Memristive Structure-Based Chaotic System for PRNG
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of Mathematical Model and Solutions Simulation
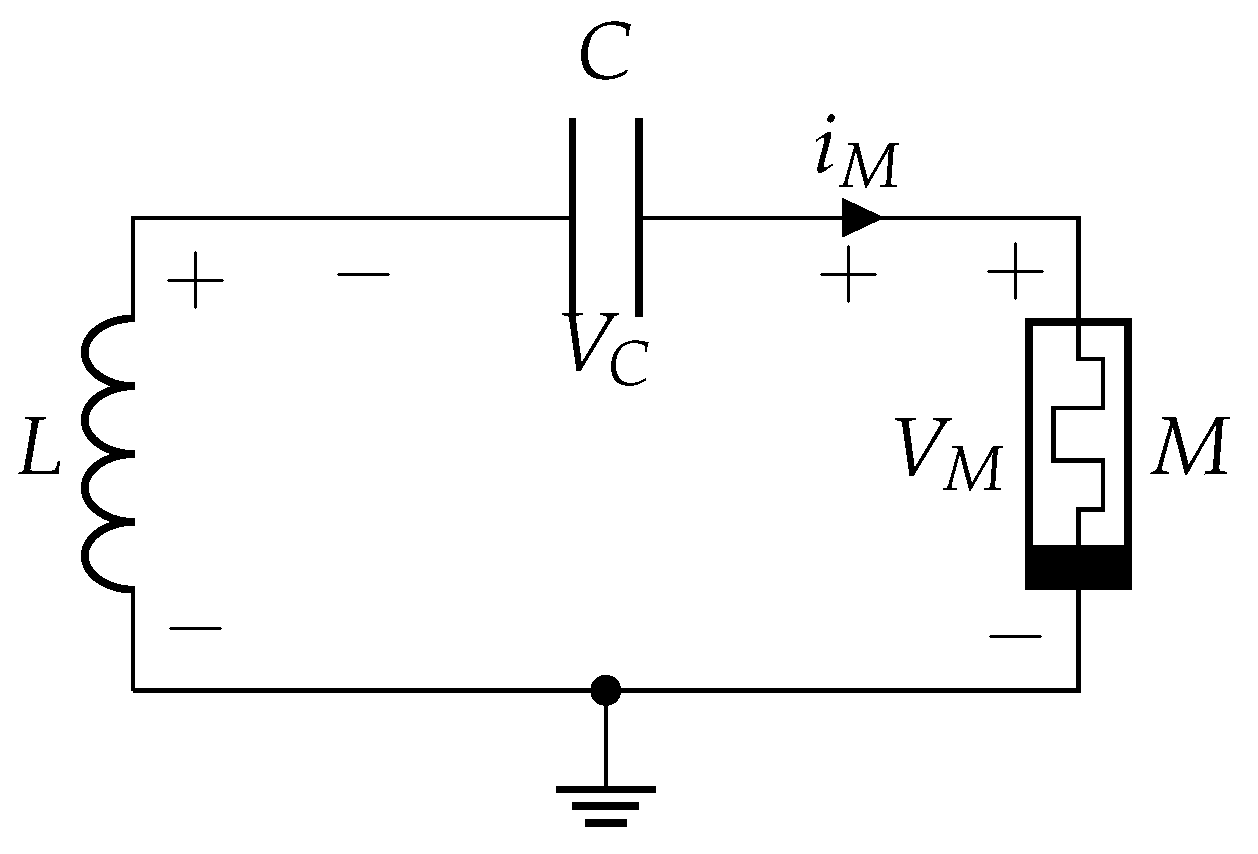
2.1. Memristive Structure-Based Chaotic System
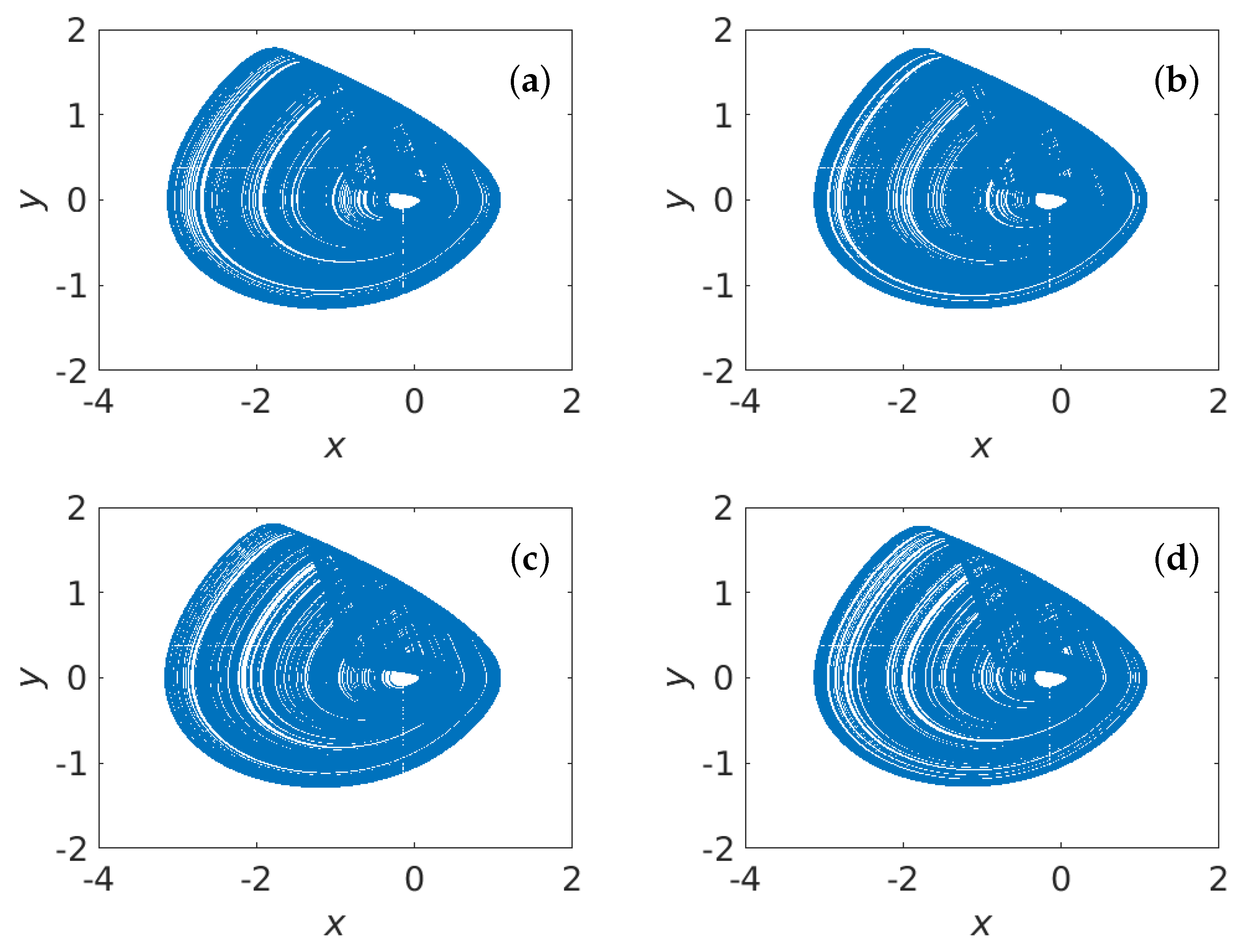
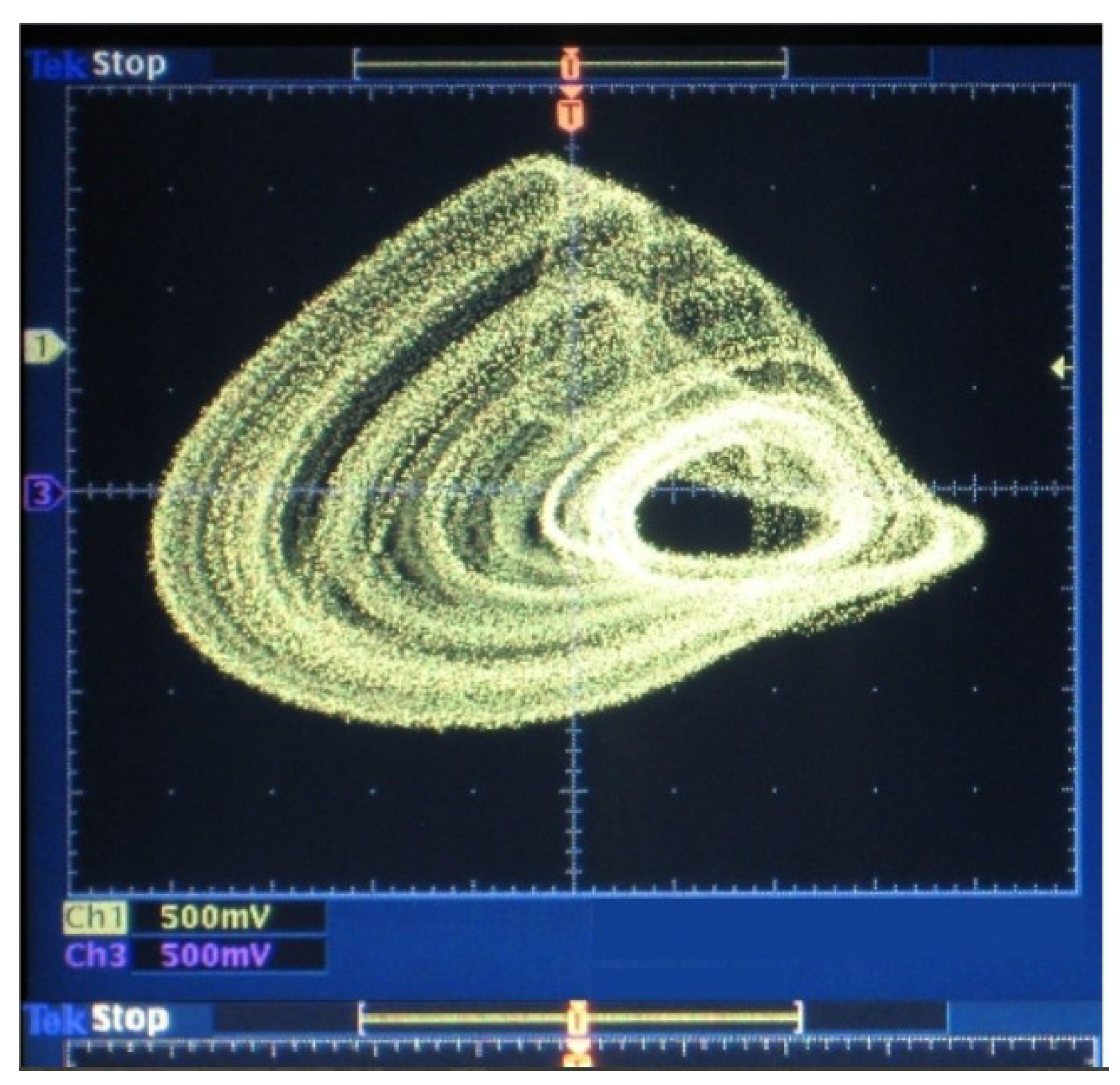
2.2. Solutions Simulation
3. Generating of Pseudorandom Sequences
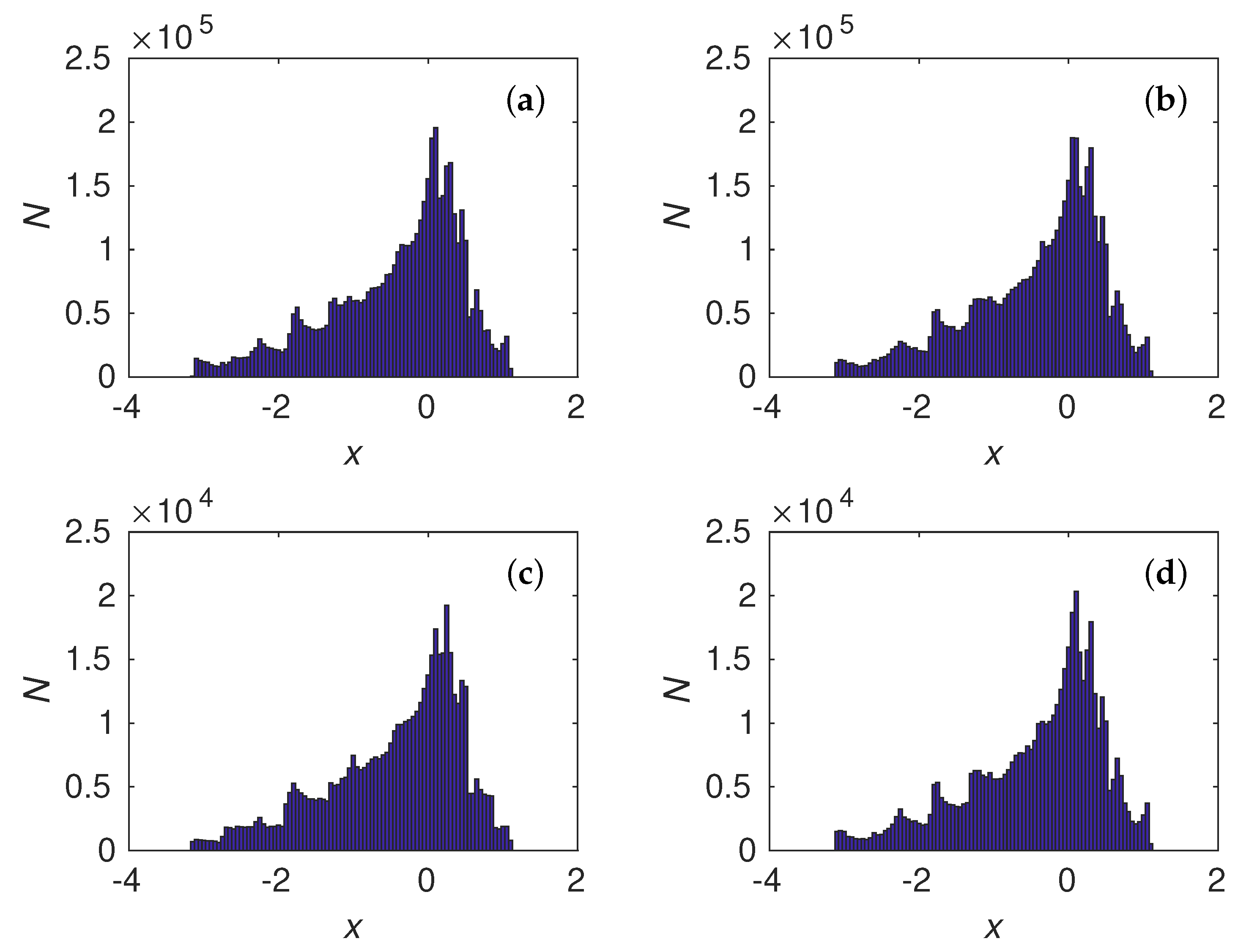
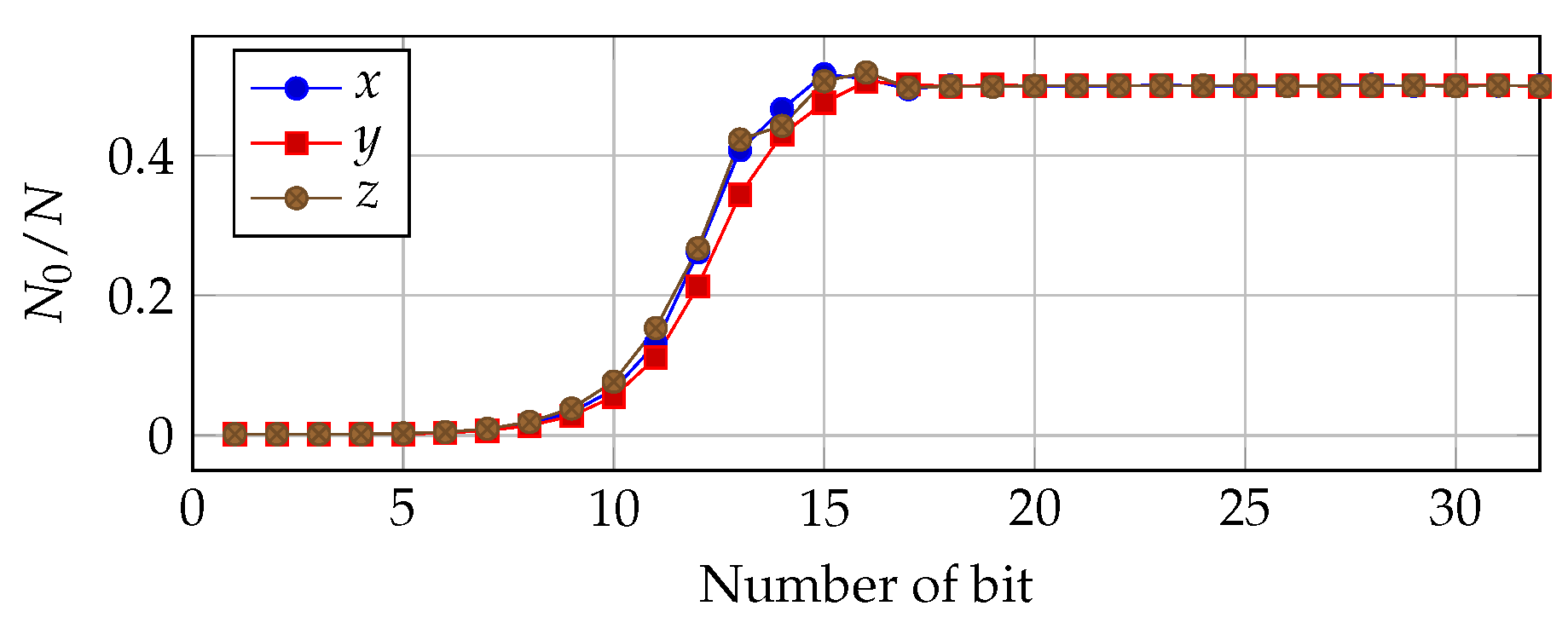
3.1. Time Series Balance Property
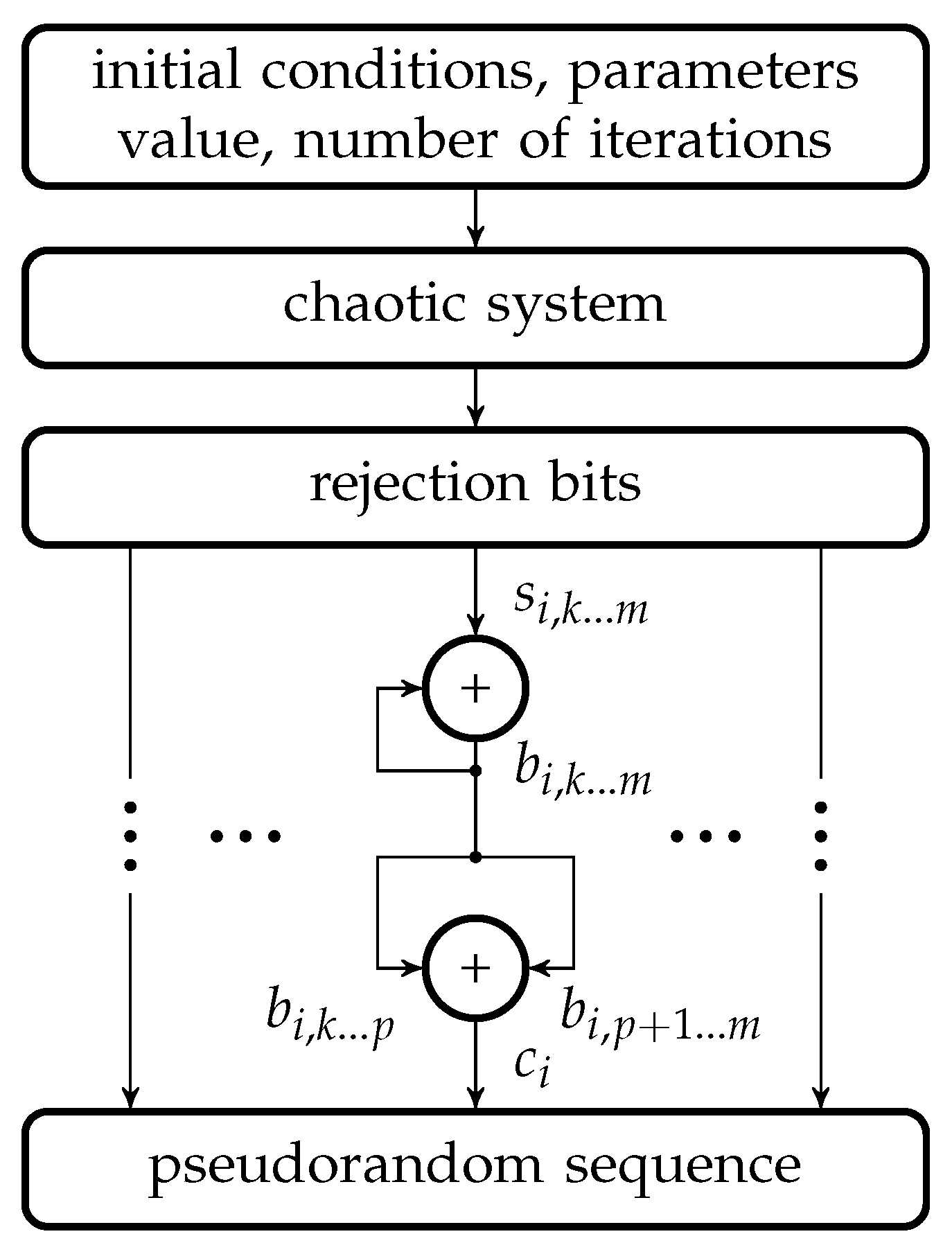
3.2. Design of CPRNG
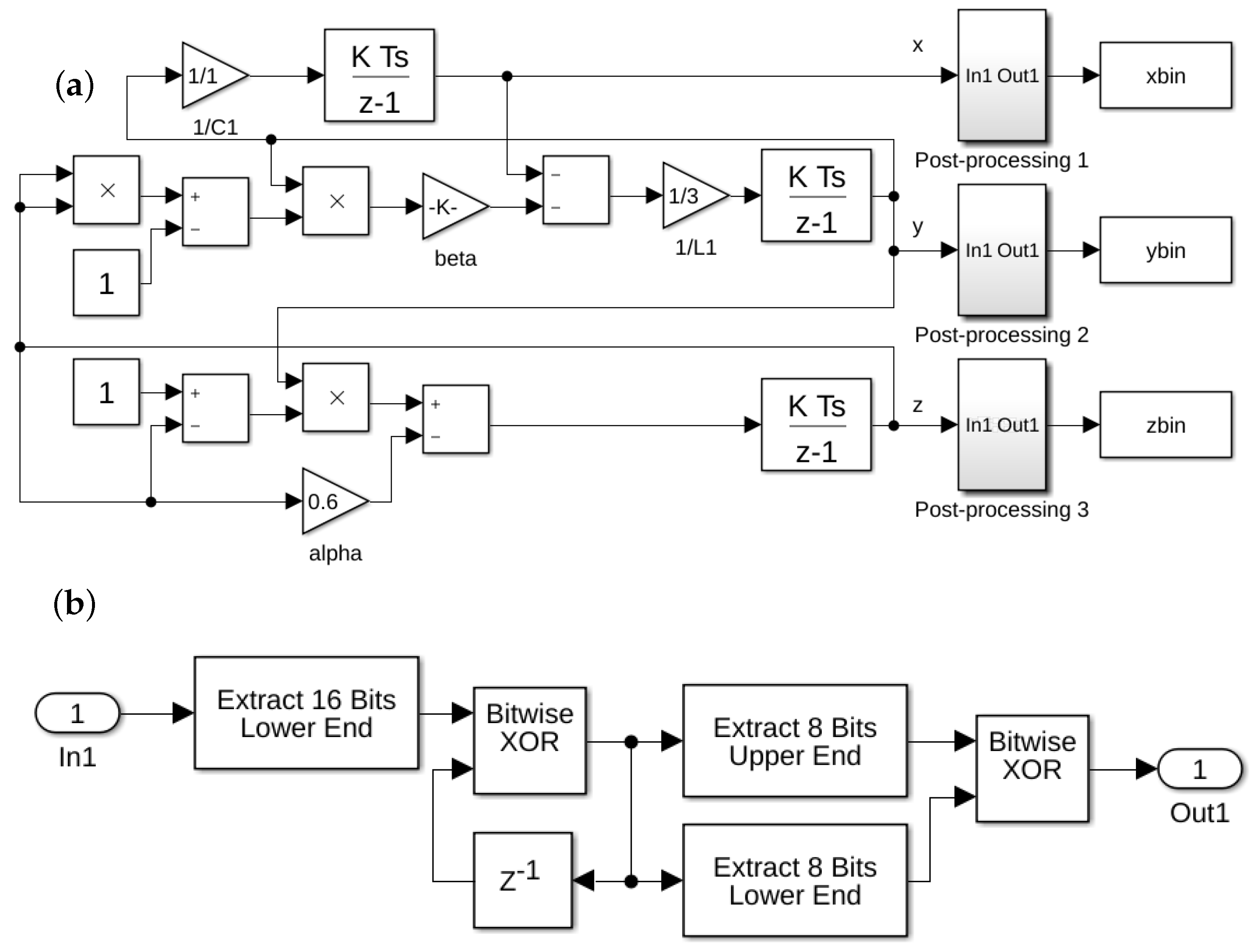
3.3. FPGA-Implementation
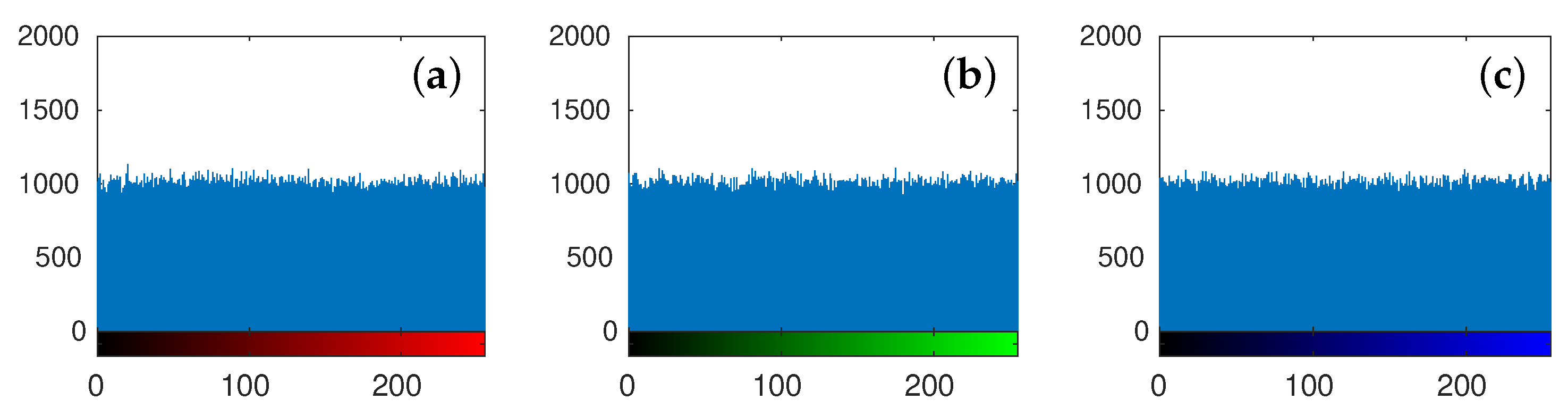
3.4. Testing of CPRNG Based on One System
- 1 bit defined the sign;
- 5 bits were used for the integer part;
- 26 bits were used for the fractional part.
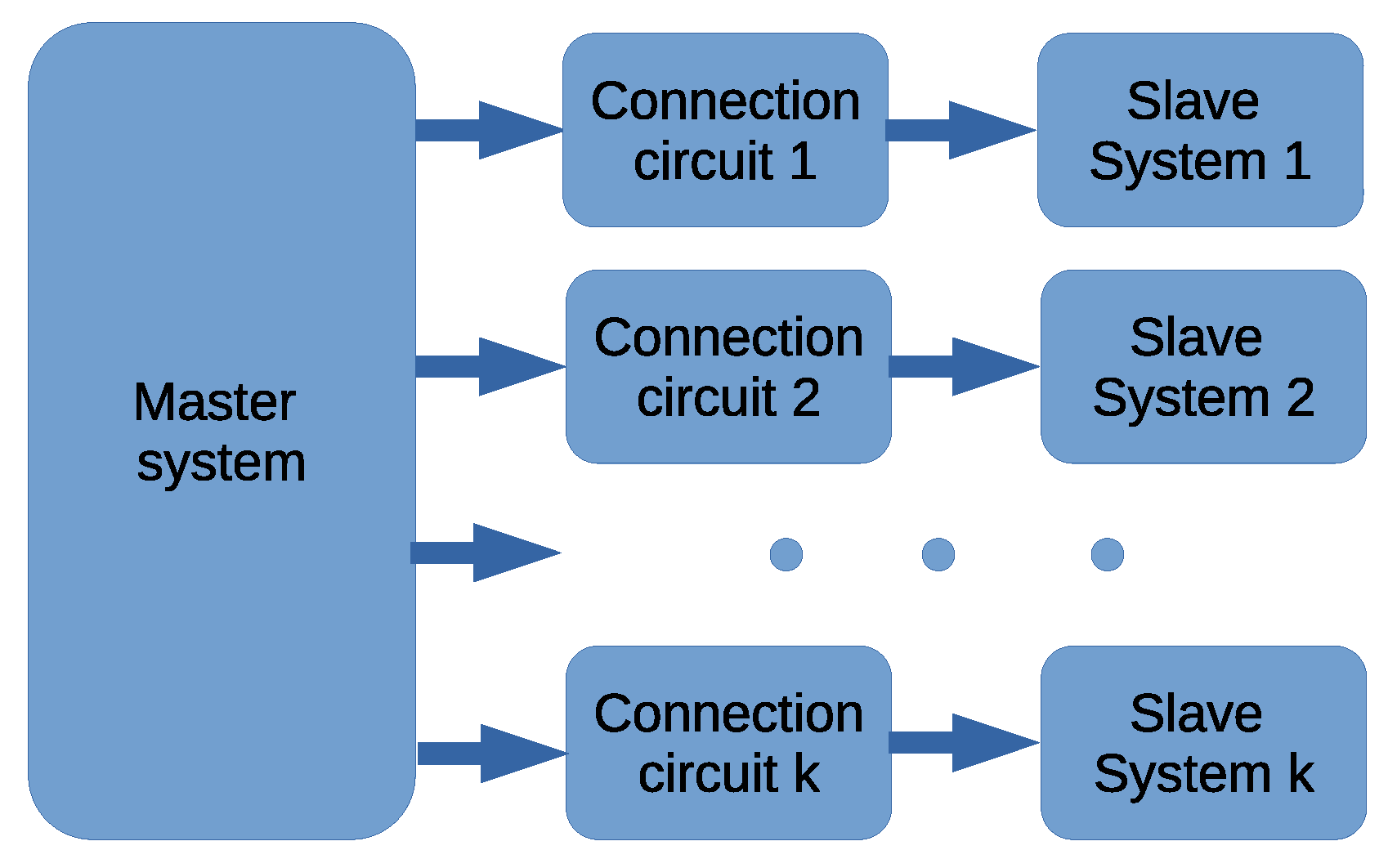
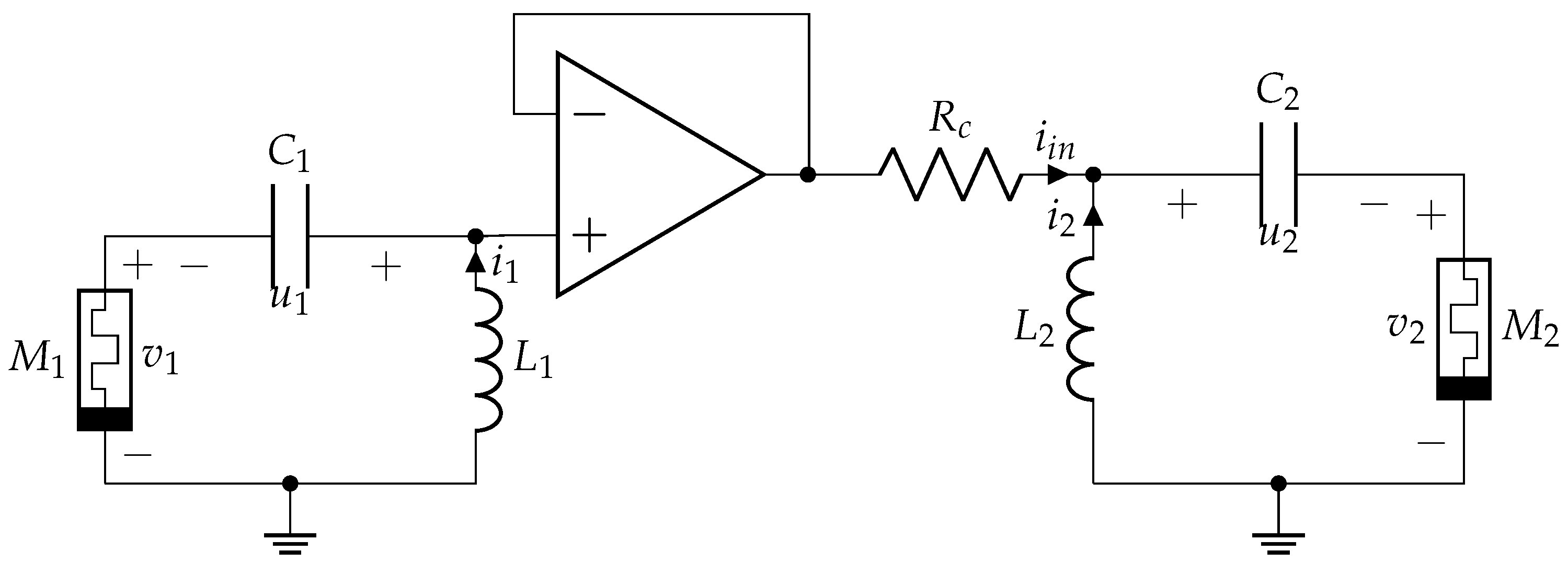
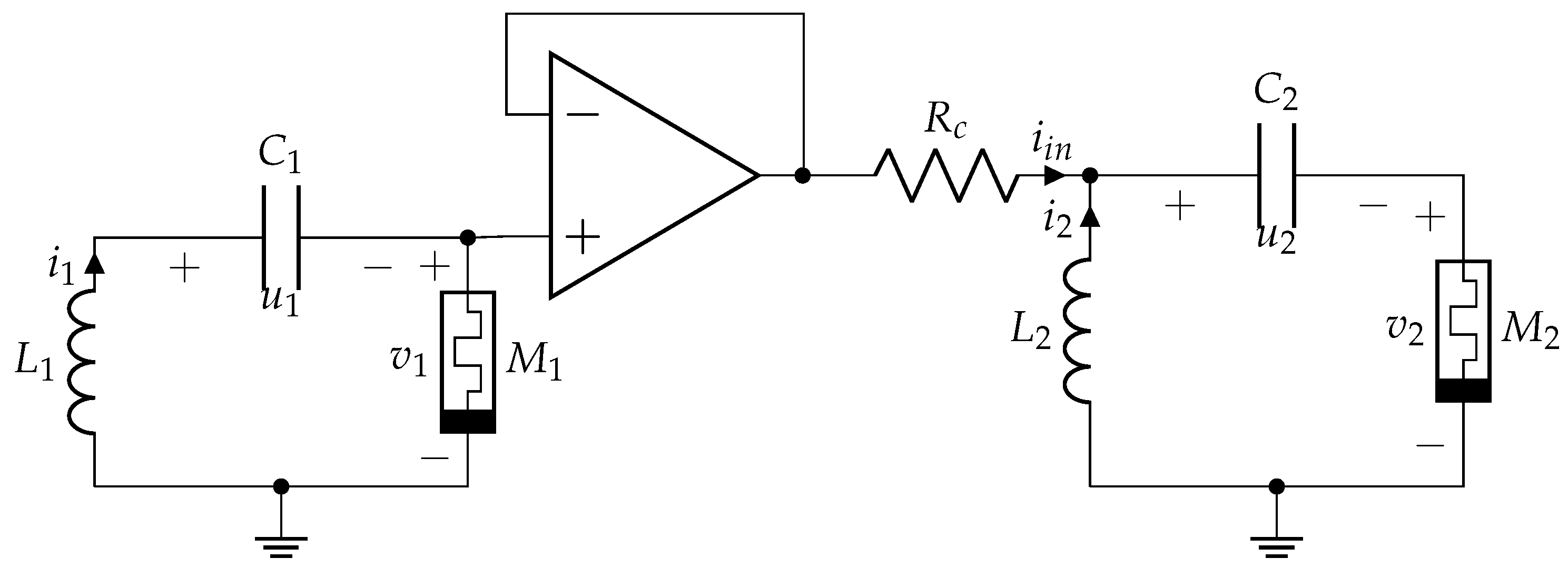
4. Coupled Memristive Structure-Based Chaotic Circuits for PRNG
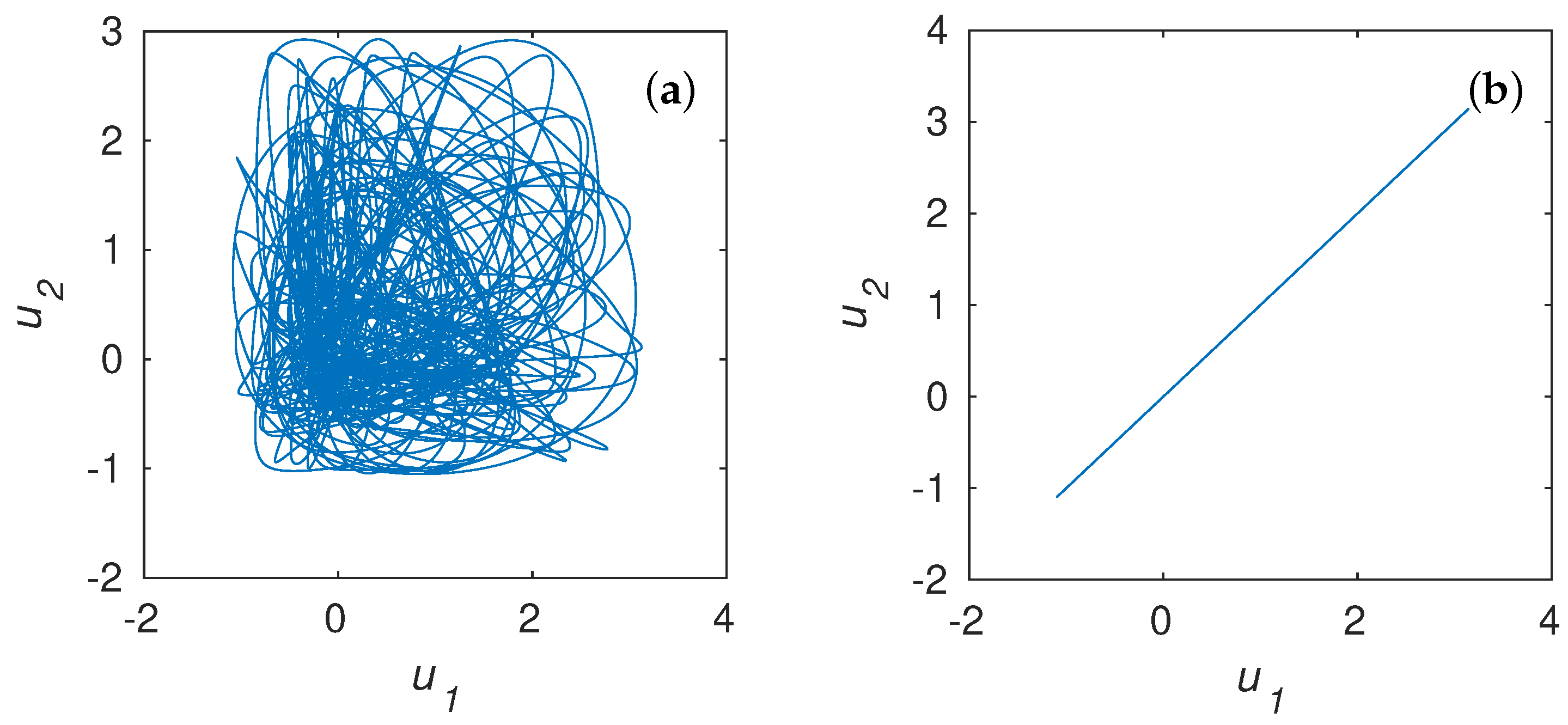
4.1. Coupled Chaotic Systems without Synchronization
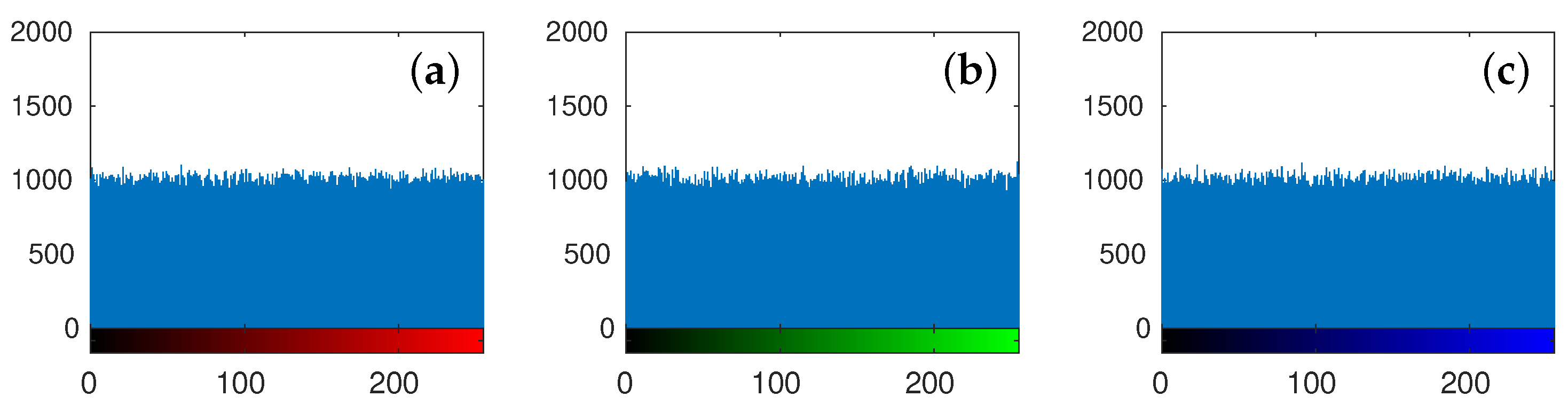
4.2. Testing of CPRNG Based on Coupled System
5. Application
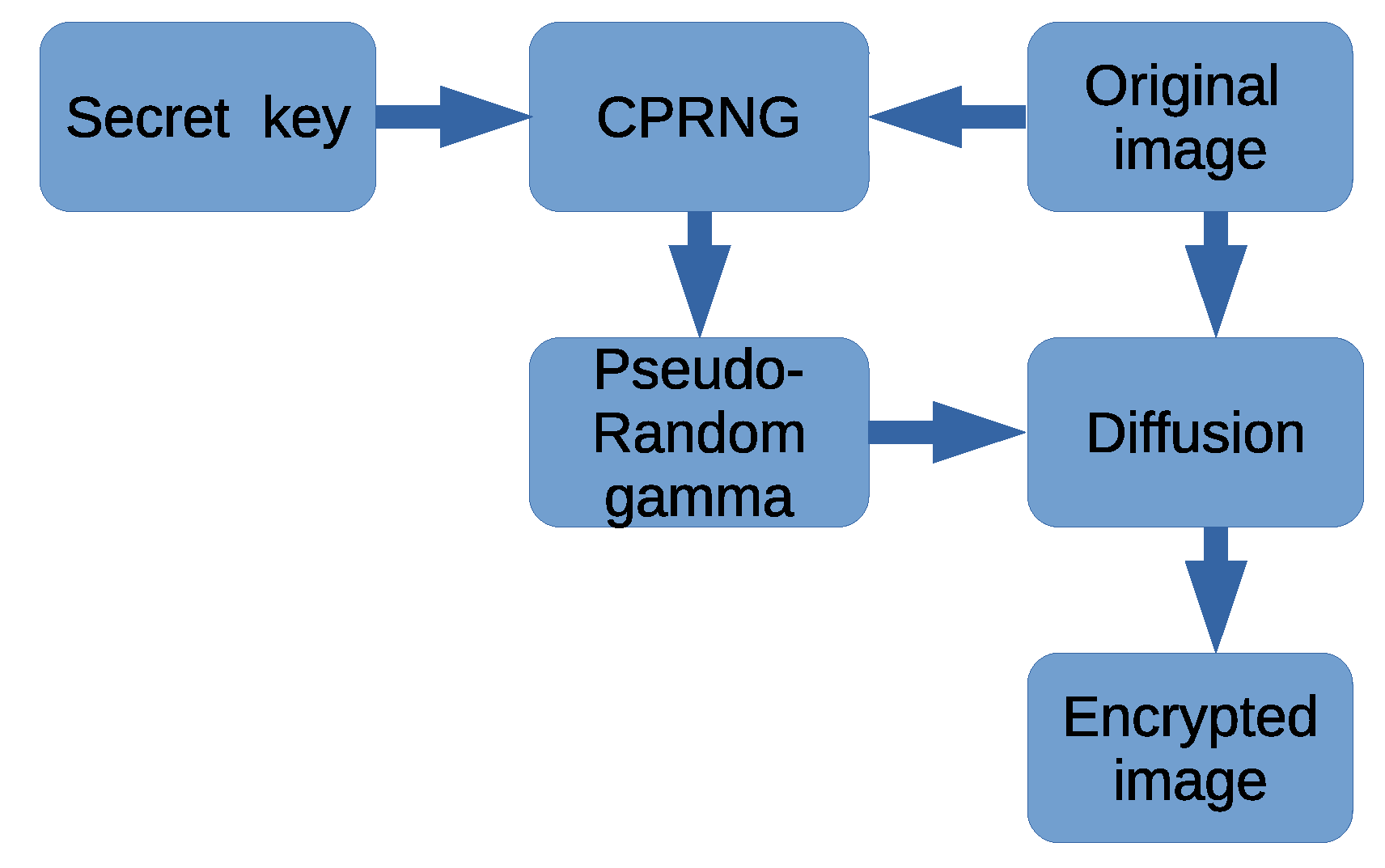
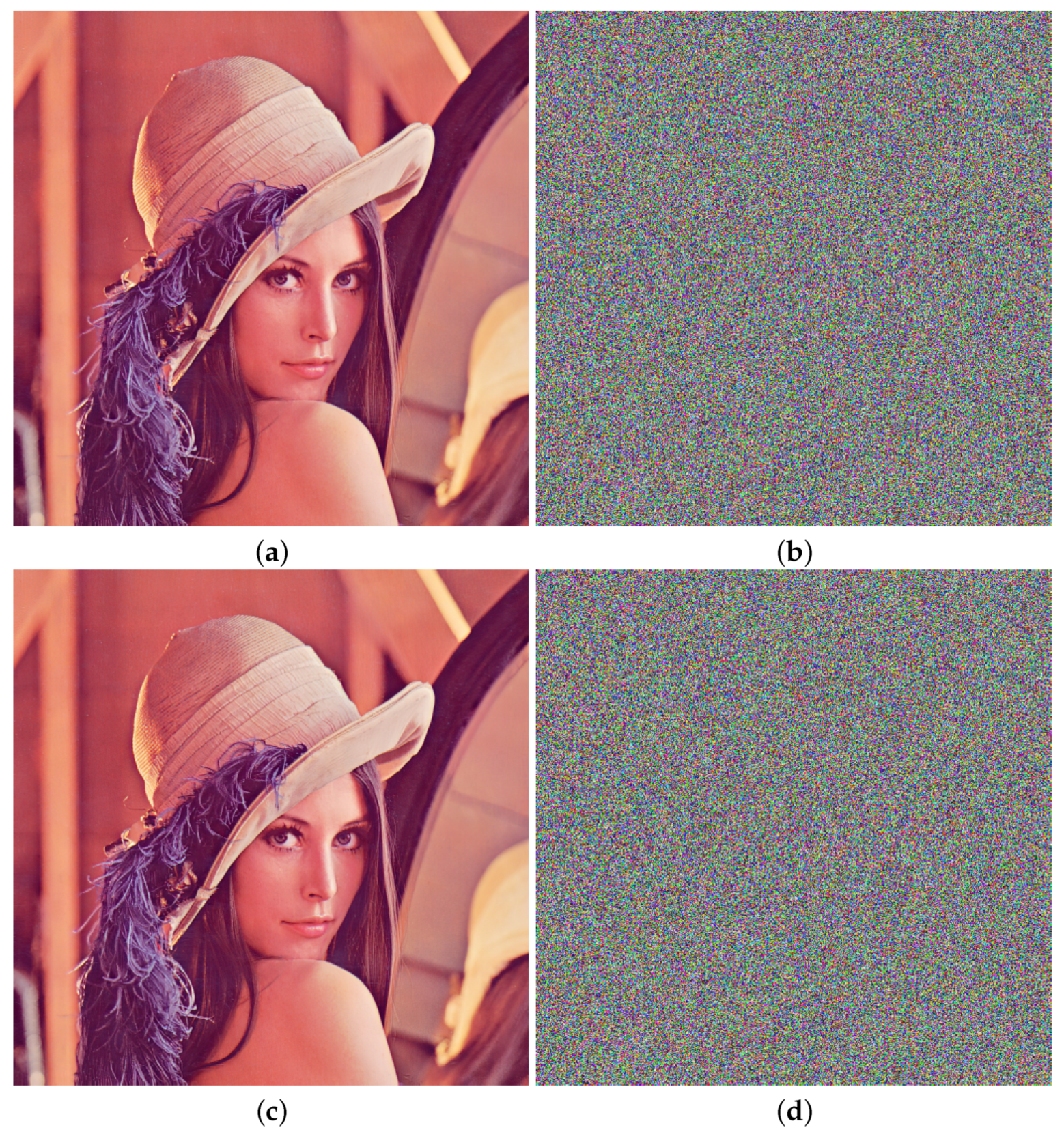
5.1. Image Encryption
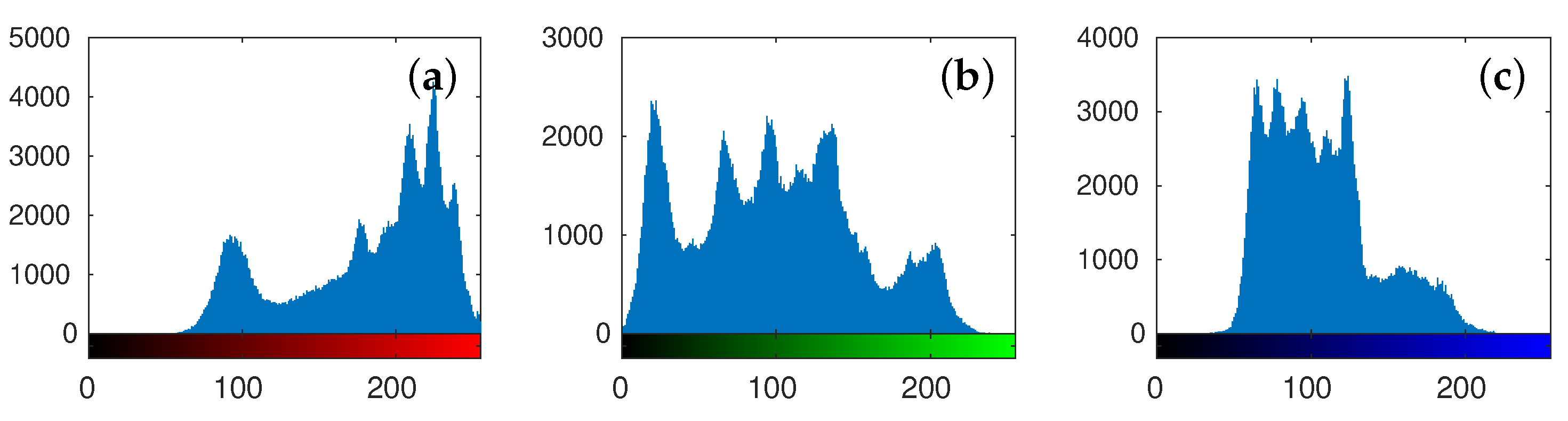
5.2. Security Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kocamaz, U.E.; Çiçek, S.; Uyaroǧlu, Y. Secure Communication with Chaos and Electronic Circuit Design Using Passivity-Based Synchronization. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2018, 27, 1850057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, A. Optical Communication with Chaotic Lasers: Applications of Nonlinear Dynamics and Synchronization; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Eisencraft, M.; Attux, R.; Suyama, R. Chaotic Signals in Digital Communications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kocarev, L.; Lian, S. Chaos-Based Cryptography: Theory, Algorithms and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 354. [Google Scholar]
- James, A. An overview of memristive cryptography. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 228, 2301–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergün, S.; Özoguz, S. Truly random number generators based on non-autonomous continuous-time chaos. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2010, 38, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Vazquez, A.; Delgado-Restituto, M. CMOS design of chaotic oscillators using state variables: A monolithic Chua’s circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 1993, 40, 596–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, S.; Rovatti, R.; Setti, G. Embeddable ADC-based true random number generator for cryptographic applications exploiting nonlinear signal processing and chaos. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtierra, J.L.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, A. A switched-capacitor skew-tent map implementation for random number generation. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2017, 45, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addabbo, T.; Alioto, M.; Fort, A.; Rocchi, S.; Vignoli, V. A feedback strategy to improve the entropy of a chaos-based random bit generator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2006, 53, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, L.; Tang, Q.; Cai, S.; Song, Y.; Xu, Q. A Survey on True Random Number Generators Based on Chaos. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2019, 2019, 25451237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hua, S.H.; Du, X.L. FPGA-Based Logistic Chaotic Pseudo-Random Sequence Generator Design. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Mechanical, Control and Computer Engineering (ICMCCE), Harbin, China, 25–27 December 2020; pp. 834–837. [Google Scholar]
- Cang, S.; Kang, Z.; Wang, Z. Pseudo-random number generator based on a generalized conservative Sprott-A system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 104, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, A.A.; Madian, A.H.; Radwan, A.G.; Soliman, A.M. Multiplierless chaotic Pseudo random number generators. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2020, 113, 152947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, M.; Defour, D.; Negre, C. A Fast Chaos-Based Pseudo-Random Bit Generator Using Binary64 Floating-Point Arithmetic. Informatica 2014, 38, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Erdem, E.; Garipcan, A.M. Hardware Implementation of Chaotic Zigzag Map Based Bitwise Dynamical Pseudo Random Number Generator on Field-Programmable Gate Array. J. Microelectron. Electron. Components Mater. 2020, 50, 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Hobincu, R.; Datcu, O. A Novel Chaos Based PRNG Targeting Secret Communication. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Communications (COMM), Singapore, 24–26 February 2018; pp. 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Moysis, L.; Tutueva, A.; Volos, C.K.; Butusov, D. A Chaos Based Pseudo-Random Bit Generator Using Multiple Digits Comparison. Chaos Theory Appl. 2020, 2, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rössler, O.E. An equation for continuous chaos. Phys. Lett. A 1976, 57, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, J.C. Some simple chaotic flows. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 50, R647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L. Memristor-The missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.; Snider, G.; Stewart, D.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, R. Memristors and Memristive Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Soell, C.; Reichenbach, M.; Roeber, J.; Hagelauer, A.; Weigel, R.; Fey, D. Case study on memristor-based multilevel memories. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2018, 46, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinto, F.; Ascoli, A.; Gilli, M. Nonlinear Dynamics of Memristor Oscillators. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2011, 58, 1323–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinto, F.; Forti, M. Nonlinear dynamics of memristor oscillators via the flux-charge analysis method. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Baltimore, MD, USA, 28–31 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Brenna, A.; Corinto, F.; Noori, S.; Ormellese, M.; Pedeferri, M.; Diamanti, M.V. Memristive Anodic Oxides: Production, Properties and Applications in Neuromorphic Computing. In Advances in Memristor Neural Networks; Ciufudean, C., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ascoli, A.; Slesazeck, S.; Mähne, H.; Tetzlaff, R.; Mikolajick, T. Nonlinear Dynamics of a Locally-Active Memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2015, 62, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascoli, A.; Tetzlaff, R.; Chua, L.O.; Strachan, J.P.; Williams, R.S. History Erase Effect in a Non-Volatile Memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2016, 63, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuswamy, B.; Kokate, P.P. Memristor-Based Chaotic Circuits. IETE Tech. Rev. 2009, 26, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyriakides, E.; Georgiou, J. A Compact, Low-frequency, Memristor-based Oscillator. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2015, 43, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Karthikeyan, A.; Duraisamy, P. Difference equations of a memristor higher order hyperchaotic oscillator. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2018, 10, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezayyin, H.G.; Ahmed, G.M.; Fouda, M.E.; Said, L.A.; Madian, A.H.; Radwan, A.G. A generalized family of memristor-based voltage controlled relaxation oscillator. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2018, 46, 1311–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuswamy, B.; Chua, L.O. Simplest chaotic circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2010, 20, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Wang, C. A New Simple Chaotic Circuit Based on Memristor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2016, 26, 1650145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volos, C.K.; Pham, V.T.; Nistazakis, H.E.; Stouboulos, I.N. A Dream that has Come True: Chaos from a Nonlinear Circuit with a Real Memristor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2020, 30, 2030036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, B.; Xu, Q.; Wu, H.; Chen, M. Parameter and initial offset boosting dynamics in two-memristor-based Colpitts system. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, M.; Roy, B.K. Hidden multistability in four fractional-order memristive, meminductive and memcapacitive chaotic systems with bursting and boosting phenomena. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ontañón-García, L.J.; García-Martínez, M.; Campos-Cantón, E.; Čelikovský, S. Grayscale image encryption using a hyperchaotic unstable dissipative system. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST-2013), London, UK, 9–12 December 2013; pp. 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- Borah, M.; Roy, B.K. Systematic construction of high dimensional fractional-order hyperchaotic systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 131, 109539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari-Chenaghlu, M.; Balafar, M.A.; Feizi-Derakhshi, M.R. A novel image encryption algorithm based on polynomial combination of chaotic maps and dynamic function generation. Signal Process. 2019, 157, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynnyk, V.; Sakamoto, N.; Čelikovský, S. Pseudo random number generator based on the generalized Lorenz chaotic system. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machicao, J.; Bruno, O.M. Improving the pseudo-randomness properties of chaotic maps using deep-zoom. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2017, 27, 053116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hua, Z.; Pun, C.M.; Chen, C.L. Cascade Chaotic System with Applications. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2015, 45, 2001–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Li, L.; He, B.; Liu, L.; Qian, S.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, H.; Cai, S.; Li, Y. Pseudorandom number generator based on a 5D hyperchaotic four-wing memristive system and its FPGA implementation. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozi, R. Cryptography-Based Chaos via Geometric Undersampling of Ring-Coupled Attractors. In Mathematical Models, Methods and Applications; Siddiqi, A.H., Manchanda, P., Bhardwaj, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Garasym, O.; Taralova, I.; Lozi, R. Key requirements for the design of robust chaotic PRNG. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST), Barcelona, Spain, 5–7 December 2016; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Miyano, T. Design and Test of Pseudorandom Number Generator Using a Star Network of Lorenz Oscillators. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2017, 27, 1750184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q. A Dependent Variable Exclusively Coupled Chaotic System for a Pseudorandom Bit Generator. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th Annual International Conference on Network and Information Systems for Computers (ICNISC), Wuhan, China, 19–21 April 2018; pp. 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, L.O.; Kang, S.M. Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sklar, B. Digital Communications: Fundamentals and Applications; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ergun, S. Analysis and Simulation of a Chaos-Based Random Number Generator for Applications in Security. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Nonlinear Theory and Its Applications, NOLTA2017, Cancun, Mexico, 4–7 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.; Yorke, J. Collapsing of chaos in one dimensional maps. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2000, 136, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications; Technical report; Booz-Allen and Hamilton Inc.: Mclean, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pecora, L.M.; Carroll, T.L.; Johnson, G.A.; Mar, D.J.; Heagy, J.F. Fundamentals of synchronization in chaotic systems, concepts, and applications. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 1997, 7, 520–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boccaletti, S.; Kurths, J.; Osipov, G.; Valladares, D.; Zhou, C. The synchronization of chaotic systems. Phys. Rep. 2002, 366, 1–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecora, L.M.; Carroll, T.L. Driving systems with chaotic signals. Phys. Rev. A 1991, 44, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hramov, A.E.; Koronovskii, A.A. Generalized synchronization: A modified system approach. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 067201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balcerzak, M.; Chudzik, A.; Stefanski, A. Properties of generalized synchronization in smooth and non-smooth identical oscillators. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2020, 229, 2151–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazanaro, F.I.; Suyama, R.; Soriano, D.C. Conditional lyapunov exponents for izhikevich neuronal model: Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th International Conference on Nonlinear Science and Complexity (NSC—2016), Niigata, Japan, 18–20 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kahan, W. Lecture Notes on the Status of IEEE Standard 754 for Binary Floating-Point Arithmetic. 1996. Available online: http://http.cs.berkeley.edu/~wkahan/ieee754status/ieee.ps (accessed on 30 November 2021).


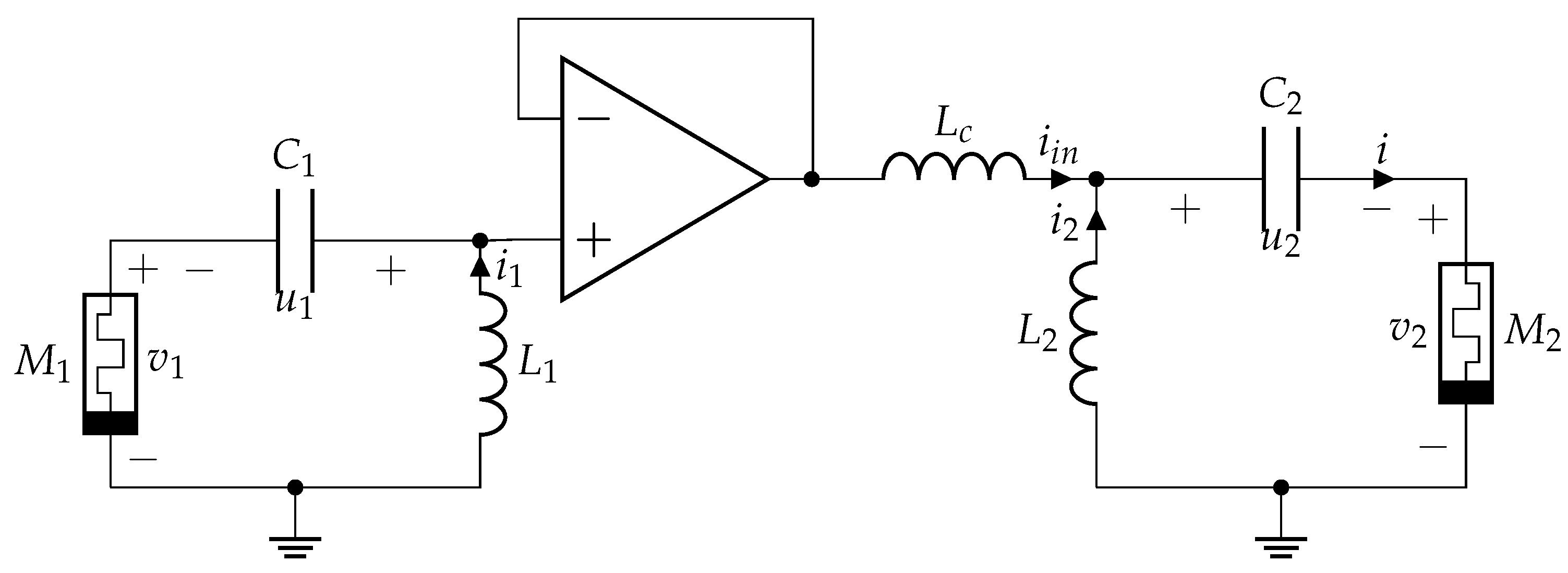
| Euler’s Method, FPGA Implementation, 32-bits Fixed-Point Arithmetic | Runge–Kutta Fourth Order Method, Matlab-Simulink Implementation, Double-Precision Floating-Point Arithmetic | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | p-Value/Proportion | Status | p-Value/Proportion | Status |
| FT | 0.504219/0.993 | Pass | 0.733899/0.986 | Pass |
| BFT | 0.922855/0.990 | Pass | 0.975644/0.987 | Pass |
| CST | 0.514124/0.993 | Pass | 0.305599/0.986 | Pass |
| CST | 0.811080/0.992 | Pass | 0.610070/0.987 | Pass |
| RuT | 0.757790/0.988 | Pass | 0.723804/0.988 | Pass |
| LRuT | 0.128132/0.990 | Pass | 0.969588/0.984 | Pass |
| RaT | 0.591409/0.991 | Pass | 0.713641/0.992 | Pass |
| FFT | 0.317565/0.990 | Pass | 0.494392/0.988 | Pass |
| NOTT | All 148 tests passed | All 148 tests are passed | ||
| OTT | 0.589341/0.984 | Pass | 0.142062/0.989 | Pass |
| UT | 0.118812/0.986 | Pass | 0.524101/0.991 | Pass |
| AET | 0.684890/0.986 | Pass | 0.508172/0.989 | Pass |
| RET | All 8 tests passed | All 8 tests are passed | ||
| REVT | All 18 tests passed | All 18 tests are passed | ||
| ST | 0.192724/0.987 | Pass | 0.686955/0.988 | Pass |
| ST | 0.182550/0.984 | Pass | 0.478839/0.993 | Pass |
| LCT | 0.522100/0.988 | Pass | 0.729870/0.987 | Pass |
| Euler’s Method, FPGA 32-bits Fixed- Point Arithmetic Implementation, Systems with Modified Coupling (14) | Euler’s Method, FPGA 32-bits Fixed- Point Arithmetic Implementation, Systems Coupled through Inductance (15) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test | p-Value/Proportion | Status | p-Value/Proportion | Status |
| FT | 0.385543/0.991 | Pass | 0.946308/0.987 | Pass |
| BFT | 0.846338/0.990 | Pass | 0.016037/0.995 | Pass |
| CST | 0.473064/0.993 | Pass | 0.377007/0.989 | Pass |
| CST | 0.136499/0.991 | Pass | 0.904708/0.988 | Pass |
| RuT | 0.522100/0.986 | Pass | 0.244236/0.990 | Pass |
| LRuT | 0.014961/0.994 | Pass | 0.538182/0.990 | Pass |
| RaT | 0.141256/0.989 | Pass | 0.044508/0.989 | Pass |
| FFT | 0.486588/0.994 | Pass | 0.603841/0.987 | Pass |
| NOTT | All 148 tests are passed | All 148 tests passed | ||
| OTT | 0.146982/0.984 | Pass | 0.820143/0.990 | Pass |
| UT | 0.266235/0.986 | Pass | 0.257004/0.985 | Pass |
| AET | 0.662091/0.991 | Pass | 0.729870/0.985 | Pass |
| RET | All 8 tests passed | All 8 tests are passed | ||
| REVT | All 18 tests passed | All 18 tests are passed | ||
| ST | 0.028244/0.998 | Pass | 0.943242/0.993 | Pass |
| ST | 0.358641/0.990 | Pass | 0.607993/0.989 | Pass |
| LCT | 0.422638/0.992 | Pass | 0.834308/0.997 | Pass |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haliuk, S.; Krulikovskyi, O.; Vovchuk, D.; Corinto, F. Memristive Structure-Based Chaotic System for PRNG. Symmetry 2022, 14, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14010068
Haliuk S, Krulikovskyi O, Vovchuk D, Corinto F. Memristive Structure-Based Chaotic System for PRNG. Symmetry. 2022; 14(1):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14010068
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaliuk, Serhii, Oleh Krulikovskyi, Dmytro Vovchuk, and Fernando Corinto. 2022. "Memristive Structure-Based Chaotic System for PRNG" Symmetry 14, no. 1: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14010068
APA StyleHaliuk, S., Krulikovskyi, O., Vovchuk, D., & Corinto, F. (2022). Memristive Structure-Based Chaotic System for PRNG. Symmetry, 14(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14010068






