Abstract
In the traditional satellite networks, network resources are mainly allocated among all the satellites based on the same allocation algorithm. This kind of symmetry model limits the increase of throughput. In this paper, we study an asymmetry resource allocation method in a satellite–terrestrial network and propose a Lotka–Volterra based predator–prey model to achieve optimal resource allocation among different satellites. In the proposed satellite–terrestrial network, we divide all the satellites into two groups, and we try to achieve load stability between these two satellites groups. Using the predator–prey model, one group is the prey–satellites, which can obtain service requirements from mobile users. The other group is considered as predator–satellites, which can only obtain the loads from the group of the prey–satellites. Once the satellites are divided into two groups using the Lotka–Volterra model, the resource allocation problem among these satellites in two groups would be asymmetry resource. We prove the existence of solutions to the proposed model. Numerical simulation results are given to show the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed model.
1. Introduction
With the development of Internet technology and the vigorous development of logistics and transportation, material exploration, and digital city, higher data communication requirements and more accurate location information have become the main characteristics of the next generation information age []. Relying only on a ground mobile network cannot bear the huge impact of data volume. Considering the rapid change of ground terminal facilities and satellite networking in recent years, with the rapid development of technology, satellite network has greater advantages in round-trip delay and coverage performance, which can provide a wide range of coverage area and remote communication []. Therefore, the joint construction of satellite ground deep integration networks by ground mobile communication networks with large transmission capacity is an efficient solution for this scenario, and it is an important direction for the development of 6G communication in the future. Through the increasingly perfect ground network and wide coverage area of a space-based network, the idea of a 6G ubiquitous connection and holographic link can be effectively realized [].
However, the integration of a cellular mobile network and satellite communication network is facing serious challenges. As for a ground cellular network, with the coverage of a 5G network and the improvement of mobile terminal mobility, there is a serious imbalance of resource allocations in small-scale cellular networks []. In the satellite communication network scenario, a complex deep space environment and satellite network topology will lead to a certain end-to-end communication delay. In addition, considering the regional problem of coverage density in the existing satellite network and the actual regional communication demand and the service allocation problem, there is an uneven distribution of satellite network traffic []. These factors will lead to network congestion in local areas of the satellite network, while the network resource in some areas are idle.
For the above problems, the traditional communication network routing algorithm is no longer applicable, and we need to consider reducing the number of congested links through a load balancing algorithm to achieve effective network load balancing []. In the communication network, load balancing technology is used to transfer the overloaded node services to the underloaded node when the network congestion occurs in order to realize the balanced distribution of services. The traditional load balancing routing algorithm is a reactive trigger, i.e., load balancing is carried out only when congestion occurs to save processing resources. However, in the face of current huge data communication and efficient business processing needs, it cannot provide effective services support. This paper constructs a new resource allocation model to achieve load balancing based on the predator–prey model for a 6G communication scenario, where the relationships among the satellites are asymmetry relations. The load balancing algorithm will keep working to stabilize the whole network service, which means that the proposed algorithm will be more practical in data processing efficiency and data transmission rates. The main contributions are as follows:
- We divide the satellites in a 6G communication scenario into two groups, and we formulate the relations between these two group satellites as a predator–prey model.
- We use the Lotka–Volterra-based predator–prey model to analyze the problem among these two groups, which is an asymmetry resource allocation problem.
- We prove the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed model.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 discusses the related works on load balancing in a satellite network. Section 3 introduces the system model and problem formulation. Section 4 provides the analysis for the proposed predator–prey model for load balancing. Numerical simulations are given in Section 5. Finally, the conclusion is provided in Section 6.
2. Related Works
The existing research on load balancing in the communication network mainly involves two aspects: terrestrial cellular network and satellite communication network. In the terrestrial cellular network, considering the inter-cell interference problem, the authors proposed a mobile load balancing algorithm compatible with ICIC method in reference [], and the spectrum utilization is significantly improved. Considering the quality of service and resource consumption, the authors proposed a distributed algorithm in reference [], which considers the neighborhood unit and non-neighborhood unit to achieve optimization. In reference [], based on the traditional MLB (mobility load balancing), the authors proposed a load allocation strategy and a target selection strategy, which realized the matching by judging the priority level, and handed over the users of the overloaded cells to the adjacent service cells. In reference [], the authors proposed a mobile load balancing algorithm based on utility and the concept of load balancing efficiency factor, which improves the sorting efficiency and load balancing efficiency of overload cells in MLB algorithm. For the failure of load balancing algorithm caused by the large difference of traffic distribution in cells, the authors proposed a multi-service load balancing algorithm in reference [], which is proven to be an effective dynamic switch algorithm for load balancing. In reference [], in the research of an adaptive algorithm for mobile load balancing in a cellular network, based on the network load, the overload cells are determined by an adaptive threshold to achieve load balancing. Based on the limitations in reference [], the authors proposed a load balancing strategy in a heterogeneous network based on clusters in reference [], which realized the load balancing optimization within the cluster and effectively improved the load balancing efficiency and throughput. In our opinion, most of the above algorithms only start the load balancing algorithm when congestion occurs, which is a static process and is not timely enough to solve the load unbalancing problem.
Considering the satellite network in reference [], the authors proposed a dynamic adaptive strategy, which considered data transmission delay and link weight to achieve dynamic routing selection and load balancing. In reference [], the authors proposed an adaptive load balancing algorithm based on the response requirements of burst hot traffic, which achieves load balancing by updating network load periodically based on congestion matrix. In reference [], the concept of on-demand routing based on satellite topology was introduced for the first time, and a location-based on-demand routing protocol was proposed to realize load balancing. In reference [], the authors proposed a distributed routing scheme, which combined the communication cost of inter satellite link and the delay of information transmission queue to realize the dynamic update of routing and effectively reduce the end-to-end delay and packet loss rate. Based on this scheme, the authors considered multiple factors to optimize the agent-based routing strategy in reference [], which is based on the on-demand allocation and priority policy of the implementation of QoS routing. In reference [], the authors proposed a distributed load balancing strategy based on the concept of virtual node routing, which realizes dynamic mapping through logical address. In reference [], the authors considered the congestion problem caused by local deviation in LEO satellite network, and proposed the resource allocation between neighboring satellites, that is, to realize the flow of redundant bandwidth resources and realize the balance of traffic resources in the domain. In reference [], the authors proposed that nodes in satellite networks store congestion information of global nodes, to realize task allocation among nodes, and to reduce the task load of high load nodes. Based on the above considerations, in reference [], the authors considered the link congestion problem caused by satellite density and proposed an explicit load balancing algorithm, that is, adjacent satellites display and exchange their congestion states to avoid congestion and improve the data transmission rate and throughput. In reference [], the authors proposed a load routing aware protocol, which can better achieve low latency load balancing by limiting the state synchronization range, reducing the discovery path time and controlling the overhead. In reference [], the authors proposed a load balancing algorithm based on the idea of intelligent optimization algorithm and linear programming and found the optimal solution through dynamic alternation of two algorithms. In reference [], the authors considered the satellite network in a polar orbit scenario and proposed that a mobile agent combined with a fixed agent to collect routing information and data transmission cost to dynamically update routing terms in the case of queuing delay and transmission delay can achieve efficient complex equalization. In reference [], the authors proposed an adaptive distributed load balancing mechanism based on historical information, which made routing selection by jointly analyzing the current and historical status of inter satellite links. In reference [], the authors proposed a hybrid load balancing algorithm for cascading congestion. Based on the existing dis-tributed mechanism and prior geographic information, a long-distance traffic bypass strategy was designed in which a long-distance traffic bypass mechanism was designed to achieve more efficient traffic load balancing. In reference [], the authors considered the congestion state of local nodes and relay nodes and updated the routing items by combining offline calculation and online dynamic adjustment strategy, as to provide load balancing efficiency.
However, most of the existing studies in satellite communication only consider load balancing based on the on-board routing strategy, which does not consider the power allocation of the satellite–terrestrial transceivers [,,] and cannot satisfy the development trends and business requirements of 6G mobile communication. Furthermore, by considering the ground communication and on-board communication to build a load balancing model, how to realize efficient data flow and business processing is still a problem that needs to be solved. In this paper, we use the Lotka–Volterra based predator–prey model to analyze the load balancing problem among these satellites in two groups, which is a dynamic control process to realize efficient data flow and business processing.
3. System Model
In this section, we mainly discuss the asymmetry resource allocation problem in satellite–terrestrial network for 6G mobile communication. In the traditional satellite–terrestrial network, the network resources are mainly allocated among all the satellites based on the symmetry model, where the resources are allocated by the same optimal allocation model to achieve matching. This kind of symmetry model limits the increase of throughput. The researched satellite–terrestrial network is composed of multiple satellites and multiple mobile users, as shown in Figure 1. The mobile users can request and obtain the 6G mobile communication services from the satellites. The satellites can provide 6G mobile communication services to mobile users. With the development of the satellite–terrestrial network, increased satellites are utilized to provide access services to mobile users. As the communication and computation capacities of different satellites are different, they would have different services loads from the mobile users. Then, how to balance the services loads among the satellites is the key problem to be solved in this paper.
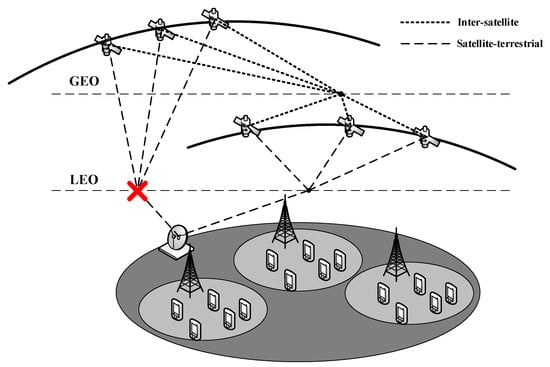
Figure 1.
System mode.
In order to describe the load balancing problem of the proposed satellite network, we model the relationships between the satellites using the predator–prey model. Under the predator–prey model, we assume the satellites can be divided into two groups. The first group is the set of satellites with higher communication and computation capacities. This kind of satellite is always geosynchronous, with high orbits, and the transmission latency would also be high. Then, we assume that this kind of satellite cannot directly provide access services to mobile users due to high transmission latency. The second group is the set of satellites with limited communication and computation capacities. They are always the low-earth orbit satellites, and they can provide access services to mobile users with lower transmission latency. However, with limited communication and computation abilities, they should offload the service requirements of the mobile users to the satellites with higher communication and computation capacities because they cannot satisfy the increasing requirements of the mobile users, due to their limited capacities. Based on the above assumptions, the second satellites group should offload the services loads to the first satellites group. We will try to balance the services loads between these two kinds of satellite group.
We use the predator–prey model to model the load balancing problem among different satellites. The satellite nodes with limited capacities are the prey–satellites denoted by , and the satellite nodes with higher capacities are considered as the predator–satellites denoted by . Assuming that, only the prey–satellites can directly serve the mobile users. The predator–satellites can only obtain the services loads offloaded from the prey–satellites . At time , assuming the services loads in the prey–satellites is . If the services load in the prey–satellites are not offloaded to the predator–satellites , the dynamic variation of the services loads in the prey–satellites can be described as follows [],
where is the variation rate of the services loads in the prey–satellites . is the action of the prey–satellites to attract the mobile users to access to the satellite network, and is the related weighted parameter to denote the conversion percent of the action.
At time , assuming the services loads in the predator–satellites is . If the services loads in the prey–satellites are not offloaded to the predator–satellites , the dynamic variation of services loads in the predator–satellites can be described as follows [],
where is the variation rate of the services loads in the predator–satellites . is the action of the predator–satellites to attract the mobile users to access to the satellite network, and is the related weighted parameter to denote the conversion percent of the action.
Assuming the computation abilities of the predator–satellites, is lower than the services loads offloading rate of the prey–satellites , and then the services loads in the predator–satellites is increased with the offloading process of the services loads from the prey–satellites , and the services loads in the prey–satellites is decreased with the offloading process of the services loads to the predator–satellites . Then, we have the following functions to denote the dynamic variation of services loads in the prey–satellites and the predator–satellites based on the Volterra model, respectively,
where is the proportion of services loads offloaded from the prey–satellites to the predator–satellites , and is the growth rate of services loads due to the offloading process from the prey–satellites to the predator–satellites .
As increased satellites are utilized to compose a hyper dense satellite network, the density of the satellite nodes in each satellite group is the influence factor need to be considered. Then the dynamic variation of the services loads in the prey–satellites and the predator–satellites should consider the effect within the satellite groups, and the dynamic variation of services loads in the prey–satellites and the predator–satellites can be re-formulated based on Lotka–Volterra model as follows,
where and are the influence factors within the satellite group. In the satellite networks, due to the impact of the communication environments, the loads in each satellite group will be inevitably interfered by external stochastic factors, such as cosmic radiation, solar spot, rain attenuation, etc. Then, the stochastic disturbances need to be added to the dynamic variation of the services loads in the prey–satellites and the predator–satellites as follows,
4. Analysis and Algorithms
In this section, let us consider the solution of the proposed model and also prove the existence and uniqueness of this solution.
Definition 1 (Asymmetry Model).
The relationships between the prey–satellites and the predator–satellites are asymmetry relations, where the predator-satellites can offload the services from the prey–satellites, and the prey–satellites cannot obtain the load from the predator–satellites.
Under the predator–prey model, the mobile satellites can be divided two groups. The first group is the set of satellites denoted by predator–satellites. We assume that this kind of satellite cannot directly provide the access services to the mobile users. The second group is the set of satellites noted by prey–satellites. They can provide the access services to the mobile users with lower transmission latency. The predator–satellites can obtain the services from the prey–satellites, where the prey–satellites cannot obtain the services from the predator–satellites.
Theorem 1 (Existing and Unique).
For any initial value, the solution of model (8) exists and is unique.
Proof.
According to the theory of stochastic differential equations, when the coefficients of Model (7) and (8) satisfy the local Lipschitz condition and the linear growth condition, the solutions of Model (7) and (8) satisfying the initial value condition are global existence and uniqueness. The coefficients of Model (7) and (8) satisfy the local Lipschitz condition, but do not satisfy the linear growth condition. Therefore, the solutions of Model (7) and (8) tend to be infinity in a finite time.
Since the coefficients of Model (7) and (8) satisfy the local Lipschitz condition, Model (7) and (8) would have unique local solutions in the time interval for the given initial conditions , where is the explosion time. We only need to prove that the solutions of Model (7) and (8) are global when . Note that in the form of Model (7) and (8), we can find the explicit solution in the interval solution as follows,
where and . In order to prove the boundedness, we construct the following comparison equation,
where the initial conditions are and . Similarly, we can obtain the explicit solution of Model (11) as follows,
□
From the comparison theorem of stochastic differential equation, we can know and . Because Model (11) is a constant function or a bounded function, and do not tend to infinity in finite time. Furthermore, and do not tend to infinity in finite time, .
5. Numerical Simulations
In this section, to verify the effectiveness of the load balancing model proposed in this paper, we use MATLAB to perform numerical simulations on the model. The hardware environment is Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-8550U CPU @ 1.80 GHz with 16.0 GB ram. The number of satellites in the simulation is two, which includes one prey–satellite and one predator satellite. The other simulation parameter settings are set in Table 1 as follows,

Table 1.
Parameters for simulations.
The load states of a prey–satellite and predator–satellite without external stochastic factors are shown in Figure 2. Figure 2 shows a comparison between the prey–satellite and predator–satellite. The load state of the prey–satellite decreases quickly at the beginning of the load balancing process due to the load balancing action between the prey–satellite and the predator–satellite. The load state of the predator–satellite increases at the beginning of the load balancing process because the load of the prey–satellite is offloaded to the predator–satellite. With the increase of time, the load state of the prey–satellite tends to be stable. The load state of the predator–satellite decreases due to the decrease of the load in the prey–satellite. It can be seen that, for both the prey-satellite and predator–satellite, the models both changed rapidly based on the proposed predator–prey model from the initial moment and reached a stable state in the observation time duration.
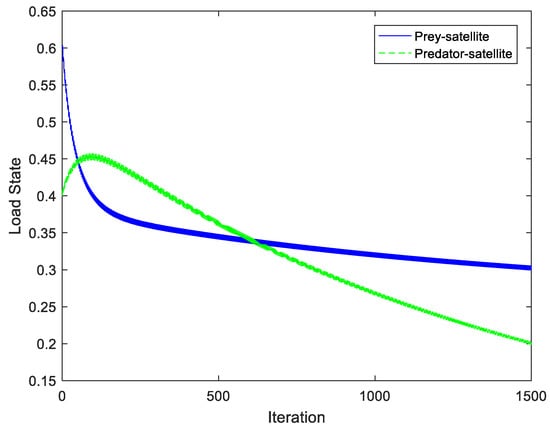
Figure 2.
Load state without external stochastic factors.
The load state with external stochastic factors for prey–satellites and predator satellites are given in Figure 3. Under the stochastic model, for both pre-satellite and predator–satellite, the models both reach a stable state in the observation time duration, which means that the proposed model can also achieve the same behaviors under the stochastic mode compared to the static mode in Figure 2. Under the external stochastic factors, the communication environments for mobile users would be different. Compared to the load state without external stochastic factors, the variation of load state with external stochastic factors are completely different. The load of the prey–satellite increases to a high value at the beginning of the time duration, then decreases to a convergence value due to the load balancing process. The load of the predator–satellite also increases at the beginning of the time duration, due to the high value of the prey–satellite. It would also converge to a stable value. In Figure 2 and Figure 3, it is assumed there are no actions of the satellites to attract mobile users to access to the satellite network.
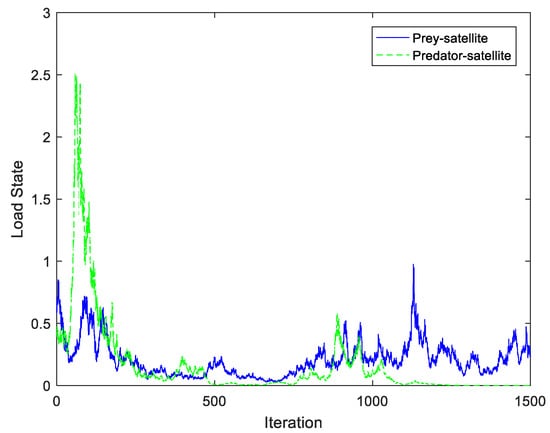
Figure 3.
Load state with external stochastic factors.
The load state of different satellites under stochastic control actions are given in Figure 4. Under the stochastic control actions, the prey–satellite and the predator–satellite decrease their load, and the load would converge to a stable value more quickly than the load without stochastic control actions. It can be concluded that both the prey–satellite and the predator–satellite can achieve sustainability under the stochastic control actions.
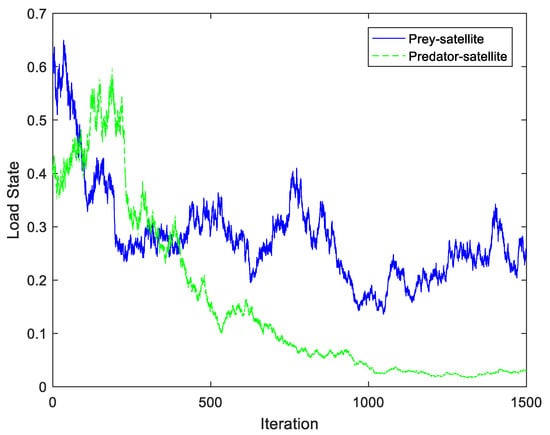
Figure 4.
Load state with stochastic control action u1 and .
6. Conclusions
This paper proposes a predator–prey-based resource allocation model in satellite–terrestrial networks, where the satellites are divided into two groups. One kind of satellite is the prey–satellite, which can obtain mobile services from users and can offload the mobile services to the other kind. The other kind of satellite is the predator–satellite. They can obtain mobile services from the prey–satellites and serve mobile users. Based on the simulations, we find that our model can achieve load balancing between prey–satellites and the predator satellites. We note that all the simulations of the paper are the numerical results under the associated parameter settings. Hence, we did not carry out the comparison with other results. In future works, we will design a simulator or a platform written in Java to evaluate our proposed schemes.
Author Contributions
Methodology, M.L.; software, Q.W.; formal analysis, Z.L.; investigation, Z.L.; resources, M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, X.; Wang, G.; Qi, B. The research content and progress of digital information resource intelligent service in the 5G era. Inf. Theory Pract. 2020, 43, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Cheng, N.; Zhou, H.; Lu, F.; Quan, W.; Shi, W.; Wu, H.; Zhou, C. Air-space-ground integration network technology: Exploration and prospect. J. Internet Things 2020, 4, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Jin, J.; Wang, Q.; Dong, J.; Lou, M.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Y. 6G vision and requirements: Digital twins, intelligent ubiquitous. Mob. Commun. 2020, 44, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama, H.; Kudoh, D.; Kato, N.; Kadowaki, N. Load Balancing and QoS Provisioning Based on Congestion Prediction for GEO/LEO Hybrid Satellite Networks. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, H.; Tada, Y.; Kato, N.; Yoshimura, N.; Toyoshima, M.; Kadowaki, N. Toward opti-mized traffic distribution for efficient network capacity utilization in two-layered satellite net-works. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y. Distributed load balancing mechanism for detouring schemes of geographic routing in wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Parallel Emerg. Distrib. Syst. 2013, 28, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, N.O.; Koca, M. Joint mobility load balancing and inter-cell interference coordination for self-organizing OFDMA networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 81st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Glasgow, UK, 11–14 May 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, N.; Mitschele-Thiel, A. Self-organized neighborhood mobility load balancing for LTE networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IFIP Wireless Days (WD), Valencia, Spain, 13–15 November 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.-R. Mobility load balancing method for self-organizing wireless networks inspired by synchronization and matching with preferences. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 67, 2594–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addali, K.M.; Melhem, S.Y.B.; Khamayseh, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kadoch, M. Dynamic mobility load balancing for 5G small-cell networks based on utility functions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 126998–127011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Shen, Q.; Wu, J.; Gan, X. A threshold-based multi-traffic load balance mechanism in LTE-A networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–12 March 2015; pp. 1273–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.; Kwon, S.; Na, J.-H. Adaptive mobility load balancing algorithm for LTE small-cell networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 2205–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Kwon, S. Cluster-Based Load Balancing Algorithm for Ultra-Dense Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 2153–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gu, X. Adaptive ATM routing in Walker delta satellite communication networks. In Proceedings of the 2006 1st International Symposium on Systems and Control in Aerospace and Astronautics, Harbin, China, 19–21 January 2006; pp. 6–373. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Pelagatti, S. CRT: An Adaptive Routing Protocol for LEO Satellite Networks. In Proceedings of the 2006 2nd International Conference on Information & Communication Technologies, Damascus, Syria, 24–28 April 2006; pp. 2496–2501. [Google Scholar]
- Papapetrou, E.; Karapantazis, S.; Pavlidou, F.-N. Distributed on-demand routing for LEO satellite systems. Comput. Netw. 2007, 51, 4356–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, Y.; Wang, R.-C. Agent-based load balancing routing for LEO satellite networks. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 3187–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, C.-A.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Fu, L.-Y.; Shao, X.; Wang, R.-C. Agent-based multi-service routing for polar-orbit LEO broadband satellite networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2014, 13, 575–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, E.; Akyildiz, I.; Bender, M. A distributed routing algorithm for datagram traffic in LEO satellite networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2001, 9, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Bae, Y.-H.; Kim, Y.; Park, C.H. Traffic load balancing in low Earth orbit satellite networks. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (Cat. No.98EX226), Lafayette, LA, USA, 15–15 October 1998; pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Franck, L.; Maral, G. Static and adaptive routing in ISL networks from a constellation perspective. Int. J. Satell. Commun. 2002, 20, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, T.; Mashimo, D.; Jamalipour, A.; Hashimoto, K.; Nemoto, Y.; Kato, N. SAT04-3: ELB: An Explicit Load Balancing Routing Protocol for Multi-Hop NGEO Satellite Constellations; IEEE Globecom: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, Q.; Li, H. A load-balanced on-demand routing for LEO satellite networks. J. Networks 2014, 9, 3305–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.H.; Wang, T.; Li, H. Research on load balancing method of LEO satellite network routing. Comput. Eng. 2011, 37, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Rao, Y.; Fu, L.; Chen, W.; Shao, X. Load balancing routing based on agent for polar-orbit LEO satellite networks. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2012, 9, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X. Adaptive distributed load balancing routing mechanism for LEO satellite IP networks. J. Netw. 2014, 9, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Wei, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, Z. Hybrid-Traffic-Detour based load balancing for onboard routing in LEO satellite networks. China Commun. 2018, 15, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, F. Load balancing strategy and its lookup-table enhancement in deterministic space delay/disruption tolerant networks. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panic, S.; Stefanovic, M.; Anastasov, J.; Spalevic, P. Fading and Interference Mitigation in Wireless Communications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Trakadas, P.; Sarakis, L.; Giannopoulos, A.; Spantideas, S.; Capsalis, N.; Gkonis, P.; Karkazis, P.; Rigazzi, G.; Antonopoulos, A.; Cambeiro, M.A.; et al. A cost-efficient 5G non-public network architectural approach: Key concepts and enablers, building blocks and potential use cases. Sensors 2021, 21, 5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannopoulos, A.; Spantideas, S.; Kapsalis, N.; Karkazis, P.; Trakadas, P. Deep reinforcement learning for energy-efficient multi-channel transmissions in 5G cognitive hetnets: Centralized, decentralized and transfer learning based solutions. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 129358–129374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellemans, T.; Bodas, T.; Van Houdt, B. Performance analysis of workload dependent load balancing policies. Proc. ACM Meas. Anal. Comput. Syst. 2019, 3, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).