Identification of Magnetorheological Layer Properties by Using Refined Plate Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
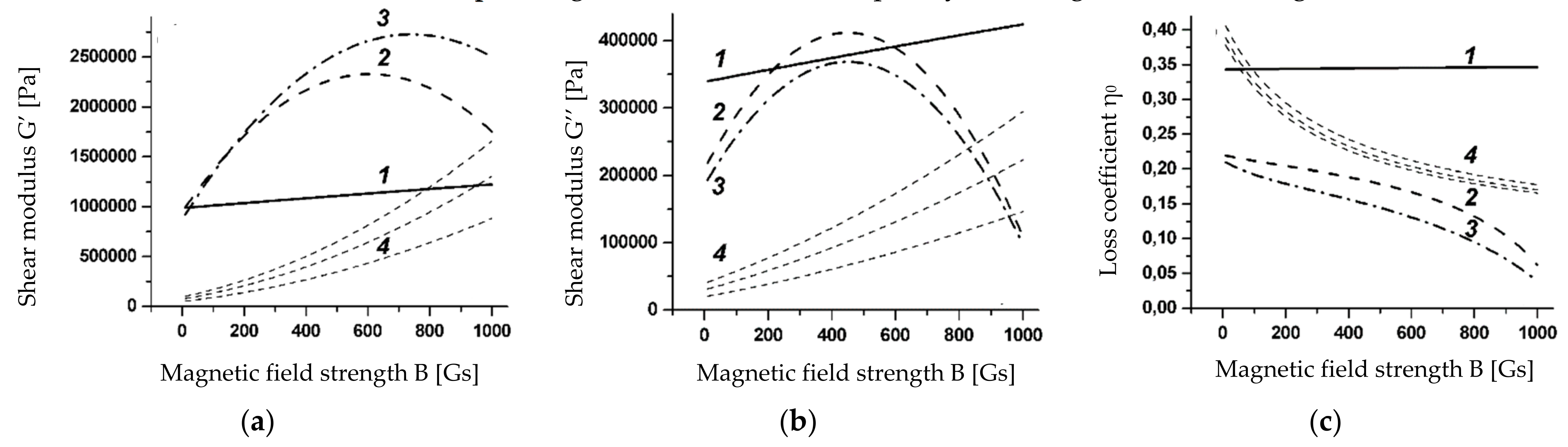
3.1. Modeling of Mechanical Properties of the MR Layer
- (1).
- The value of the modules are given in [19]:
- (2).
- The value of the modules are given in [9]:
- (3).
- The value of the modules are given in [20]:
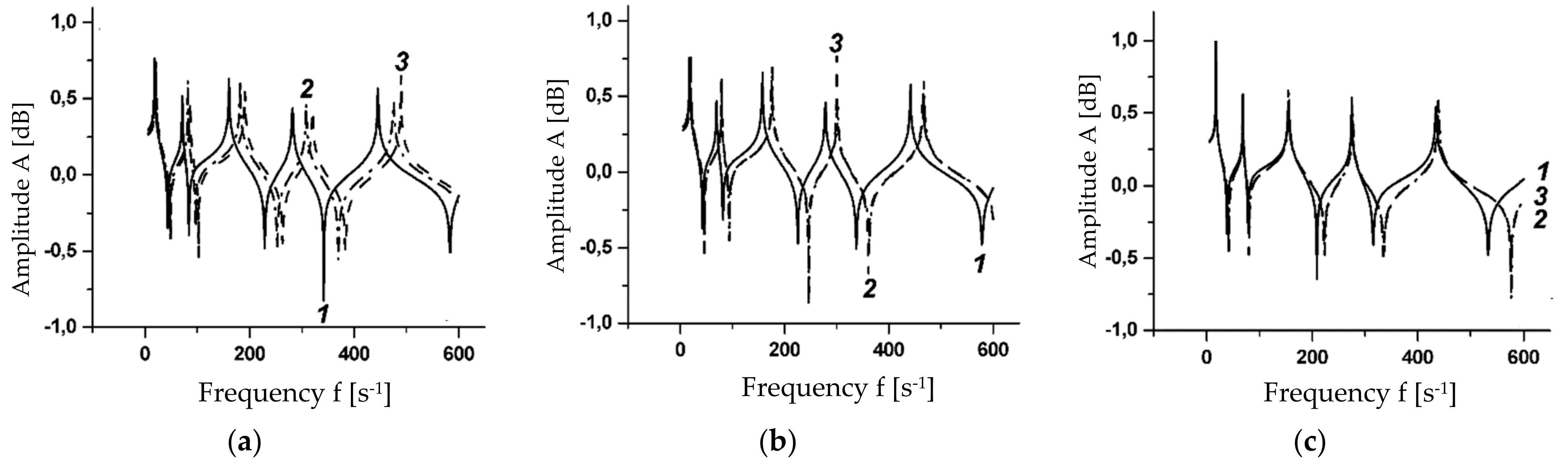
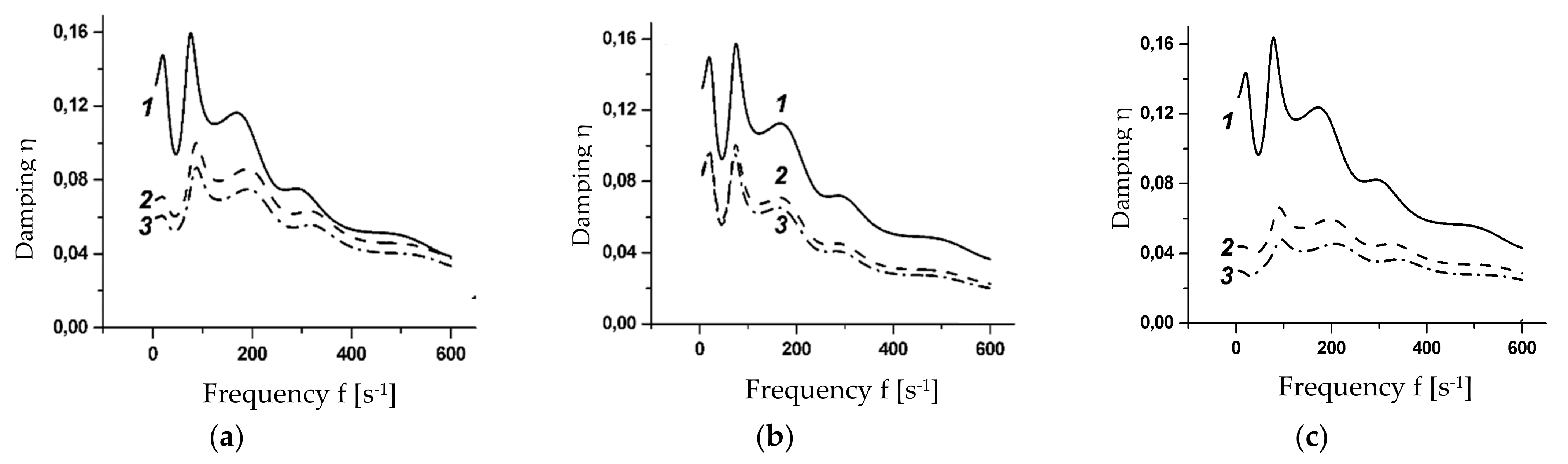
3.2. Laminated Symmetric Beams with Inner MR Layer
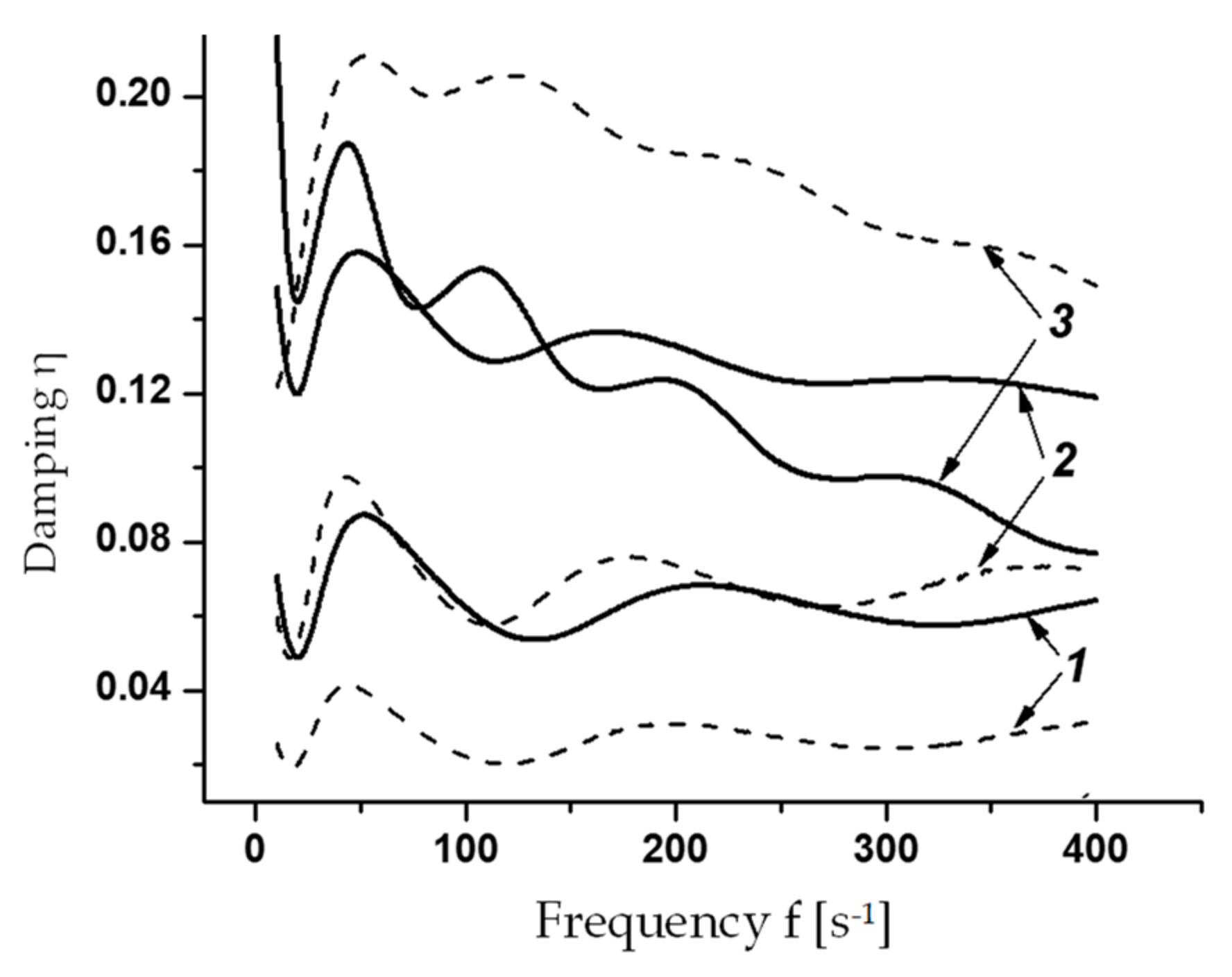
3.3. Five-Layered Beam
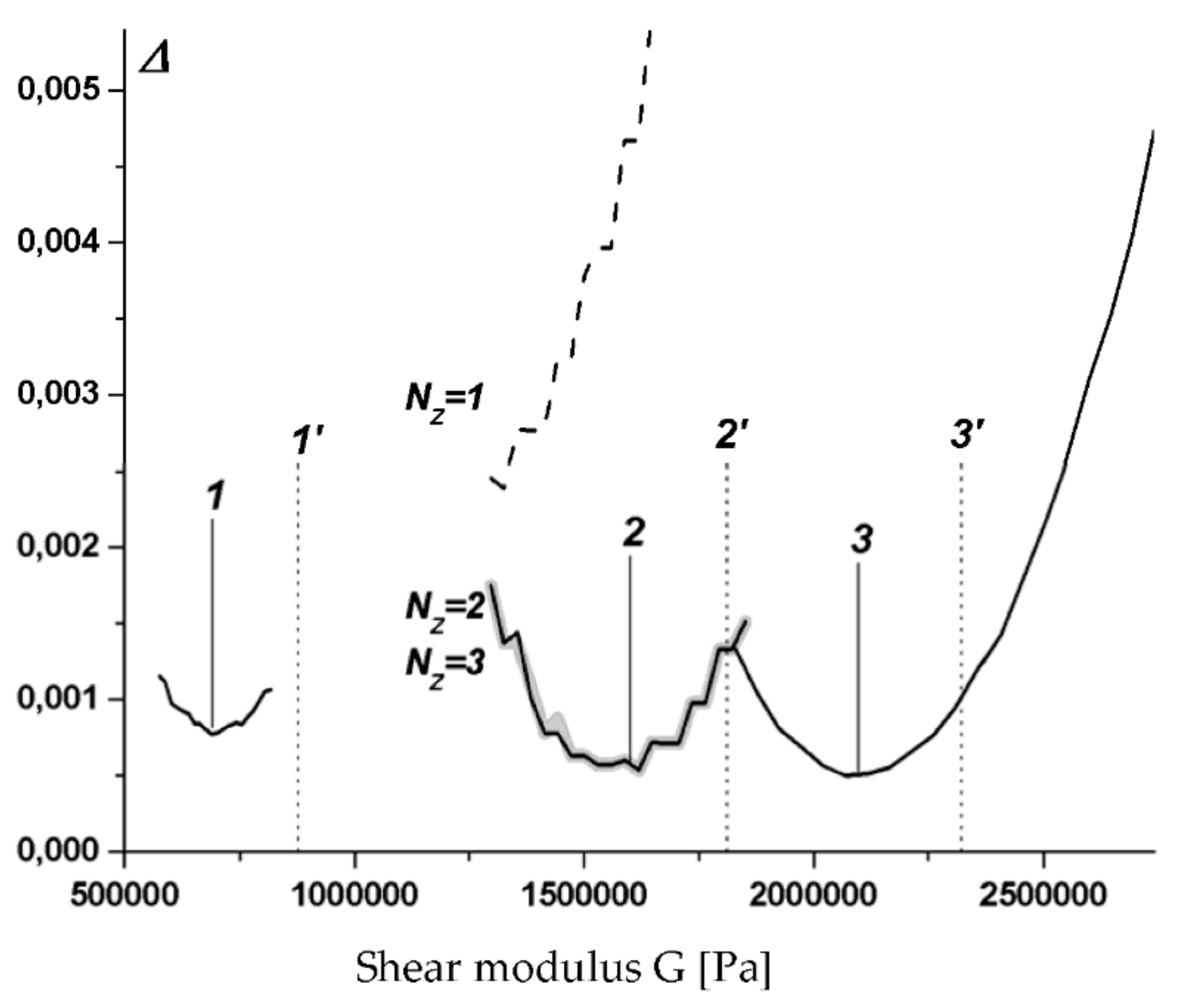
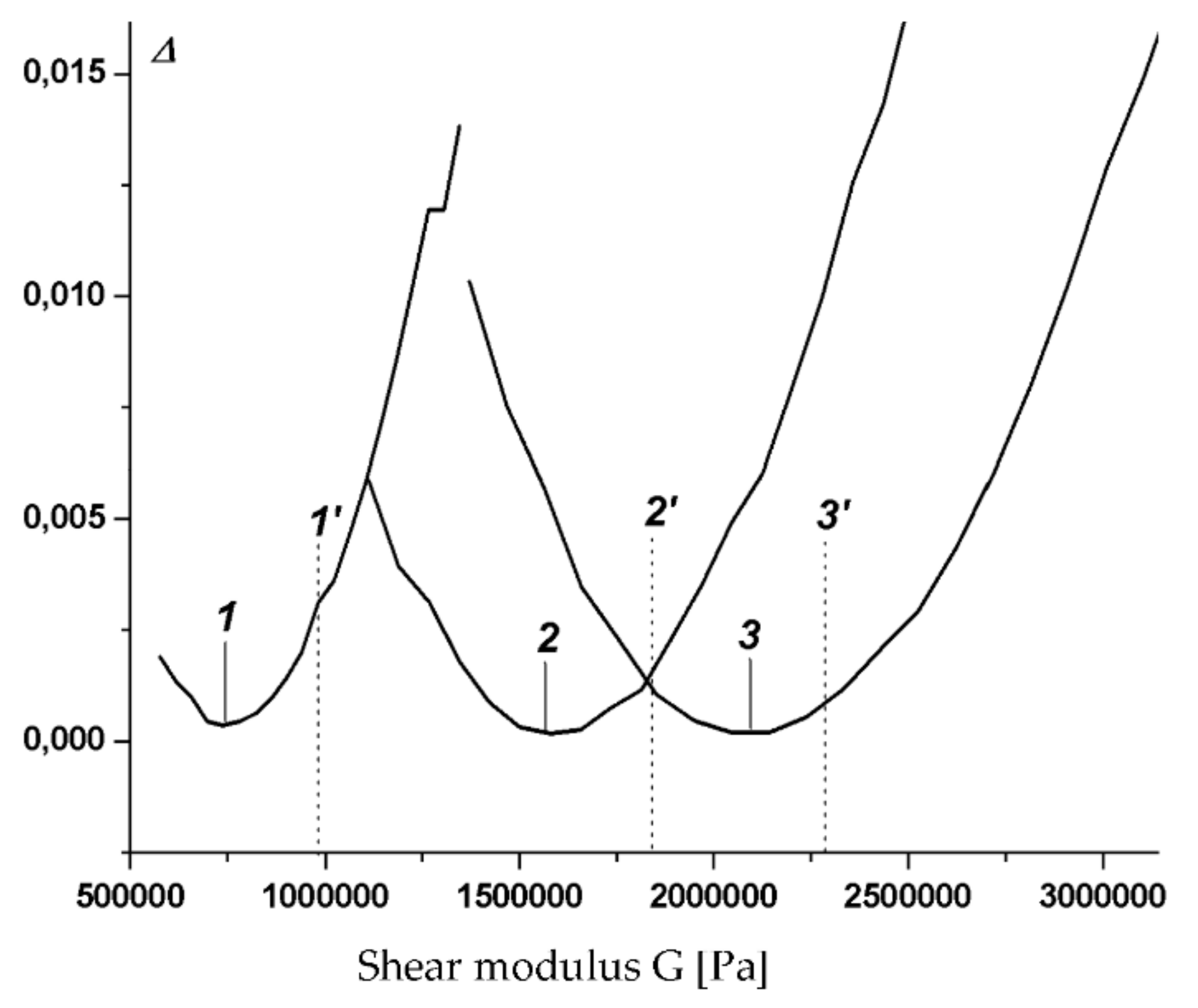
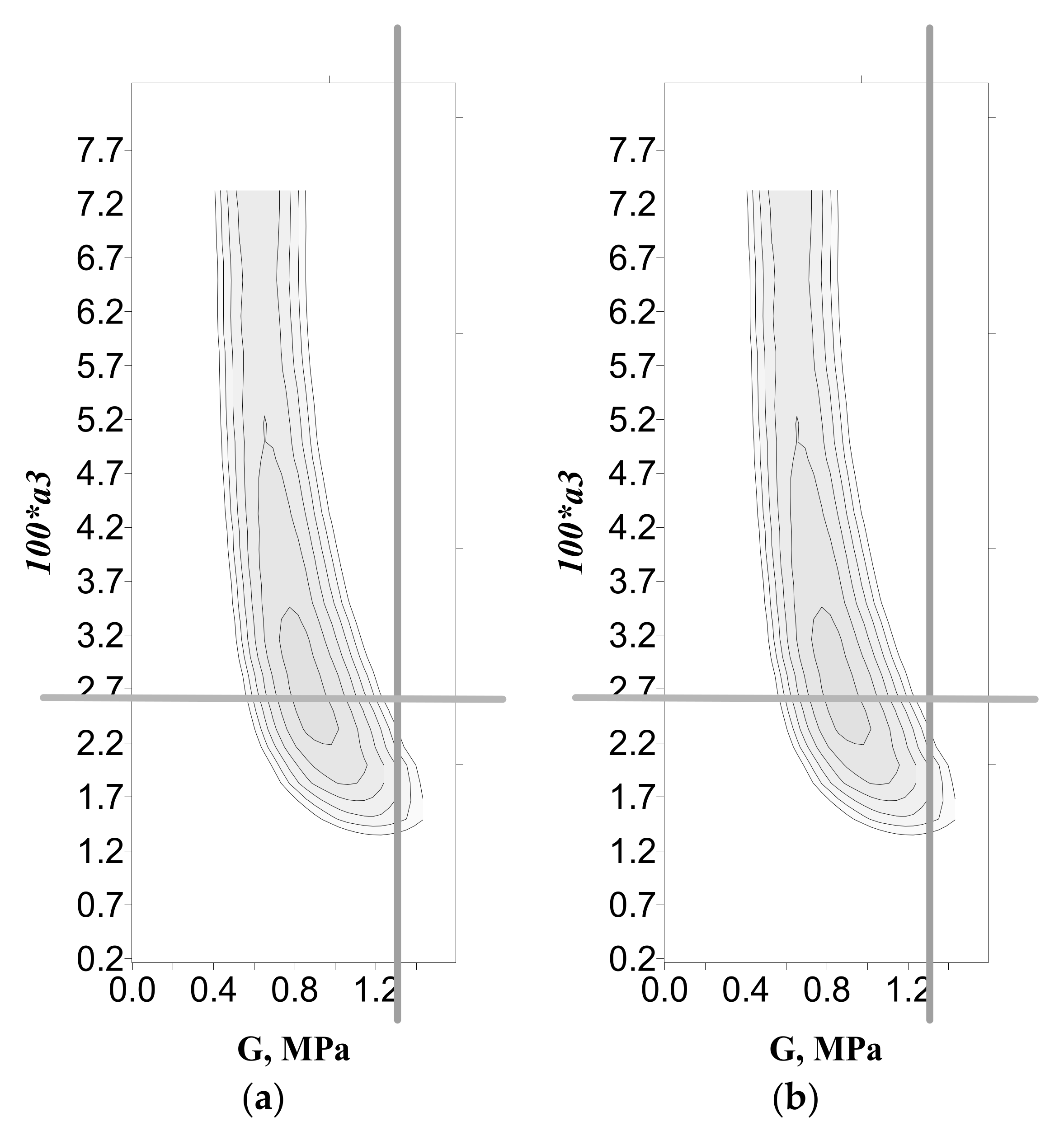
3.4. Identification of MR Layer Modules
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacob, R. Magnetic Fluid Torque and Force Transmitting Device. US Patent 2575360, 30 November 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Shiga, T.; Okadam, A.; Kurauchi, T. Magnetoviscoelastic behavior of composite gels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 58, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.R.; Carlson, J.D.; Munoz, B.C.; Bullions, A. The magnetoviscoelastic response of elastomer composites consisting of ferrous particles embedded in a polymer matrix. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1996, 7, 613–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcintas, M.; Dai, H. Magnetorheological and electrorheological materials in adaptive structures and their performance comparison. Smart Mater. Struct. 1999, 8, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, C.; Bossis, G. Filed dependence of viscoelastic properties of magnetorheological elastomers. Inter. J. Mod. Phys. 2002, 16, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.Y.; Wang, Q. Study on the adjustable rigidity of magnetorheological-elastomer-based sandwich beams. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.G.; Ni, Y.Q. Micro-vibration response of a stochastically excited sandwich beam with a magnetorheological elastomer core and mass. Smart Mater. Struct. 2009, 18, 095005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Dwivedy, S.K.; Murthy, K.S. Dynamic analysis of magnetorheological elastomer-based sandwich beam with conductive skins under various boundary conditions. J. Sound Vibration 2011, 330, 1837–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamohan, V.; Sedaghati, R.; Rakheja, S. Vibration analysis of a multi-layer beam containing magnetorheological fluid. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 015013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcintas, M.; Dai, H. Vibration suppression capabilities of magneto-rheological materials based adaptive structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, J.X.; Zhang, L. An adaptive beam model and dynamic characteristics of magnetorheological materials. J. Sound Vibration 2003, 261, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Z.F.; Shih, Y.S. Dynamic characteristics and dynamic instability of magnetorheological based adaptive beams. J. Compos. Mater. 2006, 40, 1333–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, E. Historical review of zig-zag theories for multilayered plates and shells. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2003, 56, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Belouettar, S.; Potier-Ferry, M.; Daya, E.M. Review and assessment of various theories for modeling sandwich composites. Compos. Struct. 2008, 84, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diveyev, B.; Butyter, I.; Shcherbyna, N. High order theories for elastic modules identification of composite plates. Part 1. Theoretical approach. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2008, 1, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diveyev, B.; Butyter, I.; Shcherbyna, N. High order theories for elastic modules identification of composite plates. Part 2. Theoretical-experimental approach. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2008, 2, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butyter, I.; Diveyev, B.; Kogut, I.; Marchuk, M.; Shcherbyna, N. Identification of elastic moduli of composite beams by using combined criteria. Mech. Compos. Mater. 2013, 6, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diveyev, B.; Konyk, S.; Crocker, M.J. Dynamic properties and damping predictions for laminated plates: High order theories—Timoshenko beam. J. Sound Vibration 2018, 413, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, V.R.; Vasudevan, R. Dynamic analysis of tapered laminated composite magnetorheological elastomer (MRE) sandwich plates. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, R.; Vasudevan, R.; Jeevanantham, A.K. Dynamic characterization of a laminated composite magnetorheological fluid sandwich plate. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 025022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaghi, M.; Rakheja, S.; Sedaghati, R. An accurate technique for pre-yield characterization of MR fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 065018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snitynskyy, V.; Kernytskyy, I.; Diveyev, B.; Horbay, O.; Koruniak, P.; Humenyuk, R.; Kokhana, T. Impact and particle vibration absorbers optimal design. Acta Sci. Pol. Arch. 2020, 19, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barretta, R.; Čanađija, M.; Sciarra, F.M.D. Nonlocal mechanical behavior of layered nanobeams. Symmetry 2020, 12, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, N.; Chu, F.; Luo, J. A finite element model for the vibration analysis of sandwich beam with frequency-dependent viscoelastic material core. Materials 2019, 12, 3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasik, T.; Chalecki, M.; Koda, E. Analysis of embedded retaining wall using the subgrade reaction method. Studia Geotech. Mech. 2015, 37, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Semenyuk, M.; Trach, V.; Zhukova, N. On the method of calculation of buckling and post-buckling behavior of laminated shells with small arbitrary imperfections. Acta Sci. Pol. Archit. 2021, 20, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kernytskyy, I.; Koda, E.; Diveyev, B.; Horbay, O.; Sopilnyk, L.; Humenuyk, R.; Sholudko, Y.; Osinski, P. Identification of Magnetorheological Layer Properties by Using Refined Plate Theory. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091601
Kernytskyy I, Koda E, Diveyev B, Horbay O, Sopilnyk L, Humenuyk R, Sholudko Y, Osinski P. Identification of Magnetorheological Layer Properties by Using Refined Plate Theory. Symmetry. 2021; 13(9):1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091601
Chicago/Turabian StyleKernytskyy, Ivan, Eugeniusz Koda, Bohdan Diveyev, Orest Horbay, Lyubomyr Sopilnyk, Ruslan Humenuyk, Yaroslav Sholudko, and Piotr Osinski. 2021. "Identification of Magnetorheological Layer Properties by Using Refined Plate Theory" Symmetry 13, no. 9: 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091601
APA StyleKernytskyy, I., Koda, E., Diveyev, B., Horbay, O., Sopilnyk, L., Humenuyk, R., Sholudko, Y., & Osinski, P. (2021). Identification of Magnetorheological Layer Properties by Using Refined Plate Theory. Symmetry, 13(9), 1601. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091601






