Application of a Novel Automatic Method for Determining the Bilateral Symmetry Midline of the Facial Skeleton Based on Invariant Moments
Abstract
1. Introduction
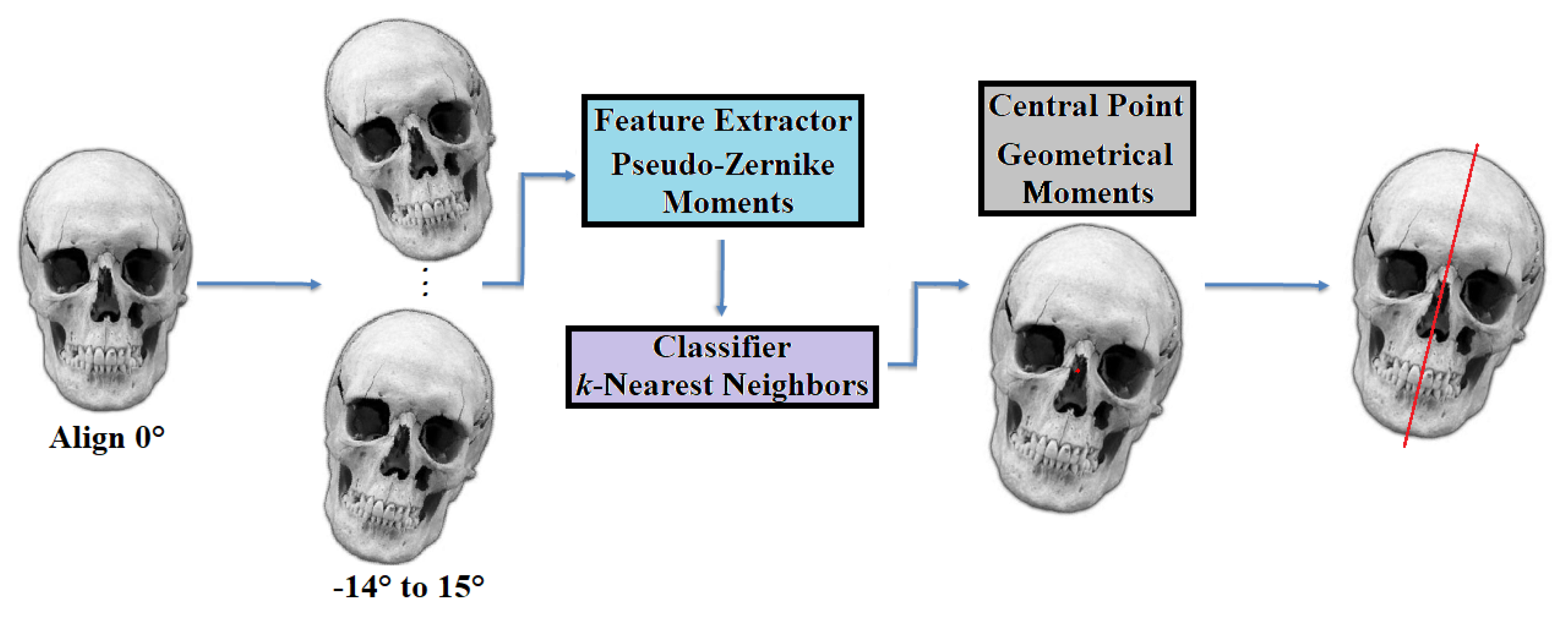
2. Materials and Methods
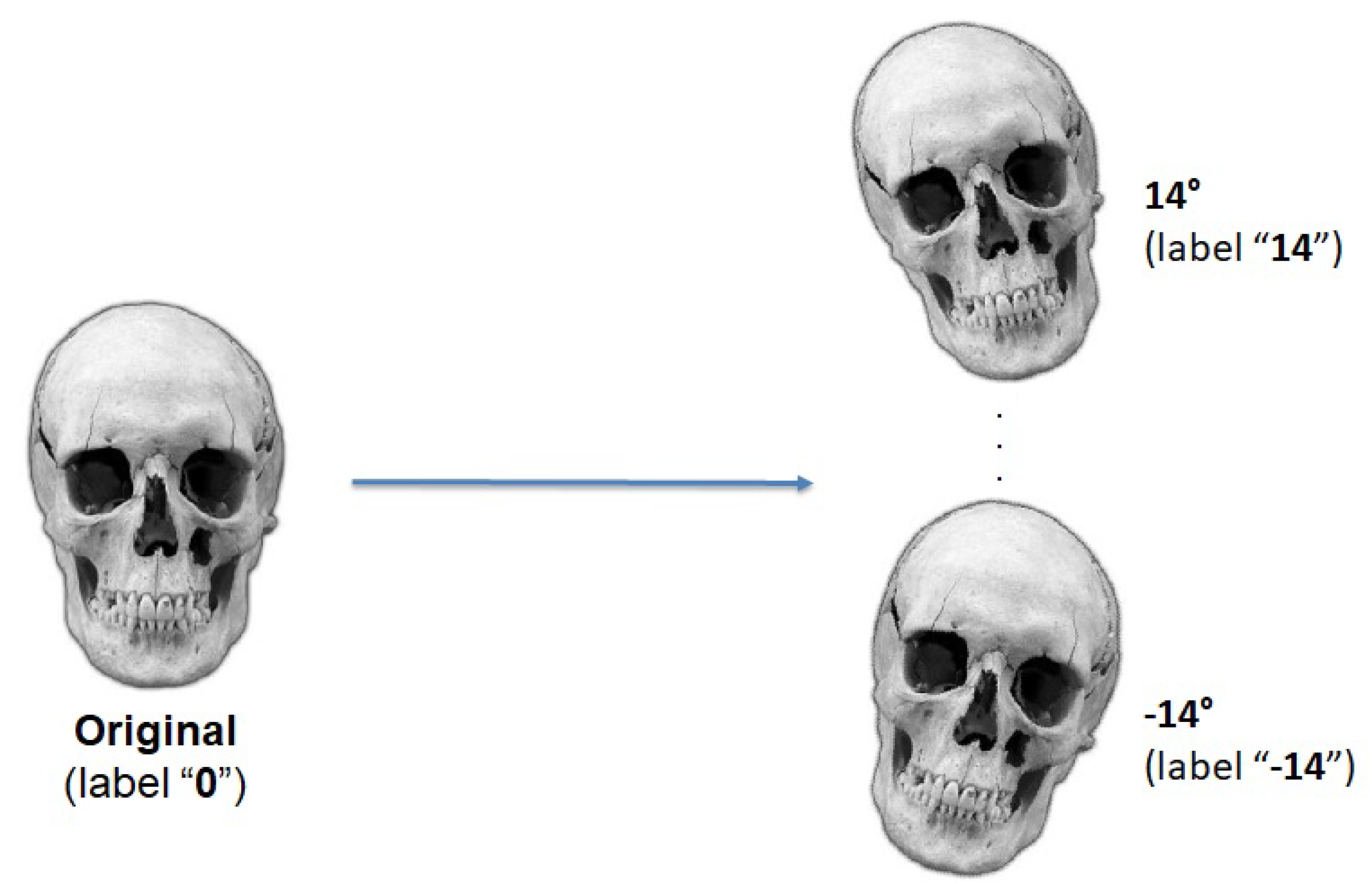
2.1. Image Creation
2.2. Feature Extractors
2.2.1. Pseudo-Zernike Moments-PZMs
2.2.2. Independent Component Analysis—ICA
2.2.3. Principal Component Analysis—PCA
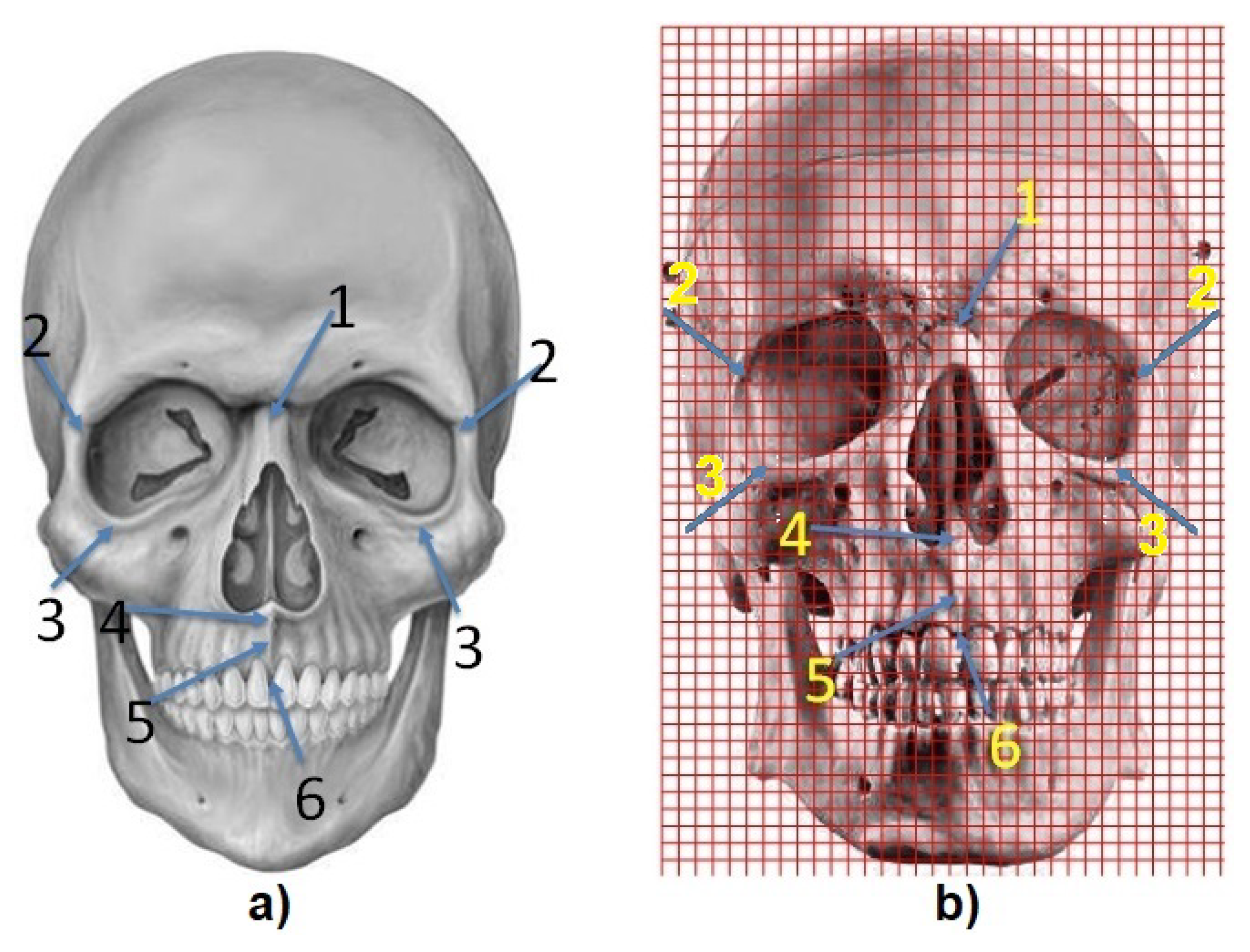
2.3. Geometric Moments—Central Point
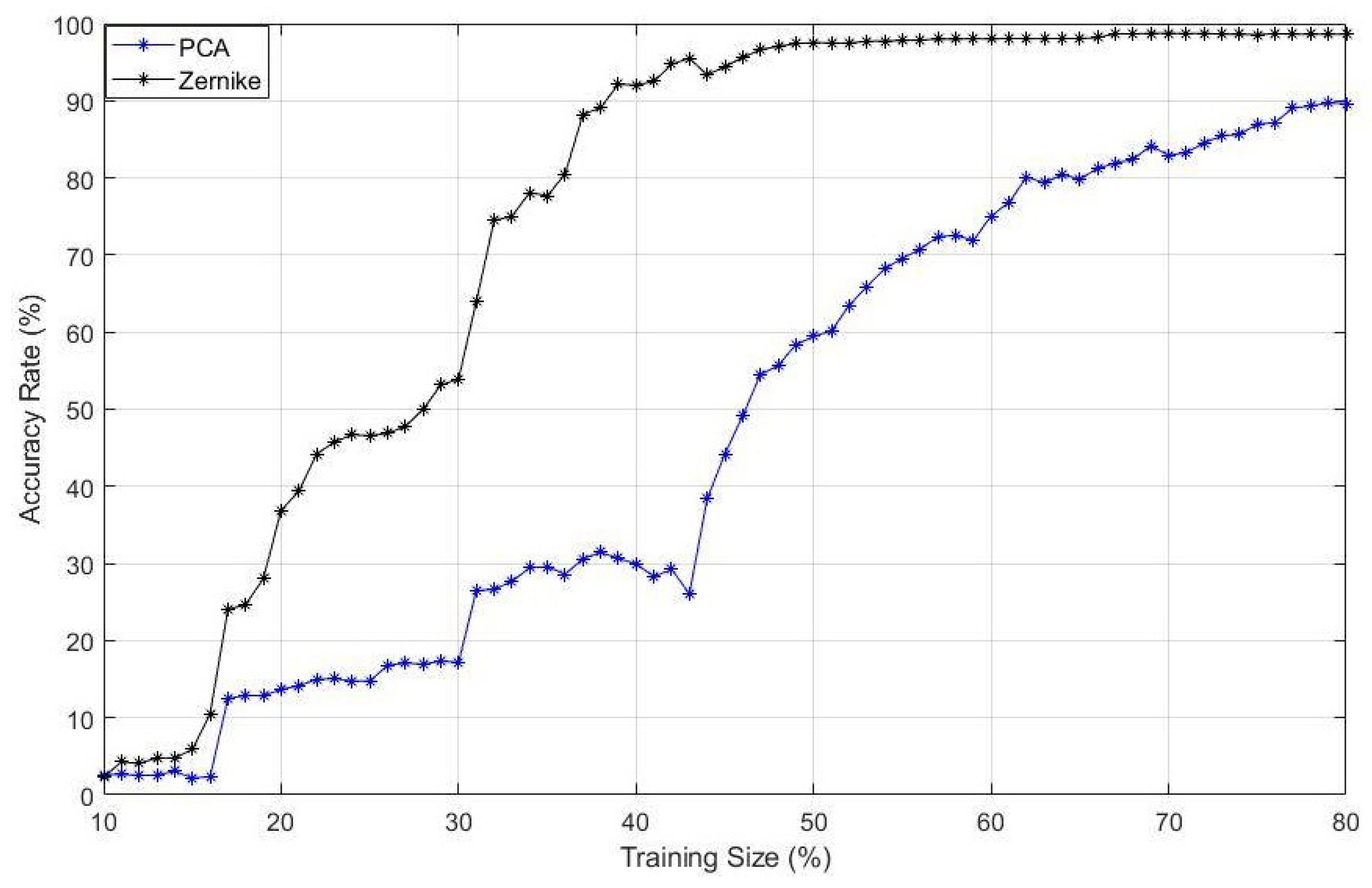
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Classification
3.2. Midpoint Calculation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosure Statement
References
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, S.; Chang, X.; Wu, L.; Ding, Y. Threedimensional analysis of craniofacial asymmetry and integrated, modular organization of human head. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 101, 1424–11431. [Google Scholar]
- Romanet, I.; Graillon, N.; Roux, M.K.L.; Guyot, L.; Chossegros, C.; Boutray, M.D.; Foletti, J.M. Hooliganism and maxillofacial trauma: The surgeon should be warned. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 120, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyot, L.; Saint-Pierre, F.; Bellot-Samson, V.; Chikhani, L.; Garmi, R.; Haen, P.; Jammet, P.; Meningaud, J.P.; Savant, J.; Thomassin, J.M.; et al. Facial surgery for cosmeti purposes: Practice guidelines. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 120, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, M.; Klausing, A.; Junger, M.; Luchters, G. The self-defining axis of symmetry: A new method to determine optimal symmetry and its application and limitation in craniofacial surgery. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Fac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damstra, J.; Fourie, Z.; De Wit, M. A three-dimensional comparison of a morphometric and conventional cephalometric midsagittal planes for craniofacial asymmetry. Clin. Oral Investig. 2012, 16, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Baik, J.; Park, J.; Chae, H.; Huh, K. Determination of midsagittal plane for evaluation of facial asymmetry using three-dimensional computer tomography. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2011, 41, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, G.; Willing, R.; Neuert, M.; Ahluwali, R.; Jenkyn, T.; Yazdani, A. Application of a novel semi-automatic technique for determining the bilateral symmetry plane of the facial skeleton of normal adult males. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2015, 26, 1997–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Momi, E.; Chapuis, J.; Pappas, I.; Ferrigno, G.; Hallermann, W.; Schramm, A.; Caversaccio, M. Automatic extraction of the mid-facial plane for cranio-maxillofacial surgery planning. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willing, R.; Roumeliotis, G.; Jenkyn, T.; Yazdani, A. Development and evaluation of a semi-automatic technique for determining the bilateral symmetry plane of the facial skeleton. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Razdan, A.; Farin, G.; Femiani, J.; Bae, M.; Lockwood, C. 3d face authentication and recognition based on bilateral symmetry analysis. Vis. Comput. 2006, 22, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, L.D.; Stefano, P.D.; Governi, L.; Marzola, A.; Volpe, Y. A robust and automatic method for the best symmetry plane detection of craniofacial skeletons. Symmetry 2019, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, L.D.; Stefano, P.D. A Computational Method for Bilateral Symmetry Recognition in Asymmetrically Scanned Human Faces. Comput.-Aided Des. Appl. 2014, 11, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, S.; Singh, M.; Jain, A.; Singh, R.; Vatsa, M.; Noore, A. On Matching Skulls to Digital Face Images: A Preliminary Approach. CoRR abs/1710.02866. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.02866. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1710.02866 (accessed on 1 August 2018).
- Teague, M. Image analysis via the general theory of moments. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1980, 70, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Walia, E.; Pooja, U.R. Analysis of algorithms for fast computation of pseudo zernike moments and their numerical stability. Digit. Signal Process. 2012, 22, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee-Way, C.; Raveendran, P.; Ramakrishnan, M. An effcient algorithm for fast computation of pseudo-zernike moments. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2011, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Singh, C. Automatic cephalometric landmark detection using zernike moments and template matching. Signal Image Video Process. 2013, 9, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams-Baboli, A.; Ezoji, M. A zernike moment based method for classification of alzheimer’s disease from structural mri. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, Faro, Portugal, 20–23 June 2017; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashar, A. Detection of alzheimer disease using zernike moments. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2017, 8, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; Phillips, P.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Alzheimer’s disease detection by pseudo-zernike moment and linear regression classification. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, B.; Latha, M.; Mohan, P.; Reddy, V. Medical image retrieval using moments. Int. J. Appl. Innov. Eng. Manag. 2013, 2, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iscan, Z.; Dokur, Z.; Olmez, T. Tumor detection by using zernike moments on segmented magnetic resonance brain images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapaliya, K.; Kwon, G. Identification and extraction of brain tumor from mri using local statistics of zernike moments. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2014, 24, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallasivan, G.; Janakiraman, S. Detection and classification of brain tumors as benign and malignant using mri scan images and zernike moment feature set with som. J. Comp. Sci. 2016, 10, 24–36. [Google Scholar]
- Akkoca, B.; Gökmen, M. Facial expression recognition using local zernike moments. In Proceedings of the 21st Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference, Haspolat, Turkey, 24–26 April 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, M.; Azimifar, Z.; Boostani, R. Facial age estimation using zernike moments and multi-layer perception. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, London, UK, 23–25 August 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathika, N.; Suresh, P.; Sakthieswaran, N. Face recognition using zernike moments with illumination variations. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2017, 25, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, E.; Gokmen, M.; Kamasak, M. An efficient multiscale scheme using local zernike moments for face recognition. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.D.C.; Thé, G.A.P.; de Medeiros, F.N.S. Geometrical and statistical feature extraction of images for rotation invariant classification systems based on industrial devices. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Automation and Computing (ICAC), Glasgow, UK, 11–12 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawi, M.S. Fast computation of pseudo zernike moments. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2010, 8, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvarinen, A.; Karhunen, J.; Oja, E. Independent Component Analysis; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 1933, 24, 417–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I. Principal Component Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Ni, R.; Zhu, Z. RST transforms resistant image watermarking based on centroid and sector-shaped partition. Sci. China Inform. Sci. 2012, 55, 650–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.; Velho, L.; Carvalho, P. Image moments-based structuring and tracking of objects. In Proceedings of the XV Brazilian Symposium on Computer Graphics and Image Processing, Fortaleza Ce, Brazil, 7–10 October 2002; pp. 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercimek, M.; Gulez, K.; Mumcu, T.V. Real object recognition using moment invariants. Sadhana 2005, 30, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, H. Geometric Moments Invariants. Pattern Recognit. 2008, 41, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.D.C.; Thé, G.A.P.; de Medeiros, F.N.S. Rotation-invariant image description from independent component analysis for classification purposes. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO), Colmar, France, 21–23 July 2015; pp. 210–216. [Google Scholar]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dalvit Carvalho da Silva, R.; Richard Jenkyn, T.; Alexander Carranza, V. Application of a Novel Automatic Method for Determining the Bilateral Symmetry Midline of the Facial Skeleton Based on Invariant Moments. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091448
Dalvit Carvalho da Silva R, Richard Jenkyn T, Alexander Carranza V. Application of a Novel Automatic Method for Determining the Bilateral Symmetry Midline of the Facial Skeleton Based on Invariant Moments. Symmetry. 2020; 12(9):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091448
Chicago/Turabian StyleDalvit Carvalho da Silva, Rodrigo, Thomas Richard Jenkyn, and Victor Alexander Carranza. 2020. "Application of a Novel Automatic Method for Determining the Bilateral Symmetry Midline of the Facial Skeleton Based on Invariant Moments" Symmetry 12, no. 9: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091448
APA StyleDalvit Carvalho da Silva, R., Richard Jenkyn, T., & Alexander Carranza, V. (2020). Application of a Novel Automatic Method for Determining the Bilateral Symmetry Midline of the Facial Skeleton Based on Invariant Moments. Symmetry, 12(9), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12091448





