Weight Queue Dynamic Active Queue Management Algorithm
Abstract
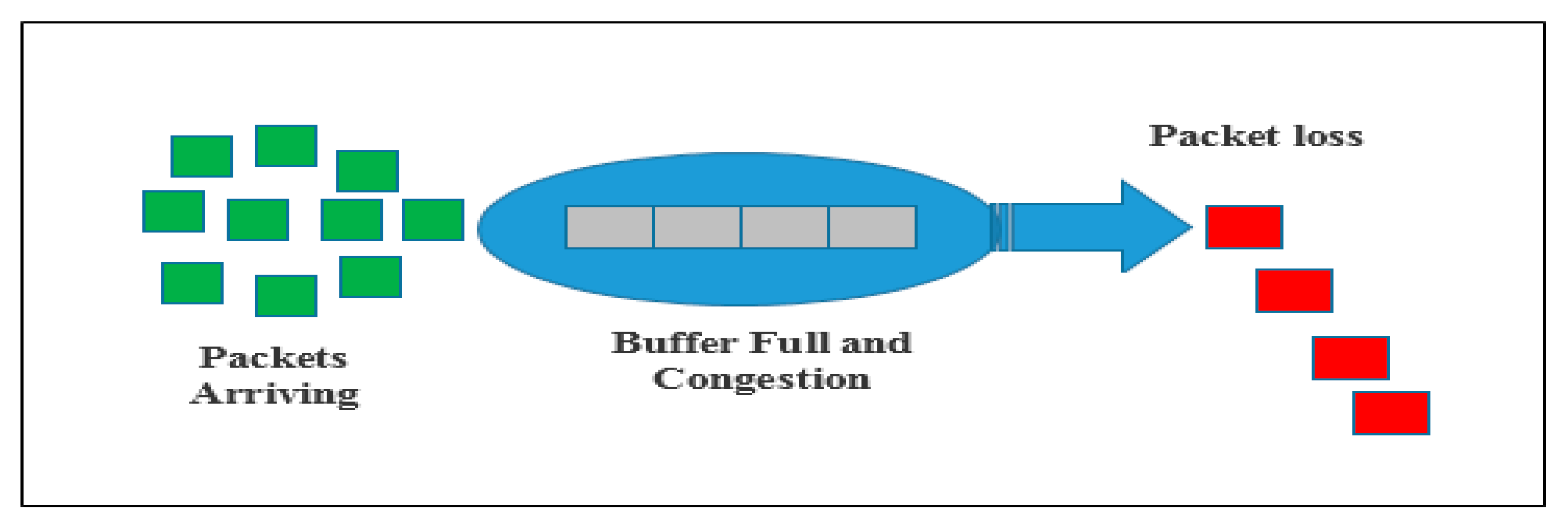
:1. Introduction
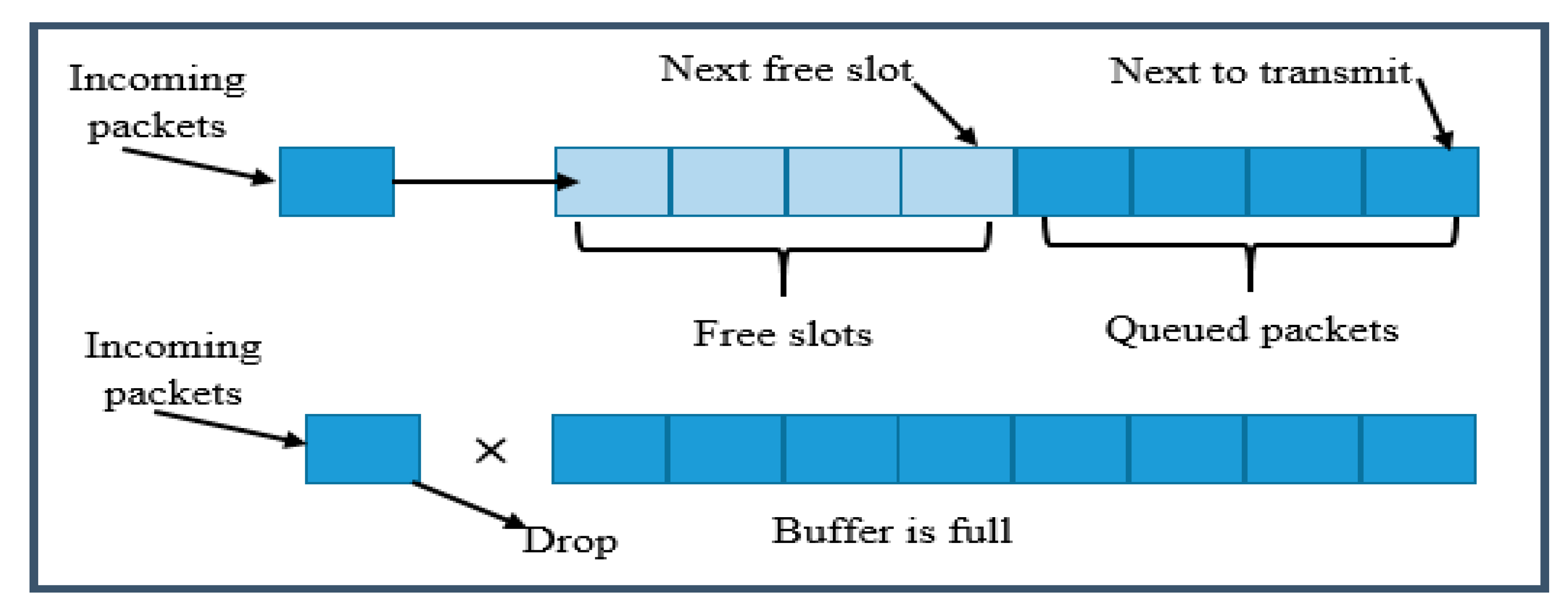
2. Related Works
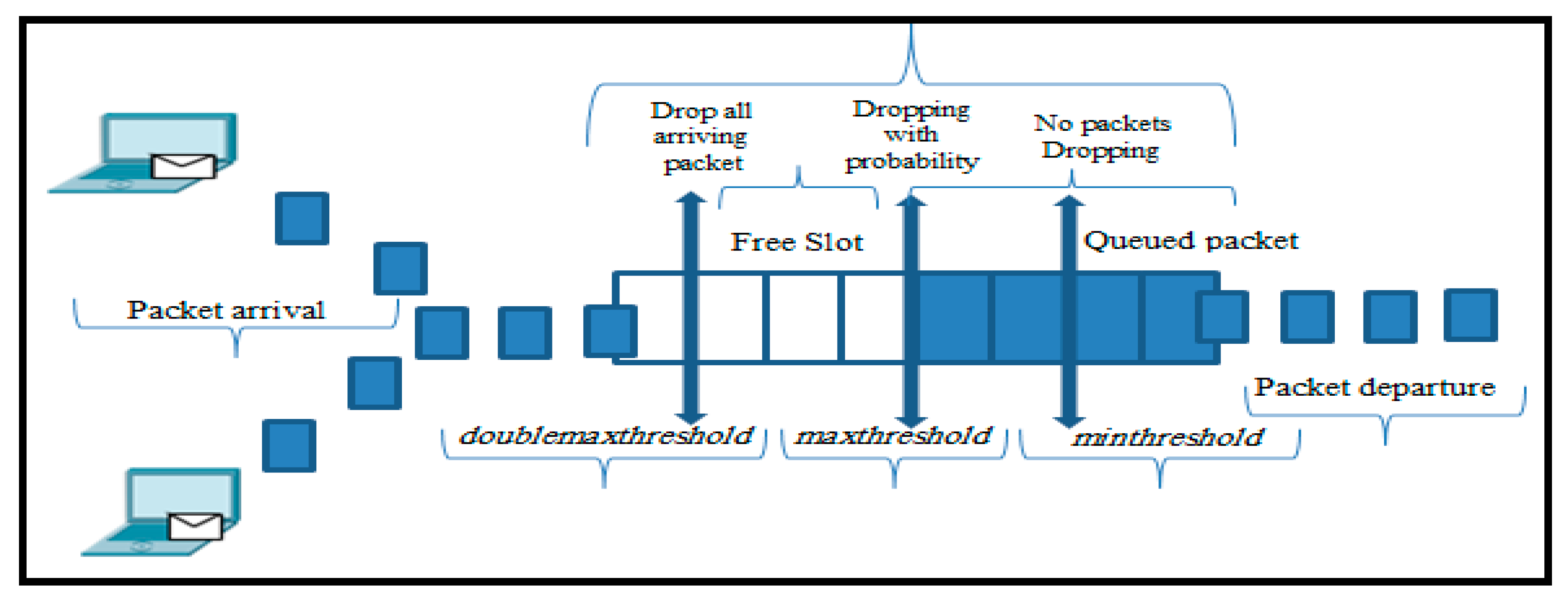
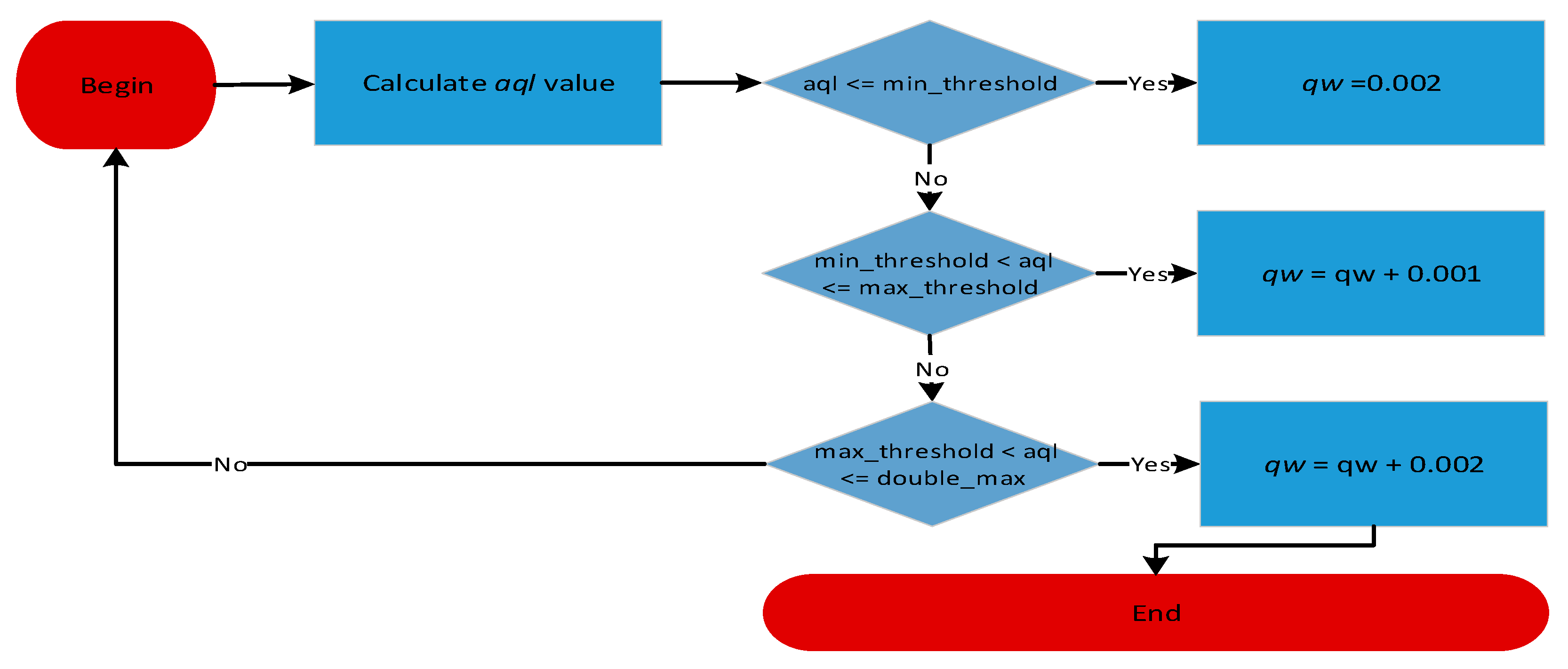
3. Proposed Algorithm
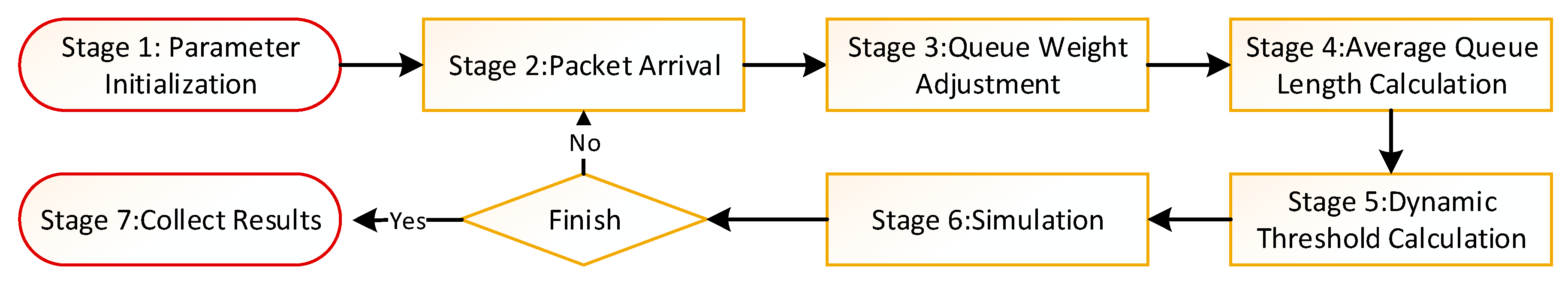
Phases of the WQDAQM Algorithm
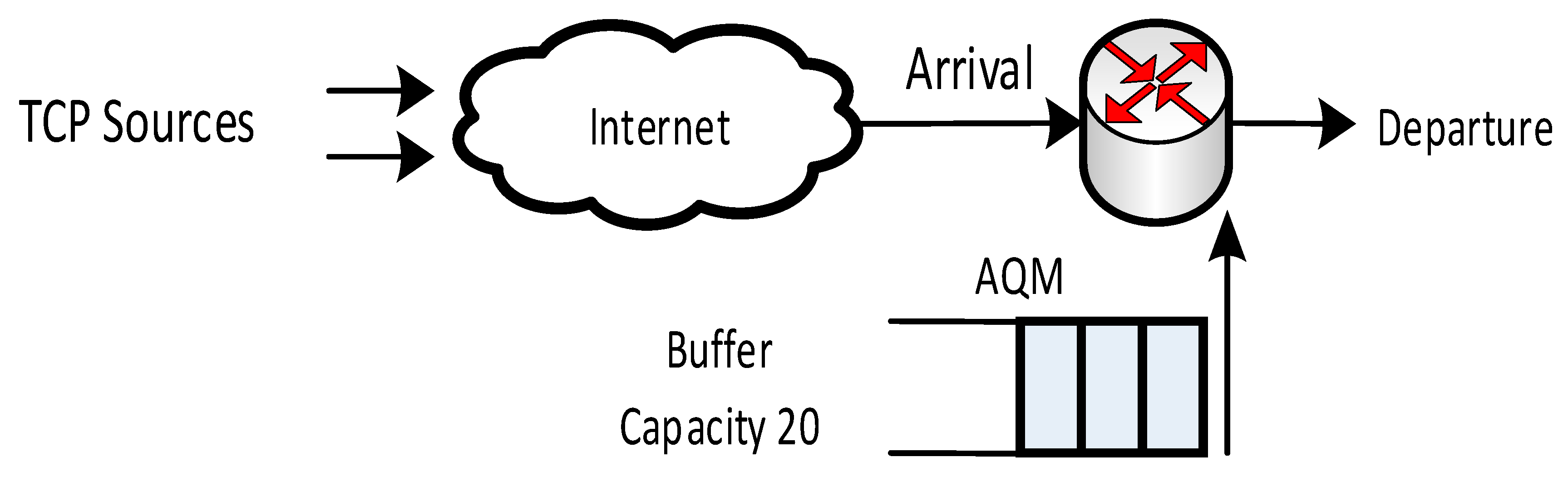
4. Simulation
5. Evaluation Results
5.1. mql
5.2. D
5.3. T
5.4. PL and DP
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Zubi, M.; Abu Shareha, A.A. Efficient signcryption scheme based on El-Gamal and Schnorr. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 78, 11091–11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welzl, M. Network Congestion Control: Managing Internet Traffic, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Baklizi, M.; Ababneh, J.M.; Abdallah, N. Performance investigations of flred and agred active queue management methods. In Proceedings of the Academicsera 13th International Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–24 February 2018; p. 14. [Google Scholar]
- Khatari, M.; Samara, G. Congestion control approach based on effective random early detection and fuzzy logic. MAGNT 2015, 3, 180–193. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Zhao, K.; Fang, Y.; Cui, J. Dynamic Traffic Scheduling and Congestion Control across Data Centers Based on SDN. Futur. Internet 2018, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abu Shareha, A.A.; Mandava, R.; Khan, L.; Ramachandram, D. Multimodal concept fusion using semantic closeness for image concept disambiguation. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2011, 61, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklizi, M.; Ababneh, J. A Survey in Active Queue Management Methods According to Performance Measures. Int. J. Comput. Trends Technol. 2016, 38, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shareha, A.A. Enhanced Random Early Detection using Responsive Congestion Indicators. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrycz, W.; Vasilakos, A. Computational Intelligence in Telecommunications Networks; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; p. 528. [Google Scholar]
- Abdeljaber, H.; Ababneh, J.; Daoud, A.; Baklizi, M. Performance Analysis of the Proposed Adaptive Gentle Random Early Detection Method under NonCongestion and Congestion Situations. In International Conference on Digital Enterprise and Information Systems (DEIS); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 592–603. [Google Scholar]
- Abualhaj, M.M.; Abu Shareha, A.A.; Al-Tahrawi, M.M. FLRED: An efficient fuzzy logic based network congestion control method. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 30, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklizi, M.; Abdel-Jaber, H.; Abu-Shareha, A.A.; Abualhaj, M.M.; Ramadass, S. Fuzzy Logic Controller of Gentle Random Early Detection Based on Average Queue Length and Delay Rate. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 16, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ababneh, J.; Abdel-Jaber, H.; Thabtah, F.; Hadi, W.; Badarneh, E. Derivation of Three Queue Nodes Discrete-Time Analytical Model Based on DRED Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2010 Seventh International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 12–14 April 2010; pp. 885–890. [Google Scholar]
- Chintam, J.R.; Daniel, M. Real-Power Rescheduling of Generators for Congestion Management Using a Novel Satin Bowerbird Optimization Algorithm. Energies 2018, 11, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baklizi, M.; Ababneh, J. Performance Evaluation of the Proposed Enhanced Adaptive Gentle Random Early Detection Algorithm in Congestion Situations. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2016, 6, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Baklizi, M. Stabilizing Average Queue Length in Active Queue Management Method. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklizi, M.; Ababneh, J.; Abualhaj, M.M.; Abdullah, N.; Abdullah, R. Markov-Modulated Bernoulli Dynamic Gentle, Random Early Detection. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2018, 9, 6688–6698. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yang, O.W.W. Using Fuzzy Logic Control to Provide Intelligent Traffic Management Service for High-Speed Networks. In IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management; June 2013; Volume 10, pp. 148–161. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6514996 (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Baklizi, M. FLACC: Fuzzy Logic Approach for Congestion Control. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baklizi, M.; Abdeljaber, H.; Abualhaj, M.M.; Abdullah, N.; Ramadass, S.; Almomani, A. Dynamic Stochastic Early Discovery: A New Congestion Control Technique to Improve Networks Performance. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2013, 9, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Wen, Y.; Foh, C.H.; Niyato, D.; Xie, H. A Survey on Software-Defined Networking. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 27–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Shareha, A.A. Controlling Delay at the Router Buffer Using Modified Random Early Detection. Int. J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2019, 11, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaaidah, A.; Zalisham, M.; Fadli, M.; Abdeljaber, H. Markov-Modulated Bernoulli-Based PErformence Analysis for Gentle Blue and Blue Algorithms under Bursty and Correlated traffic. J. Comput. Sci. 2016, 12, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brandauer, C.; Iannaccone, G.; Diot, C.; Fdida, S. Comparison of Tail Drop and Active Queue Management Performance for Bulk-Data and Web-Like Internet Traffic. In Proceedings of the Sixth IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications, Hammamet, Tunisia, 5 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, S. Recommendations on Using the Gentle Variant of RED. Available online: http://www.aciri.org/floyd/red/gentle.html (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Loukas, R.; Kohler, S.; Andreas, P.; Phuoc, T.G. Fuzzy RED: Congestion control for TCP/IP Diff-Serv. In Proceedings of the 10th Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference, Information Technology and Electrotechnology for the Mediterranean Countries, Lemesos, Cyprus, 29–31 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Floyd, S.; Jacobson, V. Random early detection gateways for congestion avoidance. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 1993, 1, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.H.; Yuan, L.; Fu, L.; Zhang, L. Research note: Methodology for traffic modeling using two-state Markov-modulated Bernoulli process. Comput. Commun. 1999, 22, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, M.E. Communication and Computer Networks: Modelling with Discrete-Time Queues; Wiley-IEEE Computer Society Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-jaber, H.; Thabtah, F.; Woodward, M. Traffic Management for the Gentle Random Early Detection Using Discrete-Time Queueing. In Proceedings of the International Business Information Management Conference (9th IBIMA), Marrakech, Morocco, 4–6 January 2008; pp. 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Abdeljaber, H.; Thabtah, F.; Woodward, M.; Ababneh, J.; Bazar, H. Random Early Dynamic Detection Approach for Congestion Control Baltic. J. Mod. Comput. 2014, 2, 16–31. [Google Scholar]











| Algorithms | Metric(s) | Adaptive/Non Adaptive | Dropping Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drop tail | Queue length (q) | Non Adaptive | Drop all packets only after the buffer gets overloaded | Simple and low computation overhead requirements | High PL, high delay and low throughput, and leads to global synchronization |
| RED | (Qavg) | Non Adaptive | Drop packets stochastically | Eliminate global synchronization problems | Sensitive to sudden congestion |
| GRED | (Qavg) | adaptive | Drop packets stochastically | More robust to sudden congestion | Several threshold values, parameterization and overflow |
| DGRED | Qavg | adaptive | Drop packets stochastically | Stabilize Qavg partially | Several threshold values, parameterization and overflow |
| SDGRED | Qavg | adaptive | Uses dynamic thresholds based on the value of aql to detect congestion at an early stage | Stabilize Qavg partially | Several threshold values, parameterization and overflow |
| Parameters | GRED Algorithm | DGRED Algorithm | SDGRED Algorithm | WQDAQM Algorithm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha | 0.33–0.93 | 0.33–0.93 | 0.33–0.93 | 0.33–0.93 |
| qw | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | Dynamic |
| Beta | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Maximum probability | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Slot | 2 million | 2 million | 2 million | 2 million |
| Buffer size | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Minimum T | 3 | .. | .. | .. |
| Maximum T | 9 | .. | .. | .. |
| Double MT | 18 | .. | .. | .. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baklizi, M. Weight Queue Dynamic Active Queue Management Algorithm. Symmetry 2020, 12, 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12122077
Baklizi M. Weight Queue Dynamic Active Queue Management Algorithm. Symmetry. 2020; 12(12):2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12122077
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaklizi, Mahmoud. 2020. "Weight Queue Dynamic Active Queue Management Algorithm" Symmetry 12, no. 12: 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12122077
APA StyleBaklizi, M. (2020). Weight Queue Dynamic Active Queue Management Algorithm. Symmetry, 12(12), 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12122077




