1. Introduction
For integer valued matrices, the notion of decomposability can be stated analogously to the real case (see Definition 1). The main difference here is that unimodularity is required for the transformation matrices. This is necessary to preserve the -module structure generated by the columns of the matrix. Thus, if one wants to keep the group structure unchanged, pure linear algebra techniques cannot be applied to study the decomposability of an integer matrix.
Let
be two positive integers. Given an
integer matrix
A, we can consider the submonoid
S of
generated by the non-negative combinations of the columns of
A. A decomposition of
A yields a decomposition of
S, and vice versa. In [
1], the authors deal with the computation of the decompositions of
S, if possible, using the (integer) Hermite normal form as the main tool. Following this idea, we relate the decomposition of any integer matrix and the decomposition of its Hermite normal form (Proposition 1). This leads to our main result (Theorem 1) which states that if
H is the Hermite normal form of an integer matrix
A, the necessary and sufficient condition for
A to be decomposable is that a certain symmetric matrix is reducible in the usual sense (see Definition 3). Now, we can adapt the combinatorial and linear algebra machinery to determine if
A is decomposable: note that, for a symmetric real matrix, it is possible to decide if it can be decomposed into a direct sum of smaller symmetric real matrices by analyzing the connectivity of a certain associated graph, which is closely related to the spectral properties of the graph. All this allows us to propose an algorithm (Algorithm 1) for the computation of the decomposition of the matrix
A, if possible.
Apart from practical computational considerations, we emphasize that, given an integer matrix
A, we propose a new approach by associating
A with a simple graph whose connectivity determines its decomposition. Consequently, this can be used to determine the decomposition of any finitely generated commutative submonoid of
, as an alternative method to [
1]. Recall that the study of finitely generated commutative submonoids of
is of great interest due to its close relation with Toric Geometry (see [
2,
3] or [
4], and the references therein). Moreover, in this context, integer decomposable matrices have their own importance; to mention a couple of illustrative examples we observe that decomposable graphical models have associated integer decomposable matrices, as can be deduced from [
5] (Theorem 4.2), and that decomposable semi-groups correspond to direct products of certain algebraic (toric, in a wide sense) varieties.
| Algorithm 1: HNF-decomposition. |
Input: An integer matrix A.
Output: A unimodular matrix P and a permutation matrix Q such that
with into Hermite normal form for every i.
1. Set and let be a unimodular matrix, such that ;
2. Define the square matrix and set ;
3. Let D be the diagonal matrix whose elements in the main diagonal are entries of and define . If then return and Q equal to the identity matrix;
4. Let R be the reduced row echelon form of L and let ;
5. For to n do
If the j-th column, , of R is a non-pivot column; then
i. Set and equal to the cardinality of ;
ii. Let be the -matrix whose columns are where denotes the n-dimensional vector that has the i-th coordinate equal to 1 and all the other coordinates equal to 0.
6. Set ;
7. Let be the unimodular matrix such that ;
8. Return and Q. |
2. On Decomposable and Reducible Integer Matrices
Let be two positive integers.
Definition 1. Let . We say that A is decomposable if there exist a unimodular matrix P and a permutation matrix Q such that decomposes into a direct sum of matrices.
As mentioned in the introduction, the main purpose of this note is to study decomposable matrices in terms of their Hermite normal form. Let us recall the notion of Hermite normal form of an integer matrix.
Definition 2. Let of rank r. The Hermite normal form of , is the unique matrix , such that , for a unimodular matrix P, satisfying the following three conditions:
- (a)
there exists a sequence of integers such that , and for each we have for all (row echelon form);
- (b)
for we have (the pivot element is the greatest along its column and the coefficients above are non-negative);
- (c)
the last rows of H are zero.
We say that A is in Hermite normal form when .
There are well-known efficient algorithms for the computation of the Hermite normal form of an integer matrix (see, e.g., [
6]). They are implemented in the usual computer algebra systems; for example, in GAP ([
7]) and Mathematica ([
8]), the commands
HermiteNormalFormIntegerMat and
HermiteDecomposition, respectively, compute the Hermite normal form of an integer matrix.
Example 1. The Hermite normal form ofiswhere the matrix is the product of the elementary matrices transforming the matrix A into its reduced row echelon form as above, in such a way that the unimodular matrix in Definition 2 is The next propositions provide necessary and sufficient conditions for an integer matrix to be decomposable in terms of its Hermite normal form.
Proposition 1. Let and let . Then, A is decomposable if and only if H is decomposable.
Proof. Let be a unimodular matrix such that . If A is decomposable, then , for a unimodular matrix and a permutation matrix Q. Now, since is unimodular, we have that H is decomposable. Conversely, assume that H is decomposable, so there exist a unimodular matrix and a permutation matrix , such that . Thus, and we are done. □
In the following, we use the symbol ⊤ to denote the transpose operation.
Proposition 2. Let H be an integer matrix in Hermite normal form. Then, H is decomposable if and only if there exist permutation matrices P and Q, such that decomposes into a direct sum of matrices.
Proof. First, we observe that if the rank of H is , then the last rows of H are zero. As these rows do not affect the condition of H to be decomposable, we assume that H has rank m.
The sufficiency part is obvious since the permutation matrix
P is unimodular and
. Conversely, if
H is decomposable, there exist a unimodular matrix
R and a permutation matrix
Q such that
For simplicity, we assume that
. Let
and
be unimodular matrices, such that
and
are in Hermite normal form, and define the following matrix
Since the rank of B is m, each row of B contains a pivot element of or . If we move the row containing the first (leftmost) pivot element to the first place, the row containing the second pivot element to the second place and so forth, the resulting matrix is necessarily in Hermite normal form. Thus, there exists a permutation matrix P such that , by the uniqueness of the Hermite normal form. Therefore, and we conclude that decomposes into . □
Example 2. By Proposition 2, we can easily see that the matrix A in Example 1 is decomposable. Indeed, For symmetric matrices, decomposability can be refined to the more restrictive notion of reducibility. This notion has a rich combinatorial nature, because of its relationship with graph theory, as we will see later on.
Definition 3. A symmetric matrix is reducible if there exists a permutation matrix Q such that decomposes into a direct sum of square matrices. Otherwise B is said to be irreducible.
The following result gives a necessary and sufficient condition for an integer matrix to be decomposable in terms of the reducibility of a certain related symmetric matrix. To state our result we need a piece of notation.
Notation 1. Let H be an integer matrix in Hermite normal form. With the same notation as in Definition 2, we write for the triangular integer matrix whose -th row is the i-row of , and zeros elsewhere.
The following example illustrates the above notation.
Observe that the matrix is not necessarily in Hermite normal form.
Lemma 1. Let H be an integer matrix in Hermite normal form. If H is decomposable, then there exists a permutation matrix Q such that decomposes into a direct sum of triangular matrices; in particular, is decomposable.
Proof. By Proposition 2, there exist permutation matrices
and
Q, such that
decomposes into a direct sum of matrices. Clearly, adding rows and columns to
conveniently, we may construct an
permutation matrix
such that
. Matrices
are not necessarily triangular. However, since
is triangular, there exists a permutation matrix
such
where
is triangular for every
. Now, since
and
are both triangular, we conclude that
and
Q are identical up to permutation of the zero rows of
. □
Theorem 1. Let A be an integer matrix. If , then A is decomposable if and only ifis reducible. Proof. By Proposition 1, we may assume that
. Now, if
H is decomposable, by Lemma 1, there exists a permutation matrix
Q, such that
, with
triangular. Therefore,
and we conclude that
is reducible.
Conversely, if
is reducible, then there exists a permutation matrix
Q, such that
. Now, since
is triangular, we have that
, with
having the same order than
, for each
, respectively. So, it follows that
and we conclude that
is decomposable. □
Example 4. We already know that the matrix A in Example 1 is decomposable. Thus, in the light of Theorem 1, the symmetric matrix must be reducible. Indeed, 3. The Simple Graph of a Integer Matrix. HNF-Decomposition Algorithm
An important advantage of dealing with symmetric matrices is their strong combinatorial meaning: any symmetric matrix can be considered as the adjacency matrix of an undirected graph with n vertices , such that is an edge of if and only if and .
Note that we are not concerned with diagonal elements and magnitudes of B to construct .
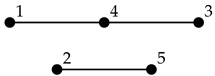
Example 5. The graph corresponding to the matrix B in Example 4 is ![Symmetry 13 01125 i001]()
Notice that is not connected in this case.
Clearly, a symmetric matrix B is reducible if and only if the graph is not connected. Thus, by Theorem 1, we can study the reducibility of an integer matrix A by means of the graph for as follows.
Corollary 1. Let and set Then A is decomposable if and only if is not connected.
Note 1. Given , the graph , with , can be constructed directly from . Indeed, with the notation of Definition 2, it suffices to observe that if, and only if, . Therefore, all the information concerning the decomposability of A is encoded in H.
We finalize this note by giving an algorithm for the computation (if possible) of the decomposition of an integer matrix into the direct sum matrices in Hermite normal form.
Let
G be the adjacency matrix of an undirected simple graph
. Recall that the degree of the
i-vertex of
is
and the Laplacian matrix of
is
, where
D is the diagonal matrix with diagonal entries
.
The second part of the following result is well-known; however, for lack of a reference we sketch a proof.
Proposition 3. Let be an undirected simple graph on n vertices. Then, has t connected components if and only if the Laplacian matrix of has rank . In this case, the connected components of are completely determined by the reduced row echelon form of the Laplacian matrix of .
Proof. The first statement follows from the well-known matrix-tree theorem (see, e.g., [
9] (
Section 1) and the references therein). Let us analyze the second statement with a little more detail. First, we observe that the Laplacian matrix of a connected graph on
n vertices is an order
n symmetric matrix of rank
whose columns sum to zero. So, its reduced row echelon form is equal to
Thus, if V is the reduced row echelon of the Laplacian matrix of a (non-necessarily connected) undirected simple graph on n vertices, then if the j-th column, , of V is not a pivot column, the set of vertices of the connected component containing the vertex j is , where denotes the support of □
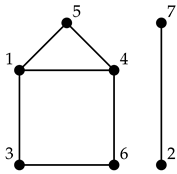
Example 6. Consider the graph with vertex-set and edges . The Laplacian matrix of is and its reduced row echelon form is Now, we can read from R that has the following two connected components: the subgraph with vertices and the subgraph with vertices .
The previos proposition is the last piece needed to ensure the correctness of Algorithm 1. We discuss below some aspects of Algorithm 1.
Comments to Algorithm 1:
Steps (1)–(6) provide unimodular matrices and Q, such that , for some permutation matrix ;
Clearly ; moreover, we have that ;
If then A is not decomposable. In this case and Q is the identity matrix. Otherwise, if A is decomposable, we cannot guarantee that and that the matrices , are in Hermite normal form. However, since , by the uniqueness of the Hermite normal form, step (7) provides the matrix such that is in Hermite normal form as desired;
By Note
Section 3, we may replace the Step (2) by
- (2)
Let B be the adjacency matrix of the graph with vertices such that if and only if .
This is advantageous for small n.
An HNF-decomposition, if it exists, is not unique. It depends on the choice of the order of the columns of the matrices and the order in which these matrices are placed.
Example 7. The matrixis in Hermite normal form and its associated graph (see Note 1) is ![Symmetry 13 01125 i002]()
Therefore, H is a decomposable matrix. Of course, we do not need to construct the graph to compute an HNF-decomposition of H.
In order to compute effectively two matrices P and Q such that is in HNF-decomposed form, we compute the reduced row echelon form, R, of the Laplacian matrix of for , Now, following Steps (5)–(7) in Algorithm 1, we may take the matrix Q equal to in this case, the corresponding matrix P is As mentioned above, other choices of Q determine a different P and, consequently, another HNF-decomposition, equivalent to the one given.
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Using the Hermite normal form as the main tool, we have obtained a theoretical criterion to determine whether a given integer matrix decomposes into a direct sum of lower order integer matrices.
This criterion allows us to associate a simple graph to the integer matrix whose connectedness determines the decomposition of the integer matrix and facilitates the formulation of an algorithm to decompose an integer matrix into a direct sum of matrices in Hermite normal form, provided such decomposition exists.
Our results have immediate applications to the study of affine semi-groups and semi-group algebras; in fact, this was our original motivation for tackling this problem. However, we believe that our results can be generalized to matrices with entries in any Euclidean ring further than .
Since we were only interested in decomposition issues, we underestimated a lot of information from B when constructing the graph . Alternatively, B can be considered as the adjacency matrix of an (undirected) weighted graph with n vertices , where the weight of the edge is . This alternative graph is sensitive to all the information recorded in the entries of B. One might wonder if this alternative graph can be used to provide information for integer matrices, beyond decomposability and reducibility.