Human Action Recognition Using Bone Pair Descriptor and Distance Descriptor
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The development of the Bone Pair Descriptor.
- The application of the Distance Descriptor to the human action recognition problem.
- The original experiments with the selection of joints, bones, and features.
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Distance Descriptor
- For each joint , do:
- (a)
- Calculate distances (Euclidean or city block) between the other joints , .
- (b)
- Sort joints by the calculated distances from the closest to the farthest.
- (c)
- Assign consecutive integers to the sorted joints , starting from 1.
- Assemble a feature vector consisting of integer values assigned to the joints in step 1c) in the following order: .
- Reduce the feature vector assembled in step 2 by adding together integers a corresponding to the same pair of indices i, j: .
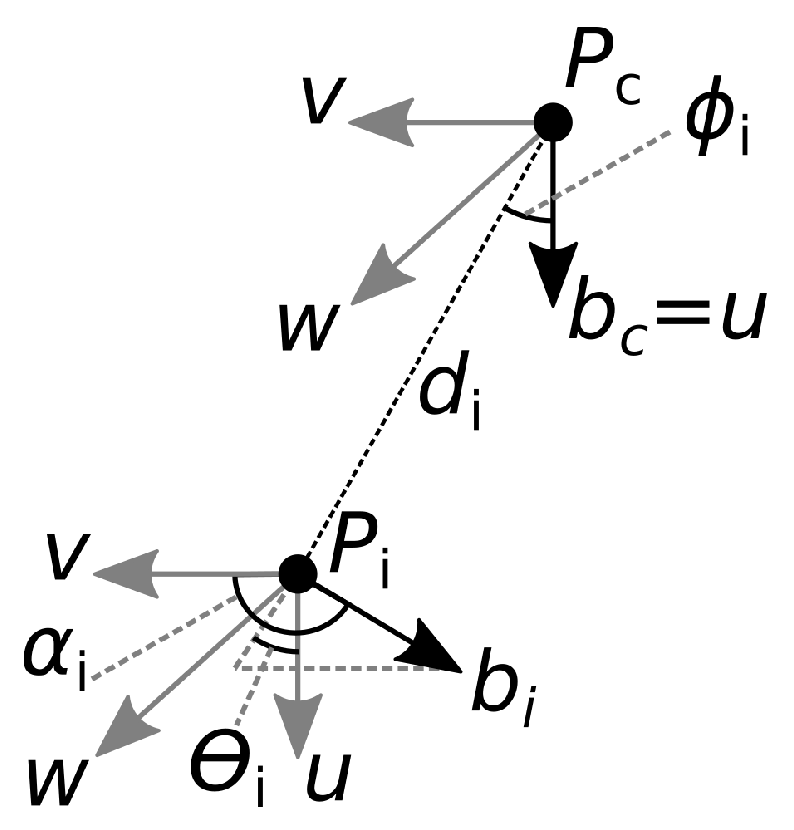
3.2. Bone Pair Descriptor
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset, Classifiers and Hardware
- right arm swipe to the left
- right arm swipe to the right
- right hand wave
- two hand front clap
- right arm throw
- cross arms in the chest
- basketball shoot
- right hand draw x
- right hand draw circle (clockwise)
- right hand draw circle (counter-clockwise)
- draw triangle
- bowling (right hand)
- front boxing
- baseball swing from right
- tennis right hand forehand swing
- arm curl (two arms)
- tennis serve
- two hand push
- right hand knock on door
- right hand catch an object
- right hand pick up and throw
- jogging in place
- walking in place
- sit to stand
- stand to sit
- forward lunge (left foot forward)
- squat (two arms stretch out)
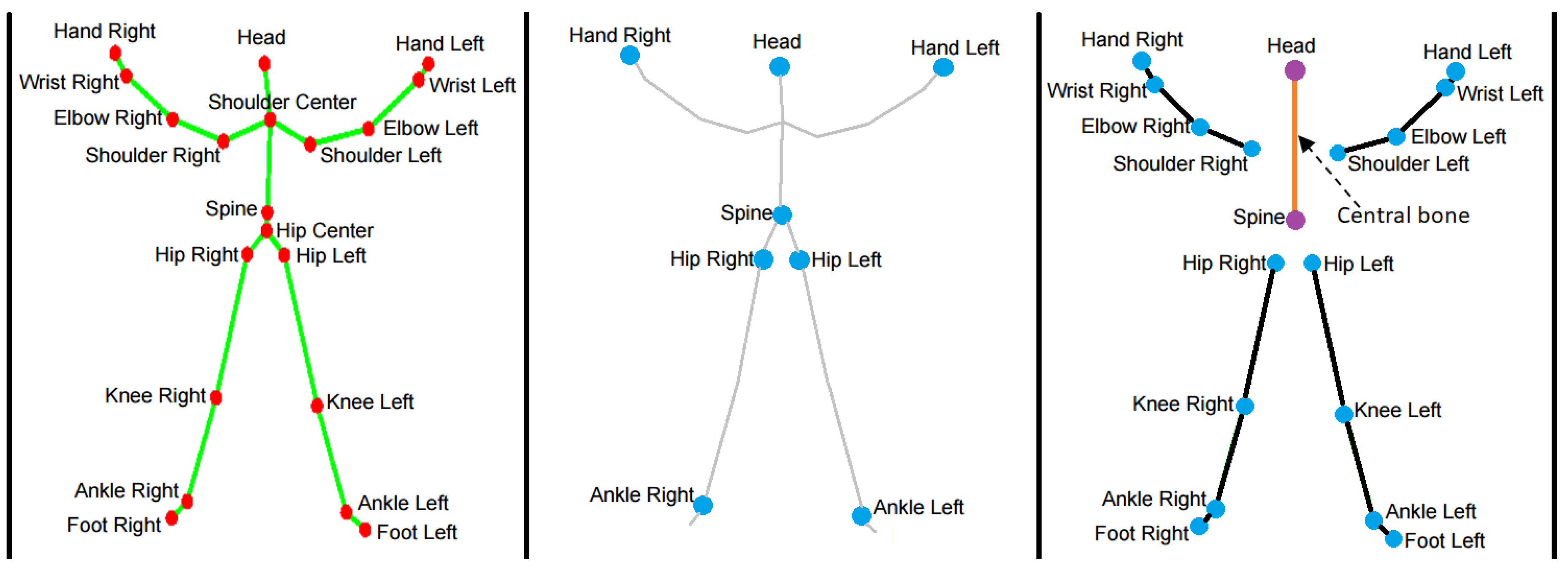
- Hand Left
- Hand Right
- Shoulder Left
- Shoulder Right
- Head
- Spine
- Hip Left
- Hip Right
- Ankle Left
- Ankle Right
- Spine—Head (central joints)
- Elbow Right—Wrist Right
- Wrist Right—Hand Right
- Shoulder Right—Elbow Right
- Elbow Left—Wrist Left
- Wrist Left—Hand Left
- Shoulder Left—Elbow Left
- Hip Right—Knee Right
- Knee Right—Ankle Right
- Ankle Right—Foot Right
- Hip Left—Knee Left
- Knee Left—Ankle Left
- Ankle Left—Foot Left
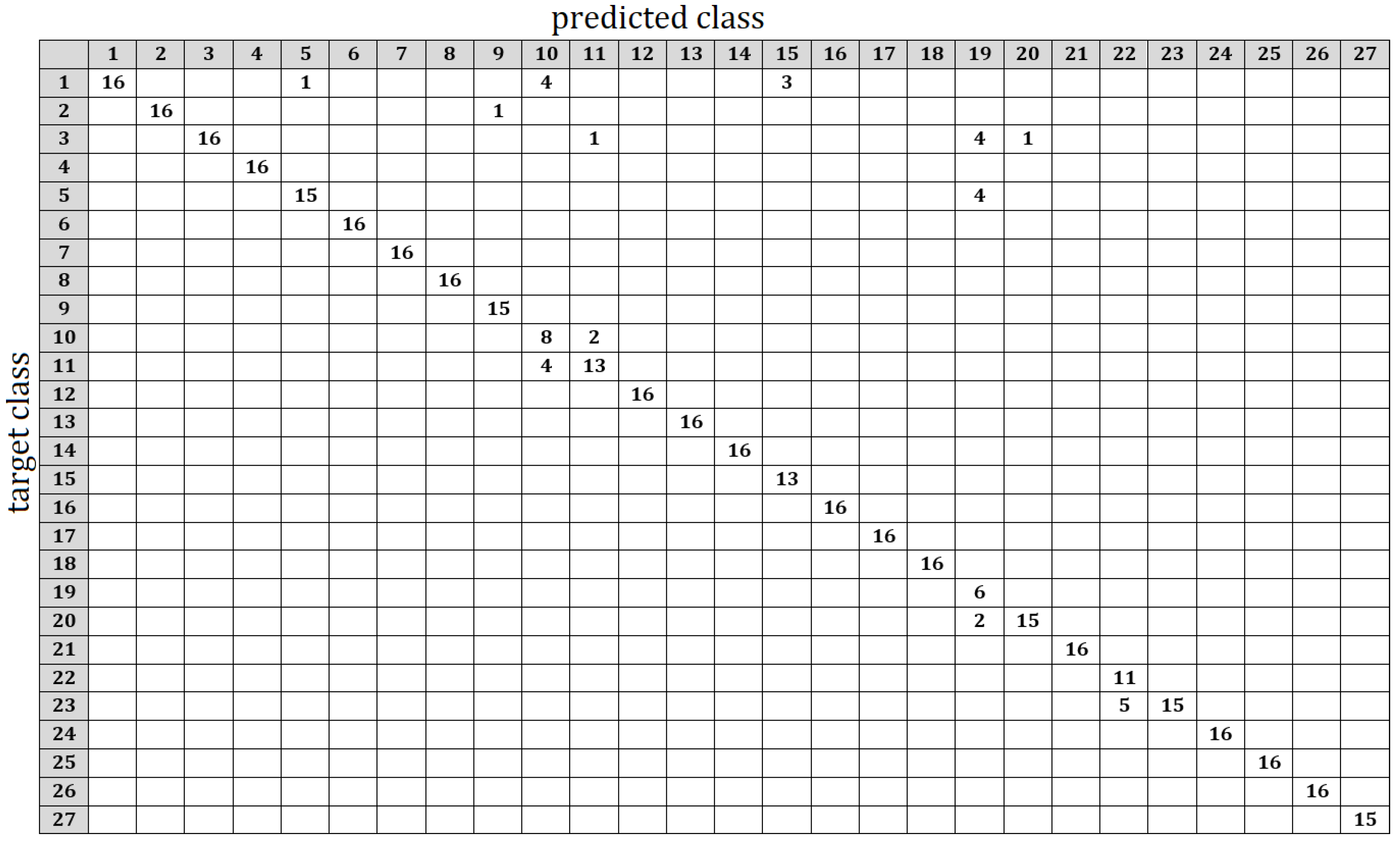
4.2. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussein, M.E.; Torki, M.; Gowayyed, M.A.; El-Saban, M. Human Action Recognition Using a Temporal Hierarchy of Covariance Descriptors on 3D Joint Locations. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Third International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence; AAAI Press: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 2466–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ogunbona, P.; Nguyen, D.T.; Zhang, H. Discriminative Key Pose Extraction Using Extended LC-KSVD for Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 25–27 November 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Jafari, R.; Kehtarnavaz, N. UTD-MHAD: A multimodal dataset for human action recognition utilizing a depth camera and a wearable inertial sensor. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 27–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Hou, Y.; Li, W. Action Recognition Based on Joint Trajectory Maps Using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Joint Distance Maps Based Action Recognition With Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Xu, W.; Su, H.; Ji, Q. Bayesian Hierarchical Dynamic Model for Human Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7733–7742. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Y. Recognizing actions using depth motion maps-based histograms of oriented gradients. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nara, Japan, 27–31 October 2012; pp. 1057–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Liu, K.; Kehtarnavaz, N. Real-time human action recognition based on depth motion maps. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2016, 12, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z. Action recognition based on a bag of 3D points. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition—Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13-18 June 2010; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Bulbul, M.F.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, J. Human action recognition based on DMMs, HOGs and Contourlet transform. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia Big Data, Beijing, China, 20–22 April 2015; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Han, J.; Kehtarnavaz, N. Multi-temporal depth motion maps-based local binary patterns for 3-D human action recognition. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 22590–22604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, L.; Han, J.; Shao, L. Action recognition using 3D histograms of texture and a multi-class boosting classifier. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 4648–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tian, Y. Super normal vector for activity recognition using depth sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 804–811. [Google Scholar]
- Slama, R.; Wannous, H.; Daoudi, M. Grassmannian representation of motion depth for 3D human gesture and action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; pp. 3499–3504. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H. Depth context: A new descriptor for human activity recognition by using sole depth sequences. Neurocomputing 2016, 175, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, C. Robust 3D action recognition through sampling local appearances and global distributions. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 20, 1932–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cai, H.; Ju, Z.; Liu, H. RGB-D sensing based human action and interaction analysis: A survey. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 94, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Liu, L.; Shen, C.; van den Hengel, A. Learning discriminative trajectorylet detector sets for accurate skeleton-based action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 66, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanne, M.; Wannous, H.; Berretti, S.; Pala, P.; Daoudi, M.; Del Bimbo, A. 3-d human action recognition by shape analysis of motion trajectories on riemannian manifold. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 45, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazhoumand-Dar, H.; Lam, C.P.; Masek, M. Joint movement similarities for robust 3D action recognition using skeletal data. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2015, 30, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillo, I.; Niebles, J.C.; Soto, A. Sparse composition of body poses and atomic actions for human activity recognition in RGB-D videos. Image Vis. Comput. 2017, 59, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J. Learning actionlet ensemble for 3D human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, N.; Maybank, S.J. Activity recognition using a supervised non-parametric hierarchical HMM. Neurocomputing 2016, 199, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahroudy, A.; Ng, T.T.; Yang, Q.; Wang, G. Multimodal multipart learning for action recognition in depth videos. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Ponce, C.; Selman, B.; Saxena, A. Unstructured human activity detection from rgbd images. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 842–849. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Song, R.; Rong, X.; Tian, X.; Tian, G.; Li, Y. Deep learning based human action recognition: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 3780–3785. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L. Skeleton based action recognition with convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3–6 November 2015; pp. 579–583. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y.; He, M. Skeleton based action recognition using translation-scale invariant image mapping and multi-scale deep CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 601–604. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, D.; Pu, S. Skeleton-based action recognition with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 597–600. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Q.; An, S.; Bennamoun, M.; Sohel, F.; Boussaid, F. Skeletonnet: Mining deep part features for 3-d action recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2017, 24, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Bennamoun, M.; An, S.; Sohel, F.; Boussaid, F. A new representation of skeleton sequences for 3d action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3288–3297. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, P.; Ogunbona, P.O.; Li, W. Investigation of different skeleton features for cnn-based 3d action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Hong Kong, China, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 617–622. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, J.; Kumar, P. Human action recognition using RGB-D sensor and deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Jaipur, India, 21–24 September 2016; pp. 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, W. Skeleton Optical Spectra-Based Action Recognition Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L. Hierarchical recurrent neural network for skeleton based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1110–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Shahroudy, A.; Liu, J.; Ng, T.T.; Wang, G. Ntu rgb+ d: A large scale dataset for 3d human activity analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1010–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L. Modeling Temporal Dynamics and Spatial Configurations of Actions Using Two-Stream Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3633–3642. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Shahroudy, A.; Xu, D.; Wang, G. Spatio-temporal lstm with trust gates for 3d human action recognition. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 816–833. [Google Scholar]
- Karpathy, A.; Toderici, G.; Shetty, S.; Leung, T.; Sukthankar, R.; Li, F.-F. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1725–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Mahadevan, V.; Vasconcelos, N. Vlad3: Encoding dynamics of deep features for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1951–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Yue-Hei Ng, J.; Hausknecht, M.; Vijayanarasimhan, S.; Vinyals, O.; Monga, R.; Toderici, G. Beyond short snippets: Deep networks for video classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4694–4702. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Marks, T.K.; Jones, M.; Tuzel, O.; Shao, M. A multi-stream bi-directional recurrent neural network for fine-grained action detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1961–1970. [Google Scholar]
- Mahasseni, B.; Todorovic, S. Regularizing long short term memory with 3D human-skeleton sequences for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3054–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, M.; Yuan, D. ARCH: Adaptive recurrent-convolutional hybrid networks for long-term action recognition. Neurocomputing 2016, 178, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Zhang, H.; Sun, M.; Yuan, D. Recurrent Temporal Sparse Autoencoder for attention-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 456–463. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, J.; Hendricks, L.A.; Rohrbach, M.; Venugopalan, S.; Guadarrama, S.; Saenko, K.; Darrell, T. Long-Term Recurrent Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition and Description. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, J.; Ryoo, M. Human Activity Analysis: A Review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2011, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapuściński, T.; Warchoł, D. Hand Posture Recognition Using Skeletal Data and Distance Descriptor. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapuściński, T.; Organiściak, P. Handshape Recognition Using Skeletal Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, R.B.; Marton, Z.C.; Blodow, N.; Beetz, M. Learning informative point classes for the acquisition of object model maps. In Proceedings of the 2008 10th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision, Hanoi, Vietnam, 17–20 December 2008; pp. 643–650. [Google Scholar]
- Spivak, M. A Comprehensive Introduction to Differential Geometry, 3rd ed.; Publish or Perish: Houston, TX, USA, 1999; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Matlab Scripts for Distance Descriptor and Bone Pair Descriptor. Available online: http://vision.kia.prz.edu.pl (accessed on 9 February 2020).
- Celebi, S.; Aydin, A.S.; Temiz, T.T.; Arici, T. Gesture Recognition using Skeleton Data with Weighted Dynamic Time Warping. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications—VISAPP 2013, Barcelona, Spain, 21–24 February 2013; pp. 620–625. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Jaitly, N.; Mohamed, A. Hybrid speech recognition with Deep Bidirectional LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Olomouc, Czech Republic, 8–12 December 2013; pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Aceto, G.; Ciuonzo, D.; Montieri, A.; Pescape, A. Mobile Encrypted Traffic Classification Using Deep Learning: Experimental Evaluation, Lessons Learned, and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2019, 16, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Liu, M.; Karimi, H.R.; Gao, H. LogDet Divergence-Based Metric Learning with Triplet Constraints and Its Applications. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 4920–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Classifier | Parameter Name | Parameter Value | Recognition Rate [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| BiLSTM | number of hidden units | 150 | 76.7 |
| number of epochs | 500 | ||
| mini-batch size | 45 | ||
| initial learn rate | 0.001 | ||
| DTW-cb | window size | 5 | 81.4 |
| FCN | number of layers | 3 | 84.3 |
| number of epochs | 2000 | ||
| batch size | 16 | ||
| DTW-euc | window size | 5 | 86.1 |
| LDMLT | triplets factor | 20 | 92.1 |
| maximum cycle | 15 | ||
| alpha factor | 5 |
| K = 1 | K = 2 | K = 3 | K = 4 | K = 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DD | 86.3 | 83 | 82.8 | 79.1 | 79.3 |
| BPD (all features) | 87.2 | 86.5 | 84.9 | 83.5 | 81.6 |
| DD + BPD (all features) | 92.1 | 92.6 | 89.5 | 88.8 | 87.9 |
| DD + BPD (, ) | 91.9 | 91.6 | 89.8 | 88.4 | 86.5 |
| DD + BPD (, ) | 88.8 | 84.4 | 82.8 | 80.2 | 81.4 |
| DD + BPD (, ) | 92.1 | 92.6 | 89.5 | 88.8 | 88.1 |
| DD + BPD () | 92.3 | 91.6 | 90 | 88.4 | 87 |
| Method | Recognition Rate [%] |
|---|---|
| Label Consistent K-SVD [2,4] | 76.2 |
| Covariance Joint Descriptors [1,4] | 85.6 |
| Optical Spectra-based CNN [34] | 87 |
| Joint Trajectory Maps [4] | 87.9 |
| Joint Distance Maps [5] | 88.1 |
| Our method (DD + BPD) | 92.6 |
| Bayesian HDM [6] | 92.8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Warchoł, D.; Kapuściński, T. Human Action Recognition Using Bone Pair Descriptor and Distance Descriptor. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12101580
Warchoł D, Kapuściński T. Human Action Recognition Using Bone Pair Descriptor and Distance Descriptor. Symmetry. 2020; 12(10):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12101580
Chicago/Turabian StyleWarchoł, Dawid, and Tomasz Kapuściński. 2020. "Human Action Recognition Using Bone Pair Descriptor and Distance Descriptor" Symmetry 12, no. 10: 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12101580
APA StyleWarchoł, D., & Kapuściński, T. (2020). Human Action Recognition Using Bone Pair Descriptor and Distance Descriptor. Symmetry, 12(10), 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12101580






