Thixotropic Behavior in Defining Particle Packing Density of Highly Filled AP/HTPB-Based Propellant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
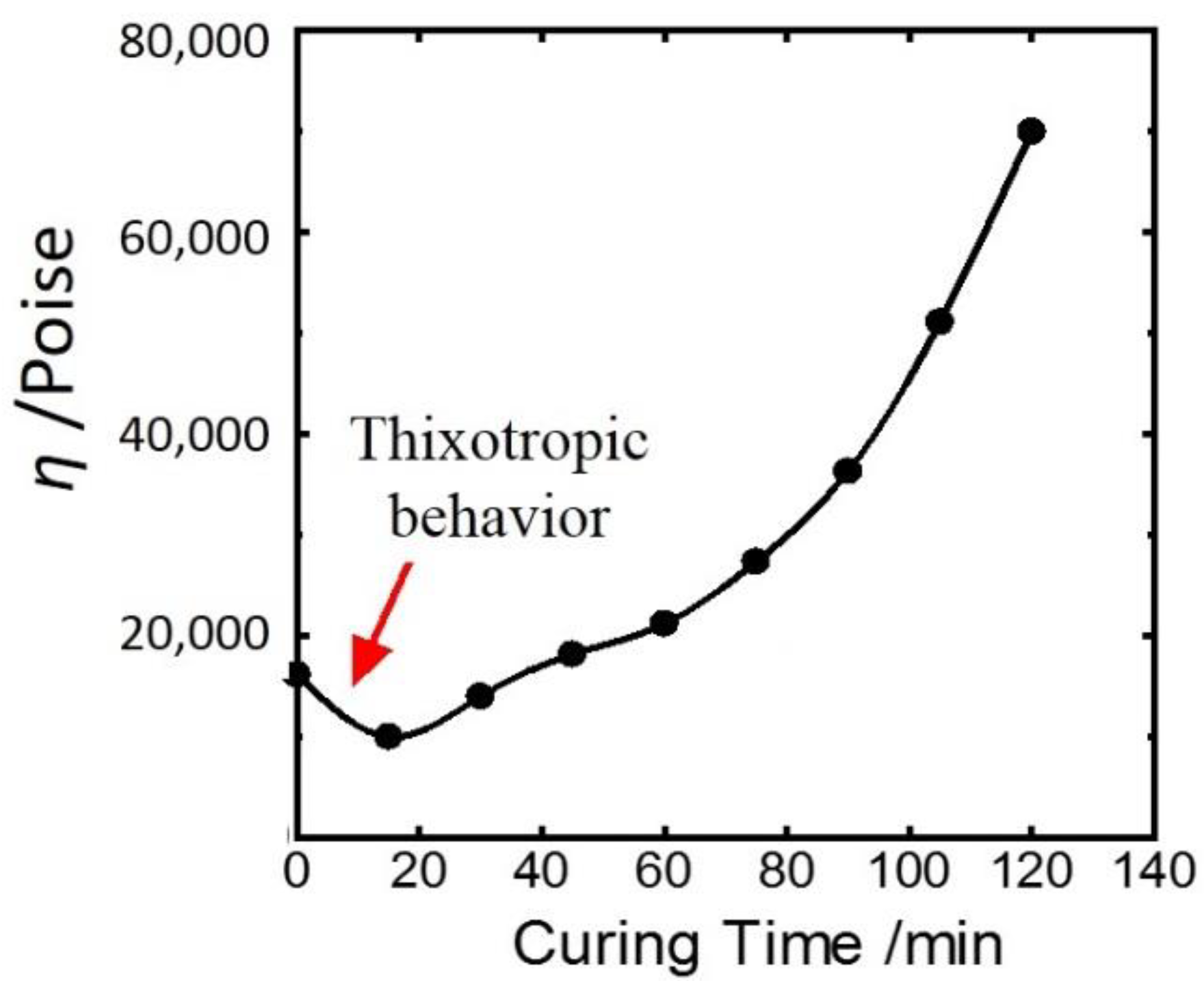
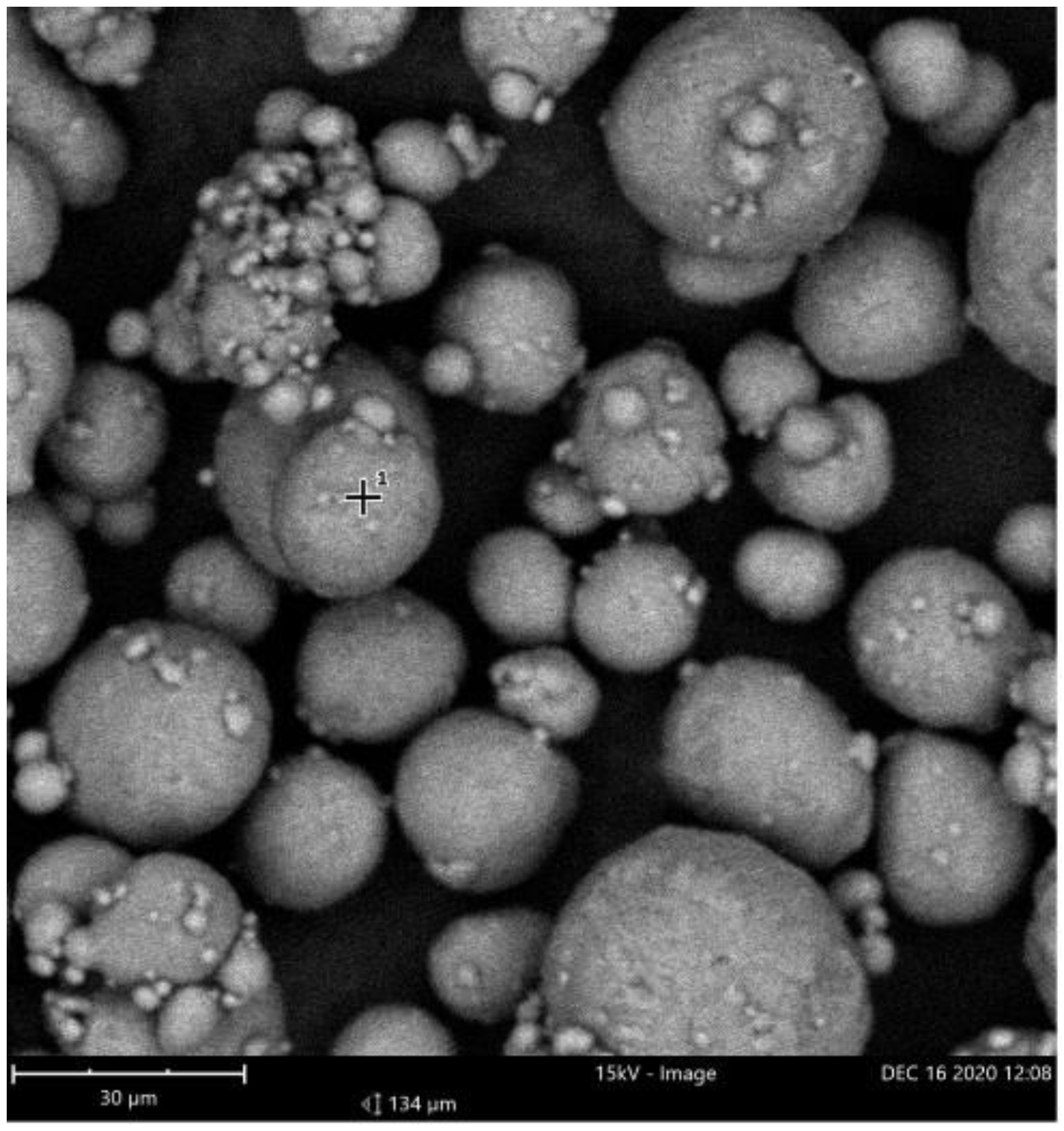
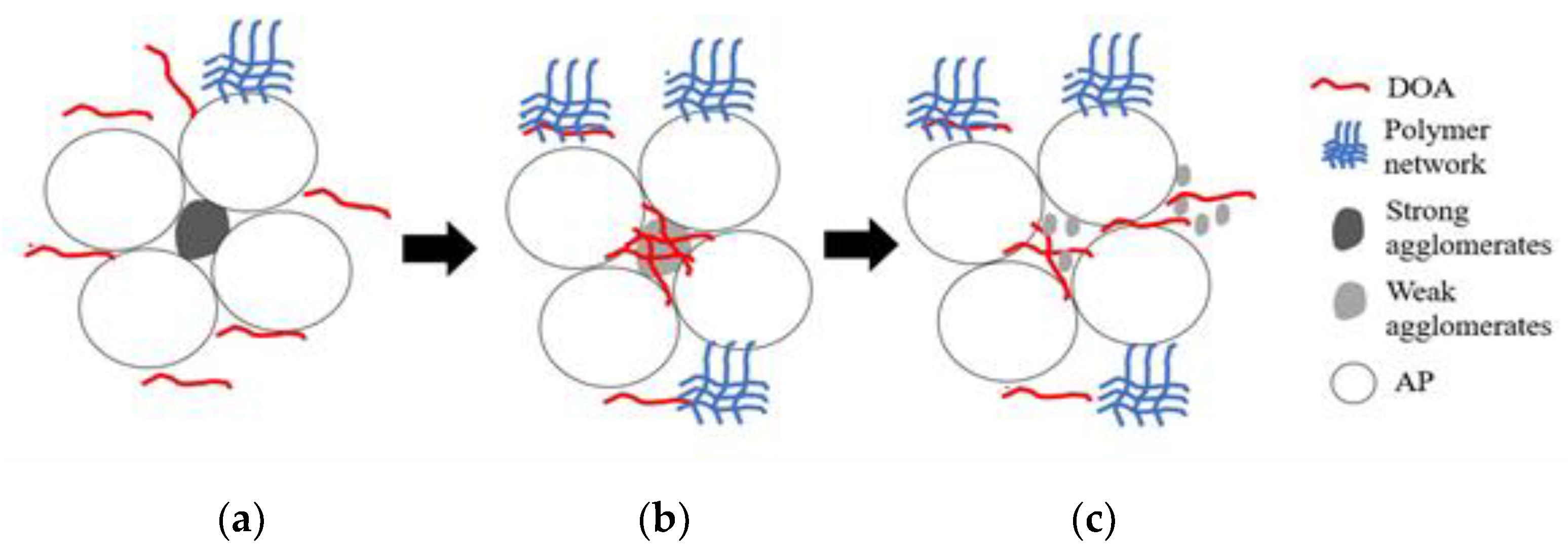
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeLuca., L.T. Evolution of Solid Rocket Propellant Formulation for Space Propulsion. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on R&D of Energetic Materials (RDEM); Research Center of Energetic Material Genome Science: Chengdu, China, 2016; pp. 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Ban, R.; Yoshihama, S.; Nakamura, T.; Habu, H. The Continuous Mixing Process of Composite Solid Propellant Slurry by an Artificial Muscle Actuator. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Sp. Sci. Aerosp. Technol. Jpn. 2016, 14, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mason, B.P.; Roland, C.M. Solid Propellants. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2019, 92, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, N.; Srivastava, P.K.; Varma, M. Recent Advances in Catalytic Combustion of AP-based Composite Solid Propellants. Def. Technol. 2021, 17, 1013–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakavas-Papaniaros, P.A. On The Distribution of Particles in Propellant Solids. Acta Mech. 2020, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restasari, A.; Budi, R.S.; Hartaya, K. Pseudoplasticity of Propellant Slurry with Varied Aluminium Content for Castability Development. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1005, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohga, M.; Hagihara, Y. Rheology of Concentrated AP/HTPB Suspensions Prepared at The Upper Limit of AP Content. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2000, 25, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdillah, L.H.; Winardi, S.; Sumarno, S.; Nurtono, T. Effect of Mixing Time to Homogeneity of Propellant Slurry. IPTEK J. Proc. Ser. 2018, 4, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dombe, G.; Jain, M.; Singh, P.P.; Radhakrishnan, K.K.; Bhattacharya, B. Pressure Casting of Composite Propellant. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2008, 15, 420–423. [Google Scholar]
- Hosomi, N.; Otake, K.; Uegaki, N.; Iwasaki, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Asakawa, M.R.; Habu, H.; Yamaguchi, S. Analysis of Mixed State of AP/HTPB Composite Propellant by X-ray Computed Tomography. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Aeronaut. Sp. Sci. Aerosp. Technol. Jpn. 2019, 17, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilmart, G.; Dorval, N.; Devillers, R.; Fabignon, Y.; Attal-Trétout, B.; Bresson, A. Imaging Aluminum Particles in Solid-Propellant Flames Using 5 kHz LIF of Al Atoms. Materials 2019, 12, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.; Radhakrishnan, S.; Vijayalakshmi, R.; Talawar, M.B.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D. Screening of Polymer-Plasticizer Systems for Propellant Binder Applications: An Experimental and Simulation Approach. J. Energ. Mater. 2019, 37, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypych, G. Handbook of Plasticizers, 3rd ed.; ChemTec Publishing: Toronto, ON, Cananda, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restasari, A.; Abdillah, L.H.; Ardianingsih, R.; Wicaksono, B.; Budi, R.S. The Compatibility of Model for Low Shear Flow Analysis in Developing Plasticized Htpb-Based Binder. Spektra J. Fis. Dan Apl. 2020, 5, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golofit, T.; Ganczyk-Specjalska, K.; Jamroga, K.; Kufel, L. Rheological and Thermal Properties of Mixtures of Hydroxyl-Terminated Polybutadiene and Plasticizer. Polimery 2018, 63, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restasari, A.; Abdillah, L.H.; Budi, R.S.; Hartaya, K. Pengaruh Dioctyl Adipate Terhadap Sifat Rheologi HTPB Terplastisasi. J. Teknol. Dirgant. 2018, 16, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandgar, B.M.; Krishnamurthy, V.N.; Mukundan, T.; Sharma, K.C. Mathematical Modeling of Rheological Properties of Hydroxyl-Terminated Polybutadiene Binder and Dioctyl Adipate Plasticizer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 85, 1002–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restasari, A.; Abdillah, L.H. Pengaruh Dioctyl Adipate Terhadap Pot-Life Proopelan Berformula AP Trimoda. In Proceedings of the Prosiding SIPTEKGAN XXI; Pusat Teknologi Penerbangan, LAPAN: Tangerang, Indonesia, 2017; pp. 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda, M.M.; Auscher, M.C.; Fulchiron, R.; Périé, T.; Martin, G.; Sonntag, P.; Cassagnau, P. Rheology and Applications of Highly Filled Polymers: A Review of Current Understanding. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 66, 22–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombe, G.; Yadav, N.K.; Lagade, R.M.; Bhongale, C. Studies on Measurement of Yield Stress of Propellant Suspensions Using Forced Falling Ball and Slump Test. Appl. Rheol. 2017, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutný, O.Ĝ.; Kratochvíl, J.Ĝ.; Švec, J.Ĝ.; Bednárek, J. Modelling of Packing Density for Particle Composites Design. In Proceedings of the Procedia Engineering; Elsevier: Brno, Czech Republic, 2016; Volume 151, pp. 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eilers, H. Die Viskositäts-Konzentrationsabhängigkeit Kolloider Systeme in Organischen Lösungsmitteln. Kolloid Z 1943, 102, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, M. The Viscosity of a Concentrated Suspension of Spherical Particles. J. Colloid Sci. 1951, 6, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, I.; Dougherty, T. Mechanism for Non-Newtonian Flow in Suspensions of Rigid Spheres. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1959, 3, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Christiansen, E.; Baer, A. Rheology of Concentrated Suspensions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1971, 15, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemada, D. Rheology of Concentrated Disperse Systems and Minimum Energy Dissipation Principle. Rheol. Acta. 1977, 16, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisken, C.; Gocmez, A.; Yilmazer, U.; Pekel, F.; Ozkar, S. Modeling and Rheology of HTPB Based Composite Solid Propellants. Polym. Compos. 1998, 19, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, K.H.; Geckler, R.D. The Rheology of Suspensions. J. Appl. Phys. 1954, 1135, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthiah, R.; Krishnamurthy, V.N.; Gupta, B.R. Rheology of HTPB Propellant. 1. Effect of Solid Loading, Oxidizer Particle Size, and Aluminum Content. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1992, 44, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lade, R.; Wasewar, K.; Sangtyani, R.; Kumar, A. Effect of Aluminum Nanoparticles on Rheological Behavior of HTPB-Based Composite Rocket Propellant. J. Energ. Mater. 2018, 37, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesar, R.; Romano, D.O.; Rebmann, M.S.; Montefusco, H.; Raucci, J.; Massucato, C.; Pileggi, R.G. Impact of Particle Packing on The Rheological Properties of Cementitious Pastes Dispersed with Polycarboxylate. Annu. Trans. Nord. Rheol. Soc. 2017, 25, 398–404. [Google Scholar]
- Mahaut, F.; Mokéddem, S.; Chateau, X.; Roussel, N.; Ovarlez, G. Effect of Coarse Particle Volume Fraction on The Yield Stress and Thixotropy of Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mbasha, W.; Masalova, I.; Haldenwang, R.; Malkin, A. The Yield Stress of Cement Pastes as Obtained by Different Rheological Approaches. Appl. Rheol. 2015, 25, 53517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-Farías, O.; Hebraud, P.; Lootens, D.; Liard, M.; Mendoza-Rangel, J.M. Thixotropy of Reactive Suspensions: The Case of Cementitious Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Singh, D.; Balasubramanian, K.; Singh, P.P.; Bhattacharya, B.; Advanced, H.S. Studies on Prediction of Rheological Behaviour of Composite Propellant Formulations Based on Rheological Models. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2015, 7, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.T.K.; Rojas, M.L.; Miano, A.C.; Augusto, P.E.D. Rheological Properties of Tomato Products. In Tomato Chemistry, Industrial Processing and Product Development; Porretta, S., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Croydon, UK, 2019; p. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandgar, B.M.; Sharma, K.C.; Mukundan, T.; Krishnamurthy, V.N. Rheokinetic Modeling of HTPB-TDI and HTPB-DOA-TDI Systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 89, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szycher, M. Szycher’s Handbook of Polyurethanes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Kawashima, S.; Marchon, D.; Vasilic, K.; Wolfs, R. Recent Advances on Yield Stress and Elasticity of Fresh Cement-based Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florczak, B.; Białek, M.; Cholewiak, A. Determination of the Internal Ballistic Properties of Solid Heterogeneous Rocket Propellants. Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 2014, 11, 589–601. [Google Scholar]
- Florczak, B.; Bednarczyk, E.; Maranda, A. Studies of Rheological Properties of Suspension of Heterogeneous Rocket Propellant Based on HTPB Rubber. CHEMIK 2015, 69, 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, M.A.; Atallah, A.; Schweizer, T.; Öttinger, H.C. Particle–Particle and Particle-Matrix Interactions in Calcite Filled High-Density Polyethylene—Steady Shear. J. Rheol. 2004, 48, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, N. Rheology of Fresh Concrete : From Measurements to Predictions of Casting Processes. Mater. Struct. 2007, 40, 1001–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.A. The Phenomena of Rupture and Flow in Solids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 1921, 221, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metzner, A.B. Rheology of Suspensions in Polymeric Liquids. J. Rheol. 1985, 29, 739–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillard, J.; Henry, F.; Marchal, P. Rheology of Powders and Nanopowders Through The Use of A Couette Four-Bladed Vane Rheometer: Flowability, Cohesion Energy, Agglomerates and Dustiness. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llusa, M.; Levin, M.; Snee, R.D.; Muzzio, F.J. Shear-Induced APAP De-agglomeration. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bika, D.G.; Gentzler, M.; Michaels, J.N. Mechanical Properties of Agglomerates. Powder Technol. 2001, 117, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Wu, A.; Qi, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, B. Mechanical Properties of Paste Slurry under Constant Shear Rate in Initial Structure Failure Process. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2019, 2971563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallier, S. A Stochastic Pocket Model for Aluminum Agglomeration in Solid Propellants. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2009, 34, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Polymer Additives and Solubility Parameters. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 51, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruellan, A.; Guinault, A.; Sollogoub, C.; Ducruet, V.; Domenek, S. Solubility Factors as Screening Tools of Biodegradable Toughening Agents of Polylactide. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Hori, Y.; Fei, H.; Inamine, I.; Asai, K.; Kiguchi, T.; Tsubaki, J. Experimental Study About the Agglomeration Behavior in Slurry Prepared by Adding Excess Polyelectrolyte Dispersant. Adv. Powder Technol. 2012, 23, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Hioki, K.; Kono, K.; Hiejima, Y.; Nitta, K. Effects of Liquid Paraffin on Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Linear High-Density Polyethylene. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 8459–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Lin, Y.G.; Yang, W.L.; Kang, C.H.; Niu, L. Application of Nanometer Antimony Trioxide Modified by Dioctyl Phthalate in Polyvinyl Chloride Flame Retardant Materials. Mater. Res. 2020, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, S.; Balzer, P.S.; Becker, D. Role of Plasticizer and Dispersion Methods on The Properties of Poly(vinyl chloride) and Clay Nanocomposites. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2018, 24, E172–E176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polowczyk, I.; Szubert, A.; Sadowski, Z.; Jażdżyk, E. Effect of Polymer-Surfactant Interaction onto The Spherical Agglomeration. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2004, 38, 351–358. [Google Scholar]









| Authors | Model |
|---|---|
| Eilers (1941) [22] | ηr = (1 + )2 |
| Mooney (1951) [23] | Ln (ηr) = () |
| Krieger and Dougherty (1959) [24] | ηr = (1 − PF)−[η]ϕm |
| Chong (1971) [25] | ηr = (1 + 0.75 ())2 |
| Quemada (1977) [26] | ηr = (1 − PF)−2 |
| No. | Al/DOA | HTPB (%.wt) | TDI (%.wt) | Tepanol (%.wt) | AP (%.wt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12.00 | 10.547 | 0.753 | 0.2 | 75.5 |
| 2 | 12.73 | 10.547 | 0.753 | 0.1 | 73.5 |
| 3 | 13.64 | 10.547 | 0.753 | 0.1 | 72.5 |
| 4 | 15.89 | 10.775 | 0.77 | 0.2 | 75.5 |
| 5 | 19.74 | 10.817 | 0.773 | 0.15 | 72.5 |
| 6 | 23.68 | 10.817 | 0.77 | 0.15 | 69.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Restasari, A.; Abdillah, L.H.; Ardianingsih, R.; Sitompul, H.R.D.; Budi, R.S.; Hartaya, K.; Wibowo, H.B. Thixotropic Behavior in Defining Particle Packing Density of Highly Filled AP/HTPB-Based Propellant. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101767
Restasari A, Abdillah LH, Ardianingsih R, Sitompul HRD, Budi RS, Hartaya K, Wibowo HB. Thixotropic Behavior in Defining Particle Packing Density of Highly Filled AP/HTPB-Based Propellant. Symmetry. 2021; 13(10):1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101767
Chicago/Turabian StyleRestasari, Afni, Luthfia Hajar Abdillah, Retno Ardianingsih, Hamonangan Rekso Diputro Sitompul, Rika Suwana Budi, Kendra Hartaya, and Heri Budi Wibowo. 2021. "Thixotropic Behavior in Defining Particle Packing Density of Highly Filled AP/HTPB-Based Propellant" Symmetry 13, no. 10: 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101767
APA StyleRestasari, A., Abdillah, L. H., Ardianingsih, R., Sitompul, H. R. D., Budi, R. S., Hartaya, K., & Wibowo, H. B. (2021). Thixotropic Behavior in Defining Particle Packing Density of Highly Filled AP/HTPB-Based Propellant. Symmetry, 13(10), 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13101767







