A Haptic Model for the Quantum Phase of Fermions and Bosons in Hilbert Space Based on Knot Theory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
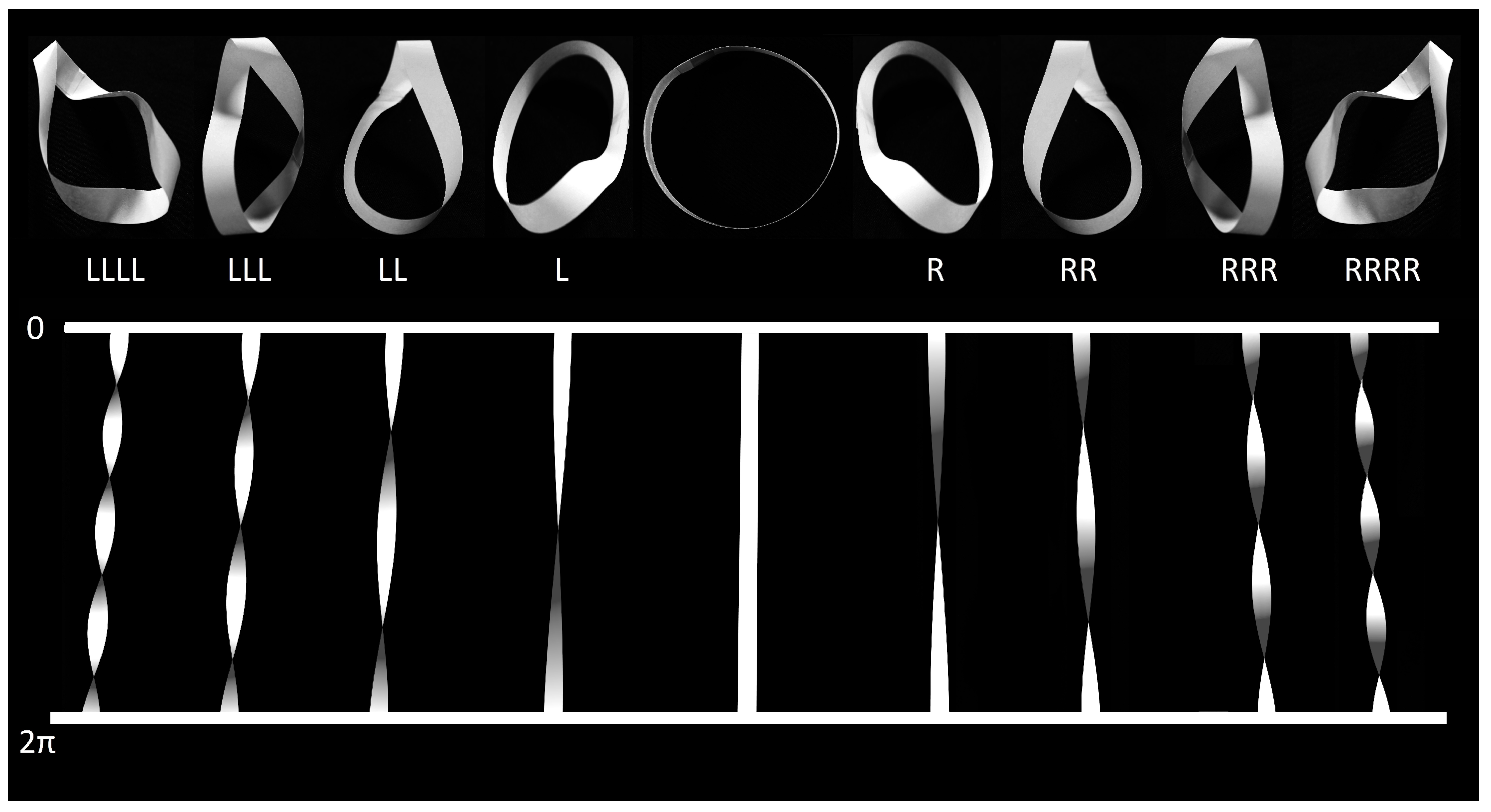
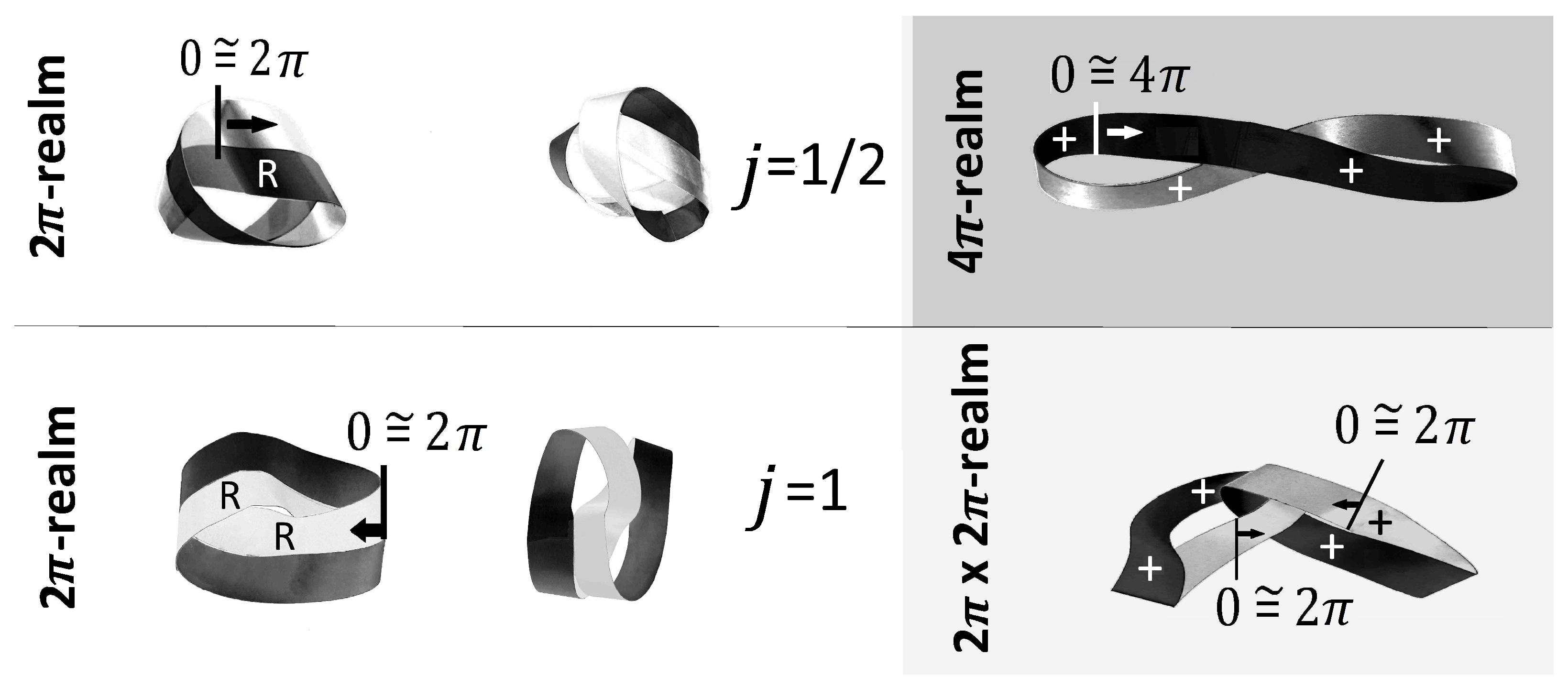
2. Great Circles and Double Windings in the -Realm
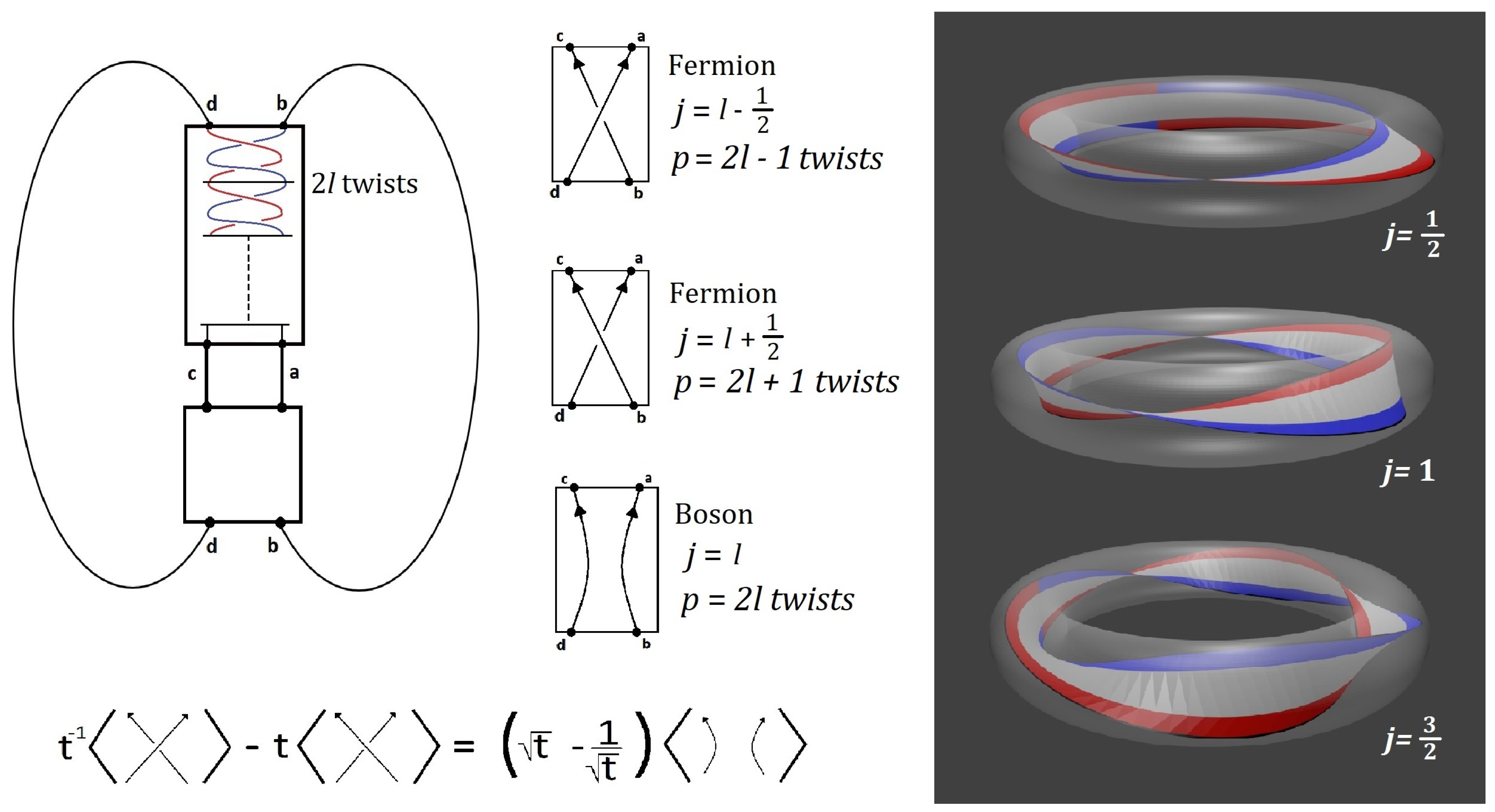
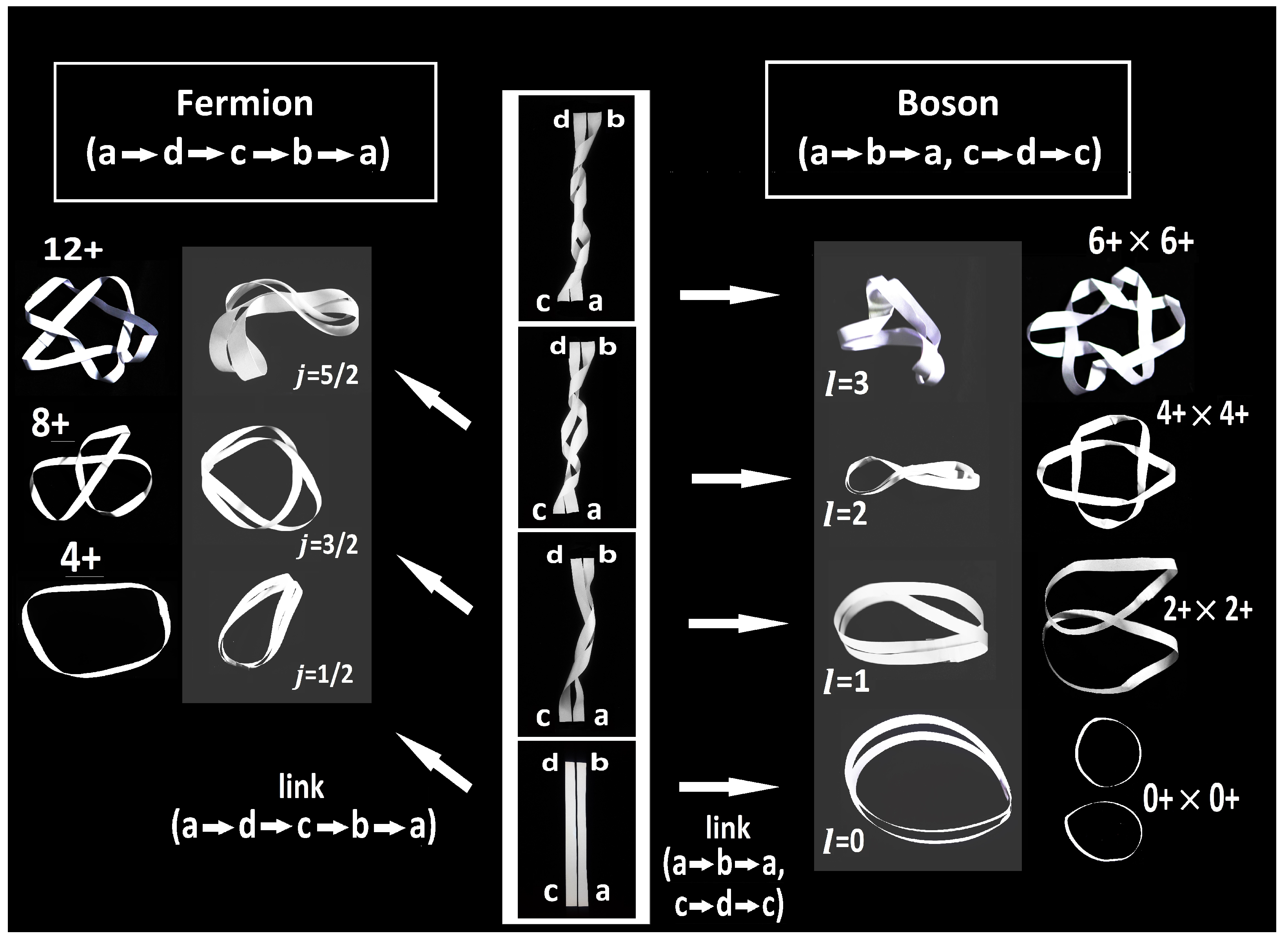
3. Jones Polynomials of Bosonic and Fermionic States in the -Realm
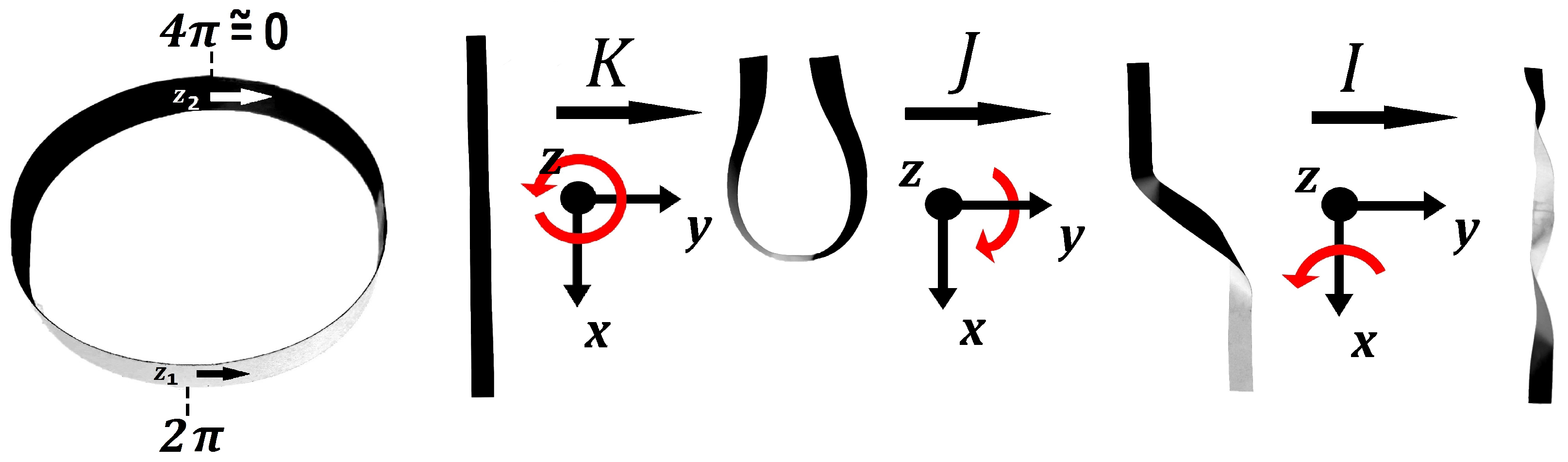
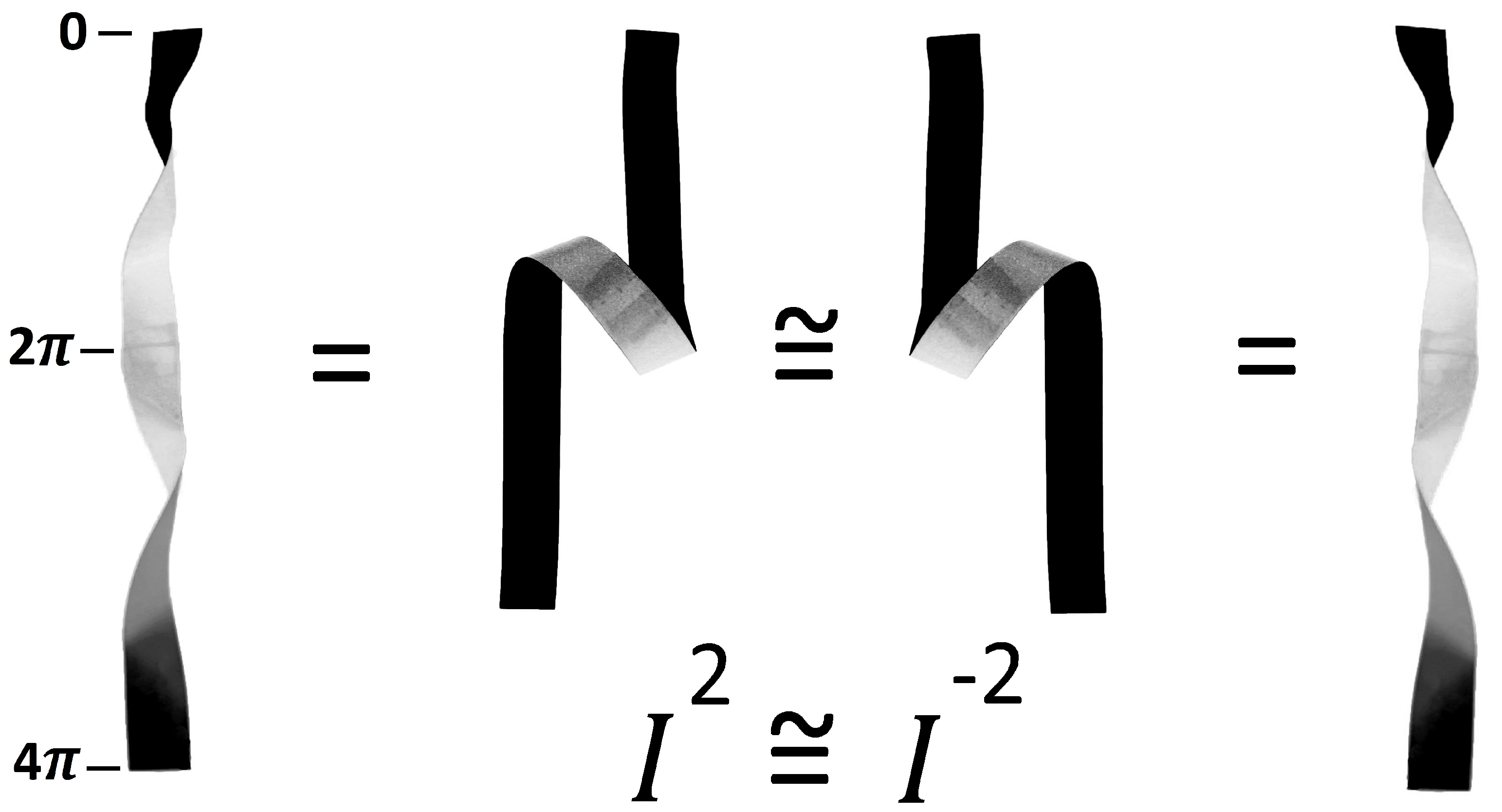
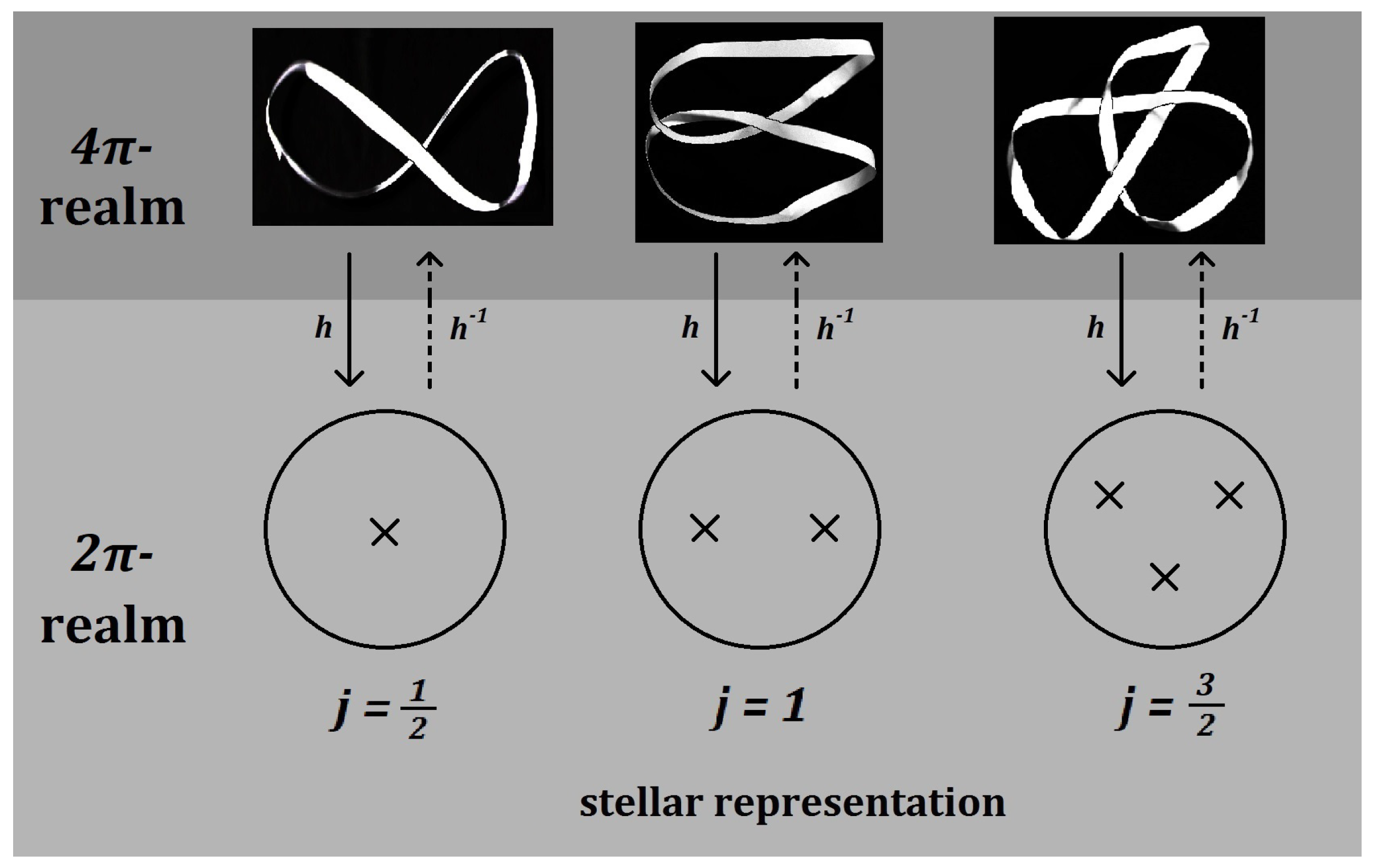
4. A Generalization of the “Dirac Belt” Trick in the -Realm
5. Relation Between Nodes, Twists and Knots
6. Observable Effects of the Möbius-Strip Topology
7. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Staley, M. Understanding Quaternions and the Dirac Belt Trick. Eur. J. Phys. 2010, 31, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heusler, S.; Ubben, M. Modelling spin. Euro. J. Phys. 2018, 39, 065405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrin, J. Knots on a Torus: A model of the Elementary particles. Symmetry 2012, 4, 39–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milnor, J. Singular Points of Complex Hypersurfaces; Princton University Press: Princton, NJ, USA, 1928. [Google Scholar]
- Brauner, K. Zur Geometrie der Funktionen zweier komplexer Veränderlichen. Abh. Math. Semin. Hambg. 1928, 6, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, I.; Zyczkowski, K. Geometry of Quantum States; Cambridge University Press: Camebridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman, L. The mathematics and physics of knots. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, I.; Penkov, I.; Serganova, V. A Categorification of the Boson–Fermion Correspondence via Representation Theory of sl(∞). Commun. Math. Phys. 2016, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, H.C. Applications of Spinor Invariants in Atomic Physics; North Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Majorana, E. Atomi orientati in campo magnetico variabile. Nuovo Cimento 1932, 9, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, H. Spin precession during interferometry of fermions and the phase factor associated with rotations through 2p radians. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1967, 18, 1102–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Colella, R.; Overhauser, A.; Eagen, C. Observation of the phase shift of a neutron due to precession in a magnetic field. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1975, 35, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, D.; Rubinstein, J. Connection between spin, statistics, and kinks. J. Math. Phys. 1968, 9, 1762–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heusler, S.; Ubben, M. A Haptic Model for the Quantum Phase of Fermions and Bosons in Hilbert Space Based on Knot Theory. Symmetry 2019, 11, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11030426
Heusler S, Ubben M. A Haptic Model for the Quantum Phase of Fermions and Bosons in Hilbert Space Based on Knot Theory. Symmetry. 2019; 11(3):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11030426
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeusler, Stefan, and Malte Ubben. 2019. "A Haptic Model for the Quantum Phase of Fermions and Bosons in Hilbert Space Based on Knot Theory" Symmetry 11, no. 3: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11030426
APA StyleHeusler, S., & Ubben, M. (2019). A Haptic Model for the Quantum Phase of Fermions and Bosons in Hilbert Space Based on Knot Theory. Symmetry, 11(3), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11030426





