Numerical Method for Dirichlet Problem with Degeneration of the Solution on the Entire Boundary
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
- (a)
- (b)
- () are differentiable functions on , such that the inequalitieshold,
- (c)
- the function satisfies the inequalities
3. The Scheme of the Finite Element Method
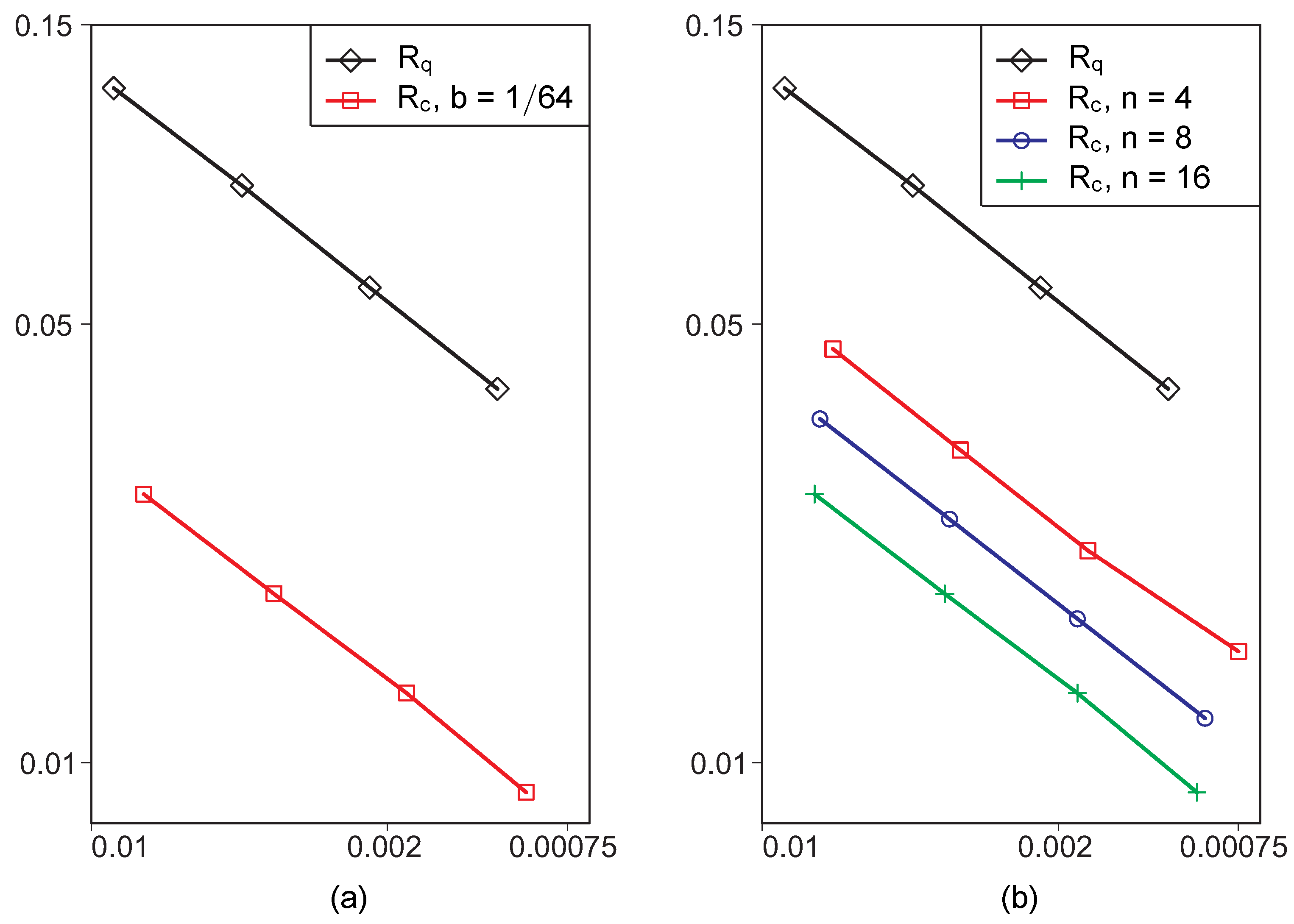
4. Numerical Experiments
5. Conclusions
- to reduce the absolute value of the error it is more expedient to increase the number of layers n than to reduce the width of the boundary ring domain; in this case the absolute value of the error decreases faster;
- for meshes of large dimensionality it is advisable to use the weighted finite element method.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ciarlet, P. The Finite Element Method for Elliptic Problems; Studies in Mathematics and Its Applications, North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Samarskii, A.A.; Lazarov, R.D.; Makarov, V.L. Finite Difference Schemes for Differential Equations with Generalized Solutions; Visshaya Shkola: Moscow, Russia, 1987; 296p. [Google Scholar]
- Kondrat’ev, V.A. Boundary problems for elliptic equations in domains with conical or angular points. Trans. Mosc. Math. Soc. 1967, 16, 227–313. [Google Scholar]
- Kondrat’ev, V.A.; Oleinik, O.A. Boundary-value problems for partial differential equations in non-smooth domains. Rus. Math. Surv. 1983, 38, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maz’ya, V.G. On weak solutions of the Dirichlet and Neumann problems. Trans. Mosc. Math. Soc. 1971, 20, 135–172. [Google Scholar]
- Maz’ya, V.G.; Plamenevskii, B.A. On coeffcients in the asymptotics of solutions of elliptic problems in domains with conical points. Math. Nachr. 1977, 76, 29–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikol’skij, S.M. A Variational Problem for an Equation of Elliptic Type with Degeneration on the Boundary. Proc. Steklov Inst. Math. 1981, 150, 227–254. [Google Scholar]
- Lizorkin, P.I.; Nikol’skij, S.M. Elliptic equations with degeneracy. Differential properties of solutions. Sov. Math. Dokl. 1981, 23, 268–271. [Google Scholar]
- Lizorkin, P.I.; Nikol’skij, S.M. Coercive properties of an elliptic equation with degeneracy (the case of generalized solutions). Sov. Math. Dokl. 1981, 24, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A. The Dirichlet problem with the noncoordinated degeneration of the initial data. Dokl. Akad. Nauk 1994, 337, 447–449. [Google Scholar]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A. The Dirichlet problem for a second-order elliptic equation with noncoordinated degeneration of the input data. Differ. Equ. 1996, 32, 406–412. [Google Scholar]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A. On the uniqueness of the Rν-generalized solution of boundary value problems with noncoordinated degeneration of the initial data. Dokl. Math. 2001, 63, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Ereklintsev, A.G. On the coercivity of the Rν-generalized solution of the first boundary value problem with coordinated degeneration of the input data. Differ. Equ. 2005, 41, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Kuznetsova, E.V. Coercive estimate for a boundary value problem with noncoordinated degeneration of the data. Differ. Equ. 2007, 43, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A. On the existence and uniqueness of an Rν-generalized solution of a boundary value problem with uncoordinated degeneration of the input data. Dokl. Math. 2014, 90, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A. The weight estimation of the speed of difference scheme convergence. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1986, 288, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikova, E.I. Finite-Element Method for the 1St Boundary-Value Problem with the Coordinated Degeneration of the Initial Data. Dokl. Akad. Nauk 1994, 338, 731–733. [Google Scholar]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A. Methods of numerical analysis for boundary value problem with strong singularity. Rus. J. Numer. Anal. Math. Model. 2009, 24, 565–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikova, H.I. The finite element method for a boundary value problem with strong singularity. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2010, 234, 2870–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikova, H.I. On the error estimation of the finite element method for the boundary value problems with singularity in the Lebesgue weighted space. Numer. Funct. Anal. Opt. 2013, 34, 1328–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Nikolaev, S.G. Weighted finite element method for an elasticity problem with singularity. Dokl. Math. 2013, 88, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikova, H.I. Weighted Finite-Element Method for Elasticity Problems with Singularity, p razvan ed.; Finite Element Method. Simulation, Numerical Analysis and Solution Techniques, IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2018; pp. 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Mosolapov, A.O. New numerical method for solving time-harmonic Maxwell equations with strong singularity. J. Comput. Phys. 2012, 231, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Mosolapov, A.O. Weighted edge finite element method for Maxwell’s equations with strong singularity. Dokl. Math. 2013, 87, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikov, A.V. Weighted finite element method for the Stokes problem with corner singularity. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 341, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikov, A.V. New Numerical Method for the Rotation form of the Oseen Problem with Corner Singularity. Symmetry 2019, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikova, E.I. Numerical Method for the First Boundary Value Problem with Degeneration. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Computational mathematics, Differential Equations, Information Technologies”, Lake Baikal, Russia, 22–24 August 2009; East Siberia State University of Technology and Management: Ulan-Ude, Russia, 2009; pp. 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikova, E.I. On the isomorphic mapping of weighted spaces by an elliptic operator with degeneration on the domain boundary. Differ. Equ. 2014, 50, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikova, E.I. The automation tracing of mesh with condensed to the boundary of domain. Inf. Sci. Control Syst. 2011, 30, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Liseikin, V.D. Grid Generation Methods; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999; 362p. [Google Scholar]
- Apel, T.; Sandig, A.M.; Whiteman, J.R. Graded mesh refinement and error estimates for finite element solutions of elliptic boundary value problems in non-smooth domains. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 1996, 19, 63–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soghrati, S.; Xiao, F.; Nagarajan, A. A conforming to interface structured adaptive mesh refinement technique for modeling fracture problems. Comput. Mech. 2017, 59, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikova, H.I. Dirichlet Problem with Degeneration of the Input Data on the Boundary of the Domain. Differ. Equ. 2016, 52, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
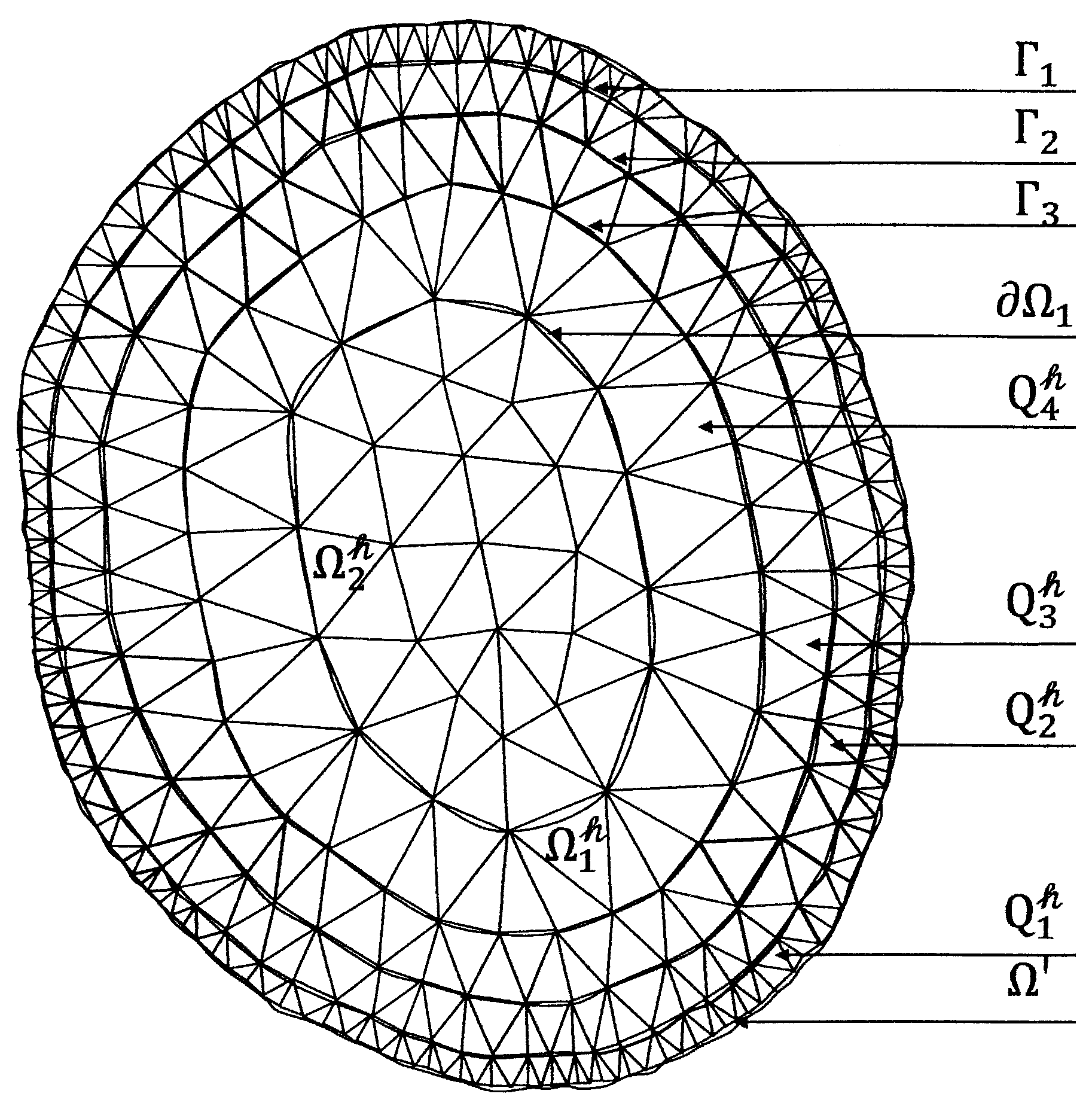
| Quasi-Uniform Mesh () | Absolute Error Distribution | Specified Limited Error | Percent | Number of Nodes | |
| Number of nodes N | 10,849,474 |  |  | 0.00% | 69 |
 | 89.37% | 9,696,362 | |||
 | 10.61% | 1,151,232 | |||
| h | 0.00055 |  | 0.01% | 1196 | |
 | 0.00% | 372 | |||
 | 0.00% | 243 | |||
| Refined Mesh () | Absolute Error Distribution | Specified Limited Error | Percent | Number of Nodes | |
| N | 10,755,478 | 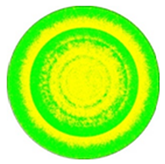 |  | 0.00% | 0 |
| Number of nodes in domain | 10,661,162 |  | 0.00% | 0 | |
 | 0.00% | 4 | |||
| h | 0.000556 |  | 44.46% | 4,781,879 | |
| n | 3 |  | 55.44% | 5,962,761 | |
| b | 1/1024 |  | 0.10% | 10,834 | |
| Refined Mesh () | Absolute Error Distribution | Specified Limited Error | Percent | Number of Nodes | |
| N | 4,974,486 | 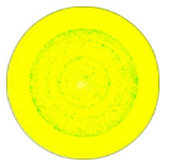 |  | 0.00% | 0 |
| Number of nodes in domain | 4,241,164 |  | 0.00% | 0 | |
 | 0.00% | 0 | |||
| h | 0.00087 |  | 2.75% | 136,821 | |
| n | 18 |  | 83.18% | 4,137,684 | |
| b | 1/128 |  | 14.07% | 699,981 | |
| Quasi-Uniform Mesh () | Refined Mesh (), | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0022 | 0.0035 | ||||||||
| 1.68 | 1.85 | 4.21 | 2.06 | ||||||
| 0.0011 | 0.00169 | ||||||||
| 1.83 | 1.72 | 4.11 | 2.03 | ||||||
| 0.00055 | 0.00083 | ||||||||
| Specified Limited Error | Quasi-Uniform Mesh () | ||
 |  |  |  |
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
| N | 338,449 | 1,355,498 | 5,427,739 |
| h | 0.0031 | 0.0015 | 0.00078 |
| Specified Limited Error | Refined Mesh (), | ||
 |  |  |  |
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
| N | 425,760 | 1,569,052 | 6,129,755 |
| Number of nodes in domain | 386,628 | 1,375,684 | 5,200,079 |
| h in domain | 0.0029 | 0.0015 | 0.00079 |
| Quasi-Uniform Mesh () | Absolute Error Distribution | Specified Limited Error | Percent | Number of Nodes | |
| N | 2,713,152 | 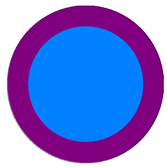 |  | 50.40% | 1,367,499 |
 | 49.60% | 1,345,653 | |||
 | 0.00% | 0 | |||
| h | 0.00055 |  | 0.00% | 0 | |
 | 0.00% | 0 | |||
| Refined Mesh () | Absolute Error Distribution | Specified Limited Error | Percent | Number of Nodes | |
| N | 3,254,432 | 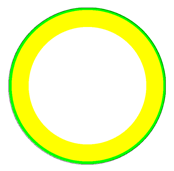 |  | 0.00% | 0 |
| Number of nodes in domain | 2,484,744 |  | 0.00% | 0 | |
| h in domain | 0.0011 |  | 26.32% | 856,521 | |
| n | 27 |  | 31.94% | 1,039,571 | |
| b |  | 41.74% | 1,358,340 | ||
| Quasi-Uniform Mesh () | Refined Mesh (), | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in domain | ||||||
| 0.0022 | 0.065816 | 3 | 0.0068 | 0.04562 | ||
| 1.43 | 2.08 | |||||
| 0.0011 | 0.046016 | 8 | 0.0032 | 0.021939 | ||
| 1.43 | 2.00 | |||||
| 0.00055 | 0.032220 | 18 | 0.0016 | 0.010989 | ||
| Specified Limited Error | Quasi-Uniform Mesh () | ||
 |  |  | 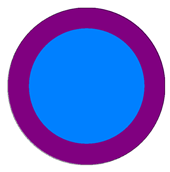 |
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
| N | 168,670 | 677,704 | 2,713,152 |
| h | 0.0044 | 0.0022 | 0.0011 |
| Specified Limited Error | Refined Mesh () | ||
 | 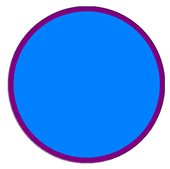 | 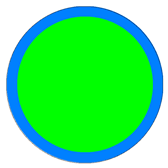 | 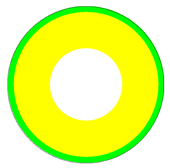 |
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
 | |||
| N | 166,751 | 643,498 | 2,567,442 |
| Number of nodes in domain | 139,635 | 514,952 | 1,972,944 |
| h in domain | 0.0050 | 0.0025 | 0.00127 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rukavishnikov, V.A.; Rukavishnikova, E.I. Numerical Method for Dirichlet Problem with Degeneration of the Solution on the Entire Boundary. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11121455
Rukavishnikov VA, Rukavishnikova EI. Numerical Method for Dirichlet Problem with Degeneration of the Solution on the Entire Boundary. Symmetry. 2019; 11(12):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11121455
Chicago/Turabian StyleRukavishnikov, Viktor A., and Elena I. Rukavishnikova. 2019. "Numerical Method for Dirichlet Problem with Degeneration of the Solution on the Entire Boundary" Symmetry 11, no. 12: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11121455
APA StyleRukavishnikov, V. A., & Rukavishnikova, E. I. (2019). Numerical Method for Dirichlet Problem with Degeneration of the Solution on the Entire Boundary. Symmetry, 11(12), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11121455




