A Computational Study of a Spatiotemporal Mean Field Model Capturing the Emergence of Alpha and Gamma Rhythmic Activity in the Neocortex
Abstract
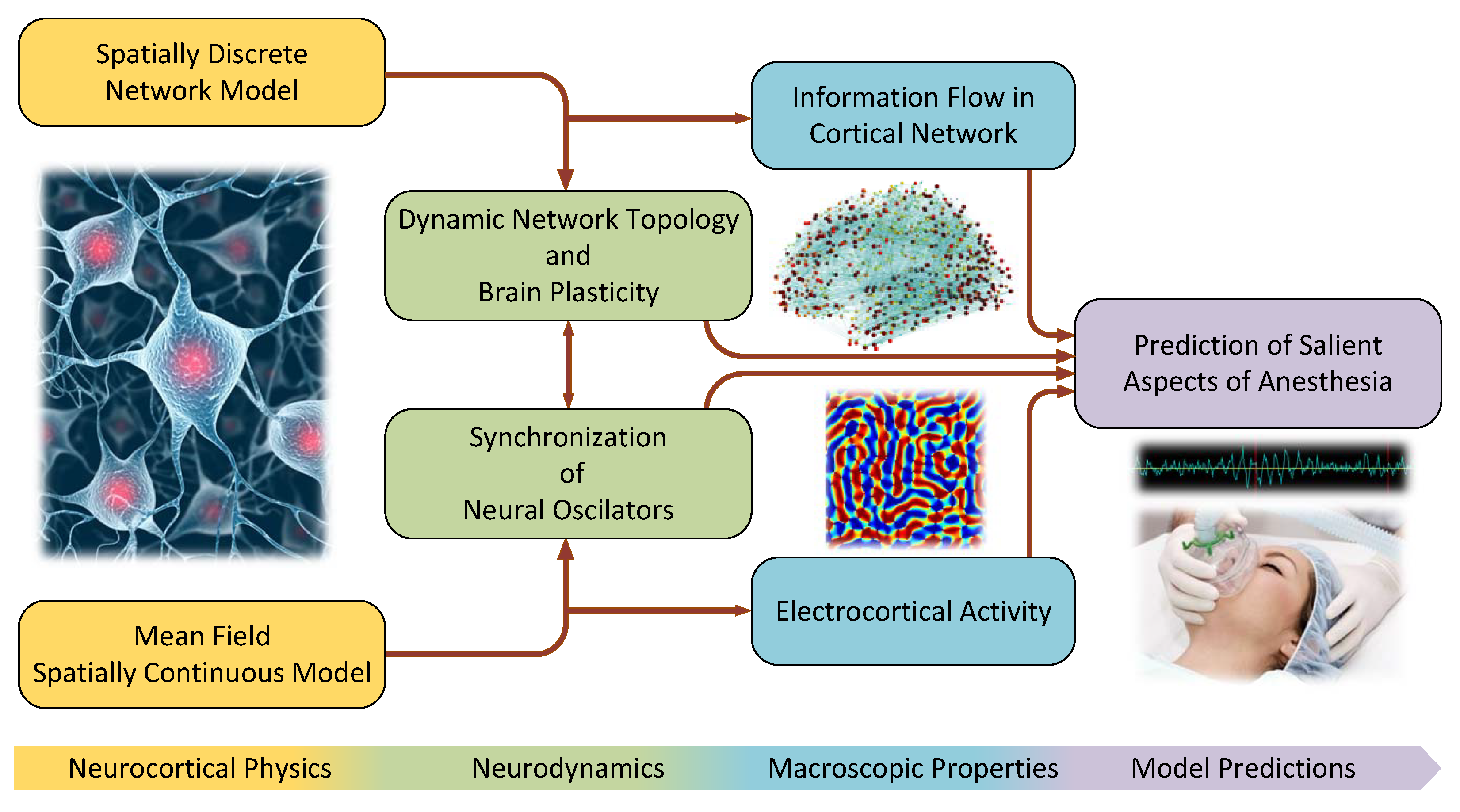
1. Introduction
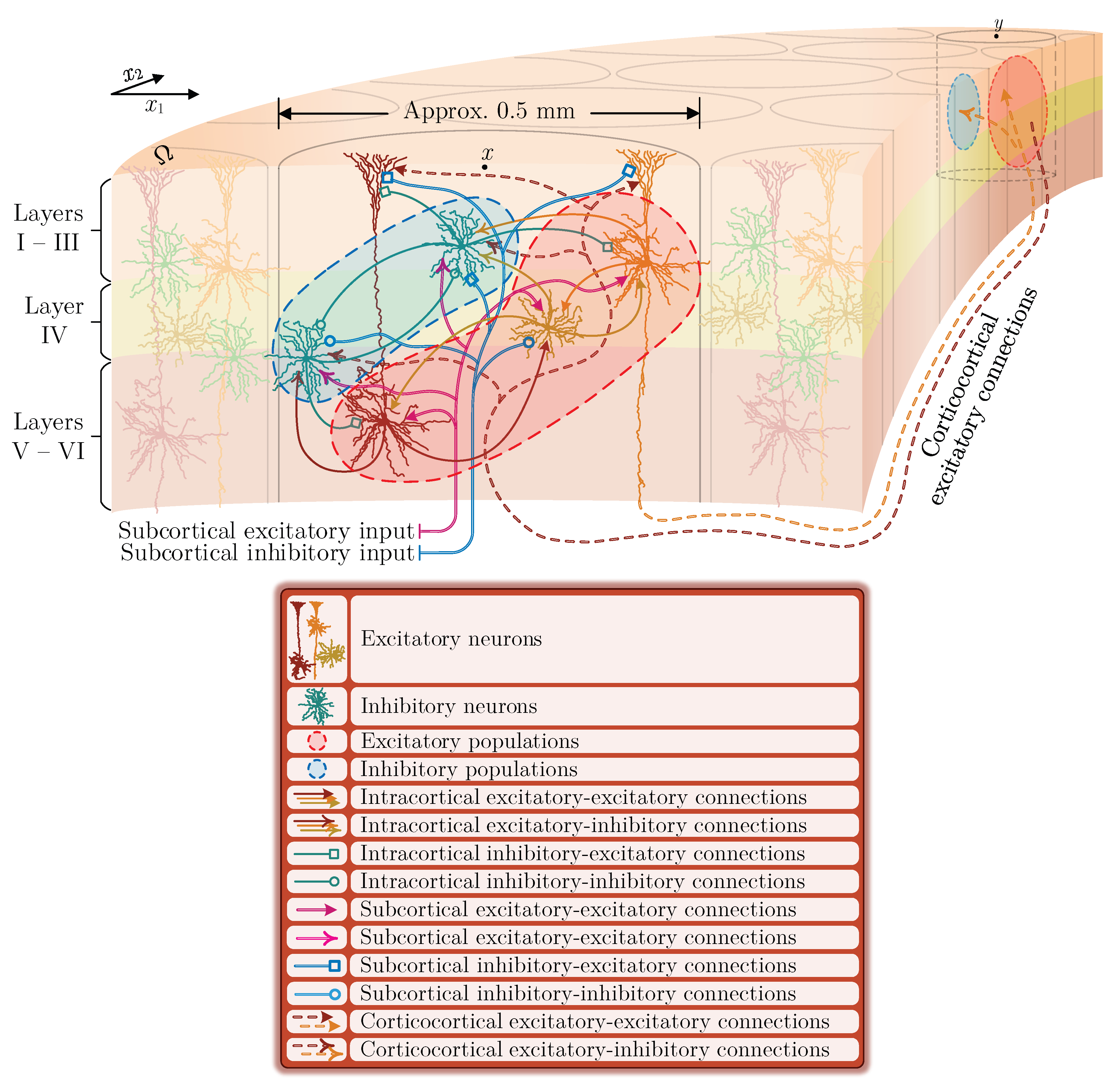
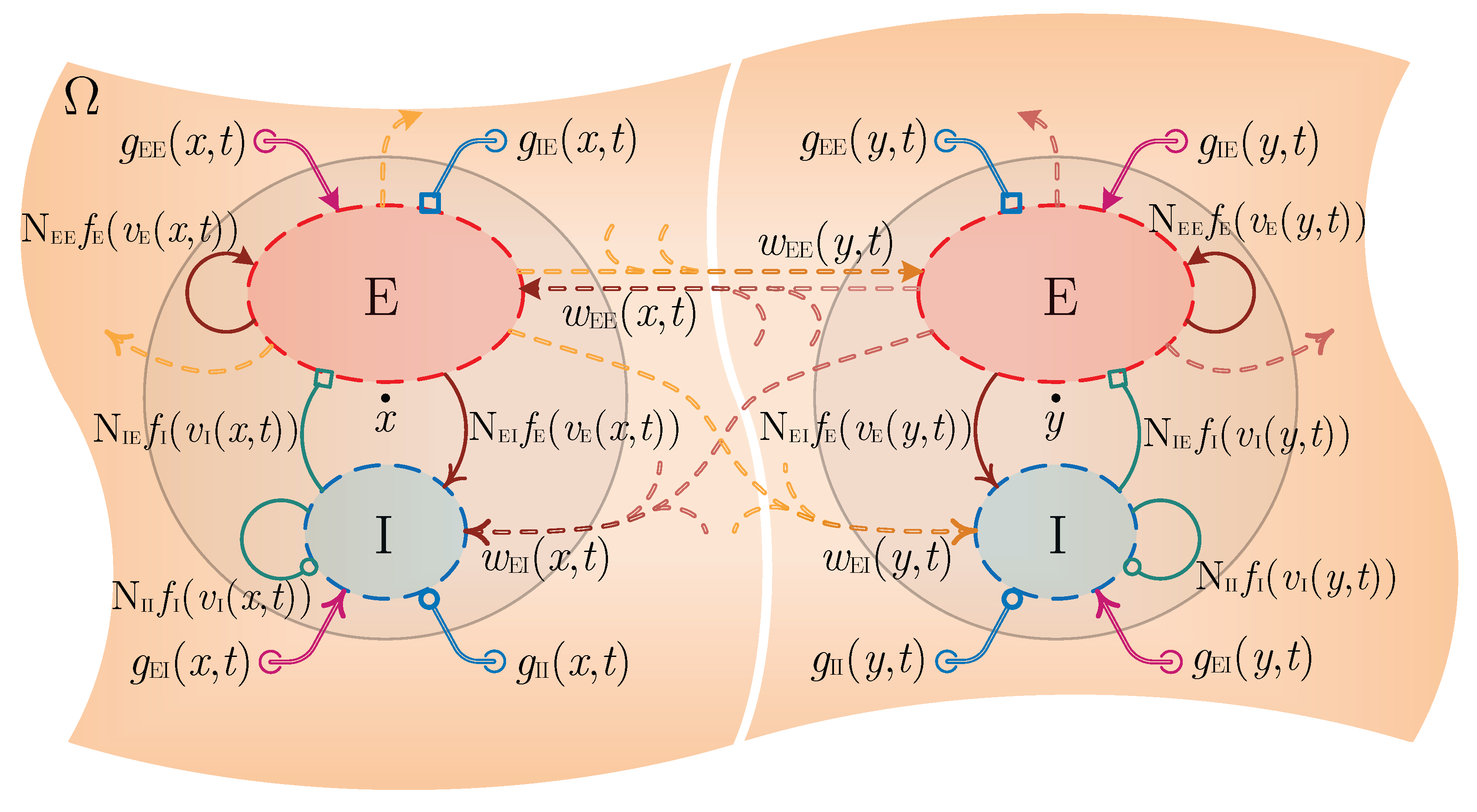
2. A Continuum Mean Field Model of Electrocortical Activity
3. Computational Framework
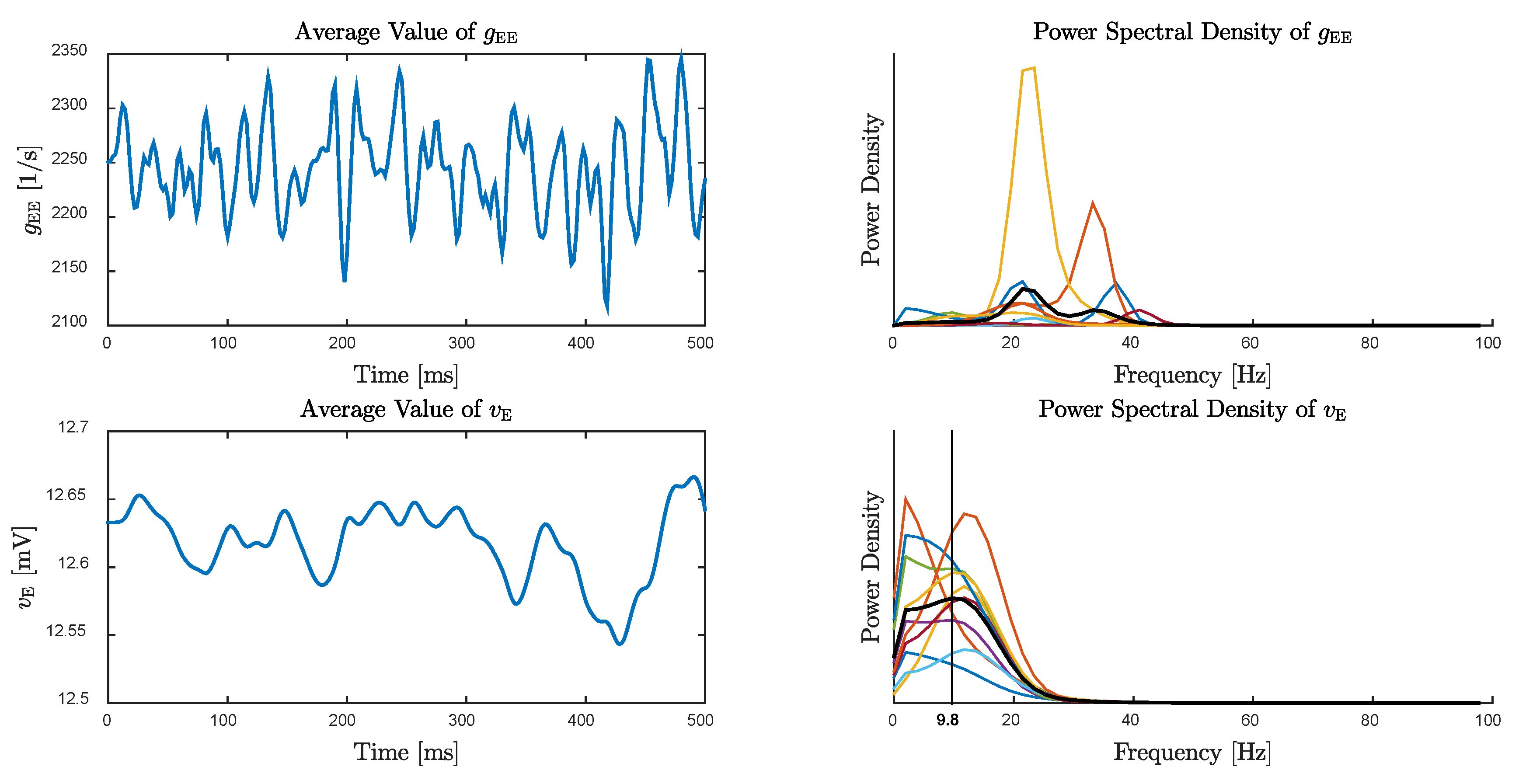
4. Alpha Rhythms in the Resting State
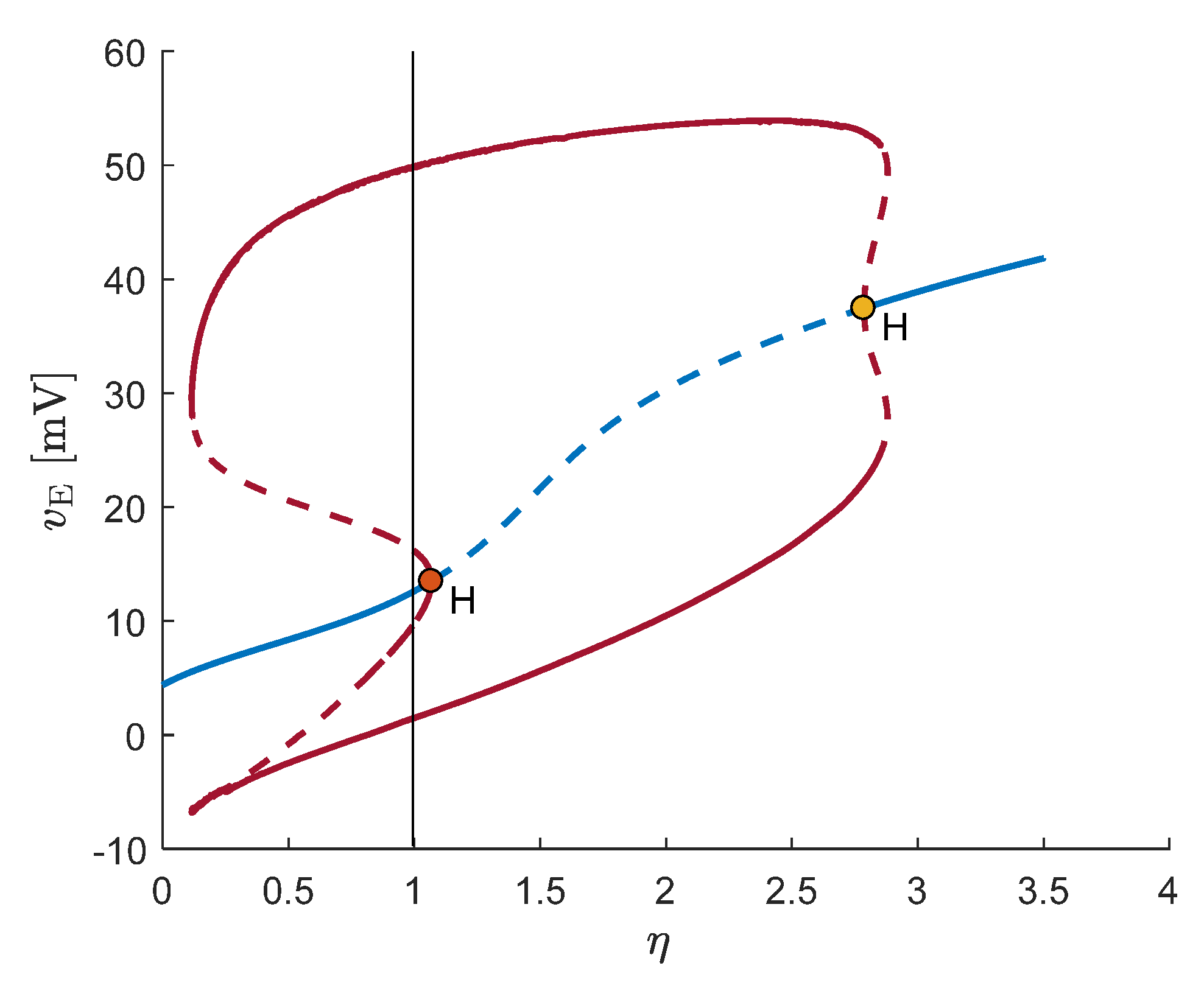
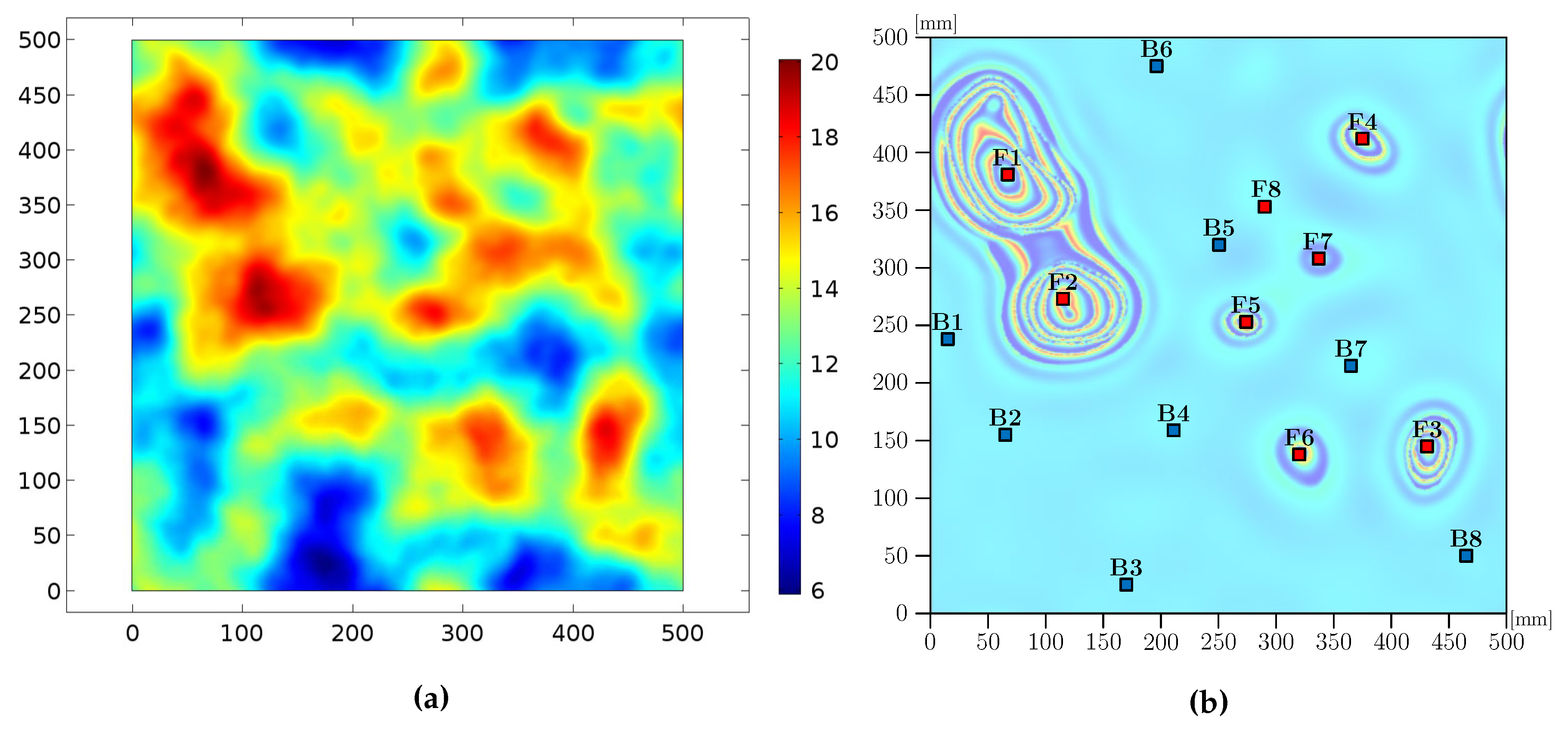
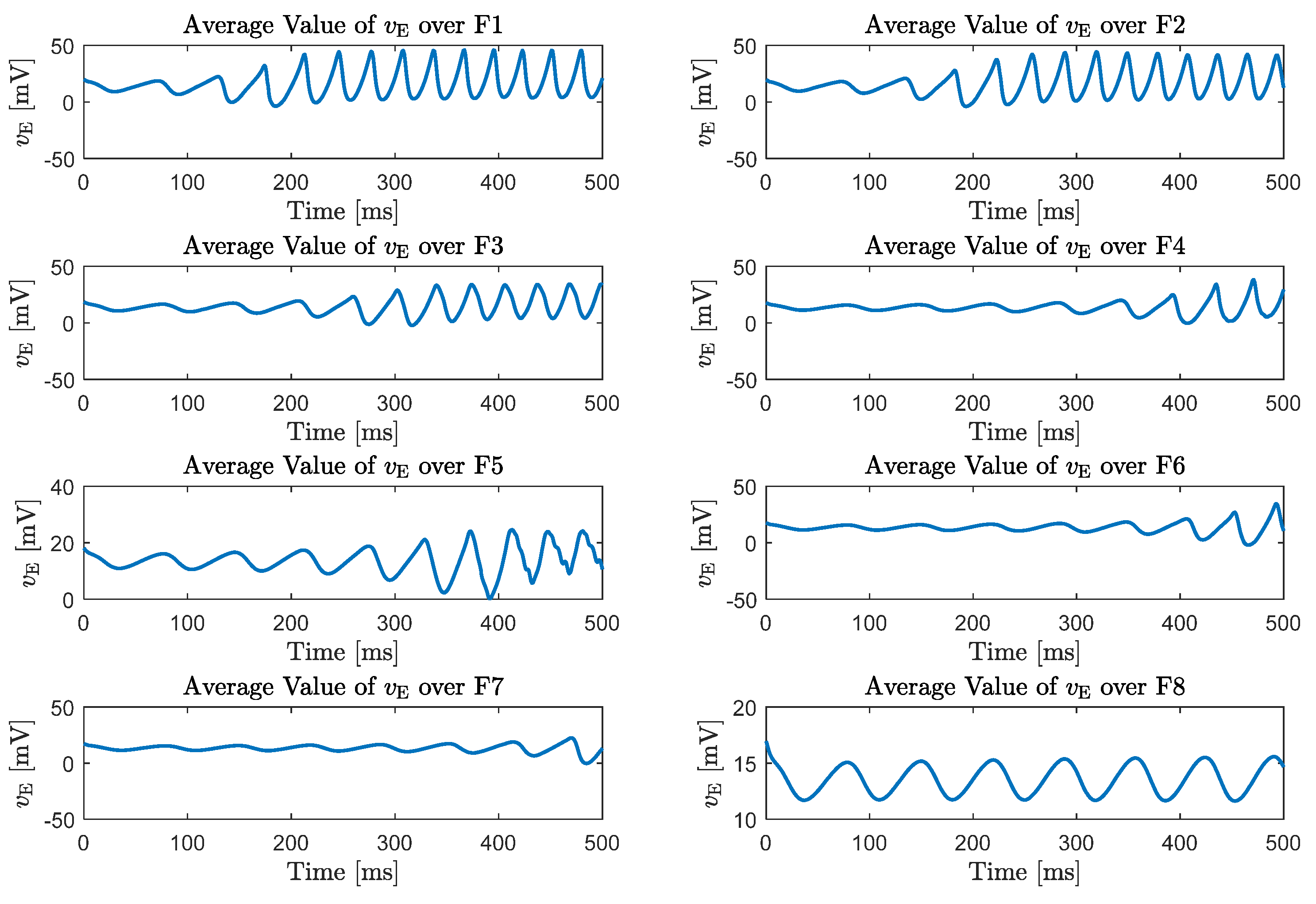
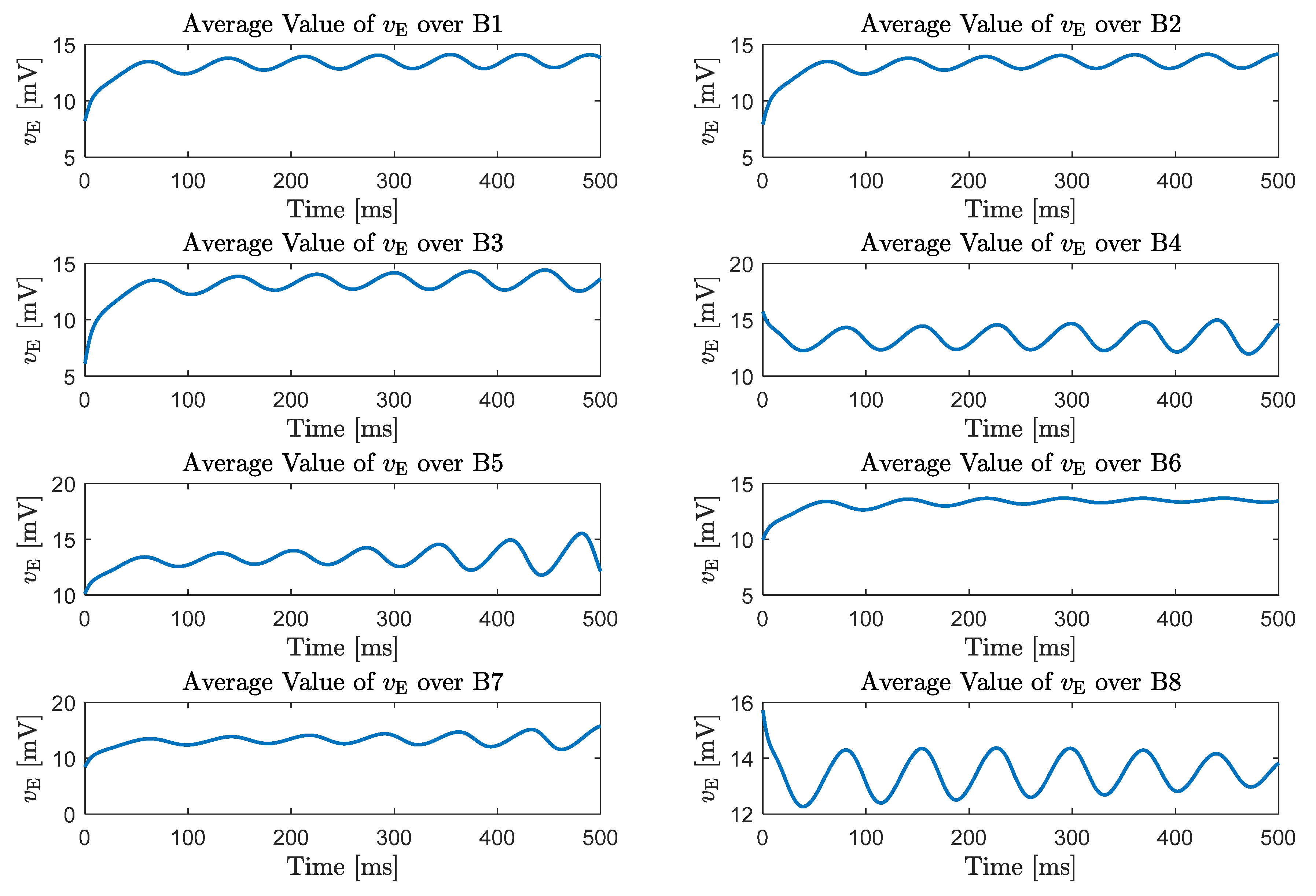
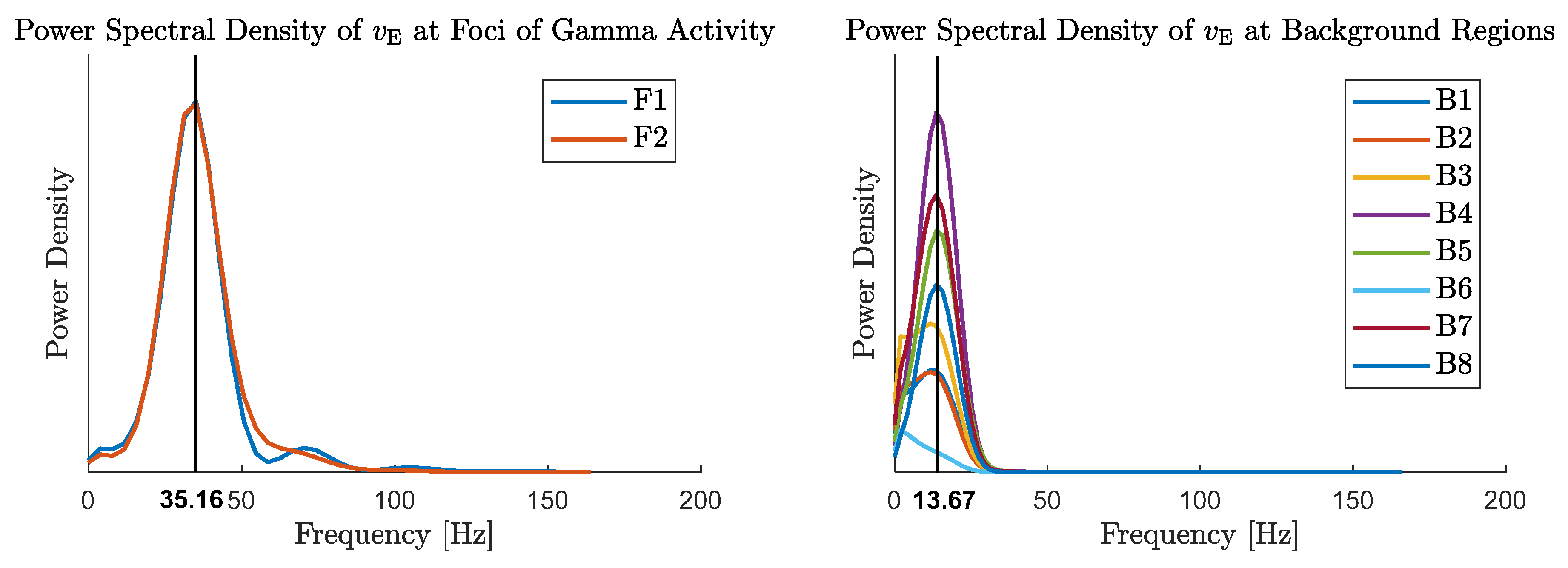
5. Emergence of Gamma Rhythms
6. Conclusions and Future Research Directions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 1952, 117, 500–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutt, A.; Griffiths, J.D.; Herrmann, C.S.; Lefebvre, J. Effect of stimulation waveform on the non-linear entrainment of cortical alpha oscillations. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.; Brown, E.N. Modeling the dynamical effects of anesthesia on brain circuits. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 25, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyamura, A.; Marszalec, W.; Yeh, J.Z.; Narahishi, T. Effects of halothane and propofol on excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in rat cortical neurons. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 304, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Hutt, A.; Longtin, A. Effects of the anesthetic agent propofol on neural populations. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2009, 4, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyn-Ross, M.L.; Steyn-Ross, D.A.; Sleigh, J.W. Modelling general anaesthesia as a first-order phase transition in the cortex. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2004, 85, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.P.; Haddad, W.M.; Meskin, N.; Bailey, J.M. A mechanistic neural mean field theory of how anesthesia suppresses consciousness: Synaptic drive dynamics, system stability, attractors, partial synchronization, and the anesthetic cascade. J. Math. Neurosci. 2015, 2015, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bojak, I.; Liley, D.T.J. Modeling the effects of anesthesia on the electroencephalogram. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 041902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermentrout, G.B.; Terman, D.H. Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gutkin, B.; Pinto, D.; Ermentrout, G.B. Mathematical neuroscience: From neurons to circuits to systems. J. Physiol. 2003, 97, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, Q.; Haddad, W.M.; Bailey, J.M. Multistability, bifurcations, and biological neural networks: A synaptic drive firing model for cerebral cortex transition in the induction of general anesthesia. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 2011, 5, 554–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Q.; Haddad, W.M.; Bailey, J.M.; Hayakawa, T. A stochastic mean field model for an excitatory and inhibitory synaptic drive cortical neuronal network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2014, 24, 751–763. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, W.M.; Hui, Q.; Bailey, J.M. Human brain networks: Spiking neuron models, multistability, synchronization, thermodynamics, maximum entropy production, and anesthetic cascade mechanisms. Entropy 2014, 16, 3939–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liley, D.T.J.; Cadusch, P.J.; Dafilis, M.P. A spatially continuous mean field theory of electrocortical dynamics. Netw. Comput. Neural Syst. 2002, 13, 67–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.R.; Cowan, J.D. Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons. Biophys. J. 1972, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.R.; Cowan, J.D. A mathematical theory of the functional dynamics of cortical and thalamic nervous tissue. Kybernetik 1973, 13, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojak, I.; Liley, D.T.J. Self-organized 40 Hz synchronization in a physiological theory of EEG. Neurocomputing 2007, 70, 2085–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, F.; Haddad, W.M.; de la Llave, R. On the global dynamics of an electroencephalographic mean field model of the neocortex. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 2017, 16, 1969–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R.; Schwartz, J.H.; Jessell, T.M.; Siegelbaum, S.A.; Hudspeth, A.J. Principles of Neural Science, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mountcastle, V.B. The columnar organization of the neocortex. Brain 1997, 120, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.C.; Adams, D.L. The cortical column: A structure without a function. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2005, 360, 837–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liley, D.T.J.; Walsh, M. The mesoscopic modelling of burst suppression during anaesthesia. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojak, I.; Stoyanov, Z.V.; Liley, D. Emergence of spatially heterogeneous burst suppression in a neural field model of electrocortical activity. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frascoli, F.; van Veen, L.; Bojak, I.; Liley, D.T.J. Metabifurcation analysis of a mean field model of the cortex. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2011, 240, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashour, G.A. Consciousness and the 21st Century Operating Room. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, D.; Ilg, R.; Riedl, V.; Schorer, A.; Grimberg, S.; Neufang, S.; Omerovic, A.; Berger, S.; Untergehrer, G.; Preibisch, C.; et al. Simultaneous electroencephalographic and functional magnetic resonance imaging indicate impaired cortical top-down processing in association with anesthetic-induced unconsciousness. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Mashour, G.A.; Kim, S.; Lee, U. Reconfiguration of network hub structure after propofol-induced unconsciousness. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 1347–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, S.; Cimenser, A.; Purdon, P.L.; Brown, E.N.; Kopell, N.J. Thalamocortical model for a propofol-induced α-rhythm associated with loss of consciousness. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22665–22670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuizenga, K.; Wierda, J.; Kalkman, C. Biphasic EEG changes in relation to loss of consciousness during induction with thiopental, propofol, etomidate, midazolam or sevoflurane. Br. J. Anaesth. 2001, 86, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojak, I.; Day, H.C.; Liley, D.T.J. Ketamine, Propofol, and the EEG: A neural field analysis of HCN1-mediated interactions. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, B.L.; Bojak, I.; Liley, D.T.J. Population based models of cortical drug response: Insights from anaesthesia. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2008, 2, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.A.; Kirsch, H.E.; Szeri, A.J. Pathological pattern formation and cortical propagation of epileptic seizures. J. R. Soc. Interface 2005, 2, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.A.; Szeri, A.J.; Sleigh, J.W.; Kirsch, H.E. Mechanisms of seizure propagation in a cortical model. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2006, 22, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liley, D.T.J.; Bojak, I. Understanding the transition to seizure by modeling the epileptiform activity of general anesthetic agents. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 22, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, K.R.; van Veen, L. Open-source tools for dynamical analysis of Liley’s mean-field cortex model. J. Comput. Sci. 2014, 5, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.A.; Truccolo, W.; Eden, U.T.; Lepage, K.Q.; Hochberg, L.R.; Eskandar, E.N.; Madsen, J.R.; Lee, J.W.; Maheshwari, A.; Halgren, E.; et al. Human seizures self-terminate across spatial scales via a critical transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21116–21121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dafilis, M.P.; Frascoli, F.; Cadusch, P.J.; Liley, D.T.J. Four dimensional chaos and intermittency in a mesoscopic model of the electroencephalogram. Chaos 2013, 23, 023111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dafilis, M.P.; Frascoli, F.; Cadusch, P.J.; Liley, D.T.J. Extensive four-dimensional chaos in a mesoscopic model of the electroencephalogram. J. Math. Neurosci. 2015, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Veen, L.; Green, K.R. Periodic solutions to a mean-field model for electrocortical activity. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2014, 223, 2979–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, L.; Liley, D.T.J. Chaos via Shilnikov’s Saddle-Node Bifurcation in a Theory of the Electroencephalogram. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 208101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhooge, A.; Govaerts, W.; Kuznetsov, Y.A.; Meijer, H.G.E.; Sautois, B. New features of the software MatCont for bifurcation analysis of dynamical systems. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 2008, 14, 147–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimburg, T.; Jackson, A.D. On soliton propagation in biomembranes and nerves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9790–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaki, I. Evidence for phase transitions in nerve fibers, cells and synapses. Ferroelectrics 1999, 220, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Definition | Range | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passive excitatory membrane decay time constant | s | ||
| Passive inhibitory membrane decay time constant | s | ||
| , | Mean excitatory Nernst potentials | mV | |
| , | Mean inhibitory Nernst potentials | [–– | mV |
| , | Excitatory postsynaptic potential rate constants | s | |
| , | Inhibitory postsynaptic potential rate constants | s | |
| , | Amplitude of excitatory postsynaptic potentials | mV | |
| , | Amplitude of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials | mV | |
| , | Number of intracortical excitatory connections | — | |
| , | Number of intracortical inhibitory connections | — | |
| Corticocortical conduction velocity | cm/s | ||
| , | Decay scale of corticocortical excitatory connectivities | cm | |
| , | Number of corticocortical excitatory connections | — | |
| Maximum mean excitatory firing rate | s | ||
| Maximum mean inhibitory firing rate | s | ||
| Excitatory firing threshold potential | mV | ||
| Inhibitory firing threshold potential | mV | ||
| Standard deviation of excitatory firing threshold potential | mV | ||
| Standard deviation of inhibitory firing threshold potential | mV |
| Parameter | ||||||||
| Value | ||||||||
| Parameter | ||||||||
| Value | ||||||||
| Parameter | ||||||||
| Value | 3228 | |||||||
| Parameter | ||||||||
| Value | 0 | 0 |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haddad, W.M. A Computational Study of a Spatiotemporal Mean Field Model Capturing the Emergence of Alpha and Gamma Rhythmic Activity in the Neocortex. Symmetry 2018, 10, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10110568
Haddad WM. A Computational Study of a Spatiotemporal Mean Field Model Capturing the Emergence of Alpha and Gamma Rhythmic Activity in the Neocortex. Symmetry. 2018; 10(11):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10110568
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaddad, Wassim M. 2018. "A Computational Study of a Spatiotemporal Mean Field Model Capturing the Emergence of Alpha and Gamma Rhythmic Activity in the Neocortex" Symmetry 10, no. 11: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10110568
APA StyleHaddad, W. M. (2018). A Computational Study of a Spatiotemporal Mean Field Model Capturing the Emergence of Alpha and Gamma Rhythmic Activity in the Neocortex. Symmetry, 10(11), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10110568




