Symmetric Potentiometric Cells for the Measurement of Unified pH Values
Abstract
1. Introduction
LJP1 LJP2
LJP

2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Ideal Symmetrical Conditions
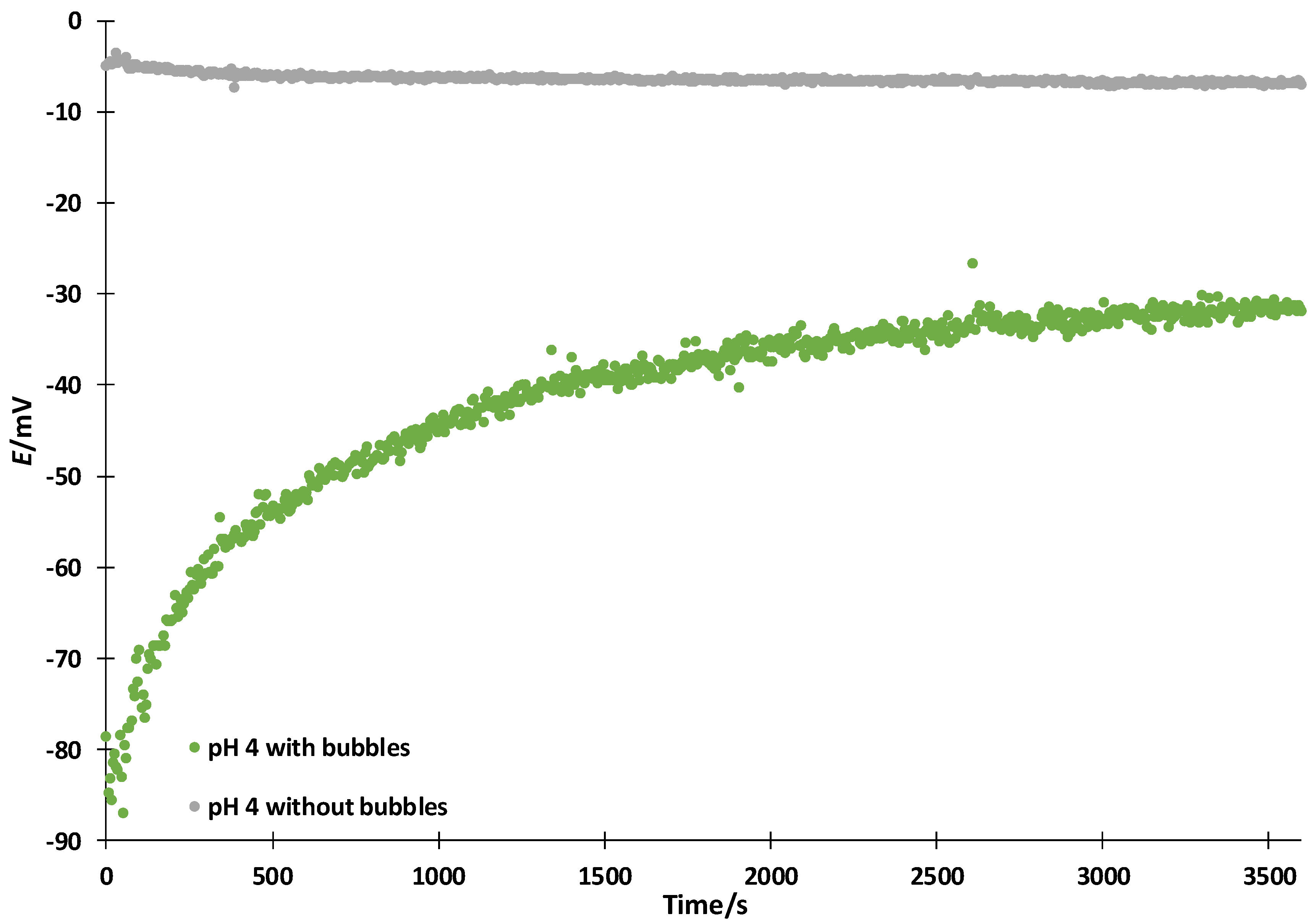
3.2. Influence of the Bubbles
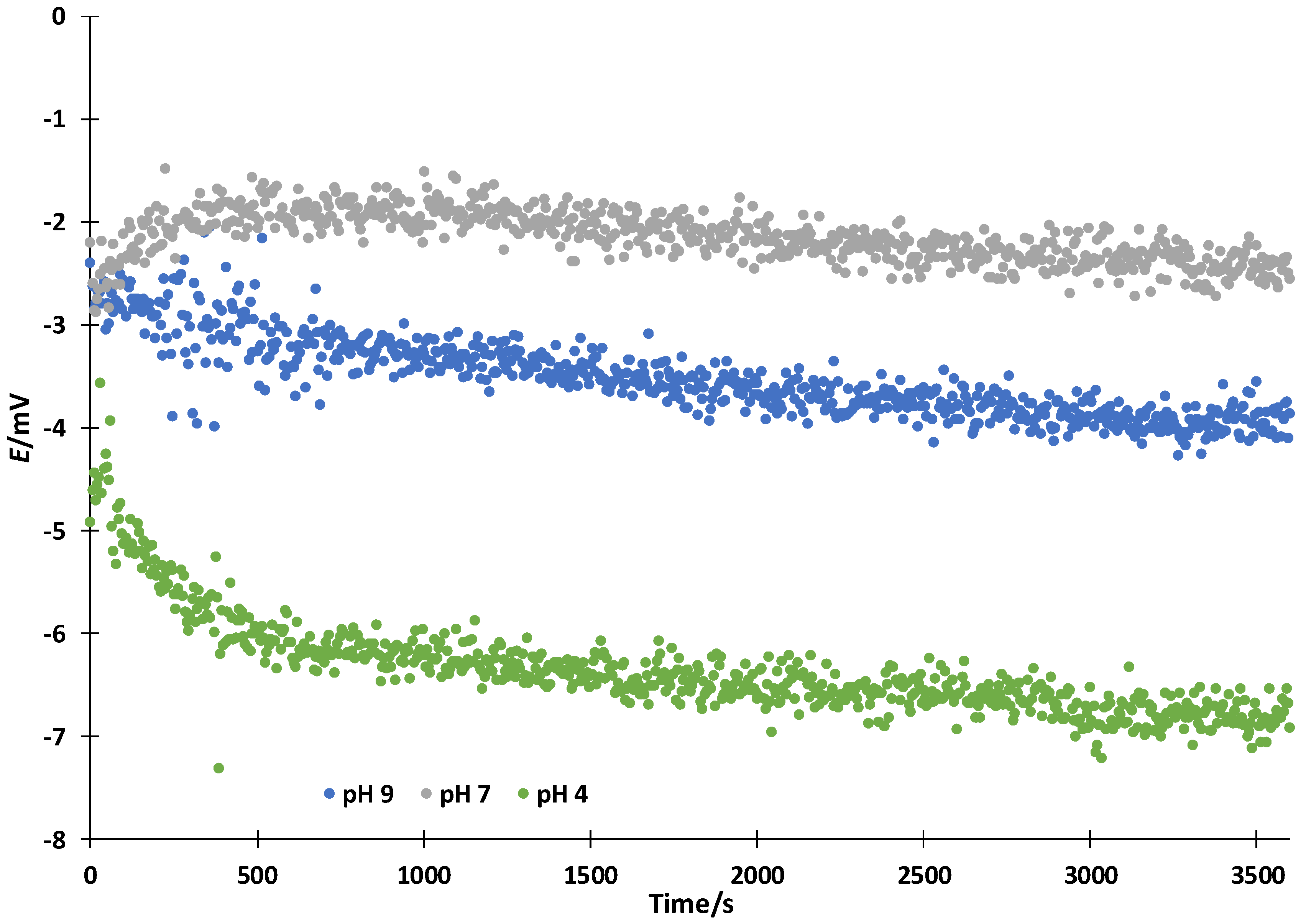
3.3. Influence of the Instrument Used to Measure the Potential Difference: Potentiostat vs. pH Meter
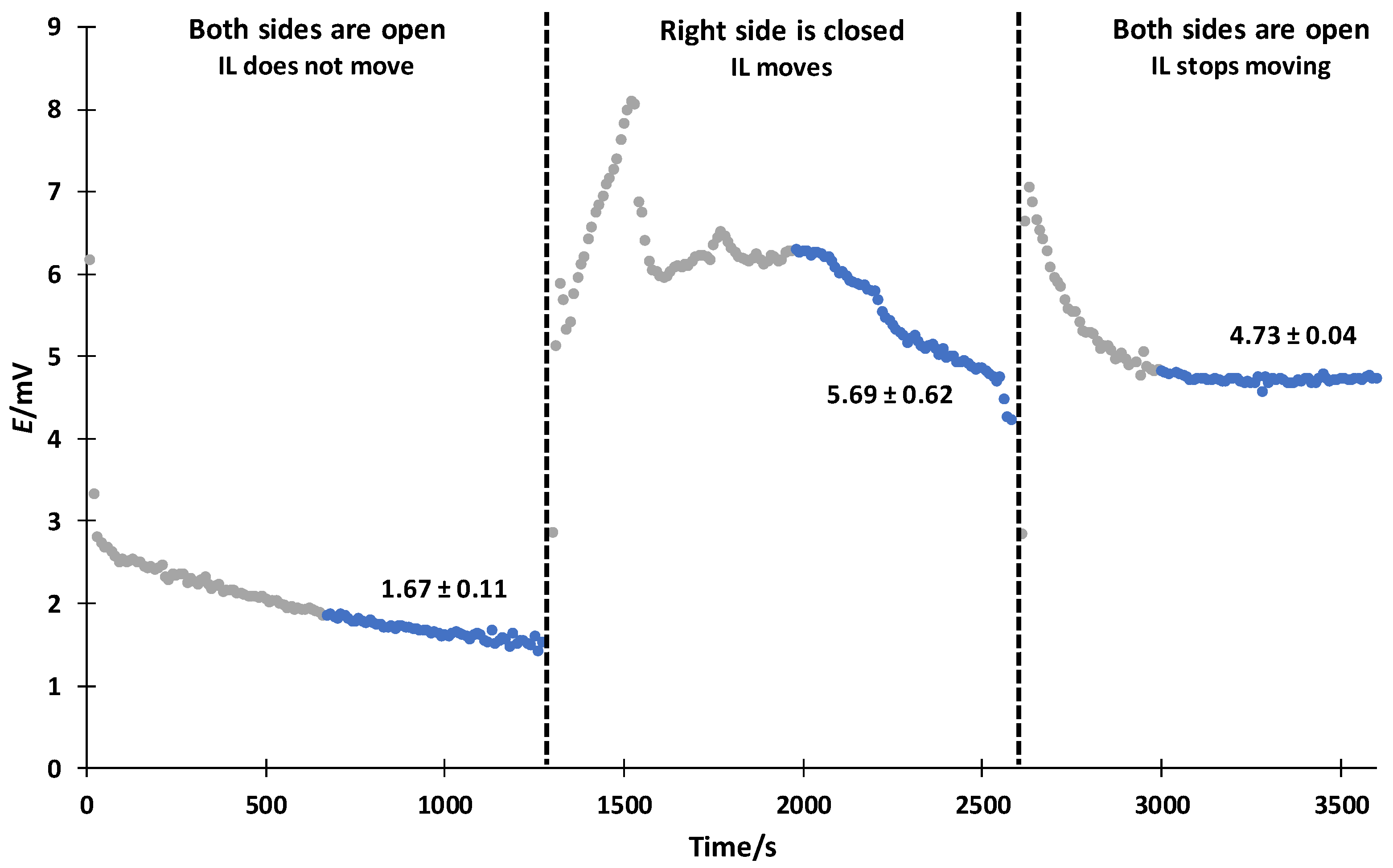
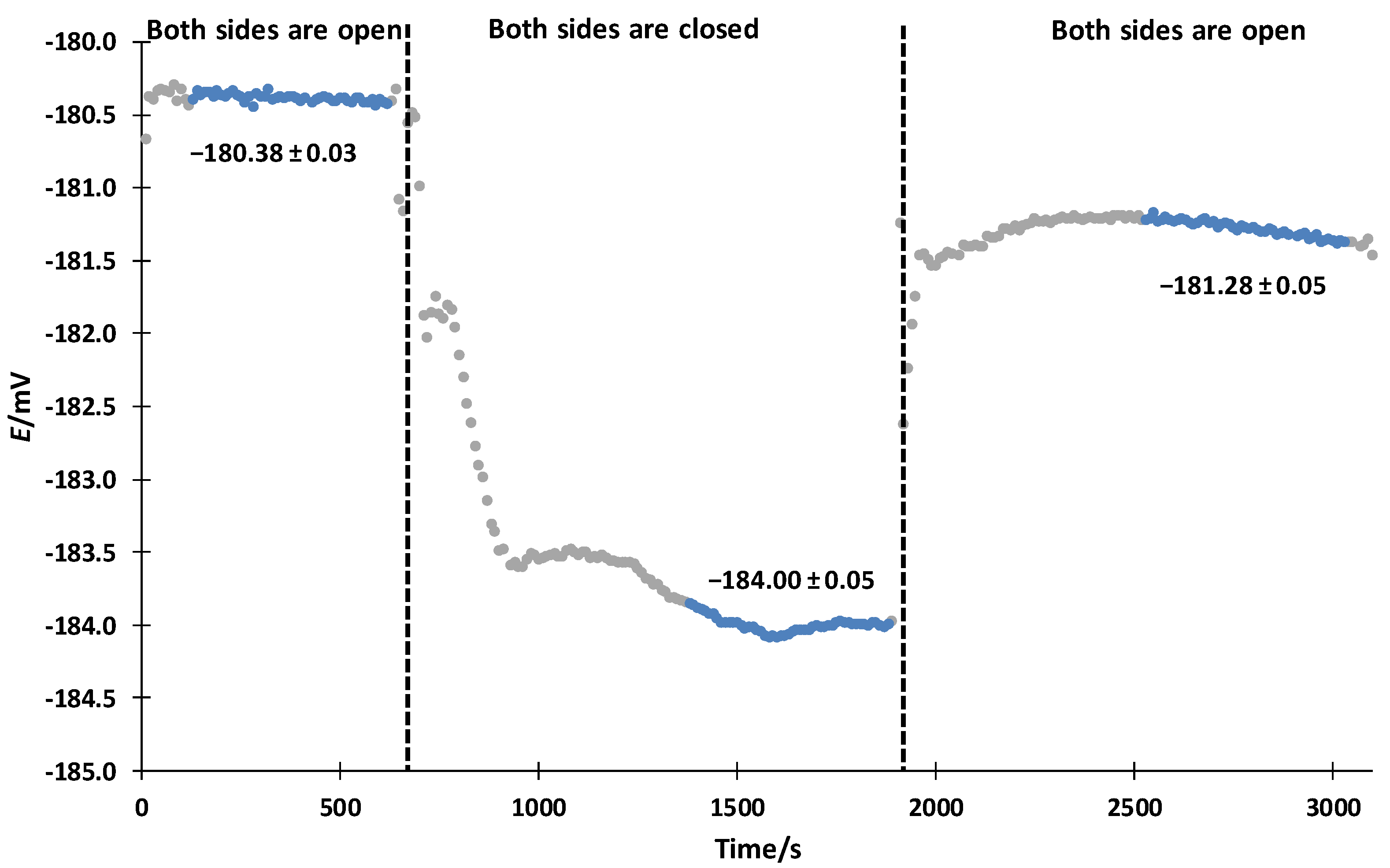
3.4. Influence of the Pressure and IL Movement within the Cell
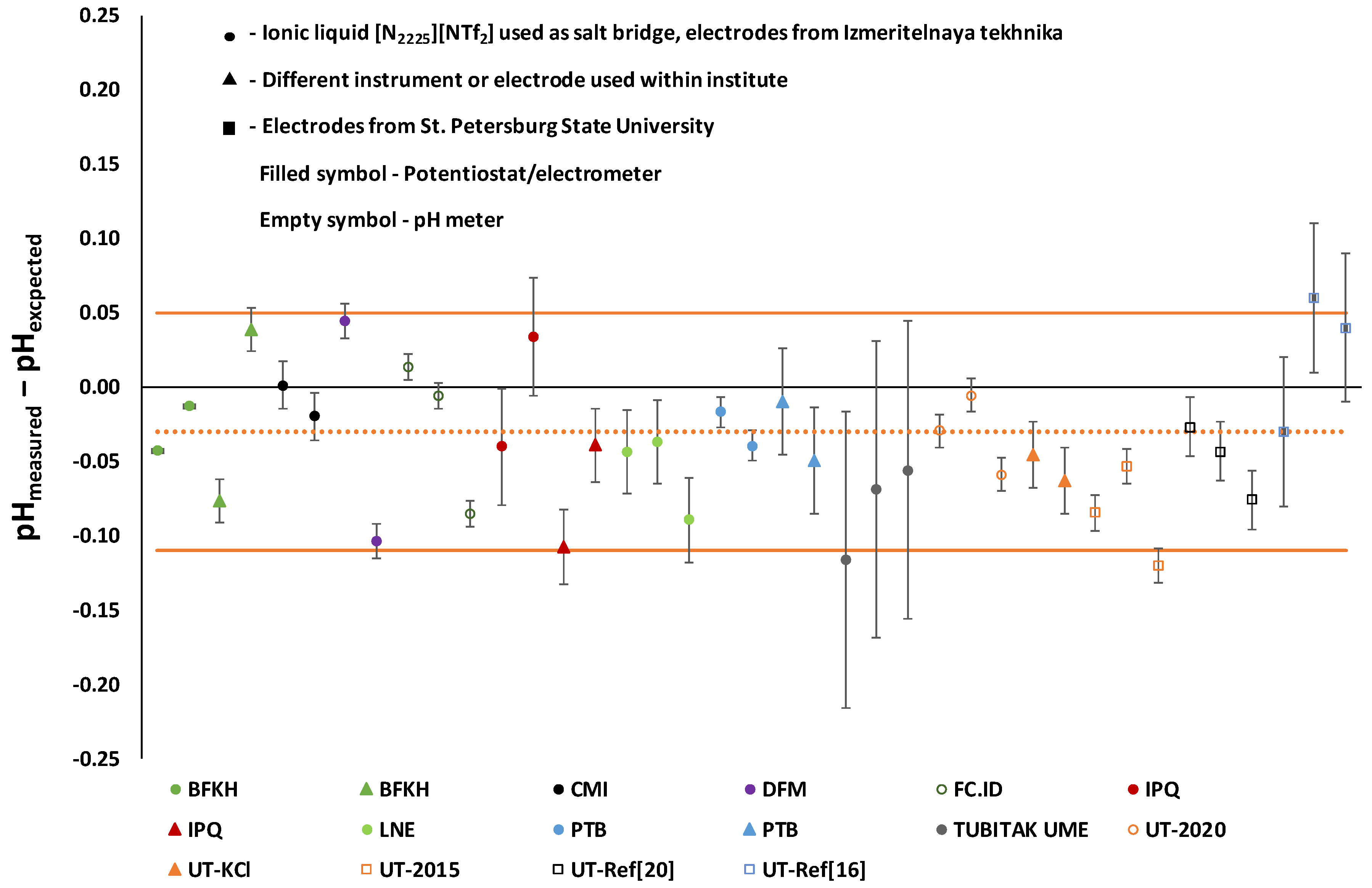
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Measurement Procedures Used
| [16] | [20] | 2015 | 2018 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Device | Metrohm | Metrohm | Metrohm | Gamry | Metrohm |
| calibration of device | No | no | no | yes | no |
| electrodes from | St. Petersburg State University | St. Petersburg State University | St. Petersburg State University | Izmeritelnaya tekhnika | Izmeritelnaya tekhnika |
| glass cell | Figure 1A, in-house | Figure 1B, in-house | Figure 1C, same as in [21], in-house | Figure 1D, in-house | Figure 1E, Rettberg |
| salt bridge position | Above | above | below | below | below |
| Faraday cage | from Al foil | from Al foil | from Al foil | Gamry VistaShield™ | Gamry VistaShield™ |
| auxiliary electrode | separate Pt electrode | Pt wire soldered into capillary | Pt wire soldered into capillary | none | separate Pt wire inserted from side port |
| thermostated | Room | room | room | solution compartments | whole cell |
| salt bridge electrolyte | saturated KCl | saturated KCl | [N2225][NTf2] | saturated KCl | [N2225][NTf2] |
| pre-soaking (30 min) | No | no | no | yes | yes |
| duration of meas. | 15 min | 15 min | 15 min | 35 min | 35 min |
| data collection interval | None | none | none | 1 s | 3 s |
| definition of potential | final data point | final data point | final data point | average of last 5 min (301 data points) | average of last 5 min (101 data points) |
| used for minimization | average of four or two potentials with opposite polarities | average of two potentials with opposite polarities | average of two potentials with opposite polarities | single potential | average of two potentials with opposite polarities |
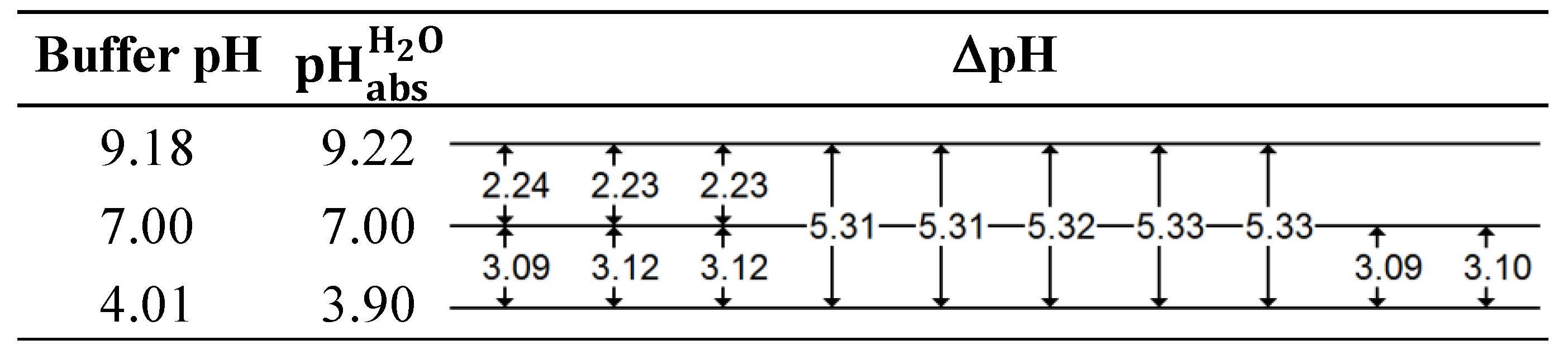
Appendix A.2. Explanation of the “Ladder” Approach
| Electrode | Intercept/mV | Slope/mV | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | −1896.34 | −57.61 | 0.99996 |
| M6 | −1898.39 | −57.08 | 0.99993 |
| System | ΔEmeasured/mV | |
|---|---|---|
| pH 7 vs. pH 4 | −177.00 | 3.09 |
| pH 7 vs. pH 4 | −178.76 | 3.12 |
| pH 7 vs. pH 4 | −179.09 | 3.12 |
| pH 7 vs. pH 4 | −177.11 | 3.09 |
| pH 7 vs. pH 4 | −177.69 | 3.10 |
| pH 9 vs. pH 4 | −304.64 | 5.31 |
| pH 9 vs. pH 4 | −304.30 | 5.31 |
| pH 9 vs. pH 4 | −305.06 | 5.32 |
| pH 9 vs. pH 4 | −305.64 | 5.33 |
| pH 9 vs. pH 4 | −305.67 | 5.33 |
| pH 9 vs. pH 7 | −128.39 | 2.24 |
| pH 9 vs. pH 7 | −127.71 | 2.23 |
| pH 9 vs. pH 7 | −127.78 | 2.23 |
| 9.225 | −0.011 | −0.017 | −0.004 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 0.002 | 0.003 |
| 7.000 | −0.012 | 0.018 | 0.024 | −0.010 | 0.000 | |||
| 3.901 | ||||||||
| Sum of squares = 0.002 | ||||||||
| n = 13 number of measurements | ||||||||
| m = 2 number of assigned values | ||||||||
| s = 0.013 consistency standard deviation | ||||||||
References
- Buck, R.P.; Rondinini, S.; Covington, A.K.; Baucke, F.G.K.; Brett, C.M.A.; Camoes, M.F.; Milton, M.J.T.; Mussini, T.; Naumann, R.; Pratt, K.W.; et al. Measurement of pH. Definition, standards, and procedures. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 2169–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Activity (Relative Activity). Available online: https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.A00115 (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Pingarrón, J.M.; Labuda, J.; Barek, J.; Brett, C.M.A.; Camões, M.F.; Fojta, M.; Hibbert, D.B. Terminology of electrochemical methods of analysis (IUPAC Recommendations 2019). Pure Appl. Chem. 2020, 92, 641–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izutsu, K. Electrochemistry in Nonaqueous Solutions; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mussini, T.; Covington, A. Criteria for standardization of pH measurements in organic solvents and water + organic solvent mixtures of moderate to high permittivities. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondinini, S.; Mussini, P.; Mussini, T. Reference value standards pH measurements in organic solvents and water + organic solvent mixtures of moderate to high permittivities. Pure Appl. Chem. 1987, 59, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.; Sanz-Nebot, V. Assignment of reference pH-values to primary standard buffer solutions for standardization of potentiometric sensors in acetonitrile-water mixtures. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1995, 353, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussini, P.; Mussini, T.; Rondinini, S. Reference value standards and primary standards for pH measurements in D2O and aqueous-organic solvent mixtures: New accessions and assessments. Pure Appl. Chem. 1997, 69, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.; Barron, D.; Marques, I. Assignment of pHS values of reference buffer solutions for standardization of potentiometric sensors in THF-water. Polyhedron 1999, 18, 3361–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, D.; Falciola, L.; Mussini, P.; Mussini, T. Medium effects, comparability and predictability of pH-standards in aqueous+organic solvent mixtures: Behavior of the (ethylene carbonate+water) and (propylene carbonate+water) systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 503, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciola, L.; Mussini, P.R.; Mussini, T.; Pelle, P. Determination of primary and secondary standards and characterization of appropriate salt bridges for pH measurements in formamide. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrel, D.; Falciola, L.; Liotto, M.; Mussini, P.R.; Mussini, T.; Rossi, M. Determination of primary and secondary standards for pH measurements in N-Methylacetamide and its 0.50 mass fraction in admixture with water, with characterization of appropriate salt bridges. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciola, L.; Fierro, A.; Mussini, P.R.; Mussini, T.; Rossi, M.; Dumitrel, D. Medium effects and determination of primary and secondary standards for pH measurements in (Glycerol + Water) solvent media at normal and subzero temperatures, with characterization of appropriate salt bridges †. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.A.; Yates, K. Acidity functions: An update. Can. J. Chem. 1983, 61, 2225–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmel, D.; Goll, S.K.; Leito, I.; Krossing, I. A unified pH scale for all phases. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6885–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suu, A.; Jalukse, L.; Liigand, J.; Kruve, A.; Himmel, D.; Krossing, I.; Rosés, M.; Leito, I. Unified pH values of liquid chromatography mobile phases. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liquid Junction. Available online: http://goldbook.iupac.org/terms/view/L03584 (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Bates, R.G. Determination of pH: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA; London, UK; Sydney, Australia; Toronto, Japan, 1973; ISBN 0-471-05647-2. [Google Scholar]
- Popovych, O.; Bates, R.G. Estimation of medium effects for single ions in non-aqueous solvents. CRC Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1970, 1, 73–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liigand, P.; Heering, A.; Kaupmees, K.; Leito, I.; Girod, M.; Antoine, R.; Kruve, A. The evolution of electrospray generated droplets is not affected by ionization mode. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 28, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lõkov, M.; Tshepelevitsh, S.; Heering, A.; Plieger, P.G.; Vianello, R.; Leito, I. On the basicity of conjugated nitrogen heterocycles in different media. European J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 4475–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, V.; Ermantraut, A.; Himmel, D.; Koslowski, T.; Leito, I. The Ideal ionic liquid salt bridge for the direct determination of gibbs energies of transfer of single ions, Part I: The concept. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2344–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermantraut, A.; Radtke, V.; Gebel, N.; Himmel, D.; Koslowski, T.; Leito, I. The ideal ionic liquid salt bridge for direct determination of Gibbs Energies of transfer os single ions, part II: Evaluation of the role of ion solvation and ion mobilities. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2348–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veigure, R.; Lossmann, K.; Hecht, M.; Parman, E.; Born, R.; Leito, I.; Herodes, K.; Kipper, K. Retention of acidic and basic analytes in reversed phase column using fluorinated and novel eluent additives for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1613, 460667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, V.; Gebel, N.; Priester, D.; Ermantraut, A.; Bäuerle, M.; Himmel, D.; Koslowski, T.; Leito, I. Krossing the ideal ionic liquid salt bridge for the direct determination of Gibbs Energies of transfer of single ions, part III: Evidence and Implications of the absence of solvent-solvent interactions. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. Submitted.

| Institution a | Buffer pH | Uncertainty b | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| BFKH | 9.180; 6.865; 4.008 | 0.005–0.01 | National CRMs c |
| CMI | 9.180; 7.000; 4.000 | 0.02 | National CRMs |
| DFM | 9.180; 7.000; 4.005 | 0.01 | Radiometer/Hach |
| FC.ID | 9.21; 9.00; 7.00; 4.00 | 0.02 | Metrohm |
| IPQ | 9.00; 7.00; 4.00 | 0.02 | Metrohm |
| LNE | 10.012; 9.180; 7.000; 4.005 | 0.01 | Radiometer/Hach |
| PTB | 9.00; 7.00; 4.01 | 0.02 | Merck |
| TUBITAK UME | 12.00; 10.00; 7.00; 4.01; 1.68 | 0.02 | Merck |
| UT | 10.00; 7.00; 4.00; 2.00 | 0.02 | Fluka |
| Institution a | Water Jacket | Auxiliary Electrode | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| BFKH | none | Yes | Budapest University of Technology and Economics (BME, Budapest, Hungary) |
| CMI | solution compartments | No | Hubert Košťál, Brno, Czech |
| DFM | whole cell | No | Scholers Glasblæseri (Regstrup. Denmark) |
| FC.ID | none | Yes | IST-UL (Lisbon, Portugal) |
| IPQ | none | No | Research Unit VICARTE, Glass and Ceramics for the Arts (FCT-UNL, Monte de Caparica, Portugal) |
| LNE | solution compartments | No | Sklotech (Sázava, Czech) |
| PTB | whole cell | No | Gebr. Rettberg GmbH (Göttingen, Germany) |
| TUBITAK UME | none | Yes | LAB-CAM (İstanbul, Turkey) |
| UT | none/solution compartments/whole cell | Yes/ No | several in-house (Tartu, Estonia) and commercial (Gebr. Rettberg GmbH, Göttingen, Germany) cells |
| Institution a | Instrument | Input Impedance/Ω |
|---|---|---|
| BFKH | Keithley 6430 Sub-Femtoamp remote sourcemeter/multimeter | >1016 |
| CMI | Bio-Logic SP200 potentiostat with a low current module | 1014 |
| DFM | Zahner IM6ex potentiostat with the HiZ (high impedance) probe | 1015 |
| FC.ID | Metrohm 713 pH meter | >1013 |
| IPQ | Agilent 3458A reference multimeter, with an impedance converter based on AD8627 (PTB); Keithley 6514 electrometer | >1013; >2 × 1014 |
| LNE | Bio-Logic SP200 potentiostat with a low current module | 1014 |
| PTB | Keysight B2987A Electrometer/High Resistance Meter | >2 × 1014 |
| TUBITAK UME | Metrohm 916 Ti-touch potentiometric titration system with differential amplifier (Metrohm 6.5104.030) | >1012 |
| UT | Gamry Reference 3000™ potentiostat/galvanostat/ZRA (zero resistance ammeter); Metrohm 713 pH meter | >1014; >1013 |
| Institution a | s |
|---|---|
| BFKH | 0.0001 |
| BFKH | 0.01 |
| CMI | 0.02 |
| DFM | 0.01 |
| FC.ID | 0.01 |
| IPQ | 0.04 |
| IPQ | 0.02 |
| LNE | 0.03 |
| PTB | 0.01 |
| PTB | 0.04 |
| TUBITAK UME | 0.10 |
| UT-2020 | 0.01 |
| UT-KCl | 0.02 |
| UT-2015 | 0.01 |
| UT [20] | 0.02 |
| UT [16] | 0.05 |
| Inter-Group Variance (SCF) | 0.006 |
|---|---|
| Degree of freedom inter-group (dofinter) | 1 |
| Intra-group variance (SCR) | 0.060 |
| Degree of freedom intra-group (dofintra) | 38 |
| F calculated | 3.398 |
| P | 0.073 |
| F critical 5% | 4.105 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heering, A.; Stoica, D.; Camões, F.; Anes, B.; Nagy, D.; Nagyné Szilágyi, Z.; Quendera, R.; Ribeiro, L.; Bastkowski, F.; Born, R.; et al. Symmetric Potentiometric Cells for the Measurement of Unified pH Values. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071150
Heering A, Stoica D, Camões F, Anes B, Nagy D, Nagyné Szilágyi Z, Quendera R, Ribeiro L, Bastkowski F, Born R, et al. Symmetric Potentiometric Cells for the Measurement of Unified pH Values. Symmetry. 2020; 12(7):1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071150
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeering, Agnes, Daniela Stoica, Filomena Camões, Bárbara Anes, Dániel Nagy, Zsófia Nagyné Szilágyi, Raquel Quendera, Luís Ribeiro, Frank Bastkowski, Rasmus Born, and et al. 2020. "Symmetric Potentiometric Cells for the Measurement of Unified pH Values" Symmetry 12, no. 7: 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071150
APA StyleHeering, A., Stoica, D., Camões, F., Anes, B., Nagy, D., Nagyné Szilágyi, Z., Quendera, R., Ribeiro, L., Bastkowski, F., Born, R., Nerut, J., Saame, J., Lainela, S., Liv, L., Uysal, E., Roziková, M., Vičarová, M., Snedden, A., Deleebeeck, L., ... Leito, I. (2020). Symmetric Potentiometric Cells for the Measurement of Unified pH Values. Symmetry, 12(7), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12071150







