Spectral Kurtosis of Choi–Williams Distribution and Hidden Markov Model for Gearbox Fault Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. SK Based on CWD
2.1. Definition of SK
2.2. Algorithm of CWD-SK
2.3. Impact of Window Functions
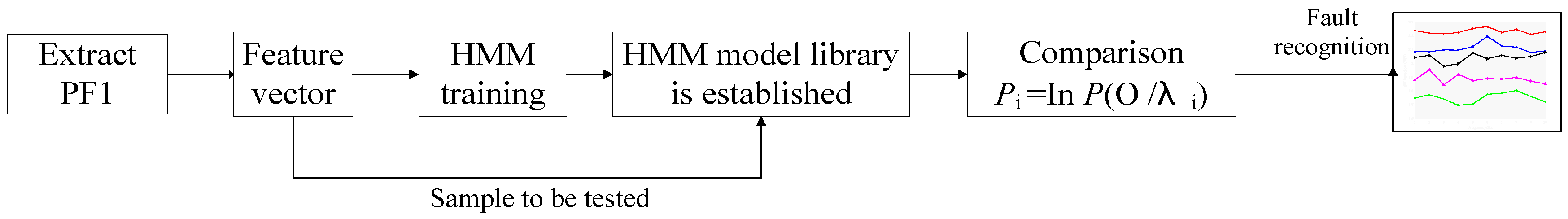
3. Diagnosis Flow Based on HMM
4. Experimental Data Analysis
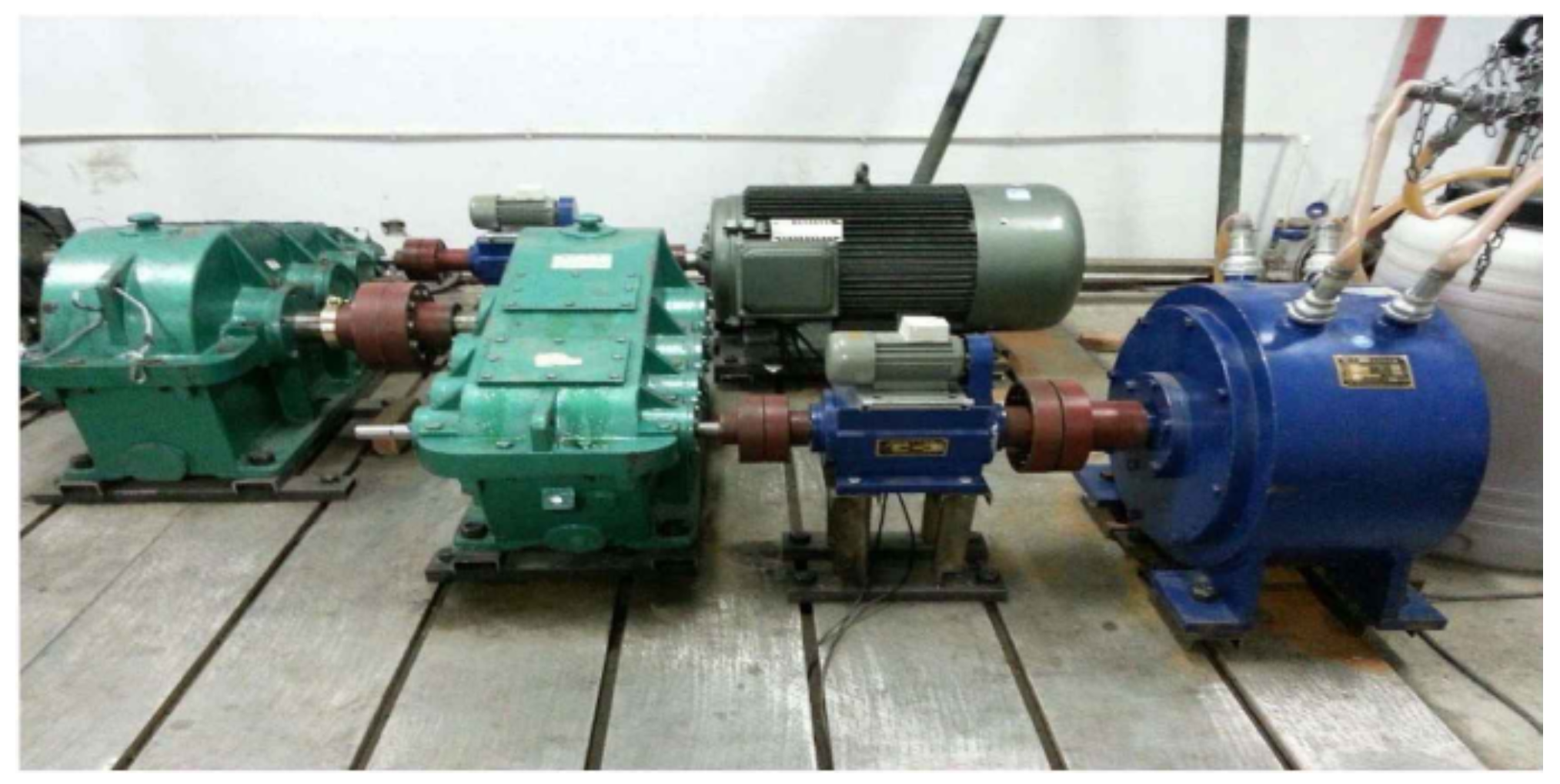
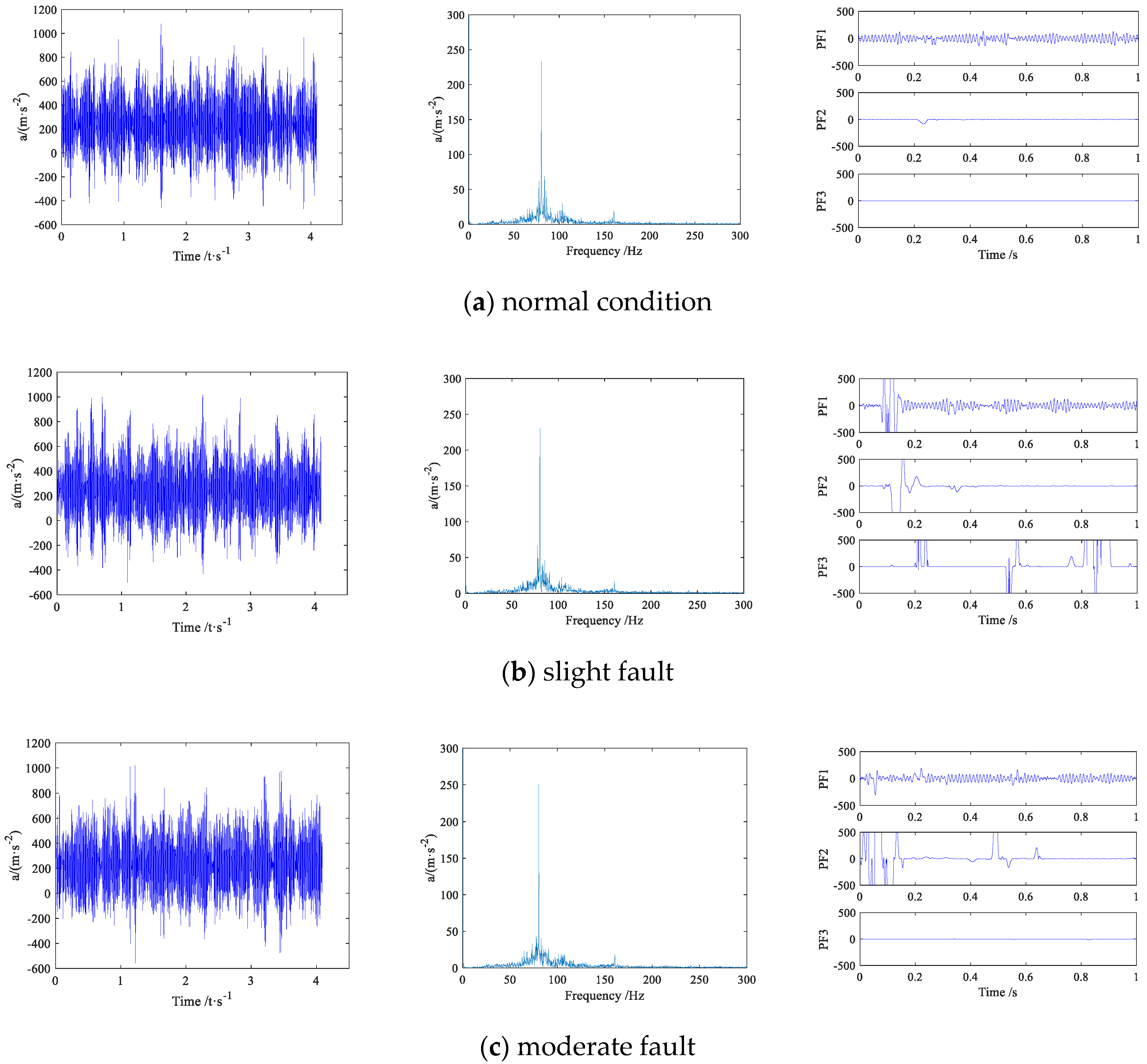
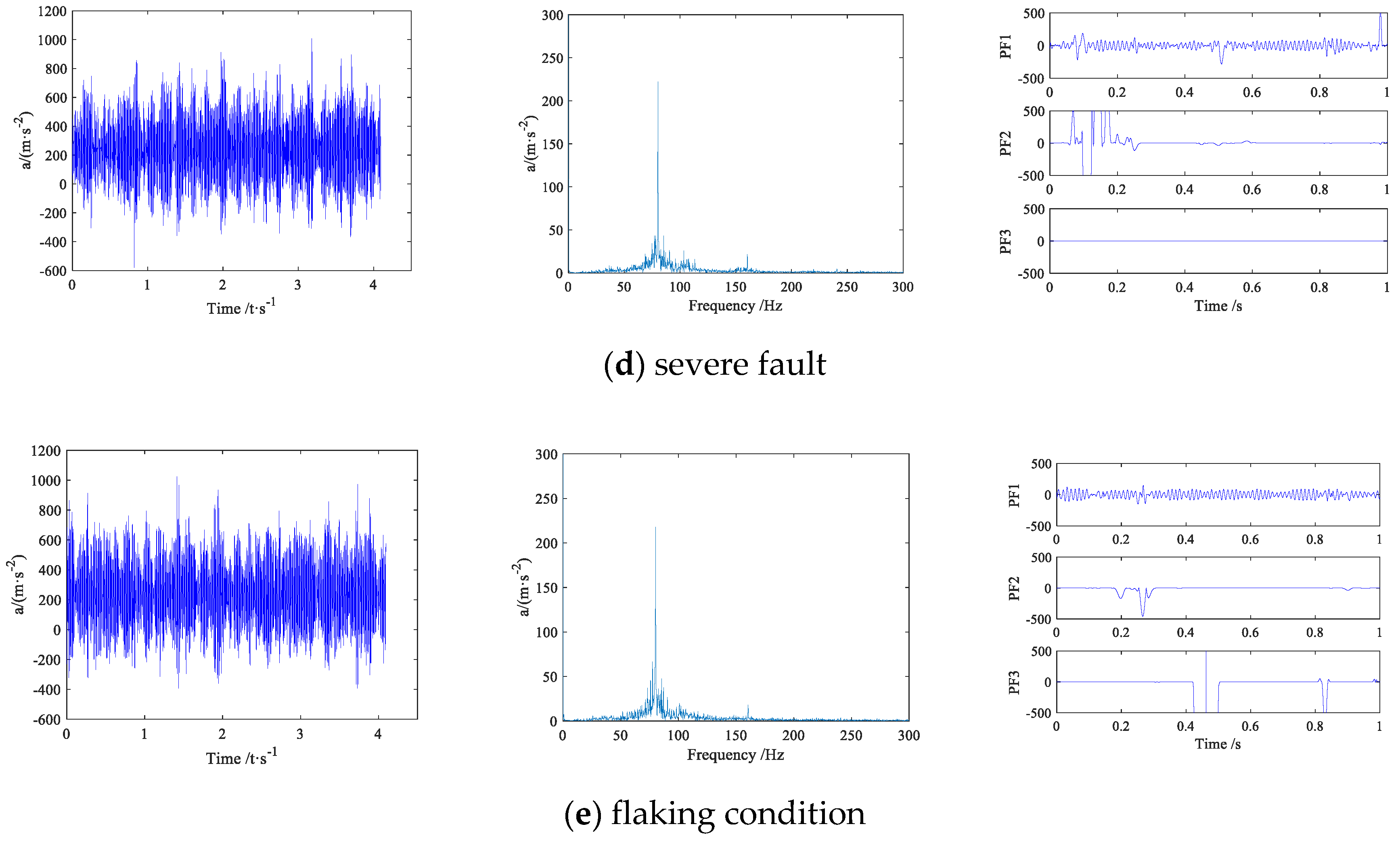
4.1. Experiment Platform and Data Preprocessing
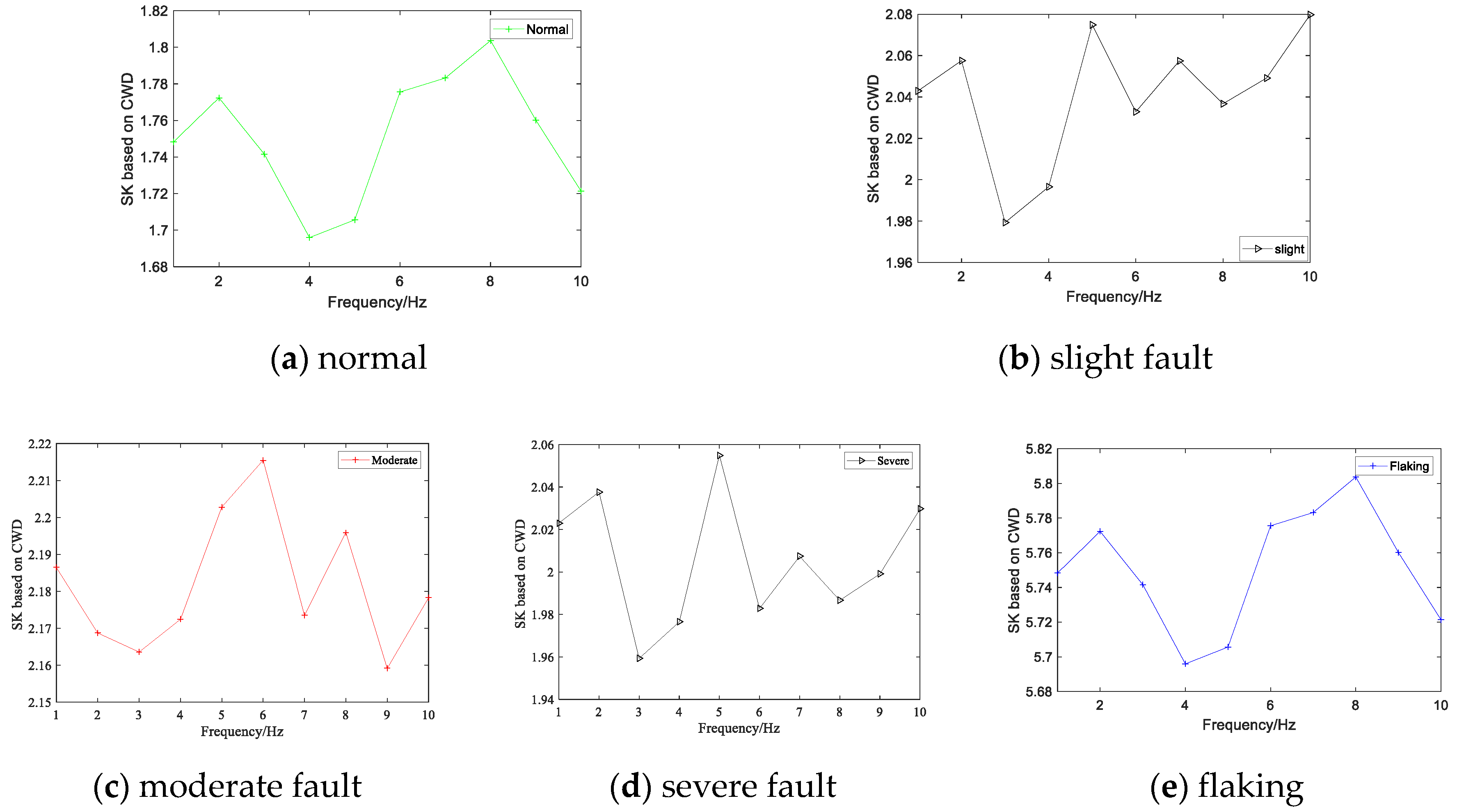
4.2. Initial Fault Feature Extraction Based on CWD-SK
4.3. Selection of Window Function
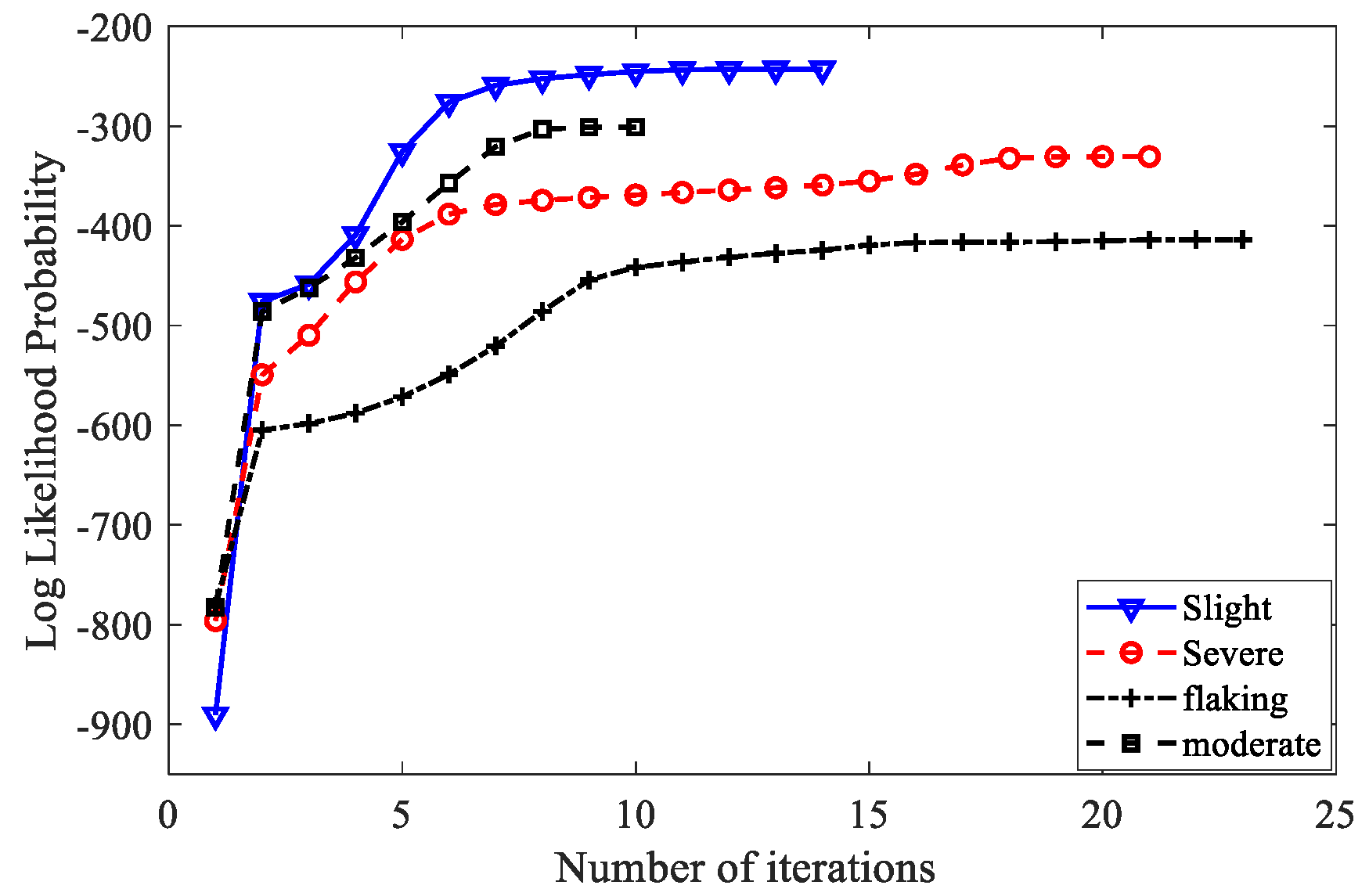
4.4. Five Types of Gear Fault Characteristics Classification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Man, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. A modified normal contact stiffness model considering effect of surface topography. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. J. Eng. Tribol. 2014, 229, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, B.; Pang, J.; Steven, Y. High Speed Grinding of HIP-SiC Ceramics on Transformation of Microscopic Features. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Carlo, C.; Chi, C. Multifractional Brownian Motion and Quantum-Behaved Particle Swarm Optimization for Short Term Power Load Forecasting: An Integrated Approach. Energy 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Chen, X.; Carlo, C. Multi-Fractional Brownian Motion and Quantum-Behaved Partial Swarm Optimization for Bearing Degradation Forecasting. Complexity 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Song, W.; Li, M.; Aleksey, K.; Enrico, Z. Fractional Lévy stable motion: Finite difference iterative forecasting model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Song, L.; Cui, L.; Wang, H. A three-dimensional geometric features-based SCA algorithm for compound faults diagnosis. Measurement 2018, 134, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Yang, J.; Tang, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, H. Parallel processing algorithm of temperature and noise error for micro-electro-mechanical system gyroscope based on variational mode decomposition and augmented nonlinear differentiator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2018, 89, 076107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J.; Du, W. Research of novel bearing fault diagnosis method based on improved krill herd algorithm and kernel Extreme Learning Machine. Complexity 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Du, W. A novel method for intelligent fault diagnosis of bearing based on capsule neural network. Complexity 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Villecco, F.; Li, M.; Song, W. Multi-Scale Permutation Entropy Based on Improved LMD and HMM for Rolling Bearing Diagnosis. Entropy 2017, 19, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Sun, G.; Jiang, X.; Guo, M.; Liang, S. Predictive Modeling of Microgrinding Force Incorporating Phase Transformation Effects. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, W.; Zhou, J.; Du, W.; Wang, J.; He, G.; He, H. Application of an Improved Ensemble Local Mean Decomposition Method for Gearbox Composite Fault Diagnosis. Complexity 2019, 2019, 1564243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, R. Detection of non-Gaussian signals by frequency domain Kurtosis estimation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP’83. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Boston, MA, USA, 14–16 April 1983; Volume 2, pp. 607–610. [Google Scholar]
- Antoni, J. The spectral kurtosis: A useful tool for characterising non-stationary signals. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2006, 20, 282–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tse, P.; Tsui, K.-L. An enhanced Kurtogram method for fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 35, 176–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Lei, Y.; Shan, H.; Lin, J. Early Fault Diagnosis of Bearings Using an Improved Spectral Kurtosis by Maximum Correlated Kurtosis Deconvolution. Sensors 2015, 15, 29363–29377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combet, F.; Gelman, L. Optimal filtering of gear signals for early damage detection based on the spectral kurtosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2009, 23, 652–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Gabbar, H.A. A novel method for real time gear fault detection based on pulse shape analysis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, G.; Zhao, Q.; Zuo, M. Maximum correlated Kurtosis deconvolution and application on gear tooth chip fault detection. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2012, 33, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Chen, X.; He, Z. Sparsity-enabled signal decomposition using tunable Q-factor wavelet transform for fault feature extraction of gearbox. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 41, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. An Approach to Recognize the Transient Disturbances with Spectral Kurtosis. Instrumentation and Measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher, P.; Weibel, R.; Burghardt, D. Integrating ontological modelling and Bayesian inference for pattern classification in topographic vector data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2009, 33, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Liu, C.-L. Evaluation of weighted Fisher criteria for large category dimensionality reduction in application to Chinese handwriting recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 2599–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binsen, P.; Hong, X. A mixed intelligent condition monitoring method for nuclear power plant. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2020, 140, 107307. [Google Scholar]
- Melin, P.; Castillo, O. A review on the applications of type-2 fuzzy logic in classification and pattern recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 5413–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, A. Neural network algorithm to pattern recognition in inverse problems: Applied Mathematics and Computation. Crossmark 2013, 221, 484–490. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Qing, X. TVAR-HMM-based Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis. J. Tianjin Univ. 2010, 43, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, M.; He, D.; Banerjee, P. Equipment health diagnosis and prognosis using hidden semi Markov models. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 30, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najkar, N.; Razzazi, F.; Sameti, H. A novel approach to HMM-based speech recognition system using particle swarm optimization. Math. Comput. Model. 2010, 52, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, L.; Chu, Z. Traffic Incident Prediction on Intersections Based on HMM. J. Transp. Syst. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2013, 13, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xue, Z.; Wang, C. Motion correction for cellular-resolution multi-photon fluorescence microscopy imaging of awake head-restrained mice using speed embedded HMM. Comput. Med Imaging Graph. 2012, 36, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.; Ching, W.-K.; Chan, L. Detection of machine failure: Hidden Markov Model approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 57, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. A Classification Method for Complex Power Quality Disturbances Using EEMD and Rank Wavelet SVM. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 6, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; Rao, K. Excitation modelling using epoch features for statistical parametric speech synthesis. Comput. Speech Lang. 2019, 60, 101029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Piero, B.; Sameer, A.; Enrico, Z. Fault prognostics by an ensemble of Echo State Networks in presence of event based measurements. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 87, 103346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PF | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kurtosis(normal) | 3.730 | 3.212 | 3.098 |
| Kurtosis (slight fault) | 3.980 | 3.402 | 3.196 |
| Kurtosis (moderate fault) | 4.645 | 4.320 | 4.089 |
| Kurtosis (severe fault) | 4.966 | 4.781 | 4.342 |
| Kurtosis(flaking) | 5.905 | 5.455 | 5.403 |
| Condition | The Mean of CWD-SK |
|---|---|
| Normal | 1.756 |
| Slight | 2.023 |
| Moderate | 2.187 |
| Severe | 2.019 |
| Flaking | 5.746 |
| Window Functions | Smoothness |
|---|---|
| Rectangular | 0.447 |
| Hanning | 0.449 |
| Hamming | 0.508 |
| Blackman | 0.458 |
| Fault Case | Logarithm Likelihood Probabilities of the Input Sample Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recognition Result | |||||
| Slight fault | −15.114 | ||||
| Moderate fault | −54.124 | -55.964 | |||
| Severe fault | −62.14 | −76.44 | −134.82 | ||
| Flaking | −132.67 | −199.211 | −211.342 | ||
| Recognition Model | Slight Fault | Moderate Fault | Severe Fault | Flaking | Recognition Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CWD-SK | HMM | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 95% |
| BP | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 90% | |
| SK | HMM | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 90% |
| BP | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 85% | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Song, W.; Wu, F.; Zio, E.; Zhang, Y. Spectral Kurtosis of Choi–Williams Distribution and Hidden Markov Model for Gearbox Fault Diagnosis. Symmetry 2020, 12, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020285
Li Y, Song W, Wu F, Zio E, Zhang Y. Spectral Kurtosis of Choi–Williams Distribution and Hidden Markov Model for Gearbox Fault Diagnosis. Symmetry. 2020; 12(2):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020285
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yufei, Wanqing Song, Fei Wu, Enrico Zio, and Yujin Zhang. 2020. "Spectral Kurtosis of Choi–Williams Distribution and Hidden Markov Model for Gearbox Fault Diagnosis" Symmetry 12, no. 2: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020285
APA StyleLi, Y., Song, W., Wu, F., Zio, E., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Spectral Kurtosis of Choi–Williams Distribution and Hidden Markov Model for Gearbox Fault Diagnosis. Symmetry, 12(2), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020285







