An Improved Analytical Tuning Rule of a Robust PID Controller for Integrating Systems with Time Delay Based on the Multiple Dominant Pole-Placement Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Proposed Method
2.1. Performance Indices
2.2. Theoretical Statements
2.3. The Process Model
2.4. Controller Design
2.5. Condition for PIPTD System
2.6. Selection of the Tuning Parameter and the Tuning Rules
3. Robustness, Input Usage and Performance Index
3.1. Integral Performance Index
3.2. Total Variation Index
4. Simulation and Analysis Studies
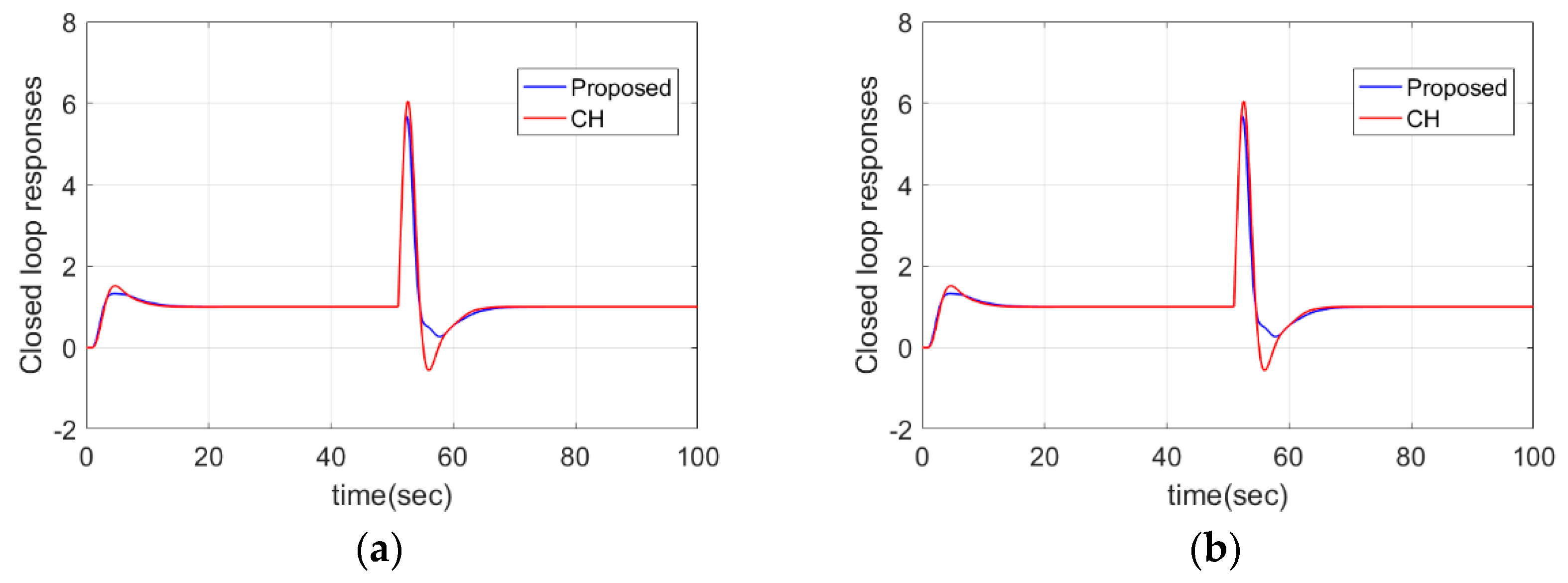
4.1. PIPTD System
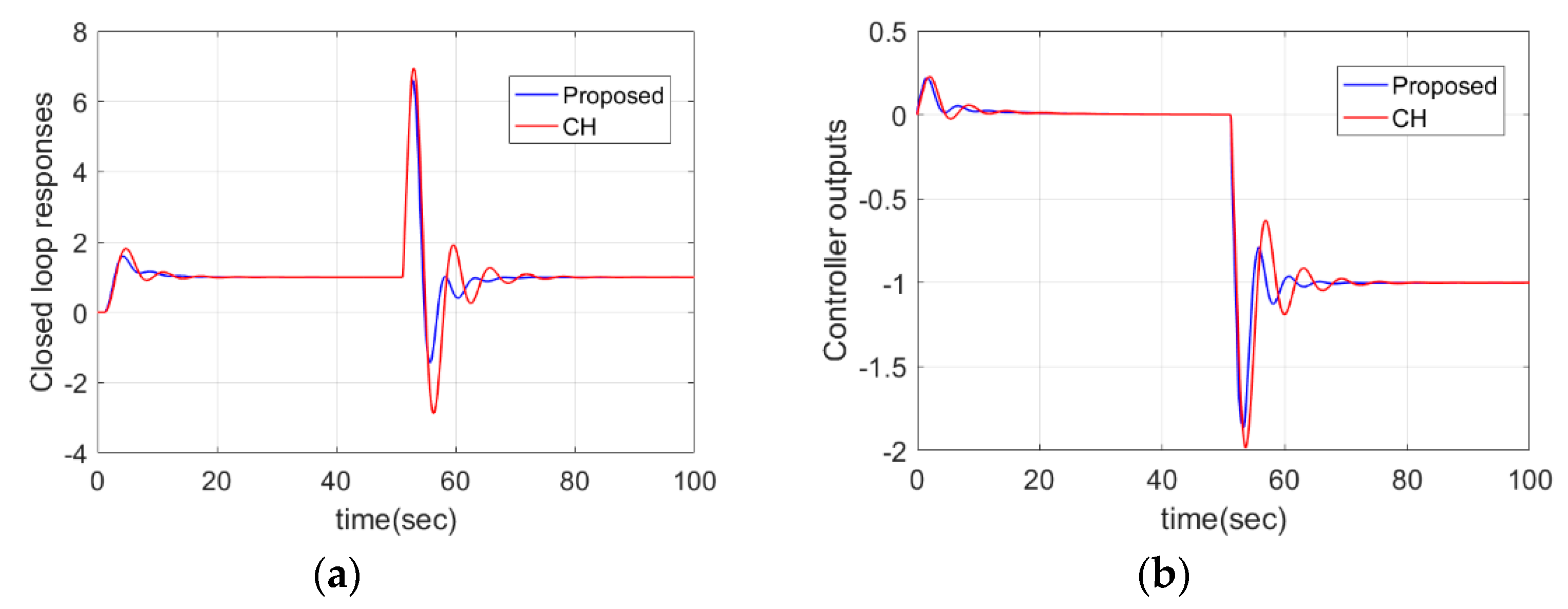
4.2. DIPTD System
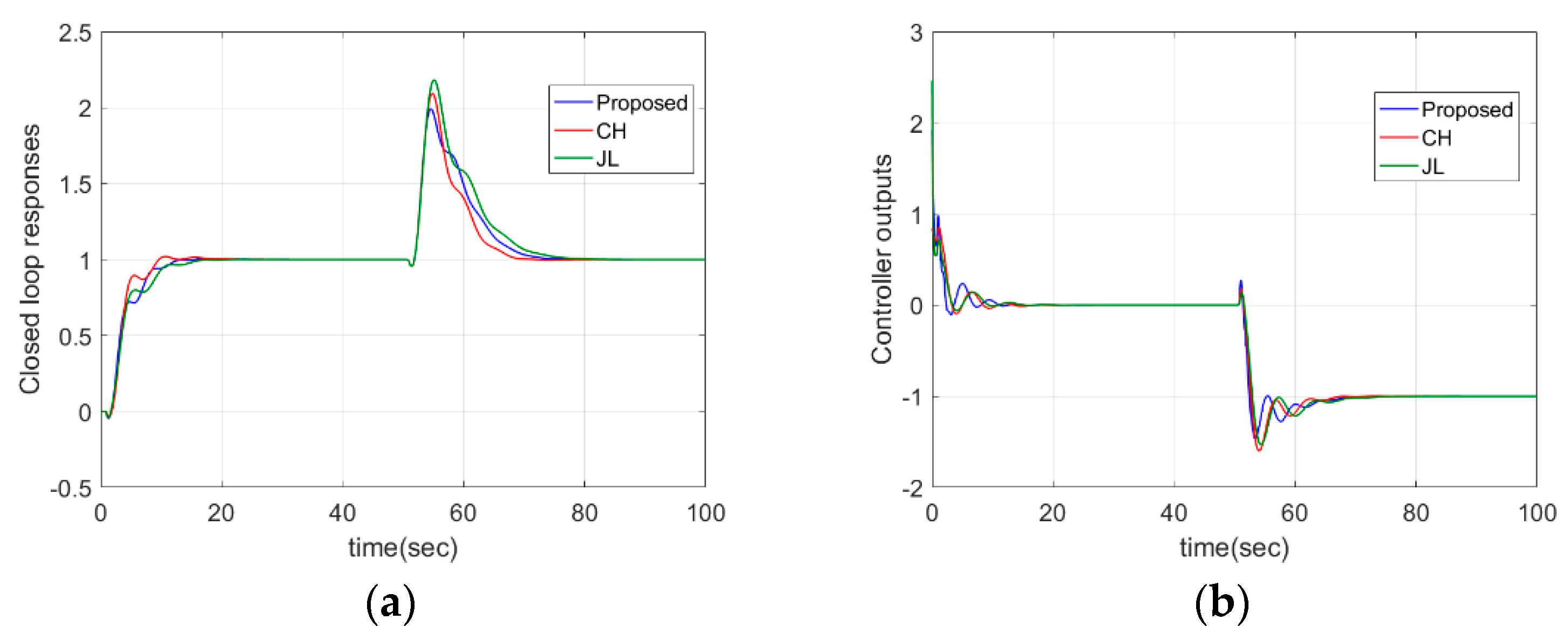
4.3. Stable FOPTDI System
4.4. Stable FOPTD System with a Negative Zero
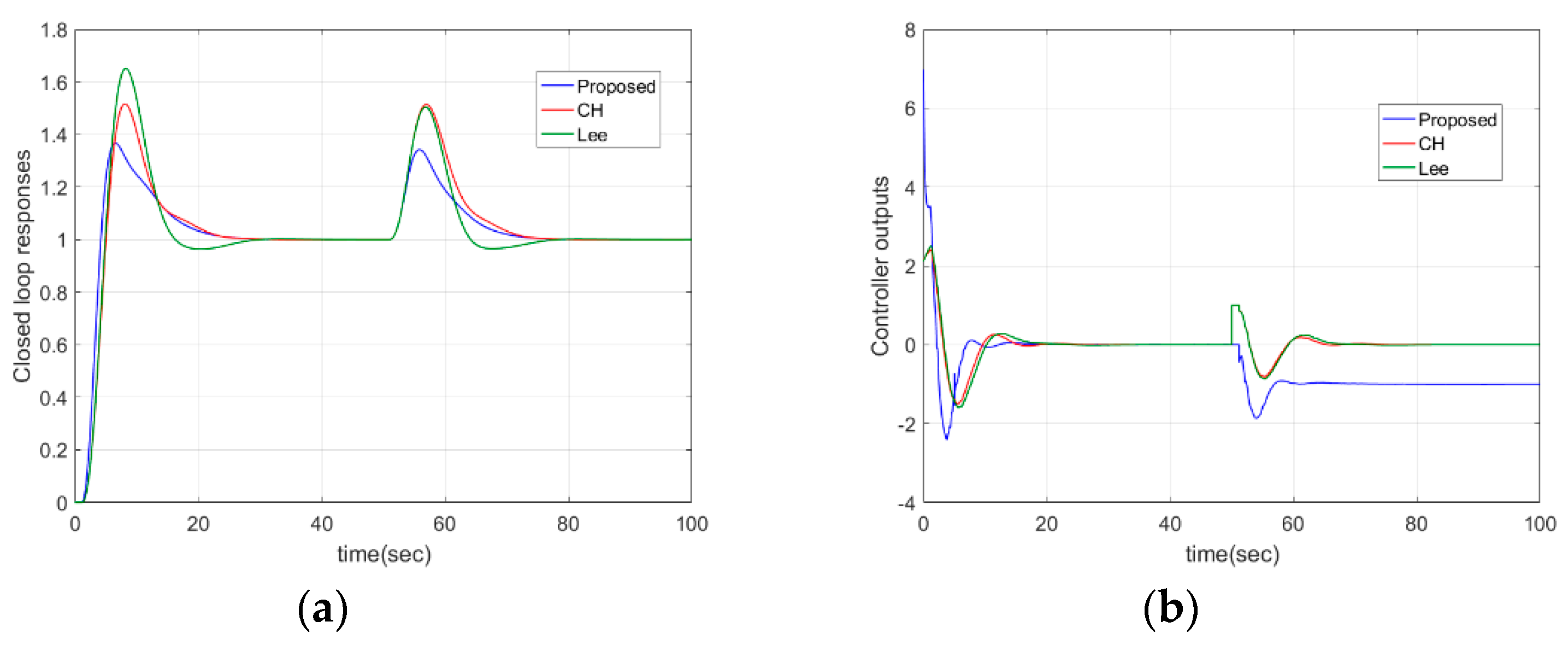
4.5. High-Order System
4.6. Non-Linear Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, D.B.S.; Padma Sree, R. Tuning of IMC based PID controllers for integrating systems with time delay. ISA Trans. 2016, 63, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.D. Quantitative Process Control Theory; CRC Press Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Majhi, S. PID controller tuning for integrating processes. ISA Trans. 2010, 49, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, D.; Suryanarayana, K.; Aparna, G.; Padma Sree, R. Tuning of PID controllers for continuous stirred tank reactors. Indian Chem. Eng. 2012, 54, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaremi, I.; Labibi, B. Control of a distillation column: A decentralized approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Computer Aided Control System Design, Anchorage, AK, USA, 25–27 September 2000; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Sun, X. The study of boiler control system of water level of steam drum based on new immune PID controller. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Digital Manufacturing & Automation, Zhangjiajie, Hunan, China, 5–7 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.X.; Wang, X.J.; Teng, F. The PID control system of steam boiler drum water level based on genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the Guidance, Navigation & Control Conference, Yantai, Shandong, China, 8–10 August 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Cluett, W.R. Tuning PID controllers for integrating processes. IEE Proc. Control. Theory Appl. 1997, 144, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bequette, B.W. Process Control: Modeling, Design, and Simulation; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, I. Two-degree-of-freedom IMC structure and controller design for integrating processes based on gain and phase-margin specifications. IEE Proc. Control. Theory Appl. 2004, 151, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.V.N.; Padma Sree, R. IMC based controller design for integrating systems with time delay. Indian Chem. Eng. 2011, 52, 194–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.S.; Rao, V.S.R.; Chidambaram, M. Direct synthesis-based controller design for integrating processes with time delay. J. Frankl. Inst. 2009, 346, 38–56. [Google Scholar]
- Vanavil, B.; Chaitanya, K.K.; Rao, A.S. Improved PID controller design for unstable time delay processes based on direct synthesis method and maximum sensitivity. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2015, 46, 1349–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.R.D.; Flesch, R.C.C.; Normey-Rico, J.E. Controlling industrial dead-time systems: When to use a PID or an advanced controller. ISA Trans. 2020, 99, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiser, J.; Zitek, P. PID Controller Tuning via Dominant Pole-placement in Comparison with Ziegler-Nichols Tuning. In Proceedings of the 15th IFAC Workshop on Time Delay Systems (TDS) Jointly Held with the 7th IFAC Symposium on System Structure and Control (SSSC), Sinaia, Romania, 9–11 September 2019; IFAC: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro, V.M.; Vilanova, R. Model reference robust tuning of 2DoF PI controllers for integrating controlled processes. In Proceedings of the Control & Automation, Barcelona, Spain, 3–6 July 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alfaro, V.M.; Vilanova, R. Robust tuning and performance analysis of 2DoF PI controllers for integrating controlled processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 13182–13194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chriss, G.; Sigurd, S. Optimal pi and pid control of first-order plus delay processes and evaluation of the original and improved simc rules. J. Proc. Control 2018, 70, 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Madhuranthakam, C.R.; Singh, J.; Elkamel, A.; Budman, H. Optimal PID controller parameters for first order and second order systems with time delay using a connectionist approach. Eng. Opt. 2010, 42, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boskovic, M.; Sekara, T.B.; Rapaic, M.R. Novel tuning rules for PIDC and PID load frequency controllers considering robustness and sensitivity to measurement noise. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2020, 114, 105416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, P.; Aström, K.J. PID control revisited. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1993, 26, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma Sree, R.; Chidambaram, M. Set point weighted PID controllers for unstable systems. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2005, 192, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma, S.; Chidambaram, M.; Rao, A.S.; Yoo, C.K. Enhanced control of integrating cascade processes with time delays using modified Smith predictor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuzzoha, M.; Lee, M. PID controller design for integrating processes with time delay. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 25, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.N.L.; Lee, M. A unified approach to the design of advanced proportional-integral-derivative controllers fortime delay processes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cho, W.; Edgar, T.F. Simple analytic PID controller tuning rules revisited. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 5038–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.B.; Liu, Q. Analytical IMC-PID design in terms of performance/robustness tradeoff for integrating processes: From 2-Dof to 1-Dof. J. Proc. Control 2014, 24, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh, S.; Chidambaram, M. A simple method of tuning parallel cascade controllers for unstable FOPTD systems. ISA Trans. 2016, 65, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuzzoha, M. Closed-loop PI/PID controller tuning for stable and integrating process with time delay. Indust. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 12973–12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentine, C.C.; Chidambaram, M. PID Control of unstable time delay systems. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1997, 162, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.G.; Zhang, Z.; Astrom, K.J.; Chek, L.S. Guaranteed dominant pole-placement with PID controllers. J. Proc. Control 2009, 19, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viteckova, M.; Vitecek, A. Use of multiple dominant pole method for controller tuning. In Proceedings of the Carpathian Control Conference, High Tatras, Slovakia, 28–31 May 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Viteckova, M.; Vitecek, A. Two-degree of freedom controller tuning for integral plus time delay plants. ICIC Exp. Lett. 2008, 2, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Viteckova, M.; Vitecek, A. 2DOF PID controller tuning for integrating plants. In Proceedings of the Carpathian Control Conference, Tatranska Lomnica, Slovakia, 29 May–1 June 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Anil, C.; Padma Sree, R. PID control of integrating systems using multiple dominant pole-placement method. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 10, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmeri, M.; Ali, A. Direct synthesis based tuning of the parallel control structure for integrating processes. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2015, 46, 2461–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, C.; Padma Sree, R. Tuning of PID controllers for integrating systems using direct synthesis method. ISA Trans. 2015, 57, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
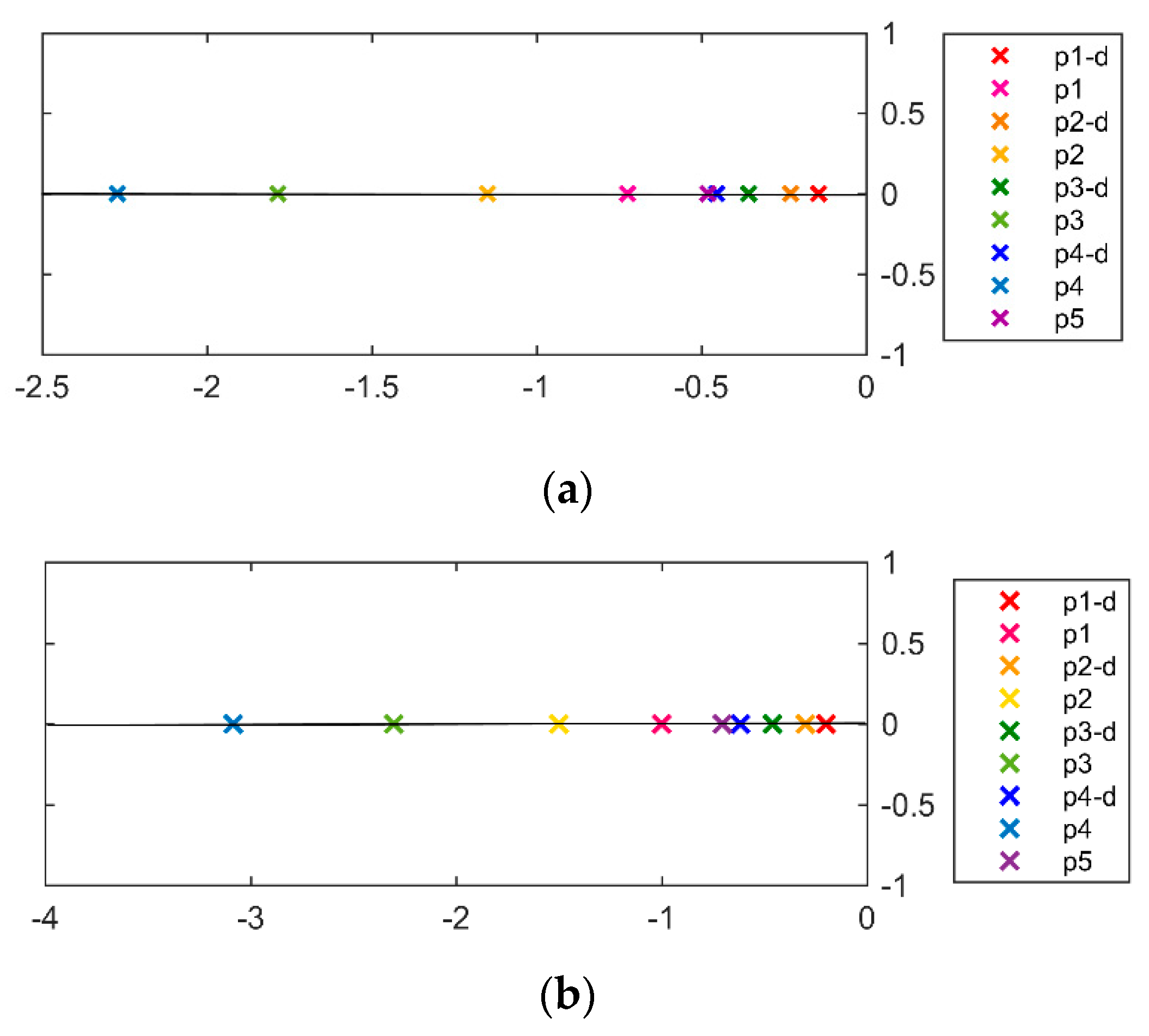
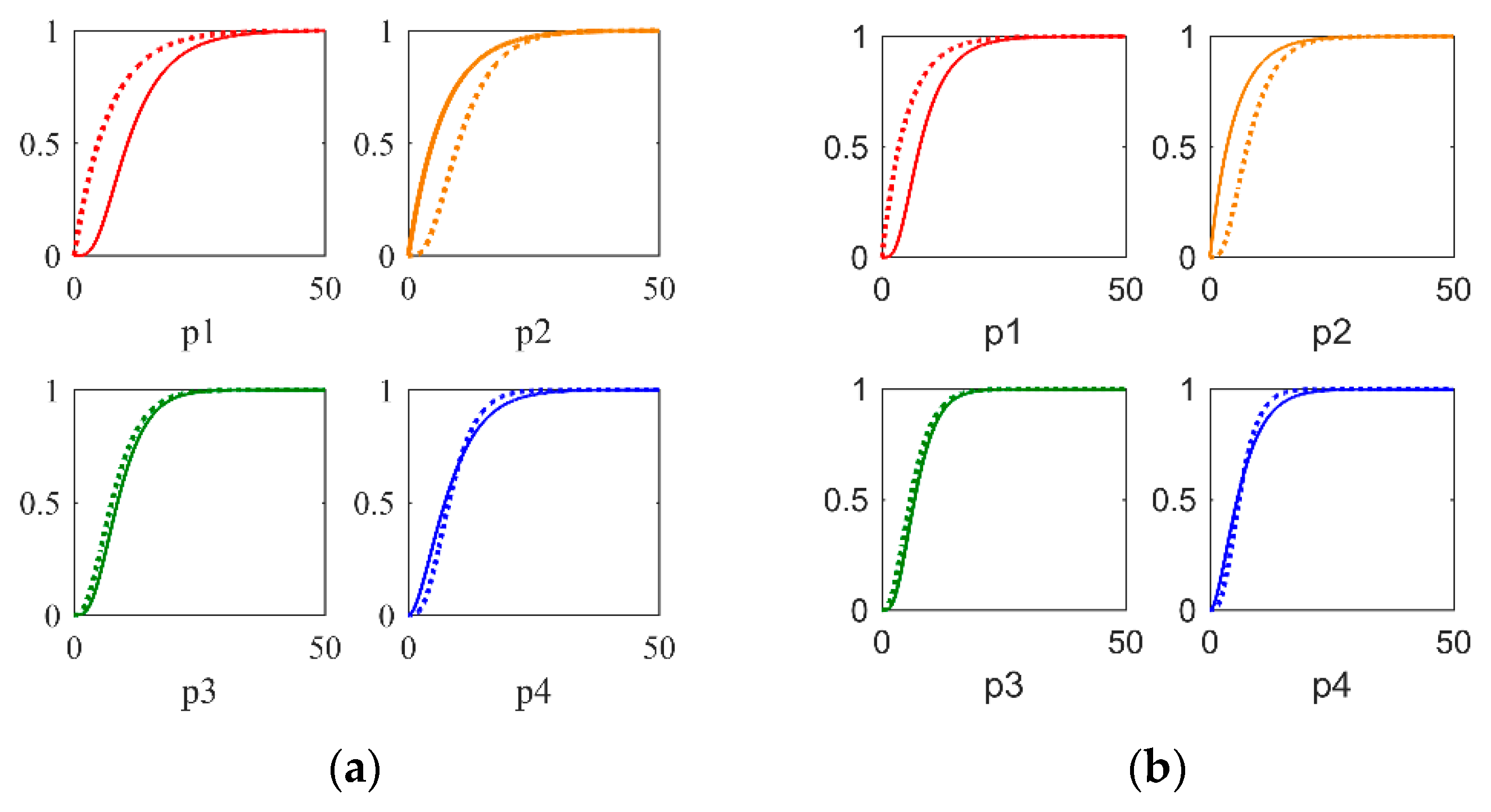
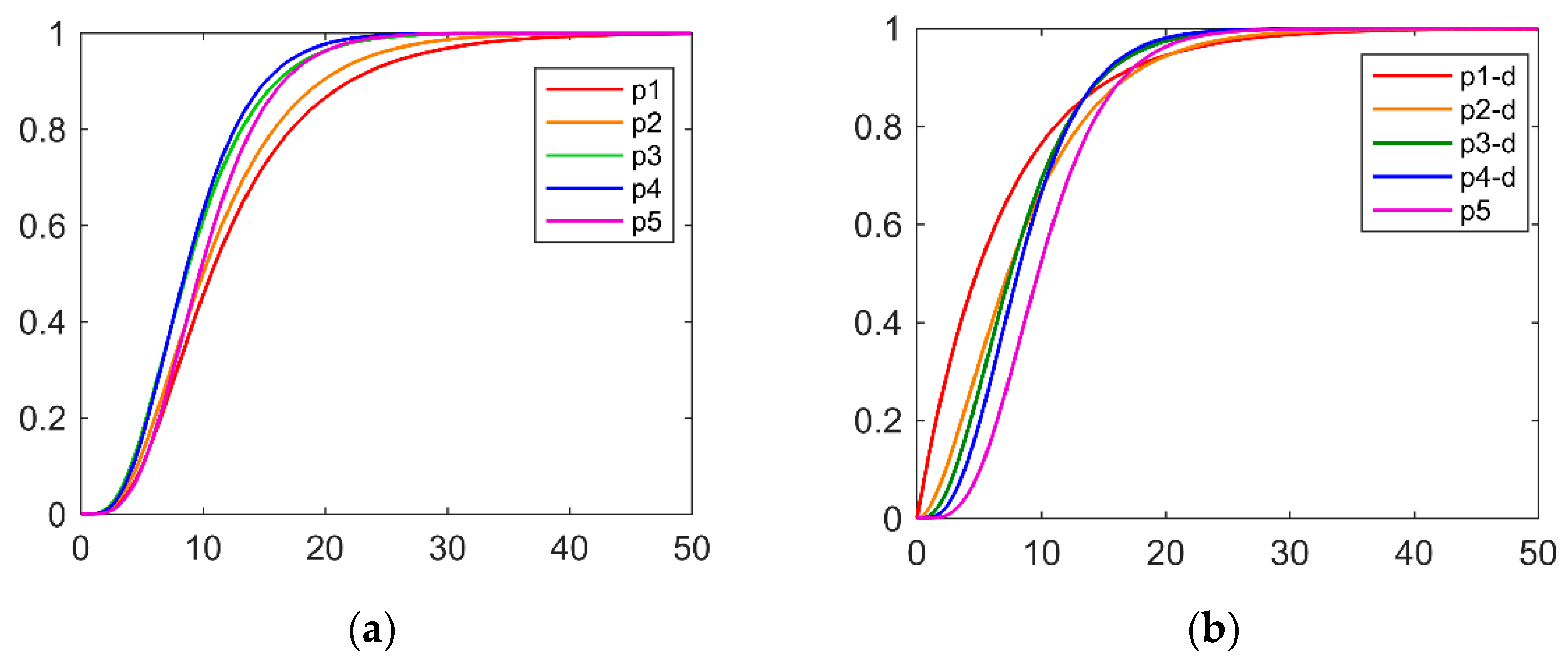
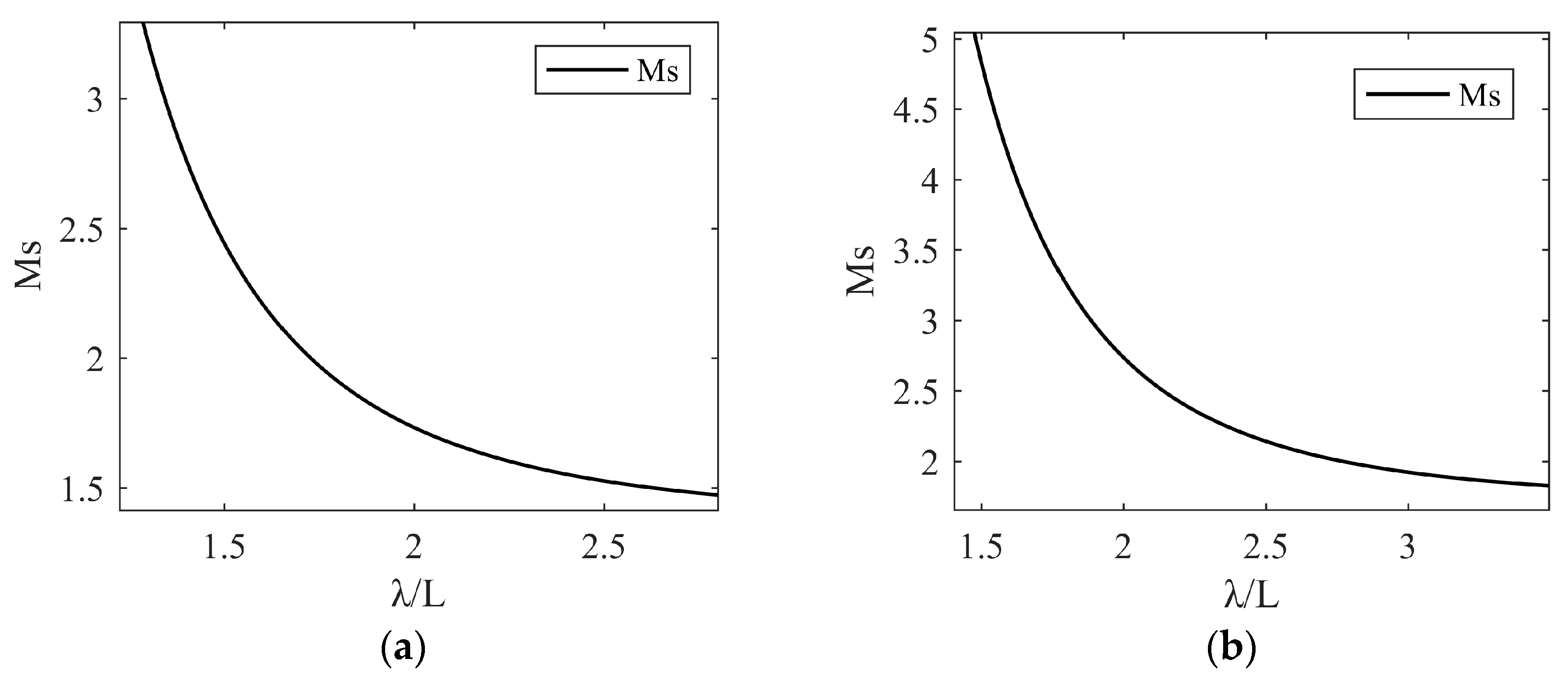
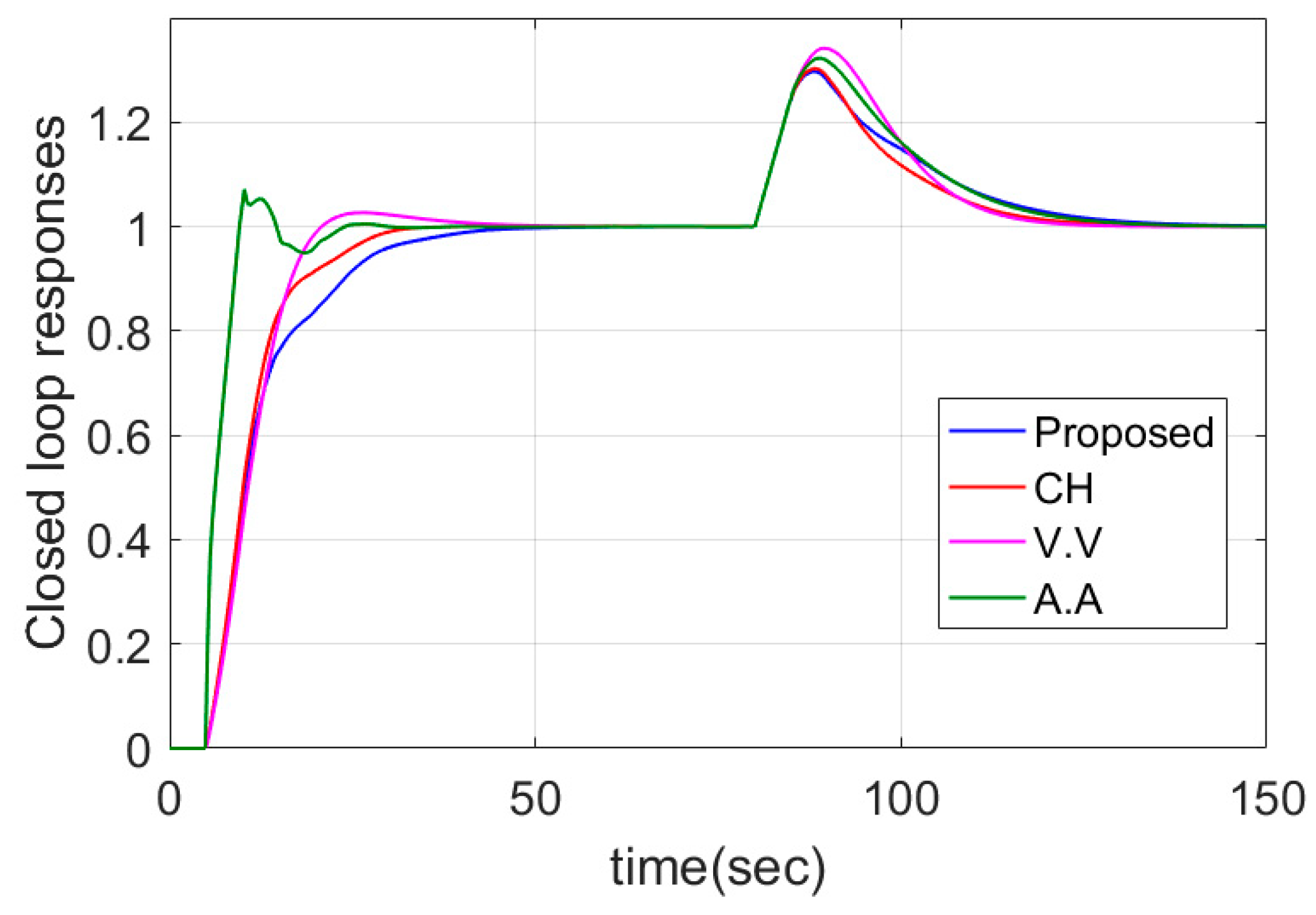
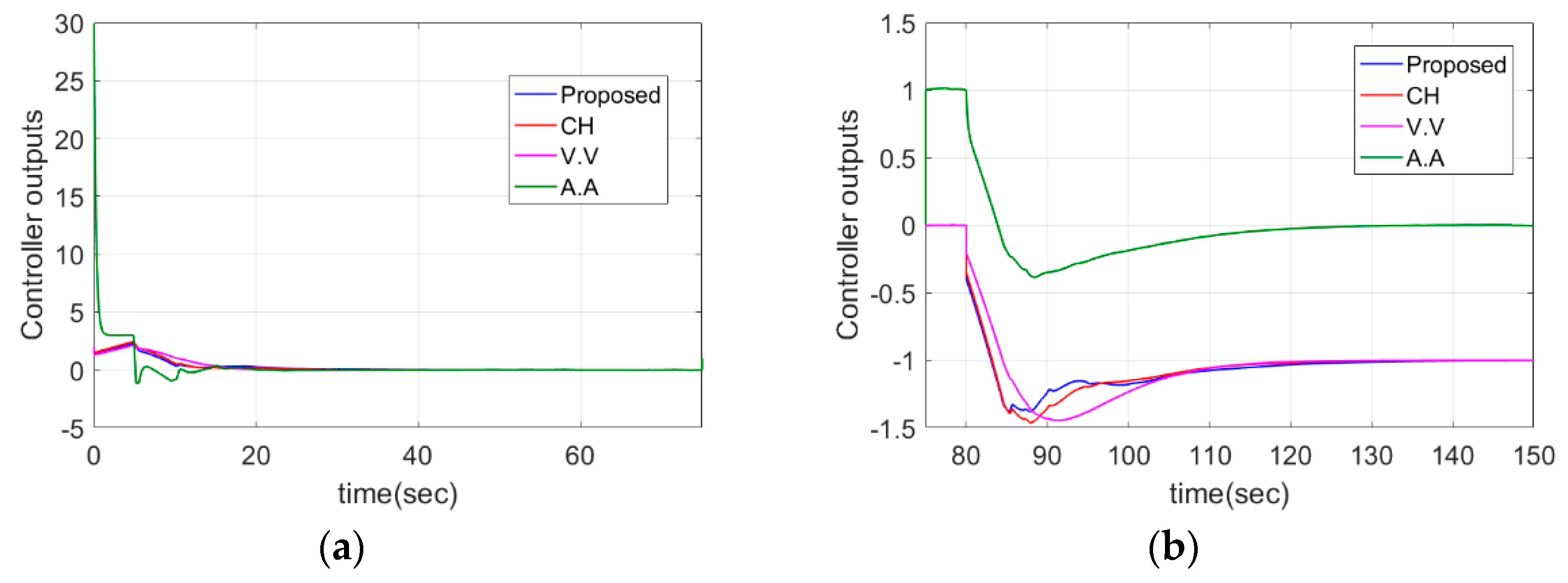
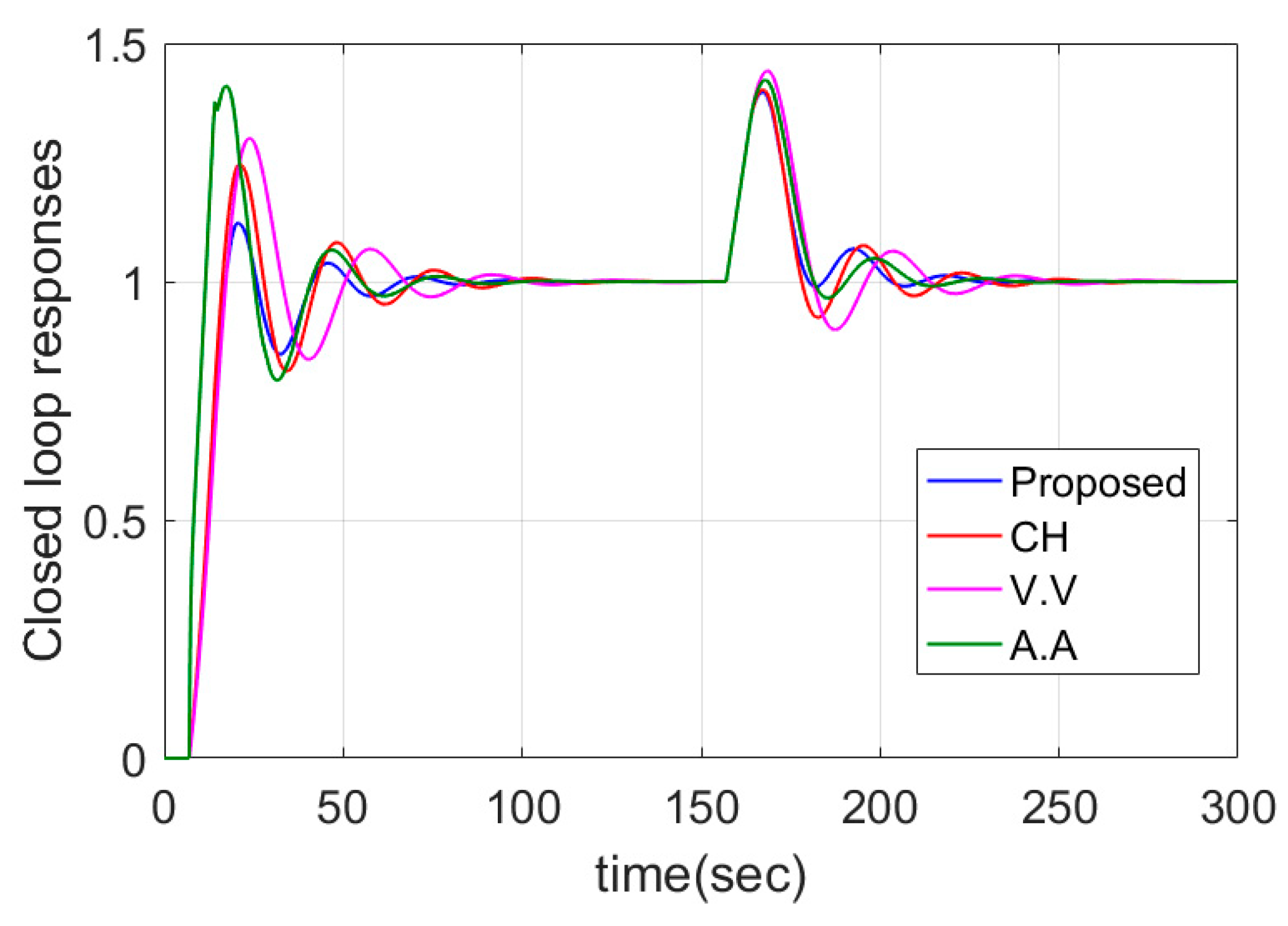
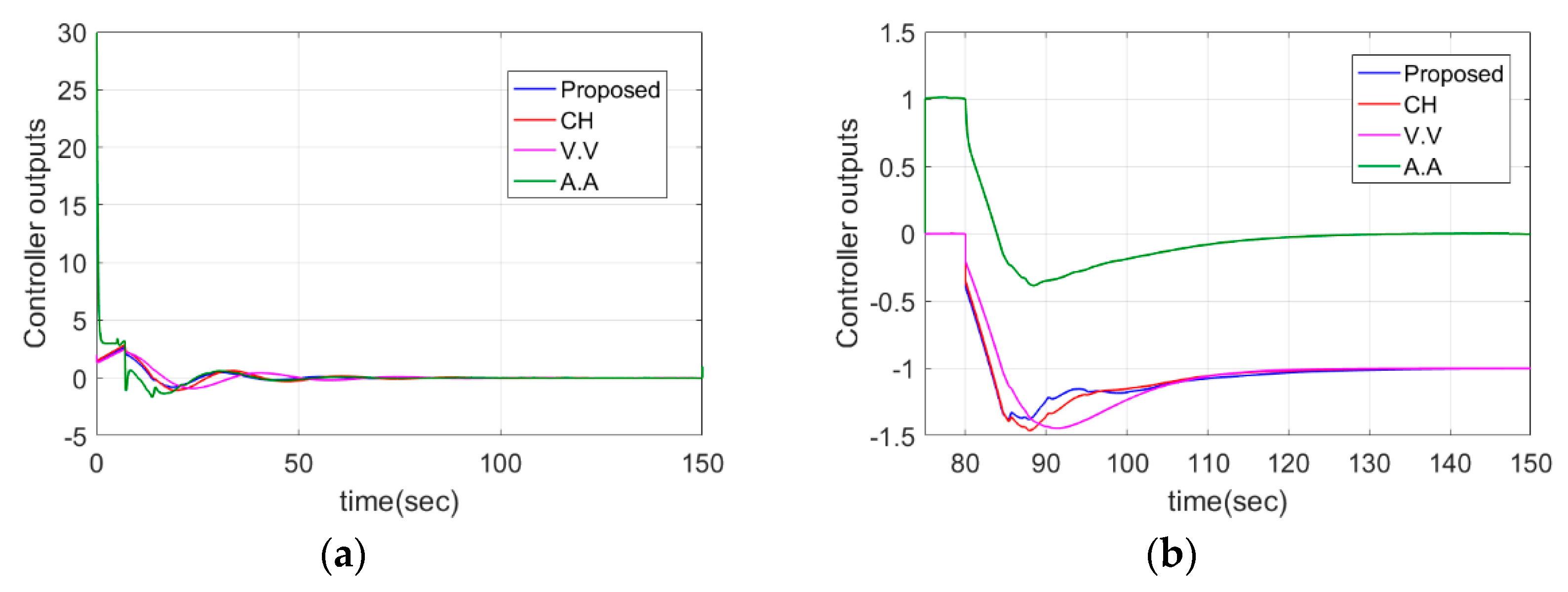
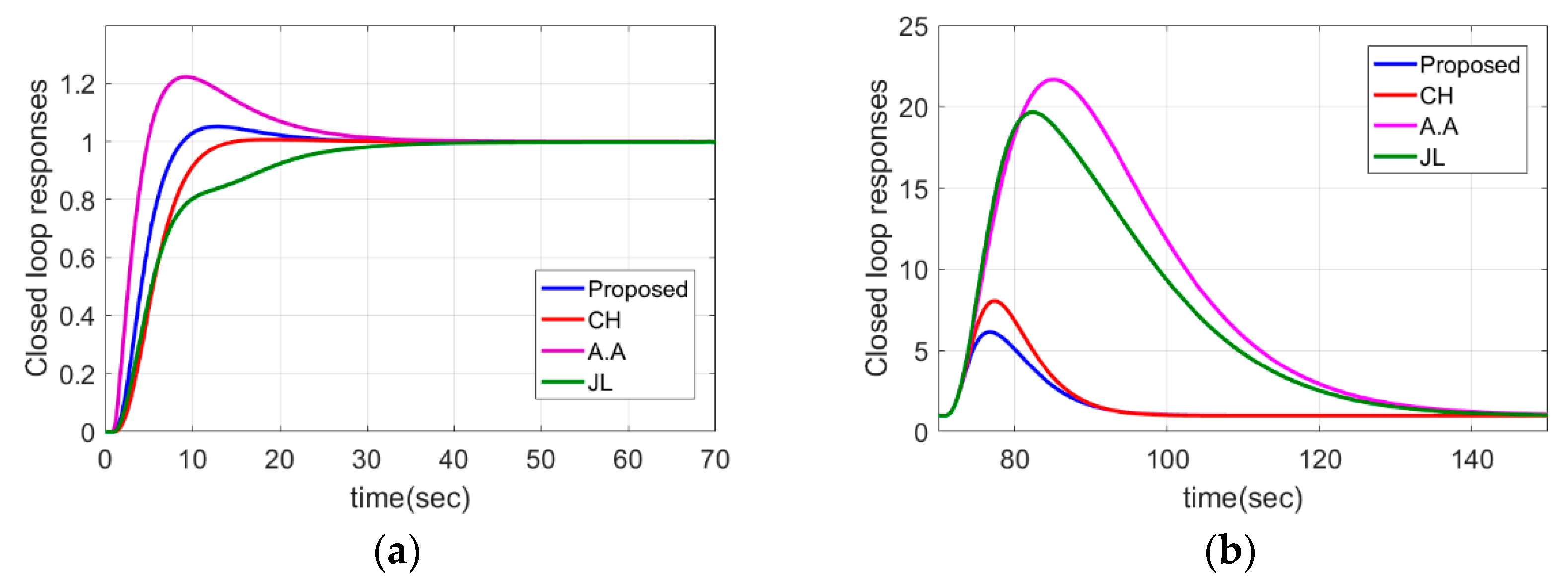
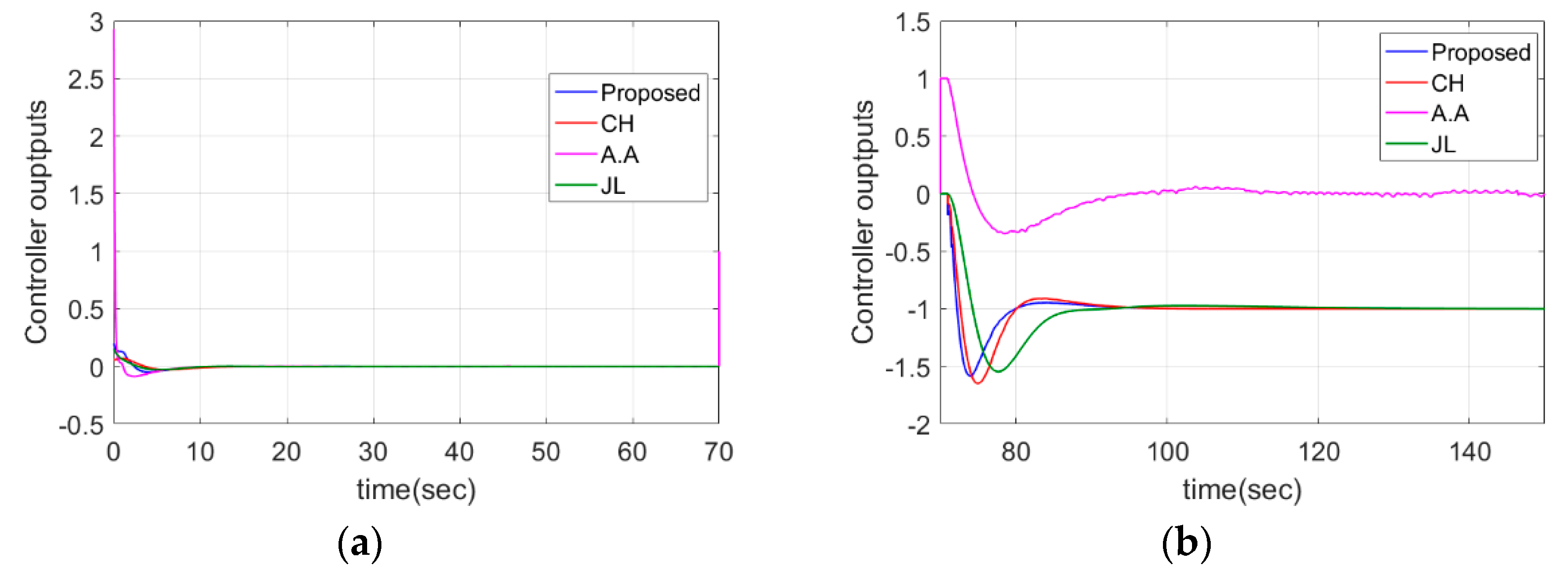
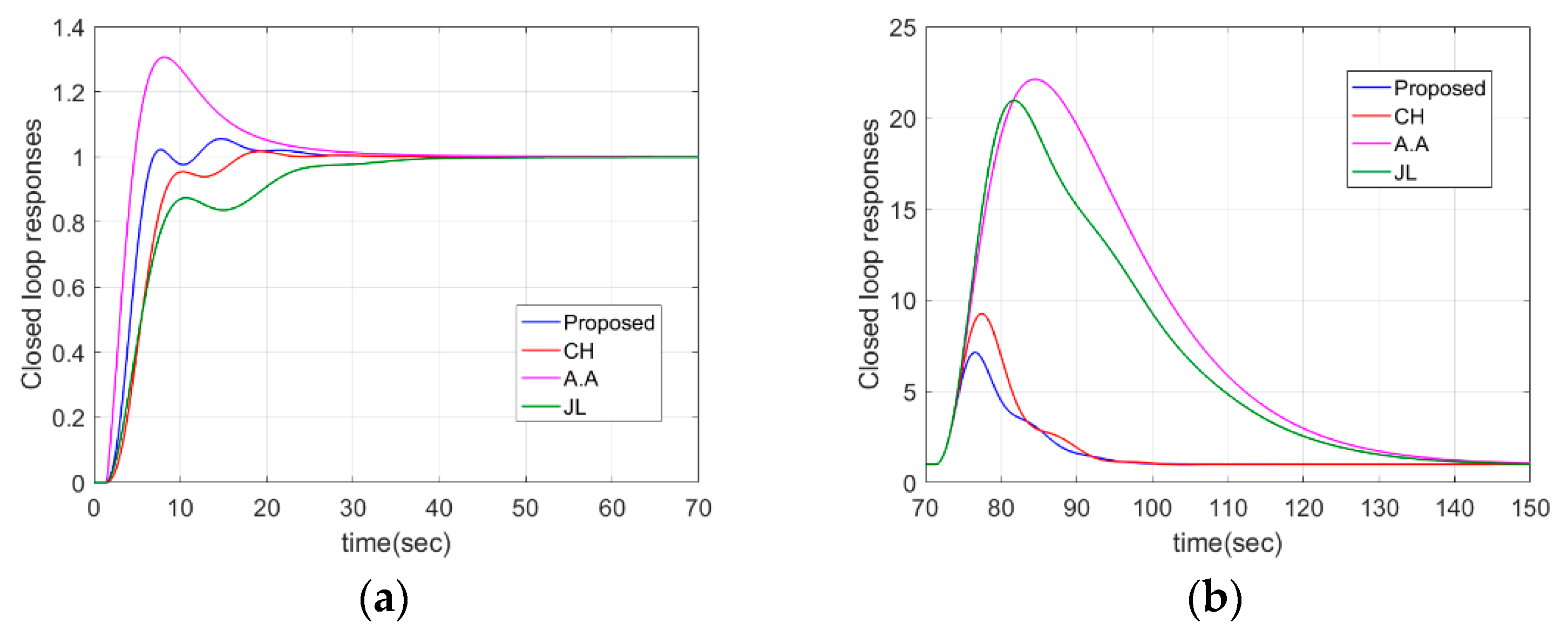
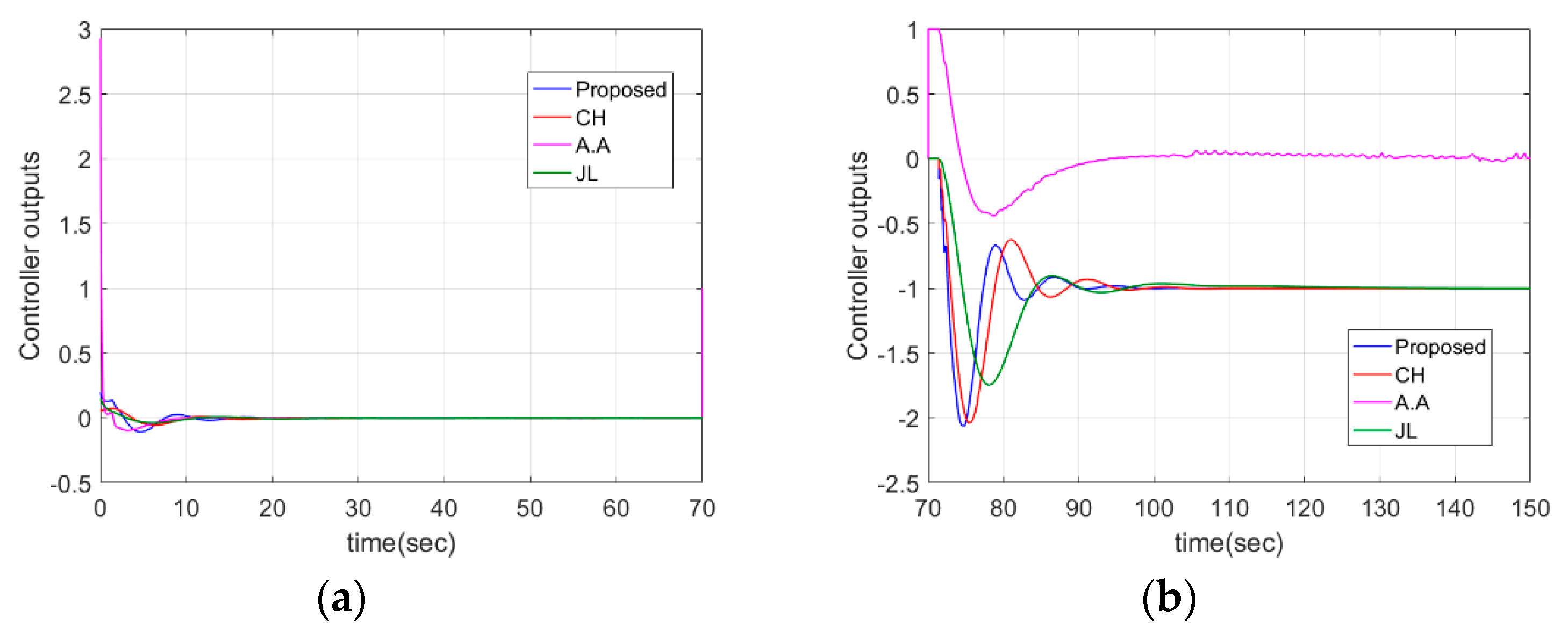
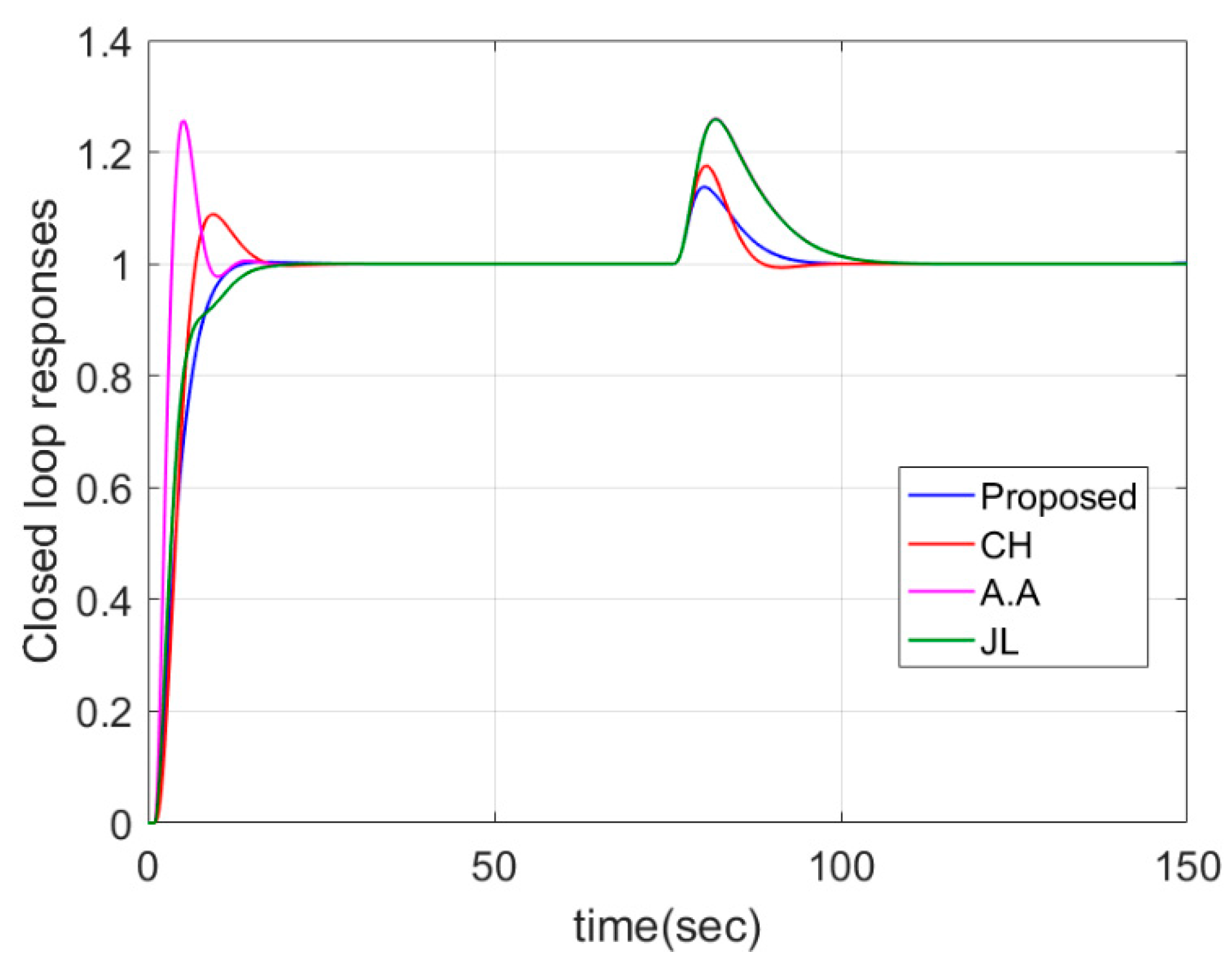
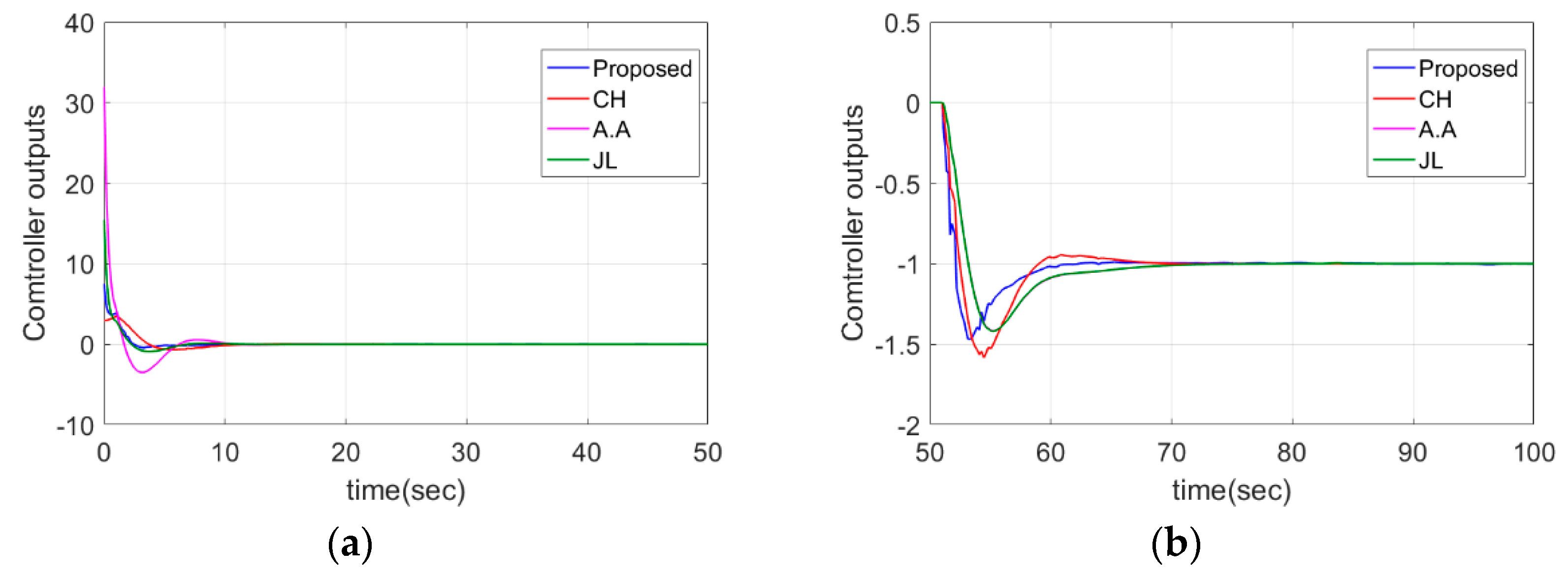
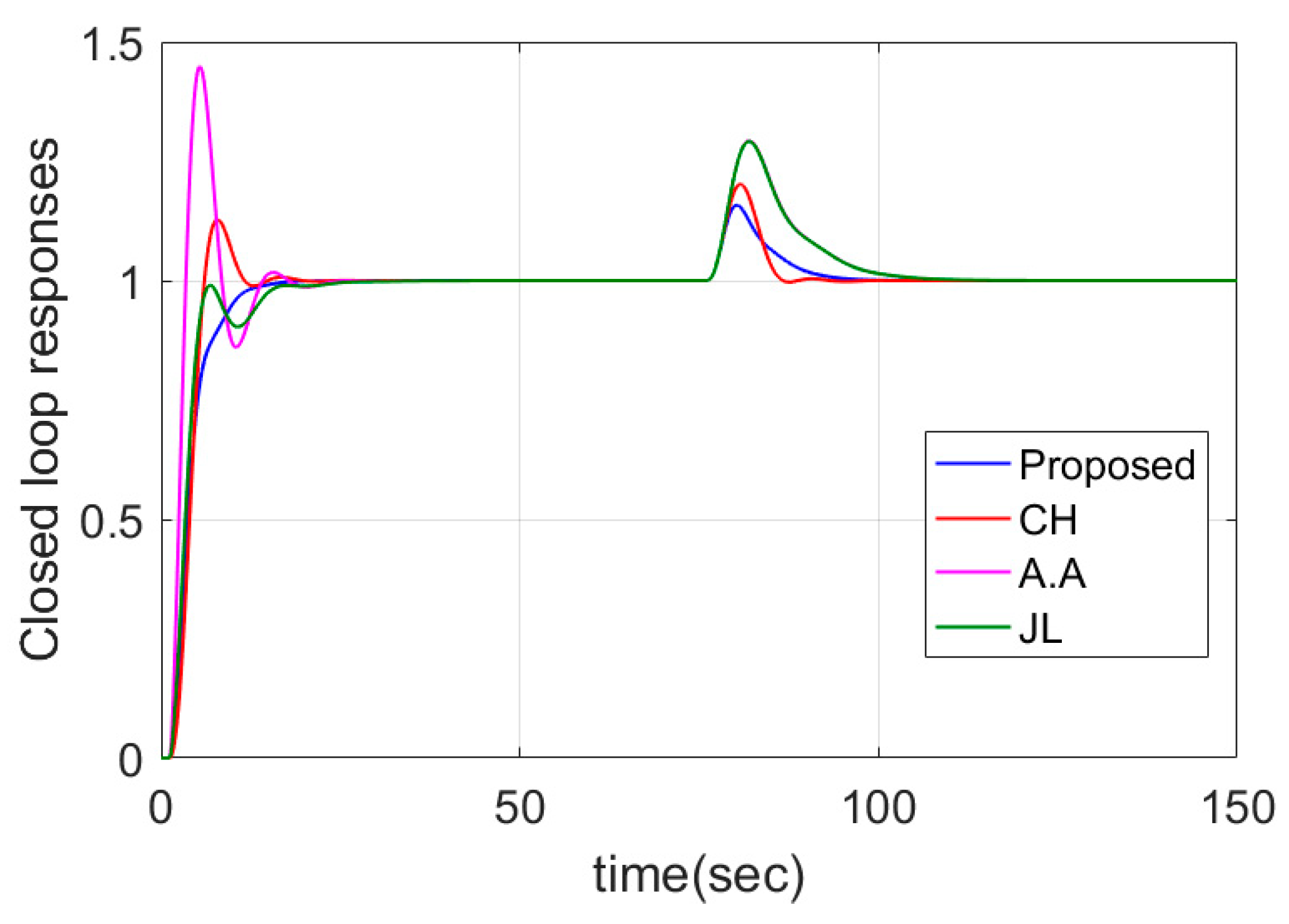
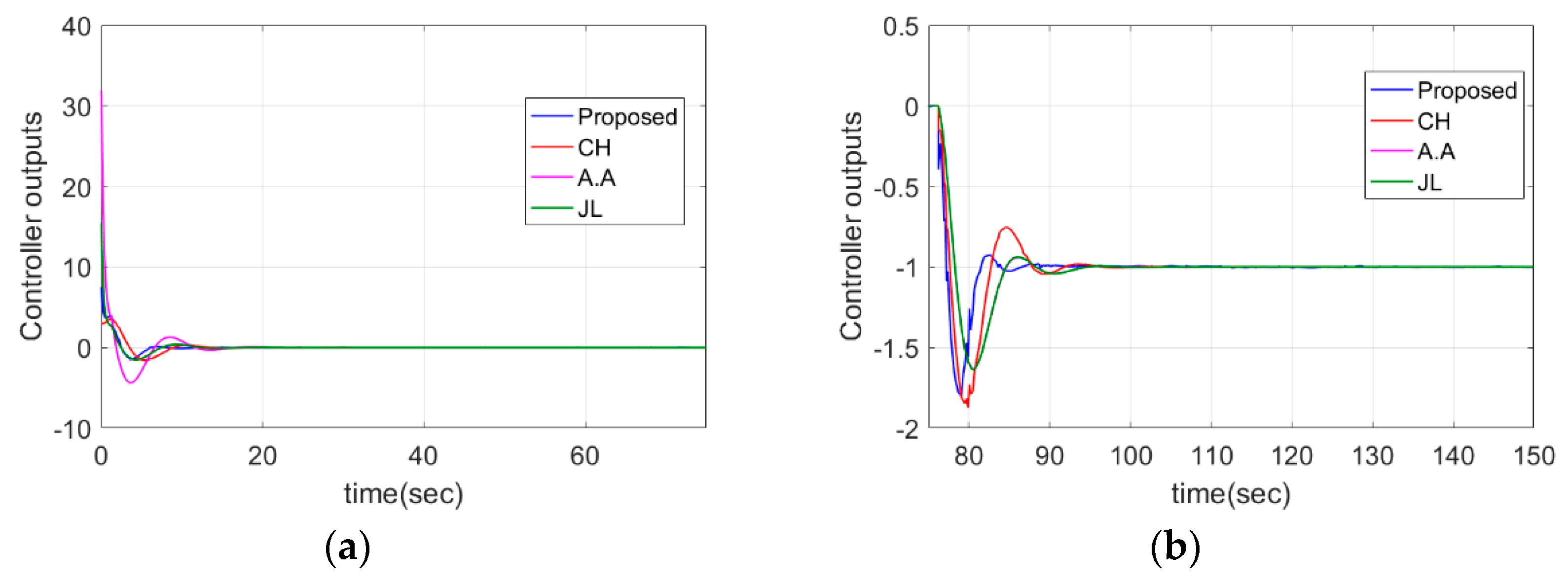



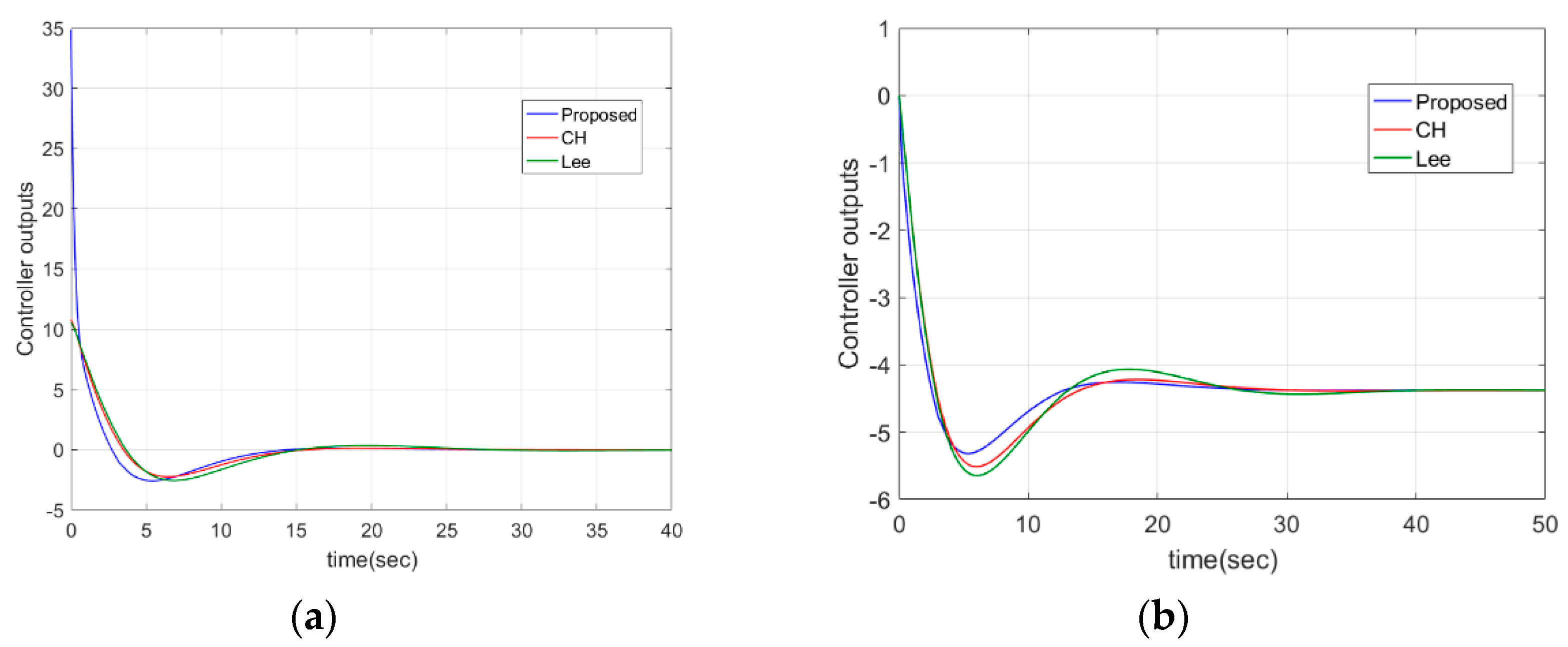
| Process | Controller | PID Parameters with Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Controller | PID Parameters with Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Transfer Function | Method | τi | τd | kc | α | β | Ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1: | Proposed | 21.4 | 2.1493 | 3.6627 | - | - | 2 |
| V.V a | 18.66 | 1.3200 | 3.1400 | - | - | 2 | |
| A.A | 20.575 | 1.7705 | 3.3209 | - | - | 2 | |
| CH | 18.94 | 1.89 | 3.727 | - | - | 2 | |
| Case 2: | Proposed | 9.5912 | 3.5403 | 0.1768 | 0.4967 | 0.2638 | 2 |
| CH | 9.7264 | 3.8211 | 0.1378 | 1.0761 | 1.0392 | 2 | |
| JL b | 21.281 | 7.2550 | 0.0460 | - | - | 2 | |
| A.A | 22.48 | 7.8415 | 0.0414 | - | - | 2 | |
| Case 3: | Proposed | 7.4369 | 2.035 | 6.6735 | 0.4937 | 0.176 | 2 |
| CH | 5.9046 | 1.9519 | 5.7422 | 0.6320 | 0.4915 | 2 | |
| A.A | 10.4221 | 2,4769 | 3.67 | - | - | 2 | |
| JL c | 10.392 | 2.4730 | 3.6860 | - | - | 1.998 | |
| Case 4: | Proposed d | 5.6594 | 1.2956 | 1.2179 | - | - | 2.350 |
| CH e | 5.1536 | 1.2458 | 1.1601 | - | - | 2.350 | |
| Case 5: | Proposed | 7.1991 | 0.6422 | 0.9684 | 1.0399 | 0.2098 | 2.81 |
| JL f | 8.6980 | 1.1200 | 0.9700 | - | - | 2.81 | |
| CH | 6.3792 | 0.6573 | 1.0030 | 1.1608 | 0.549 | 2.81 | |
| Case 6: | Proposed | 8.5000 | 2.8034 | 3.0021 | 0.5000 | 0.2153 | 2 |
| CH | 2.1307 | 8.9775 | 3.1033 | 1.0119 | 1 | 2 | |
| Lee | 2.1171 | 6.3630 | 3.1860 | - | - | 2 |
| Transfer Function | Method | Servo Problem | Regulation Problem | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAE | TV | OS | IAE | TV | OS | ||
| Case 1: | Proposed | 12.84 | 3.81 | 0 | 5.79 | 2.00 | 0.3 |
| CH | 11.42 | 3.89 | 0.00 | 5.07 | 2.02 | 0.31 | |
| V.V | 11.56 | 3.81 | 0.03 | 5.94 | 1.90 | 0.34 | |
| A.A | 7.15 | 36.58 | 0.07 | 6.17 | 2.78 | 0.32 | |
| Case 2: | Proposed | 5.81 | 0.21 | 0 | 54.30 | 3.75 | 5.17 |
| CH | 5.98 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 70.76 | 2.54 | 7.06 | |
| A.A | 5.46 | 3.16 | 0.22 | 541.19 | 3.10 | 20.27 | |
| JL | 7.76 | 0.22 | 0 | 486.06 | 2.15 | 18.66 | |
| Case 3: | Proposed | 4.52 | 20.56 | 0.00 | 1.12 | 2.82 | 0.14 |
| CH | 4.51 | 9.92 | 0.089 | 1.10 | 2.35 | 0.17 | |
| A.A | 3.13 | 40.21 | 0.256 | 2.84 | 1.85 | 0.26 | |
| JL | 4.13 | 17.54 | 0.00 | 2.83 | 1.86 | 0.26 | |
| Case 4: | Proposed | 4.05 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 13.66 | 2.05 | 4.67 |
| CH | 4.34 | 0.40 | 0.52 | 17.04 | 2.22 | 5.03 | |
| Case 5: | Proposed | 4.43 | 3.45 | 0.01 | 7.53 | 3.06 | 0.97 |
| CH | 4.10 | 1.67 | 0.02 | 6.51 | 2.75 | 1.07 | |
| JL | 4.68 | 3.20 | 0.00 | 9.03 | 2.57 | 1.15 | |
| Transfer Function | Method | Servo Problem | Regulation Problem | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAE | TV | OS | IAE | TV | OS | ||
| Case 1: Time delay +40% | Proposed | 14.95 | 7.57 | 0.12 | 6.08 | 4.20 | 0.39 |
| CH | 16.95 | 9.27 | 0.25 | 6.79 | 4.97 | 0.40 | |
| V.V | 18.53 | 7.81 | 0.30 | 8.49 | 4.13 | 0.44 | |
| A.A | 15.28 | 42.61 | 0.41 | 6.79 | 4.96 | 0.42 | |
| Case2: Time delay +40% | Proposed | 4.70 | 0.56 | 0.06 | 54.33 | 4.56 | 6.13 |
| CH | 6.03 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 70.86 | 4.16 | 8.25 | |
| A.A | 6.04 | 3.22 | 0.31 | 542.56 | 4.63 | 21.12 | |
| JL | 7.76 | 0.25 | 0 | 462.71 | 2.83 | 19.98 | |
| Case3: parameters +20% | Proposed | 4.46 | 16.52 | 0 | 1.11 | 3.98 | 0.16 |
| CH | 4.41 | 10.03 | 0.13 | 1.05 | 3.34 | 0.20 | |
| A.A | 4.40 | 44.14 | 0.45 | 2.84 | 2.49 | 0.29 | |
| JL | 4.13 | 19.48 | 0 | 2.83 | 2.51 | 0.29 | |
| Case 4: parameters +20% | Proposed | 4.37 | 0.53 | 0.60 | 17.36 | 3.47 | 5.50 |
| CH | 5.08 | 0.66 | 0.82 | 25.68 | 4.34 | 5.87 | |
| Case 5: parameters +20% | Proposed | 4.58 | 5.39 | 0.05 | 7.58 | 6.00 | 1.35 |
| CH | 5.97 | 4.83 | 0.21 | 8.31 | 8.12 | 1.47 | |
| JL | 5.65 | 5.35 | 0.10 | 9.96 | 7.10 | 1.56 | |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Volume, V | 50 m3 |
| Feed flow rate, F | 5 m3/s |
| Feed temperature, TF | 580 K |
| Feed concentration, CAF | 15.61 K mol/m3 |
| Heat transfer coefficient, hA | 2600 kJ/(min K) |
| Specific heat, Cp | 1.8 kJ/(kg K) |
| Heat of reaction, −ΔH | 20,000 kJ/kmol |
| Universal gas law constant, R | 8.314 kJ/(kmol K) |
| Activation energy, E | 80,000 kJ/kmol |
| Frequency factor, k | 680,000 min−1 |
| Density, ρ | 800 kg/m3 |
| Temperature, Tc | 401.6 K |
| Transfer Function | Method | Servo Problem | Regulation Problem | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAE | TV | OS | IAE | TV | OS | ||
| Proposed | 5.79 | 10.95 | 0.32 | 2.83 | 2.95 | 0.30 | |
| CH | 6.99 | 4.94 | 0.43 | 4.22 | 3.32 | 0.46 | |
| Lee | 7.63 | 5.45 | 0.55 | 3.70 | 3.57 | 0.45 | |
| parameters +20% | Proposed | 5.96 | 13.79 | 0.37 | 2.83 | 3.55 | 0.34 |
| CH | 7.18 | 6.57 | 0.52 | 4.22 | 3.97 | 0.51 | |
| Lee | 7.67 | 6.83 | 0.65 | 3.54 | 4.13 | 0.50 | |
| Method | For Step Change of Operating Temperature from 590 to 595 K | For Load Change of Feed Concentration from 15.61 to 20 K mol/m3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IAE | TV | OS | IAE | TV | OS | |
| Proposed | 26.62 | 40.36 | 0.0024 | 12.41 | 6.51 | 1.2 |
| CH | 31.38 | 15.57 | 0.0029 | 18.74 | 6.98 | 1.7 |
| Lee | 34.20 | 16.55 | 0.0036 | 16.69 | 7.67 | 1.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Cui, Y.; Ding, X. An Improved Analytical Tuning Rule of a Robust PID Controller for Integrating Systems with Time Delay Based on the Multiple Dominant Pole-Placement Method. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091449
Zhang W, Cui Y, Ding X. An Improved Analytical Tuning Rule of a Robust PID Controller for Integrating Systems with Time Delay Based on the Multiple Dominant Pole-Placement Method. Symmetry. 2020; 12(9):1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091449
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wei, Yue Cui, and Xiangxin Ding. 2020. "An Improved Analytical Tuning Rule of a Robust PID Controller for Integrating Systems with Time Delay Based on the Multiple Dominant Pole-Placement Method" Symmetry 12, no. 9: 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091449
APA StyleZhang, W., Cui, Y., & Ding, X. (2020). An Improved Analytical Tuning Rule of a Robust PID Controller for Integrating Systems with Time Delay Based on the Multiple Dominant Pole-Placement Method. Symmetry, 12(9), 1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091449





