Abstract
A better understanding of the connection between risk factors associated with pain and function may assist therapists in optimizing therapeutic programs. This study applied mathematical modeling to analyze the relationship of psychological, psychophysical, and motor variables with pain, function, and symptom severity using Bayesian linear regressions (BLR) and self-organizing maps (SOMs) in carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). The novelty of this work was a transfer of the symmetry mathematical background to a neuropathic pain condition, whose symptoms can be either unilateral or bilateral. Duration of symptoms, pain intensity, function, symptom severity, depressive levels, pinch tip grip force, and pressure pain thresholds (PPTs) over the ulnar, radial, and median nerve trunks, the cervical spine, the carpal tunnel, and the tibialis anterior were collected in 208 women suffering from CTS. The first BLR model revealed that symptom severity, PPTs over the radial nerve, and function had significant correlations with pain intensity. The second BLR showed that symptom severity, depressive levels, pain intensity, and years with pain were associated with function. The third model demonstrated that pain intensity and function were associated with symptom severity. The SOMs visualized these correlations among variables, i.e., clinical, psychophysical, and physical, and identified a subgroup of women with CTS exhibiting worse clinical features, higher pressure sensitivity, and lower pinch tip grip force. Therefore, the application of mathematical modeling identified some interactions among the intensity of pain, function, and symptom severity in women with CTS.
1. Introduction
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is probably the most common entrapment neuropathy of the upper extremity. A recent study reported a lifetime prevalence of 3.1% and an incidence rate of 1.73 per 1000 persons per year [1], although these data depend on the definition of CTS [2]. In middle-age workers, this prevalence can reach up to 9–10% [3,4]. This condition is associated with substantial economic costs and burden for society, particularly associated with loss of work [5].
Pain, numbness, tingling, and/or paresthesia within the median nerve-innervated areas are the symptoms most commonly experienced by individuals with CTS [6]. In addition, people with CTS may also experience motor symptoms, such as strength or motor control deficits. Although CTS has been traditionally considered a peripheral localized neuropathy, recent theories support the presence of mechanisms involving the central nervous system [7]. The heterogeneity in clinical presentation observed in patients has led to the investigation of the associations of psychological, psychophysical, and physical outcomes with clinical outcomes. The hypothesis was that a better understanding of the influence of modifiable risk variables on pain intensity and pain-related disability in individuals with CTS could assist therapists in determining more specific therapeutic programs for these patients.
Previous studies reported associations between pain intensity and function with psychological (e.g., depressive levels), psychophysical (i.e., pressure pain sensitivity), and physical (lower pinch tip grip force) outcomes in a sample of women with CTS [8,9,10]. Previous studies used linear regression analyses to determine the associations between the dependent variable(s) and independent variables. Linear regressions usually used frequentist models, which consider different statistical assumptions to employ ordinary least square estimations. Another mathematical approach comes from Bayesian statistics, where additional information is included in the form of a priori probability distribution. In particular, a priori distribution is chosen over all unknown parameters and combined with the data′s likelihood function according to the Bayes theorem to obtain the distribution over all parameters [11]. In addition to the ability of incorporating prior information, a potential additional advantage of Bayesian models, as compared to frequentist analysis, arises from the fact that the learned parameter distributions are more plastic and can deal with more complex relationships [12]. The Bayes method is considered a pragmatic choice, since it naturally allows additional contextual information and, therefore, the models are more precise and restrictive than those obtained with a frequentist approach [13]. Finally, since both parameters and predictions are treated as a distribution, Bayesian models enable direct calculation of the predictive intervals. In the current paper, the use of mathematical Bayesian modeling attempts to confirm or refute previous associations observed with frequentist analysis in patients with CTS [8,9,10]. Furthermore, in order to justify the use of a linear model for this particular pain condition, the modeling capabilities of BLR are compared with more powerful nonlinear predictors, and it is shown that these models do not outperform the simpler BLR, thereby justifying its use.
To complement the findings of the BLR and to develop further insights into the data, we propose the use of self-organizing maps (SOMs). An SOM is an artificial neural network for clustering and visualization of data in an easily readable informative form that allows projecting high-dimensional datasets into a simpler two-dimensional map, thus providing a compressed visual representation of the data. The SOM results in a map that preserves similarity relations existing in the dataset; hence, the information included in the high-dimensional space can be easily visualized and understood [14].
In addition, symmetry is a key concept when developing models in physical systems, and there are a plethora of examples in the literature. For instance, there are some applications of SOMs in problems related to symmetry [15,16,17]; however, no study previously applied these mathematical models in CTS. The novelty of this work was the transfer of the symmetry mathematical background to a neuropathic pain condition, whose symptoms can be either unilateral or bilateral.
Therefore, the objectives of this study were (1) to analyze the potential associations of psychological, psychophysical, and physical variables with dependent variables pain intensity, function, and symptom’s severity in women with CTS using Bayesian linear regressions (BLR), and (2) to identify subgroups of patients with CTS with similar characteristics, analyze nonlinear relationships, and visualize similarities or differences in the dependent variables as depicted by SOMs.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
Consecutive women with symptoms compatible with CTS, i.e., pain and/or paresthesia in the median nerve distribution, attending a regional hospital in Madrid (Spain) from January 2017 to June 2019 were screened for eligibility criteria. To be included in the study, patients had to exhibit symptoms and positive findings during clinical and electro-diagnostic examinations.
In particular, participants had to exhibit pain and/or numbness in the median nerve distribution which increased during the night and positive Tinel and Phalen signs during physical examination. Additionally, the electro-diagnostic examination had to reveal deficits of sensory/motor median nerve conduction according to the international guidelines [18]: (1) median nerve distal sensory latency of the index finger >3.6 ms and/or (2) median nerve distal motor latency >4.2 ms. Sensory and motor conduction studies of the radial and ulnar nerves were also performed and should be negative.
Exclusion criteria included (1) motor and/or sensory deficits in ulnar or radial nerves, (2) previous surgery on the upper extremity, (3) previous steroid injections, (4) diagnoses on the upper extremity mimicking CTS symptoms (e.g., cervical radiculopathy), (5) previous trauma in the upper quadrant (i.e., neck, shoulder, or arm), (6) any underlying systemic disease, e.g., diabetes mellitus, potentially causing CTS, (7) any comorbid systemic medical condition, e.g., rheumatoid arthritis or fibromyalgia, affecting pain sensitivity, or (8) pregnancy. Participants were informed prior to their inclusion in the study and signed a written informed consent form. The Ethic Local Human Research Committee of the Hospital (PI14/00364-HUFA12/14) evaluated and approved the study design.
2.2. Pain and Related Disability Outcomes
The output features (dependent variables) included in this Bayesian analysis were pain intensity and pain-related disability. A 10-point (0: no pain, 10: maximum pain) numerical pain rate scale [19] (NPRS) was used to evaluate the different levels of pain: mean level of hand pain, worst level of pain, and the least level of pain experienced in the preceding week. The mean of the three pain scores was calculated and used in the analyses. The Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire [20] (BCTQ) was used for assessing pain-related disability. The BCTQ functional status scale assesses the patient’s ability to perform eight common hand-related tasks. The BCTQ symptoms’ severity scale assesses the severity of pain, numbness, and weakness at night and during the day throughout 11 items [20]. Patients answer each question on a five-point scale (1: no complaint; 5: severe complaint). Higher scores suggest greater pain-related disability or symptom severity. This questionnaire was shown to be valid and reliable for use in individuals with CTS [21]. In the current study, the validated Spanish version [22] of the BCTQ was used. Each domain was analyzed independently in the statistical analysis.
2.3. Pressure and Thermal Pain Threshold Assessment
Pressure and thermal pain thresholds were used to determine pain sensitivity in our sample. Pressure pain threshold (PPT), the minimal amount of pressure where the patient first perceives pain, was measured bilaterally with an electronic algometer (Somedic AB©, Farsta, Sweden) over the three main nerve trunks of the upper extremity (i.e., median, ulnar, and radial nerves), the cervical spine at C5–C6 levels, carpal tunnel, and tibialis anterior following previous guidelines [23]. Heat (HPT) and cold (CPT) pain thresholds were also bilaterally assessed with a Thermotest System (Somedic AB© Farsta, Sweden) over the carpal tunnel and thenar eminence as previously described [24]. The order of trials was randomized between participants, and the mean of three trials of each measured point was used in the main analysis. Previous studies [23,24] and our data showed no side-to-side differences; thus, the mean of both sides was used in the analysis. The reliability of PPT was shown to be excellent [25], whereas the reliability for thermal pain thresholds ranges from fair to excellent [26] in the upper extremity.
2.4. Pinch Tip Grip Force Assessment
Pinch tip grip force (pounds) between the thumb and the second, third, fourth, and fifth fingers was measured with a pinch grip dynamometer (Psymptec©, Madrid, Spain) following previous studies [27]. Participants were able to see a digital display for visual feedback. The mean of three trials was calculated and used in the further analysis. The reliability of this outcome was reported to be excellent [28].
2.5. Psychological Assessment
Finally, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) was used for determining the level of depressive symptoms. The BDI-II is a 21-item patient-reported outcome measure assessing different aspects (affective, cognitive, and somatic symptoms) of depression [29]. This questionnaire is easily adapted for detecting potential symptoms of depression in most clinical conditions [30].
2.6. Data Overview and Preprocessing
Before performing statistical analysis, data were cleaned and prepared. First, 12 participants out of the 220 recruited for this study were discarded due to missing or erroneous values. Second, the categorical features of electromyographic (EMG) affectation (minimal, moderate, severe) and affected side (left, right, bilateral) were one-hot encoded, as required by further algorithms, such as BLR and SOM. This processing step consisted of transforming a categorical feature into a set of indicator features, which take a value of either one or zero. As an example, for EMG affectation, i.e., minimal, moderate, or severe, two new indicator features were created, minimal affectation and severe affectation, such that a patient with minimal affectation would be assigned a value of one to the “minimal affectation” indicator and zero to the “severe affectation” indicator. Fourth, all features were standardized by applying Equation (1) (where is the original value of a feature, and is the normalized value of that feature). Feature standardization consists of shifting the distribution of a feature so that it is centered around zero and scaling it so that it has a standard deviation of one. This is a prerequisite for BLR and SOM. It also helps with the interpretation of the results, since all features now lay in a similar range and, thus, the importance of each one can be directly compared with the others.
2.7. Bayesian Linear Regression (BLR)
Bayesian statistics is a branch of statistics first proposed by Thomas Bayes in 1763, wherein probabilities are interpreted as a degree of belief. Despite the advantages of these kinds of methods, they were not usually adopted until recently due to their generally high computational requirements.
2.7.1. Method Overview
BLR is a translation of traditional LR to the Bayesian framework. A standard BLR model, along with its priors, is defined in Equation (3), where is the intercept term of the BLR, is the vector of parameters (or weights), represents the input features, and is the variable to predict, which has a mean (just like in regular LR) and a standard deviation . Please note that weakly informative priors were employed, so as to add as little bias as possible.
By developing Bayes theorem using the parameters from Equation (2), and realizing that does not actually depend on , we finally arrive at Equation (3), where is the posterior probability distribution of the parameters and the intercept of the BLR model, which is proportional to the prior probability of and , and the likelihood , both of which are known.
Since the sought-after posterior distribution is known up to a normalization constant, Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods can be employed to efficiently sample from it, thus obtaining a numerical, yet unbiased, estimation of this distribution. For our purposes, the Python library PyMC3 [31] was employed. Internally, it uses the NoU-Turn Sampler [32], which is an advanced kind of MCMC method that presents a number of empirical advantages: higher sampling efficiency, less correlated samples, self-tuning capabilities, etc.
2.7.2. Bayesian vs. Frequentist Statistics
As it can be observed, , and , rather than being just a number (or a vector) like in traditional linear regression (LR), are probability distributions, which is an extremely powerful feature of the BLR models. The distributions in Equation (1) are just the priors, but once the model has been trained (that is, the posterior distribution has been inferred from data), the predictions that BLR produces are also a probability distribution, which allows very easily assessing the credibility of the prediction. Moreover, the weights of the model can be interpreted by visualizing their credible interval, which is the region where a given percentage (e.g., ) of the distribution falls.
In the frequentist (traditional) approach to statistics, a confidence interval for the parameters would mean that, if we were to randomly sample from a population multiple times, of all those times, the true value for would fall inside the interval. In contrast to this unintuitive definition, a Bayesian credible interval for the parameter means exactly what it seems, i.e., the interval of the distribution of where of its values lay. These properties allow for a very visual interpretation of feature significance in BLR models.
2.7.3. Bayesian Linear Models LR vs. Nonlinear Models
Although the parameters of a BLR provide excellent explainability of the importance of each feature over the predicted variable (which is highly desirable), BLR is still a linear model and, hence, unable to model complex relationships among the input features and the prediction. By contrast, nonlinear algorithms such as xgboost [33] (which is a kind of random forest) or neural networks (NNs) can learn these complex relationships extremely well, but at the cost of explainability.
Therefore, it would be ideal to have a very explainable model (such as BLR) that is able to model the input–output relationship very well (such as xgboost or NNs). To analyze this trade-off, the three algorithms (BLR, xgboost, and NNs) were trained and tenfold cross-validated (CV) on the current dataset. The mean correlation coefficient from the 10 training and validation folds can be observed in Table 1. The CV correlation reveals how well each algorithm performs when applied to data that it has not seen during training; by contrast, train correlation can be deceiving, as xgboost and NNs are powerful enough to learn the training data by heart, which is a problem known as overfitting. Hence, CV correlations in Table 1 show how each algorithm was able to capture the sought-after relationships, allowing us to assess the trade-off in modeling power that we incur by using the simpler BLR to analyze the data. To control overfitting, a hyperparameter sweep was performed to maximize CV correlation for both xgboost and NN.

Table 1.
Mean correlation coefficient from 10 training and cross-validation (CV) folds for all output features. Despite the performance differences in training, all algorithms seem to be similarly capable in validation. BLR, Bayesian linear regression; NN, neural network.
As can be observed, the mean train correlation was almost 1 for xgboost for all output features and between 0.6 and 0.75 for BLR. However, the mean CV correlations were almost identical for xgboost and BLR (except for predicting pain intensity). This means that xgboost learned the training data well (overfitted) and, when trying to predict unseen data, it was no better than the simpler BLR. NN, which was heavily regularized to perform as well as possible in the CV dataset, showed no improvement over the simpler BLR either.
In conclusion, since BLR is just as able as xgboost or NNs to model the relationships in the data, there was no performance trade-off, and the simple BLR was finally used, thus allowing us to also leverage its superior explainability and other desirable properties.
2.8. Self-Organizing Maps (SOM)
Self-organizing maps (SOMs) are an unsupervised learning mathematical method proposed by Kohonen [34] for visualizing and interpreting high-dimensional datasets. An SOM is a net of nodes (or neurons) connected by following a pattern, which in our particular case had a hexagonal shape. Each neuron has a weight associated with it which has the same dimensionality as any data sample (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Visualization of a self-organizing map (SOM) and its parameters.
After training the SOM, any sample in the dataset would have a (winner) neuron whose weight is closest to it. Therefore, the SOM would have transformed a mapping from a high-dimensional space (where each sample has many features) into a plane (a two-dimensional hexagonal grid). A trained SOM provides several representations that can help better understanding the data. In this paper, a toroidal hexagonal grid (which means that the nodes are connected from left to right, and from the bottom to the top) and a modified version of the Pyhton SimpSOM [35] library were used.
3. Results
3.1. Participants
Three hundred (n = 300) subjects with symptoms compatible with CTS were screened and assessed for eligibility criteria. Of these, 220 women with CTS satisfied all inclusion criteria and signed the written informed consent. Eighty patients were excluded for the following reasons: previous hand surgery (n = 25), steroid hand injection (n = 25), diabetes (n = 10), previous whiplash injury (n = 10), and men (n = 10). During data overview and preprocessing, 12 were excluded because of missing data. A total of 208 women with CTS were finally included in the analyses. Eighty-three (40%) reported unilateral symptoms (58 right side, 25 left side), whereas 125 (60%) showed bilateral symptoms. Sixty-one (29%) had minimal CTS, 69 (33%) had moderate CTS, and 78 (38%) had severe CTS. Table 2 summarizes the clinical and neurophysiological data of the total sample.

Table 2.
Clinical and neurophysiological data of the sample (n = 208).
3.2. Bayesian Linear Regression
Three different BLR models (one for each output feature) were trained on the whole dataset in order to analyze the importance of every feature on the prediction of the outputs. Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the distribution of all parameters learned by BLR. For every parameter, the caps at the beginning and the end of the distribution enclose the 95% credible interval. This allows for a very simple visual assessment of the significance; if the credible interval does not cross the zero line, that parameter can be said to be significant with a 95% credibility. Note that BLR has no actual notion of significance, and the previous definition is only provided to assist the interpretation of the results.
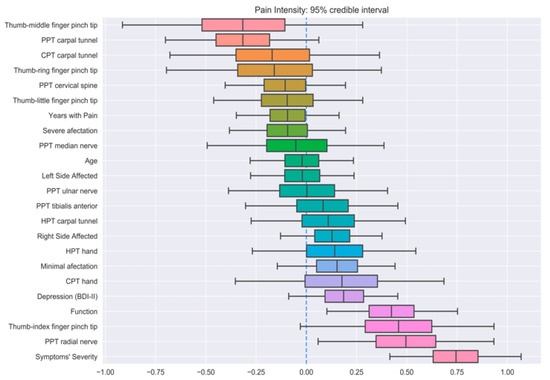
Figure 2.
Credible intervals for all the parameters in the Bayesian linear regression (BLR) model for pain intensity prediction.
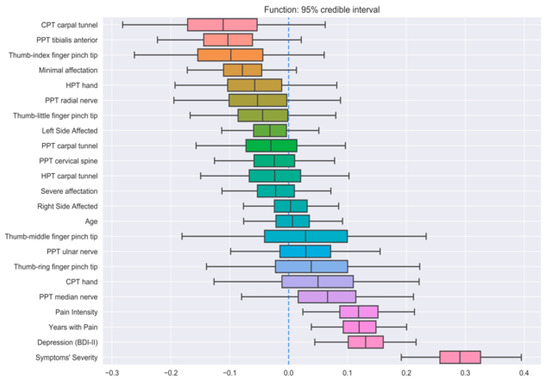
Figure 3.
Credible intervals for all the parameters in the Bayesian linear regression (BLR) model for function prediction.
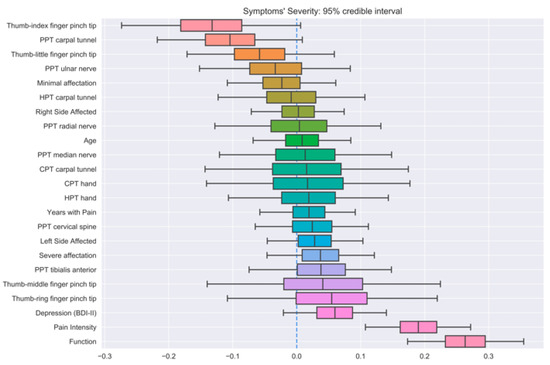
Figure 4.
Credible intervals for all the parameters in the Bayesian linear regression (BLR) model for symptom severity prediction.
The first model revealed that symptom severity, PPTs over the radial nerve, and function had significant correlations with pain intensity (Figure 2). Additionally, thumb–index finger pinch and PPTs over the carpal tunnel also exhibited strong positive and negative correlations, respectively, although they did not reach the 95% credibility threshold. Similarly, symptom severity, depressive levels, pain intensity, and years with pain had significant correlations with function (Figure 3), with minimal EMG affectation and PPT over the tibialis anterior muscle displaying a strong, yet not significant, negative correlation. Finally, the last BLR revealed that function and pain intensity presented a significant association with symptom severity (Figure 4). In this BLR model, depressive levels also laid just below the significance threshold, but did not reach significance. Finally, thumb–index finger pinch and PPT over the carpal tunnel also showed a negative correlation, but not statistically significant.
3.3. Self-Organizing Maps
Figure 5 shows the mean distance between the parameters of each node and its neighbors as a color map, such that dark-blue points represent lower values (the neighboring nodes are similar to the given node) and yellow points represent higher values (the neighboring nodes are different). Furthermore, the number of samples that “fall” into (are closest to) each node is represented inside of each hexagonal area. The interpretation is as follows: similar samples are clustered together in the dark-blue areas, while yellow areas act as barriers separating the different potential clusters.
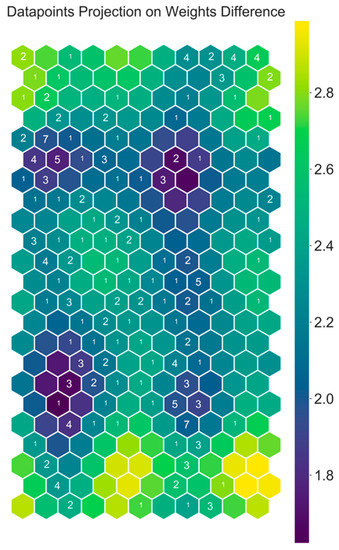
Figure 5.
Self-organizing map weight difference plot with number of data points overlaid.
Figure 6 provides a color map of the weight-vector component of each feature included in this study. For instance, for the map associated with the variable age (top left corner of Figure 6), blue areas correspond with younger age, whereas yellow areas correspond with older age. Hence, all samples that fell in the top right corner of any SOM (including the weight difference plot in Figure 5) correspond to older patients, as evidenced by the big yellow spot in the age SOM. Furthermore, it can be observed that all SOMs of features about PPTs (second line) were highly similar; in those areas of the SOM where PPT over the median nerve had high values, the remaining PPT-related features also had high values. The opposite also happened; in those places where PPTs over the median nerve had low values, the remaining PPT features also had low values. Thus, the SOMs demonstrate visually that PPT features are highly positively correlated.
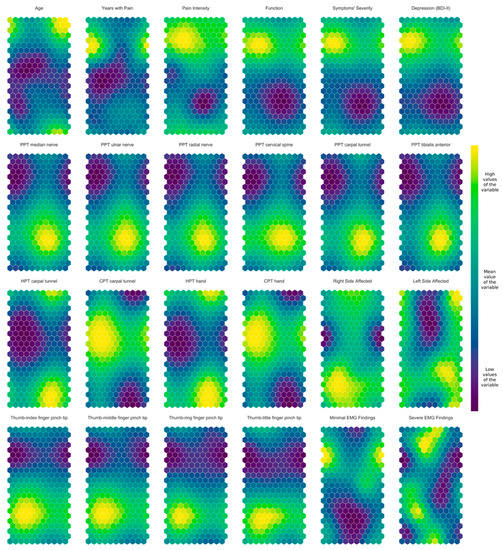
Figure 6.
Self-organizing maps of the clinical, neuro-physiological, psychological, and motor features in women with carpal tunnel syndrome.
The SOM also showed that both HPT features are negatively correlated with both CPT features, since CPT SOMs were all quite similar and almost exact opposites to HPT SOMs (third line by the top). In general, the SOMs support an association among clinical features (e.g., pan intensity, function, symptom severity), pressure pain thresholds (PPTs), thermal pain thresholds (HPT vs. CPT), and pinch tip grip force (Figure 6).
4. Discussion
This is the first study applying mathematical modeling for identifying the potential associations of psychological, psychophysical, and physical variables with pain, function, and symptom severity in a sample of women with CTS.
The BLR showed that clinical outcomes, e.g., pain intensity, function, and symptom severity, were intrinsically associated in all models. Additionally, variables such as PPTs over the radial nerve were associated with pain intensity, while depressive levels and years with pain were associated with function. Although PPTs over the carpal tunnel were found to be negatively correlated with pain intensity and symptom severity, these associations did not reach the established credible interval. Similarly, thumb–index finger pinch showed a strong negative correlation with pain intensity and symptom severity, again laying just below the significance level. It was previously reported that function, thumb–middle finger pinch, thumb–little finger pinch, depressive levels, PPTs over radial nerve and carpal tunnel, and HPT carpal tunnel were partly associated with pain intensity in women with CTS [9]. These findings were mostly corroborated in the current study, except for thumb–middle finger pinch which, according to BLR, is not significant for pain intensity prediction. This could be explained by the difference in how significance is interpreted between frequentist linear regression and BLR. In BLR, all parameters have an associated distribution which, for the case of thumb–middle finger pinch, was extremely wide (Figure 2). This suggests that the correlation, even if large in magnitude, is unreliable and, hence, no significance can be guaranteed. It is interesting to note that those variables significantly associated with pain intensity in linear regression models [9], but not in BLR, are related to peripherally localized sensitization mechanisms [7], suggesting that, perhaps, these kinds of features are all important yet untrustworthy pain intensity predictors.
Similarly, linear regression model revealed that that pain intensity, thumb–little finger pinch grip force, and depressive symptoms were associated with function score [10]. When BLRs were applied, function was associated with symptom severity, depressive levels, pain intensity, and years with pain. In this comparison, pain intensity and depressive levels were deemed significant by both models, supporting that these features are clearly associated with pain-related disability. The application of BLR also revealed a negative, but not significant, association between function and PPT on the tibialis anterior muscle. Lower PPTs over the tibialis anterior are a clinical manifestation of widespread pressure pain sensitivity [23]. It is probable that, albeit not significant in our BLR, the presence of altered central pain processing, as expressed by widespread pressure hyperalgesia, could have a negative effect on function in these patients.
Finally, the last BLR revealed that function and the intensity of pain were significantly associated with symptom severity, which would be expected due to the interactions between these output variables. In addition, some outcomes such as depressive levels, thumb–index finger pinch, and PPT over the carpal tunnel were also associated, but did not reach statistical significance.
The application of a mathematical model such as BLR supports an intrinsic relation among pain intensity, function, and symptom severity in all the analyzed models, which is expected since pain intensity is directly correlated with patient-reported outcome measure (PROM) of function in individuals with chronic neuropathic pain [36]. From a clinical point of view, our results would support the relevance of treating pain symptoms in patients with neuropathic conditions, such as CTS, with the aim of getting an effect on related function. However, since the relationship can be obviously bidirectional, it is also possible that application of functional interventions leads to improvements in pain intensity. Nevertheless, in this latest scenario, it is also important to consider that depression plays a relevant role in function. In fact, depression is one of the most prevalent mood disorders associated with pain-related disability [37]; it is, therefore, unsurprising that both linear regression and BLR identified depression as a contributor to function in women with CTS.
The application of SOMs is able to find similar behaviors, with typical profiles represented in the same area of the map, while simultaneously depicting the results in an easily interpretable two-dimensional map. As expected, SOMs permitted us to highlight predictable correlations between the different variables, i.e., clinical, psycho-physical, or physical. In fact, expected correlations were confirmed by the SOM analysis, e.g., PPTs were almost identical independently of the area where they were assessed, whereas HPT output was opposite to CPT output.
When examining the overall information of the SOMs, an interesting subgrouping of women with CTS can be inferred from Figure 6. For instance, we observed a cluster of women with CTS in the upper portion of the maps (on top line) with worse function and more severe symptoms (higher value of the output variables) with higher pressure pain sensitivity, i.e., lower PPTs (second line) and lower pinch tip grip force (fourth line). This strongly suggests an interaction among clinical, neuro-physiological, and motor output variables.
These results, obtained using mathematical models, have potential implications for clinical practice. The presence of interactions between clinical outcomes (pain intensity, function, symptom severity) and mood disorders (depressive levels) suggests that treatment of women with CTS should include multimodal therapeutic approaches targeting pain and function, i.e., physical therapy, psychological disturbances, i.e., cognitive behavior, and mechanical hypersensitivity, i.e., pharmacological, neuro-modulatory pain approaches.
Despite the described positive aspects of the use of mathematical methods in the current study, potential limitations must be acknowledged. Firstly, BLR is still a linear model and, as such, it is unable to capture more complex relationships among independent or dependent variables, assuming those were present in the data. An analysis was performed to confirm that more complex models are marginally more capable than the much simpler linear analysis, yet a more exhaustive analysis could be performed, and more complex relationships might be uncovered. Secondly, the SOM analysis mostly confirmed what was already known. More powerful clustering techniques could be employed to better divide the patients, potentially leading to further insights into the syndrome. Finally, these results can only be applied to women with CTS and should not be extrapolated to men with this pain condition. Future studies investigating gender differences could reveal other associations.
5. Conclusions
The current study identified a potential interaction between pain intensity, function, and symptom severity in women with CTS by applying BLR and SOMs as mathematical models. In addition, variables such as PPTs over the radial nerve, depressive levels, and years with symptoms were also associated with function. The SOMs revealed correlations among the different types of output variables, i.e., clinical, psycho-physical, or physical, as well as a potential group of women with CTS showing worse clinical features, higher pressure pain sensitivity, and lower pinch tip grip force.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, all authors; methodology, all authors; software, O.J.P.-V. and J.D.M.-G.; validation, all authors; formal analysis, O.J.P.-V. and J.D.M.-G.; investigation, all authors; resources, C.F.-d.-l.-P.; data curation, O.J.P.-V. and J.D.M.-G.; writing—original draft preparation, all authors; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, all authors; supervision, C.F.-d.-l.-P. and E.N.-P.; project administration; funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pourmemari, M.H.; Heliövaara, M.; Viikari-Juntura, E.; Shiri, R. Carpal tunnel release: Lifetime prevalence, annual incidence, and risk factors. Muscle Nerve 2018, 58, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiese, M.S.; Gerr, F.; Hegmann, K.T.; Harris-Adamson, C.; Dale, A.M.; Evanoff, B.; Eisen, E.A.; Kapellusch, J.; Garg, A.; Burt, S.; et al. Effects of varying case definition on carpal tunnel syndrome prevalence estimates in a pooled cohort. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 2320–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, S.; Sparer, E.H.; Tran, B.N.; Ruan, Q.Z.; Dennerlein, J.T.; Singhal, D.; Lee, B.T. Prevalence of Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Among Surgeons and Interventionalists: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, e174947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, A.M.; Harris-Adamson, C.; Rempel, D.; Gerr, F.; Hegmann, K.; Silverstein, B.; Burt, S.; Garg, A.; Kapellusch, J.; Merlino, L.; et al. Prevalence and incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome in US working populations: Pooled analysis of six prospective studies. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2013, 39, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, M.; Silverstein, B. The long-term burden of work-related carpal tunnel syndrome relative to upper-extremity fractures and dermatitis in Washington State. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2015, 58, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genova, A.; Dix, O.; Saefan, A.; Thakur, M.; Hassan, A. Carpal tunnel syndrome: A review of literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e7333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Plaza-Manzano, G. Carpal tunnel syndrome: Just a peripheral neuropathy? Pain Manag. 2018, 8, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, F.; Vranceanu, A.M.; Ring, D. Determinants of pain in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 3328–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Muñoz, J.J.; Palacios-Ceña, M.; Cigarán-Méndez, M.; Ortega-Santiago, R.; de-la-Llave-Rincón, A.I.; Salom-Moreno, J.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C. Pain is associated to clinical, psychological, physical, and neurophysiological variables in women with carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Cleland, J.A.; Plaza-Manzano, G.; Ortega-Santiago, R.; de-la-Llave-Rincón, A.I.; Martínez-Perez, A.; Arroyo-Morales, M. Clinical, physical, and neurophysiological impairments associated with decreased function in women with carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2013, 43, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permai, S.D.; Tanty, H. Linear regression model using bayesian approach for energy performance of residential building. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 135, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunson, D.B.; Neelon, B. Bayesian inference on order-constrained parameters in generalized linear models. Biometrics 2003, 59, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Taylor, J.M.G.; Vokonas, P.S.; Park, S.K.; Mukherjee, B. Improving estimation and prediction in linear regression incorporating external information from an established reduced model. Stat. Med. 2018, 37, 1515–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohonen, T. Self-Organizing Maps, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Riesenhuber, M.; Bauer, H.U.; Brockmann, D.; Geisel, T. Breaking rotational symmetry in a self-organizing map model for orientation map development. Neural Comput. 1998, 10, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, T.; Ota, K.; Kurata, K.; Aoyagi, T. Ordering process of self-organizing maps improved by asymmetric neighborhood function. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2009, 3, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, R.; Rativa, D.; Lima Neto, F. Clustering of Self-Organizing Maps as a means to support gait kinematics analysis and symmetry evaluation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2018, 62, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablecki, C.K.; Andary, M.T.; Floeter, M.K.; Miller, R.G.; Quartly, C.A.; Vennix, M.J.; Wilson, J.R. Practice parameter: Electro-diagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome. Report of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, American Academy of Neurology, American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. Neurology 2002, 58, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P.; Turbner, J.A.; Romano, J.M.; Fisher, L. Comparative reliability and validity of chronic pain intensity measures. Pain 1999, 83, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D.W.; Simmons, B.; Koris, M.; Daltroy, L.; Hohl, G.; Fossel, A.; Katz, J. A self-administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1993, 75, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Leite, J.; Jerosch-Herold, C.; Song, F. A systematic review of the psychometric properties of the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2006, 7, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Rosales, R.S.; Benseny, E.; Díez de la Lastra-Bosch, I. Evaluation of the Spanish version of the DASH and carpal tunnel syndrome health-related quality of life instruments: Cross cultural adaptation process and reliability. J. Hand Surg. 2002, 27, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; de la Llave-Rincón, A.I.; Fernández-Carnero, J.; Cuadrado, M.L.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Pareja, J.A. Bilateral widespread mechanical pain sensitivity in carpal tunnel syndrome: Evidence of central processing in unilateral neuropathy. Brain 2009, 132, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-la-Llave-Rincón, A.I.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Fernández-Carnero, J.; Padua, L.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Pareja, J.A. Bilateral hand/wrist heat and cold hyperalgesia, but not hypoesthesia, in unilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 198, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.H.; Kilgour, R.D.; Comtois, A.S. Test-retest reliability of pressure pain threshold measurements of the upper limb and torso in young healthy women. J. Pain 2007, 8, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, N.A.; Hall, T.M.; O’Sullivan, T.C.; Doody, C.M. Reliability of thermal quantitative sensory testing of the hand in a cohort of young, healthy adults. Muscle Nerve 2011, 44, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Pérez-de-Heredia-Torres, M.; Martínez-Piédrola, R.; De-la-Llave-Rincón, A.I.; Cleland, J.A. Bilateral deficits in fine motor control and pinch grip force in patients with unilateral carpal tunnel syndrome. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 194, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuders, T.; Roebroeck, M.; Goumans, J.; Van Nieuwenhuijzen, J.; Stijnen, T. Measurement error in grip and pinch force measurements in patients with hand injuries. Phys. Ther. 2003, 83, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. Beck Depression Inventory, 2nd ed.; The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.P.; Gorenstein, C. Assessment of depression in medical patients: A systematic review of the utility of the Beck Depression Inventory-II. Clinics 2013, 68, 1274–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatier, J.; Wiecki, T.V.; Fonnesbeck, C. Probabilistic programming in Python using PyMC3. Peer J. Comput. Sci. 2016, 2, e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.D.; Gelman, A. The no-U-turn sampler: Adaptively setting path lengths in Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1593–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Association for Computing Machinery, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Kohonen, T. The Self-Organizing Map. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 1464–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comitani, F. SimpSOM, a lightweight Python library for Kohonen Self Organising Maps. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/2621560 (accessed on 29 August 2020).
- Seventer, R.V.; Serpell, M.; Bach, F.W.; Morlion, B.; Zlateva, G.; Bushmakin, A.G.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Nimour, M. Relationships between changes in pain severity and other patient-reported outcomes: An analysis in patients with posttraumatic peripheral neuropathic pain. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2011, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWilliams, L.A.; Cox, B.J.; Enns, M.W. Mood and anxiety disorders associated with chronic pain: An examination in a nationally representative sample. Pain 2003, 106, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).