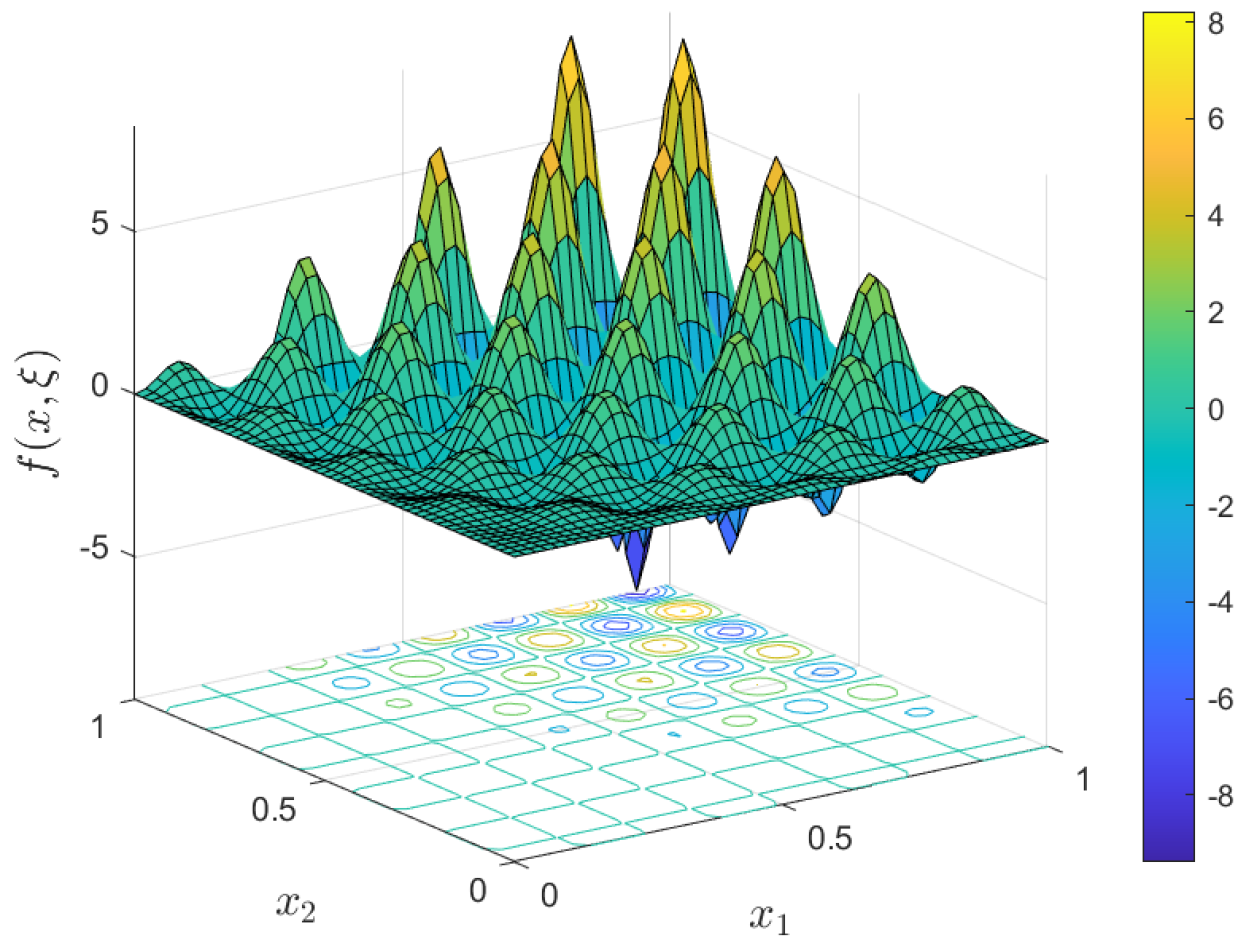
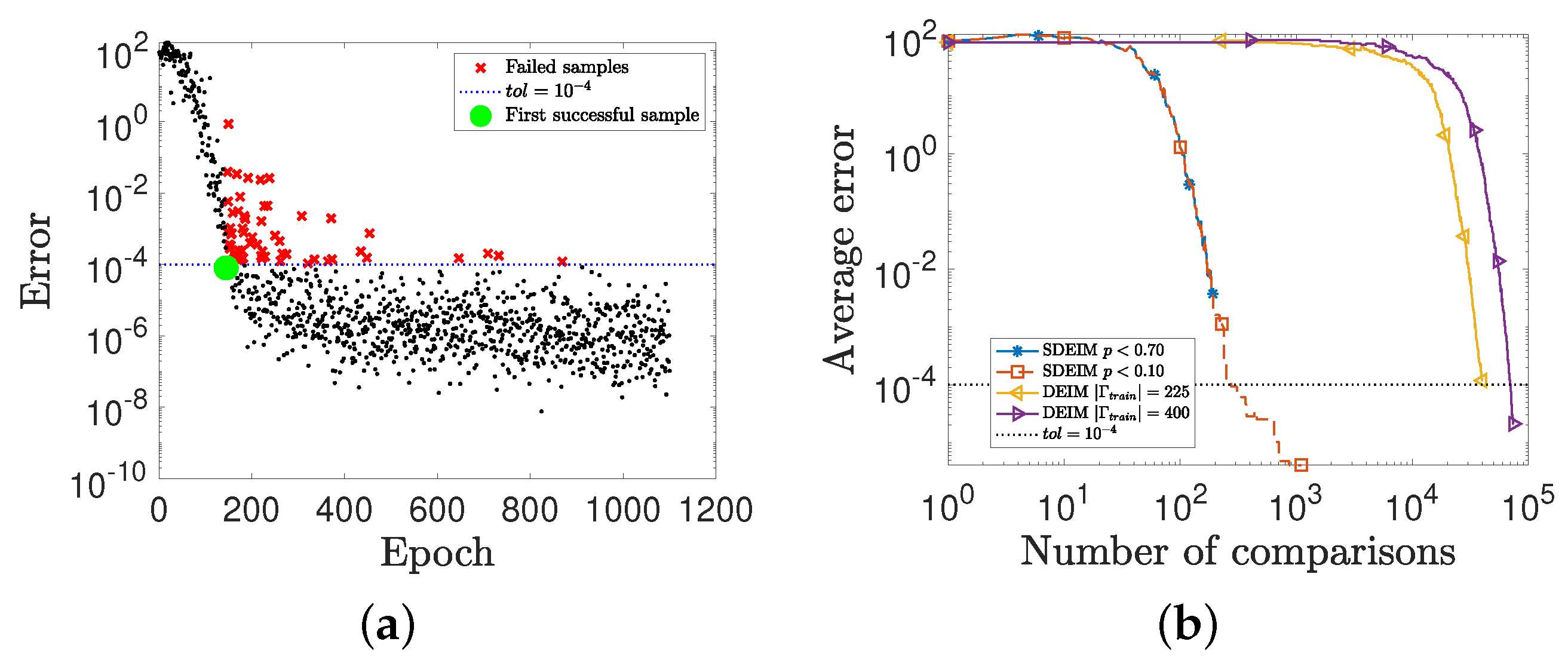
4.2. A Nonlinear Parameterized Function with Spatial Points in Two Dimensions
4.3. Random Fields
4.4. The FitzHugh–Nagumo (F-N) System
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benner, P.; Gugercin, S.; Willcox, K. A survey of projection-based model reduction methods for parametric dynamical systems. SIAM Rev. 2015, 57, 483–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrault, M.; Maday, Y.; Nguyen, N.C.; Patera, A.T. An ‘empirical interpolation’ method: Application to efficient reduced-basis discretization of partial differential equations. C. R. Math. 2004, 339, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maday, Y.; Mula, O. A generalized empirical interpolation method: Application of reduced basis techniques to data assimilation. In Analysis and Numerics of Partial Differential Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Quarteroni, A.; Rozza, G. A weighted empirical interpolation method: A priori convergence analysis and applications. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 2014, 48, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elman, H.C.; Forstall, V. Numerical solution of the parameterized steady-state Navier–Stokes equations using empirical interpolation methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2017, 317, 380–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturantabut, S.; Sorensen, D.C. Nonlinear model reduction via discrete empirical interpolation. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2010, 32, 2737–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peherstorfer, B.; Butnaru, D.; Willcox, K.; Bungartz, H.J. Localized discrete empirical interpolation method. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2014, 36, A168–A192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, L. A novel variable-separation method based on sparse and low rank representation for stochastic partial differential equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2017, 39, A2879–A2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veroy, K.; Rovas, D.V.; Patera, A.T. A posteriori error estimation for reduced-basis approximation of parametrized elliptic coercive partial differential equations: “Convex inverse” bound conditioners. ESAIM Control. Optim. Calc. Var. 2002, 8, 1007–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarteroni, A.; Rozza, G. Numerical solution of parametrized Navier–Stokes equations by reduced basis methods. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. Int. J. 2007, 23, 923–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Quarteroni, A.; Rozza, G. Comparison between reduced basis and stochastic collocation methods for elliptic problems. J. Sci. Comput. 2014, 59, 187–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.; Narayan, A. A goal-oriented reduced basis methods-accelerated generalized polynomial chaos algorithm. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2016, 4, 1398–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, H.C.; Liao, Q. Reduced basis collocation methods for partial differential equations with random coefficients. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2013, 1, 192–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liao, Q.; Lin, G. Reduced basis ANOVA methods for partial differential equations with high-dimensional random inputs. J. Comput. Phys. 2016, 317, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.; Dahmen, W.; DeVore, R.; Nichols, J. Reduced basis greedy selection using random training sets. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 2020, 54, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocsoreanu, C.; Georgescu, A.; Giurgiteanu, N. The FitzHugh–Nagumo Model: Bifurcation and Dynamics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Grepl, M.A.; Maday, Y.; Nguyen, N.C.; Patera, A.T. Efficient reduced-basis treatment of nonaffine and nonlinear partial differential equations. ESAIM Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 2007, 41, 575–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maday, Y.; Stamm, B. Locally adaptive greedy approximations for anisotropic parameter reduced basis spaces. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2013, 35, A2417–A2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temlyakov, V.N. Nonlinear Kolmogorov widths. Math. Notes 1998, 63, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, N.N.; Veroy, K.; Patera, A.T. Certified real-time solution of parametrized partial differential equations. In Handbook of Materials Modeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1529–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Kristoffersen, S. The Empirical Interpolation Method. Master’s Thesis, Institutt for Matematiske Fag, Trondheim, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dudley, R.M. Real Analysis and Probability; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffding, W. Probability inequalities for sums of bounded random variables. In The Collected Works of Wassily Hoeffding; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 409–426. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem, R.G.; Spanos, P.D. Stochastic Finite Elements: A Spectral Approach; Courier Corporation: Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, G.J.; Powell, C.E.; Shardlow, T. An Introduction to Computational Stochastic PDEs; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; Volume 50. [Google Scholar]
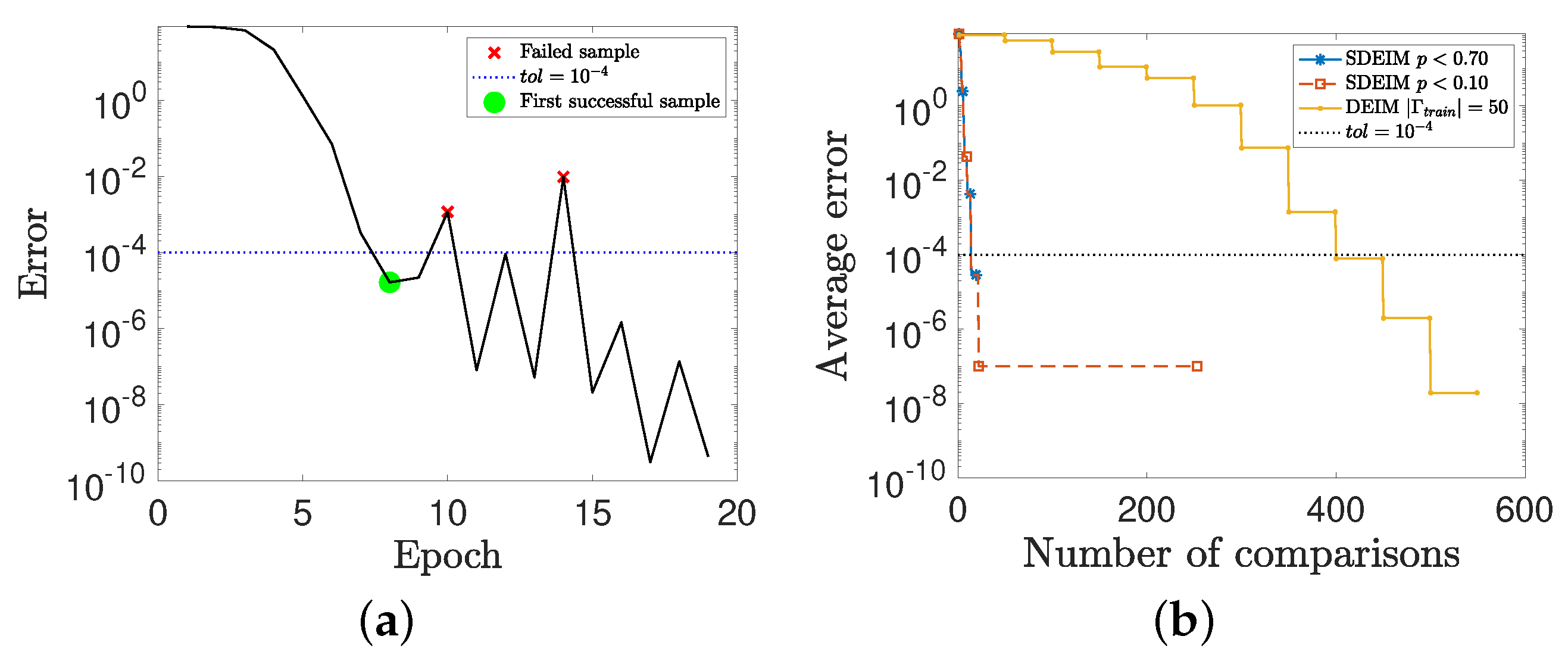




| n | Number of Comparisons | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDEIM | 9 | ||||
| 10 | 0 | ||||
| DEIM | 10 | 0 | 550 |
| n | Number of Comparisons | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDEIM | 173 | ||||
| 204 | |||||
| DEIM | 177 | 40,050 | |||
| 184 | 74,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, D.; Yao, C.; Liao, Q. A Stochastic Discrete Empirical Interpolation Approach for Parameterized Systems. Symmetry 2022, 14, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14030556
Cai D, Yao C, Liao Q. A Stochastic Discrete Empirical Interpolation Approach for Parameterized Systems. Symmetry. 2022; 14(3):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14030556
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Daheng, Chengbin Yao, and Qifeng Liao. 2022. "A Stochastic Discrete Empirical Interpolation Approach for Parameterized Systems" Symmetry 14, no. 3: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14030556
APA StyleCai, D., Yao, C., & Liao, Q. (2022). A Stochastic Discrete Empirical Interpolation Approach for Parameterized Systems. Symmetry, 14(3), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14030556






