Kramers Degeneracy and Spin Inversion in a Lateral Quantum Dot
Abstract
1. Introduction
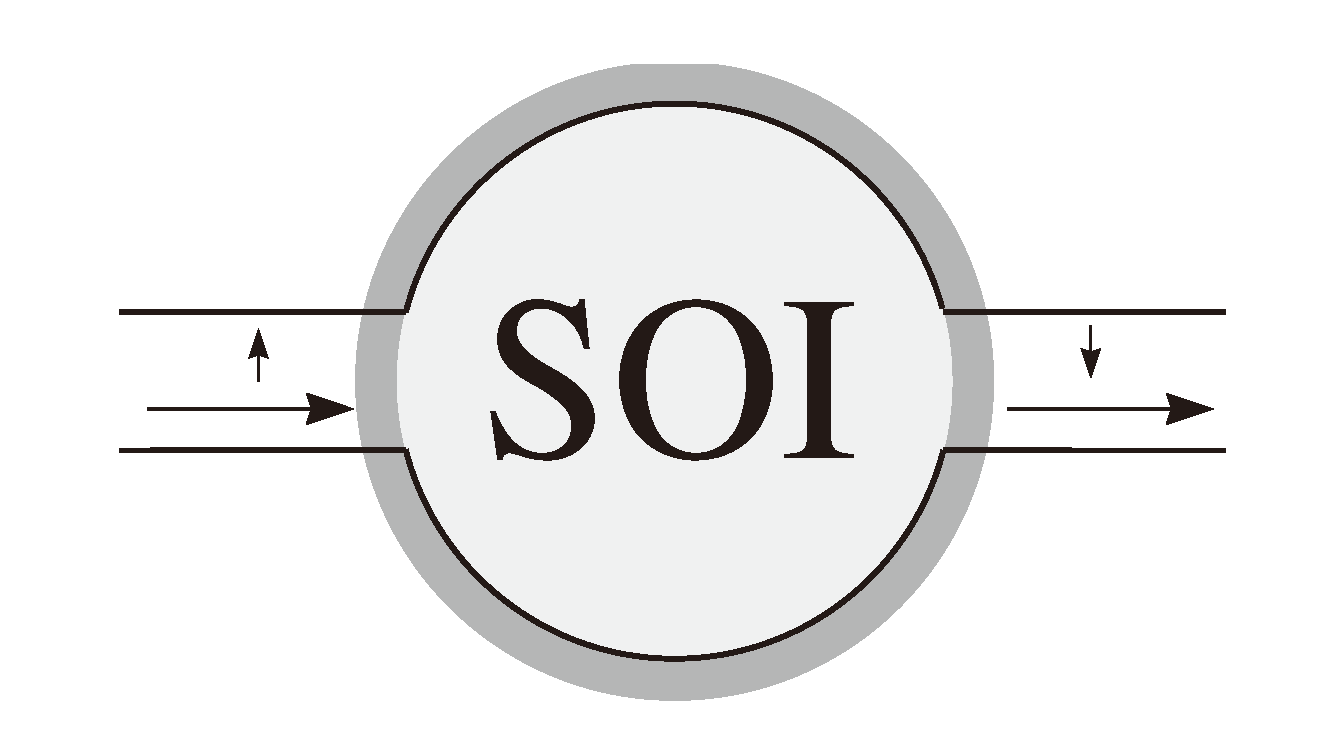
2. Symmetry of Rashba SOI
3. Effective Hamiltonian Model
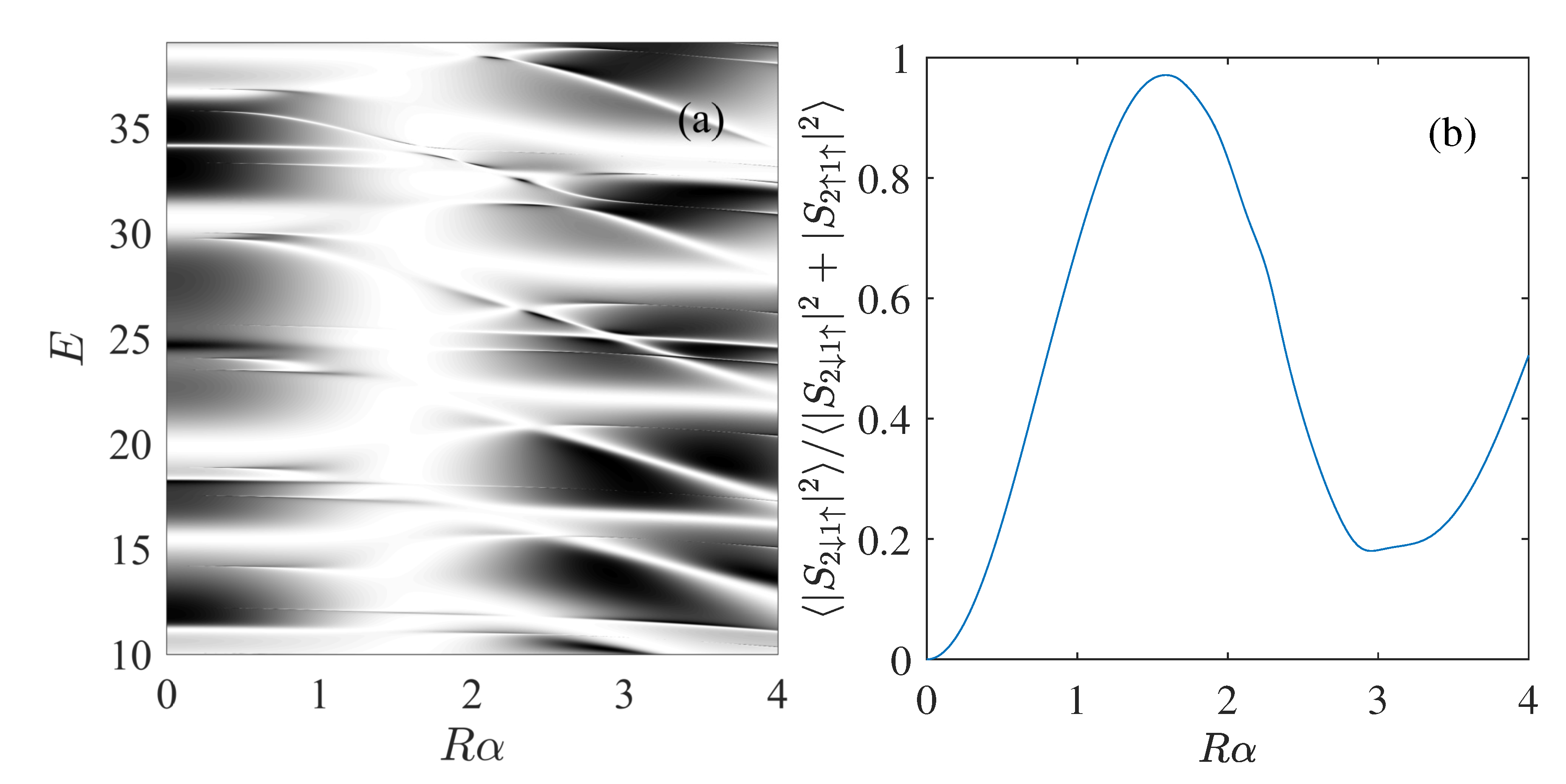
4. The 2D Model
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Derivation of Effective Hamiltonian on 2D Square Lattice
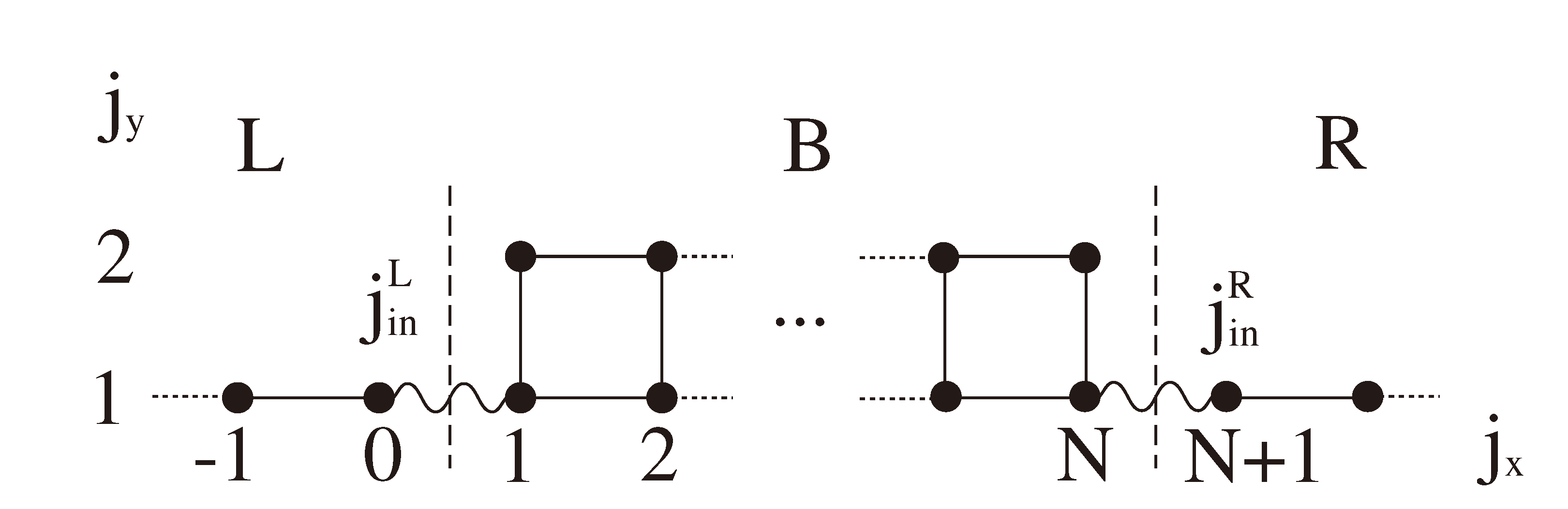
Appendix A.1. Normalization Constant of the Electrode Eigenfunctions
Appendix A.2. Integral Over Zone
References
- Wolf, S.A. Spintronics: A Spin-Based Electronics Vision for the Future. Science 2001, 294, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žutić, I.; Fabian, J.; Sarma, D.S. Spintronics: Fundamentals and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2004, 76, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, R.; Kouwenhoven, L.P.; Petta, J.R.; Tarucha, S.; Vandersypen, L.M.K. Spins in few-electron quantum dots. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2007, 79, 1217–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, H.A.; Loss, D. Detection of Single Spin Decoherence in a Quantum Dot via Charge Currents. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 4648–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghan, E.; Khoshnoud, D.S.; Naeimi, A. Logical spin-filtering in a triangular network of quantum nanorings with a Rashba spin-orbit interaction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2018, 529, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattari, F.; Mirershadi, S. Spin-dependent transport properties in strained silicene with extrinsic Rashba spin-orbit interaction. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 445, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudlak, M.; Nazmitdinov, R.G. Spin-dependent electron transmission across the corrugated graphene. Physica E 2020, 118, 113846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Adelmann, C.; Crooker, S.A.; Garlid, E.S.; Zhang, J.; Reddy, K.S.M.; Flexner, S.D.; Palmstrm, C.J.; Crowell, P.A. Electrical detection of spin transport in lateral ferromagnet-semiconductor devices. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.P.; Sharma, S.; Patel, R.S.; de Jong, M.P.; Jansen, R. Electrical creation of spin polarization in silicon at room temperature. Nature 2009, 462, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciorga, M.; Einwanger, A.; Wurstbauer, U.; Schuh, D.; Wegscheider, W.; Weiss, D. Electrical spin injection and detection in lateral all-semiconductor devices. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 165321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valín-Rodríguez, M.; Nazmitdinov, R.G. Model for spin-orbit effects in two-dimensional semiconductors in magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 235306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, J.; Matos-Abiague, A.; Ertler, C.; Stano, P.; Žutić, I. Semiconductor spintronics. Acta Phys. Slovaca 2007, 57, 565–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmitdinov, R.G.; Pichugin, K.N.; Valín-Rodríguez, M. Spin control in semiconductor quantum wires: Rashba and Dresselhaus interaction. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 193303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliemann, J. Colloquium: Persistent spin textures in semiconductor nanostructures. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2017, 89, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, Y.A.; Rashba, E.I. Oscillatory effects and the magnetic susceptibility of carriers in inversion layers. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1984, 17, 6039–6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashba, E.I. Electron spin operation by electric fields: Spin dynamics and spin injection. Phys. Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2004, 20, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, J.; Akazaki, T.; Takayanagi, H.; Enoki, T. Gate Control of Spin-Orbit Interaction in an Inverted In0.53Ga0.47As/In0.52Al0.48As Heterostructure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundler, D. Large Rashba splitting in InAs quantum wells due to electron wave function penetration into the barrier layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 6074–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.; Nitta, J.; Akazaki, T.; Takayanagi, H.; Osaka, J.; Pfeffer, P.; Zawadzki, W. Zero-field spin splitting in an inverted In0.53Ga0.47As/In0.52Al0.48As heterostructure: Band nonparabolicity influence and the subband dependence. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 7736–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutchyn, R.M.; Sau, J.D.; Das Sarma, S. Majorana Fermions and a Topological Phase Transition in Semiconductor-Superconductor Heterostructures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 077001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreg, Y.; Refael, G.; von Oppen, F. Helical Liquids and Majorana Bound States in Quantum Wires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 177002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourik, V.; Zuo, K.; Frolov, S.M.; Plissard, S.R.; Bakkers, E.P.A.M.; Kouwenhoven, L.P. Signatures of Majorana Fermions in Hybrid Superconductor-Semiconductor Nanowire Devices. Science 2012, 336, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucignano, P.; Mezzacapo, A.; Tafuri, F.; Tagliacozzo, A. Advantages of using high-temperature cuprate superconductor heterostructures in the search for Majorana fermions. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 144513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinovaja, J.; Loss, D. Time-reversal invariant parafermions in interacting Rashba nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 045118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.R.; Franz, M. Colloquium: Majorana fermions in nuclear, particle, and solid-state physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2015, 87, 137–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.D.; Freedman, M.; Nayak, C. Majorana zero modes and topological quantum computation. Quantum Inf. 2015, 1, 15001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, D.; Hell, M.; Mishmash, R.V.; Higginbotham, A.; Danon, J.; Leijnse, M.; Jespersen, T.S.; Folk, J.A.; Marcus, C.M.; Flensberg, K.; et al. Milestones Toward Majorana-Based Quantum Computing. Phys. Rev. X 2016, 6, 031016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Nitta, J.; Akazaki, T.; Takayanagi, H. Rashba spin-orbit coupling probed by the weak antilocalization analysis in InAlAs/InGaAs/InAlAs quantum wells as a function of quantum well asymmetry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 046801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governale, M.; Boese, D.; Zülicke, U.; Schroll, C. Filtering spin with tunnel-coupled electron wave guides. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 140403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohe, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Ohtsuki, T.; Nitta, J. Mesoscopic Stern-Gerlach spin filter by nonuniform spin-orbit interaction. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 041308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Vasilopoulos, P. Spin-dependent transmission in waveguides with periodically modulated strength of the spin-orbit interaction. App. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, J.J. Modern Quantum Mechanics; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Heiss, W.D.; Nazmitdinov, R.G. Orbital magnetism in small quantum dots with closed shells. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 1998, 68, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Könemann, J.; Haug, R.J.; Maude, D.K.; Fal’ko, V.I.; Altshuler, B.L. Spin-Orbit Coupling and Anisotropy of Spin Splitting in Quantum Dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 226404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valín-Rodríguez, M.; Puente, A.; Serra, L. Role of spin-orbit coupling in the far-infrared absorption of lateral semiconductor dots. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 045317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaux, C.; Weidenmüller, H.A. Shell-Model Approach to Nuclear Reactions; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Dittes, F.M. The decay of quantum systems with a small number of open channels. Phys. Rep. 2000, 339, 215–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadreev, A.F.; Rotter, I. S-matrix theory for transmission through billiards in tight-binding approach. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2003, 36, 11413–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiselev, A.A.; Kim, K.W. Prohibition of equilibrium spin currents in multiterminal ballistic devices. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71, 153315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.; Xu, H.Q. Symmetry of Spin Transport in Two-Terminal Waveguides with a Spin-Orbital Interaction and Magnetic Field Modulations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 246601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, E.N.; Sadreev, A.F. Spin polarization in quantum dots by radiation field with circular polarization. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 2001, 73, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihn, T. Semiconductor Nanostructures: Quantum States and Electronic Transport; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, T. Quantum point contacts in magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. B 1991, 44, 8017–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazmitdinov, R.G.; Pichugin, K.N.; Rotter, I.; Šeba, P. Whispering gallery modes in open quantum billiards. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 056214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazmitdinov, R.G.; Pichugin, K.N.; Rotter, I.; Šeba, P. Conductance of open quantum billiards and classical trajectories. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 085322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandalov, I.; Nazmitdinov, R.G. Shell effects in nonlinear magnetotransport through small quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 075315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
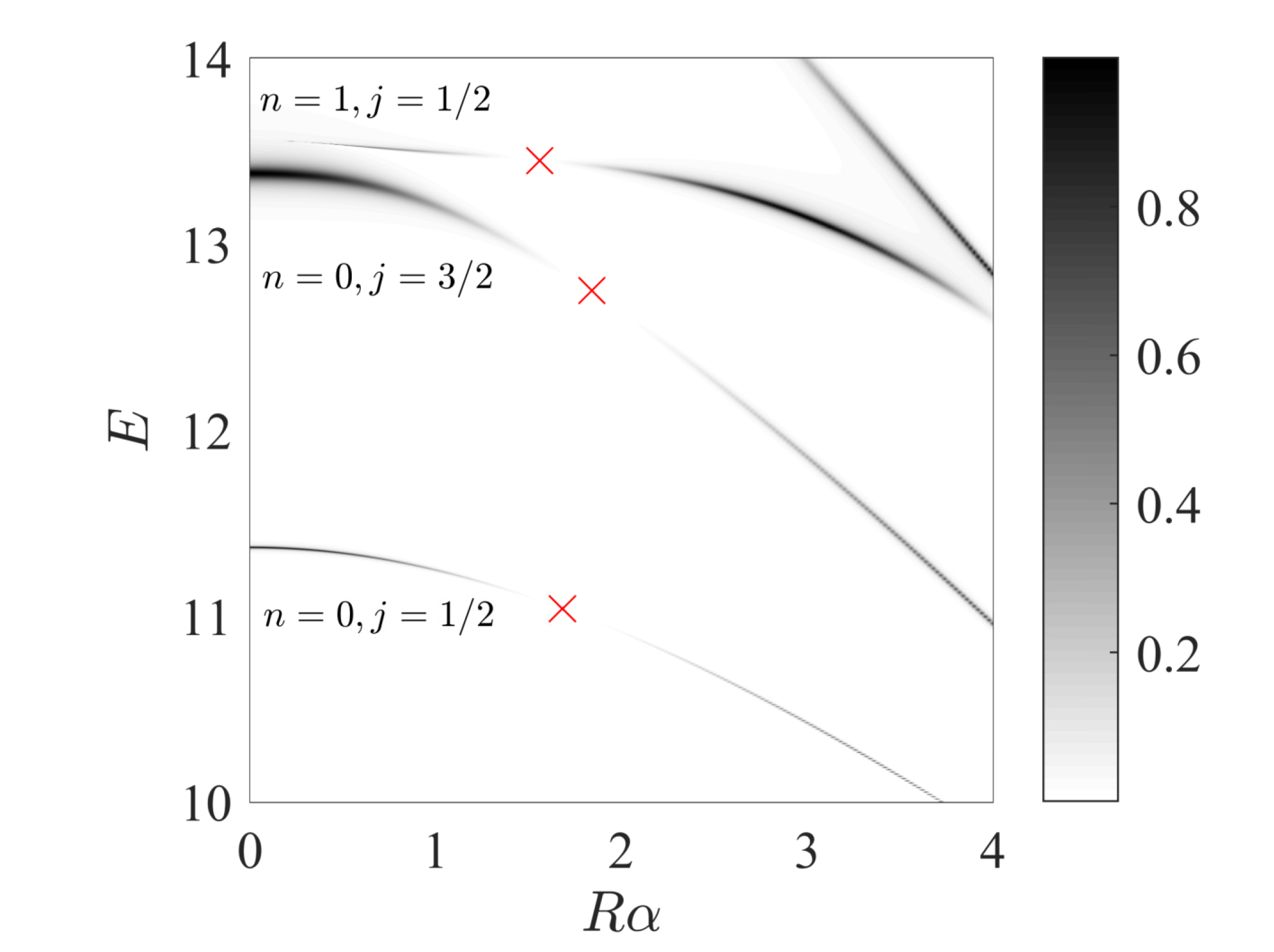
| n | j | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1/2 | 1.68 |
| 0 | 3/2 | 1.85 |
| 1 | 1/2 | 1.57 |
| 0 | 5/2 | 1.98 |
| 1 | 3/2 | 1.61 |
| 2 | 1/2 | 1.59 |
| 0 | 7/2 | 2.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pichugin, K.; Puente, A.; Nazmitdinov, R. Kramers Degeneracy and Spin Inversion in a Lateral Quantum Dot. Symmetry 2020, 12, 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12122043
Pichugin K, Puente A, Nazmitdinov R. Kramers Degeneracy and Spin Inversion in a Lateral Quantum Dot. Symmetry. 2020; 12(12):2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12122043
Chicago/Turabian StylePichugin, Konstantin, Antonio Puente, and Rashid Nazmitdinov. 2020. "Kramers Degeneracy and Spin Inversion in a Lateral Quantum Dot" Symmetry 12, no. 12: 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12122043
APA StylePichugin, K., Puente, A., & Nazmitdinov, R. (2020). Kramers Degeneracy and Spin Inversion in a Lateral Quantum Dot. Symmetry, 12(12), 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12122043






