Abstract
Recent advancements in wireless technology have created an exponential rise in the number of connected devices leading to the internet of things (IoT) revolution. Large amounts of data are captured, processed and transmitted through the network by these embedded devices. Security of the transmitted data is a major area of concern in IoT networks. Numerous encryption algorithms have been proposed in these years to ensure security of transmitted data through the IoT network. Tiny encryption algorithm (TEA) is the most attractive among all, with its lower memory utilization and ease of implementation on both hardware and software scales. But one of the major issues of TEA and its numerous developed versions is the usage of the same key through all rounds of encryption, which yields a reduced security evident from the avalanche effect of the algorithm. Also, the encryption and decryption time for text is high, leading to lower efficiency in IoT networks with embedded devices. This paper proposes a novel tiny symmetric encryption algorithm (NTSA) which provides enhanced security for the transfer of text files through the IoT network by introducing additional key confusions dynamically for each round of encryption. Experiments are carried out to analyze the avalanche effect, encryption and decryption time of NTSA in an IoT network including embedded devices. The results show that the proposed NTSA algorithm is much more secure and efficient compared to state-of-the-art existing encryption algorithms.
1. Introduction
Internets of things (IoT) includes millions of connected devices that can sense, compute and communicate data [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Every second, large amounts of data are transferred among these devices. Considering the sensitivity of applications in the IoT network, such as connected vehicles or wearable health devices, security of transmitted information has remained a major area of concern [7,8,9]. The increasing number of intruders and hackers has made this task very challenging. Over the years, numerous cryptographic algorithms have been used to ensure the security of transmitted data. The strength of the cryptographic algorithms depended on the techniques used for managing, establishing and distributing the secret keys. Secret keys that are poorly maintained make the cryptographic algorithm useless, even if the algorithm is theoretically and also, practically ideal [10,11]. Cryptographic algorithms proposed for IoT networks can be classified into the symmetric and asymmetric algorithms. Symmetric algorithms use the same key for both encryption and decryption. The strength of the symmetric algorithms truly depends on how the key is securely exchanged between the sender and receiver. Asymmetric algorithms indeed avail two different keys including the public and private keys. The private key is never transmitted through the network and hence it is secure. The public key is sent through the network to the receiver. During encryption, the sender encrypts the plaintext using the public key of the receiver and sends the resultant cipher text to the receiver using the network. Even if the public key is known to the hacker, he cannot read the scrambled (or hashed) message because secret key is not known for him. During decryption, the receiver will use his private key to decrypt the cipher text. Asymmetric algorithms are more complex to implement and utilize more resources than symmetric algorithms [12,13]. Thus, most of the modern applications in IoT networks use symmetric algorithms to provide security to the transmitted information. Further, they are easy to implement, utilize fewer resources with low overhead and are secure as long as the key is kept secret.
Symmetric algorithms are classified into block and stream ciphers. Encryption of plaintext is done bit-by-bit in case of stream cipher [14] and a group of bits (i.e., 64 bits) is taken for encryption in block cipher as a unit. The block cipher algorithm is preferred to the stream cipher for faster computations. Most of the symmetric algorithms use Feistel ciphers [15,16]. In the Feistel cipher, the encrypted plaintext is decomposed into two parts. A transformation function known as the round function is applied to one half using a sub-key and the output of the round function is XOR'ed with the other half. These two parts are then swapped with each other. This step is performed iteratively on the number of times specified in the algorithm. The Feistel cipher is an efficient method for implementing block symmetric algorithms. So, we focus on improving the security of symmetric algorithms that use the Feistel ciphers for encryption of text files.
With numerous IoT devices having different computational capabilities, one of the major requirements for an efficient security protocol in IoT networks is that it should be light weight. The processing time taken by the protocol should be minimal for less delay and better performance. Also, the security algorithm needs to be less complex with minimal overhead. Because of these reasons many protocols used with normal computer networks do not give good performance in IoT networks and are not preferred. Considering these features, tiny encryption algorithm (TEA) [17,18,19] is the most widely used symmetric algorithm with a Feistel cipher for secure transmission of data through the IoT network. The popularity of TEA is mainly due to the ease of implementation and less memory utilization compared to all other encryption algorithms. But one of the major issues with TEA is the usage of the same keys through all the rounds of encryption which leads to reduced security. This is undoubtedly observed from the avalanche effect of TEA. Moreover, the time taken for encryption and decryption is high, leading to reduced efficiency of TEA. Although many versions of TEA have been proposed over these years [20,21,22,23], none of them have given concrete solutions to the above problems.
This paper proposes an algorithm named NTSA (novel tiny symmetric encryption algorithm) that improves the security features of TEA by introducing more key confusions. Most of the works with TEA and its variations has focused only on decreasing the delay in delivery. Very few researches have been done on key alteration as a method to enhance the security of the transmission algorithm. In the proposed method we introduce multiple key alterations dynamically and secure the key from intruders. Since the key is computed dynamically, the key values are changed during the execution time and cannot be pre-computed. Furthermore, our proposed algorithm (NTSA) takes less time for encryption and decryption compared to TEA and thus provides both better security and efficiency for all the modern applications in IoT networks. The rest of the research is organized into four sections as follows. Section 2 discusses different existing encryption mechanisms for the secure transmission of data through IoT networks. This section further explains the implementation of the TEA algorithm in detail. Few variations of the TEA algorithm are also discussed in this section. Our proposed NTSA is explained in the Section 3. Section 4 presents the experimental results of the NTSA algorithm and we conclude in Section 5 and express some potential future works.
2. Related Work
In here, we discuss the major encryption algorithms proposed for transmission of data in IoT networks. Specifically, we discuss the design and implementation of these algorithms and highlight their issues and drawbacks. We also discuss the design, implementation and issues with the TEA and its latest versions in detail.
One of the earliest works in this area was the RC5 symmetric key block cipher [24]. RC5 uses variable sized blocks, 32, 64, 128 bits etc. The rounds used are 0–255 with key size of 0 to 2040 bits. The case RC5 is determined suitable for wireless sensor network (WSN) applications, but the key schedule must be calculated a priori based on 104 additional bytes of RAM for each key. Also, the variable-bit rotation instruction used by RC5 is rarely supported by the embedded systems [24]. Skipjack algorithm is another block cipher algorithm developed by the US National Security Agency. Skipjack and its variants, TinySec and MiniSec, are used for transmission of data in WSNs. But the algorithm is not efficient in embedded IoT devices with multiple issues in implementation [25,26,27]. Standaert et al. gave the scalable encryption algorithm (SEA) [28] generated for processing units that have limited the instruction set. It provides cost-effective encryption and authentication, but does not address secure search of the substring. Hong et al. proposed the HIGHT algorithm [29] that is very useful for pervasive computing devices like devices of a wireless sensory system or network. It uses Feistel network and basic operations like addition mod 28 or XOR. There are 32 rounds with 128-bit key and 64-bit block size. But the noted algorithm is vulnerable to saturation attack. Usman et al. proposed SIT—a lightweight encryption algorithm [30] that provides enhanced security for data transmission between IoT devices. SIT uses a combinational form of Feistel structure and network with a uniform substitution-permutation. But the detailed study on performance evaluation and cryptanalysis for possible attacks have not been performed. Liang C et al. [31] proposed the hybrid encryption algorithm for lightweight data in cloud storage. This was an improved method on the RSA algorithm and it combined with advanced encryption standard (AES) to introduce a hybrid encryption algorithm. The proposed algorithm improves the efficiency of generating large primes. But the algorithm was mainly focused on enhancing the data confidentiality in the cloud. M-SSE proposed by Chongzhi Gao et al. [32] is different from existing searchable symmetric encryption algorithms as it provides privacy in both forward and backward directions using a technique of multi-cloud computing. But the algorithms and its variations are prone to information leakage. International data encryption algorithm (IDEA) [33] is a block symmetric algorithm that uses 64-bit plain text and a key size of 128 permuted into 52 sub-keys of 128 bits. It includes a Feistel structure and has eight rounds. The degree of diffusion and non-linearity properties of the round function decides the strength of the Feistel structure. IDEA does not use substitution and permutation boxes and is based on operations like XOR, addition and multiplication, thus reducing the memory overhead. The use of the multiplication operation provides diffusion. IDEA does not support any change in the Feistel structure and hence is not flexible. MARS [34] is another symmetric block algorithm that uses 128-bit plaintext with key size varying between 128–448 bits. It follows Feistel structure and has only one substitution box. This algorithm is faster than DES and it is susceptible to many attacks. The involvement of various components makes MARS very complex to analyze and implement in hardware. Abdelhalim et al. proposed the modified TEA algorithm (MTEA) [35], which improves the security of TEA and power consumption. The linear feedback shift register (LFSR) is used as a pseudo-random number generator to improve the security of the TEA and power utilization. The pseudo-random number generator frequently changes the MTEA key in each round. Zhdanov and Sokolov proposed an algorithm [36] based on the principles of many-valued logic and variable block length. The encryption process is performed iteratively with five rounds. The number of rounds can be varied, with round 1 consisting of gamma and permutations procedures, remaining rounds include substitution and gamma procedures. The proposed method can process binary information after representing as a ternary vector. But there is no method developed that does this conversion directly. LEA (lightweight encryption algorithm) is a block encryption algorithm [37] that is designed to provide confidentiality in lightweight environment like mobile devices. This algorithm uses plain text of 128 bits and varying modes can be selected depending on the size of the key (128, 192, or 256 bits). Based on the modes, the number of rounds can be changed between 24, 28, and 32 bits. This algorithm does not use S-box, instead addition, rotation and XOR arithmetic operation is processed in 32-bit unit [38]. Abdullah et al. proposed a super-encryption cryptography [39] with IDEA (international data encryption algorithm) and WAKE (word auto key encryption) algorithm. The technique of super encryption combines two or more symmetric cryptographic algorithms so as to provide more security to data. Anderson et al. proposed the serpent algorithm [40] that was an AES candidate. The main aim of this algorithm is to maximize the avalanche effect within the cipher text. Serpent has substitution permutation structure that uses 128-bit plain text and accepts keys of 128, 192, or 256 bits. The 32 rounds of serpent make it a bit slower and complex to implement on small blocks. Data encryption standard (DES) is one of the widely used symmetric key block cipher that uses the Feistel structure. The plaintext of 64-bit and a key size of 56 bits are used for the encryption process that includes 16 rounds. The DES algorithm does not allow flexibility in Feistel structure and hence does not support any changes in it [41].
Tiny encryption algorithm (TEA) developed by David Wheeler and Roger Needham [42] is the most efficient for use with embedded devices in IoT networks compared to all the discussed encryption algorithms. Some of the interesting features of TEA are ease of implementation, the absence of specialized tables, good performance and short enough to integrate into any embedded device. The main focus of TEA is reduced memory usage and maximized speed. Encryption routine of TEA is shown in Figure 1 and the decryption routine is shown in Figure 2.
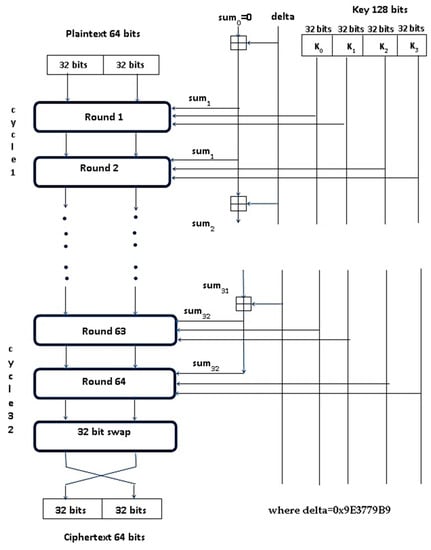
Figure 1.
Encryption routine of the tiny encryption algorithm (TEA).
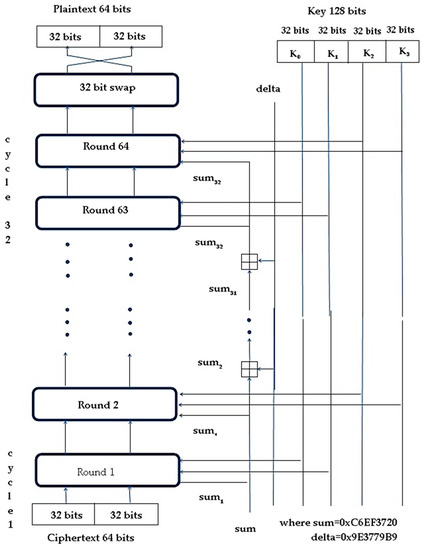
Figure 2.
Decryption routine of TEA.
TEA uses Feistel structure with 64 rounds or 32 cycles where one cycle is composed of two rounds [43]. The plaintext block size is 64 bits (operate on two 32-bit unsigned integers and stored in v[0] and v[1]). The recommended key size is 128 bits. The key is split into four 32-bit blocks, k[0] to k[3]. The XOR and AND operations are used alternatively. Also repeated mixing of all the bits of plaintext and key is achieved by the dual shift operation. A simple key schedule is used for both encryption and decryption and the four 32-bit blocks of the key are mixed exactly the same way for each cycle. Magic constant is used to compute the key. For preventing the attacks caused by the symmetry of rounds, each cycle (one cycle constitutes of two rounds) uses different multiples of magic constants. Magic constant is 2,654,435,769 or 9E3779B916 and would be selected as 231/ Ø (Ø is named the golden ratio). During the encryption process, the plaintext is partitioned into two parts Left[0] and Right[0]. Each of the parts utilizes another half part for doing the encryption process. There will be 64 rounds along with two other rounds that constitute one cycle, so there are 32 cycles. After the 64th round, both parts will be composed to create the cipher text. In each of the rounds, all the inputs include “Left[i − 1]” and “Right[i − 1]” which is derived from the previous round and sub-key Ki extracted from the 128-bit key K. The constant delta =0 × 9E3779B9 is chosen to be 231/Ø. This is to confirm that the sub-keys are distinct and that the accurate value of it does not have a cryptographic significance. In each round, the integer "addition" modulo of 232 is applied instead of XOR. The round function F uses addition, bitwise XOR, left and right shift operation.
For the i-th cycle,
Left [i] = Left [i − 1] + F (Right [I − 1], key [0, 1], delta [i]),
Right [i] = Right [i − 1] + F (Left [i − 1], key [2, 3], delta [i]),
Delta [i] = Floor ((i + 1)/2)*delta
Round function F is
F(M,K[a,b],delta[i]) = ((M<<4)AND k[a]) XOR (M AND delta[i]) XOR ((M>>5)AND k[b] ).
The 128-bit key is divided into four 32-bit blocks K=(k[0], k[1], k[2], k[3]) where odd rounds use keys k[0] and k[1] and even rounds use k[2] and k[3]. One cycle constitutes two rounds and the i-th round is shown in Figure 3.
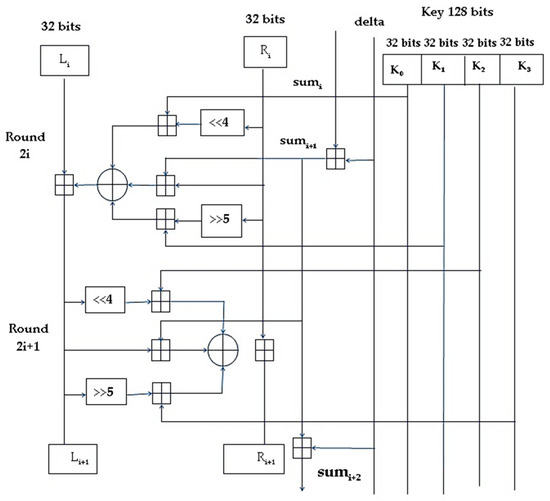
Figure 3.
The i-th cycle of TEA.
Many variations of the TEA algorithm have been proposed recently. Dian Rachmawati et al. proposed an algorithm [44] that uses a combined asymmetric and symmetric encryption for secure file transfer. The security of the file is taken care by the symmetric algorithm TEA and security of the key by the asymmetric algorithm LUC based on Lucas function. But the method used the same key for all rounds of encryption leading to reduced security. Novelan et al. developed an SMS security system for mobile devices using the Tiny Encryption algorithm [45]. This system ensures that the confidential messages are encrypted in the presence of a key to obtain the encrypted SMS message that is sent to the destination mobile number. Cipher text at the receiver side can be decrypted using the same key to get the SMS. The drawback with this method is that the size of the SMS decides the encryption and decryption time taken for the process. XTEA is a block symmetric encryption algorithm that uses the Feistel structure [46]. This algorithm uses 64-bit block plaintext, 128-bit key and 64 rounds of encryption. This algorithm uses a more complex key-schedule than TEA with rearrangements of the shifts, XOR’s and additions [47]. XXTEA, also called block TEA uses the same round function as XTEA but applies it cyclically across an entire message for several iterations [48]. Table 1 presents a summary of all the existing security algorithms.

Table 1.
Summary of the symmetric encryption techniques.
Of all the discussed algorithms, TEA remains the most efficient for use in IoT networks for secure and quick transfer of text files between simple embedded devices. But one of the major issues with TEA and its latest variations is the usage of same keys through all rounds of encryption, resulting in reduced security, which is evident from the avalanche effect of the algorithm. Also, the encryption and decryption time for text is high, leading to lower efficiency in IoT networks with embedded devices. This paper proposes a NTSA which provides enhanced security for the transfer of text files through the IoT network by introducing additional key confusions dynamically for each round of encryption.
3. Novel Tiny Symmetric Encryption Algorithm (NTSA)
The TEA algorithm and its variations use the same key in all rounds of encryption and are thus more prone to relative key attack where the attacker tries to realize some relationship between different keys used by the user. The proposed NTSA algorithm is intended to provide more confusion to the keys in each round dynamically. It uses 64-bit plaintext and key of 128 bits. There are 32 cycles and each cycle is composed of two rounds, resulting in 64 rounds. The plaintext is divided into two halves, v0 and v1, with 32 bits each. The round function op is applied to each half of plaintext. The 128-bit key is divided into four 32-bit partial keys k1, k2, k3, and k4. Partial keys k1 and k3 are applied to the odd numbered round and partial keys k2 and k4 are applied to even numbered round. Compute key schedule constant ksc = floor (231/Ø) where Ø is the golden ratio. The golden ratio Ø is 1.618033988749895 and computed as (1 + √ 5)/2.
NTSA round function is as follows:
Round i (i is odd):
v0 += ((v1 LSHIFT 4) AND k0) XOR (v1 AND kc) XOR ((v1 RSHIFT 5) AND k1)
Round i (i is even):
v1 += ((v0 LSHIFT 4) AND k2) XOR (v0 AND kc) XOR ((v0 RSHIFT 5) AND k3)
For 1st cycle: the partial keys are k0, k1, k2 and k3.
From 2nd cycle onwards:
For odd round k0 is kept constant but k1 changes for all odd rounds as follows,
k1 = k1 + (k0 XOR(xtract(v0)))
For even round k2 is kept constant but k3 changes for all even rounds as follows,
k3 = k3 + (k2XOR(xtract(v1)))
The function xtract() will compute an integer in the range 0 to 32 from v0 or v1 depending upon the parameter being passed. This integer value is an index to an array that is generated dynamically based on the key value selection. The xtract() function will return the value from the array that is pointed by the index value computed. Thus, the key confusion is created dynamically and cannot be predicted prior to execution and the value changes on each execution of the algorithm. The NTSA encryption and decryption model is shown in Figure 4.
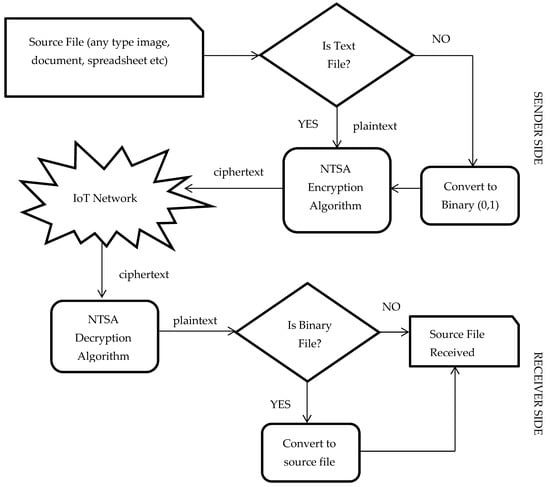
Figure 4.
System model: novel tiny symmetric encryption algorithm (NTSA) encryption and decryption.
The source file can be a file of any type such as a document, spreadsheet, pdf, presentation, image, text file etc. The text file can be sent directly to the NTSA encryption algorithm to obtain the cipher text. All the other types of files are converted into binary, the streams of ones and zeros. This binary stream is sent to the NTSA encryption algorithm to get the cipher text using the secret key which has already been agreed upon by the sender and the receiver. On reception of cipher text at the receiver end, the NTSA decryption algorithm converts the cipher text to plaintext. If the converted file is binary (that is streams of zeros and ones) the file is converted to the respective source file, otherwise the plaintext is already received. The NTSA Encryption technique is presented as Algorithm 1 and Decryption technique is presented as Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 1 Novel tiny symmetric encryption algorithm (NTSA) symmetric encryption algorithm |
| Encrypt (plaintext v, key k): |
| 1: Start 2: Assign key constant kc = 0 3: Assign cycle = 0 4: kc = kc + ksc 5: 32-bit block v0 is recomputed as v0 += ((v1 LSHIFT 4) AND k0) XOR (v1 AND kc) XOR ((v1 RSHIFT 5) AND k1) 6: Partial key k1 is recomputed as k1 += (k0 XOR(xtract(v0))) where function xtract() returns value of array indexed v0. 7: 32-bit block v1 is recomputed as v1 += ((v0 LSHIFT 4) AND k2) XOR (v0 AND kc) XOR ((v0 RSHIFT 5) AND k3) 8: Partial key k3 is recomputed as k3 += (k2 XOR(xtract(v1))) where function xtract() returns value of array indexed v1. 9: Increment cycle by 1 10: Repeat step 4 through step 9 until cycle = 32 11: Assign value of k1 to newk1 and k3 to newk3 12: Return newk1 and newk3 |
The NTSA symmetric encryption algorithm uses the plaintext to encrypt with the key that was already agreed upon by the two parties in communication. The key constant is initialized to zero. The key schedule constant ksc is computed as floor (231/Ø) where Ø is the golden ratio. The golden ratio Ø is 1.618033988749895. The 32-bit block plaintext v0 and v1 are recomputed each time for 32 cycles and partial keys k1 and k3 are recomputed for even and odd rounds respectively to induce key confusion. The computation of v0, k1, v1, k3 are shown in the following equations.
v0 += ((v1 LSHIFT 4) AND k0) XOR (v1 AND kc) XOR ((v1 RSHIFT 5) AND k1)
k1 += (k0 XOR(xtract(v0))) where function xtract() returns value of array indexed v0.
v1 += ((v0 LSHIFT 4) AND k2) XOR (v0 AND kc) XOR ((v0 RSHIFT 5) AND k3)
k3 += (k2 XOR(xtract(v1))) where function xtract() returns value of array indexed v1.
kc is recomputed each time as kc = kc + ksc
This process is repeated for 32 cycles and after the last cycle the values of partial keys k1 and k3 are the new values computed and these new partial keys and the cipher text are sent to the decryption process. The NTSA symmetric decryption algorithm uses the cipher text, the key that was already agreed upon by the two parties in communication and the newly computed partial keys k1 and k3 for the decryption purpose. The key constant is initialized to 0XC6EF3720. The key schedule constant ksc is computed as floor (231/Ø). The golden ratio Ø is 1.618033988749895. The 32-bit blocks v1 and v0 are recomputed each time for 32 cycles and partial keys k3 and k1 are recomputed for odd and even rounds respectively to induce key confusion. The computation of k3, v1, k1 and v0 are shown in the following equations.
k3 - = (k2 XOR(xtract(v1))) where function xtract() returns value of array indexed v1
v1 - = ((v0 LSHIFT 4) AND k2) XOR (v0 AND kc) XOR ((v0 RSHIFT 5) AND k3)
k1 - = (k0 XOR(xtract(v0))) where function xtract() returns value of array indexed v0
v0 - = ((v1 LSHIFT 4) AND k0) XOR (v1 AND kc) XOR ((v1 RSHIFT 5) AND k1)
kc is recomputed each time as kc = kc − ksc
This process is repeated for 32 cycles and after the last cycle the 32-bit block v0 and v1 contains the decrypted contents.
| Algorithm 2. NTSA symmetric decryption algorithm |
| Encrypt (plaintext v, key k): |
| 1: Start 2: Assign key constant kc = 0XC6EF3720 3: Assign k1 = newk1 and k3 = newk3 4: Assign cycle=0 5: Partial key k3 is recomputed as k3 - = (k2 XOR(xtract(v1))) where function xtract() returns value of array indexed v1. 6: 32-bit block v1 is recomputed as v1 - = ((v0 LSHIFT 4) AND k2) XOR (v0 AND kc) XOR ((v0 RSHIFT 5) AND k3) 7: Partial key k1 is recomputed as k1 - = (k0 XOR(xtract(v0))) where function xtract() returns value of array indexed v0. 8: 32-bit block v0 is recomputed as v0 - = ((v1 LSHIFT 4) AND k0) XOR (v1 AND kc) XOR ((v1 RSHIFT 5) AND k1) 9: kc = kc − ksc 10: Increment cycle by 1 11: Repeat step 5 through step 10 until cycle=32 12: Return |
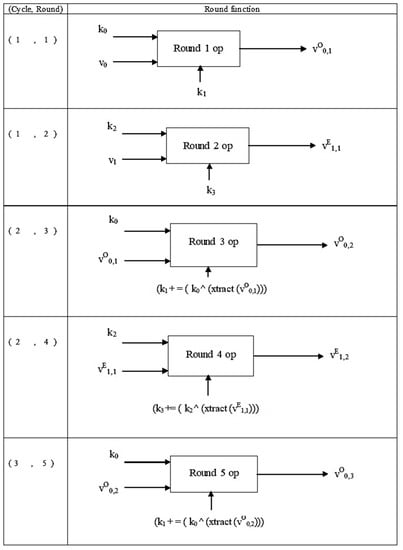
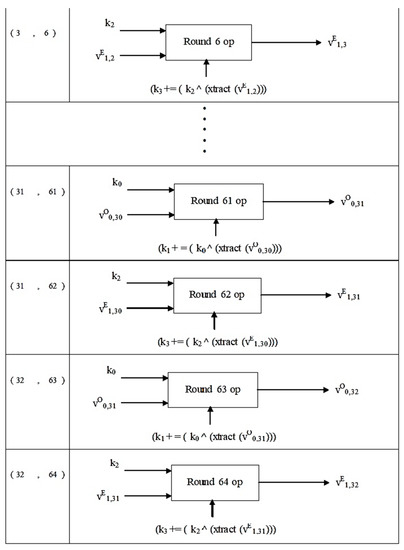
Figure 5.
Structure of NTSA encryption algorithm.
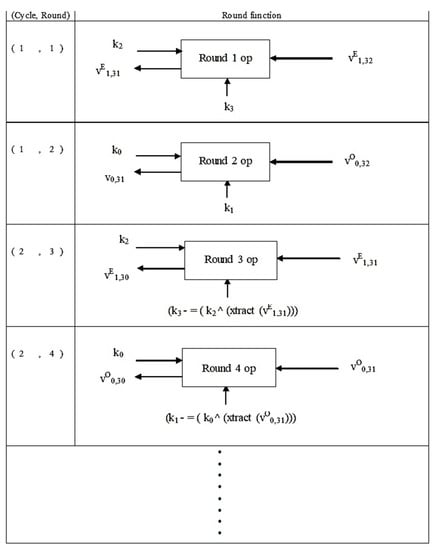
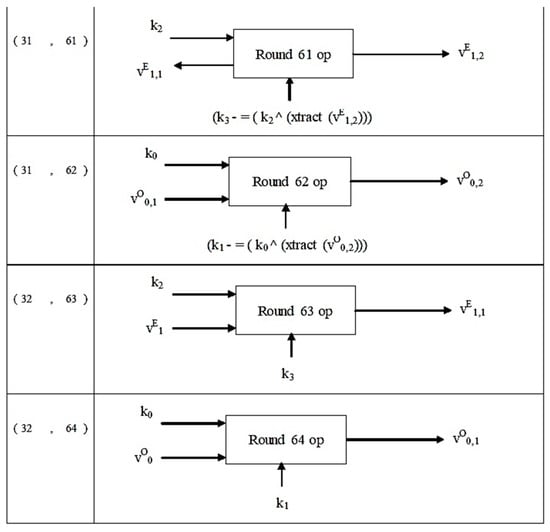
Figure 6.
Structure of NTSA decryption algorithm.
The notation:
in vO0,1; O indicates an odd round, and 0,1 indicate the 0th cycle, round 1;
in vE1,1; E indicates an even round, and 1,1 indicate the 1st cycle, round 1.
For computing vO0,1, the second half of the plaintext v1 is used and shift, AND, and XOR operations are performed on v1. Similarly, for computing vE1,1, the first half (32 bits) of plain text v0 is used and shift, AND and XOR operations are performed on v0.
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
In this section we discuss the results obtained with our experiments. The performance of NTSA is analyzed and compared with TEA and its latest variations XTEA and XXTEA. A network with LPWAN and IoT infrastructures was set up in our lab. NTSA, TEA, XTEA and XXTEA algorithms were implemented in embedded devices. System architecture similar to [51] was used for the experimental set up. IoT configured mobile devices connected with LPWAN and interfaced with IoT cloud via the IoT gateway was set up. The text files were then transmitted from these devices to the IoT cloud configured in a mobile device through the IoT gateway platform. The text files were then stored in the database in the cloud server. The text files were then encrypted using the four algorithms separately in four different scenarios and were send to the IoT configured mobile devices. The encryption and decryption times for each algorithm was measured for varying file sizes and key sizes.
4.1. Performance Comparison of NTSA with TEA, XTEA and XXTEA
Table 2 and 3 presents the encryption and decryption times of the various security algorithms for 48-bit key with varying file sizes from 0.37 kilobytes to 26.7 kilobytes. It is evident from Table 2 that the encryption time for text files using the proposed method NTSA was lower than the other existing security algorithms. NTSA achieved an encryption time of 0.041 ms for a 0.37 kB text file which is much lower compared to 0.059 ms obtained by the TEA algorithm. The two other variations of TEA, XTEA and XXTEA had much higher encryption times because of their complexity in design and implementation. It is observed from the results that, even when the text file size increased, NTSA maintained a lower encryption time compared to the other existing security encryption schemes. NTSA achieved a much lower encryption time of 0.857 ms, 1.211 ms and 1.603 ms for text file size 12.2 kB, 16.2 kB, and 26.7 kB, respectively. This asserts the excellent performance of NTSA even with higher text file sizes.

Table 2.
Encryption time for key size of 48 bits.
From the results presented in Table 3, it is evident that NTSA achieved a lower decryption time for various text file sizes compared to the other three existing security algorithms in IoT networks. NTSA achieved a decryption time of 0.055 ms for a 0.37 kB text file, which is much lower than the decryption time achieved by other algorithms. For higher file sizes of 12.2 kB, 16.2 kB and 26.7 kB, NTSA achieved 0.890 ms, 1.234 ms, and 1.645 ms decryption times, respectively. So even with higher text file sizes, NTSA achieved lower decryption times similar to the results obtained during encryption. Lower encryption and decryption times are a very important parameter determining the efficiency of a security algorithm in an IoT network. With most of the devices having limited computational capabilities, it is very much required to have a security algorithm that can provide maximum security with less complexity and minimum encryption and decryption times. Thus, the results obtained from our experiments with 48-bit key encryption confirms that the proposed method achieves much lower encryption and decryption times compared to the existing security algorithms in IoT networks. This result is achieved, especially due to the simplicity in design of the proposed algorithm, without compromising the strength in security. The improved strength in security of the algorithm was later verified using the avalanche effect parameter. With lower encryption and decryption time, this algorithm would be highly beneficial for the users to transmit text files through the IoT networks more efficiently.

Table 3.
Time for key size of 48 bits.
Table 4 and Table 5 present the comparison of encryption and decryption time of NTSA with TEA, XTEA and XXTEA for a 128-bit key with varying file sizes from 0.37 kilobytes to 26.7 kilobytes. It is interesting to observe from the results presented in Table 4 that with a larger key size, NTSA achieved lower encryption time compared to all the existing security algorithms in IoT networks. The encryption time for a text file of size 0.37 kB with 128-bit key is 0.51 ms for NTSA which was much lower compared to the encryption time achieved by TEA, XTEA and XXTEA algorithms. The simplicity in design of NTSA helped the algorithm to achieve lower encryption time with varying key and file sizes.

Table 4.
Time for key size of 128 bits.

Table 5.
Time for key size of 128 bits.
This scenario was also observed with the decryption times presented in Table 5. With decryption also, NTSA achieved lower times compared to its compatriots with a 128-bit key and varying file sizes. NTSA achieved a decryption time of 0.49 ms for a 0.37 kB text file compared to 0.058 ms, 0.143 ms and 0.068 ms achieved by TEA, XTEA and XXTEA respectively for similar text file size. For higher file sizes of 12.2 kB, 16.2 kB, and 26.7 kB, NTSA achieved 1,03 ms, 1.10 ms, and 1.989 ms decryption times, respectively. So even with higher text file sizes, NTSA achieved lower decryption times similar to the results obtained during encryption. With lower encryption and decryption times at 128-bit key, NTSA can become the preferred security algorithm for hand held devices and other embedded IoT devices with different computational capabilities for efficiently transferring text files.
Table 6 and Table 7 show the encryption and decryption times of the security algorithms for the transfer of a text file with size 0.95 kB. The better performance of NTSA compared to all the existing security algorithms is evident from the obtained results. This is because the NTSA algorithm has a very simple implementation strategy. The TEA and its different variations use complex computations with the key and hence the encryption and decryption time is greater. In Table 6, the encryption time obtained by NTSA for a file size of 0.95 kB with varying key size is compared with the existing algorithms. The key size is varied from 32 bits to 240 bits and the corresponding encryption time is observed. TEA achieved an encryption time of 0.125 ms for a key size of 32 bits while XTEA and XXTEA achieved 0.287ms and 0.145 ms, respectively. For the same key size, NTSA had an encryption time of 0.07 ms which was much lower compared to all the other security algorithms. For the 96-bit key, XTEA had an encryption time of 0.126 ms, while XTEA and XXTEA had encryption times of 0.265 ms and 0.158 ms, respectively. The encryption time obtained by NTSA for similar key size was 0.093 ms which was much lower than the time achieved by the existing algorithms. This demonstrates the better performance of the proposed approach NTSA, compared to all the existing security algorithms in IoT networks with varying key sizes.

Table 6.
Encryption time for file size 0.95 kB.

Table 7.
Time for file size 0.95 kB.
Table 8 and Table 9 show the encryption and decryption times of the security algorithms for the transfer of a text file with size 12.2 kB with varying key sizes. The encryption time achieved by TEA, XTEA and XXTEA for a key size of 32 bits was 1.173 ms, 2.287 ms, and 1.649 ms, respectively, which was much higher compared to 1.009 ms obtained by NTSA for a similar key size. Even for a key size of 96 bits, NTSA achieved an encryption time of 1.10 ms which is lower than the values obtained by all the other existing security algorithms for similar file size. For a key size of 240 bits, NTSA had an encryption time of 1.2 ms which was much lower compared to all the existing algorithms. Thus, for smaller and larger key sizes, NTSA achieved lower encryption time compared to all the existing security algorithms in IoT networks. This scenario is also observed with the decryption times presented in Table 9. NTSA achieved a decryption time of 1.025 ms, 1.155 ms, and 1.388 ms for a key size 160 bits, 192 bits, and 240 bits, respectively. This time achieved by NTSA was lower than the times obtained by TEA, XTEA and XXTEA for similar key sizes in the IoT network. This assures the better performance of NTSA compared to all the existing algorithms with varying key sizes in IoT networks.

Table 8.
Time for file size 12.2 kB.

Table 9.
Decryption time for file size 12.2 kB.
Table 10 and Table 11 presents the results obtained in encryption and decryption time with NTSA, TEA, XTEA and XXTEA for a text file size of 26.7 kB with varying key sizes from 32 bits to 240 bits. The encryption time achieved by TEA, XTEA and XXTEA for a key size of 32 bits is 2.253 ms, 4.459 ms, and 2.339 ms, respectively, which is much higher compared to 1.772 ms obtained by NTSA for a similar key size. Even for a key size of 96 bits, NTSA achieved an encryption time of 1.856 ms which was lower than the values obtained by all the other existing security algorithms for similar file size. NTSA also achieved an encryption time of 1.887 ms, 1.662 ms, and 1.912 ms for 160 bits, 192 bits and 240 bits’ key sizes. Thus, from the results it is evident that NTSA achieved much lower encryption times compared to all the existing algorithms in IoT networks. This scenario is also verified in Table 11 which presents the decryption time obtained by these algorithms for varying key sizes. The simplicity in design enables NTSA to achieve much lower encryption and decryption times in IoT networks. This would definitely enable IoT devices with varying computational and storage capabilities to efficiently and securely transmit text files through the network.

Table 10.
Time for file size 26.7 kB.

Table 11.
Time for file size 26.7 kB.
From the results presented in Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10 and Table 11, it is very evident that the NTSA algorithm give better performance compared to all the existing algorithms with variable file sizes and key sizes. NTSA gave much lower encryption and decryption times for variable size text files using multiple key sizes in IoT networks. This is due to the simple and efficient design of NTSA. One of the most important features of NTSA is that it provides enhanced security to all the applications in IoT devices with lower encryption and decryption times. Thus, the proposed approach NTSA can be used for efficient and secure transfer of text files between devices in IoT networks.
Avalanche Effect
The avalanche effect is the property wherein a very small change in input results in significant changes on the output. An encryption algorithm is considered good if a one-bit change in key results in significant changes in the cipher text. With reference to the avalanche effect, we compared the strength of NTSA and TEA algorithms.
Experiment 1: an encryption was performed for NTSA and TEA algorithms using keys with varying key sizes of 48, 64 and 128 bits and same plaintext. Then one bit was changed on the key and the experiment was repeated. It is observed that for every 64-bit block, a one-bit change in key resulted in significant changes on the cipher text. Drastic changes were observed for the NTSA algorithm when compared to TEA. Figure 7 shows, for every 64-bit block, a change in one bit of the key with various key sizes and the corresponding change in cipher text for NTSA and TEA.
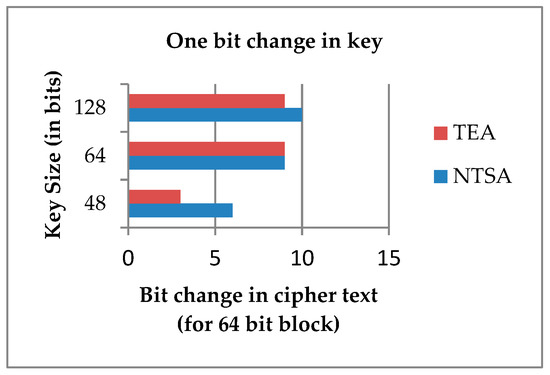
Figure 7.
Change in key and the corresponding change in cipher text for a 64-bit block.
From Figure 7, it is very evident that when a bit in the key was changed, the cipher text generated using NTSA algorithm had more drastic change than the cipher text created using TEA. This shows the increased security offered by the NTSA algorithm compared to TEA.
Experiment 2: an encryption was performed for NTSA and TEA algorithms using keys with varying key sizes 48, 64 and 128 bits. Then one bit was changed on the plaintext and the experiment is repeated. It was observed that for every 64-bit block, one-bit change in plaintext resulted in significant changes on the cipher text. Drastic changes were observed for the NTSA algorithm when compared to the tiny encryption algorithm. Figure 8 shows that for every 64-bit block a change in one bit of key with various key sizes and the corresponding change in cipher text for NTSA and TEA.
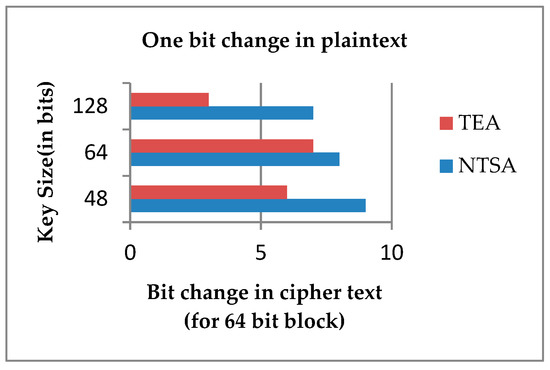
Figure 8.
One-bit change in plaintext corresponding change in cipher text for 64-bit block.
From Figure 8 it is very evident that when a bit in the plaintext was changed, the cipher text generated using NTSA algorithm had more drastic change than the cipher text created using TEA. This verifies the increased security offered by the NTSA algorithm compared to TEA. Thus, the proposed method NTSA is more efficient and secure than all previously proposed encryption schemes for transfer of text files between embedded devices in IoT network.
5. Conclusions
TEA showed better performance in terms of both encryption and decryption execution times than XTEA and XXTEA. The XTEA was proposed to set the key schedule and XXTEA was proposed in order to present the key material slowly. The proposed algorithm NTSA does the same, and experiments performed proved that the performance of NTSA is better than TEA. In addition to this, NTSA created more confusion on the key than the tiny encryption algorithm. The avalanche effect showed a positive result to NTSA when compared to TEA. Thus, NTSA can be used by all the latest applications in IoT devices with different computational and storage facilities to transfer text files efficiently and securely through the network. The NTSA algorithm security can be further increased by encrypting the compressed file. In future we also aim to integrate and implement this algorithm for data transfer in ad hoc, sensor and fog networks [8,52,53,54,55,56,57].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.R.; formal analysis, S.R. and V.M.; funding acquisition, V.M.; investigation, S.R.; methodology, S.R.; project administration, V.P., V.M. and M.K.; resources, V.P. and V.M.; software, M.K.; supervision, V.P.; validation, S.R. and M.K.; visualization, S.R.; writing—original draft, S.R., V.P. and V.M.; writing—review and editing, V.M. and M.K.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank the Management and Principal of SCMS School of Engineering and Technology for providing the infrastructure and facilities to carry out the research. Authors would also like to thank Linda Cui, Assistant Editor for all the support handling the manuscript and the reviewers for providing valuable suggestions and comments in improving the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Porambage, P.; Okwuibe, J.; Liyanage, M.; Ylianttila, M.; Taleb, T. Survey on Multi-Access Edge Computing for Internet of Things Realization. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2961–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploennigs, J.; Cohn, J.; Stanford-Clark, A. The Future of IoT. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2018, 1, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, V.; Suman, V.K.; Menon, V.G.; Dhanya, K. A Review on latest Internet of Things based Healthcare Applications. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. 2017, 15, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Deshkar, S.; Thanseeh, R.A.; Menon, V.G. A Review on IoT based m-Health Systems for Diabetes. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Telecommun. 2017, 8, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Vinoj, P.G.; Jacob, S.; Menon, V.G. Hybrid brainactuated muscle interface for the physically disabled. In Basic and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 123. [Google Scholar]
- Keerthi, K.S.; Mahapatra, B.; Menon, V.G. Into the World of Underwater Swarm Robotics: Architecture, Communication, Applications and Challenges. Recent Pat. Comput. Sci. 2019, 12, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bordel, B.; Alcarria, R.; De Andres, D.M.; You, I.; Martin, D. Securing Internet-of-Things Systems through Implicit and Explicit Reputation Models. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 47472–47488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.G.; Prathap, J. Vehicular Fog Computing: Challenges applications and future directions. Int. J. Veh. Telemat. Infotain. Syst. 2017, 1, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frustaci, M.; Pace, P.; Aloi, G.; Fortino, G. Evaluating Critical Security Issues of the IoT World: Present and Future Challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 2483–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, Z. Cryptanalysis of a Symmetric Fully Homomorphic Encryption Scheme. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimuț, D.; Reyhanitabar, R. Authenticated Encryption: Toward Next-Generation Algorithms. IEEE Secur. Privacy 2014, 12, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Alam, K.M.R.; Rahman, H.; Tamura, S. A comparison between symmetric and asymmetric key encryption algorithm based decryption mixnets. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Networking Systems and Security (NSysS), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5–7 January 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yassein, M.B.; Aljawarneh, S.; Qawasmeh, E.; Mardini, W.; Khamayseh, Y. Comprehensive study of symmetric key and asymmetric key encryption algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lamba, C.S. Design and Analysis of Stream Cipher for Network Security. In Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Singapore, 26–28 February 2010; pp. 562–567. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, S.I.B.; Al-Hamami, A.H. Novel Algorithm in Symmetric Encryption (NASE): Based on Feistel Cipher. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on New Trends in Computing Sciences (ICTCS), Amman, Jordan, 9–11 October 2017; pp. 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Rebeiro, C.; Nguyen, P.H.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Poschmann, A. Formalizing the Effect of Feistel Cipher Structures on Differential Cache Attacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2013, 8, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.; Needham, R. TEA, a tiny encryption algorithm. In Proceedings of the 1995 Fast Software En-Cryption Workshop, Leuven, Belgium, 14–16 December 1995; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Amrutha George, A.; Riyadh, M.; Prajitha, M.V. Secure image transferring using KBRP and TEA algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems (ICIIECS), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 March 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhalim, M.B.; El-Mahallawy, M.; Ayyad, M.; Elhennawy, A. Implementation of a modified lightweight cryptographic TEA algorithm in RFID system. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 11–14 December 2011; pp. 509–513. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, S.J. The Tiny Encryption Algorithm. Cryptologia 2007, 31, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, I.; Tarmurean, D.; Greu, V.; Diaconu, A. XXTEA, an alternative replacement of KASUMI cipher algorithm in A5/3 GSM and f8, f9 UMTS data security functions. In Proceedings of the 2012 9th International Conference on Communications (COMM), Bucharest, Romania, 21–23 June 2012; pp. 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J. Related-key rectangle attack on 36 rounds of the XTEA block cipher. Int. J. Inf. Sec. 2009, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Holden, J. Demitasse: A “Small” Version of the Tiny Encryption Algorithm and Its Use in a Classroom Setting. Cryptologia 2013, 37, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dormale, G.M.; Bass, J.; Quisquater, J.-J. On Solving RC5 Challenges with FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 15th Annual IEEE Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines (FCCM 2007), Napa, CA, USA, 23–25 April 2007; pp. 281–282. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Bao, F. SenSec Design Technical Report-TR v1.1; InfoComm Security Department, Institute for Infocomm Research: Singapore, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Karlof, C.; Sastry, N.; Wagner, D. TinySec: A link layer security architecture for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (SenSys ’04), Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–5 November 2004; pp. 162–175. [Google Scholar]
- Luk, M.; Mezzour, G.; Perrig, A.; Gligor, V. MiniSec: A secure sensor network communication architecture. In Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN ’07), Cambridge, MA, USA, 25–27 April 2007; pp. 479–488. [Google Scholar]
- Standaert, F.-X.; Piret, G.; Gershenfeld, N.; Quisquater, J.-J. SEA: A scalable encryption algorithm for small embedded applications. In Proceedings of the Workshop on RFIP and Light weight Crypto, Graz, Austria, 14–15 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.; Sung, J.; Hong, S.; Lim, J.; Lee, S.; Koo, B.-S.; Lee, C.; Chang, D.; Lee, J.; Jeong, K.; et al. HIGHT: A new block cipher suitable for low-resource device. In Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2006: 8th International Workshop, Yokohama, Japan, 10–13 October 2006; Volume 4249 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Usman, M.; Ahmed, I.; Aslam, M.I.; Khan, S.; Shah, U.A. SIT: A Lightweight Encryption Algorithm for Secure Internet of Things. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Ye, N.; Malekian, R.; Wang, R. The hybrid encryption algorithm of lightweight data in cloud storage. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd International Symposium on Agent, Multi-Agent Systems, and Robotics (ISAMSR), Bangi, Malaysia, 23–24 August 2016; pp. 160–166. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Lv, S.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, X. M-SSE: An Effective Searchable Symmetric Encryption with Enhanced Security for Mobile Devices. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 38860–38869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneier, B. The IDEA Encryption Algorithm. Dr. Dobb’s J. 1990, 18, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Burwick, C.; Coppersmith, D.; D’Avignon, E.; Gennaro, R.; Halevi, S.; Jutla, C.; Matyas, S.M.; O’Connor, L.; Peyravian, M.; Safford, D.; et al. MARS—A candidate cipher for AES. 1998. Available online: http://www.research.ibm.com/security/mars.html (accessed on 29 April 2018).
- Abdelhalim, M.B.; El-Mahallawy, M.; Elhennawy, M.A.A. Design and Implementation of an Encryption Algorithm for use in RFID System. Int. J. RFID Secur. Cryptogr. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, O.N.; Sokolov, A.V. Block Symmetric Cryptographic Algorithm based on Principles of variable block length and many-valued logic. Far East J. Electron. Commun. 2016, 16, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Telecommunication Technology Association. 128 Bit Light Weight Block Cipher LEA, Information Telecommunication Organization Standard (Korean Standard). 2013.
- Park, J.H. 128 bit block cipher LEA. TTA J. 2015, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, D.; Rahim, R.; Siahaan, A.P.U.; Ulva, A.F.; Fitri, Z.; Malahayati, M.; Harun, H. Super-Encryption Cryptography with IDEA and WAKE Algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1019, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Biham, E.; Knudsen, L. Serpent: A Proposal for the Advanced Encryption Standard. In Proceedings of the First Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Conference, Ventura, CA, USA, 20–22 August 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Miao, Z. A Hybrid Encryption Algorithm Based on DES and RSA in Bluetooth Communication. In Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Modeling, Simulation and Visualization Methods, Sanya, China, 15–16 May 2010; pp. 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.; Needham, R. TEA, A Tiny Encryption Algorithm. Available online: http://www.cix.co.uk/~klockstone/tea.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2018).
- Andem, V.R. A Cryptanalysis of the Tiny Encryption Algorithm; The University of Alabama: Tuscaloosa, AL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rachmawati, D.; Sharif, A.; Jaysilen; Budiman, M.A. Hybrid Cryptosystem Using Tiny Encryption Algorithm and LUC Algorithm. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 300, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelan, M.S.; Husein, A.M.; Harahap, M.; Aisyah, S. SMS Security System on Mobile Devices Using Tiny Encryption Algorithm. IOP Conf. Ser. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1007, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, R.M.; Wheeler, D.J. TEA Extensions; Technical Report; Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kaps, J.-P. Chai-tea, Cryptographic Hardware Implementations of XTEA. In Proceedings of the INDOCRYPT 08 Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Cryptology in India: Progress in Cryptology, Kharagpur, India, 14–17 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.; Needham, R. XXTEA: Correction to XTEA; Technical report; Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Coppersmith, D.; Johnson, D.B.; Matyas, S.M. A proposed mode for triple-DES encryption. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1996, 40, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milad, A.A.; Muda, H.Z.; Noh, Z.A.; Algaet, M.A. Comparative Study of Performance in Cryptography Algorithms (Blowfish and Skipjack). J. Comput. Sci. 2012, 8, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Wu, T.; Yuce, M.R. An Internet-of-Things (IoT) Network System for Connected Safety and Health Monitoring Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, V.G.; Prathap, J.; Priya, J. Ensuring reliable communication in disaster recovery operations with reliable routing technique. Mobile Inf. Syst. 2016, 2016, 9141329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.G.; Prathap, J. Comparative analysis of opportunistic routing protocols for underwater acoustic sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Emerging Technological Trends (ICETT), Kollam, India, 21–22 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, V. Optimized Opportunistic Routing in Highly Dynamic Ad hoc Networks. Preprints 2019, 2019, 020130. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, V.G.; Prathap, J. Performance of various Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks-A Survey. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2013, 6, 4181–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.G.; Prathap, J. Analyzing the behavior and performance of opportunistic routing protocols in highly mobile wireless ad hoc networks. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2016, 8, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.G.; Prathap, P.M.J. Opportunistic routing with virtual coordinates to handle communication voids in mobile ad hoc networks. In Advances in Signal Processing and Intelligent Recognition Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 323–334. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).