Abstract
Variation of the meristic characteristics of pholidosis in the sand lizard, Lacerta agilis, was studied both in laboratory experiments and in natural populations. The total phenotypic variability was assessed by the variation of the sum of the number of scales on the left and on the right sides of the body (l + r), while the measure of developmental stability, providing insight into the degree of fluctuating asymmetry, or developmental variability, was assessed by the variation of the difference in the character values on the left and on the right (l − r). Experimental incubation of eggs at different temperatures demonstrates that the minimal level of both kinds of variability corresponds to a certain temperature, which can be characterized as an optimal one, increasing both with an increase and with a decrease in the temperature from this regime. The data demonstrate the crucial role of the temperature impact for the phenotypic variation under study. An increase in the level of developmental variability to the north and to the south from the center part of the species range, in the absence of an obvious trend in geographic variation of the level of total phenotypic variability, assumes an increase in the role of developmental variability in the observed phenotypic diversity at the periphery of the species range. The results obtained indicate the importance of a population phenogenetic approach, based on the developmental stability study in natural populations, to provide certain information supposing the possible nature of phenotypic diversity in a species range.
1. Introduction
Study of the phenotypic variation in natural populations existing under various environmental conditions in the species range is one of the key areas for both population biology and developmental biology [1,2,3,4]. Assessment of the input of various sources for the phenotypic diversity in the center and in the periphery of the species range is among the challenging tasks in this area [5,6,7]. To answer this question, it is necessary to obtain an estimate of the role of different kinds of variation, including genetic, environmental and developmental variation, in observed phenotypic diversity under the optimal and nonoptimal environmental conditions.
Population phenogenetic analysis, based on the study of the measures of developmental stability, such as fluctuating asymmetry of morphological characters, in natural populations is a possible approach to obtain information on the nature of observed phenotypic diversity. This approach makes it possible to assess the role of developmental variability, or developmental noise, in the phenotypic diversity and its possible change under various environmental conditions [8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15].
The aim of the study is to assess possible changes in the indices of the total phenotypic variability and developmental variability in the laboratory experiment and in natural populations. The sand lizard, Lacerta agilis—as one of the widespread reptile species, whose external morphology, pholidosis, provides an appropriate model for the meristic variation analysis—was used for the study. The working hypothesis is that the level of both kinds of variability should increase under extreme environmental conditions and the role of developmental variability in the total phenotypic variability will increase under these adverse conditions.
2. Material and Methods
The variation of the meristic characters of pholidosis in the sand lizard, Lacerta agilis L. 1758, was examined both in the laboratory experiment and in natural populations. The experimental material was obtained via incubation of the eggs obtained from the pregnant females in the natural population (Voronezh region, Russia) at constant temperature regimes (20, 22, 25, 27, 30, 32 degrees Celsius). One-hundred and eighty specimens were analyzed. For the population study, samples from 32 geographic points located from the north to the south in the European part of the range (from 59.20° N in the Vologda region to 44.61° N in the Krasnodar region) were analyzed (Figure 1). Eight-hundred and five individuals were studied. The collection of the Zoological Museum of Moscow State University was used for the study.
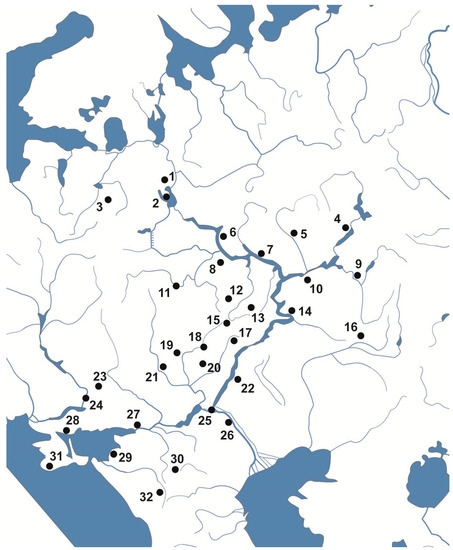
Figure 1.
Sample sites of the sand lizard in the European part of the species range (samples 1–32 are located from the north to the south, from the Vologda region to the Krasnodar region).
The meristic variation of 13 characters of pholidosis, the number of scales in different parts of the body, was analyzed (characters are described in [16]): postnasal and prezygomatic scales; preorbital scales; upper labial scales in front of the suborbital one; upper labial scales behind the suborbital one; orbitotemporal scales; supraorbital scales; upper ciliary scales; upper temporal scales; lower labial scales; mandibular scales; granules; lower ciliary scales; femoral pores. No indications were revealed for a correlation between the characters and their asymmetry, or for the presence of directional asymmetry (significant difference of the mean left minus right value from zero) and antisymmetry (significant negative interaction between the character values on the left and on the right) for their variation (as was recommended in [12,17,18,19]). Sex differences were not registered for the studied parameters.
The sum (l + r) and the difference (l − r) in the character values on the left and on the right sides of the body were accounted for. The variance of the sum () was calculated to assess the total phenotypic variability, while the variance of the difference () was calculated to assess the developmental variability, or developmental noise, as a measure of developmental stability [16,19]. To assess the variation for a whole set of characters, the value of the generalized variance was calculated ( and , respectively). In the absence of correlation between the characters and their asymmetry, the generalized variance was calculated as a geometric mean of the variance for separate characters [20,21]. As shown in the previous studies for the species—as well as for other species, including mammals—this measure () provides results similar to the other commonly used measures of fluctuating asymmetry [12,20]. In this study, the measure () was chosen to provide an opportunity to compare it with the similar measure of the total variation (). The proportion of developmental variability () in the total phenotypic variability () was assessed by the ratio between the variances (/). The F-statistic and the Friedman’s tests were used to test the differences in the studied parameters.
3. Results
In the laboratory experiment, the minimal level of both kinds of variability, including total phenotypic variability () and developmental variability (), corresponds to the temperature (25 °C), which can be characterized as optimal, increasing both with an increase and with a decrease in the temperature from this regime (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The variance value is significantly higher at extreme temperature conditions than at 25 °C (p < 0.01 for the F-statistic). An increase in the value of variability is more pronounced with a decrease than with an increase in temperature from 25 °C.
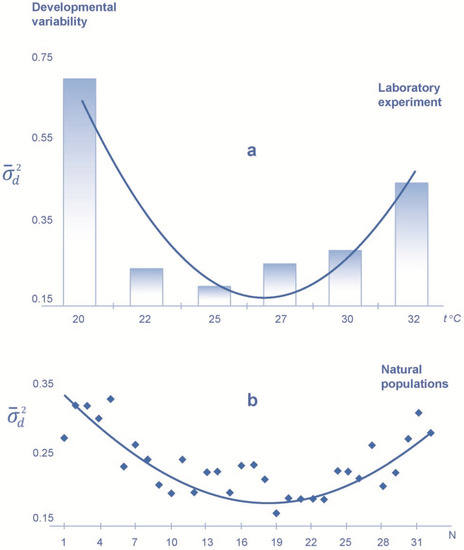
Figure 2.
Values of the developmental variability index () in the sand lizard at different incubation temperatures in the laboratory experiment (a) and in natural populations (b). Developmental variability is assessed by generalized variance of the difference in the character values on the left and on the right (for 13 meristic characters of pholidosis, number of scales). N is the number of samples from natural populations in the European part of the species range (samples 1–32 are located from the north to the south, from the Vologda region to the Krasnodar region).
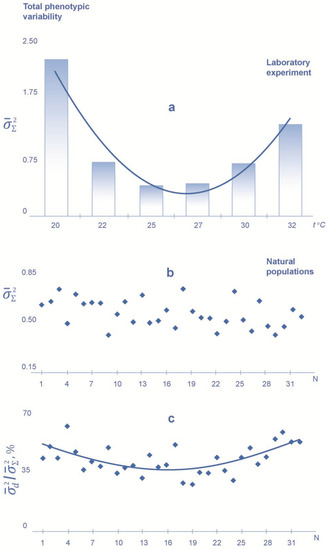
Figure 3.
Values of the total phenotypic variability index () in the sand lizard at different incubation temperatures in the laboratory experiment (a) and in natural populations (b). There is also a proportion of developmental variability (, see Figure 2) in the total phenotypic variability (/) for natural populations (c). Total phenotypic variability is assessed by generalized variance of the sum of the character values on the left and on the right (for 13 meristic characters of pholidosis, number of scales). N is the number of samples from natural populations in the European part of the species range (samples 1–32 are located from the north to the south, from the Vologda region to the Krasnodar region).
In natural populations, the level of developmental variability () increases to the north and to the south from the center part of the species range (p < 0.05 according to Friedman’s test) (Figure 2); the maximum variance value is found in the northern periphery of the range. There is no obvious trend in geographic variation of the level of total phenotypic variability () for the samples from the same natural populations (Figure 3).
Thus, similar dependence of both indices of variability on the temperature of development is accompanied by essentially different pattern of their interpopulation variation in the species range.
4. Discussion
Interpretation of the pattern of variation in the measures of intrapopulation phenotype diversity in the species range is complicated due to the uncertainty of the role of its various components (including genetic, environmental and ontogenetic ones). Certain information on the nature of the observed phenotypic variety (measured by the variance of the sum of the character values on two sides of the body) can be obtained through a study of developmental stability assessed by fluctuating asymmetry, or developmental variability (variance of the difference in the character values on the left and on the right) [22,23].
If all the observed diversity is associated only with the manifestation of developmental variability, the variance of the sum is equal to the variance of the difference and the coefficient of correlation between the sides is zero. With the increasing the role of other forms of variability, the variance of the sum is significantly higher than the variance of the difference with a positive value of the correlation coefficient [22,24,25,26,27]. Thus, the ratio of different forms of variability for bilateral characters can be represented by comparing the variance of the sum of the values of the trait on two sides of the body, which can be considered an estimate of the total phenotypic diversity and the variance of the difference, as an estimate of developmental noise.
The proportion of the variance of the difference in the variance of the sum indicates the role of developmental noise in the observed level of total phenotypic diversity. It was established that most of the intrapopulation phenotypic variability for the meristic traits results from developmental noise and genetic differences among individuals [1]. While the genotypic diversity is usually implied to be the main cause of phenotypic diversity, a significant proportion of the total phenotypic variation in natural populations can occur from developmental noise [22,23,28]. Moreover, the concordance of phenotypic variation in the species range with experimentally established dependence of the characters under study on developmental conditions may signify the role of the environment [29,30,31].
In this study, the similarity of the experimental and population data on the dependence of the level of developmental variability on temperature is manifested not only in the general trend, but also in a specific reaction for different temperature impacts. A stronger reaction of the index value on the temperature decrease than on the temperature increase from the optimal regime of about 25 °C in the laboratory experiment corresponds to the higher index values in the samples from the populations in the northern periphery of the range than in the southern one. All this demonstrates the crucial role of the temperature impact for the phenotypic variation under study.
At the same time, the maximum index values for the developmental variability in natural populations do not reach the level that we reveal at extreme temperatures in the laboratory experiment. There might be some reasons for this effect. The range of developmental temperature in nature could be narrower than those we can simulate in the laboratory. The optimal conditions for development most probably correspond not to the constant temperature regime, modeled in the experiment, but to the temperature fluctuations [32]. The effect of different temperatures’ impact on development in nature can be smoothed out by a shift in the timing of egg laying in different geographic zones.
The similarity of the minimal index values of developmental variability in the central part of the range to the index values in the experimental group under optimal conditions suggests that the development in this area occurs under conditions that are close to the optimal ones. A parallel increase in the index values at low and high temperatures in the experiment and in the northern and southern periphery of the range in nature suggests that some populations of the species exist under adverse conditions. This indicates an essential role of developmental conditions in the observed pattern of phenotypic variability in nature. Phenotypic diversity caused by developmental variability turns out to be lower under optimal conditions that apparently take place in the central part of the species range and higher under adverse conditions in the ecological periphery of the range.
Experimental and population data on the total phenotypic variability turn out to be essentially different. If, under experimental conditions, the level of total phenotypic variability has the same temperature dependence as the index of developmental variability, there is not a clear trend in the geographic variation of its value in natural populations.
An increase in the total phenotypic variability under adverse conditions in the experiment is primarily determined by deterioration in developmental stability. The fact that an increase in the value of the total diversity under extreme temperatures is not completely exhausted by an increase in the value of the developmental variability is determined by the manifestation of another component of the variability, the genotype–environment interaction, as the manifestation of the different sensitivity of genotypes to a change in environmental conditions that characterizes the canalization of development [16,33,34].
The intrapopulation phenotypic diversity in nature is caused by many factors, and primarily by genotype variety that often is higher under optimal conditions and decreases at the ecological periphery of the species range [6,7]. The absence of an obvious trend for variation in the level of the total phenotypic variability among the populations from different parts of the range, despite its clear dependence on developmental conditions in the laboratory experiment, assumes an increase in the role of the developmental variability in phenotypic diversity at the periphery of the range. Thus, the lack of concordance between the experimental and population data on the total phenotypic variability illustrates that the ratio of the level of phenotypic diversity in different parts of the species range depends on the particular proportion of different components of variation.
The results obtained indicate the importance of simultaneous study of the total phenotypic variability and developmental variability that may provide certain information supposing the possible nature of phenotypic diversity in a species range.
Author Contributions
The article was prepared at all stages, from the beginning to the end, through the collaboration of all authors: V.M.Z., N.P.Z. and I.E.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been funded by Government program of basic research in the Koltzov Institute of Developmental Biology of the Russian Academy of Sciences in 2022 № 0088-2021-0019.
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of the laboratory of postnatal ontogenesis of the Koltzov Institute of Developmental Biology of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Zoological Museum of Moscow State University for a fruitful cooperation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Leary, R.F.; Allendorf, F.W.; Knudsen, K.L. Genetic, environmental, and developmental causes of meristic variation in rainbow trout. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1992, 191, 79–95. [Google Scholar]
- Scheiner, S.M. Genetics and evolution of phenotypic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1993, 24, 35–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.F. Ecological Developmental Biology: Developmental Biology Meets the Real World. Dev. Biol. 2001, 233, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, S.F.; Barresi, M.J.F. Developmental Biology, 11th ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Soule, M.; Baker, B. Phenetics of natural populations IV. The population asymmetry parameter in the butterfly Coenonympha tullia. Heredity 1968, 23, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kat, P.W. The relationship between heterozygosity for enzyme loci and developmental homeostasis in peripheral populations of aquatic bivalves (Unionidae). Am. Nat. 1982, 119, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, P.A. Fluctuating asymmetry: A biological monitor of environmental and genomic stress. Heredity 1992, 68, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, K. Genetical control of stability in development. Heredity 1953, 7, 297–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddington, C.H. The Strategy of the Genes; George Allen & Unwin: London, UK, 1957; 262p. [Google Scholar]
- Yedier, S.; Bostanci, D.; Kontas, S.; Kurucu, G.; Polat, N. Comparison of otolith mass asymmetry in two different Solea solea populations in Mediterranean Sea. Ordu Üniversitesi Bilim Ve Teknol. Derg. 2018, 8, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Yedier, S.; Bostanci, D.; Kontas, S.; Kurucu, G.; Polat, N. Fluctuating asymmetry in otolith dimensions of Trachurus mediterraneus collected from the Middle Black Sea. Acta Biol. Turc. 2018, 31, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharov, V.M.; Shadrina, E.G.; Trofimov, I.E. Fluctuating Asymmetry, Developmental Noise and Developmental Stability: Future Prospects for the Population Developmental Biology Approach. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.H. Nature, Nurture, and Noise: Developmental Instability, Fluctuating Asymmetry, and the Causes of Phenotypic Variation. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-López, Y.; Prieto-Dueñas, I.S.; Tapia-Torres, Y.; Magno, A.Z.B.; Suazo-Ortuño, I.; Cuevas-Reyes, P. Fluctuating asymmetry and oxidative stress indicate environmental stress of Cane toads Rhinella marina. Zool. Anz. 2022, 299, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhelev, Z.; Tsonev, S.; Boyadzhiev, P. Using of fluctuating asymmetry in adult Pelophylax ridibundus (Amphibia: Anura: Ranidae) meristic traits as a method for assessing developmental stability of population and environmental quality of their habitat: Industrial area in southern Bulgaria. Turk. J. Zool. 2022, 46, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, V.M. Future Prospects for Population Phenogenetics; Soviet Scientific Reviews, Section F, Physiology and General Biology Reviews; Routledge: London, UK, 1989; Volume 4, pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Van Valen, L. A study of fluctuating asymmetry. Evolution 1962, 16, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soule, M.E. Phenetics of Natural Populations. II. Asymmetry and Evolution in a Lizard. Am. Nat. 1967, 101, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.R.; Strobeck, C. Fluctuating asymmetry: Measurement, Analysis, Patterns. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1986, 17, 391–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, V.M.; Pankakoski, E.; Sheftel, B.I.; Peltonen, A.; Hanski, I. Developmental stability and population dynamics in the common shrew, Sorex araneus. Am. Nat. 1991, 138, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhivotovsky, L.A. A measure of fluctuating asymmetry for a set of characters. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1992, 191, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharov, V.M. Population phenogenetics: Analysis of developmental stability in natural populations. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1992, 191, 7–30. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, J.H.; Raz, S.; Hel-Or, H.; Nevo, E. Fluctuating asymmetry: Methods, theory, and applications. Symmetry 2010, 2, 466–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astauroff, B.L. Analyse der erblichen Störungsfälle der bilateralen Symmetrie. Z. Ver-Erbungslehre 1930, 55, 183–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, R.S. Fluctuating Asymmetry in the Dentition of the House Mouse. Growth 1965, 29, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angus, R.A. Quantifying Fluctuating Asymmetry: Not All Methods are Equivalent. Growth 1982, 46, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Pertoldi, C.; Kristensen, T.N.; Loeschcke, V. A new method for estimating environmental variability for clonal organisms, and the use of fluctuating asymmetry as an indicator of developmental Instability. J. Theor. Biol. 2001, 210, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajus, D.L.; Graham, J.H.; Kozhara, A.V. Developmental instability and the stochastic component of total phenotypic variance. In Developmental Instability: Causes and Consequences; Polak, M., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 343–363. [Google Scholar]
- Osgood, D.W. Effects of temperature on the development of meristic characters in Natrix fasciata. Copeia 1978, 1, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, V.M. Appearance, fixation and stabilization of environmentally induced phenotypic changes as a microevoutionary event. Genetica 1993, 89, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, F.J.; Shine, R. Geographic variation in lizard phenotypes: Importance of the incubation environment. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 64, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beardmore, J.A. Developmental stability in constant and fluctuating temperatures. Heredity 1960, 14, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, G.H. Statistical methods for the analysis of genotype-environment interactions. Heredity 1973, 31, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glotov, N.V. Analysis of the genotype-environment interaction in natural populations. Acta Zool. Fenn. 1992, 191, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).