Research of the Operator’s Advisory System Based on Fuzzy Logic for Pelletizing Equipment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- More convenient storage, transportation;
- Rare adhesion of fertilizer particles;
- Even distribution of chemicals during fertilization; and
- Increased distance of fertilization.
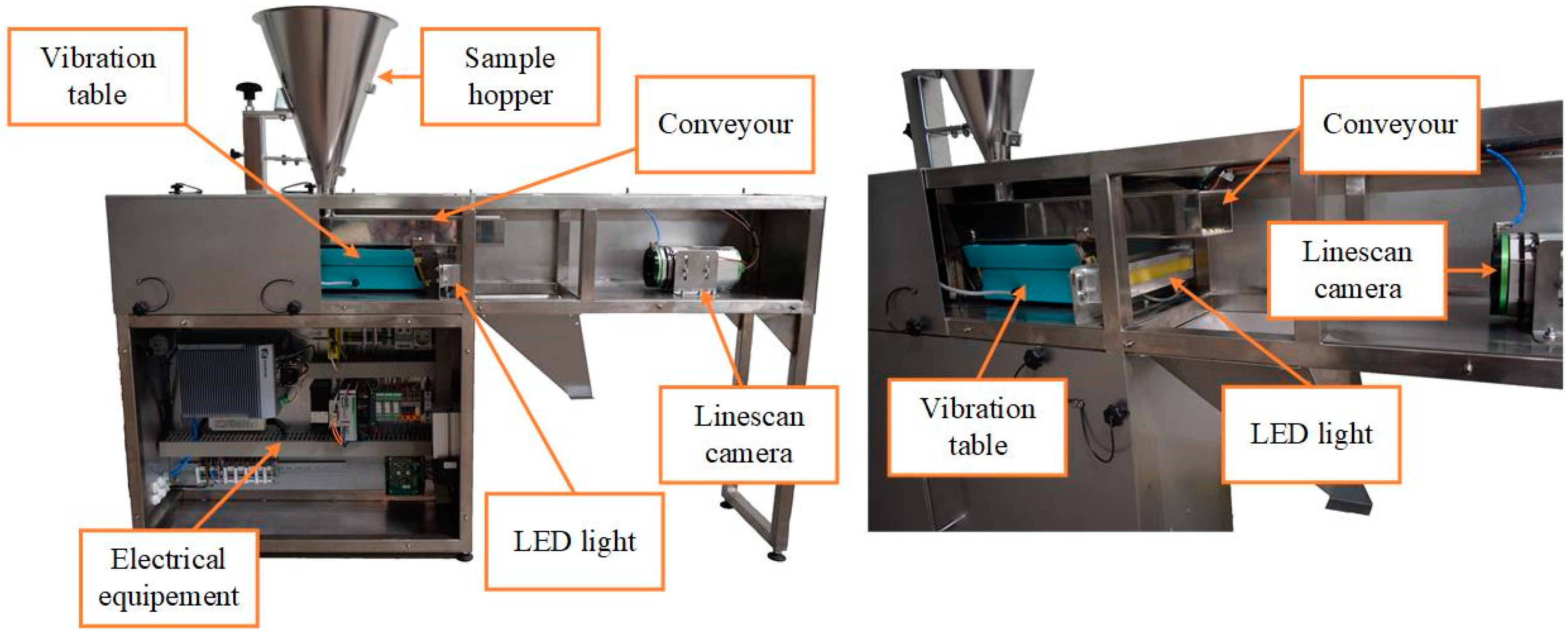
2. Materials and Methods
- Aspect ratio;
- Circularity;
- Convexity;
- Elongation;
- Sphericity;
- Surface roughness;
- Compactness;
- Symmetry;
- Length;
- Width;
- Perimeter; and
- Area.
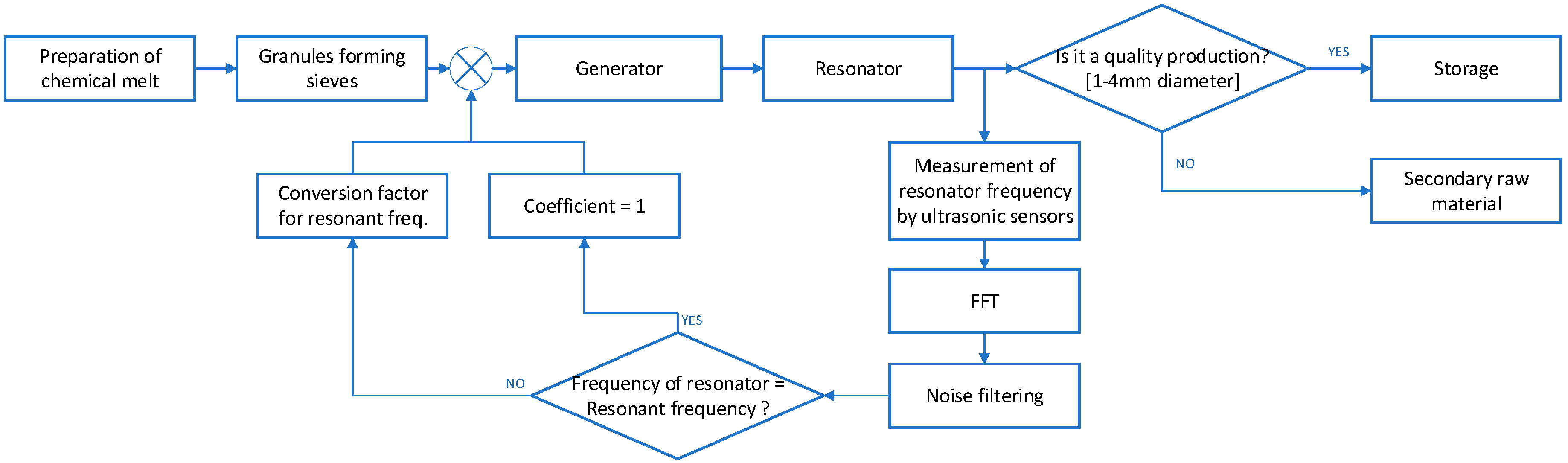
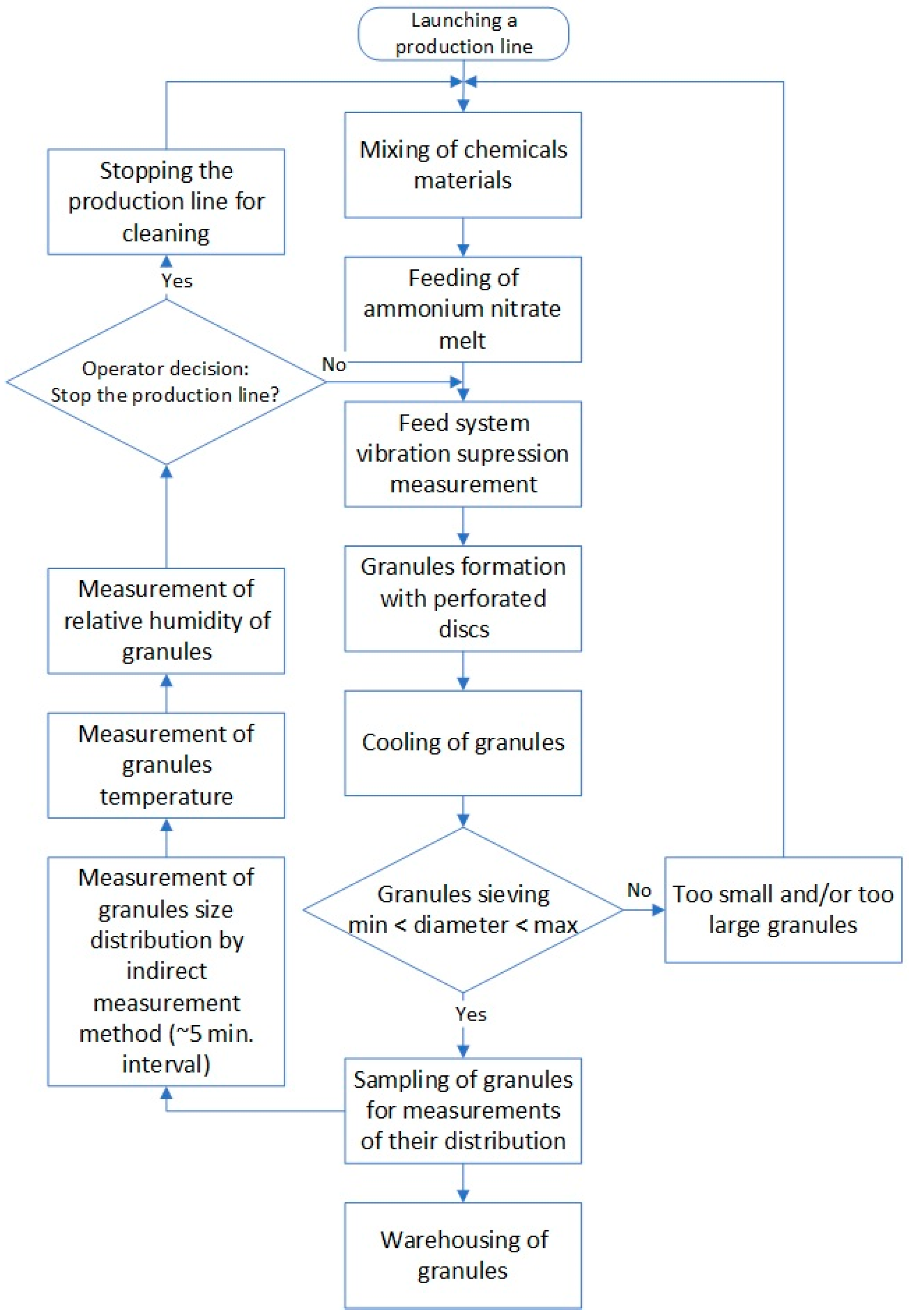
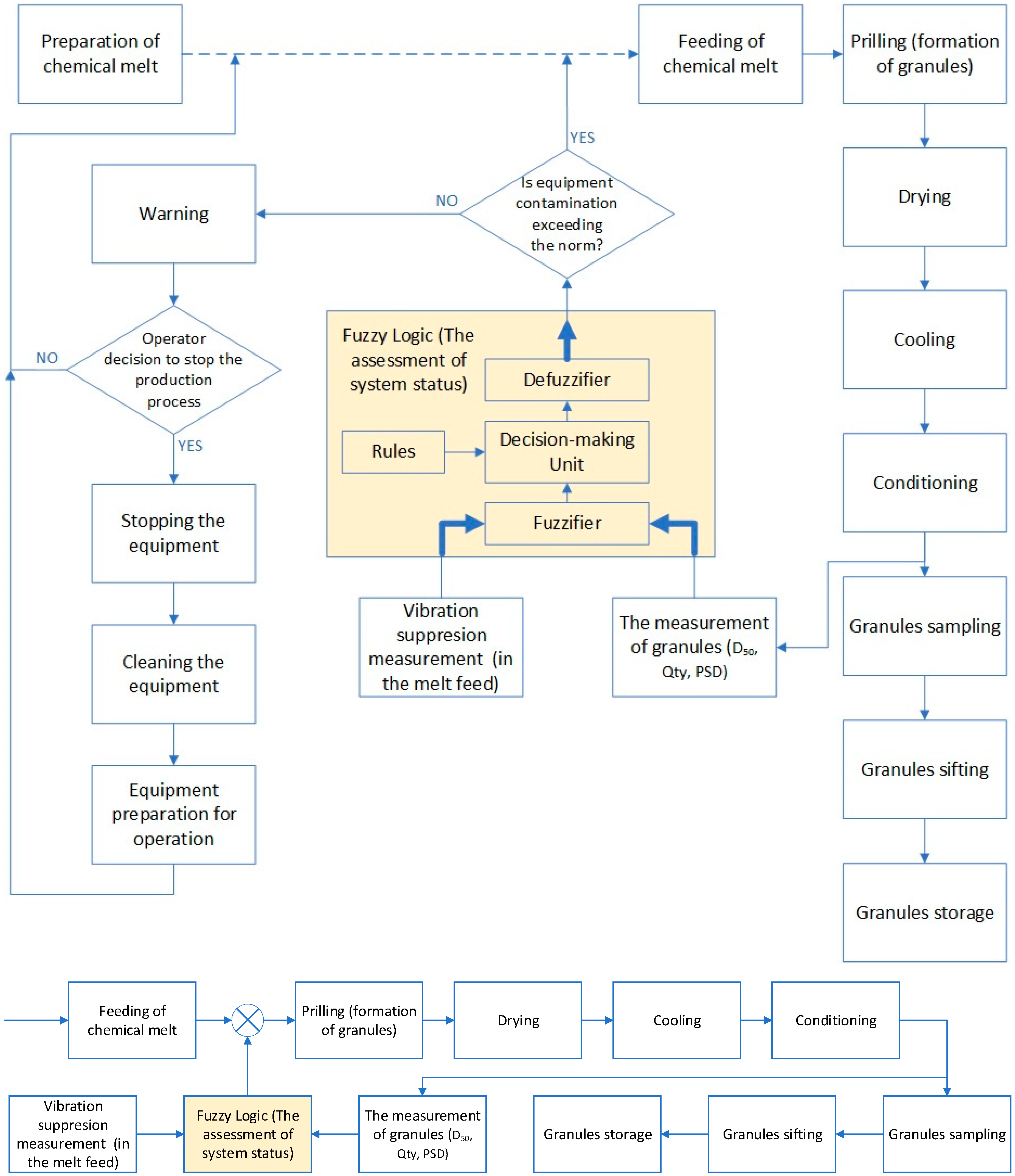
3. System Model
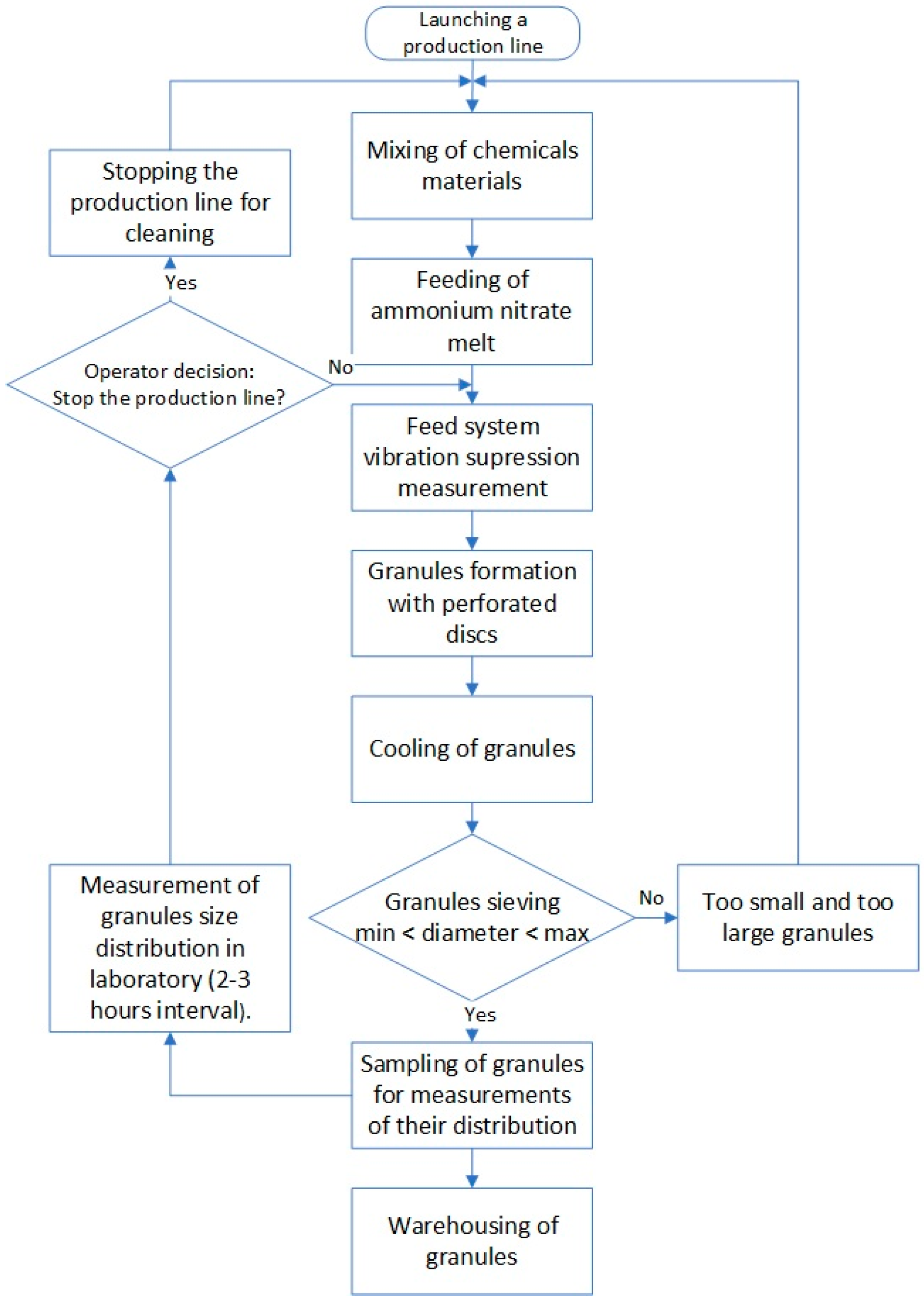
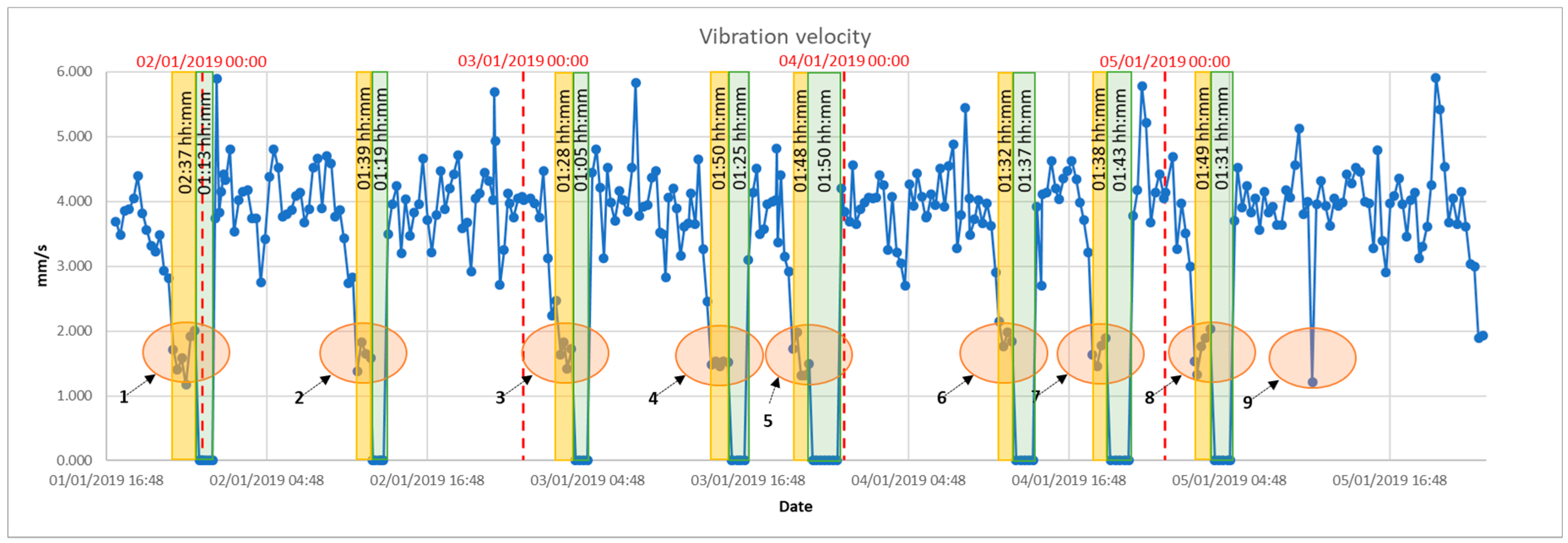
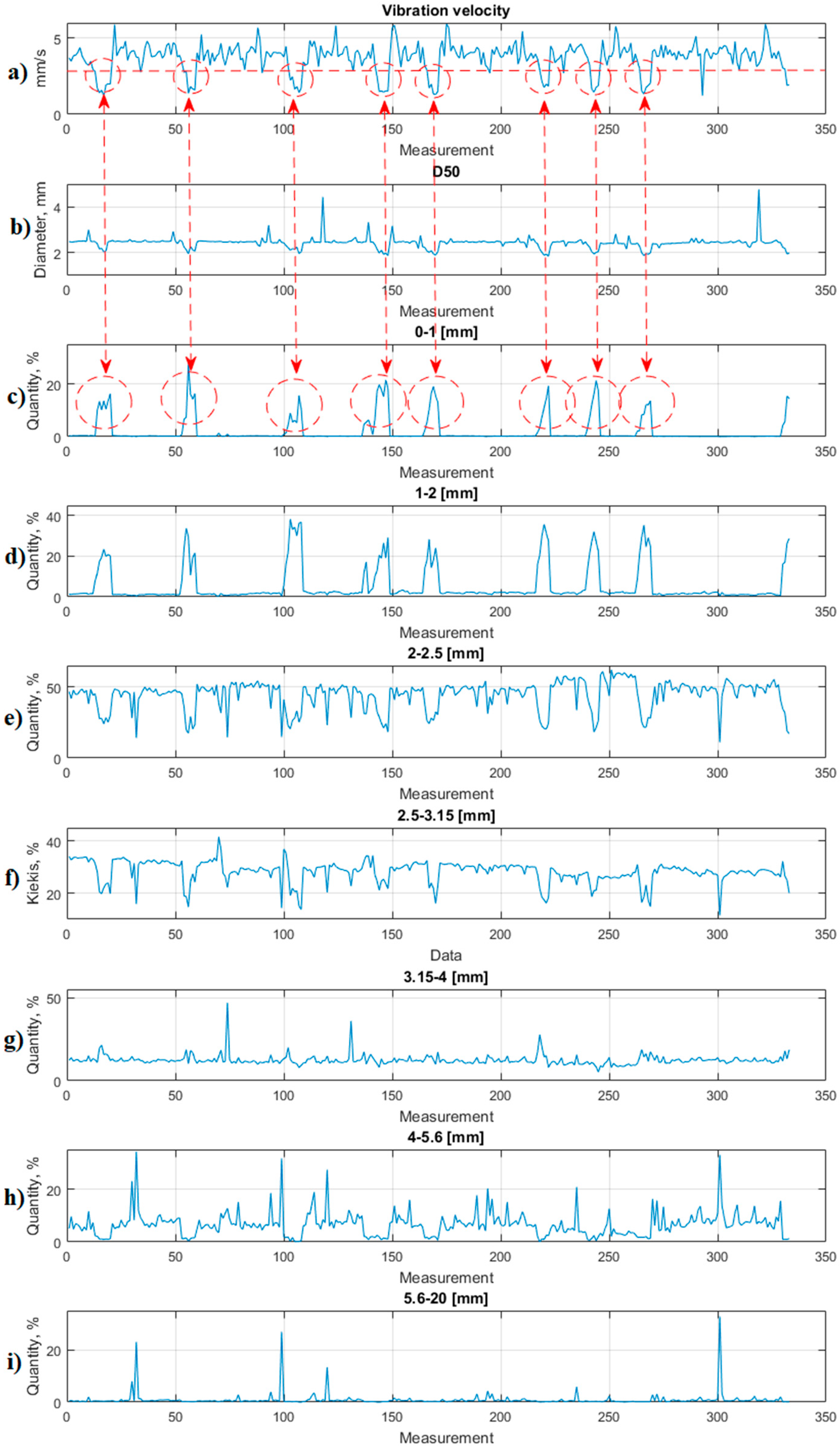
4. Evaluation of the Prilling Process
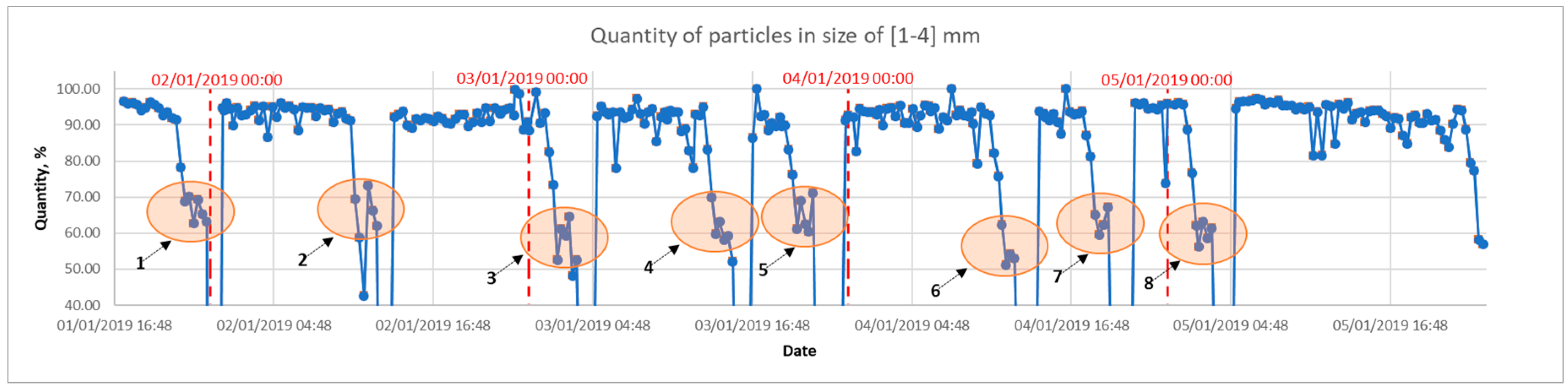
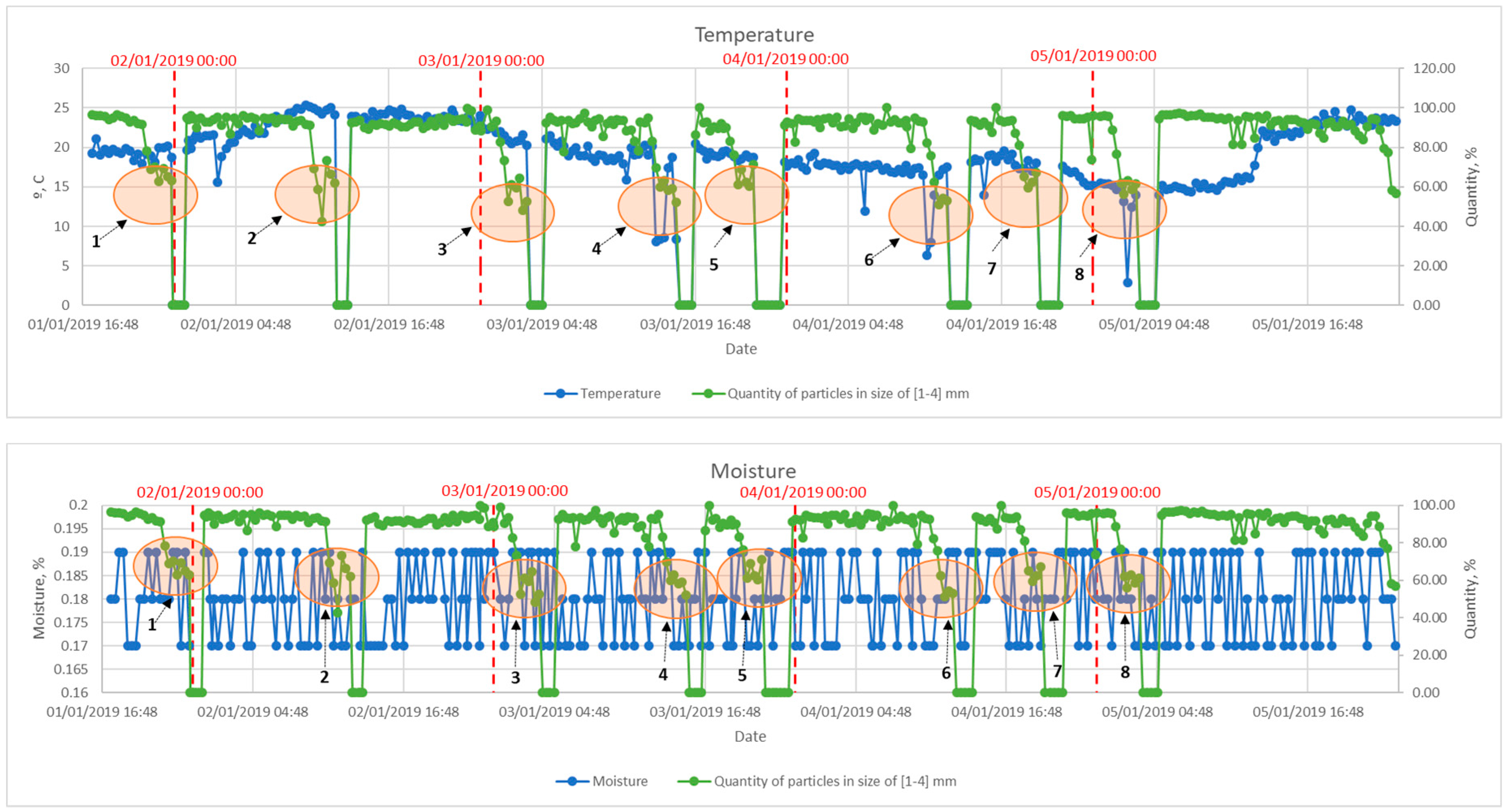
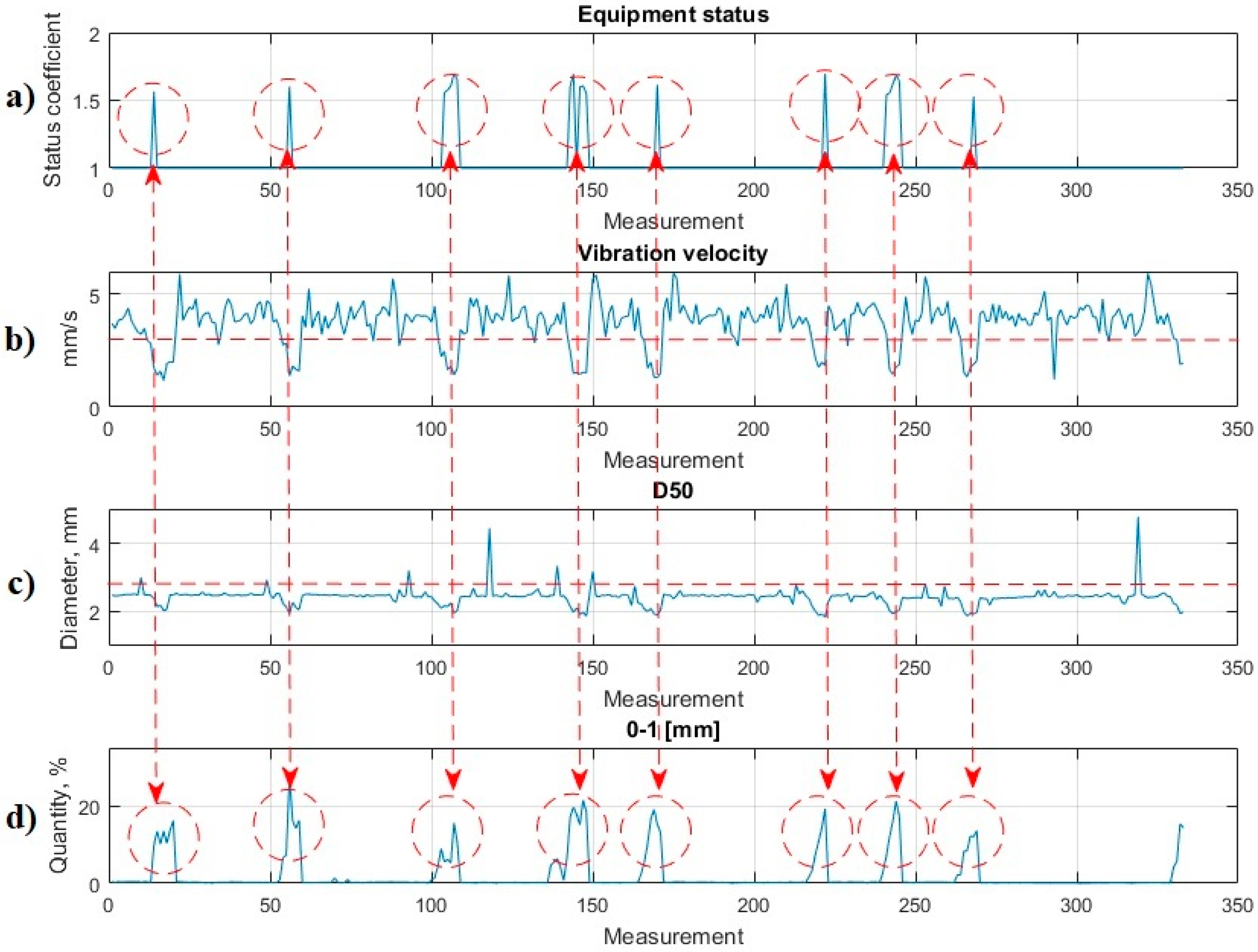
5. Combined Advisory System Model
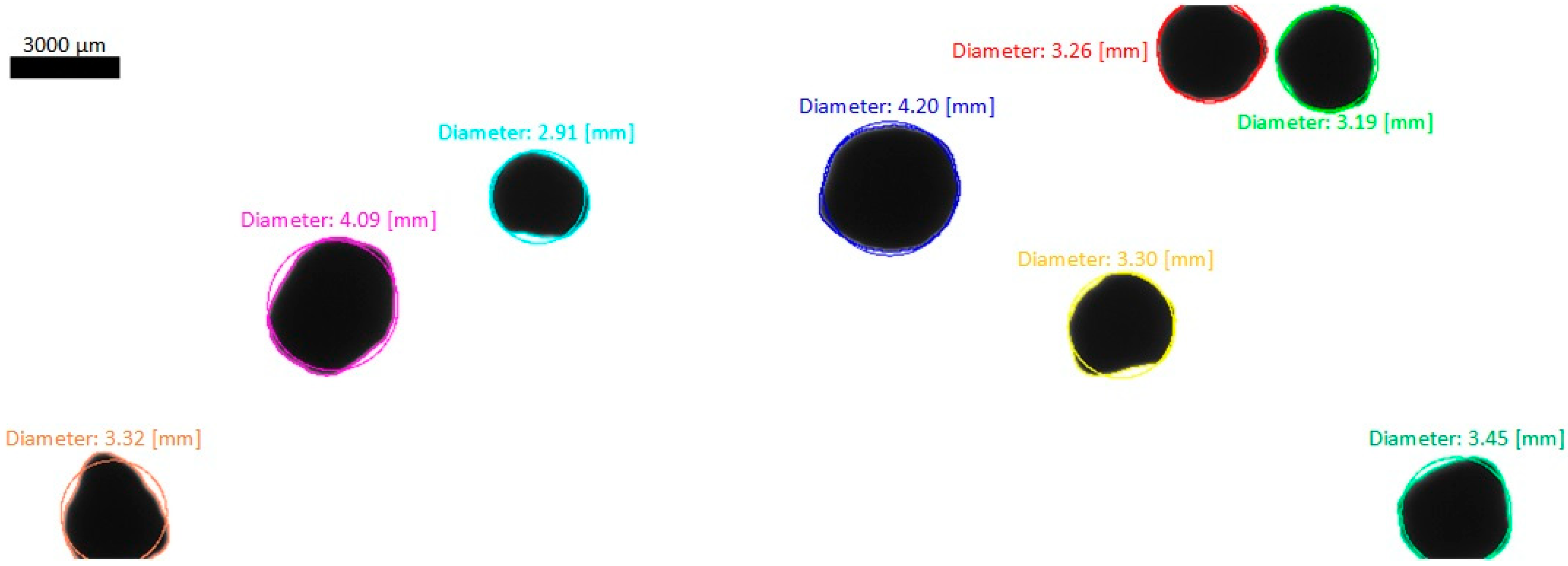
- [1–4] mm particles make > 97% of the total particles
- Average particle size D50 ≈ 2.5 mm
- During the experiment, the sample analysed consists of 40,000–50,000 particles on average
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahmanian, N.; Naderi, S.; Supuk, E.; Abbas, R.K.; Hassanpour, A. Urea Finishing Process: Prilling Versus Granulation. Procedia Eng. 2015, 102, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, C.K.; Rao, S.R.M.; Sudhakar, M.; Bhaskar, J. Advances in Granulation Technology. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2016, 9, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, J.; Port, K. Physical properties of granular fertilizers and impact on spreading. Ohioline 2016. Available online: https://fabe.osu.edu/sites/fabe/files/imce/images/Precision_Ag/Physical%20Properties%20of%20Granular%20Fertilizers%20and%20Impact%20on%20Spreading%20_%20Ohioline.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2019).
- Das, S.C.; Behara, S.R.B.; Morton, D.A.V.; Larson, I.; Stewart, P.J. Importance of particle size and shape on the tensile strength distribution and de-agglomeration of cohesive powders. Powder Technol. 2013, 249, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, R. Spray Drying Technology Review. In Proceedings of the 45th International Conference on Environmental Systems, Bellevue, DC, USA, 12–16 July 2015; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gezerman, A.O.; Corbacioglu, B.D. A New Approach to Cooling and Prilling during Fertilizer Manufacture. Int. J. Chem. 2011, 3, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrez, A.; Ali, A.H.H.; Zahra, W.K.; Ookawara, S.; Suzuki, M. Study on Heat and Mass Transfer During Urea Prilling Process. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2012, 3, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bao, C.; Zhou, Y. An Innovated Tower-fluidized Bed Prilling Process. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 15, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, N.; Homayoonfard, M.; Alamdari, A. Simulation of urea prilling process: An industrial case study. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2013, 200, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Pendyala, R.; Rahmanian, N. CFD Simulation of Droplet Formation Under Various Parameters in Prilling Process. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 625, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaergaard, O.G.; Vilstrup, P. Multiple-core encapsulation: Prilling. In Microencapsulation of Food Ingredients; Leatherhead Publishing: Surrey, UK, 2001; pp. 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov, V.V.; Grek, G.R.; Litvinenko, M.A.; Litvinenko, Y.A.; Kozlov, G.V. Round jet in a transverse shear flow. Vestnik NSU Ser. Phys. 2010, 5, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, N.; Hare, C.; Ghadiri, M.; Murtagh, M.; Oram, P.; Haber, R.A. Auto-granulation of Fine Cohesive Powder by Mechanical Vibration. Procedia Eng. 2015, 102, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstensen, M.; Bakker, P.; Matveyev, I.; Esbensen, K.H. Acoustic chemometrics monitoring of chemical production processes. In Proceedings of the European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6), Copenhagen, Denmark, 6–12 September 2007; pp. 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Atasoy, H.; Yildirim, E.; Yildirim, S.; Kutlu, Y. A Real-Time Parallel Image Processing Approach on Regular PCs with Multi-Core CPUs. Res. J. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2017, 23, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skydanenko, M.; Sklabinskyi, V.; Saleh, S.; Barghi, S. Reduction of Dust Emission by Monodisperse System Technology for Ammonium Nitrate Manufacturing. Processes 2017, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsotsas, E. Multiscale Approaches to Processes That Combine Drying with Particle Formation. Dry. Technol. 2015, 33, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastowicz, J.; Grudzinski, M.; Teclaw, M.; Okarma, K. Objective 3D Printed Surface Quality Assessment Based on Entropy of Depth Maps. Entropy 2019, 21, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, B.A.; Bhowmik, A.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, P.R.; Lazar, A.; Singh, A.P.; Sharma, M.; Singh, B. Ultrasound promoted efficient and green protocol for the expeditious synthesis of 1, 4 distributed 1, 2, 3-triazoles using Cu(II) doped clay as catalyst. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 80–81, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrak, D.; Dietrich, S.; Eckardt, G.; Köhler, M. In-line particle sizing for process control by an optical probe based on the spatial filtering technique (SFT). In Proceedings of the 6th World Congress Particle Technology, Nuremberg, Germany, 26–29 April 2011; Volume 22, pp. 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskulski, M.; Fischer, C.; Sajontz, F.; Friese, S. Particle Size Distribution and Moisture Content Inline Measurement Systems for the Spray Dryers. In Proceedings of the 22nd Polisch Conference of Chemical and Process Engineering, Spała, Poland, 5–9 September 2016; pp. 499–509. [Google Scholar]
- Okarma, K. Current Trends and Advances in Image Quality Assesment. Res. J. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2019, 25, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, Y.; Tamura, Y.; Kawaguchi, K.; Inada, K. Measuring Particle Size Distribution. U.S. Patent 4,288,162, 27 February 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Tokoyama, K. Powder and Granule Inspection Apparatus. U.S. Patent 5,309,773, 10 May 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Plate, M.; Pankratz, J. Apparatus for Determining the Particle Size Distribution of a Mixture. U.S. Patent 6,061,130, 22 January 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, I.B.; Lieber, K.J.W.; Young, L. Method and Apparatus for Sizing Particulate Material. WO Patent 1997014950A1, 16 October 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shanthi, C.; Porpatham, R.K.; Pappa, N. Image analysis for particle size distribution. Eng. Technol. 2014, 6, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen, T.; Strand, O.E.; Asbjornsen, O.A. Method and Apparatus for Performing Automatic Particle Analysis. U.S. Patent 5,011,285, 30 April 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Schumann, M. Procedure for the Determination of Particle Size Distribution in Particle Mixtures. U.S. Patent 5,309,215, 3 May 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Penumadu, D.; Zhao, R.; Steadman, E.F. Particle Size and Shape Distribution Analyzer. U.S. Patent 6,960,756, 1 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hodenberg, M.F.V. Device for Determining Parameters of a Bulk Material Particle Flow. WO Patent 2008046914A1, 20 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lech, P.; Okarma, K. Prediction of the Optical Character Recognition Accuracy based on the Combined Assessment of Image Binarization Results. Res. J. Elektron. Elektrotechnika 2015, 21, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, T.; Reinholt, F.; Johnsen, O.M. Automatic Particle Analyzing System. U.S. Patent 7,154,600, 7 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, T.K.; Miles, N.J.; Morgan, S.P.; Hayes-Gill, B.R. Improving particle size measurement using multi-flash imaging. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T. Apparatus and Method for Analyzing Particle Images Including Measuring at a Plurality of Capturing Magnifications. U.S. Patent 5,721,433, 24 February 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Uesugi, M.; Harayama, M.; Ota, K.; Kawaguchi, S.; Shibuya, H. Method of Measuring Average Particle Size of Granular Material. U.S. Patent 5,129,268, 5 April 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Althyabat, S.; Miles, N.J. An improved estimation of size distribution from particle profile measurements. Powder Technol. 2006, 166, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeloo, E.; Massinaei, M.; Mehrshad, N. Estimation of particle size distribution on an industrial conveyour belt using image analysis and neural networks. Powder Technol. 2014, 261, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.; Vicens, R. Grain-size measurement of fluvial gravel bars using Object-Based image analysis. Rev. Bras. Geomorfol. 2018, 19, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipova, N. Determining the grain size distribution of granular soils using image analysis. Acta Geotech. Slov. 2017, 14, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, J.; Ferreira, C.; McGinty, J.; Hamilton, A.W. Image analysis framework with focus evaluation for in situ characterisation of particle size and shape attributes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 191, 208–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canty, T.M.; O’Brien, P.J.; Marks, C.P.; Owen, R.E. Granular Product Inspection Device. U.S. Patent 7,009,703, 27 March 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Labati, R.D.; Genovese, A.; Ballester, E.M.; Piuri, V. 3D granulometry using image processing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepuritis, R.; Garboczi, E.J.; Ferraris, C.F.; Jacobsen, S. Measurement of particle size distribution and specific surface area for crushed concrete aggregate fines. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laucka, A.; Adaskeviciute, V.; Andriukaitis, D. Research of the Equipment Self-Calibration Methods for Different Shape Fertilizers Particles Distribution by Size Using Image Processing Measurement Method. Symmetry 2019, 11, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laucka, A.; Adaskeviciute, V.; Andriukaitis, D.; Valinevicius, A. Research of the Equipment Calibration Methods for Fertilizers Particles Distribution by Size Using Image Processing Measurement Method. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Methods & Models in Automation & Robotics (MMAR), Międzyzdroje, Poland, 27–30 August 2018; pp. 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceamag. Technical Grade Ammonium Nitrate. Available online: https://www.ceamag.com/en/technologies/ammonium-nitrate?id=56 (accessed on 12 November 2019).
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Bausys, R.; Antucheviciene, J. Civil Engineering and Symmetry. Symmetry 2019, 11, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Sieve Size, mm | Minimum Value for Granules Content, % | Minimum Value for Granules Content, % |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0–1.0 | 1.5 | 7.0 |
| 1.0–2.0 | 2.0 | 10.0 |
| 2.0–2.5 | 35.0 | 45.0 |
| 2.5–3.15 | 22.0 | 30.0 |
| 3.15–4.0 | 6.0 | 12.0 |
| 4.0–5.6 | 4.0 | 12.0 |
| 5.6–20.0 | 0.0 | 8.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andriukaitis, D.; Laucka, A.; Valinevicius, A.; Zilys, M.; Markevicius, V.; Navikas, D.; Sotner, R.; Petrzela, J.; Jerabek, J.; Herencsar, N.; et al. Research of the Operator’s Advisory System Based on Fuzzy Logic for Pelletizing Equipment. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111396
Andriukaitis D, Laucka A, Valinevicius A, Zilys M, Markevicius V, Navikas D, Sotner R, Petrzela J, Jerabek J, Herencsar N, et al. Research of the Operator’s Advisory System Based on Fuzzy Logic for Pelletizing Equipment. Symmetry. 2019; 11(11):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111396
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndriukaitis, Darius, Andrius Laucka, Algimantas Valinevicius, Mindaugas Zilys, Vytautas Markevicius, Dangirutis Navikas, Roman Sotner, Jiri Petrzela, Jan Jerabek, Norbert Herencsar, and et al. 2019. "Research of the Operator’s Advisory System Based on Fuzzy Logic for Pelletizing Equipment" Symmetry 11, no. 11: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111396
APA StyleAndriukaitis, D., Laucka, A., Valinevicius, A., Zilys, M., Markevicius, V., Navikas, D., Sotner, R., Petrzela, J., Jerabek, J., Herencsar, N., & Klimenta, D. (2019). Research of the Operator’s Advisory System Based on Fuzzy Logic for Pelletizing Equipment. Symmetry, 11(11), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111396









