Study on an Adaptive Co-Evolutionary ACO Algorithm for Complex Optimization Problems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Basic Method
3.1. The CEA
3.2. The ACO Algorithm
3.3. Adaptive ACO Algorithm
4. Adaptive Co-Evolutionary ACO (SCEACO) Algorithm
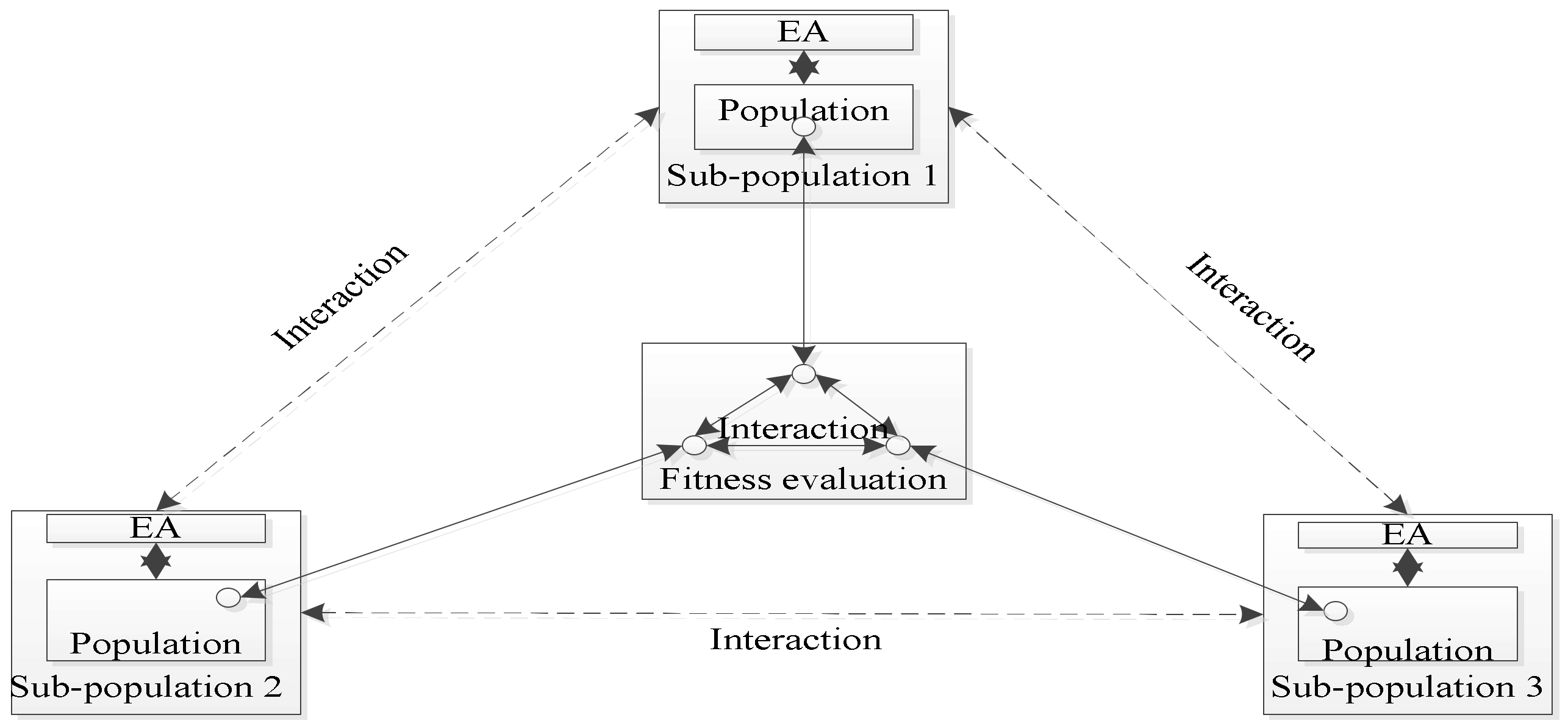
4.1. The Idea of the SCEACO Algorithm
4.2. The Model of the SCEACO Algorithm
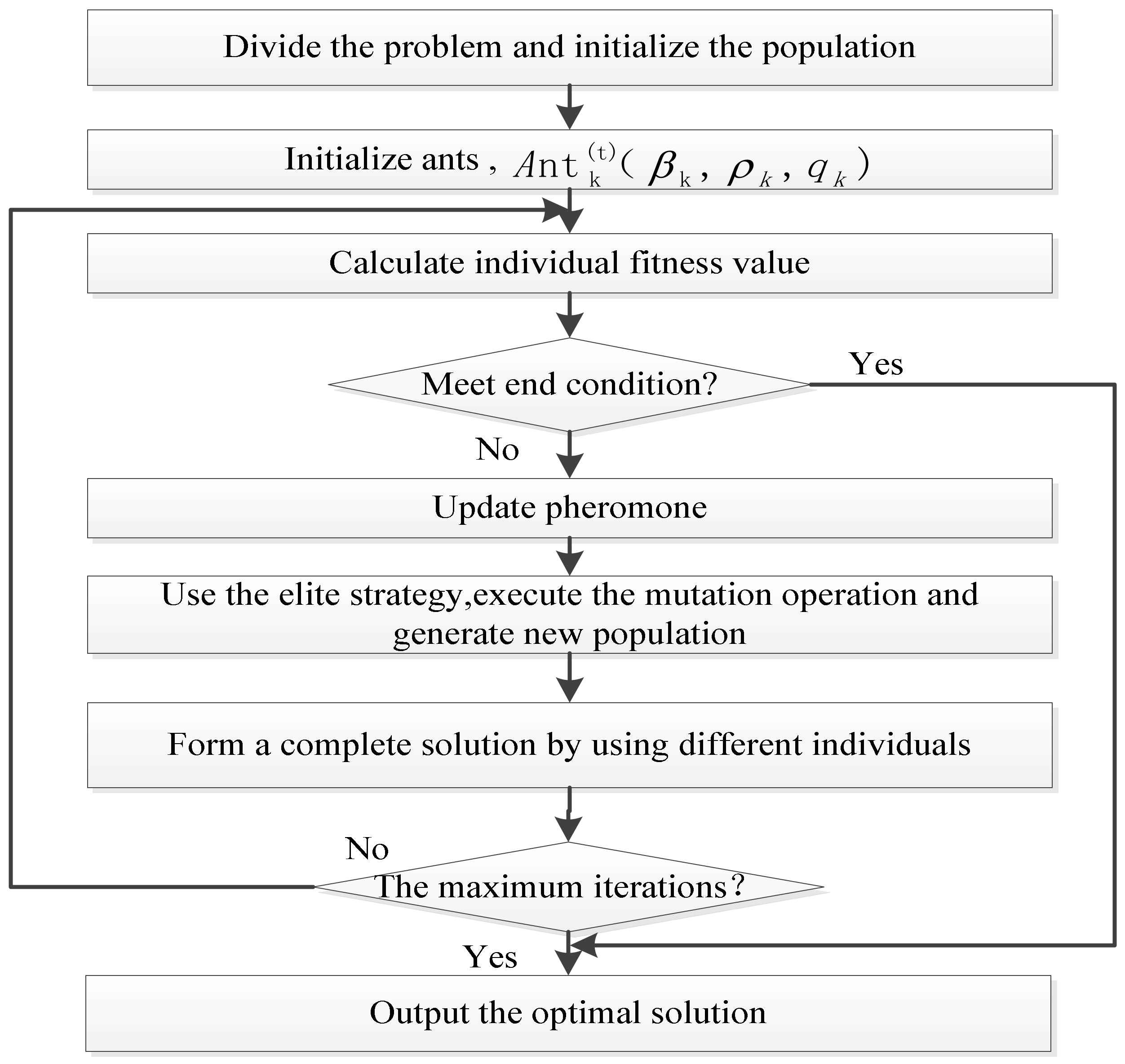
4.3. The Steps of the SCEACO Algorithm
- Step 1.
- The ant colony is divided into multiple sub-populations in a common search space, each sub-population performs the search activity and pheromone updating strategy. The multi-objective optimization problem is divided into several sub-optimization problems, then each sub optimization problem corresponds to one sub-population.
- Step 2.
- Initialize the parameters of the SCEACO algorithm. These parameters include the control parameters and , ant size , the pheromone trial evaporation rate , the maximum iteration times , and the iteration algebraic counter . For the initialized number of ants, each ant stores these parameters in the form of .
- Step 3.
- Calculate the fitness value of each individual in each sub-population, determine whether the result meets the end condition. If the result meets the end condition, then the result is output. Otherwise go to Step 4.
- Step 4.
- The pheromone is updated for each individual according to the improved pheromone updating Equations (3)–(6).
- Step 5.
- In each sub-population, the elitist strategy is used to retain some elitist individuals. The other ants are evolved to generate a new population.
- Step 6.
- Each sub-population selects the current optimal individual, which is used to form a complete solution with the individual of different sub-population in order to complete the information interaction among these sub-populations.
- Step 7.
- The min-max ant strategy is used to set pheromone concentration for each path
- Step 8.
- Determine whether the maximum number of iterations is reached. If the number of iterations is reached, then the result is output. Otherwise go to Step 3.
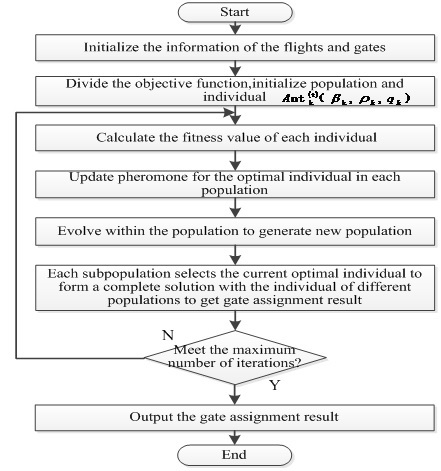
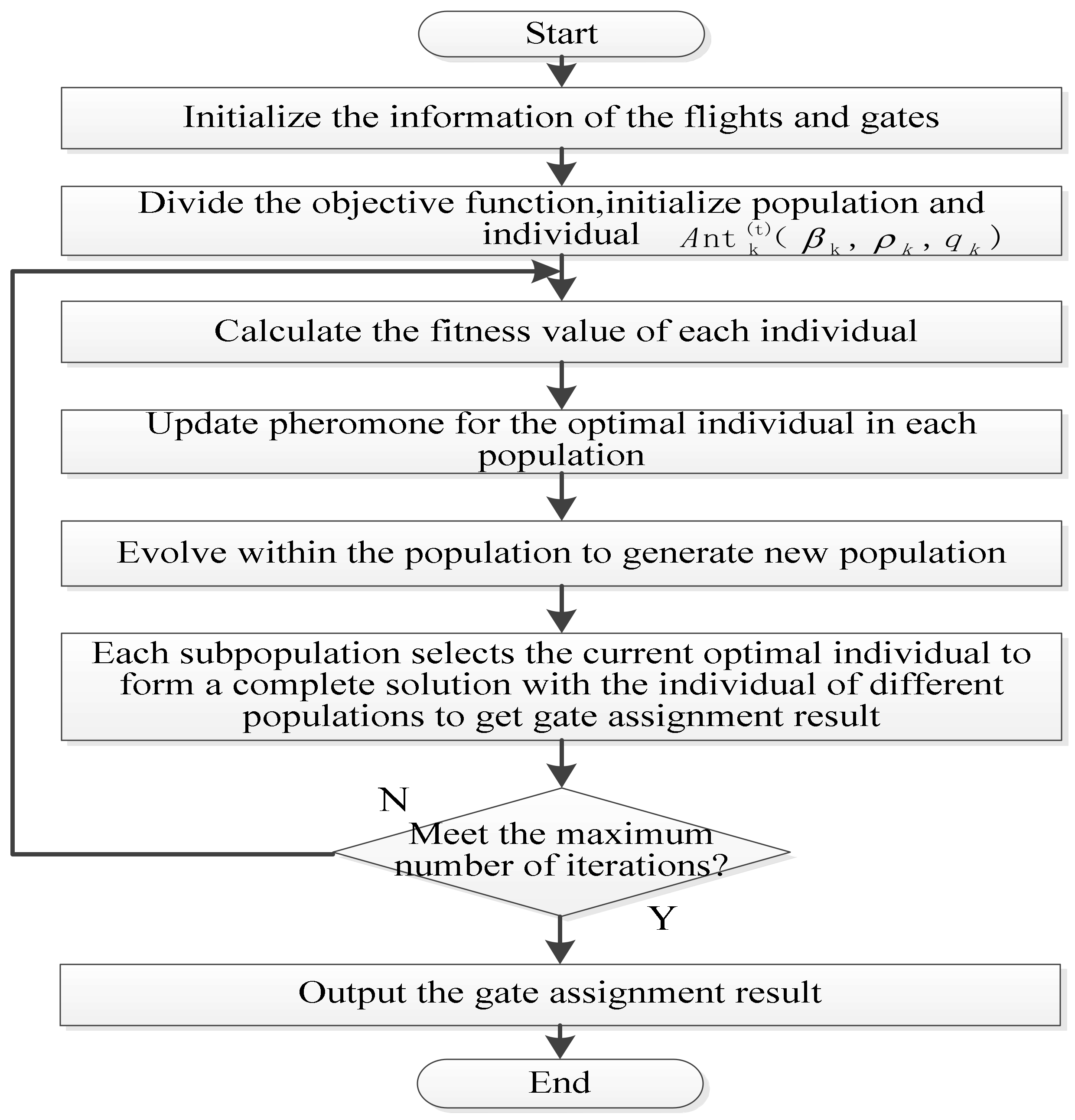
5. Application of the SCEACO Algorithm in Gate Assignment
5.1. Construct the Optimization Model of Gate Assignment
5.2. Gate Assignment Method by Using the SCEACO Algorithm
6. Case Analysis
6.1. Data Source and Experimental Environment
6.2. Experimental Result
6.3. Comparison and Analysis of the Experimental Results
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villarrubia, G.; De Paz, J.F.; Chamoso, P.; la Prieta, F.D. Artificial neural networks used in optimization problems. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Chen, R.; He, B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Yin, L.F.; Guo, J.H. A novel two-stage hybrid swarm intelligence optimization algorithm and application. Soft Comput. 2012, 16, 1707–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Li, J.C.; Gu, X.Y. Self-adaptive step fruit fly algorithm optimized support vector regression model for dynamic response prediction of magnetorheological elastomer base isolator. Neurocomputing 2016, 211, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Li, B.; Zhao, H.M. Study on an airport gate reassignment method and its application. Symmetry 2017, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Zhou, X.Q.; Lu, M.M.; Lin, J.Q.; Sun, J.B. Parameters optimization for machining optical parts of difficult-to-cut materials by genetic algorithm. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 29, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dackermann, U.; Skinner, B.; Li, J.C. Guided wave-based condition assessment of in situ timber utility poles using machine learning algorithms. Struct. Health Monit. 2014, 13, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Maniezzo, V.; Colorni, A. Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 1996, 26, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W. Heterogeneous-ants-based path planner for global path planning of mobile robot applications. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 1754–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Yang, J.G.; Li, H.P. An improved ant colony algorithm for robot path planning. Soft Comput. 2017, 21, 5829–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.C.; Wang, H.D.; Shang, R.H.; Liu, F. A co-evolutionary multi-objective optimization algorithm based on direction vectors. Inf. Sci. 2013, 228, 90–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhao, H.M.; Zou, L.; Li, G.Y.; Yang, X.H.; Wu, D.Q. A novel collaborative optimization algorithm in solving complex optimization problems. Soft Comput. 2017, 21, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercedes, E.N.; Miquel, A.P. Robust gate assignment procedures from an airport management perspective. Omega 2015, 50, 82–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.R.; Cho, S.B. Co-evolutionary learning with strategic coalition for multiagents. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2005, 5, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, L. An effective co-evolutionary particle swarm optimization for constrained engineering design problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2007, 20, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Z.; Wang, L.; He, Q. An effective co-evolutionary differential evolution for constrained optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 2007, 186, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, J.K.; Zheng, W. Co-evolutionary particle swarm optimization to solve constrained optimization problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 2009, 57, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.W.; Gu, M.Z.; Cao, C.W.; Gu, X.S. A novel competitive co-evolutionary quantum genetic algorithm for stochastic job shop scheduling problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2010, 37, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.S.; Bernert, D.L.A. A modified ant colony optimization algorithm based on differential evolution for chaotic synchronization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 4198–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.N.; Chen, Y.W.; Yang, K.W. Multi-population interactive coevolutionary algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2011, 48, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.C.; Wang, H.Y. Quantum ant colony optimization algorithm based on bloch spherical search. Neural Netw. World 2012, 22, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.W.; Kuo, R.J.; Hu, J.T.L. Hybrid ant colony optimization algorithms for mixed discrete-continuous optimization problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 219, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Frean, M.; Zhang, M.J. Crossover-based local search in cooperative co-evolutionary feedforward neural networks. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2012, 12, 2924–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.B.; Gu, X.S. A hybrid co-evolutionary cultural algorithm based on particle swarm optimization for solving global optimization problems. Neurocomputing 2012, 98, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.L.; Wang, M.M. Hybrid coding PSO-ACO co-evolutionary algorithm for solving mixed-integer programming problems. Asia-Pac. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 30, 1340001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Vargas, J.A.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Segovia-Hernández, J.G.S. An improved ant colony optimization method and its application for the thermodynamic modeling of phase equilibrium. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013, 353, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk-Allah, R.M.; Zaki, E.M.; El-Sawy, A.A. Hybridizing ant colony optimization with firefly algorithm for unconstrained optimization problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 224, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.F.; Hung, C.W.; Hsu, C.H. Rule-based cooperative continuous ant colony optimization to improve the accuracy of fuzzy system design. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 22, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.J.; Alam, S.; Abbass, H.A. MOCCA-II: A multi-objective co-operative co-evolutionary algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2014, 23, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.P.; Guan, Z.J.; Shi, Q.; Wang, J.D. A more efficient attribute self-adaptive co-evolutionary reduction algorithm by combining quantum elitist frogs and cloud model operators. Inf. Sci. 2015, 293, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Li, T.Q.; Zhang, Q. A weighted max-min ant colony algorithm for TSP instances. IEICE Trans. Fundam. Electron. Commun. Comput. Sci. 2015, 98, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, M.; Yu, Y.Y. A co-evolutionary improved multi-ant colony optimization for ship multiple and branch pipe route design. Ocean Eng. 2015, 102, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.C.; Wang, M.W.; Ye, Z.W.; Lai, X.D. A feature selection method based on modified binary coded ant colony optimization algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2016, 49, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.K. An effective co-evolutionary artificial bee colony algorithm for steelmaking-continuous casting scheduling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 250, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.T.; Wang, R.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.J.; Zha, Y.B. A multi-objective co-evolutionary algorithm for energy-efficient scheduling on a green data center. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 75, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhao, H.; Xue, D.Y. A multi-population co-evolutionary genetic programming approach for optimal mass customisation production. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2017, 55, 621–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goran, M.; Tihana, G.G. Co-evolutionary multi-population genetic programming for classification in software defect prediction: An empirical case study. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 2017, 55, 331–351. [Google Scholar]
- Nilakantan, J.M.; Li, Z.X.; Tang, Q.H.; Nielsen, P. Multi-objective co-operative co-evolutionary algorithm for minimizing carbon footprint and maximizing line efficiency in robotic assembly line systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiew, B.Y.; Tan, S.C.; Lim, W.S. A double-elimination-tournament-based competitive co-evolutionary artificial neural network classifier. Neurocomputing 2017, 249, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, W.N.; Yu, Z.T.; Gu, T.L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhang, J. Adaptive multimodal continuous ant colony optimization. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2017, 21, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.L.; You, X.M.; Liu, S. A novel heuristic communication heterogeneous dual population ant colony optimization algorithm. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 18506–18515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.P.; Lin, C.T.; Chen, S.B.; Zhang, X.F.; Hu, B. Multiagent-consensus-MapReduce-based attribute reduction using co-evolutionary quantum PSO for big data applications. Neurocomputing 2018, 272, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Jiang, J.M.; Zhao, B.P.; Ma, T.H. A self-adaptive artificial bee colony algorithm based on global best for global optimization. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 2935–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.C.; Li, J.C. Nonparametric modeling of magnetorheological elastomer base isolator based on artificial neural network optimized by ant colony algorithm. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhao, H.M.; Yang, X.H.; Xiong, J.X.; Sun, M.; Li, B. Study on an improved adaptive PSO algorithm for solving multi-objective gate assignment. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 59, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvar, M.N.; Li, X.D.; Mei, Y.; Yao, X. Cooperative Co-Evolution with differential grouping for large scale optimization. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2014, 18, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzle, T.; Dorigo, M. A short convergence proof for a class of ant colony optimization algorithms. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 2000, 6, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, C.; Stützle, T.; Dorigo, M.; Manfrin, M.; Birattari, M. An analysis of communication policies for homogeneous multi-colony ACO algorithms. Inf. Sci. 2010, 180, 2390–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; See, P.C. A new minimum pheromone threshold strategy (MPTS) for max-min ant system. Appl. Soft Comput. 2009, 9, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
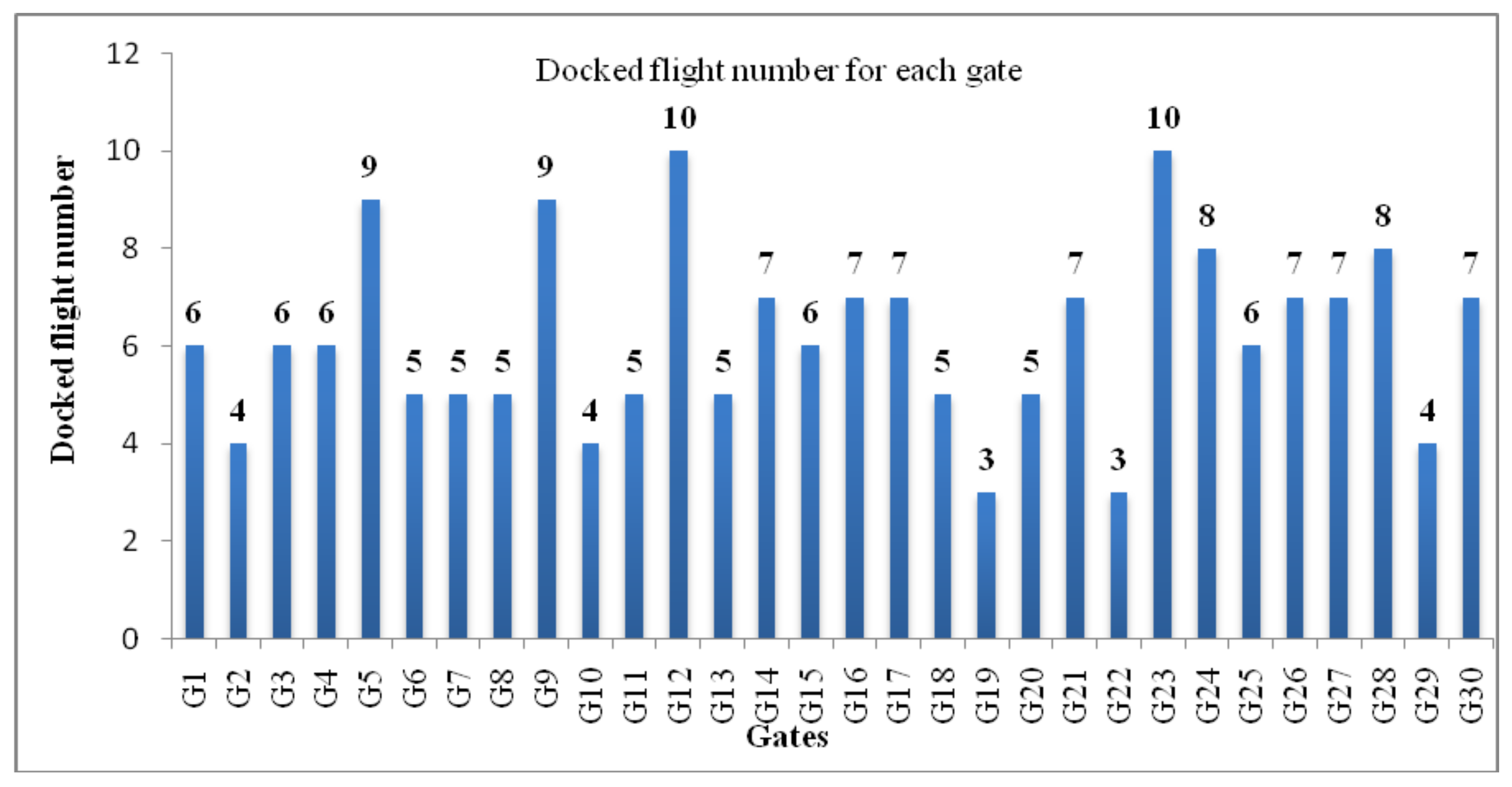
| Gate | Type | Walking Distance (m) | Gate | Type | Walking Distance (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | M | 190 | G16 | L | 115 |
| G2 | M | 975 | G17 | M | 215 |
| G3 | L | 400 | G18 | S | 535 |
| G4 | M | 333 | G19 | M | 1050 |
| G5 | L | 260 | G20 | M | 170 |
| G6 | S | 135 | G21 | L | 585 |
| G7 | M | 1100 | G22 | M | 1250 |
| G8 | M | 150 | G23 | L | 500 |
| G9 | L | 384 | G24 | L | 920 |
| G10 | M | 960 | G25 | L | 270 |
| G11 | S | 1000 | G26 | M | 230 |
| G12 | L | 235 | G27 | L | 265 |
| G13 | S | 1200 | G28 | L | 450 |
| G14 | M | 580 | G29 | M | 1300 |
| G15 | M | 440 | G30 | L | 426 |
| Flight | Arrival Time | Departure Time | Walking Distance (m) | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 26 July 2015 0:05:00 | 26 July 2015 1:15:00 | 482 | M |
| F2 | 26 July 2015 0:05:00 | 26 July 2015 1:45:00 | 273 | S |
| F3 | 26 July 2015 0:10:00 | 26 July 2015 1:30:00 | 261 | S |
| F4 | 26 July 2015 0:15:00 | 26 July 2015 1:30:00 | 116 | S |
| F5 | 26 July 2015 0:15:00 | 26 July 2015 3:15:00 | 244 | S |
| F6 | 26 July 2015 0:20:00 | 26 July 2015 1:30:00 | 312 | M |
| F7 | 26 July 2015 0:25:00 | 26 July 2015 2:40:00 | 340 | M |
| F8 | 26 July 2015 0:30:00 | 26 July 2015 1:00:00 | 198 | S |
| F9 | 26 July 2015 0:35:00 | 26 July 2015 8:10:00 | 184 | S |
| F10 | 26 July 2015 0:35:00 | 26 July 2015 10:55:00 | 494 | M |
| F11 | 26 July 2015 0:40:00 | 26 July 2015 7:00:00 | 19 | L |
| F12 | 26 July 2015 0:45:00 | 26 July 2015 6:40:00 | 443 | L |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| F200 | 26 July 2015 19:30:00 | 26 July 2015 20:25:00 | 252 | S |
| F201 | 26 July 2015 19:35:00 | 26 July 2015 20:25:00 | 378 | M |
| Gate | Flights | Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | F38 | F59 | F78 | F96 | F140 | F172 | 6 | ||||
| G2 | F36 | F116 | F135 | F159 | 4 | ||||||
| G3 | F34 | F74 | F95 | F107 | F134 | F148 | 6 | ||||
| G4 | F8 | F32 | F101 | F110 | F147 | F173 | 6 | ||||
| G5 | F15 | F41 | F56 | F71 | F94 | F100 | F113 | F129 | F157 | 9 | |
| G6 | F31 | F51 | F126 | F141 | F169 | 5 | |||||
| G7 | F17 | F65 | F89 | F124 | F179 | 5 | |||||
| G8 | F1 | F30 | F46 | F60 | F164 | 5 | |||||
| G9 | F10 | F29 | F40 | F58 | F70 | F88 | F139 | F146 | F156 | 9 | |
| G10 | F16 | F48 | F90 | F161 | 4 | ||||||
| G11 | F13 | F37 | F53 | F145 | F171 | 5 | |||||
| G12 | F14 | F61 | F72 | F92 | F106 | F115 | F131 | F144 | F155 | F193 | 10 |
| G13 | F3 | F133 | F151 | F160 | F189 | 5 | |||||
| G14 | F28 | F39 | F50 | F132 | F152 | F163 | F198 | 7 | |||
| G15 | F18 | F44 | F68 | F166 | F185 | F192 | 6 | ||||
| G16 | F26 | F42 | F108 | F119 | F123 | F162 | F184 | 7 | |||
| G17 | F6 | F45 | F55 | F67 | F109 | F150 | F195 | 7 | |||
| G18 | F25 | F82 | F86 | F167 | F199 | 5 | |||||
| G19 | F4 | F112 | F197 | 3 | |||||||
| G20 | F24 | F43 | F57 | F69 | F187 | 5 | |||||
| G21 | FF23 | F87 | F105 | F118 | F125 | F158 | F188 | 7 | |||
| G22 | F22 | F177 | F183 | 3 | |||||||
| G23 | F9 | F21 | F33 | F47 | F52 | F64 | F73 | F168 | F181 | F191 | 10 |
| G24 | F2 | F99 | F111 | F122 | F130 | F149 | F170 | F190 | 8 | ||
| G25 | F11 | F35 | F54 | F63 | F83 | F194 | 6 | ||||
| G26 | F12 | F27 | F117 | F128 | F138 | F176 | F182 | 7 | |||
| G27 | F20 | F49 | F62 | F80 | F85 | F153 | F196 | 7 | |||
| G28 | F7 | F75 | F91 | F104 | F120 | F127 | F137 | F201 | 8 | ||
| G29 | F19 | F66 | F154 | F200 | 4 | ||||||
| G30 | F5 | F93 | F114 | F121 | F136 | F165 | F186 | 7 | |||
| Total | 186 | ||||||||||
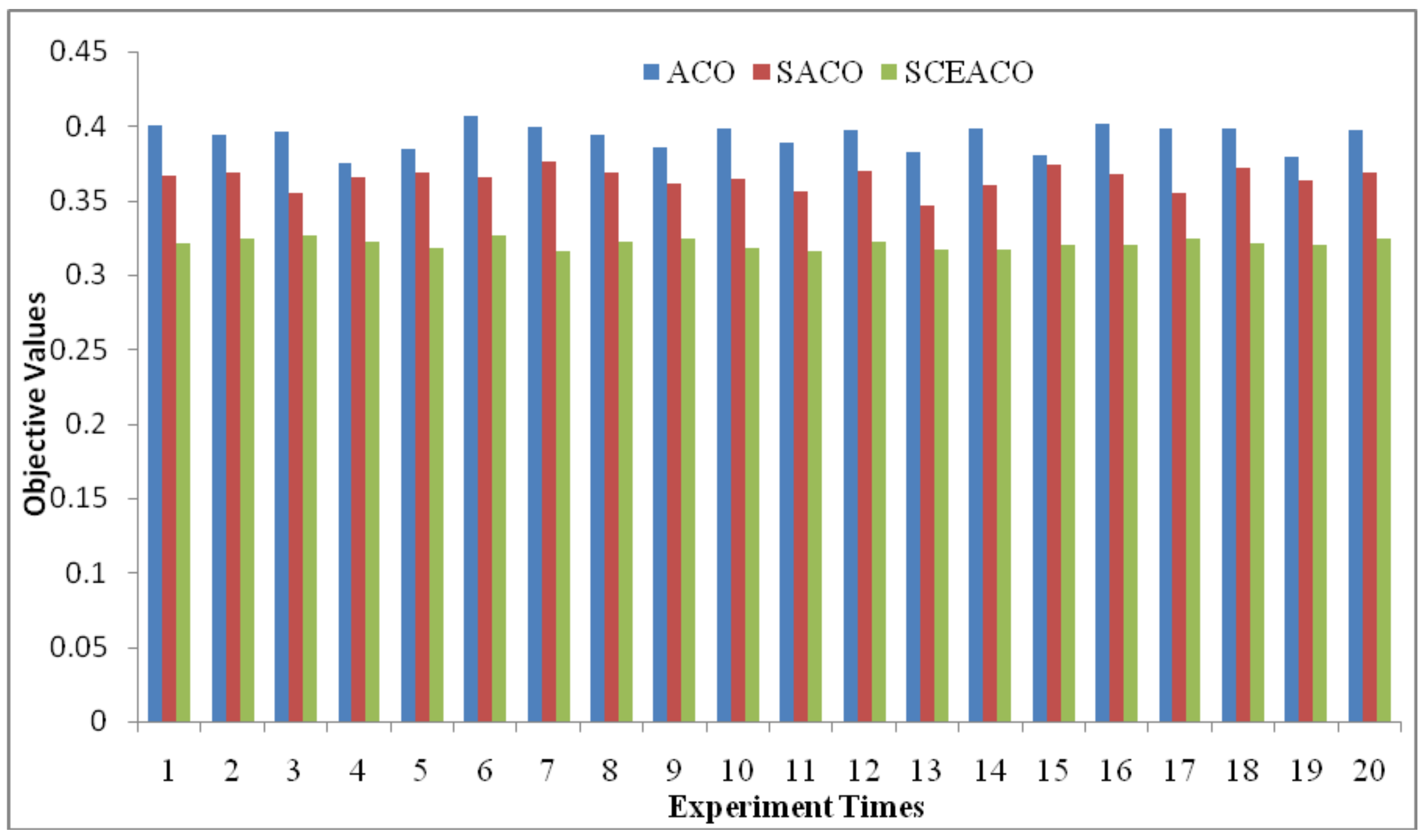
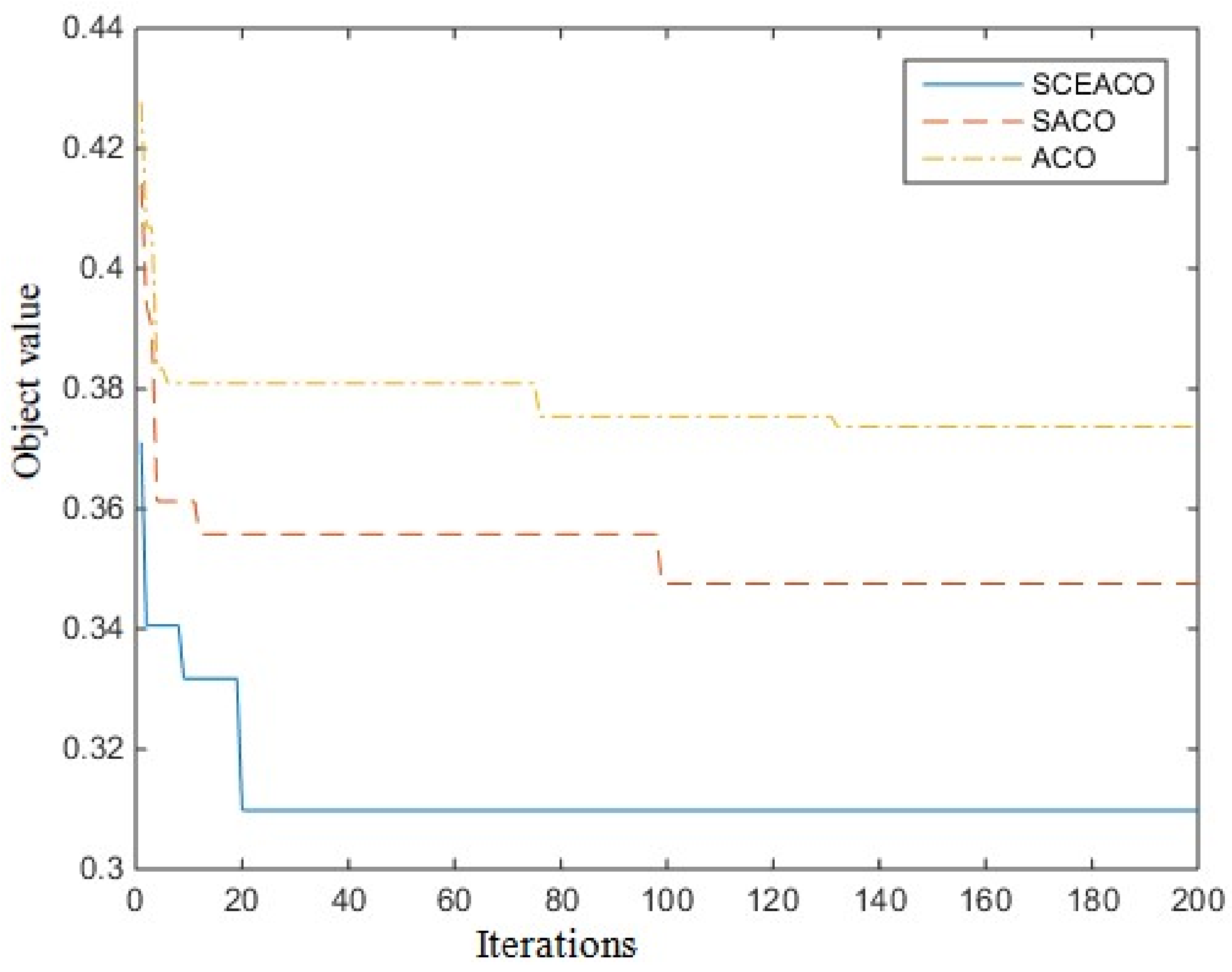
| Algorithms | ACO Algorithm | SACO Algorithm | SCEACO Algorithm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Times | Iterations | Optimal Value | Flights | Iterations | Optimal Value | Flights | Iterations | Optimal Value | Flights |
| 1 | 103 | 0.4010 | 155 | 32 | 0.3665 | 165 | 76 | 0.3216 | 181 |
| 2 | 126 | 0.3941 | 158 | 93 | 0.3686 | 161 | 83 | 0.3243 | 174 |
| 3 | 115 | 0.3962 | 153 | 98 | 0.3553 | 156 | 60 | 0.3269 | 171 |
| 4 | 58 | 0.3755 | 162 | 85 | 0.3662 | 151 | 21 | 0.322 | 177 |
| 5 | 64 | 0.3847 | 166 | 79 | 0.3689 | 170 | 58 | 0.3182 | 182 |
| 6 | 149 | 0.4070 | 155 | 61 | 0.3658 | 168 | 33 | 0.3266 | 173 |
| 7 | 121 | 0.3998 | 157 | 82 | 0.3764 | 162 | 64 | 0.3160 | 186 |
| 8 | 158 | 0.3938 | 166 | 114 | 0.3689 | 180 | 88 | 0.3225 | 175 |
| 9 | 74 | 0.3855 | 163 | 77 | 0.3613 | 162 | 18 | 0.3246 | 173 |
| 10 | 143 | 0.3987 | 167 | 83 | 0.3648 | 153 | 96 | 0.3185 | 183 |
| 11 | 69 | 0.3891 | 162 | 105 | 0.3565 | 167 | 10 | 0.3165 | 181 |
| 12 | 79 | 0.3973 | 154 | 100 | 0.3698 | 162 | 20 | 0.3227 | 180 |
| 13 | 156 | 0.3826 | 159 | 39 | 0.3471 | 167 | 37 | 0.3168 | 175 |
| 14 | 37 | 0.3990 | 163 | 74 | 0.3609 | 164 | 43 | 0.3169 | 176 |
| 15 | 103 | 0.3805 | 163 | 168 | 0.3742 | 164 | 88 | 0.3198 | 177 |
| 16 | 138 | 0.4016 | 155 | 41 | 0.3676 | 155 | 80 | 0.3207 | 183 |
| 17 | 65 | 0.3984 | 161 | 80 | 0.3556 | 163 | 76 | 0.3244 | 182 |
| 18 | 97 | 0.3988 | 157 | 73 | 0.3718 | 158 | 34 | 0.3217 | 183 |
| 19 | 141 | 0.3793 | 166 | 11 | 0.3632 | 155 | 28 | 0.3200 | 183 |
| 20 | 109 | 0.3974 | 158 | 73 | 0.3689 | 167 | 44 | 0.3244 | 173 |
| Average | 105.5 | 0.3930 | 160 | 78.4 | 0.3649 | 162.5 | 52.85 | 0.3213 | 178.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Gao, W.; Deng, W.; Sun, M. Study on an Adaptive Co-Evolutionary ACO Algorithm for Complex Optimization Problems. Symmetry 2018, 10, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10040104
Zhao H, Gao W, Deng W, Sun M. Study on an Adaptive Co-Evolutionary ACO Algorithm for Complex Optimization Problems. Symmetry. 2018; 10(4):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10040104
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Huimin, Weitong Gao, Wu Deng, and Meng Sun. 2018. "Study on an Adaptive Co-Evolutionary ACO Algorithm for Complex Optimization Problems" Symmetry 10, no. 4: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10040104
APA StyleZhao, H., Gao, W., Deng, W., & Sun, M. (2018). Study on an Adaptive Co-Evolutionary ACO Algorithm for Complex Optimization Problems. Symmetry, 10(4), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10040104