Abstract
Using different chaotic systems in secure communication, nonlinear control, and many other applications has revealed that these systems have several drawbacks in different aspects. This can cause unfavorable effects to chaos-based applications. Therefore, presenting a chaotic map with complex behaviors is considered important. In this paper, we introduce a new 2D chaotic map, namely, the 2D infinite-collapse-Sine model (2D-ICSM). Various metrics including Lyapunov exponents and bifurcation diagrams are used to demonstrate the complex dynamics and robust hyperchaotic behavior of the 2D-ICSM. Furthermore, the cross-correlation coefficient, phase space diagram, and Sample Entropy algorithm prove that the 2D-ICSM has a high sensitivity to initial values and parameters, extreme complexity performance, and a much larger hyperchaotic range than existing maps. To empirically verify the efficiency and simplicity of the 2D-ICSM in practical applications, we propose a symmetric secure communication system using the 2D-ICSM. Experimental results are presented to demonstrate the validity of the proposed system.
1. Introduction
Numerous phenomena have been comprehended by studying the complex behaviors in many natural and non-natural dynamical systems. Understanding the chaotic behavior, which is a kind of nonlinear complex dynamical behavior, has provided a significant description of these systems. Although dynamical systems with chaotic behaviors are deterministic, long-term prediction of their behaviors is impossible [1]. Moreover, the sensitivity, topological mixing, and orbits density are the main characteristics of the chaotic systems [2,3,4]. Therefore, chaotic systems have valuable applications in various fields including computer science, telecommunication, physics, engineering, etc. [5,6,7,8,9,10]. In particular, due to the similarity between the characteristics of chaotic systems and the diffusion and confusion properties of cryptography [11], a wide body of chaos-based cryptographic applications has been presented in the last few years [12,13,14,15,16,17].
For the time being, discrete-time systems and continuous-time systems are the major types of chaotic systems. The former type is described by a difference equation, and it can be implemented through an iterative procedure, while the latter one is usually represented by a partial and/or ordinary differential equation. Edward Lorenz was the first to present a chaotic system with continuous- time [18]. Subsequently, several well-known continuous-time chaotic and hyperchaotic systems have been proposed such as Rössler [19], Sprott [20], Chen [21], and Lü [22] systems. On the other hand, the Logistic map, which was presented by Robert May, is the first clear example of a discrete-time system with chaotic behavior [23]. Since then various discrete-time chaotic and hyperchaotic systems have been presented in the literature [24,25,26,27,28].
During the past recent years, significant efforts in the prediction of chaotic systems’ behaviors have been devoted through determining their parameters [29], or estimating their states [30]. Predicting the behavior of a chaotic system can render chaos-based cryptosystem insecure [31]. This has raised the need for measuring the complexity of the employed chaotic systems [32,33]. Therefore, numerous algorithms have emerged to measure the complexity of the systems’ time series such as Fuzzy Entropy [34], Modified Permutation-Entropy [35], and Sample Entropy [36].
Due to the performance drawbacks of many existing chaotic systems in some attributes, for instance, frail chaos (i.e., chaotic behavior appears only in insulated zones of the system’ parameters), it motivated researchers to propose systems with robust chaos that can encourage chaos-based cryptographic applications. An example of such weakness is that through a slight perturbation to a single parameter, it could make the system collapse into a non-chaotic zone of the system [37].
Based on the aforementioned description, this paper proposes a new chaotic discrete-time system, called the 2D infinite-collapse-Sine model (2D-ICSM). The 2D-ICSM exhibits a wide hyperchaotic range, good ergodicity, high complexity, and sensitivity. Therefore, 2D-ICSM could be an ideal source for chaos-based cryptographic applications. The main contributions of this work are as follows.
- We introduce an analytical framework to understand the dynamical behavior of the 2D-ICSM including stability of its fixed points, bifurcation diagram, and Lyapunov Exponents.
- We experimentally evaluate the complexity, sensitivity, and randomness of the 2D-ICSM using Sample Entropy, cross-correlation coefficient, and NIST-800-22 statistical test, respectively.
- To demonstrate the efficiency and simplicity of the 2D-ICSM in practical applications, we design a secure communication system, and then experimented tested it on an optical channel with Arduino microcontrollers.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the 2D-ICSM and studies the stability of its equilibria. In Section 3, we analyze the dynamics of the 2D-ICSM. Section 4 demonstrates the high sensitivity and randomness of the 2D-ICSM. Section 5 demonstrates the detailed complexity performance of the 2D-ICSM. In Section 6, we introduce the proposed secure communication system. Section 7 illustrates the implementation of the communication system. Conclusions are presented in Section 8.
2. The 2D Infinite-Collapse-Sine Model
In this section, we introduce a new 2D chaotic map, called the 2D infinite-collapse-Sine model (2D-ICSM), and then discusses its stability analysis.
2.1. Definition of 2D-ICSM
Among existing 1D discrete-time dynamical systems, the infinite collapse model is considered as one of the best maps that show robust chaotic performance [38]. Mathematically, its dynamical equation is given by
where is the control parameter and x is the state variable. The dynamical behavior of this map can be illustrated by depicting its bifurcation diagram and trajectory in the phase plane, as shown in Figure 1. It can be seen that the numerical solution of this map is in the range of . Besides that, the bifurcation diagram of this map shows that the chaotic attractor appears in limited regions of its parameter. Meanwhile, several non-chaotic regions can be observed as the parameter increasing. Furthermore, Figure 1b demonstrates that its trajectory only occupies a small space in the phase plane. Such behaviors are widely observed in the existing 1D chaotic maps such as Logistic, Tent, and Sine maps.

Figure 1.
Dynamical behavior of the infinite collapse map (1) with : (a) bifurcation diagram for and (b) chaotic attractor for .
To tackle the aforementioned issues, we propose a new 2D chaotic map, which consists of four terms with two control parameters. Mathematically, it is defined as follows,
where is the amplitude parameter and is the internal frequency parameter. It can be seen that the proposed 2D infinite-collapse-Sine model (2D-ICSM) is mainly designed by using three components including a linear variable, 1D Sine map, and 1D infinite collapse map. The linear state variable is used to modulate the output of a 1D infinite collapse map. Therefore, it can enhance the chaotic behavior of the state variable . Meanwhile, the 1D Sine map is employed to boost randomness to the state variable .
2.2. Stability Analysis
For discrete-time systems, the fixed point of a function form a graphical point of view is an element in the domain that maps to itself by the function. For instance, P is a fixed point of the function only when . To simplify the calculation of the fixed points of 2D-ICSM, we reduce its dimension to become 1D as follows,
The fixed points of the 2D-ICSM are calculated for two different sets of system parameters. For each set of parameters, we obtain the fixed points of the variable y by Equation (3), and subsequently, the corresponding points of the variable x can be easily obtained by the first equation of the system (2). Figure 2 illustrates how the fixed points of the variable y can be obtained using the graphical method. From this figure, one can notice that the number of fixed points is increased as the values of the amplitude and internal frequency parameters increase. Now, let us collect some fixed points from each set of system parameters to investigate their stability. First, we have extracted the following fixed point from the first set of the system parameters,

Figure 2.
Fixed points of the 2D-ICSM: (a) for the parameters ; (b) for the parameters .
Second, we have extracted three different fixed points from the second set as follows,
The stability of the above-fixed points can be determined by obtaining the Jacobian matrix, which is given by
Using the above matrix, the 2D-ICSM is Linearized at any arbitrary fixed point as follows,
Thus, the eigenvalues are obtained by solving the following equation,
It is well-known that the stability of fixed points is dependent on the eigenvalues. When an eigenvalue is within the interval , then the fixed point exhibits a stable state. Otherwise, it shows an unstable state. Moreover, the stability of the obtained fixed points is as illustrated in Table 1. All the selected fixed points of the 2D-ICSM are unstable.

Table 1.
The fixed points of the 2D infinite-collapse-Sine model (2D-ICSM) and their stability analysis.
3. Dynamical Behaviors
This section investigates the dynamical behaviors of 2D-ICSM through the bifurcation diagram, Lyapunov Exponents, and phase space.
3.1. Bifurcation Diagram and Lyapunov Exponents
Typically, the bifurcation diagram and Lyapunov Exponents are used to determined the non-chaotic and chaotic regions of a dynamical system when one of its parameters varies. Furthermore, the Lyapunov exponent is used to evaluate the chaotic properties of a dynamical system. In other words, it could recognize the chaotic and hyperchaotic behaviors of the system. A system is recognized as chaotic when there is one positive Lyapunov Exponent value for each parameter value, whereas the hyperchaotic system has more than one positive Lyapunov Exponent value. The hyperchaotic system exhibits a higher level of randomness, and the generated sequences by the hyperchaotic system show extreme unpredictability.
To investigate the dynamics of 2D-ICSM, we depict its bifurcation diagram and Lyapunov Exponents with the initial values and for the parameters and , as shown in Figure 3. It can be seen that 2D-ICSM is hyperchaotic among the whole parameter range, which indicates that its sequences are extremely hard to be predicted.

Figure 3.
Dynamics of the 2D-ICSM with the initial values and for the parameter : (a) bifurcation diagram; (b) Lyapunov Exponents.
3.2. Hyperchaotic Attractor
The set of numerical values, which is generated by a chaotic/hyperchaotic map with specific sets of initial values and control parameters, is called chaotic/hyperchaotic attractor. For a 2D map, its attractor can be described by a group of points that occupies a particular region in the phase space. A chaotic/hyperchaotic model has better performance when its attractor is geometrically complicated and occupies a larger range in the phase space. To illustrate the hyperchaotic range of the 2D-ICSM, Figure 4f depicts its attractor in the 2D phase space with the parameters and . Besides that, this figure plots the attractors of several existing chaotic and hyperchaotic models to demonstrate the complicated behavior of the 2D-ICSM. It can be observed that the hyperchaotic attractor of 2D-ICSM fully occupies a 2D phase space ranging and . This means that 2D-ICSM can generate more unpredictable hyperchaotic sequences and it has a better competitive ergodicity property than existing models.

Figure 4.
Chaotic and hyperchaotic attractors of different 2D maps: (a) 2D-SLMM [12]; (b) 2D-SIMM [13]; (c) 2D Ushiki map [39]; (d) 2D-LASM [14]; (e) 2D-LICM [15]; (f) the 2D-ICSM.
4. Performance Evaluations
In this section, the sensitivity of the initial conditions and the control parameters is measured by the cross-correlation coefficient. Furthermore, the quantitative values of the randomness of sequences generated by the 2D-ICSM are determined using NIST-800-22 randomness tests.
4.1. Cross-Correlation Coefficient
To estimate the sensitivity of the initial conditions and the control parameters of the 2D-ICSM, we use the cross-correlation coefficient (CCF); its equation is given by
where represents the mean value of the time series , meanwhile represents the mean value of the time series . When is close to 0, then it can be indicated that these two-time series are diverging.
Figure 5 presents the sensitivity of the 2D-ICSM with the parameters and . In this figure, the sensitivity is estimated by calculating the CCF between the original time series and the modified time series. It is important to mention here that the modified time series was generated by the 2D-ICSM using a very small error, , which was added to the initial value and the parameter , as shown in Figure 5a,b, respectively. It can be observed that the 2D-ICSM has a high level of sensitivity to its initial values and control parameters.

Figure 5.
The CCF analysis of the 2D-ICSM with and : (a) the CCF with the initial values ; (b) the CCF with the initial values and for .
4.2. Chaos-Based Pseudorandom Number Generator
A chaotic map could be a suitable source to generate pseudorandom numbers when it has high sensitivity, good ergodicity, and extreme unpredictability. The existence of these features in a chaotic map can be determined by the NIST-800-22 randomness tests.
It is, therefore, crucial to determine the existence of such features in the 2D-ICSM to examine its ability to be a PRNG. In this regard, we propose a simple strategy, which directly employs the chaotic sequences as pseudorandom numbers by converting each of their values to a 32-bit binary stream using the IEEE 754 float standard. Figure 6 displays the NIST SP800-22 test results of pseudorandom numbers generated by the 2D-ICSM. In this figure, the generated sequence by 2D-ICSM has a length of binary bits. It is important to state here that a chaotic map can pass the statistical tests of NIST-800-22 only when the corresponding p-values are greater than the experimental significance level [40]. Consequently, the results in Figure 6 demonstrates the high randomness of the generated pseudo random numbers by the 2D-ICSM.

Figure 6.
The p-values of the binary sequence generated by PRNG of the 2D-ICSM with the parameters and .
5. Complexity-Based Sample Entropy
In this section, the complexity of 2D-ICSM is investigated through a fundamental algorithm, namely, Sample Entropy (SamEn). The authors of [36] presented SamEn to calculate how much extra information is required to predict the th output of a trajectory using its previous outputs. SamEn with larger values indicate a lower degree of regularity of a chaotic map. In other words, the chaotic map exhibits a high level of complexity and unpredictability.
The SamEn algorithm for a given time series is outlined as follows:
- Reconstruction: the time series can be reconstructed as follows,where m is embedding dimension and is time delay.
- Counting the vector pairs: For a given tolerance parameter r, let be the number of vectors such thathere, is the distance between and , which is defined as
- Calculating : According to the obtained number of vector pairs, we can getthen calculate by
- Calculating SamEn: Repeating the above steps we can get , then SamEn is given by
Figure 7a plots SamEn results of the 2D-ICSM when the two parameters and are varying simultaneously. This figure provides a more clear vision of the complexity of 2D-ICSM. It can be seen from this figure that the 2D-ICSM exhibits high complexity in most of its parameters setting. However, the highest SamEn values appear whenever the and are increasing.

Figure 7.
SamEn simulation: (a) SamEn values of the 2D-ICSM when its parameters vary; (b) SamEn results of different chaotic and hyperchaotic maps, where parameter represents , for the 2D-ICSM, 2D-LASM [14], 2D-SIMM [13], and 2D-SLMM [12], respectively.
Moreover, Figure 7b depicts the SamEn results of the 2D-ICSM and different chaotic and hyperchaotic maps. It is quite clear that the 2D-ICSM has the largest SamEn values, which indicates that one needs more information to predict the generated sequences by this map.
6. Chaos Based Cryptography
This section investigates the performance of 2D-ICSM in cryptography applications by designing a symmetric secure communication system. Figure 8 displays the schematic diagram of the proposed symmetric secure communication scheme. As can be observed in this figure, the proposed communication system is designed to transmit a message between two points in which the 2D-ICSM is employed to encrypt the information.

Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of the proposed secure communication scheme using the 2D-ICSM.
6.1. Arduino Transmitter
In the proposed communication system, the Arduino is considered as the core of transmission. Here, we employ the Arduino Uno R3 microcontroller boards, which are simple and implemented at a low cost. It has 14 digital input/output pins (6 of them can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz crystal oscillator, a USB connection, and a reset button [41].
First, we convert the signal from the bipolar form to the unipolar form, and this is due to the fact that the Arduino analog inputs only accept unipolar signals in the range from 0 V to 5 V. The communication starts with a message , which is sent to the analog input A0 of the Arduino transmitter, as shown in Figure 9. Second, the input signal is converted from analog to digital using an embedded 8-bit ADC at a maximum rate of 8000 samples per second. Finally, this signal is encrypted by the 2D-ICSM and Delta modulator.

Figure 9.
The transmitter circuit.
6.2. Delta Modulation
The Delta modulation is a simple and robust A / D conversion method [42]. It has a comparator in the forward path and an integrator in the feedback path of a simple control loop, as shown in Figure 10. The signal is the input of the comparator. Meanwhile, is the integrated output, which has a binary form. The value of Delta modulation depends on the current sample, if it is less than the previous sample, then zero is transmitted as a signal, whereas if the current sample is greater than the previous one, then number one is sent as a transmitted signal. Algorithm 1 illustrates the pseudocode of the Delta modulation process.
| Algorithm 1: Delta Modulation |
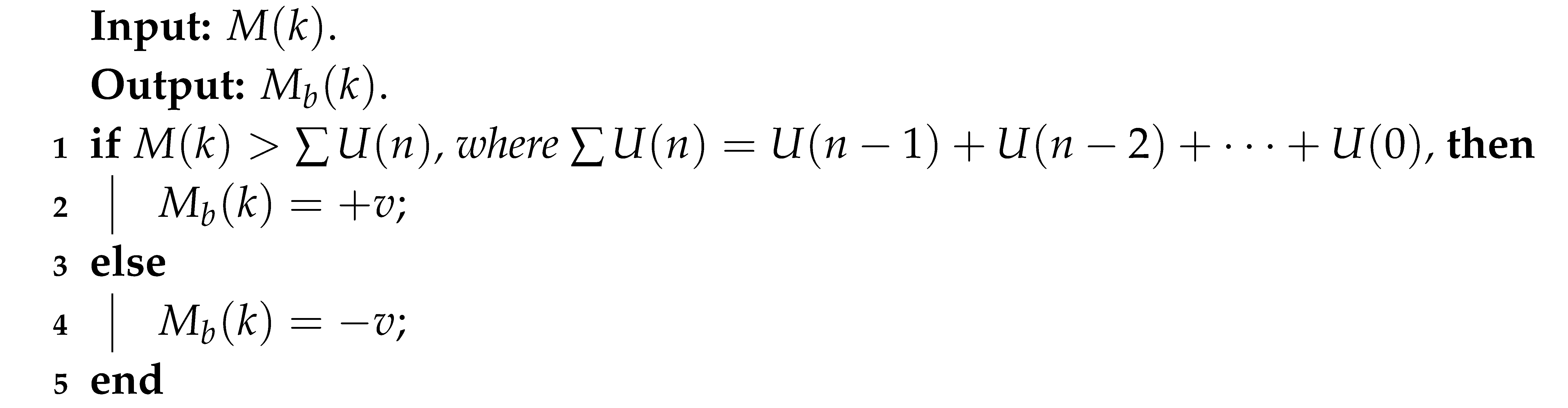 |

Figure 10.
Diagram of the Delta Modulator.
6.3. Encryption Process
The encryption process begins after obtaining the signal from the Delta modulator. First, the secret key of the proposed encryption scheme is mainly generated from the initial values and a control parameter of the 2D-ICSM, as illustrated in Figure 11. As can be seen from this figure, the secrete key consists of 5 parts with 232 bits in which and are the initial values control parameter of the 2D-ICSM. Meanwhile, s and z are added to increase the security by increasing the key space and changing the initial values and control parameters. It is crucial to state here that the proposed key is symmetric, which means that it can be used for both encryption and decryption processes.

Figure 11.
The secret key structure.
Now, the obtained signal can be encrypted using the hyperchaotic sequence generated by the 2D-ICSM. Algorithm 2 illustrates the pseudo-code of generating the secrete key and the encryption process.
| Algorithm 2: The encryption process. |
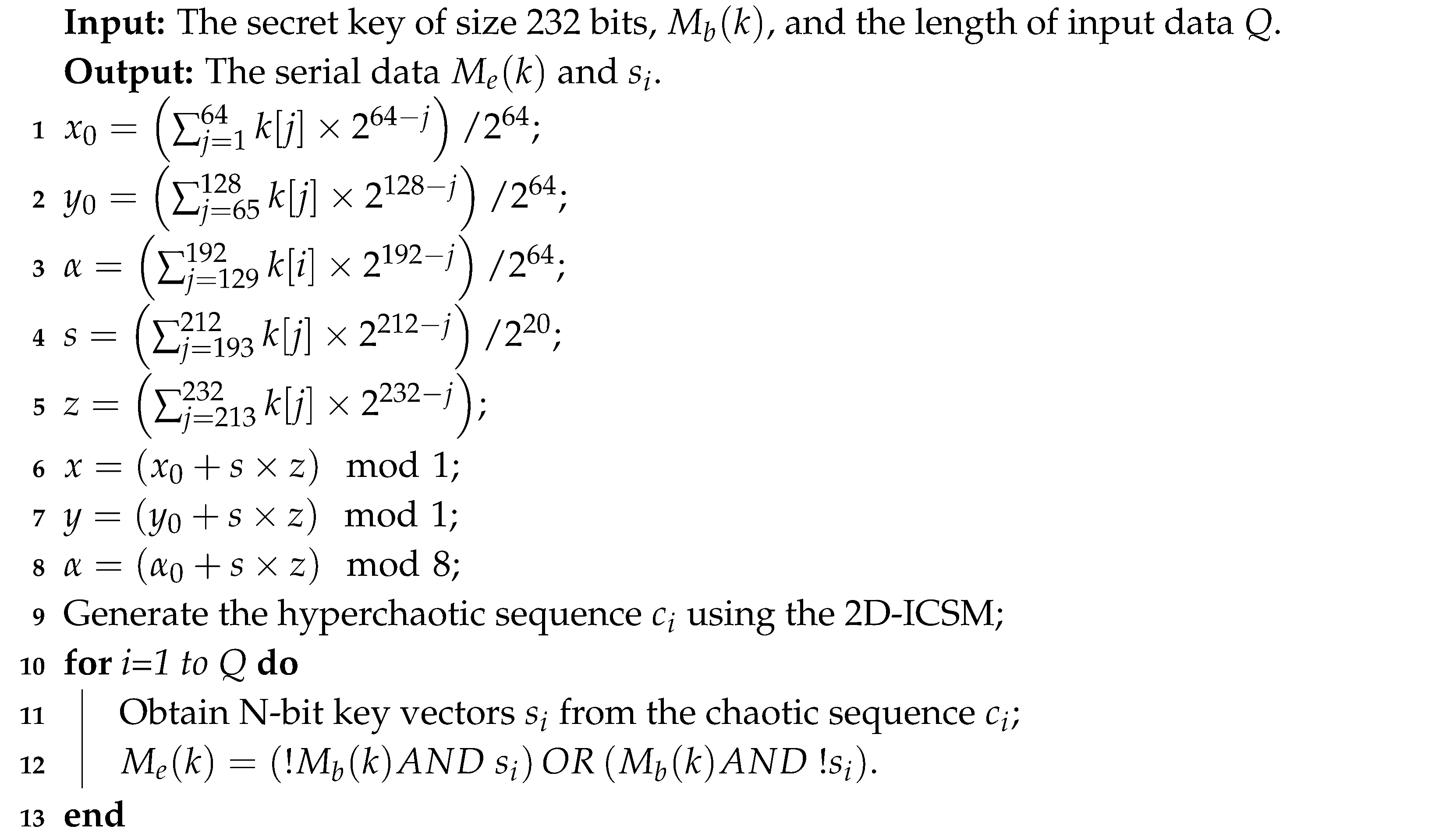 |
It is crucial to mention here that the encrypted signal will be the pulses (1’s on and 0’s off) that is sent from pin 1 in Arduino (board 1) to the electronic laser circuit as shown in Figure 9. The laser diode output depends on the diode injected current instead of voltage. The Arduino pin 1 is used to power the diode directly. Its processor draws 30 mA with 40 mA outputs. When the current enters into the laser diode circuit (LDC), it should be controlled by a modulated data stream. This current has high speed, where this circuit inverts the signal phase before the Laser diode (LD) is injected. Figure 12 shows a simulation example of the LDC. The inputs of the data stream are modulated through the LDC directly. The output of LD as an emitted light represents the reaction of “one” or “zero” logic. The direct modulation is considered as the most commonly used. It is utilized to modulate the light intensity for the transmission of information through free space.

Figure 12.
The input signal (yellow) and the output signal of the laser diode circuit (LDC) (blue).
Besides that, the laser beam transmitted by the photodiode is received in the form of light pulses. The photodiode acts as a semiconductor device used to convert light into a current that converts the received beam into an electrical signal within a voltage range between two volts (0–0.5). The encoded signal received by the photodiode passes various stages to amplify the signal voltage and return it to 5 volts, as can be seen in Figure 13. Furthermore, the binary signal is inverted and then sent it to pin 0 of Arduino (Board 2), as shown in Figure 12.

Figure 13.
The receiver circuit.
6.4. Decryption Process
The decryption signal is referred to by . This output signal is sent to Pin 5, which in turn sends it immediately to delta demodulation, which is designed by an analog electronics via the operating amplifier. Figure 13 shows the delta demodulation composite of a Delta demodulation integrator. An op-amplifier as a low pass filter is used to send the signals and obtain the final , which is equal to the original signal M(s).
7. Experimental Implementation
This section investigates the simplicity of the proposed secure communication system in simulation and hardware implementation.
7.1. Simulation Implementation
The simulation results of the proposed secure communication system are presented here by Matlab 2017b programs and implemented in a computer with specification Core i3-2.00 GHz, Intel CPU, and 4 GB RAM. The decimal values of the secret key are selected as , , , , and . Figure 14a–f depicts the simulation results of the proposed communication system. Empirical correctness of the system can be observed through the retrieved signal , which is completely identical to the original signal that has been encrypted, and then sent through a free-space optical channel.

Figure 14.
Simulation results: (a) the original signal; (b) the modulated output ; (c) the encrypted binary data ; (d) the serial binary data; (e) the decrypted binary data; (f) the retrieved signal.
Key Sensitivity Analysis
The employed key for the encryption scheme is considered highly sensitive when the encrypted message cannot be recovered, as a slight difference in one of the key components would result in an incorrect decrypted ciphertext. Therefore, we hereby investigate the key sensitivity of the proposed secure communication scheme, as shown in Figure 15. In this figure, a signal has been encrypted by , and using the same key, we could recover the signal, as shown in Figure 15a–c. However, when we change the 14th decimal place in the parameters, or initial conditions, or both to obtain three other keys, namely, , , and , respectively, Figure 15d–f demonstrates that these keys fail to recover the original signal, which means that the proposed communication system has a robust and sensitive key.

Figure 15.
Key sensitivity analysis: (a) the original signal; (b) the encrypted signal; (c) the decrypted with the right key (); (d–f) the decrypted signal with the wrong keys (, , ), in which the change occurred slightly in the parameters and initial conditions, only the parameters, and only the initial condition, respectively.
7.2. Hardware Implementation
The encryption algorithm is applied to a signal between (0 Hz–200 Hz) based on two microcontroller boards of Arduino Uno R3. The properties of these boards are non-expensive, have a simple design, and powerful microcontrollers that depend on the ATmega328 chip. The input and output pins are digital which consists of 14 digits, six of them are used as pulse width modulation (PWM) outputs, the other six are analog inputs. Besides that, the other 2 digits are used as 16 MHz crystal oscillator, the USB connection, and a reset button. These materials can be implemented by utilizing the C++ language. The computer with specification Core i3- 2.00 GHz, Intel CPU, and RAM 4 GB is used to run the software that is designed by the C++/C programing language, which is used to implement the two Arduino boards. These experiments have been implemented in a lab using a 200 MHz digital oscilloscope and a digital function generator. It is shown in Figure 16.

Figure 16.
Work environment and laboratory materials.
The experiment was conducted in the laboratory. The results presented in Figure 17a refers to the sent message that appears in blue, while the retrieved message appears in yellow, and Figure 17a refers to the serial binary data.

Figure 17.
Oscilloscope outputs: (a) the sent message appeared in blue, and the reconstructed message appeared in yellow; (b) the serial data.
8. Conclusions
In summary, this paper introduces the 2D-ICSM, which is a new hyperchaotic map designed using the 1D infinite collapse model as seed. The fixed points of certain parameters of the 2D-ICSM have been calculated, and then the stability of these points was analyzed by the graphical method. Performance evaluations including Lyapunov exponents, bifurcation diagram, cross-correlation coefficient, phase space diagram, NIST-800-22 randomness test, and Sample Entropy algorithm showed that the 2D-ICSM has a wide hyperchaotic range, high sensitivity, good ergodicity, sufficient level of randomness, and extreme complexity performance. Therefore, the 2D-ICSM could be an ideal source for many chaos-based practical applications. To demonstrate the efficiency of 2D-ICSM, we proposed a secure communication system, which is designed to transmit a message between two points. The input message is modulated using a simple Delta modulator and then encrypted using the 2D-ICSM. In the receiver side, the 2D-ICSM along with Delta demodulation are employed to retrieve the original message. It is crucial to state that the transmitted message by the proposed communication system could be an image, a text, or a sound. Simulation and empirical results have verified the efficiency and simplicity of the proposed secure communication system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.M.G.A.-S. and D.Y.; methodology, H.N.; software, H.N. and D.Y.; validation, M.A.A. and Z.M.; writing–original draft preparation, N.M.G.A.-S. and H.N.; writing–review and editing, M.R.K.A.; supervision, M.R.K.A.; project administration, M.R.K.A.; funding acquisition, M.R.K.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Casdagli, M. Nonlinear prediction of chaotic time series. Phys. Nonlinear Phenom. 1989, 35, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Takaya, M. Chaotic cryptography using augmented Lorenz equations aided by quantum key distribution. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2014, 62, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Banerjee, S.; He, S.; Said, M.R.M.; Kilicman, A. Designing an M-dimensional nonlinear model for producing hyperchaos. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 114, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Banerjee, S.; Ariffin, M.R.K.; Said, M.R.M. Can hyperchaotic maps with high complexity produce multistability? Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2019, 29, 011103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, H.; Daniel, G.P.; Olivier, T. Chaos in computer performance. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2006, 16, 013110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyris, A.; Syvridis, D.; Larger, L.; Annovazzi-Lodi, V.; Colet, P.; Fischer, I.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Mirasso, C.R.; Pesquera, L.; Shore, K.A. Chaos-based communications at high bit rates using commercial fibre-optic links. Nature 2005, 438, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natiq, H.; Said, M.R.M.; Al-Saidi, N.M.; Kilicman, A. Dynamics and complexity of a new 4d chaotic laser system. Entropy 2019, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgul, A.; Calgan, H.; Koyuncu, I.; Pehlivan, I.; Istanbullu, A. Chaos-based engineering applications with a 3D chaotic system without equilibrium points. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 84, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.K.; Ali, R.S.; Natiq, H.; Al-Saidi, N.M. A new S-box generation algorithm based on multistability behavior of a plasma perturbation model. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 124914–124924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet-Thanh, P.H.A.M.; Ali, D.S.; Al-Saidi, N.M.; Rajagopal, K.; Alsaadi, F.E.; Jafari, S. A Novel Mega-stable Chaotic Circuit. Radioengineering 2020, 29, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, G.; Li, S. Some basic cryptographic requirements for chaos-based cryptosystems. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2006, 16, 2129–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Pun, C.M.; Chen, C.P. 2D Sine Logistic modulation map for image encryption. Inf. Sci. 2015, 297, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Sun, K.; Zhu, C. A fast image encryption algorithm based on chaotic map. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 84, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, Y. Image encryption using 2D Logistic-adjusted-Sine map. Inf. Sci. 2016, 339, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Sun, K.; Liu, W. A novel bit-level image encryption algorithm based on 2D-LICM hyperchaotic map. Signal Process. 2018, 143, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Al-Saidi, N.M.G.; Said, M.R.M.; Kilicman, A. A new hyperchaotic map and its application for image encryption. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moysis, L.; Tutueva, A.; Volos, C.; Butusov, D.; Munoz-Pacheco, J.M.; Nistazakis, H. A Two-Parameter Modified Logistic Map and Its Application to Random Bit Generation. Symmetry 2020, 12, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rössler, O.E. An equation for continuous chaos. Phys. Lett. 1976, 57, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, J.C. Some simple chaotic flows. Phys. Rev. 1994, 50, R647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ueta, T. Yet another chaotic attractor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1999, 9, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Lu, J.; Lü, J.; Yu, S. Generating hyperchaotic Lü attractor via state feedback control. Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 2006, 364, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.M. Simple mathematical models with very complicated dynamics. Nature 1976, 261, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, G.; Klein, M. Maximum hyperchaos in generalized Hénon maps. Phys. Lett. 1990, 151, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Al-Saidi, M.N.; Said, M.R.M. Complexity and dynamic characteristics of a new discrete-time hyperchaotic model. In Proceedings of the 2017 Second Al-Sadiq International Conference on Multidisciplinary in IT and Communication Science and Applications (AIC-MITCSA), Baghdad, Iraq, 30–31 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, W.A.; Al-Saidi, N.M.; Natiq, H. A New 2D Hénon-Logistic Map for Producing Hyperchaotic Behavior. In Proceedings of the 2018 Third Scientific Conference of Electrical Engineering (SCEE), Baghdad, Iraq, 19–20 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Natiq, H.; Ariffin, M.R.K.; Said, M.R.M.; Banerjee, S. Enhancing the sensitivity of a chaos sensor for internet of things. Internet Things 2019, 7, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, K.; He, S. A class of higher-dimensional hyperchaotic maps. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2019, 134, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y. Sine-transform-based chaotic system with FPGA implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Leung, H. Identification of linear systems driven by chaotic signals using nonlinear prediction. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Fundam. Theory Appl. 2002, 49, 170–180. [Google Scholar]
- Skrobek, A. Cryptanalysis of chaotic stream cipher. Phys. Lett. 2007, 363, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natiq, H.; Banerjee, S.; Said, M.R.M. Cosine chaotification technique to enhance chaos and complexity of discrete systems. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2019, 228, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, A.K.; Al-Saidi, N.M.; Maolood, A.T.; Nazarimehr, F.; Hussain, I. Entropy analysis and image encryption application based on a new chaotic system crossing a cylinder. Entropy 2019, 21, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, K.; Zhao, L.; Liu, F.; Zheng, D.; Liu, C.; Liu, S. Analysis of heart rate variability using fuzzy measure entropy. Comput. Biol. Med. 2013, 43, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, C.; Qin, C.; Ma, Q.D.; Shen, Q. Modified permutation-entropy analysis of heartbeat dynamics. Phys. Rev. 2012, 85, 021906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richman, J.S.; Moorman, J.R. Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 278, H2039–H2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Y. Sine chaotification model for enhancing chaos and its hardware implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; He, C.; Jiang, L.G.; Zhu, H.W.; Hu, G.R. Chaotic characteristics of a one-dimensional iterative map with infinite collapses. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Fundam. Theory Appl. 2001, 48, 900–906. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, B. Study on the dynamical behaviors of a two-dimensional discrete system. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 2009, 70, 4209–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhin, A.; Soto, J.; Nechvatal, J.; Smid, M.; Barker, E. A Statistical Test Suite for Random and Pseudorandom Number Generators for Cryptographic Applications, Tech. rep., Booz-allen and hamilton inc mclean va 2001. Available online: https://www.nist.gov/publications/statistical-test-suite-random-and-pseudorandom-number-generators-cryptographic (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Zapateiro De la Hoz, M.; Acho, L.; Vidal, Y. An experimental realization of a chaos-based secure communication using arduino microcontrollers. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 123080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.S. Design of Continuously Variable Slope Delta Modulation Communication Systems. Motorola Technical Document AN1544. 1996. Available online: http://gamearchive.askey.org/General/DataSheets/cvsdspeechinfo/an1544cvsd.pdf (accessed on 2 November 2020).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).