Super Potent Bispecific Llama VHH Antibodies Neutralize HIV via a Combination of gp41 and gp120 Epitopes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
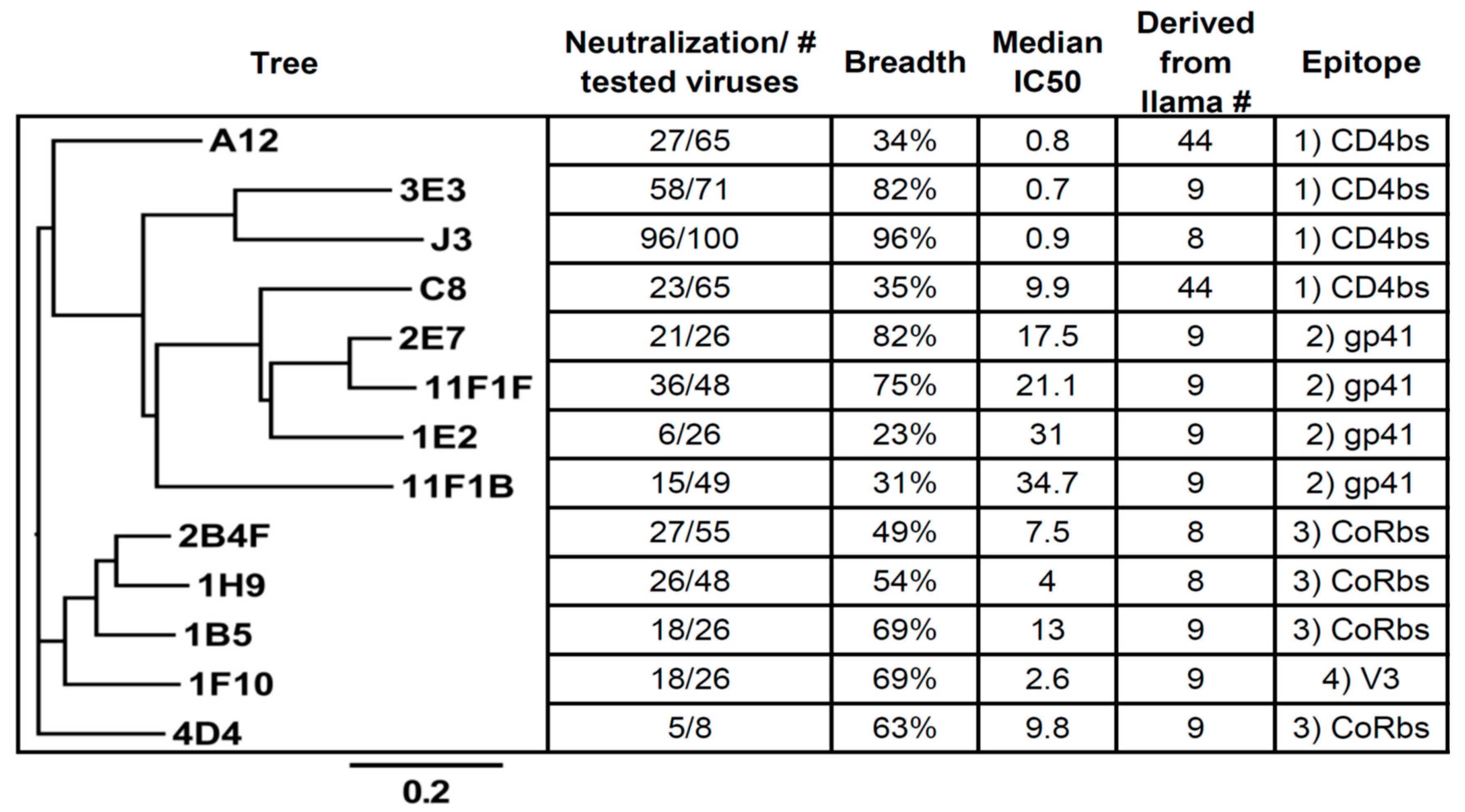
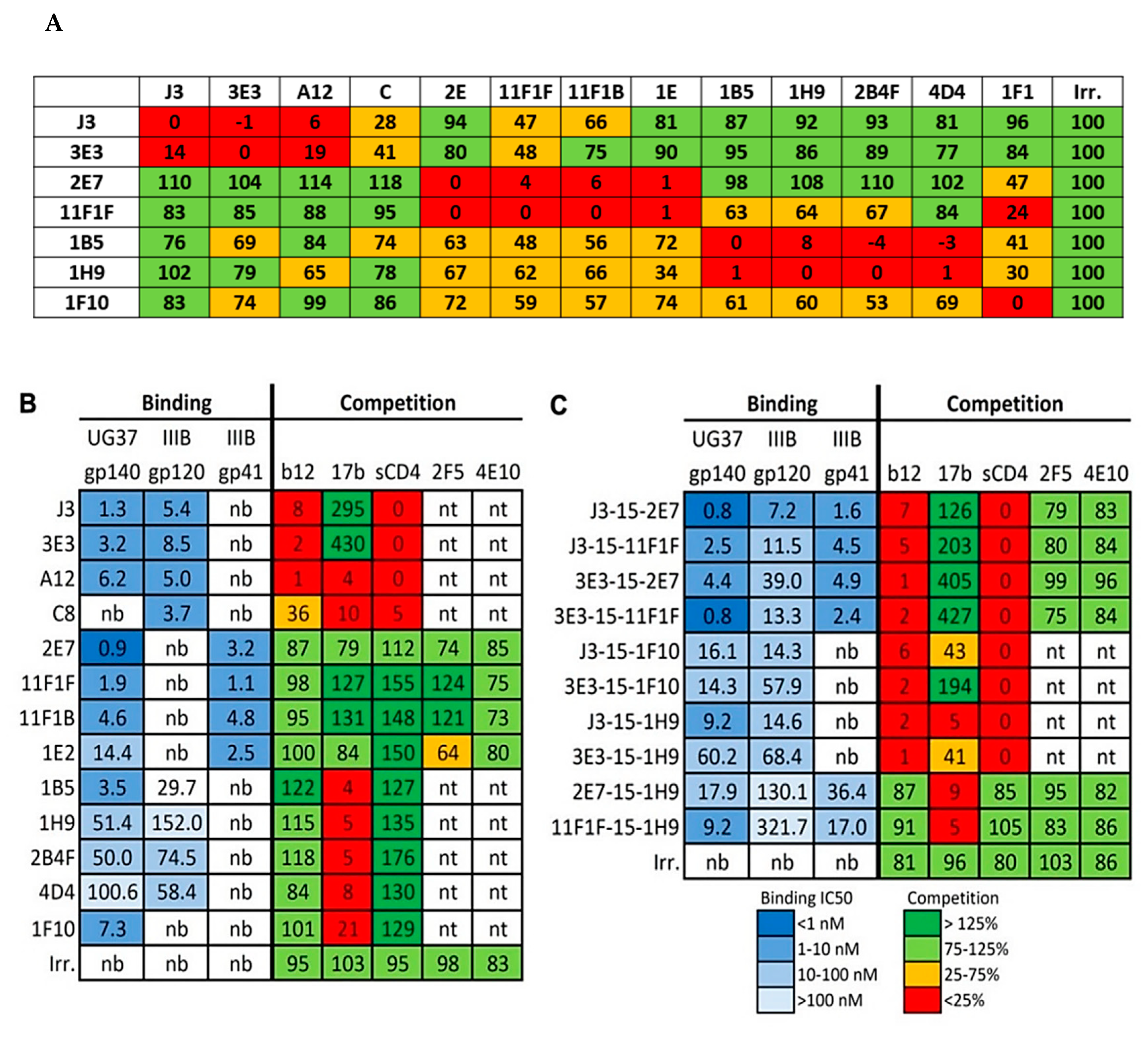
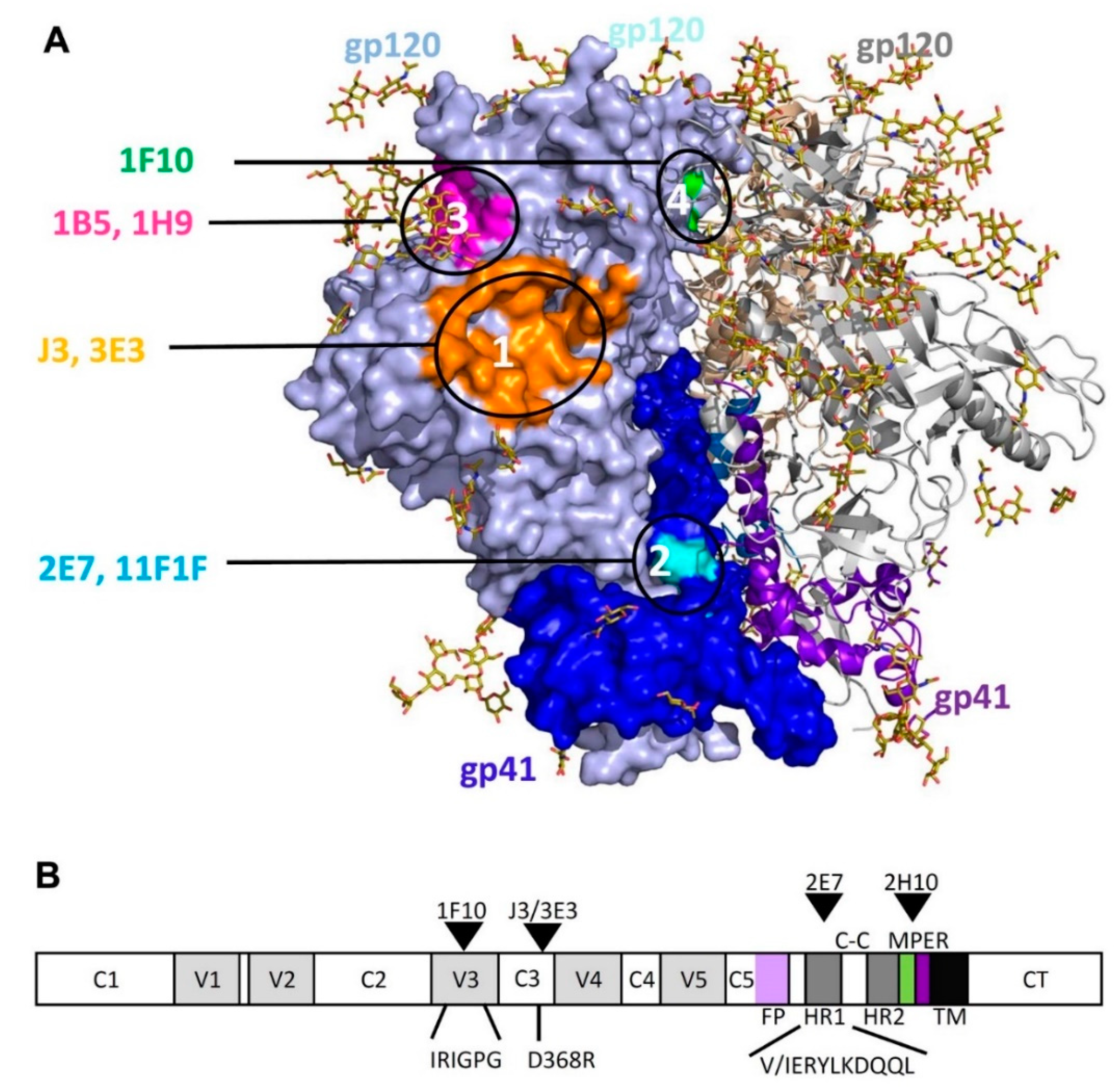
2.1. Competition-Based Determination of 4 Different Epitope Groups
2.1.1. Epitope Group I, VHH That Bind to CD4bs
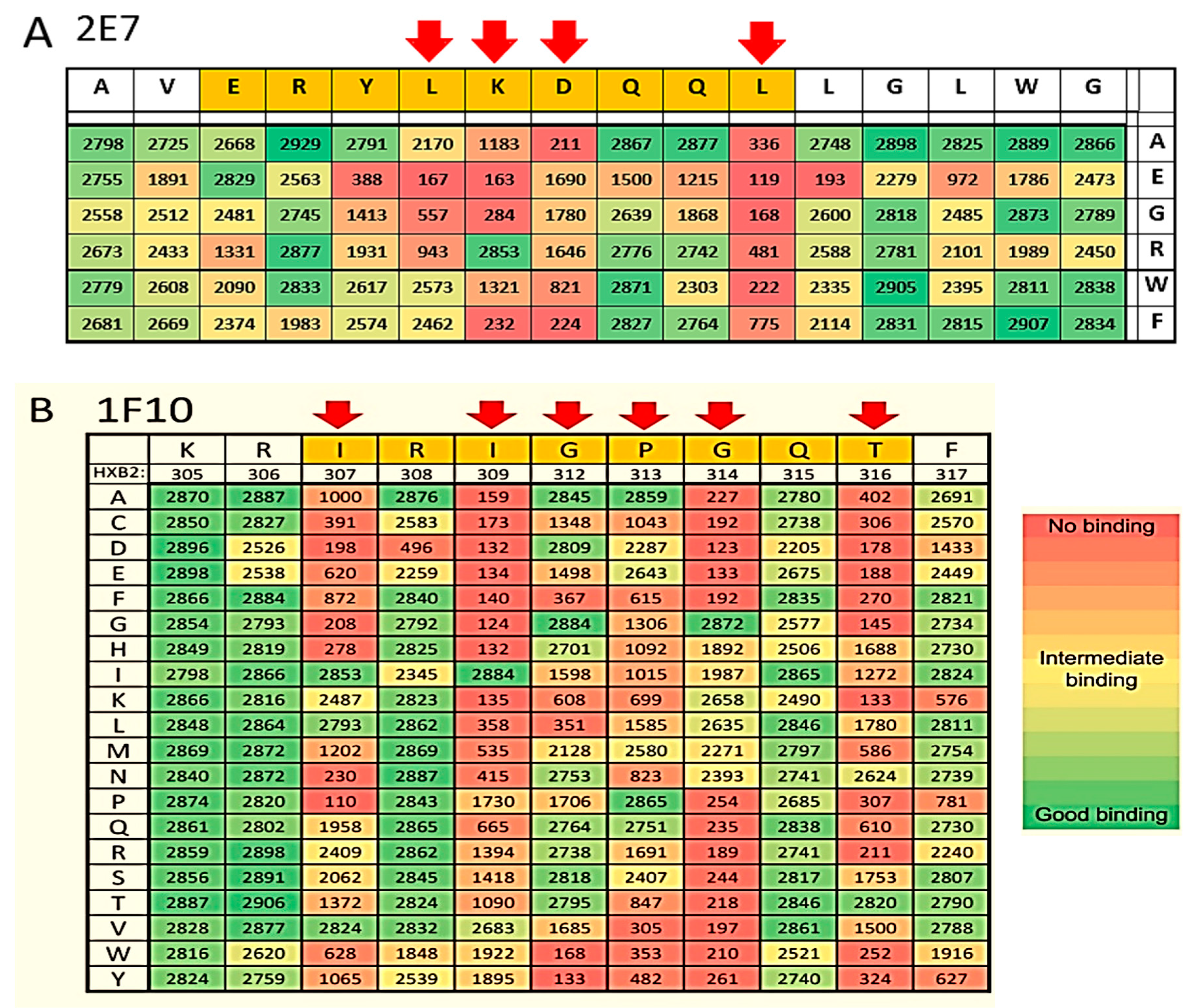
2.1.2. Epitope Group II Consisting of 2E7, 11F1F, 1E2 and 11F1B and Their Family Members
2.1.3. Epitope Group III Consisting of 1B5 and 1H9 and Family Members Recognize Part of the Co-Receptor Binding Site
2.1.4. Epitope Group IV Consisting of 1F10 Binds to the Crown of the V3 Loop
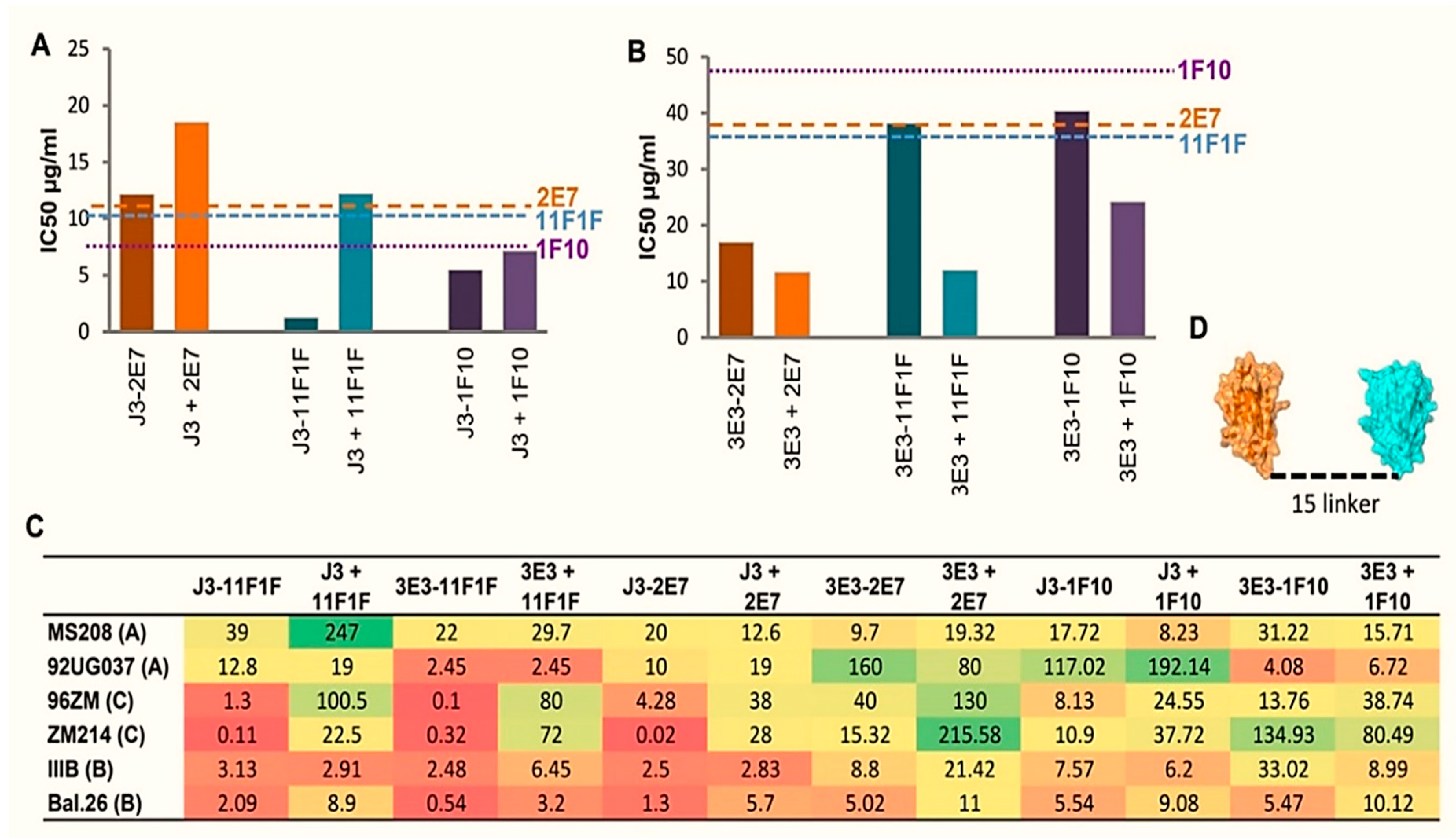
2.2. Construction of Bispecific anti-HIV VHH
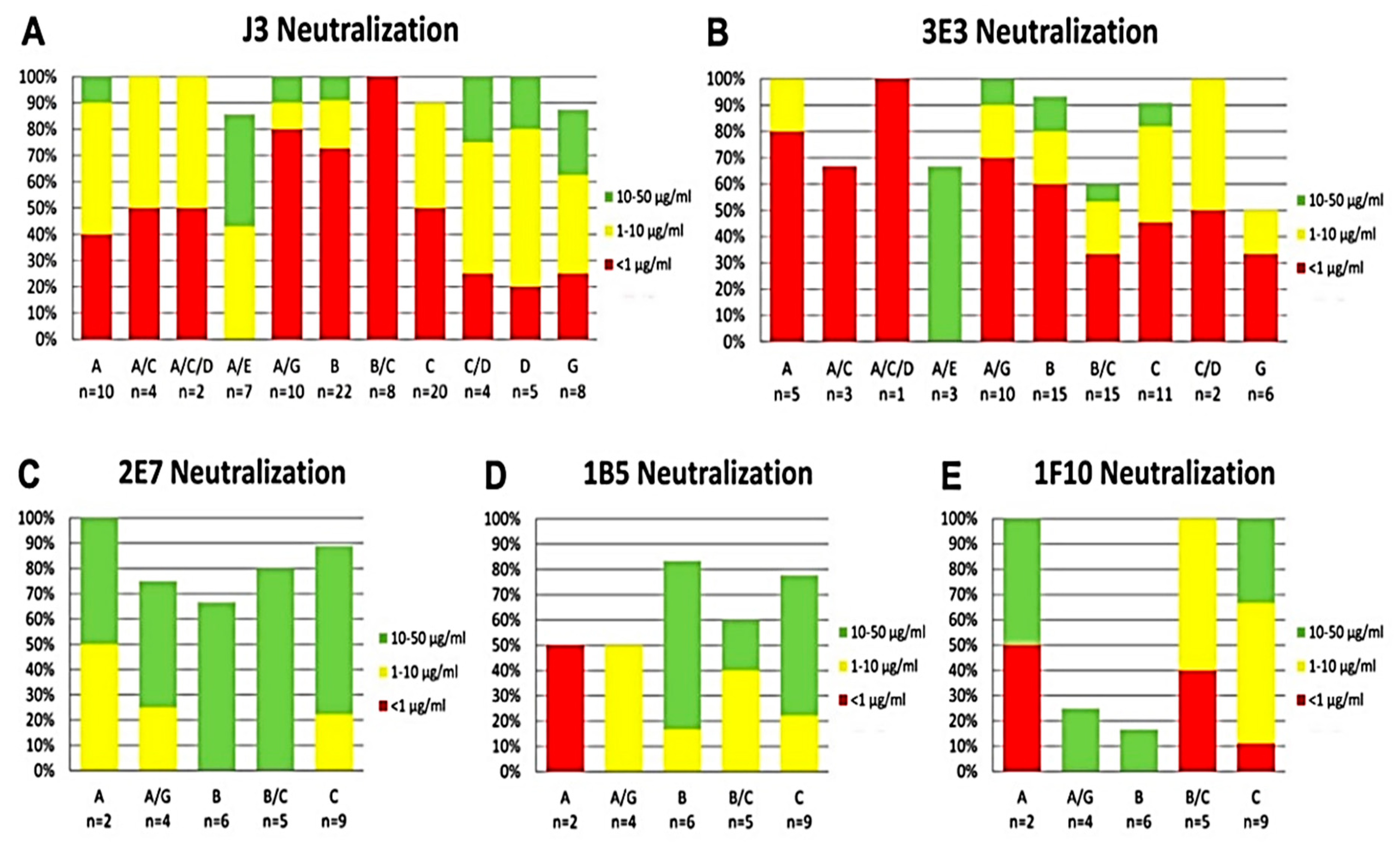
2.3. Broad and Potent HIV Neutralization by bi-Specific VHH Targeting a Combination of gp120 and gp41 Epitopes
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Materials and Methods
4.1.1. Proteins
4.1.2. Viruses
4.1.3. Cells
4.1.4. VHH
4.2. Cross-Competition Assay
4.3. Binding to Various Env Proteins
4.4. Competition Assay with mAbs and sCD4
4.5. Construction of bi-Specific VHH
4.6. HIV Neutralization Assay
4.7. Epitope Mapping
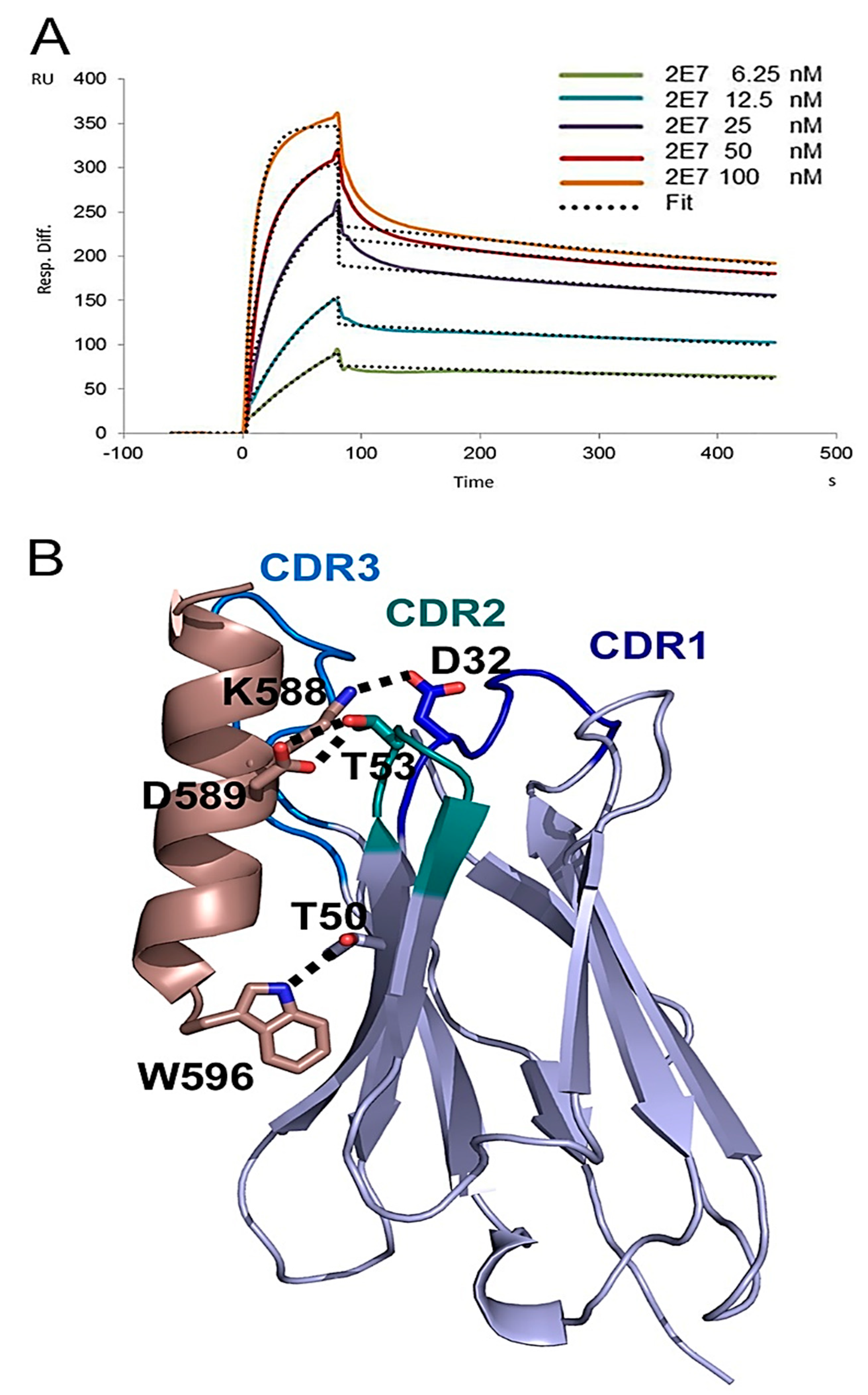
4.8. Crystal Structure of VHH 2E7 in Complex with a gp41 Peptide
4.9. SPR Analysis of 2E7 Binding to gp41int
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granelli-Piperno, A.; Pritsker, A.; Pack, M.; Shimeliovich, I.; Arrighi, J.F.; Park, C.G.; Trumpfheller, C.; Piguet, V.; Moran, T.M.; Steinman, R.M. Dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule 3-grabbing nonintegrin/CD209 is abundant on macrophages in the normal human lymph node and is not required for dendritic cell stimulation of the mixed leukocyte reaction. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4265–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdool Karim, Q.; Abdool Karim, S.S.; Frohlich, J.A.; Grobler, A.C.; Baxter, C.; Mansoor, L.E.; Kharsany, A.B.; Sibeko, S.; Mlisana, K.P.; Omar, Z.; et al. CAPRISA 004 Trial Group Effectiveness and safety of tenofovir gel, an antiretroviral microbicide, for the prevention of HIV infection in women. Science 2010, 329, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, F.; Gaebler, C.; Mouquet, H.; Sather, D.N.; Lehmann, C.; Scheid, J.F.; Kraft, Z.; Liu, Y.; Pietzsch, J.; Hurley, A.; et al. Broad neutralization by a combination of antibodies recognizing the CD4 binding site and a new conformational epitope on the HIV-1 envelope protein. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, F.; Halper-Stromberg, A.; Horwitz, J.A.; Gruell, H.; Scheid, J.F.; Bournazos, S.; Mouquet, H.; Spatz, L.A.; Diskin, R.; Abadir, A.; et al. HIV therapy by a combination of broadly neutralizing antibodies in humanized mice. Nature 2012, 492, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheid, J.F.; Mouquet, H.; Feldhahn, N.; Seaman, M.S.; Velinzon, K.; Pietzsch, J.; Ott, R.G.; Anthony, R.M.; Zebroski, H.; Hurley, A.; et al. Broad diversity of neutralizing antibodies isolated from memory B cells in HIV-infected individuals. Nature 2009, 458, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.M.; Phogat, S.K.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Wagner, D.; Phung, P.; Goss, J.L.; Wrin, T.; Simek, M.D.; Fling, S.; Mitcham, J.L.; et al. Broad and potent neutralizing antibodies from an African donor reveal a new HIV-1 vaccine target. Science 2009, 326, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheid, J.F.; Mouquet, H.; Ueberheide, B.; Diskin, R.; Klein, F.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Pietzsch, J.; Fenyo, D.; Abadir, A.; Velinzon, K.; et al. Sequence and structural convergence of broad and potent HIV antibodies that mimic CD4 binding. Science 2011, 333, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, D.; Langedijk, J.P.; Hinz, A.; Seaman, M.S.; Vanzetta, F.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, B.M.; Silacci, C.; Pinna, D.; Jarrossay, D.; Balla-Jhagjhoorsingh, S.; et al. Analysis of memory B cell responses and isolation of novel monoclonal antibodies with neutralizing breadth from HIV-1-infected individuals. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Hogerkorp, C.M.; Schief, W.R.; Seaman, M.S.; Zhou, T.; Schmidt, S.D.; Wu, L.; Xu, L.; et al. Rational Design of Envelope Identifies Broadly Neutralizing Human Monoclonal Antibodies to HIV-1. Science 2010, 329, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.M.; Huber, M.; Doores, K.J.; Falkowska, E.; Pejchal, R.; Julien, J.P.; Wang, S.K.; Ramos, A.; Chan-Hui, P.Y.; Moyle, M.; et al. Broad neutralization coverage of HIV by multiple highly potent antibodies. Nature 2011, 477, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ofek, G.; Laub, L.; Louder, M.K.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Longo, N.S.; Imamichi, H.; Bailer, R.T.; Chakrabarti, B.; Sharma, S.K.; et al. Broad and potent neutralization of HIV-1 by a gp41-specific human antibody. Nature 2012, 491, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinckmann, S.; da Costa, K.; van Gils, M.J.; Hallengard, D.; Klein, K.; Madeira, L.; Mainetti, L.; Palma, P.; Raue, K.; Reinhart, D.; et al. Rational design of HIV vaccines and microbicides: Report of the EUROPRISE network annual conference 2010. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Laar, T.; Visser, C.; Holster, M.; Lopez, C.G.; Kreuning, D.; Sierkstra, L.; Lindner, N.; Verrips, T. Increased heterologous protein production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae growing on ethanol as sole carbon source. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 96, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorlani, A.; Brouwers, J.; McConville, C.; van der Bijl, P.; Malcolm, K.; Augustijns, P.; Quigley, A.F.; Weiss, R.; De Haard, H.; Verrips, T. Llama antibody fragments have good potential for application as HIV type 1 topical microbicides. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2012, 28, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsman, A.; Beirnaert, E.; Aasa-Chapman, M.M.; Hoorelbeke, B.; Hijazi, K.; Koh, W.; Tack, V.; Szynol, A.; Kelly, C.; McKnight, A.; et al. Llama antibody fragments with cross-subtype human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-neutralizing properties and high affinity for HIV-1 gp120. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 12069–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, L.E.; Quigley, A.F.; Strokappe, N.M.; Bulmer-Thomas, B.; Seaman, M.S.; Mortier, D.; Rutten, L.; Chander, N.; Edwards, C.J.; Ketteler, R.; et al. Potent and broad neutralization of HIV-1 by a llama antibody elicited by immunization. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strokappe, N.; Szynol, A.; Aasa-Chapman, M.; Gorlani, A.; Forsman Quigley, A.; Hulsik, D.L.; Chen, L.; Weiss, R.; de Haard, H.; Verrips, T. Llama antibody fragments recognizing various epitopes of the CD4bs neutralize a broad range of HIV-1 subtypes A, B and C. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doria-Rose, N.A.; Louder, M.K.; Yang, Z.; O’Dell, S.; Nason, M.; Schmidt, S.D.; McKee, K.; Seaman, M.S.; Bailer, R.T.; Mascola, J.R. HIV-1 neutralization coverage is improved by combining monoclonal antibodies that target independent epitopes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3393–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strokappe, N.M. HIV-1, How Llamas Help Us Fight the AIDS Pandemic; Utrecht University: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matz, J.; Kessler, P.; Bouchet, J.; Combes, O.; Ramos, O.H.; Barin, F.; Baty, D.; Martin, L.; Benichou, S.; Chames, P. Straightforward selection of broadly neutralizing single-domain antibodies targeting the conserved CD4 and coreceptor binding sites of HIV-1 gp120. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, L.E.; Rutten, L.; Frampton, D.; Anderson, I.; Granger, L.; Bashford-Rogers, R.; Dekkers, G.; Strokappe, N.M.; Seaman, M.S.; Koh, W.; et al. Molecular Evolution of Broadly Neutralizing Llama Antibodies to the CD4-Binding Site of HIV-1. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultberg, A.; Temperton, N.J.; Rosseels, V.; Koenders, M.; Gonzalez-Pajuelo, M.; Schepens, B.; Itati Ibanez, L.; Vanlandschoot, P.; Schillemans, J.; Saunders, M.; et al. Llama-derived single domain antibodies to build multivalent, superpotent and broadened neutralizing anti-viral molecules. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnichen, S.; Blanchetot, C.; Maussang, D.; Gonzalez-Pajuelo, M.; Chow, K.Y.; Bosch, L.; De Vrieze, S.; Serruys, B.; Ulrichts, H.; Vandevelde, W.; et al. CXCR4 nanobodies (VHH-based single variable domains) potently inhibit chemotaxis and HIV-1 replication and mobilize stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20565–20570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouquet, H.; Warncke, M.; Scheid, J.F.; Seaman, M.S.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Enhanced HIV-1 neutralization by antibody heteroligation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balazs, A.B.; West, A.P., Jr. Antibody gene transfer for HIV immunoprophylaxis. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsman Quigley, A.; Strokappe, N.; McCoy, L.; Rutten, L.; Tan, S.; Aasa-Chapman, M.; Seaman, M.; Szynol, A.; Liu, Y.Y.; de Haard, H.; et al. Broadly neutralising single-chain llama antibody fragments targeting novel gp120 and gp41 epitopes on the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope spike. manuscript in preparation.
- McCoy, L.; Rutten, L.; Strokappe, N.; Verrips, T.; Webb, B.; Weiss, R. Broadly neutralizing VHH againstHIV-1. WO Patent WO2013036130A1, 14 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.Y.; Gorny, M.K.; Palker, T.; Karwowska, S.; Zolla-Pazner, S. Epitope mapping of two immunodominant domains of gp41, the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, using ten human monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4832–4838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pancera, M.; Zhou, T.; Druz, A.; Georgiev, I.S.; Soto, C.; Gorman, J.; Huang, J.; Acharya, P.; Chuang, G.Y.; Ofek, G.; et al. Structure and immune recognition of trimeric pre-fusion HIV-1 Env. Nature 2014, 514, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.P.; Hock, M.; Radzimanowski, J.; Tonks, P.; Hulsik, D.L.; Effantin, G.; Seilly, D.J.; Dreja, H.; Kliche, A.; Wagner, R.; et al. A fusion intermediate gp41 immunogen elicits neutralizing antibodies to HIV-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 29912–29926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luftig, M.A.; Mattu, M.; Di Giovine, P.; Geleziunas, R.; Hrin, R.; Barbato, G.; Bianchi, E.; Miller, M.D.; Pessi, A.; Carfi, A. Structural basis for HIV-1 neutralization by a gp41 fusion intermediate-directed antibody. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabin, C.; Corti, D.; Buzon, V.; Seaman, M.S.; Lutje Hulsik, D.; Hinz, A.; Vanzetta, F.; Agatic, G.; Silacci, C.; Mainetti, L.; et al. Crystal structure and size-dependent neutralization properties of HK20, a human monoclonal antibody binding to the highly conserved heptad repeat 1 of gp41. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenhorn, W.; Hinz, A.; Gaudin, Y. Virus membrane fusion. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 2150–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grupping, K. Inhibiting the CD4-gp120 Interaction to Prevent HIV Infection: Insights from Mutational Resistance Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiteit Antwerpen, Antwerp, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pennings, P.S. Standing Genetic Variation and the Evolution of Drug Resistance in HIV. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokan, M.; Rudicell, R.S.; Louder, M.; McKee, K.; O’Dell, S.; Stewart-Jones, G.; Wang, K.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Choe, M.; et al. Bispecific Antibodies Targeting Different Epitopes on the HIV-1 Envelope Exhibit Broad and Potent Neutralization. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12501–12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Patel, B.; Ghanem, M.H.; Bundoc, V.; Zheng, Z.; Morgan, R.A.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Dey, B.; Berger, E.A. Novel CD4-Based Bispecific Chimeric Antigen Receptor Designed for Enhanced Anti-HIV Potency and Absence of HIV Entry Receptor Activity. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6685–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bournazos, S.; Gazumyan, A.; Seaman, M.S.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Ravetch, J.V. Bispecific Anti-HIV-1 Antibodies with Enhanced Breadth and Potency. Cell 2016, 165, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, J.; Lanzi, A.; Yao, X.; Andrews, C.D.; Tsai, L.; Gajjar, M.R.; Sun, M.; Seaman, M.S.; Padte, N.N.; et al. Engineered Bispecific Antibodies with Exquisite HIV-1-Neutralizing Activity. Cell 2016, 165, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, B.; Del Castillo, C.S.; Berger, E.A. Neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by sCD4-17b, a single-chain chimeric protein, based on sequential interaction of gp120 with CD4 and coreceptor. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2859–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutje Hulsik, D.; Liu, Y.Y.; Strokappe, N.M.; Battella, S.; El Khattabi, M.; McCoy, L.E.; Sabin, C.; Hinz, A.; Hock, M.; Macheboeuf, P.; et al. A gp41 MPER-specific llama VHH requires a hydrophobic CDR3 for neutralization but not for antigen recognition. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, J.P.; Cupo, A.; Sok, D.; Stanfield, R.L.; Lyumkis, D.; Deller, M.C.; Klasse, P.J.; Burton, D.R.; Sanders, R.W.; Moore, J.P.; et al. Crystal structure of a soluble cleaved HIV-1 envelope trimer. Science 2013, 342, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyumkis, D.; Julien, J.P.; de Val, N.; Cupo, A.; Potter, C.S.; Klasse, P.J.; Burton, D.R.; Sanders, R.W.; Moore, J.P.; Carragher, B.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of a fully glycosylated soluble cleaved HIV-1 envelope trimer. Science 2013, 342, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissenhorn, W.; Dessen, A.; Harrison, S.C.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Atomic structure of the ectodomain from HIV-1 gp41. Nature 1997, 387, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustchina, E.; Li, M.; Louis, J.M.; Anderson, D.E.; Lloyd, J.; Frisch, C.; Bewley, C.A.; Gustchina, A.; Wlodawer, A.; Clore, G.M. Structural basis of HIV-1 neutralization by affinity matured Fabs directed against the internal trimeric coiled-coil of gp41. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholukh, A.M.; Watkins, J.D.; Vyas, H.K.; Gupta, S.; Lakhashe, S.K.; Thorat, S.; Zhou, M.; Hemashettar, G.; Bachler, B.C.; Forthal, D.N.; et al. Defense-in-depth by mucosally administered anti-HIV dimeric IgA2 and systemic IgG1 mAbs: Complete protection of rhesus monkeys from mucosal SHIV challenge. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, D.R.; Barbas, C.F., 3rd; Persson, M.A.; Koenig, S.; Chanock, R.M.; Lerner, R.A. A large array of human monoclonal antibodies to type 1 human immunodeficiency virus from combinatorial libraries of asymptomatic seropositive individuals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10134–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thali, M.; Moore, J.P.; Furman, C.; Charles, M.; Ho, D.D.; Robinson, J.; Sodroski, J. Characterization of conserved human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 neutralization epitopes exposed upon gp120-CD4 binding. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 3978–3988. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Gao, F.; Mascola, J.R.; Stamatatos, L.; Polonis, V.R.; Koutsoukos, M.; Voss, G.; Goepfert, P.; Gilbert, P.; Greene, K.M.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env clones from acute and early subtype B infections for standardized assessments of vaccine-elicited neutralizing antibodies. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 10108–10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Salazar-Gonzalez, J.F.; Derdeyn, C.A.; Morris, L.; Williamson, C.; Robinson, J.E.; Decker, J.M.; Li, Y.; Salazar, M.G.; Polonis, V.R.; et al. Genetic and neutralization properties of subtype C human immunodeficiency virus type 1 molecular env clones from acute and early heterosexually acquired infections in Southern Africa. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 11776–11790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdeyn, C.A.; Decker, J.M.; Sfakianos, J.N.; Wu, X.; O’Brien, W.A.; Ratner, L.; Kappes, J.C.; Shaw, G.M.; Hunter, E. Sensitivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to the fusion inhibitor T-20 is modulated by coreceptor specificity defined by the V3 loop of gp120. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8358–8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Decker, J.M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Arani, R.B.; Kilby, J.M.; Saag, M.S.; Wu, X.; Shaw, G.M.; Kappes, J.C. Emergence of resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in patients receiving fusion inhibitor (T-20) monotherapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, A.; Lutje Hulsik, D.; Forsman, A.; Koh, W.W.; Belrhali, H.; Gorlani, A.; de Haard, H.; Weiss, R.A.; Verrips, T.; Weissenhorn, W. Crystal Structure of the Neutralizing Llama V(HH) D7 and Its Mode of HIV-1 gp120 Interaction. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyerson, J.R.; Tran, E.E.; Kuybeda, O.; Chen, W.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Gorlani, A.; Verrips, T.; Lifson, J.D.; Subramaniam, S. Molecular structures of trimeric HIV-1 Env in complex with small antibody derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, E.; Piano, D.; Bowler, M.W. Direct cryocooling of naked crystals: Are cryoprotection agents always necessary? Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battye, T.G.; Kontogiannis, L.; Johnson, O.; Powell, H.R.; Leslie, A.G. iMOSFLM: A new graphical interface for diffraction-image processing with MOSFLM. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, P. Scaling and assessment of data quality. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2006, 62, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, A.J. Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with Phaser. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2007, 63, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrakis, A.; Morris, R.; Lamzin, V.S. Automated protein model building combined with iterative structure refinement. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1999, 6, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Vagin, A.A.; Dodson, E.J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1997, 53, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caskey, M.; Klein, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.; Seaman, M.S.; West, A.P., Jr.; Buckley, N.; Kremer, G.; Nogueira, L.; Braunschweig, M.; Scheid, J.F.; et al. Viraemia suppressed in HIV-1-infected humans by broadly neutralizing antibody 3BNC117. Nature 2015, 522, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 2E7GP41 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Native | Anisotropic Scaling ** |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.97239 | |
| Space group | P22121 | |
| Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) | 37.95, 121.26, 132.21 | |
| Resolution (Å) * | 44.68–2.95 (3.03–2.95) | 44.68–2.95 (3.03–2.95) |
| Unique reflections * | 13440 (993) | 12538 (327) |
| Rmerge (%) | 8.4 (76.4) | 7.9 (34.2) |
| I/σI * | 13.8 (2.3) | 14.6 (3.9) |
| Completeness (%) * | 99.0 (100.00) | 96.6 (34.5) |
| Redundancy * | 4.7 (5.0) | 4.3 (1.3) |
| Wilson B factor (Å2) | 63.85 | 58.0 |
| Refinement | ||
| Resolution | 44.68–2.96 (3.07–2.96) | |
| Rwork/Rfree (%) * | 19.42 (30.07)/24.91 (34.4) | |
| No. atoms | ||
| Protein | 3087 | |
| Water | 0 | |
| B factors (Å2) | ||
| Protein | 55.4 | |
| Water | 0 | |
| r.m.s. deviations | ||
| Bond lengths (Å) | 0.006 | |
| Bond angles (°) | 1.26 | |
| Ramachandran | ||
| Favored (%) | 99.0 | |
| Outliers (%) | 0.0 | |
| Clashscore *** Molprobity score *** | 3.78 (100th percentile) 1.47 (100th percentile) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strokappe, N.M.; Hock, M.; Rutten, L.; Mccoy, L.E.; Back, J.W.; Caillat, C.; Haffke, M.; Weiss, R.A.; Weissenhorn, W.; Verrips, T. Super Potent Bispecific Llama VHH Antibodies Neutralize HIV via a Combination of gp41 and gp120 Epitopes. Antibodies 2019, 8, 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8020038
Strokappe NM, Hock M, Rutten L, Mccoy LE, Back JW, Caillat C, Haffke M, Weiss RA, Weissenhorn W, Verrips T. Super Potent Bispecific Llama VHH Antibodies Neutralize HIV via a Combination of gp41 and gp120 Epitopes. Antibodies. 2019; 8(2):38. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8020038
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrokappe, Nika M., Miriam Hock, Lucy Rutten, Laura E. Mccoy, Jaap W. Back, Christophe Caillat, Matthias Haffke, Robin A. Weiss, Winfried Weissenhorn, and Theo Verrips. 2019. "Super Potent Bispecific Llama VHH Antibodies Neutralize HIV via a Combination of gp41 and gp120 Epitopes" Antibodies 8, no. 2: 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8020038
APA StyleStrokappe, N. M., Hock, M., Rutten, L., Mccoy, L. E., Back, J. W., Caillat, C., Haffke, M., Weiss, R. A., Weissenhorn, W., & Verrips, T. (2019). Super Potent Bispecific Llama VHH Antibodies Neutralize HIV via a Combination of gp41 and gp120 Epitopes. Antibodies, 8(2), 38. https://doi.org/10.3390/antib8020038






