Attention Mechanism Based Semi-Supervised Multi-Gain Image Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Algorithm
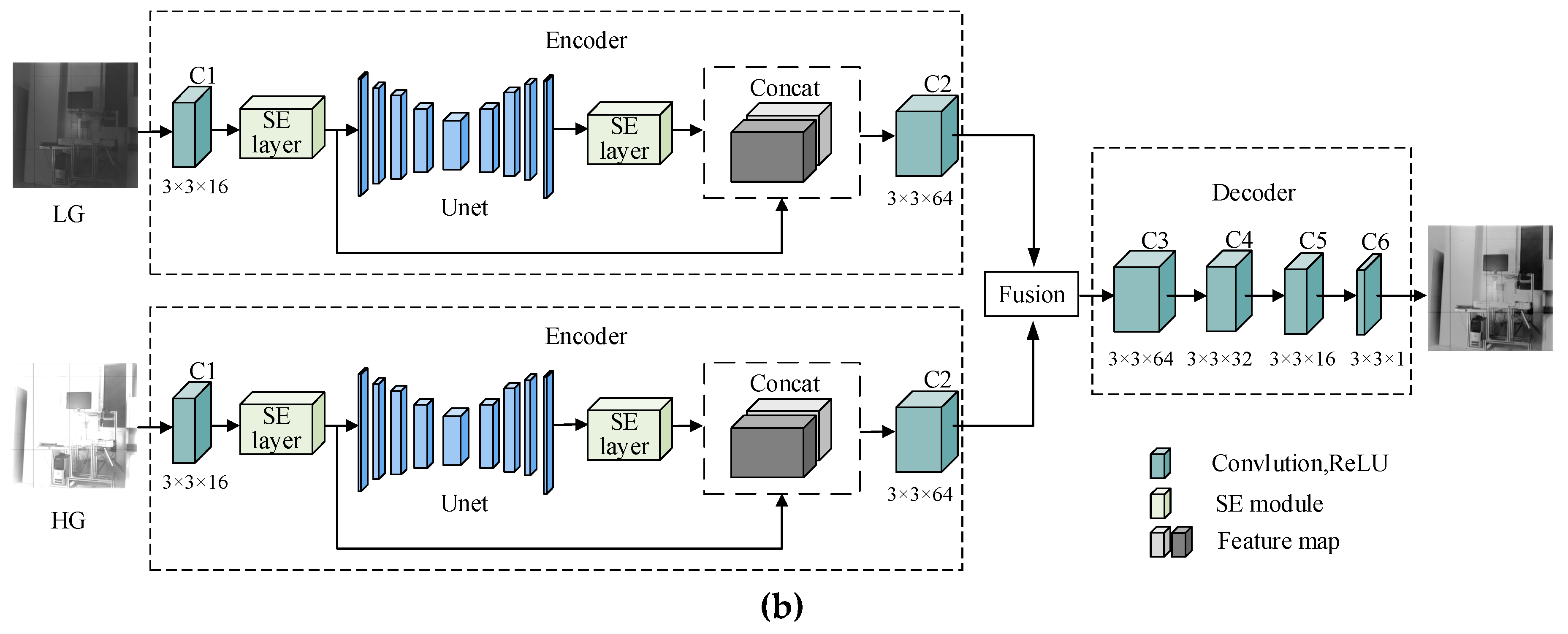
3. U-SENet Network Structure
3.1. Encoding Structure
3.2. Fusion Module
3.3. Decoding Module
3.4. Loss Function
4. Experiment Results
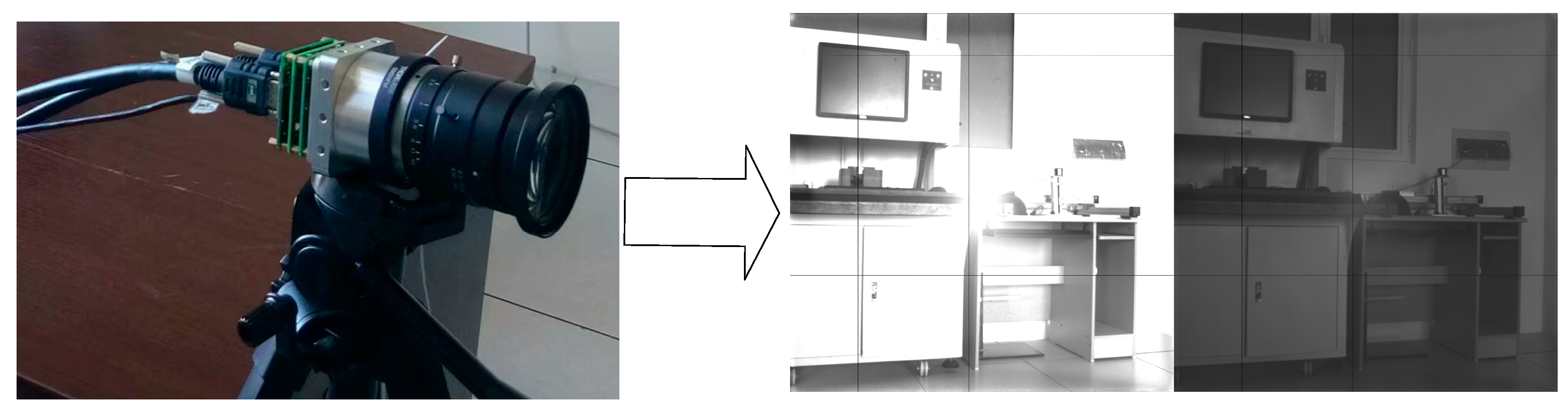
4.1. Hardware Platform
4.2. Dasetset and Training Strategy
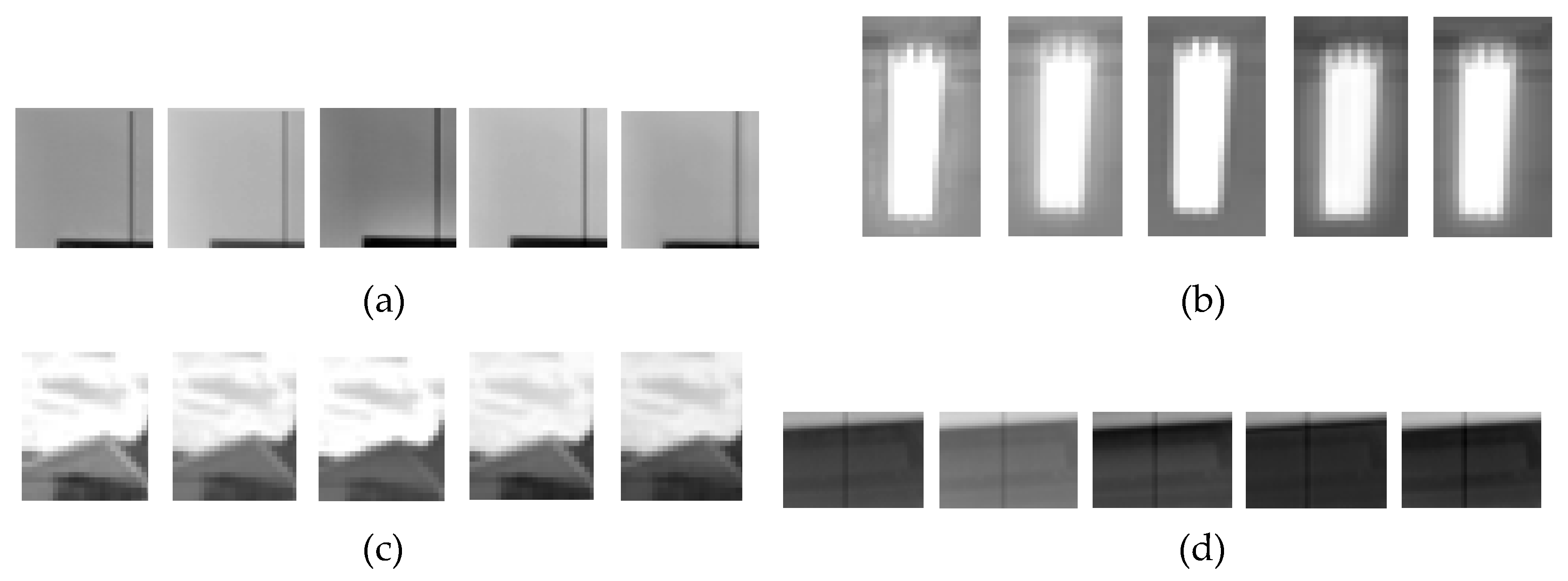
4.3. Validation
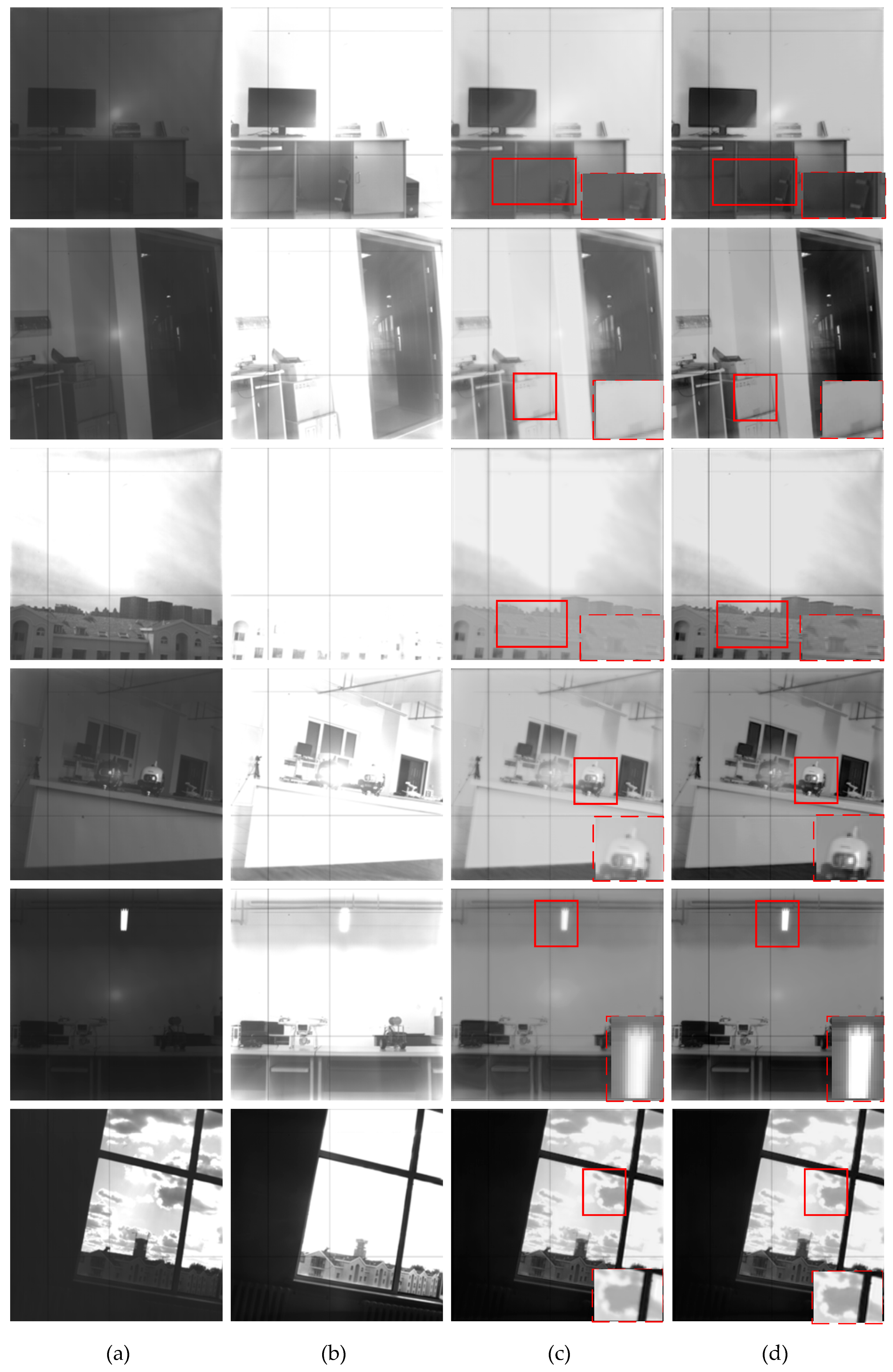
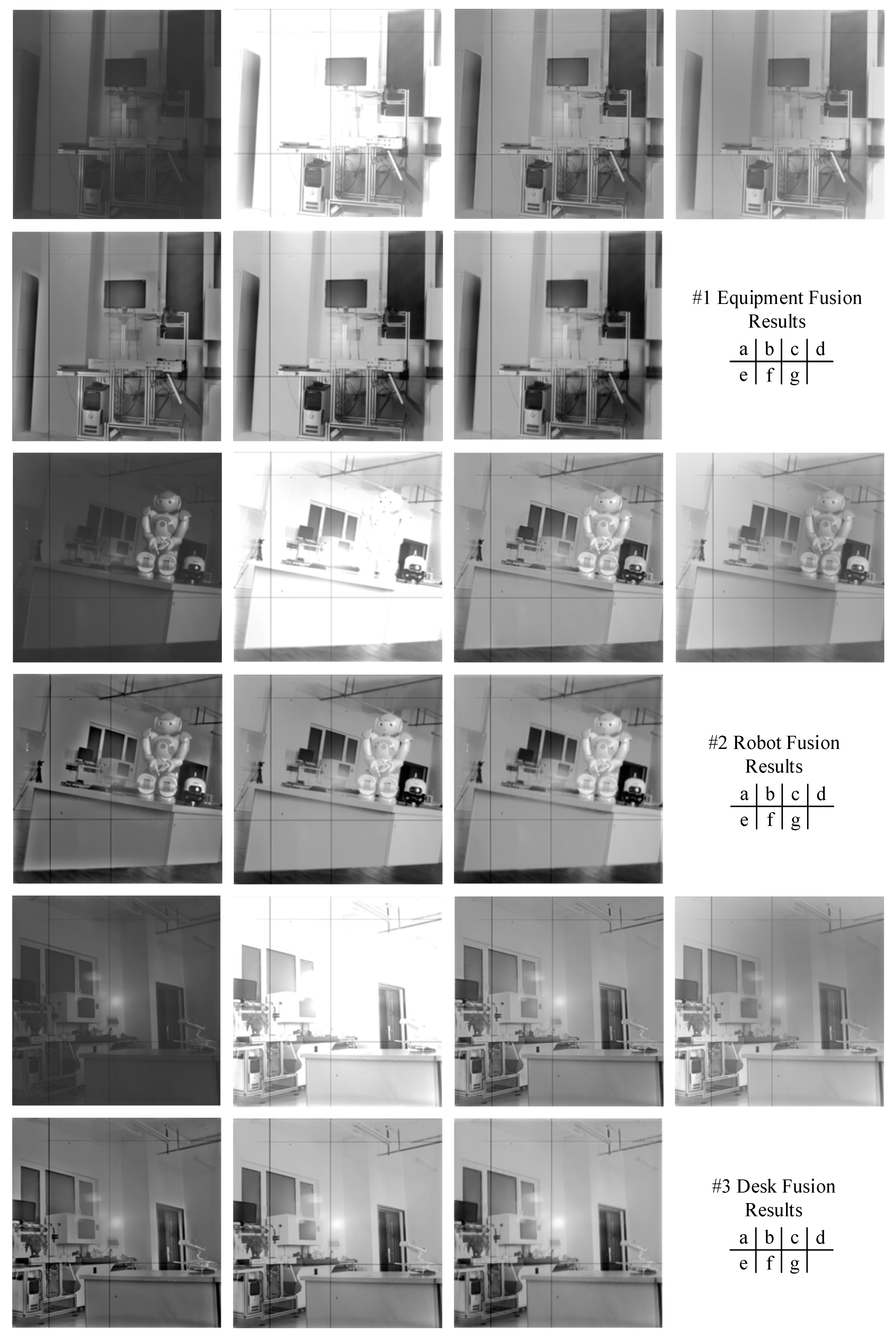
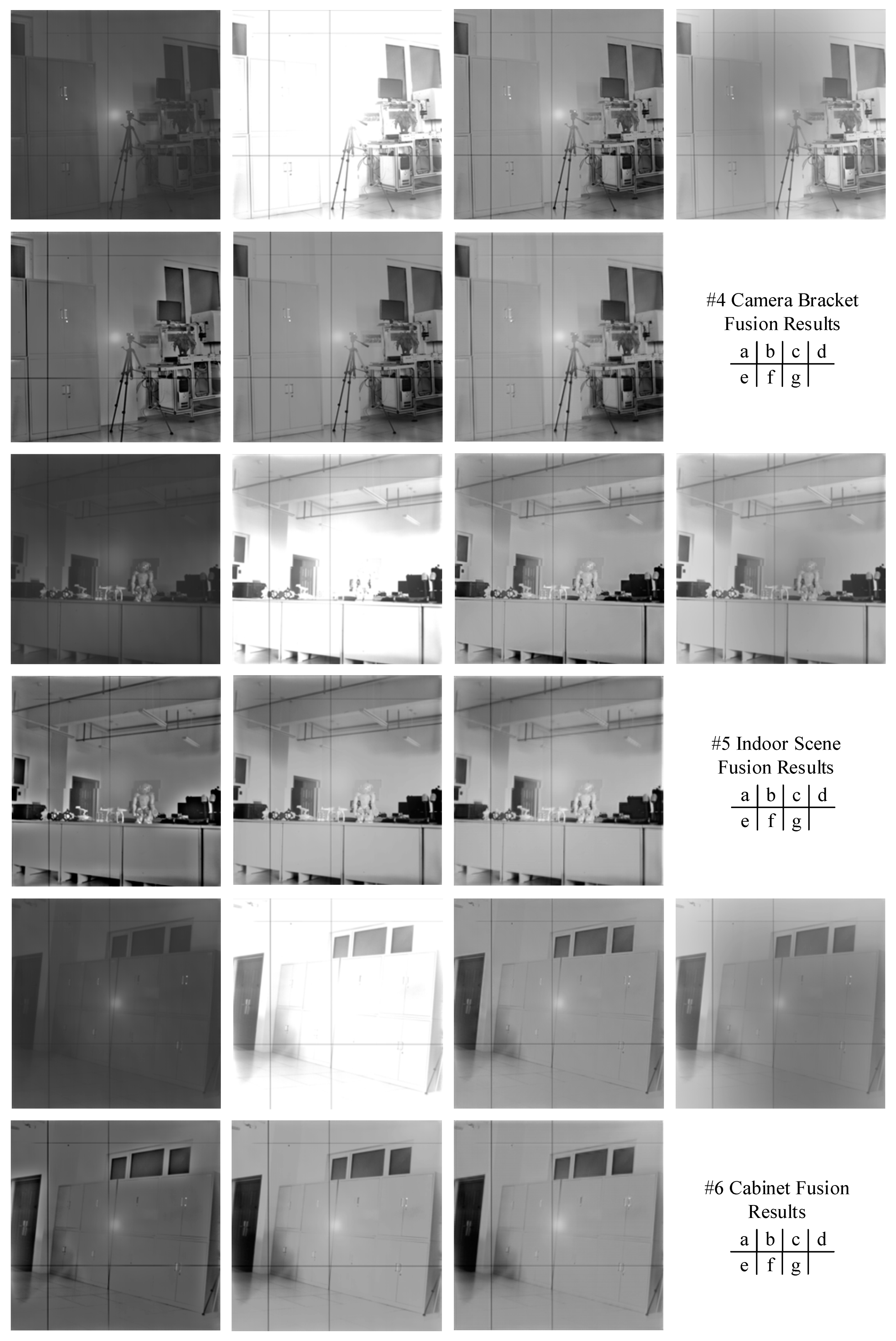
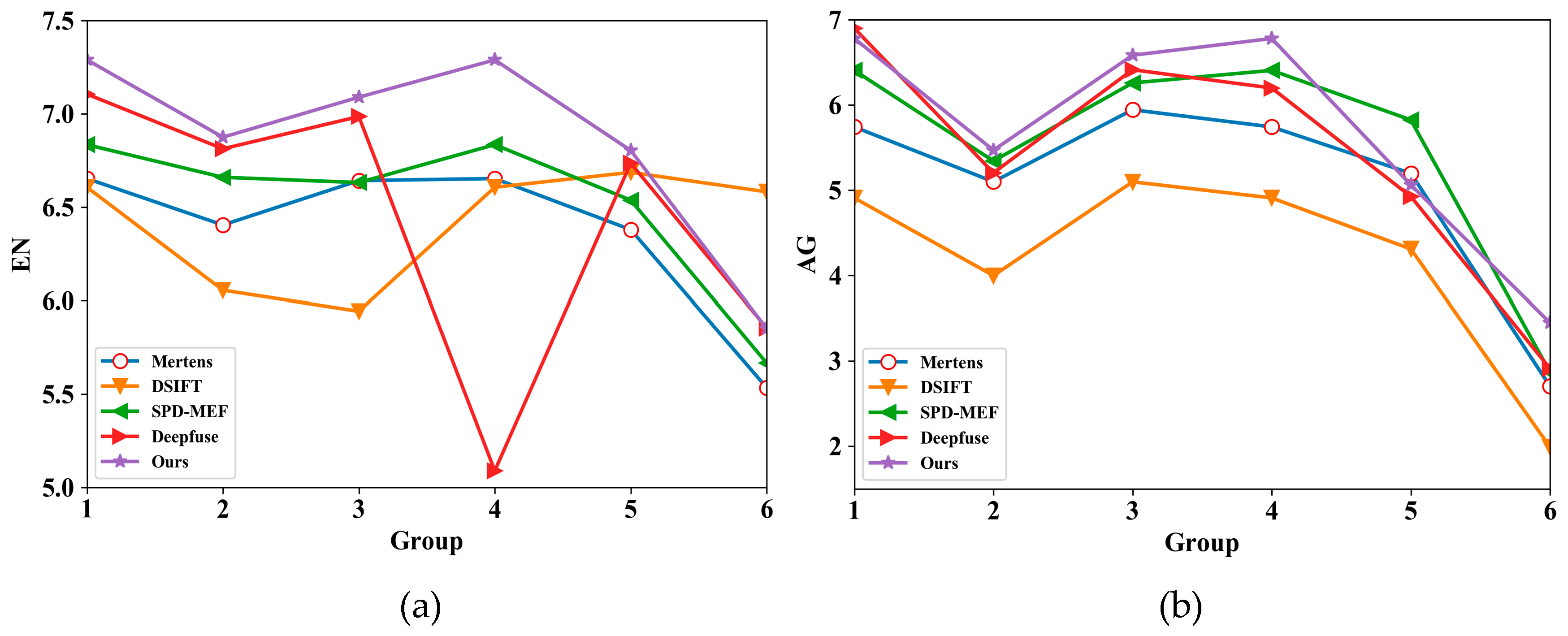
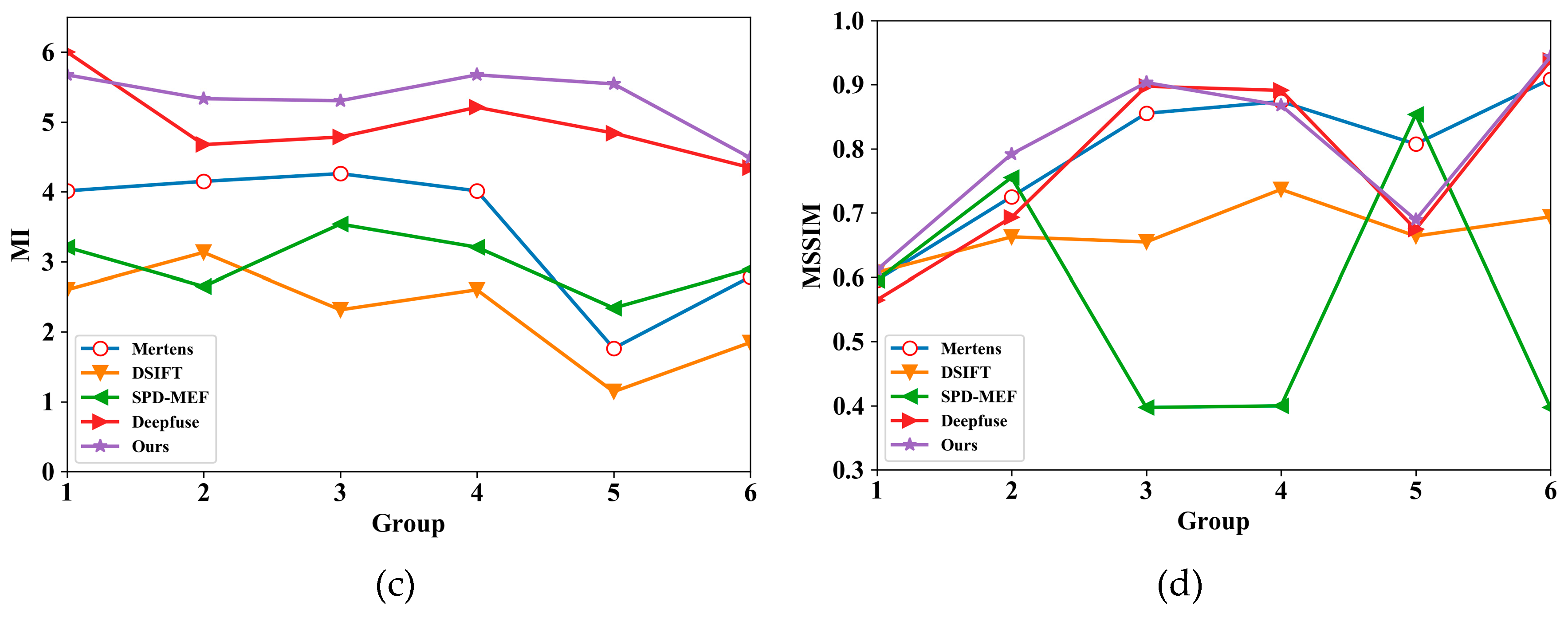
4.4. Experimental Result and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kou, F.; Li, Z.; Wen, C.; Chen, W. Edge-preserving smoothing pyramid based multi-scale exposure fusion. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2018, 53, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Ling, H. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 26, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, T.; Kautz, J.; Van Reeth, F. Exposure fusion: A simple and practical alternative to high dynamic range photography. Comput. Graph. Forum 2009, 28, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y. A fast fusion scheme for infrared and visible light images in NSCT domain. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2015, 72, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lee, H. Exposure Measurement and Fusion via Adaptive Multiscale Edge-Preserving Smoothing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Huang, J. Image fusion with local spectral consistency and dynamic gradient sparsity. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2760–2765. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Blum, R.; Han, J.; Tao, D. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: A review. Inf. Fusion 2018, 40, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Chen, C. Regional multifocus image fusion using sparse representation. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 5182–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, P.; Kolczynski, R. Enhanced image capture through fusion. In Proceedings of the 1993 (4th) International Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Germany, 11–14 May 1993; pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Hu, J. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Dense SIFT for ghost-free multi-exposure fusion. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2015, 31, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Li, H.; Yong, H.; Wang, Z.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Robust multi-exposure image fusion: A structural patch decomposition approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 2519–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Duanmu, Z.; Yeganeh, H.; Wang, Z. Multi-exposure image fusion by optimizing a structural similarity index. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2017, 4, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Manjunath, B.; Mitra, S. Multi sensor image fusion using the wavelet transform. Graph. Models Image Process. 1995, 57, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borwonwatanadelok, P.; Rattanapitak, W.; Udomhunsakul, S. Multi-focus image fusion based on stationary wavelet transform and extended spatial frequency measurement. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Electronic Computer Technology, Macau, China, 20–22 February 2009; pp. 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, P.; Canagarajah, C.; Bull, D. Image Fusion Using Complex Wavelets. In Proceedings of the BMVC, Tvbingen, Germany, 22−24 November 2002; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Hu, S.; Liu, S.; Fang, J.; Xu, S. Multi-focus image fusion based on joint sparse representation and optimum theory. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, K.; Srikar, V.; Babu, R. DeepFuse: A Deep Unsupervised Approach for Exposure Fusion with Extreme Exposure Image Pairs. In Proceedings of the ICCV, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4724–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhang, L. Multi-exposure fusion with CNN features. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1723–1727. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Gong, D.; Zhang, P.; Shi, Q.; Sun, J.; Reid, I.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Scale Dense Networks for Deep High Dynamic Range Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 7–11 January 2019; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, X. Densefuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollar, P.; Lawrence Zitnick, C. Microsoft coco: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Mei, X.; Ma, J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2020, 508, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Multi-Gain Dataset [EB/OL]. Available online: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ku7nAz0ZHxjyvNJ_z2IvfA (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Bai, X.; Zhou, F.; Xue, B. Edge preserved image fusion based on multiscale toggle contrast operator. Image Vis. Comput. 2011, 29, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Zhang, D.; Yan, P. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron. Lett. 2002, 38, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Layer | Parameter (Convolution Kernel, Step) | Numbers of Output Channels | Size of the Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convolution1 | |||
| SE layer | |||
| Convolution | |||
| Conv1 | |||
| Pool1 | |||
| Conv2 | |||
| Pool2 | |||
| Conv3 | |||
| Pool3 | |||
| Conv4 | |||
| Pool4 | |||
| Conv5 | |||
| Up6 | |||
| Conv6-1 | |||
| Conv6 | |||
| Up7 | |||
| Conv7 | |||
| Up8 | |||
| Conv8 | |||
| Up9 | |||
| Conv9 | |||
| SE layer | |||
| Convolution2 | |||
| Convolution3 | |||
| Convolution4 | |||
| Convolution5 | |||
| Convolution6 |
| Optical Format | 2.0 Inch | Full Well Capacity (FWC) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active image size | 22.528 mm × 22.528 mm | Temporal dark noise | 1.6 |
| Pixel size | 11 um × 11 um | Dynamic range | >93 db(HDR model) |
| Number of active pixels | 2048(H) × 2048(V) | Supply voltage | 3.3 V for analog 1.8 V for digital |
| Shutter type | Electronic rolling shutter | Output format | 8 pairs of LVDS drivers |
| Pixel clock rate | 25 MHz | Power consumption | <650 mW |
| Frame rate | 24 fps | Chroma | Mono |
| Data rate | 2.4 Gbit/s at 25 MHz pixel clock | Package | 115 pins PGA |
| Mertens | DSIFT | SPD-MEF | Deepfuse | Ours | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group #1 | EN | 6.6530 | 6.6065 | 6.8346 | 7.1057 | 7.2891 |
| AG | 5.7424 | 4.9093 | 6.4059 | 6.9002 | 6.7798 | |
| MI | 4.0131 | 2.6018 | 3.2064 | 6.0032 | 5.6738 | |
| MSSIM | 0.5955 | 0.6074 | 0.5955 | 0.5648 | 0.6112 | |
| Group #2 | EN | 6.4043 | 6.0553 | 6.6599 | 6.8125 | 6.8746 |
| AG | 5.0993 | 3.9978 | 5.3426 | 5.2035 | 5.4691 | |
| MI | 4.1493 | 3.1324 | 2.6489 | 4.6750 | 5.3325 | |
| MSSIM | 0.7254 | 0.6627 | 0.7554 | 0.6931 | 0.7919 | |
| Group #3 | EN | 6.6420 | 5.9434 | 6.6316 | 6.9855 | 7.0891 |
| AG | 5.9434 | 5.0982 | 6.2583 | 6.4133 | 6.5834 | |
| MI | 4.2599 | 2.3149 | 3.5373 | 4.7846 | 5.3038 | |
| MSSIM | 0.8554 | 0.6547 | 0.3972 | 0.8976 | 0.9034 | |
| Group #4 | EN | 6.6530 | 6.6065 | 6.8346 | 5.0894 | 7.2891 |
| AG | 5.7424 | 4.9093 | 6.4059 | 6.1988 | 6.7798 | |
| MI | 4.0131 | 2.6018 | 3.2064 | 5.2097 | 5.6738 | |
| MSSIM | 0.8738 | 0.7367 | 0.3997 | 0.8911 | 0.8679 | |
| Group #5 | EN | 6.3793 | 6.6863 | 6.5371 | 6.7355 | 6.8036 |
| AG | 5.1979 | 4.3104 | 5.8242 | 4.9258 | 5.0622 | |
| MI | 1.7641 | 1.1427 | 2.3402 | 4.8399 | 5.5443 | |
| MSSIM | 0.8075 | 0.6639 | 0.8534 | 0.6743 | 0.6892 | |
| Group #6 | EN | 5.5347 | 6.5820 | 5.6667 | 5.8539 | 5.8510 |
| AG | 2.7043 | 1.9913 | 2.8711 | 2.9129 | 3.4494 | |
| MI | 2.7863 | 1.8473 | 2.8905 | 4.3453 | 4.4864 | |
| MSSIM | 0.9087 | 0.6940 | 0.3972 | 0.9377 | 0.9435 |
| Parameter | Deepfuse | Ours |
|---|---|---|
| Epoch | 4 | 30 |
| Batch Size | 2 | 12 |
| Learning Rate |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, M.; Liang, X.; Fu, F.; Song, Y.; Shao, Z. Attention Mechanism Based Semi-Supervised Multi-Gain Image Fusion. Symmetry 2020, 12, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030451
Fang M, Liang X, Fu F, Song Y, Shao Z. Attention Mechanism Based Semi-Supervised Multi-Gain Image Fusion. Symmetry. 2020; 12(3):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030451
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Ming, Xu Liang, Feiran Fu, Yansong Song, and Zhen Shao. 2020. "Attention Mechanism Based Semi-Supervised Multi-Gain Image Fusion" Symmetry 12, no. 3: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030451
APA StyleFang, M., Liang, X., Fu, F., Song, Y., & Shao, Z. (2020). Attention Mechanism Based Semi-Supervised Multi-Gain Image Fusion. Symmetry, 12(3), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12030451




