Numerical Study of Natural Convection Flow of Nanofluid Past a Circular Cone with Cattaneo–Christov Heat and Mass Flux Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
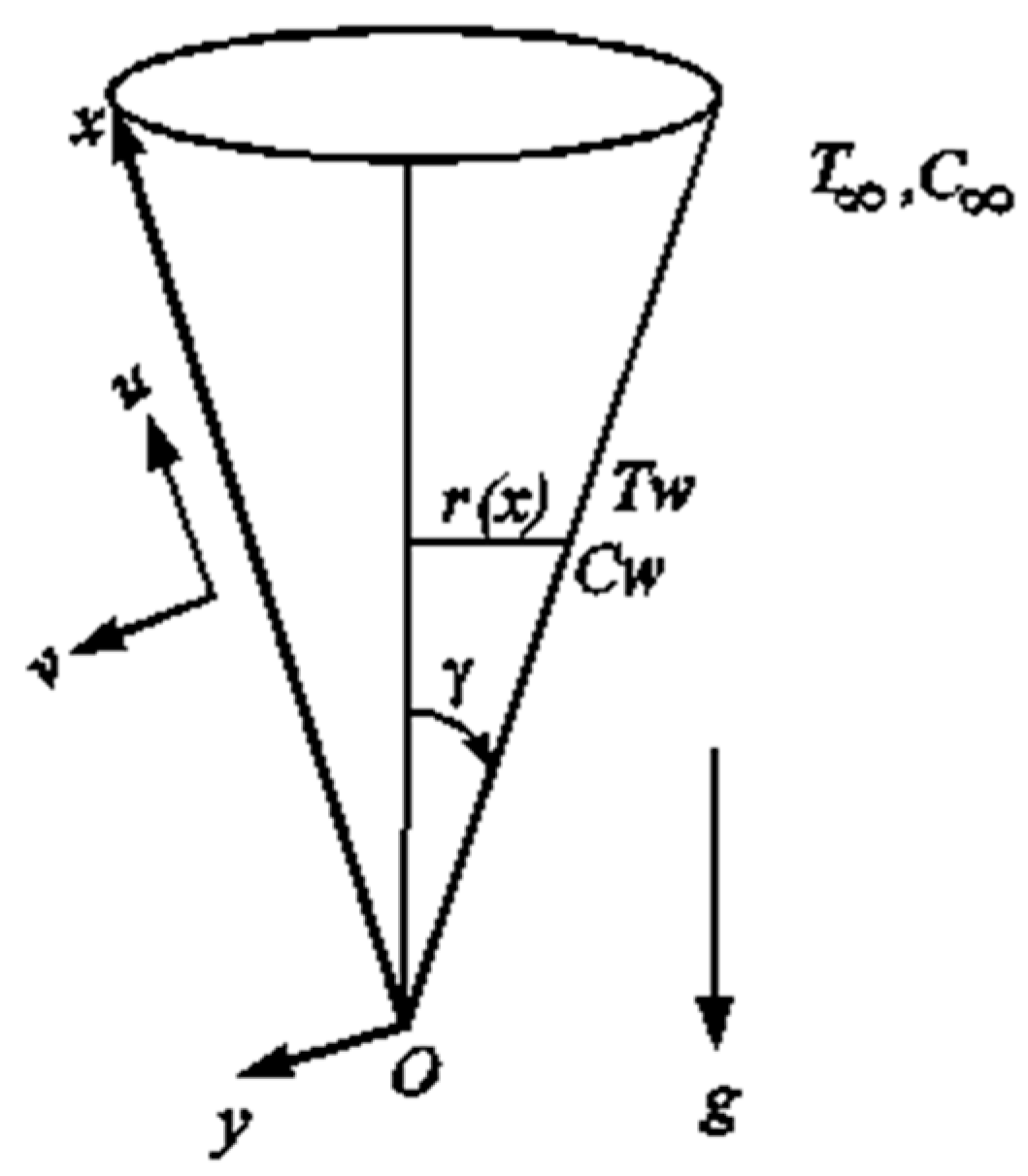
2. Mathematical Formulation
| : | Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient; | Thermal diffusivity; | |
| : | Brownian diffusion coefficient; | Gravitational acceleration; | |
| The ratio of heat capacity of a nanoparticle to the base fluid; | Concentration; | ||
| Temperature; |
3. Method of Solution
- (i)
- The higher-order differential equations are transformed into the first-order. For this purpose, lets us considerthen Equations (13)–(15) can take the following formand the boundary conditions are
- (ii)
- The derivatives are discretized by the central difference formulaand the functions are replaced by their means value like
- (iii)
- The discretized nonlinear algebraic equations are linearized with the help of Newton’s technique. For this purpose, the functions at iteration are written aswhere represents the small increment in the function’s values. The second and higher orders’ terms in are neglected.
- (iv)
- Linearized algebraic equations are finally solved through block-tridiagonal elimination method.
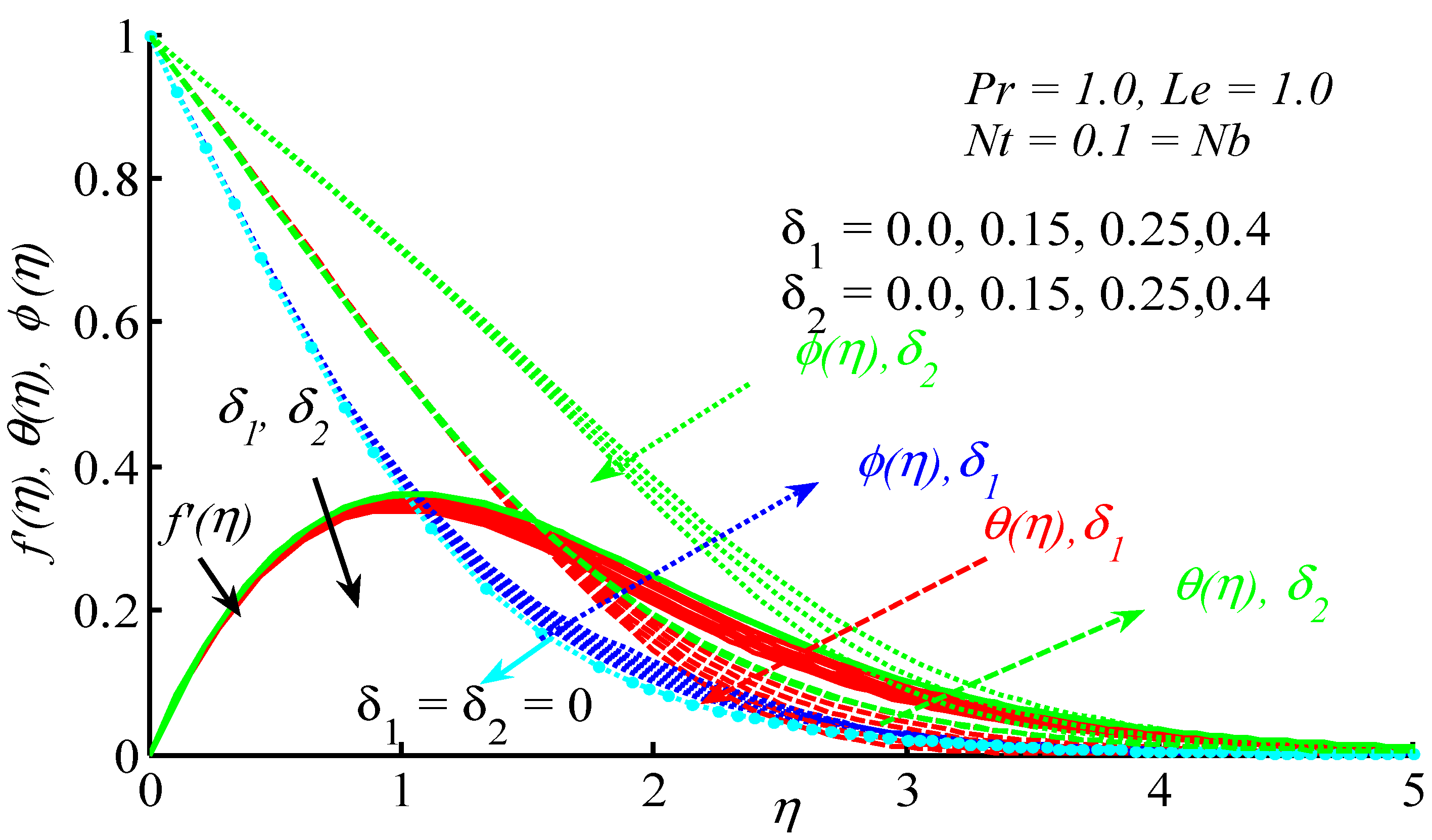
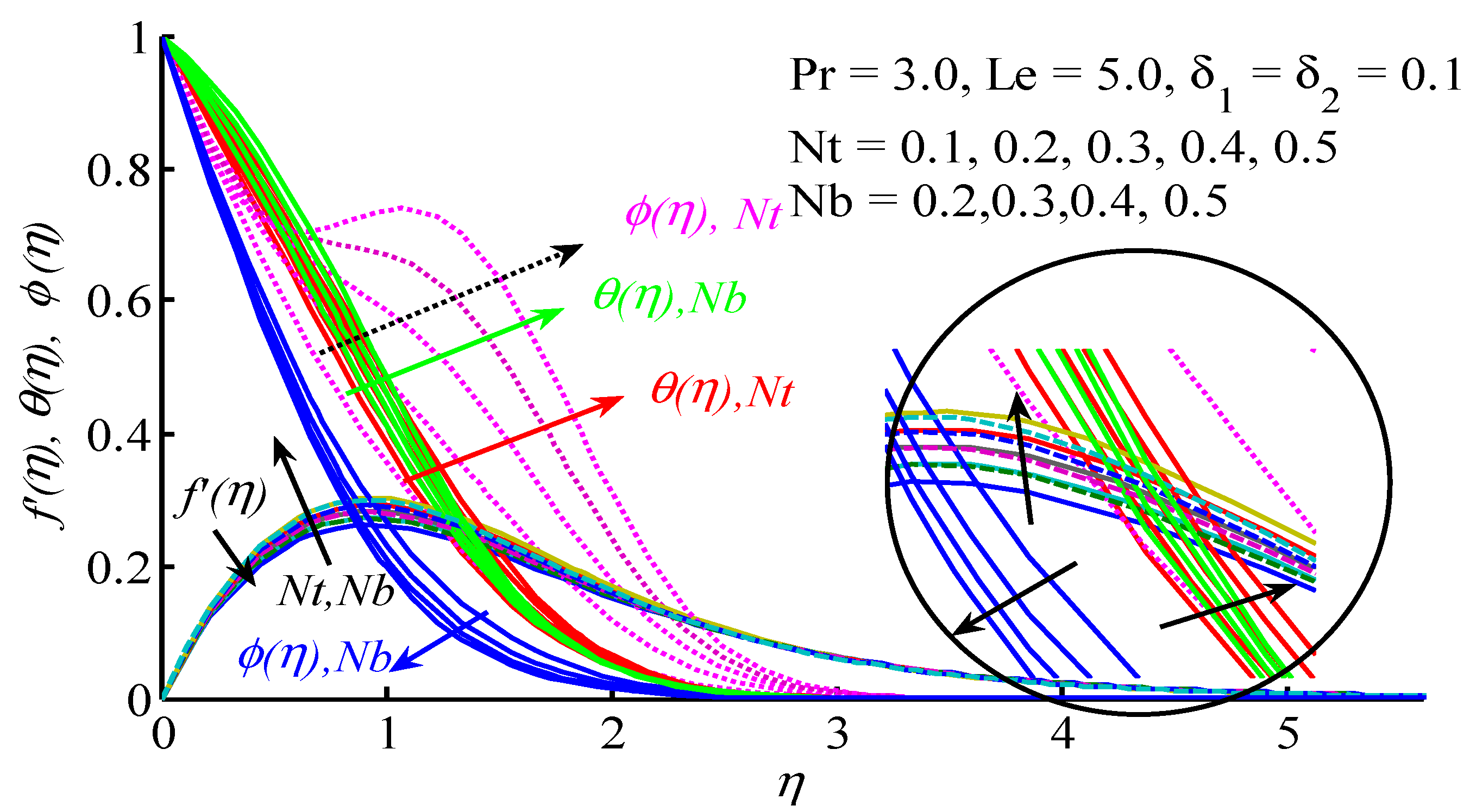
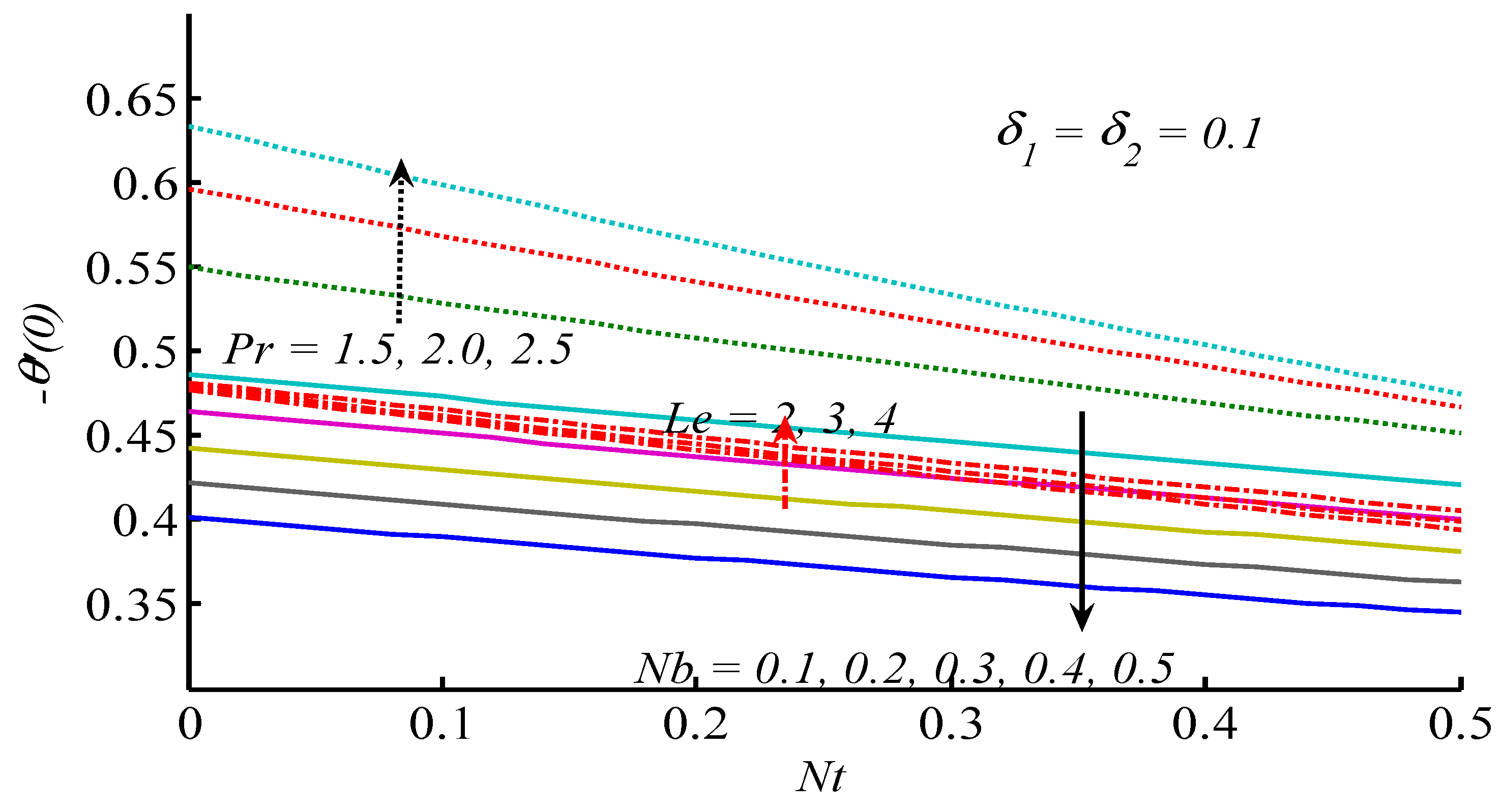
4. Results and Discussion
5. Concluding Remarks
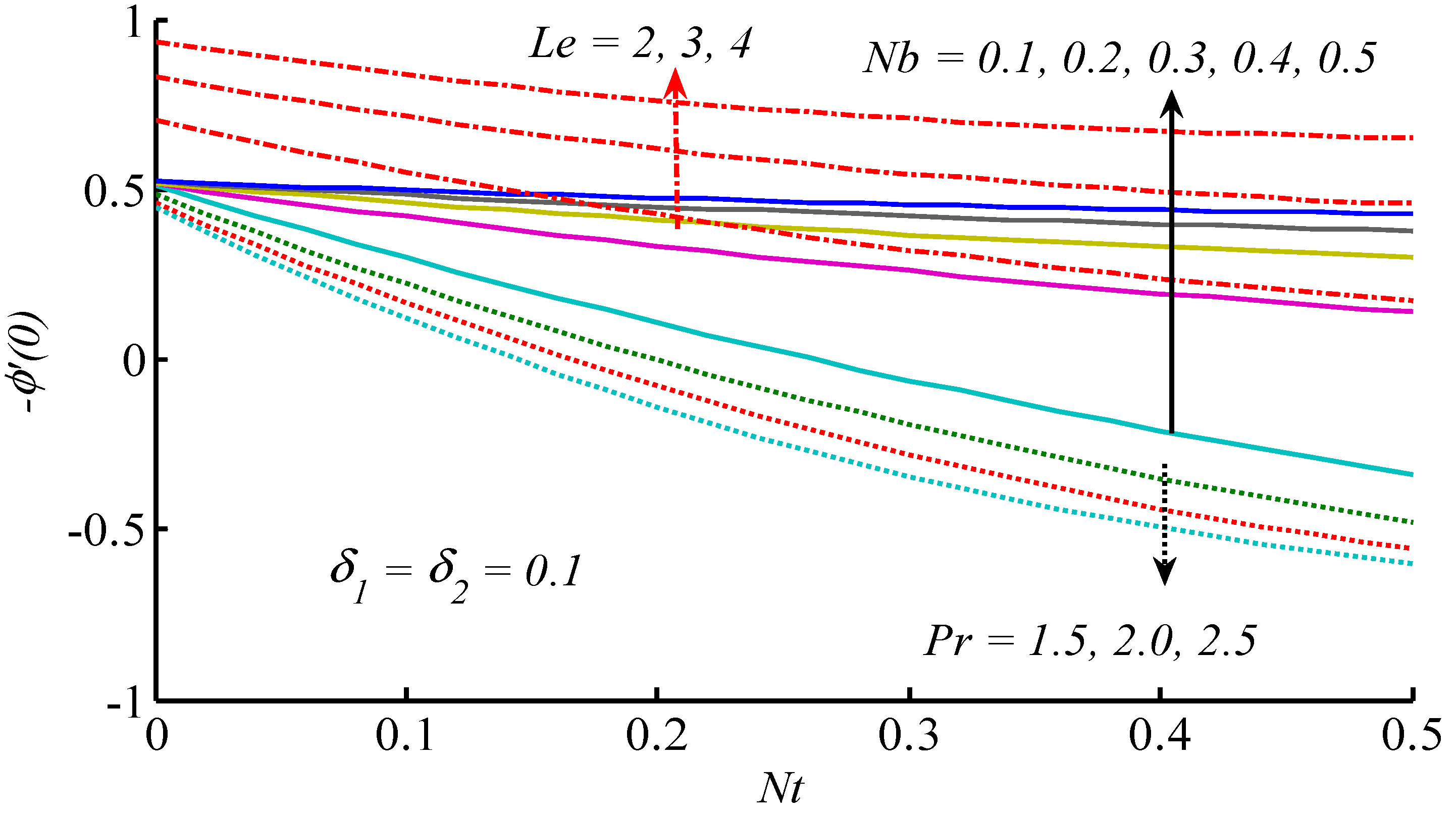
- With the increase of Brownian motion parameters, Sherwood number increases, whereas it gains reverse behavior against thermophoresis parameter.
- With the increase of thermophoresis and Brownian motion parameters, Nusselt number decreases.
- Nusselt number decreases by increasing Prandtl and Lewis numbers.
- Sherwood number increases by increasing Lewis numbers and decreasing Prandtl numbers.
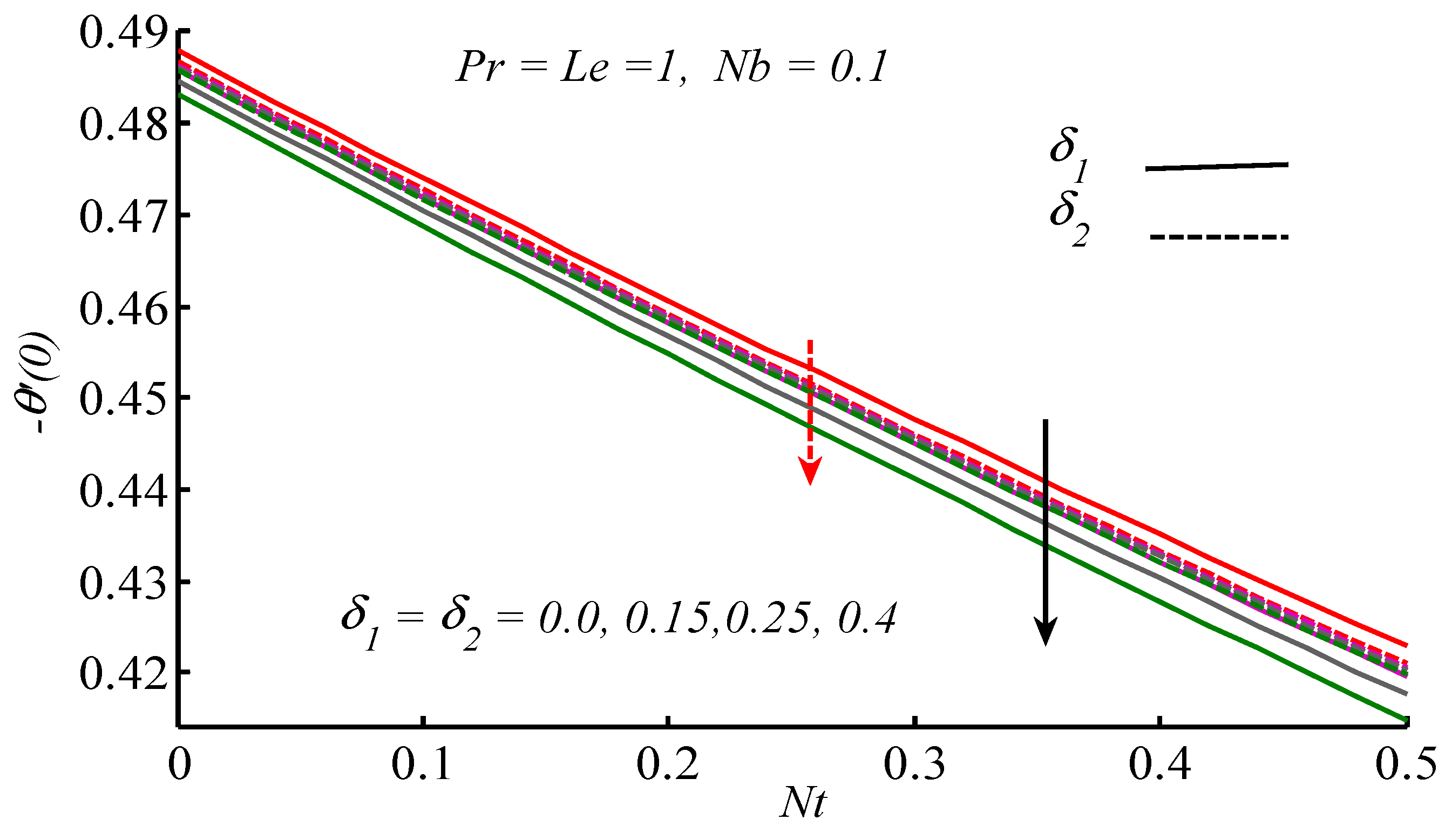
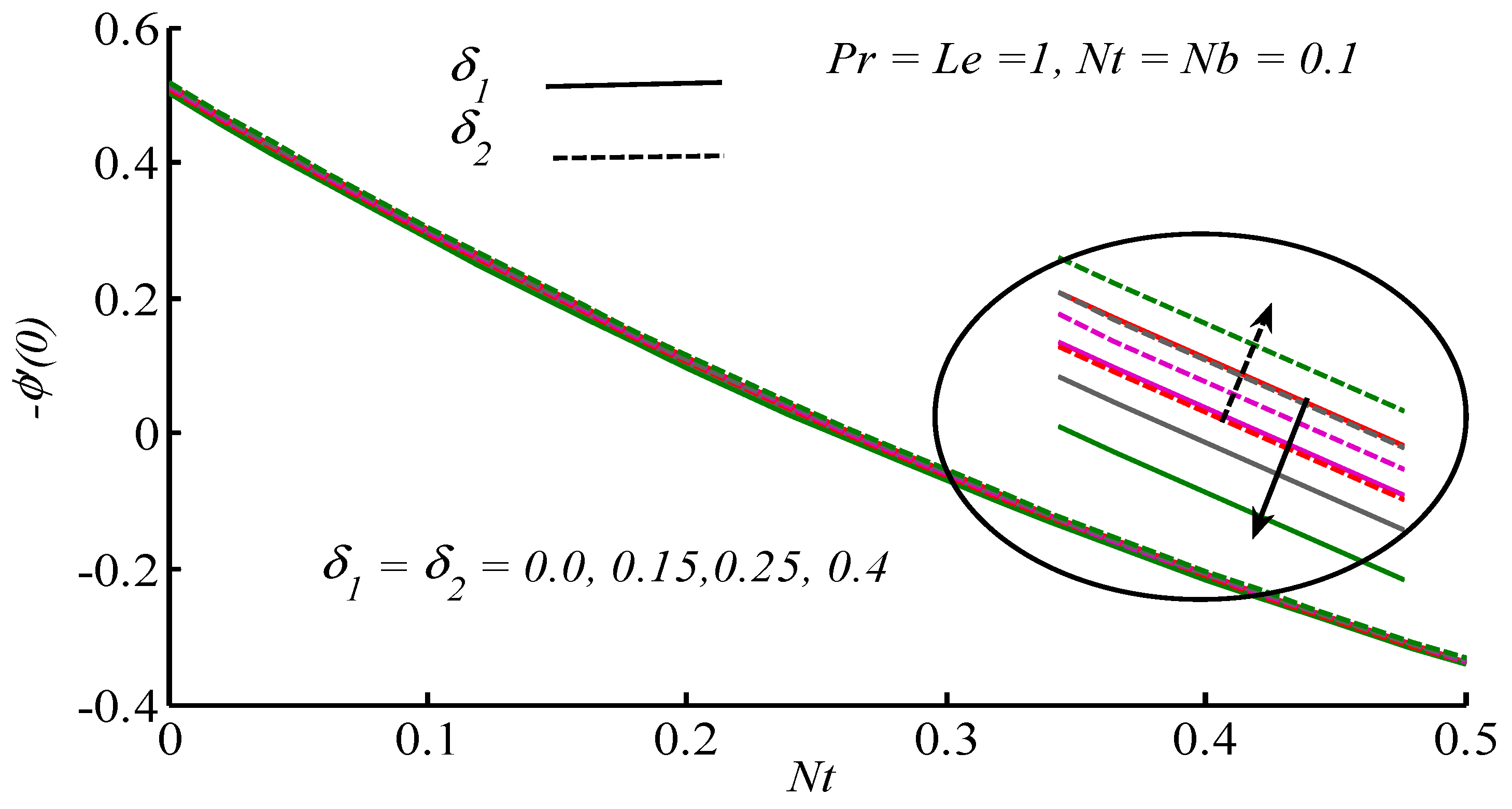
- Nusselt number decreases by increasing thermal and concentration relaxation parameters ).
- Sherwood number increases by increasing concentration relaxation parameter (.
- Sherwood number decreases by increasing thermal relaxation parameter .
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| DT | thermophoretic diffusion coefficient; |
| DB | Brownian diffusion coefficient; |
| T | Temperature; |
| α | thermal diffusivity; |
| g | Gravitational acceleration; |
| C | Concentration; |
| Nb | Brownian motion parameter |
| Nt | thermophoresis parameter |
| T | Temperature of the fluid |
| T∞ | Ambient fluid temperature |
| Tw | Surface temperature |
| C | Solutal concentration |
| C∞ | Ambient solutal concentration |
| Cf | Skin friction coefficient |
| Cw | Solutal concentration at the wall |
| Nu | Nusselt number |
| Pr | Prandtl number |
| Sc | Schmidt number |
| Sh | Sherwood number |
| Dimensional velocity components in and directions | |
| u, v | Dimensionless velocity components in x and y directions |
| Coordinates along and normal to the surface in dimensional form | |
| x, y | Coordinates along and normal to the surface in dimensionless form |
| r | Radius of the base of cone |
| Gr | Grashof number |
| Le | Lewis number |
| Greek symbols | |
| Internal half angle of the cone | |
| τ | The ratio of heat capacity of a nanoparticle to the base fluid |
| Dimensionless concentration | |
| Wall shear stress | |
| Stream function | |
| v | Kinematic viscosity |
| Dynamic viscosity | |
| ρ | Fluid density |
| Relaxation time of the mass flux | |
| Relaxation time of the heat flux | |
| Dimensionless relaxation time of the heat flux | |
| Dimension relaxation time of the mass flux | |
References
- Choi, S.U.S. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In Developments and Applications of Non-Newtonian Flows; ASME: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 66, pp. 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.U.S.; Lockwood, F.E.; Grulke, E.A.; Zhang, Z.G.; Yu, W. Anomalous thermal conductivity enhancement in nanotube suspensions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 2252–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, R.; Grosh, R. Laminar free convection from a non-isothermal cone. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1962, 5, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, R. Laminar free convection from a non-isothermal cone at low Prandtl numbers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1965, 8, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S. Free convection over a slender vertical cone at high Prandtl numbers. ASME J. Heat Transf. 1974, 101, 174–176. [Google Scholar]
- Vajravelu, K.; Nayfeh, J. Hydromagnetic convection at a cone and a wedge. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1992, 19, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafoussias, N. Effects of mass transfer on free convective flow past a vertical isothermal cone surface. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1992, 30, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yih, K. Effect of radiation on natural convection about a truncated cone. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 42, 4299–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrang, M.A.; Ghalambaz, M.; Assareh, E.; Noghrehabadi, A.R. A new solution for natural convection of Darcian fluid about a full vertical cone embedded in porous media prescribed wall temperature by using a hybrid neural network-particle swarm optimization method. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Tech. 2011, 49, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.Y. Free convection heat transfer from a non-isothermal permeable cone with suction and temperature-dependent viscosity. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 2015, 18, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Duwairi, H.M.; Zeid, O.A.; Damseh, R.A. Viscous and Joule heating effects over an isothermal cone in saturated porous media. Jordan J. Mech. Ind. Eng. 2007, 1, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Elbashbeshy, E.M.A.; Emam, T.G.; Sayed, E.A. Effect of pressure work and heat generation/absorption on free convection flow from a vertical circular cone with variable surface heat flux. World J. Eng. Phys. Sci. 2013, 1, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, W.H.; Ostrach, S.; Heighway, J.E. Free-convection similarity flows about two dimensional and axisymmetric bodies with closed lower ends. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1961, 2, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosan, T.; Postelnicu, A.; Pop, I. Free convection boundary layer over a vertical cone in a non-Newtonian fluid-saturated porous medium with internal heat generation. Tech. Mech. 2004, 24, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chamkha, A.J.; Aly, A.M.; Mansour, M.A. Effects of chemical reaction and pressure work on free convection over a stretching cone embedded in a porous medium. Int. J. Ind. Math. 2012, 4, 319–333. [Google Scholar]
- Sohouli, A.R.; Domairry, D.; Famouri, M.; Mohsenzadeh, A. Analytical solution of natural convection of Darcian fluid about a full vertical cone embedded in porous media prescribed wall temperature through HAM. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 35, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J.; Hu, W. Nanofluid coolants for advanced nuclear power plants. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Petrochemicals and Polymers, (ICAPP 05), Seoul, Korea, 15–19 May 2005; p. 5705. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 50, 2002–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdy, A. Natural convection boundary layer flow due to gyrotactic microorganisms about a vertical cone in porous media saturated by a nanofluid. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2016, 38, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behseresht, A.; Noghrehabadi, A.; Ghalambaz, M. Natural-convection heat and mass transfer from a vertical cone in porous media filled with nanofluids using the practical ranges of nanofluids thermo-physical properties. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noghrehabadi, A.; Behseresht, A.; Ghalambaz, M.; Behseresht, J. Natural-Convection Flow of Nanofluids over Vertical Cone Embedded in Non-Darcy Porous Media. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2013, 27, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hady, F.M.; Ibrahim, F.S.; Abdel-Gaied, S.M.; Eid, M.R. Boundary-layer flow in a porous medium of a nanofluid past a vertical cone. In An Overview of Heat Transfer Phenomena; Kazi, S.N., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Fauzi, E.L.A.; Ahmad, S.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary layer flow from a vertical cone in a porous medium filled with a nanofluid. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Tech. 2012, 70, 10–25. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, W.A.; Rashad, A.; Abdou, M.; Tlili, I. Natural bioconvection flow of a nanofluid containing gyrotactic microorganisms about a truncated cone. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2019, 75, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Ismail, A.I.M. Non-similar solution of free convective flow of power law nanofluids in porous media along a vertical cone/plate with thermal and mass convective boundary conditions. Can. J. Phys. 2015, 93, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straughan, B. Thermal convection with the Cattaneo–Christov model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibullo, V.; Zampoli, V. A uniqueness result for the Cattaneo-Christov heat conduction model applied to incompressible fluids. Mech. Res. Commun. 2011, 38, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.A.; Reddy, J.R.; Sugunamma, V.; Sandeep, N. Magnetohydrodynamic Cattaneo-Christov flow past a cone and a wedge with variable heat source/sink. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.; Zheng, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Coupled flow and heat transfer in viscoelastic fluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Appl. Math. Lett. 2014, 38, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Qayyum, S.; Imtiaz, M.; Alsaedi, A. Impact of Cattaneo-Christov Heat Flux in Jeffrey Fluid Flow with Homogeneous-Heterogeneous Reactions. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S. Thermal instability in Brinkman porous media with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 68, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F. Unsteady Marangoni convection heat transfer of fractional Maxwell fluid with Cattaneo heat flux. Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 44, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayat, T.; Qayyum, S.; Imtiaz, M.; Alsaedi, A. Three-dimensional rotating flow of Jeffrey fluid for Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 025012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivakumara, I.; Ravisha, M.; Ng, C.-O.; Varun, V. A thermal non-equilibrium model with Cattaneo effect for convection in a Brinkman porous layer. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2015, 71, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, H.B. Numerical methods in boundary layer theory. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1988, 10, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebeci, T.; Bradshaw, P. Physical and Computational Aspects of Convective Heat Transfer; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
| Present | Yih et al. [8] | Present | Yih et al. [8] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0001 | 1.452616 | 1.6006 | 0.033845 | 0.0079 |
| 0.001 | 1.440436 | 1.5135 | 0.038402 | 0.0246 |
| 0.01 | 1.348483 | 1.3551 | 0.075460 | 0.0749 |
| 0.1 | 1.095916 | 1.0960 | 0.211345 | 0.2116 |
| 0.7 | 0.819591 | - | 0.451095 | - |
| 1 | 0.769428 | 0.7699 | 0.510399 | 0.5109 |
| 10 | 0.487697 | 0.4877 | 1.033989 | 1.0339 |
| 100 | 0.289635 | 0.2896 | 1.922854 | 1.9226 |
| 1000 | 0.166145 | 0.1661 | 3.470171 | 3.4696 |
| 10000 | 0.094042 | 0.0940 | 6.200679 | 6.1984 |
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.47256 | 0.29844 | 0.45902 | 0.10786 | 0.44588 | −0.06091 | 0.43312 | −0.2091 | 0.42074 | −0.33788 |
| 0.2 | 0.45094 | 0.41891 | 0.43785 | 0.33380 | 0.42515 | 0.25910 | 0.41284 | 0.19421 | 0.40089 | 0.13854 |
| 0.3 | 0.42988 | 0.46077 | 0.41724 | 0.4106 | 0.40499 | 0.36703 | 0.39311 | 0.32968 | 0.38161 | 0.29816 |
| 0.4 | 0.40938 | 0.48295 | 0.39720 | 0.45007 | 0.38540 | 0.42190 | 0.37396 | 0.39814 | 0.36290 | 0.37853 |
| 0.5 | 0.38947 | 0.49724 | 0.37774 | 0.47459 | 0.36639 | 0.45551 | 0.3554 | 0.43978 | 0.34476 | 0.42718 |
| 2 | 3 | 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.54899 | 0.44100 | 0.59205 | 0.37685 | 0.63310 | 0.30480 |
| 3 | 0.53896 | 0.61442 | 0.57534 | 0.56004 | 0.6035 | 0.50459 |
| 5 | 0.52795 | 0.84874 | 0.55651 | 0.80533 | 0.5693 | 0.76937 |
| 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.47432 | 0.29986 | 0.47140 | 0.29258 | 0.47015 | 0.28898 | 0.46904 | 0.28545 |
| 0.2 | 0.47384 | 0.30440 | 0.47091 | 0.29714 | 0.46966 | 0.29351 | 0.46855 | 0.28992 |
| 0.3 | 0.47358 | 0.30685 | 0.47064 | 0.29961 | 0.46939 | 0.29597 | 0.46827 | 0.29235 |
| 0.4 | 0.47331 | 0.30945 | 0.47036 | 0.30221 | 0.46910 | 0.29857 | 0.46798 | 0.29493 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, M.S.; Khan, W.; Mustafa, I.; Ghaffari, A. Numerical Study of Natural Convection Flow of Nanofluid Past a Circular Cone with Cattaneo–Christov Heat and Mass Flux Models. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111363
Iqbal MS, Khan W, Mustafa I, Ghaffari A. Numerical Study of Natural Convection Flow of Nanofluid Past a Circular Cone with Cattaneo–Christov Heat and Mass Flux Models. Symmetry. 2019; 11(11):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111363
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Muhammad Saleem, Waqar Khan, Irfan Mustafa, and Abuzar Ghaffari. 2019. "Numerical Study of Natural Convection Flow of Nanofluid Past a Circular Cone with Cattaneo–Christov Heat and Mass Flux Models" Symmetry 11, no. 11: 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111363
APA StyleIqbal, M. S., Khan, W., Mustafa, I., & Ghaffari, A. (2019). Numerical Study of Natural Convection Flow of Nanofluid Past a Circular Cone with Cattaneo–Christov Heat and Mass Flux Models. Symmetry, 11(11), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111363





