Type 2 Fuzzy Inference-Based Time Series Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Collection and Selection of Data
2.2. Proposed Forecasting Model
2.3. Evaluation of the Performance
3. Empirical Analysis
4. Algorithm of the Proposed Method
- Step 1:
- The class interval of the universe of discourse is determined by using the sliding window method.
- Step 2:
- The observations are fuzzified into corresponding fuzzy sets.
- Step 3:
- Fuzzy logical relationship groups (FLRGs) are obtained.
- Step 4:
- Out-of-sample observations are mapped to FLRGs.
- Step 5:
- Operators and fuzzy rules obtained by using weighted subsethood-based algorithm are applied to the FLRGs for all the observations and obtain forecasts.
- Step 6:
- The forecasts are defuzzified.
- Step 7:
- Forecast values are computed for all data individually.
- Step 8:
- The method is compared with the previous method.
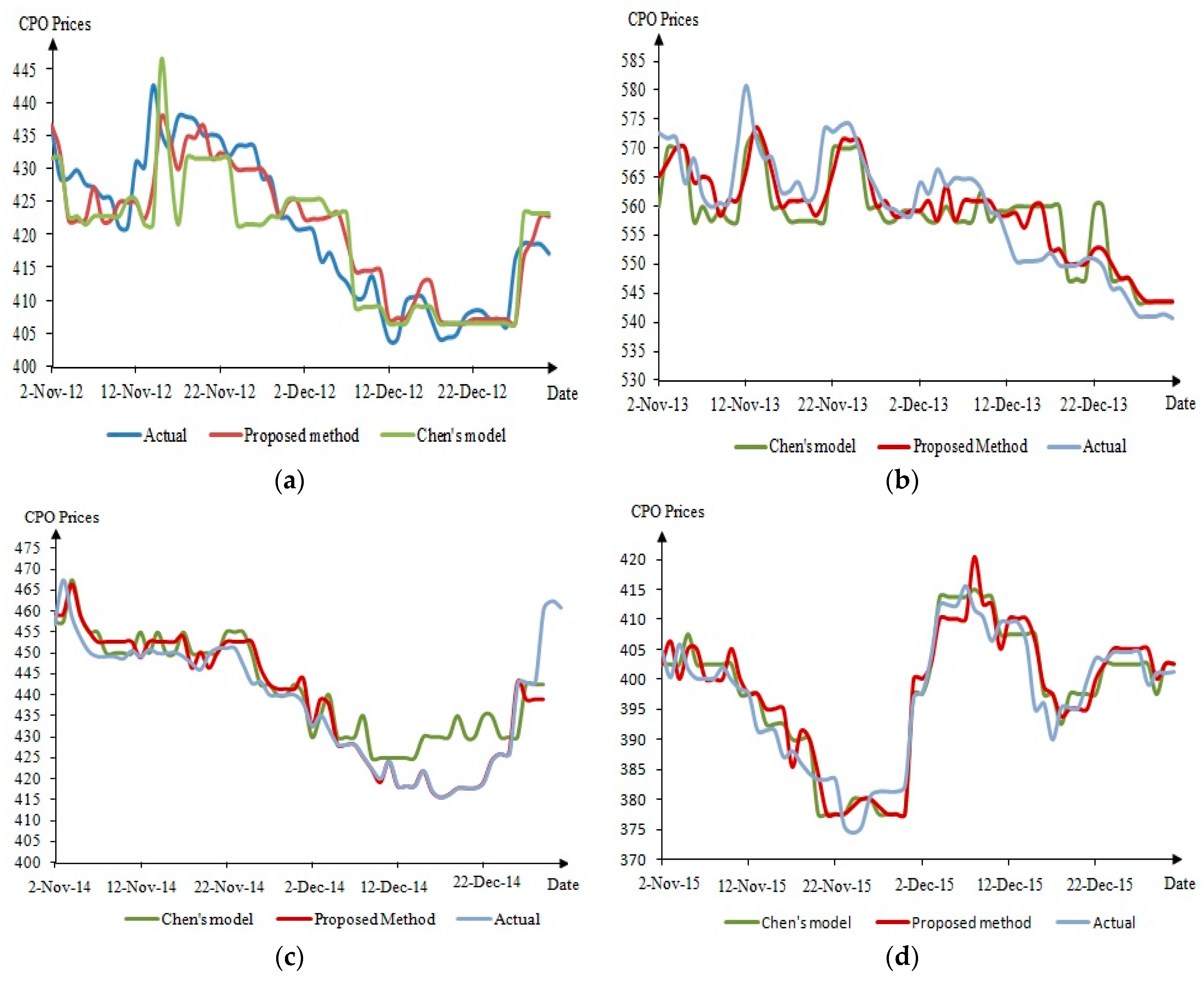
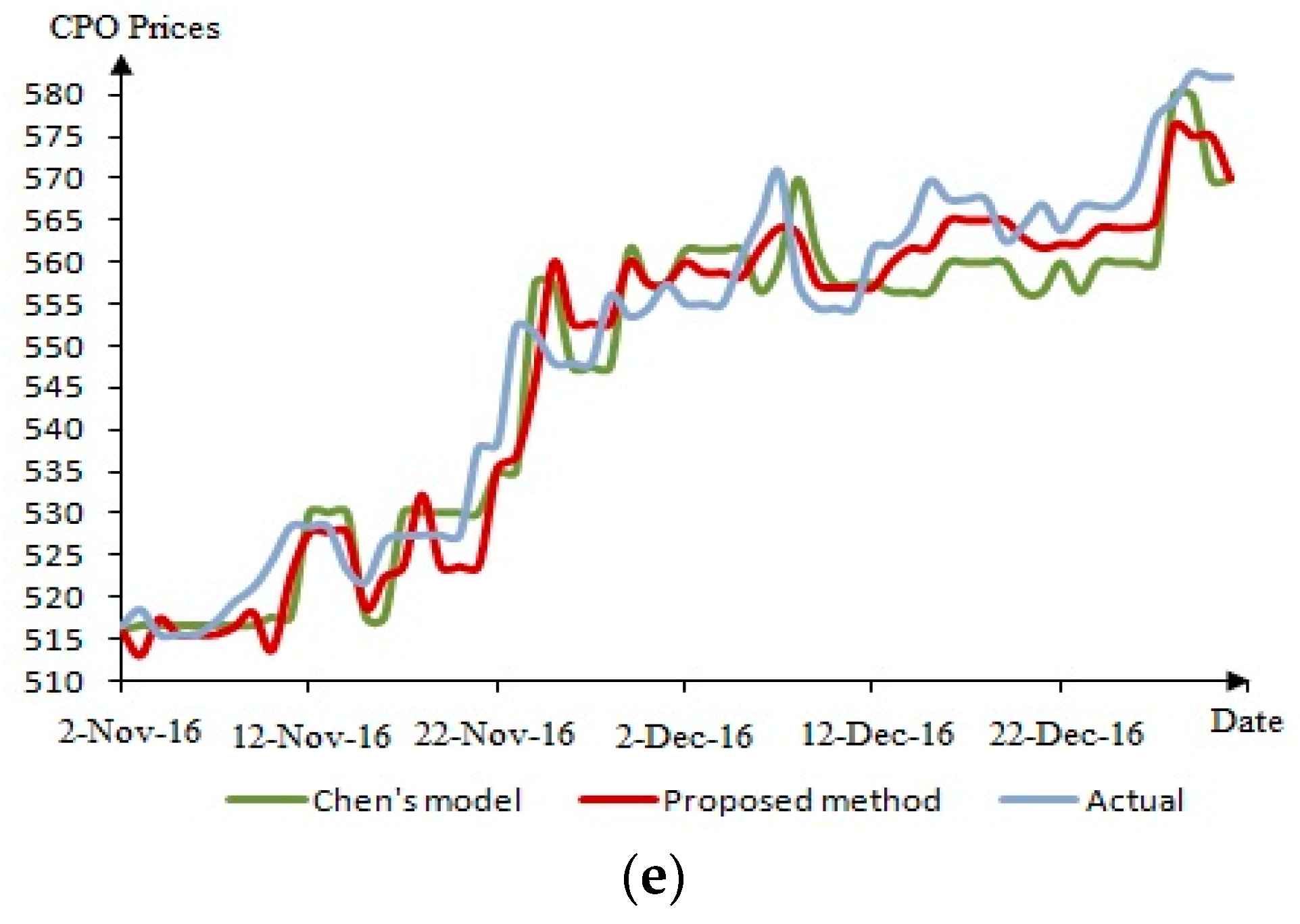
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, M.H.; Ping, P.Y.; Mahamed, N. Volatility modelling and forecasting of Malaysian crude palm oil prices. Appl. Math. Sci. 2014, 8, 6159–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karia, A.A.; Bujang, I.; Ahmad, I. Forecasting on crude palm oil prices using artificial intelligence approaches. Am. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 3, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.C.; Ball, J.E.; Sharma, A. An application of artificial neural networks for rainfall forecasting. Math. Comput. Model. 2001, 33, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, N.Q.; Babel, M.S.; Weesakul, S.; Tripathi, N.K. An artificial neural network model for rainfall forecasting in Bangkok, Thailand. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 13, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, M.A.; Hameed, A. Crude oil, palm oil stock and prices: How they link. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2013, 3, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Applanaidu, S.D.; Fatimah, M.A.; Shamsudin, M.N.; Abdel Hameed, A.A. An econometric analysis of the link between biodiesel demand and malaysian palm oil market. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2011, 6, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuwijaya, K.; Chen, S.M. A new method to forecast enrollments using fuzzy time series and clustering techniques. In Proceedings of the 2009 international conference on machine learning and cybernetics, Hebei, China, 12–15 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.N.; Lei, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, Y. Intuitionistic fuzzy time series forecasting model based on intuitionistic fuzzy reasoning. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 38, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, V.R.; Bas, E.; Yolcu, U.; Egrioglu, E. A new fuzzy time series analysis approach by using differential evolution algorithm and chronologically-determined weights. J. Soc. Econ. Stat. 2013, 2, 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaram, S.; Vamitha, V. A modified approach on fuzzy time series forecasting. Ann. Pure Appl. Math. 2012, 2, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.M.; Hsu, C.C. A new method to forecast enrollments using fuzzy time series. Int. J. Appl. Sci.& Eng. 2004, 2, 234–244. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Chissom, B.S. Fuzzy time series and its models. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1993, 54, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chissom, B.S. Forecasting enrollments with fuzzy time series—Part I. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1993, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Chissom, B.S. Forecasting enrollments with fuzzy time series—Part II. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1994, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Forecasting enrollments based on fuzzy time series. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1996, 81, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P. Forecasting enrollments based on fuzzy time series with Higher Forecast Accuracy Rate. Int. J. Comput. Technol. Appl. 2012, 3, 957–961. [Google Scholar]
- Datar, M.; Gionis, A.; Indyk, P.; Motwani, R. Maintaining stream statistics over sliding windows: (extended abstract). In Proceedings of the Thirteenth Annual {ACM-SIAM} Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–8 January 2002; pp. 635–644. [Google Scholar]
- BenYahmed, Y.; Abu, B.A.; Razak, H.A.; Ahmed, A.; Abdullah, S.M.S. Adaptive sliding window algorithm for weather data segmentation. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2015, 80, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- D’Arcy, J.A.; Collins, D.J.; Rowland, I.J.; Padhani, A.R.; Leach, M.O. Applications of sliding window reconstruction with cartesian sampling for dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. NMR Biomed. 2002, 15, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, P.; Bedi, S.S. Weather forecasting using sliding window algorithm. ISRN Signal. Process. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasu, A.; Manku, G.S. Approximate counts and quantiles over sliding windows. In Proceedings of the twenty-third ACM SIGMOD-SIGACT-SIGART symposium on Principles of database systems, Paris, France, 14–16 June 2004; pp. 286–296. [Google Scholar]
- Huarng, K. Effective lengths of intervals to improve forecasting in fuzzy time series. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2001, 123, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huarng, K.; Yu, T.H. Ratio-based lengths of intervals to improve fuzzy time series forecasting. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. B Cybern. 2006, 36, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmani, K.A.; Shen, Q. Subsethood-based fuzzy modelling and classification. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference On Fuzzy Systems, Reno, NV, USA, 25 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmani, K.A.; Shen, Q. Data-driven fuzzy rule generation and its application for student academic performance evaluation. Appl. Intell. 2006, 25, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cordón, O.; Herrera, F.; Zwir, I. Linguistic modeling by hierarchical systems of linguistic rules. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2002, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Handbook of fuzzy computation. Fuzzy Sets Syst. Dep. Comput. Sci. Artif. Intell. 2001, 123, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, A.; Ahmad, A. Fuzzy Logic and Approximate Reasoning; Blekinge Institute of Technology: Karlskrona, Sweeden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Huarng, K.; Yu, H.K. A Type 2 fuzzy time series model for stock index forecasting. Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 2005, 353, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, D.; Li, H. A comprehensive high order Type 2 fuzzy time series forecasting model. In Proceedings of the 28th Chinese control and decision conference, Shenyang, China, 28–30 May 2016; pp. 6681–6686. [Google Scholar]
- Maleki, A.; Pasha, E.; Razzaghnia, T. Possibility linear regression analysis with trapezoidal fuzzy data. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 18, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.M.; Wang, N.Y. Fuzzy forecasting based on fuzzy-trend logical relationship groups. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. Part. B Cybern. 2010, 40, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, N.F.; Othman, M.; Sokkalingam, R.; Abdul, K.E. Forecasting crude palm oil prices using fuzzy rule-based time series method. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32216–32224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Date (yyyy/mm/dd) | CPO Price | Fuzzy Sets |
|---|---|---|
| 2012/10/1 | 424.20 | A7 |
| 2012/10/2 | 424.20 | A7 |
| 2012/10/3 | 407.40 | A3 |
| 2012/10/4 | 395.20 | A1 |
| 2012/10/5 | 411.00 | A4 |
| 2012/10/6 | 412.50 | A4 |
| 2012/10/7 | 412.50 | A4 |
| 2012/10/8 | 406.80 | A3 |
| 2012/10/9 | 418.50 | A5 |
| 2012/10/10 | 418.00 | A5 |
| 2012/10/11 | 430.00 | A8 |
| 2012/10/12 | 423.00 | A6 |
| 2012/10/13 | 415.50 | A5 |
| 2012/10/14 | 415.50 | A5 |
| 2012/10/15 | 417.40 | A5 |
| 2012/10/16 | 417.00 | A5 |
| 2012/10/17 | 414.90 | A5 |
| 2012/10/18 | 419.60 | A6 |
| 2012/10/19 | 425.80 | A7 |
| 2012/10/20 | 424.00 | A6 |
| 2012/10/21 | 424.00 | A6 |
| 2012/10/22 | 435.10 | A9 |
| 2012/10/23 | 424.70 | A7 |
| 2012/10/24 | 424.70 | A7 |
| 2012/10/25 | 435.20 | A9 |
| 2012/10/26 | 435.20 | A9 |
| 2012/10/27 | 434.30 | A9 |
| 2012/10/28 | 434.30 | A9 |
| 2012/10/29 | 428.60 | A7 |
| 2012/10/30 | 426.00 | A7 |
| 2012/10/31 | 424.70 | A7 |
| Date (mm/dd) | Closing | High | Low |
|---|---|---|---|
| … | … | … | … |
| 10/11 | 430.00 | 431.10 | 419.20 |
| 10/12 | 423.00 | 428.80 | 412.80 |
| 10/13 | 415.50 | 420.30 | 413.80 |
| … | … | … | … |
| Date (mm/dd) | Forecasts | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Closing | |||
| 10/12 | High | ||
| Low | |||
| Closing | |||
| 10/13 | High | ||
| Low | |||
| Closing | |||
| 10/14 | High | ||
| Low |
| Date (mm/dd) | Forecasts | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Closing | |||
| 10/12 | High | ||
| Low | |||
| Closing | |||
| 10/13 | High | ||
| Low | |||
| Closing | |||
| 10/14 | High | ||
| Low |
| Year | Mean Square Error (MSE) | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Method | Chen’s model | Proposed Method | Chen’s model | |
| 2012 | 0.0010 | 0.0010 | 0.518 | 0.520 |
| 2013 | 0.00067 | 0.0011 | 0.457 | 0.635 |
| 2014 | 0.0019 | 0.0027 | 0.637 | 0.855 |
| 2015 | 0.00069 | 0.00079 | 0.414 | 0.462 |
| 2016 | 0.0009 | 0.0015 | 0.567 | 0.754 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahim, N.F.; Othman, M.; Sokkalingam, R.; Abdul Kadir, E. Type 2 Fuzzy Inference-Based Time Series Model. Symmetry 2019, 11, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111340
Rahim NF, Othman M, Sokkalingam R, Abdul Kadir E. Type 2 Fuzzy Inference-Based Time Series Model. Symmetry. 2019; 11(11):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111340
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahim, Nur Fazliana, Mahmod Othman, Rajalingam Sokkalingam, and Evizal Abdul Kadir. 2019. "Type 2 Fuzzy Inference-Based Time Series Model" Symmetry 11, no. 11: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111340
APA StyleRahim, N. F., Othman, M., Sokkalingam, R., & Abdul Kadir, E. (2019). Type 2 Fuzzy Inference-Based Time Series Model. Symmetry, 11(11), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111340





