AMT Starting Control as a Soft Starter for Belt Conveyors Using a Data-Driven Method
Abstract
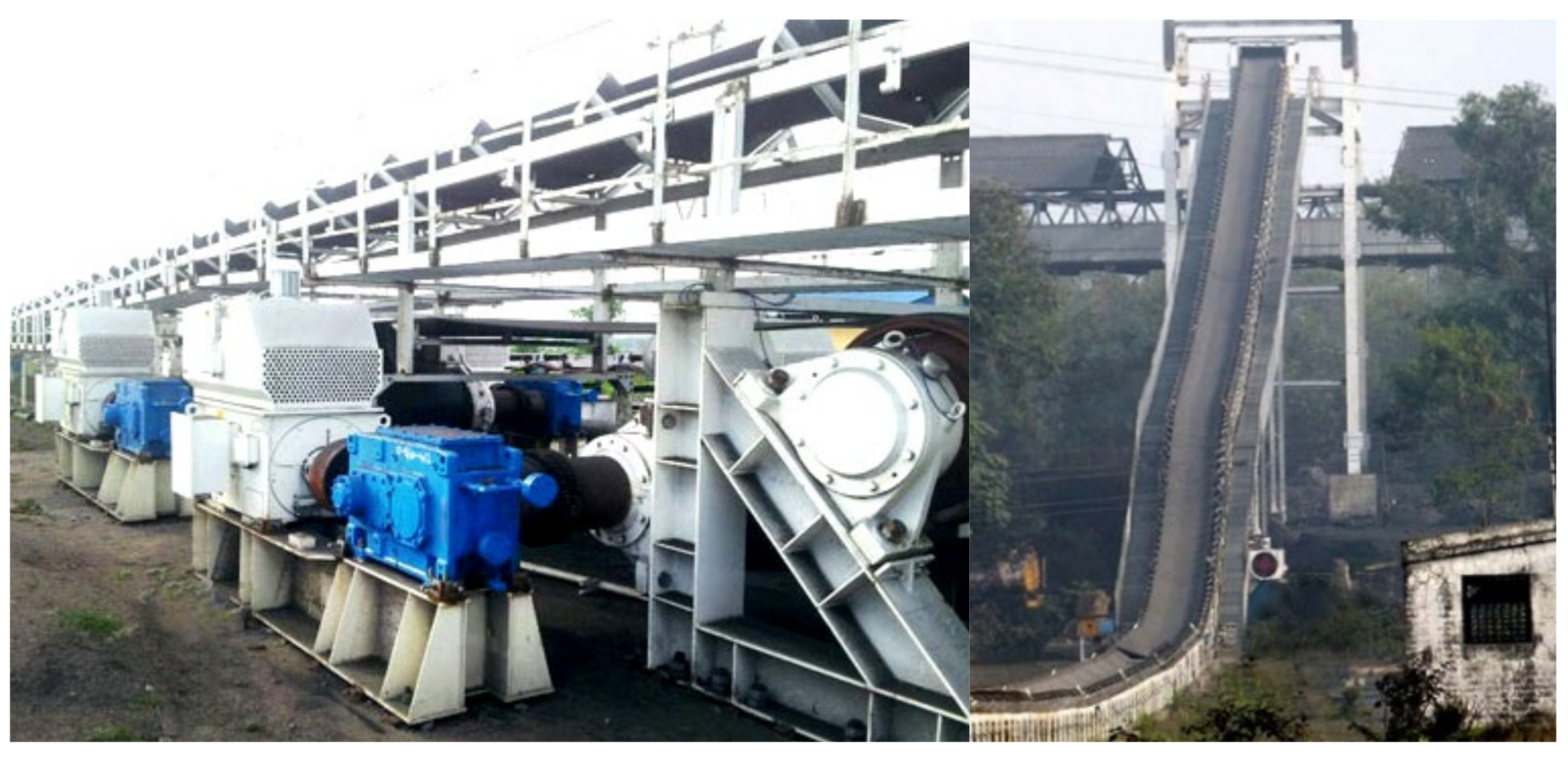
:1. Introduction
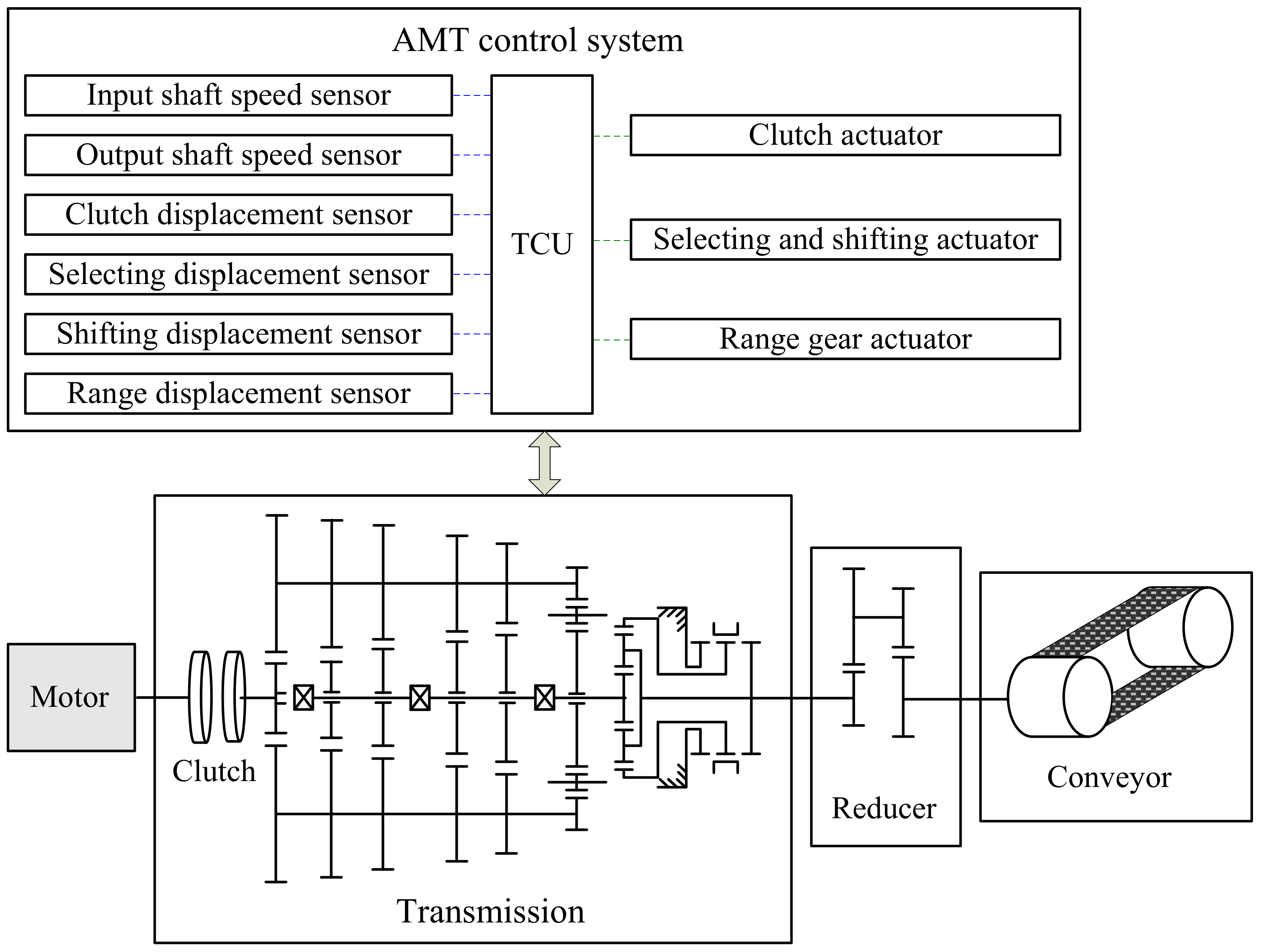
2. Starting Acceleration Curve Based on AMT
3. AMT Dynamics Analysis
3.1. Clutch Torque Transmissibility
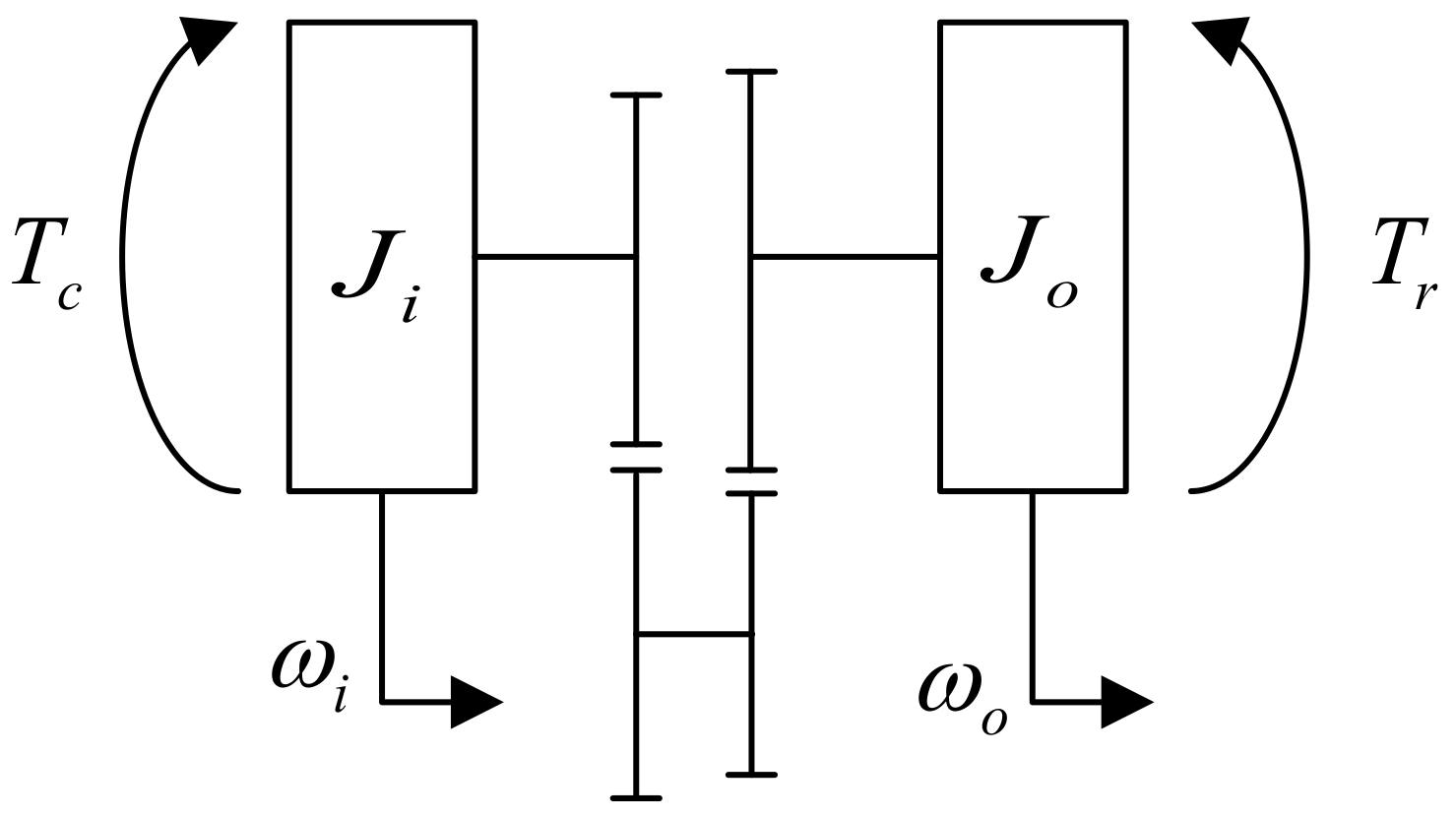
3.2. Transmission Dynamic Model
3.3. Angular Acceleration Curve of the AMT Output Shaft
4. Acceleration Control Method
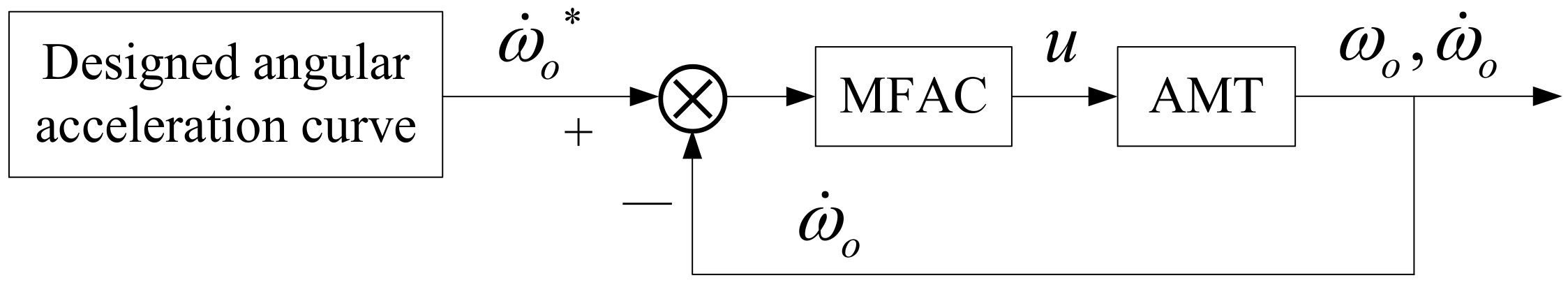
4.1. Prototype MFAC Method
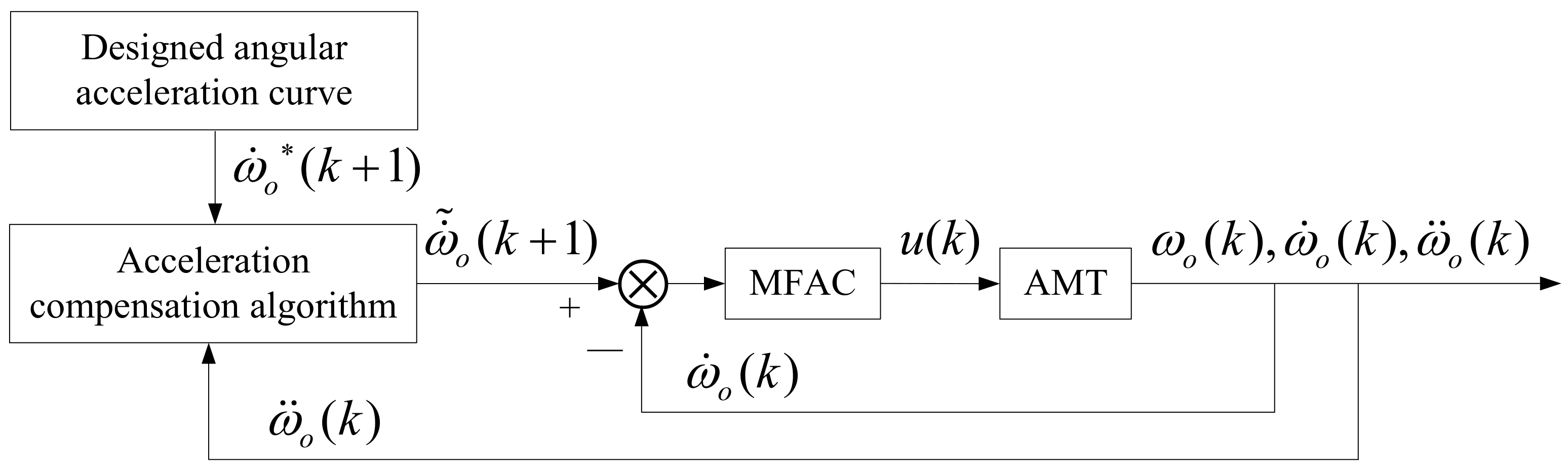
4.2. MFAC Method with Jerk Compensation
5. Simulation and Analysis
5.1. Driveline Parameters
5.2. Parameters of the Three Control Methods
5.2.1. Parameters of the Prototype MFAC Method and the Modified MFAC Method with Jerk Compensation
5.2.2. Parameters of the PID Control Method
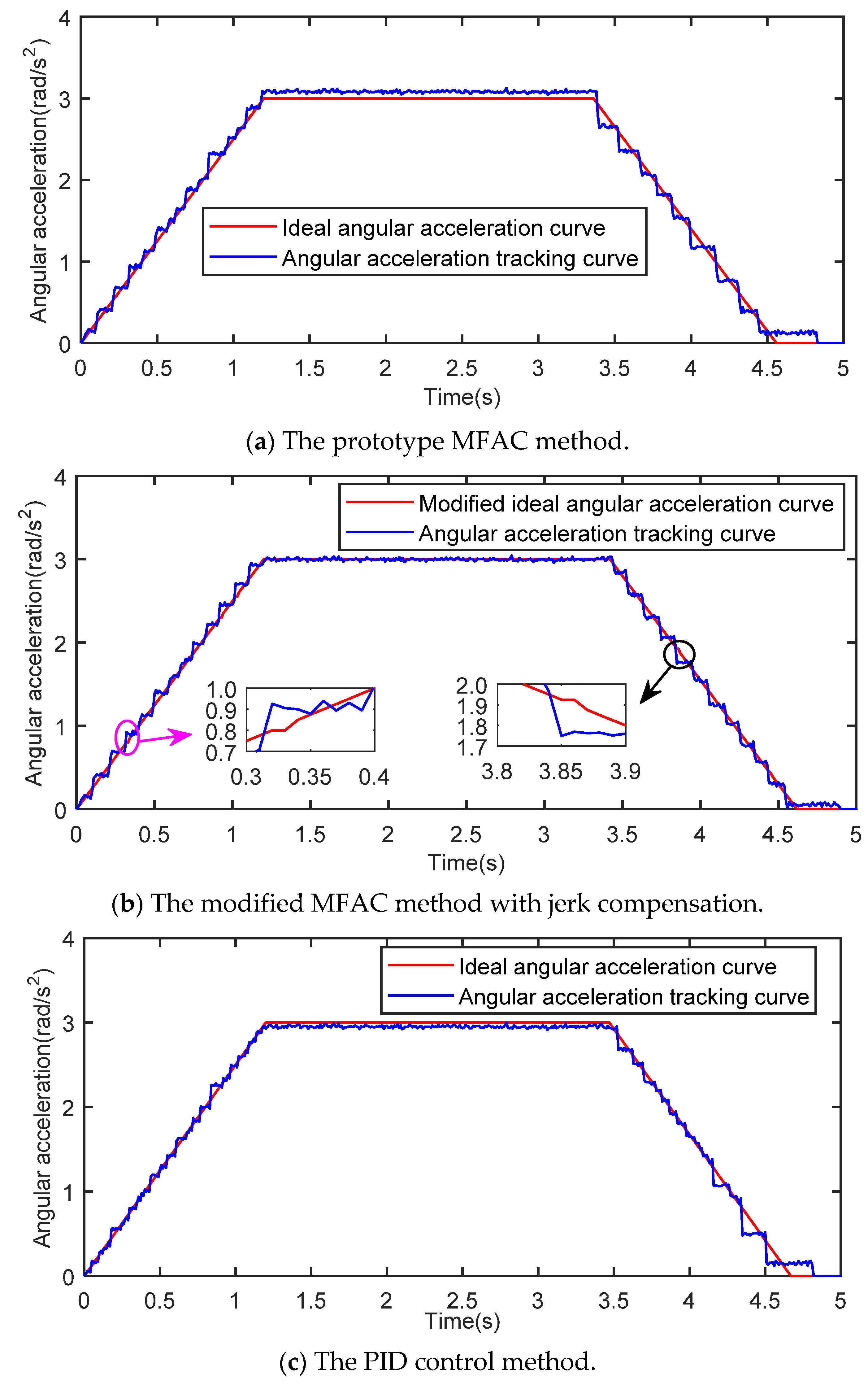
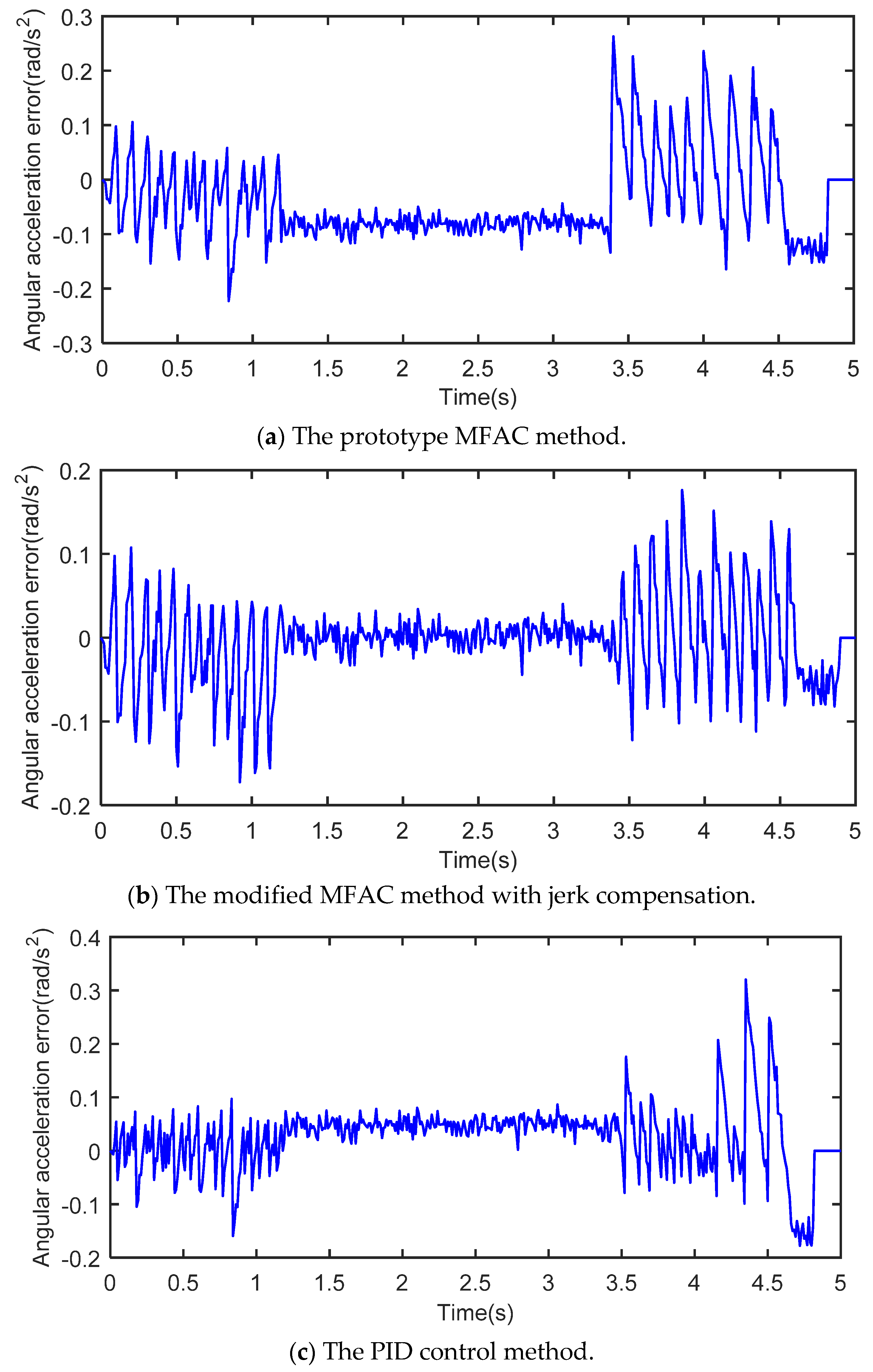
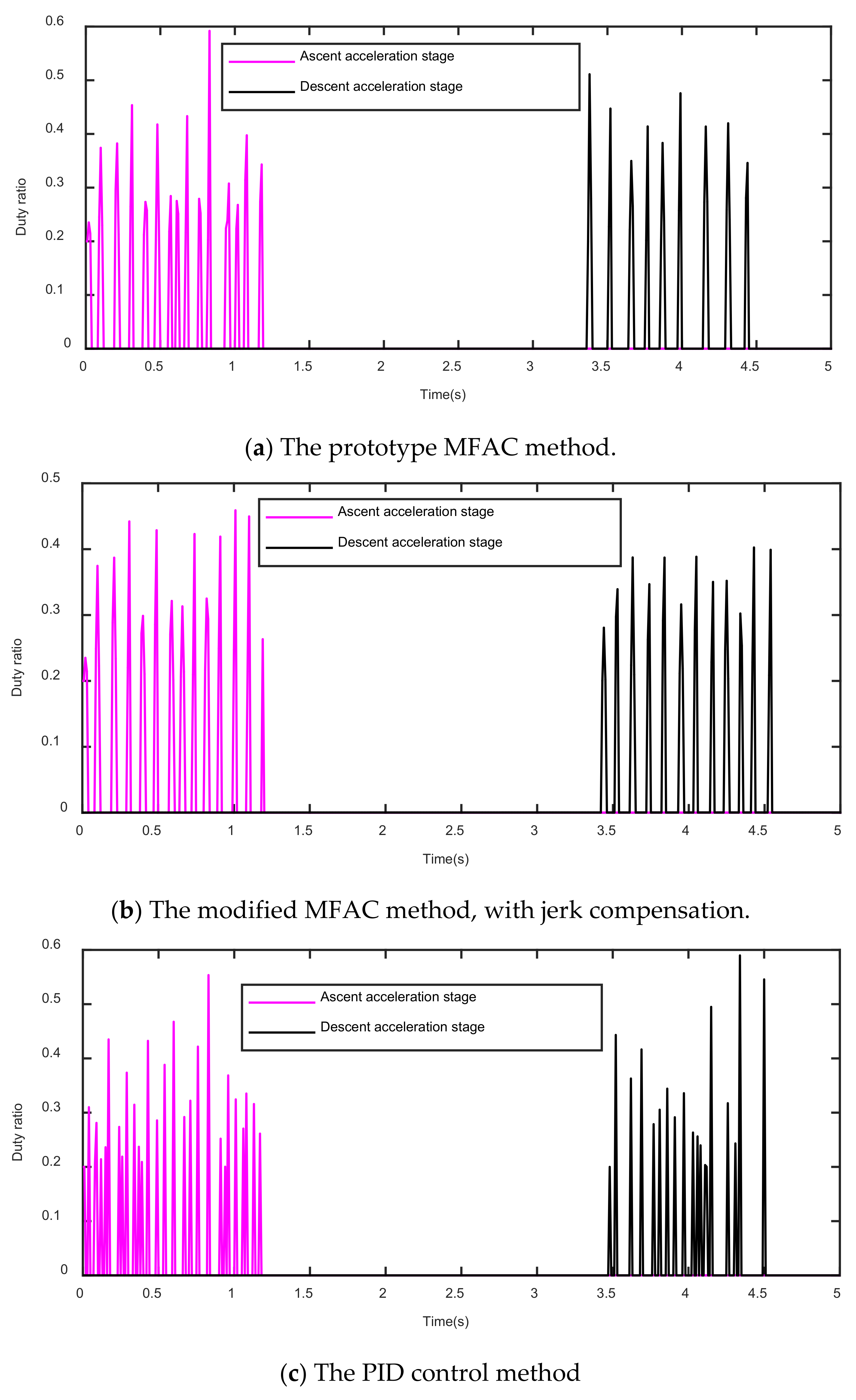
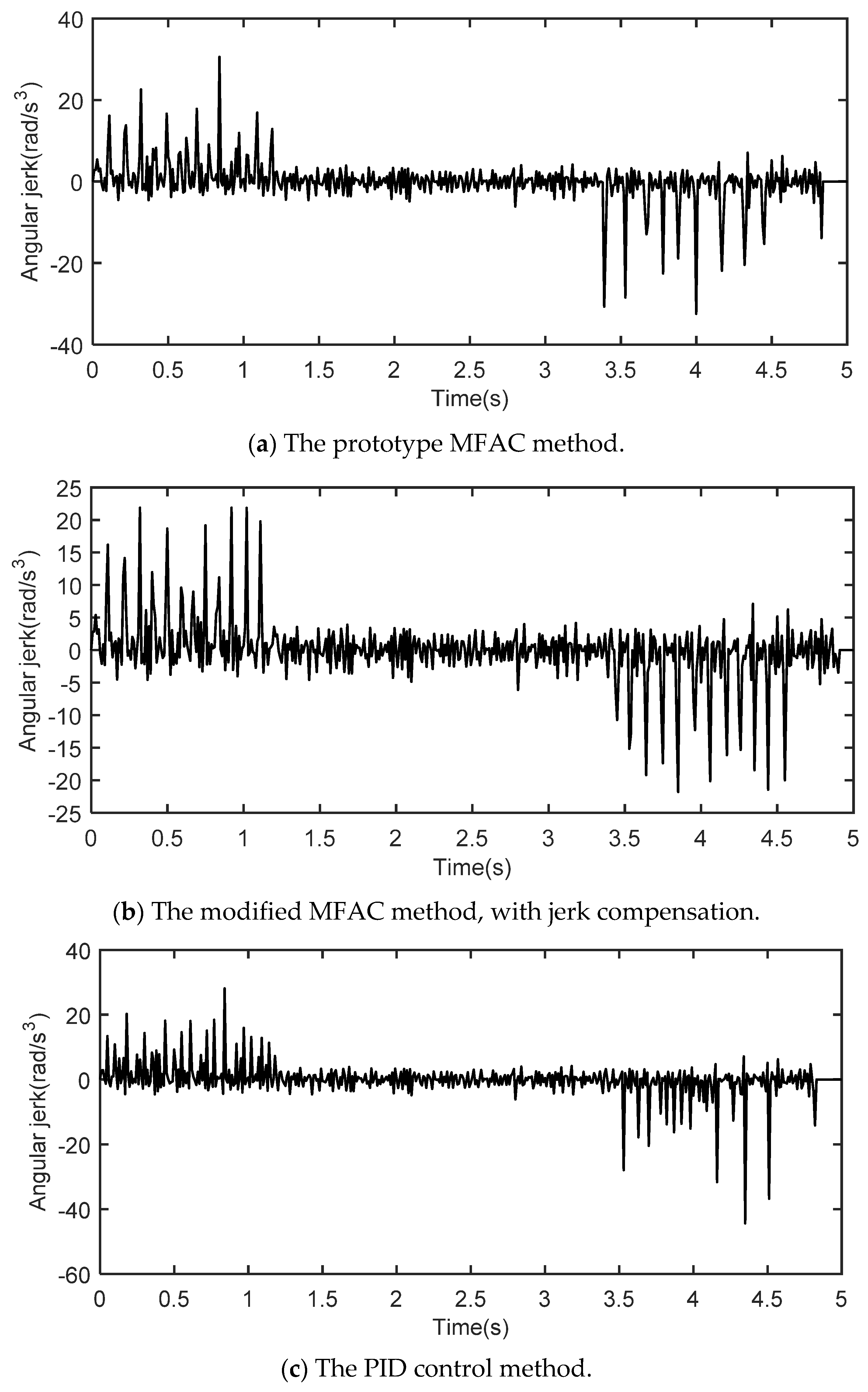
5.3. Simulation Results
5.4. Data Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, D.; Liu, X.; Zhong, B. Sustainable belt conveyor operation by active speed control. Measurement 2020, 154, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Pang, Y.; Lodewijks, G. Green operations of belt conveyors by means of speed control. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovanevskiy, V.A. Kondratiev, Elastic properties of steel-cord rubber conveyor belt. Exp. Tech. 2021, 45, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.I.; Wheeler, C.A.; Munzenberger, P.J.; Ausling, D.G. The influence of viscoelastic property measurements on the predicted rolling resistance of belt conveyors. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordell, L.K.; Ciozda, Z.P. Transient belt stresses during starting and stopping: Elastic response simulated by finite element methods. Bulk Solids Handl. 1984, 4, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Dynamics simulation of the belt conveyor possessing feedback loop during starting. J. Coal Sci. Eng. 2005, 11, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Zhu, C. Longitudinal tear detection of conveyor belt under uneven light based on Haar-AdaBoost and Cascade algorithm. Measurement 2021, 168, 108341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.Y.T.; Pang, Y. Infrared spectrum analysis method for detection and early warning of longitudinal tear of mine. Measurement 2020, 165, 107856. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Miao, C.; Li, X. Cosine-trapezoidal soft-starting control strategy for a belt conveyor. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8164247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayesh, M.H. Nonlinear transversal vibration and stability of an axially moving viscoelastic string supported by a partial viscoelastic guide. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 314, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, D.S. A tricky problem: Selection of drive systems for long-distance conveyor systems. Bulk Solids Handl. 2013, 33, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Hou, Y. Effect of oil film squeezing on hydro-viscous drive speed regulating start. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 2134–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.; Wei, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Oil-film clutch in soft-start of belt conveyor. J. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2002, 11, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Agarwal, R.K. Dynamic transmission of oil film in soft-start process of HVD considering surface roughness. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2018, 70, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, Q.; Lian, Z.; Li, L. Theoretical model and experimental research on friction and torque characteristics of hydro-viscous drive in mixed friction stage. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 32, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Pi, D. Two-layer structure control of an automatic mechanical transmission clutch during hill start for heavy-duty vehicles. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 49617–49628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Lu, X.; Chen, H. Dynamics and control of gear upshift in automated manual transmissions. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2013, 63, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, T.; Ebbesen, S.; Guzzella, L. Topology optimization for hybrid electric vehicles with automated transmissions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 61, 2442–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cong, X. Constant acceleration control for AMT’s application in belt conveyor’s soft starting. Int. J. Control Autom. 2013, 6, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yan, P. Study on load parameters estimation during AMT startup. J. Control Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 7391968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Gu, J.; He, L. Estimation of torques transited by twin-clutch during shifting process for dry dual clutch transmission. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 53, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasca, F.; Iannelli, L.; Senatore, A.; Reale, G. Torque transmissibility assessment for automotive dry-clutch engagement. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H. Optimal robust control of shifting process for hybrid electric car with dry dual clutch transmission. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 52, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Si, T.; Sun, L.; Liu, B.; Li, Z. Linear active disturbance rejection control for three-phase voltage-source PWM rectifier. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 45050–45060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakshin, P.V.; Koposov, A.S.; Emelianova, J.P. Iterative learning control of a multiagent system under random perturbations. Autom. Remote Control 2020, 81, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hou, Z.; Tian, T.; Deng, Z.; Li, Z. A novel dual successive projection-based model-free adaptive control method and application to an autonomous car. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3444–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Xiong, S. On model-free adaptive control and its stability analysis. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2019, 64, 4555–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hou, Z. Data-driven MFAC for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems with RBFNN. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2014, 25, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Wang, Z. From model-based control to data-driven control: Survey, classification and perspective. Inf. Sci. 2013, 235, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, H. Data-driven multiagent systems consensus tracking using model free adaptive control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Hou, Z. Data-driven urban traffic model-free adaptive iterative learning control with traffic data dropout compensation. IET Control Theory Appl. 2021, 15, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yan, F.; Liang, J.; Duan, Y. Detailed Modeling and experimental assessments of automotive dry clutch engagement. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59100–59113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; Qi, X.; Li, X.; Cao, D.; Zhu, Z. Automatic clutch control based on estimation of resistance torque for AMT. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2016, 21, 2682–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myklebust, A.; Eriksson, L. Modeling, observability, and estimation of thermal effects and aging on transmitted torque in a heavy duty truck with a dry clutch. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 20, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Qin, D.; Ye, X. Optimal control about AMT heavy-duty truck starting clutch. Zhongguo Gonglu Xuebao/China J. Highw. Transp. 2010, 23, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
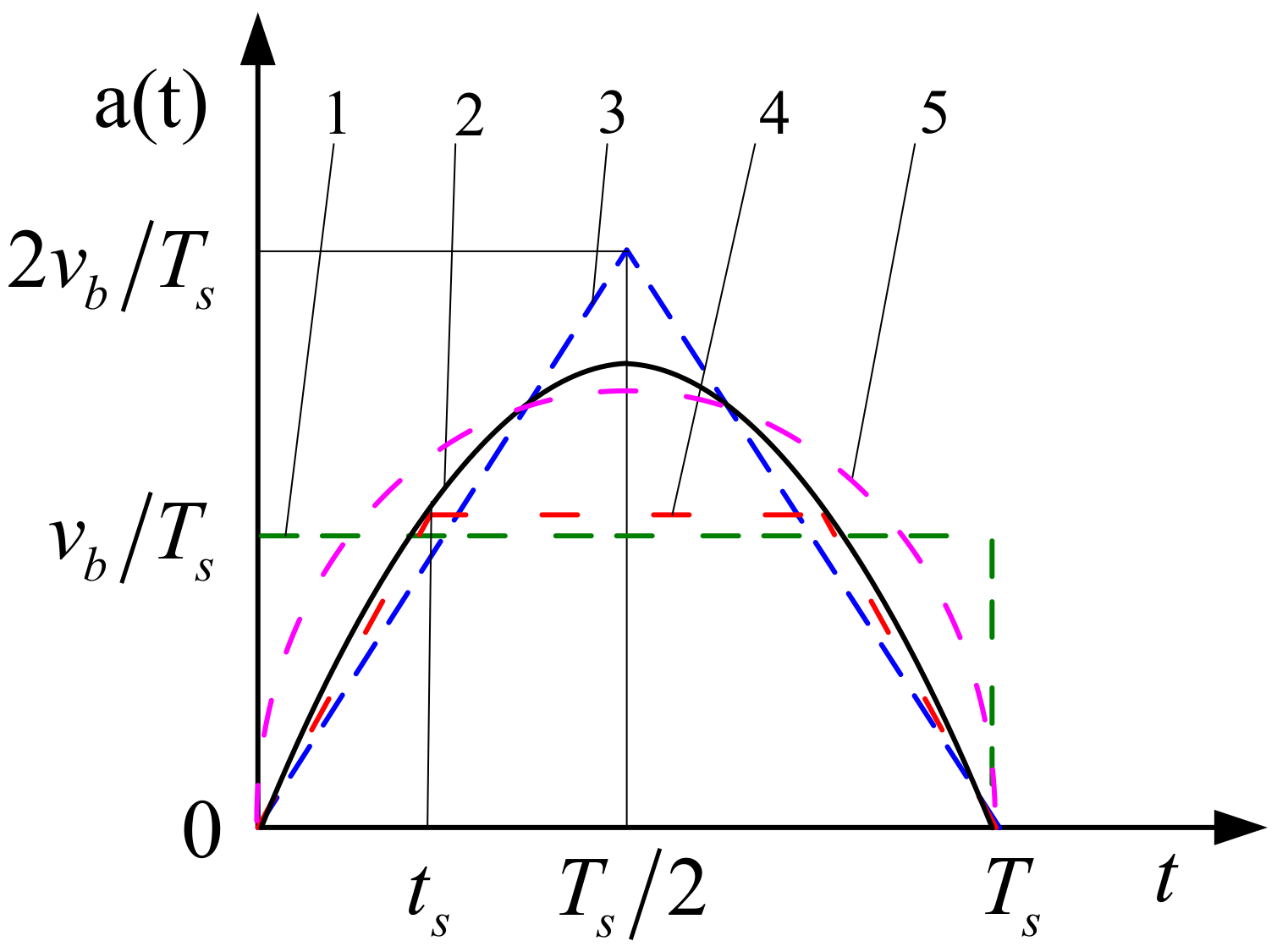
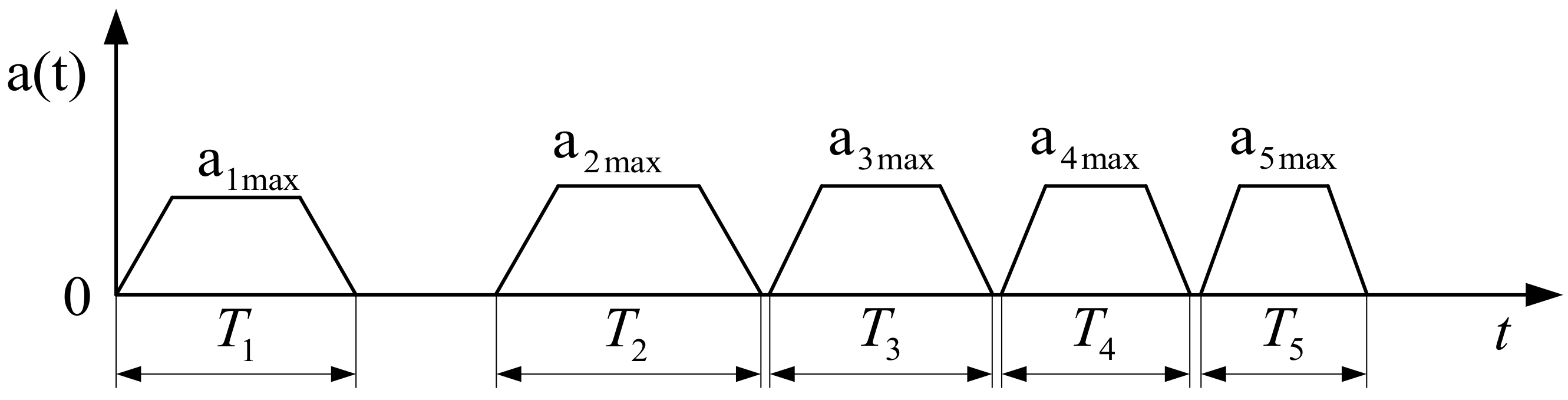

| Type | Time | Velocity | Acceleration | Jerk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant acceleration | 0 | 0 | vb/Ts | ∞ |
| Ts | vb | vb/Ts | −∞ | |
| Sine acceleration | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ts/2 | vb/2 | 0 | ||
| Ts | vb | 0 | ||
| Triangular acceleration | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ts/2 | vb/2 | |||
| Ts | vb | 0 | ||
| Trapezoidal acceleration | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | ||||
| Ts | vb | 0 | ||
| Parabola acceleration | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ts/2 | vb/2 | 0 | ||
| Ts | vb | 0 |
| Characteristic Parameter | Stage | Modified MFAC Method with Jerk Compensation | Prototype MFAC | PID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absolute maximum of the AMT output shaft’s angular acceleration error (rad/s2) | Ascent stage | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.22 |
| Descent stage | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.32 | |
| Absolute maximum of the AMT output shaft’s angular jerk (rad/s3) | Ascent stage | 21.87 | 30.60 | 28.11 |
| Descent stage | 21.79 | 32.45 | 44.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, C. AMT Starting Control as a Soft Starter for Belt Conveyors Using a Data-Driven Method. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101808
Li Y, Li L, Zhang C. AMT Starting Control as a Soft Starter for Belt Conveyors Using a Data-Driven Method. Symmetry. 2021; 13(10):1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101808
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yunxia, Lei Li, and Chengliang Zhang. 2021. "AMT Starting Control as a Soft Starter for Belt Conveyors Using a Data-Driven Method" Symmetry 13, no. 10: 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101808
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, L., & Zhang, C. (2021). AMT Starting Control as a Soft Starter for Belt Conveyors Using a Data-Driven Method. Symmetry, 13(10), 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101808






